Spatial Matching Analysis and Development Strategies of County Night-Time Economy: A Case of Anning County, Yunnan Province
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. China’s Night-Time Economic Policy and Development Background
3. Research Areas and Methods
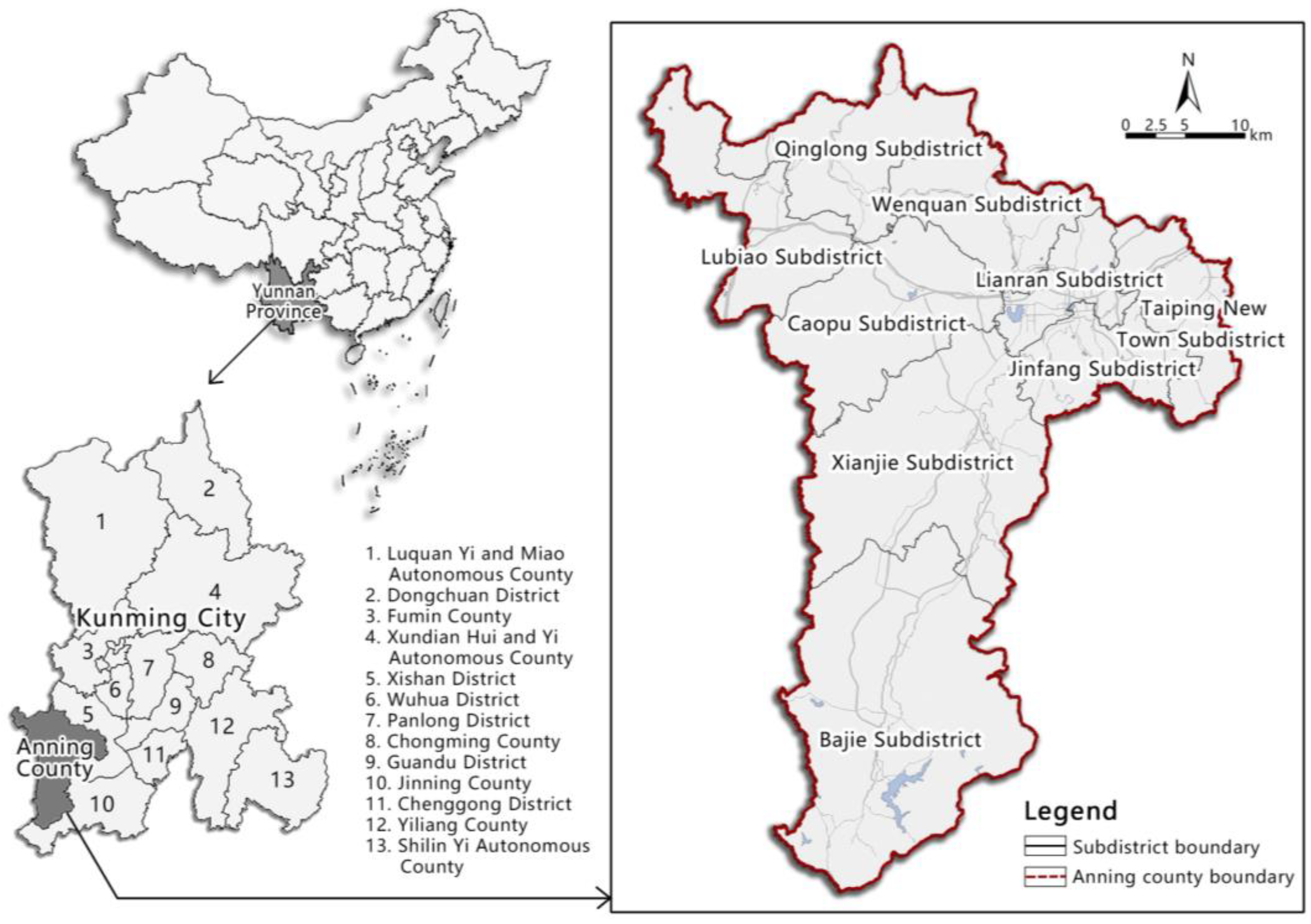
3.1. Research Area
3.2. Data Acquisition and Processing
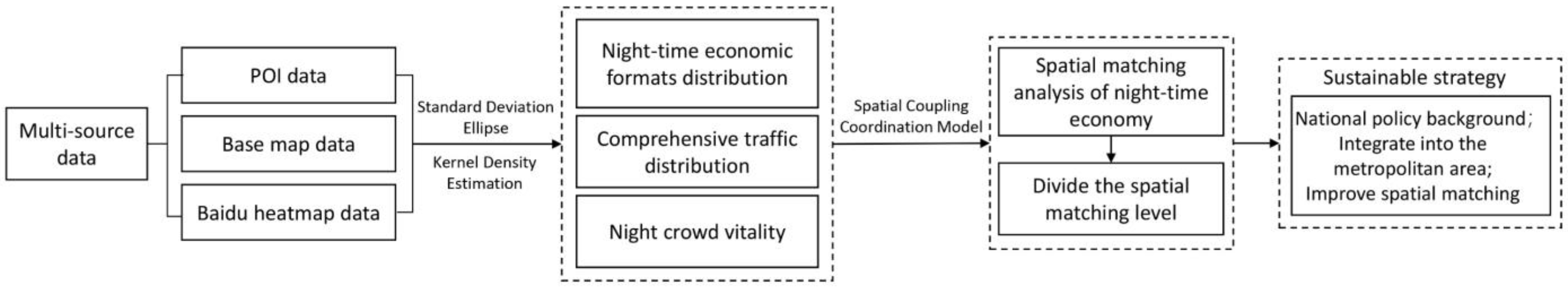
3.3. Research Methods
3.3.1. Data Analysis
3.3.2. Spatial Coupling Coordination Model
4. Results and Analysis
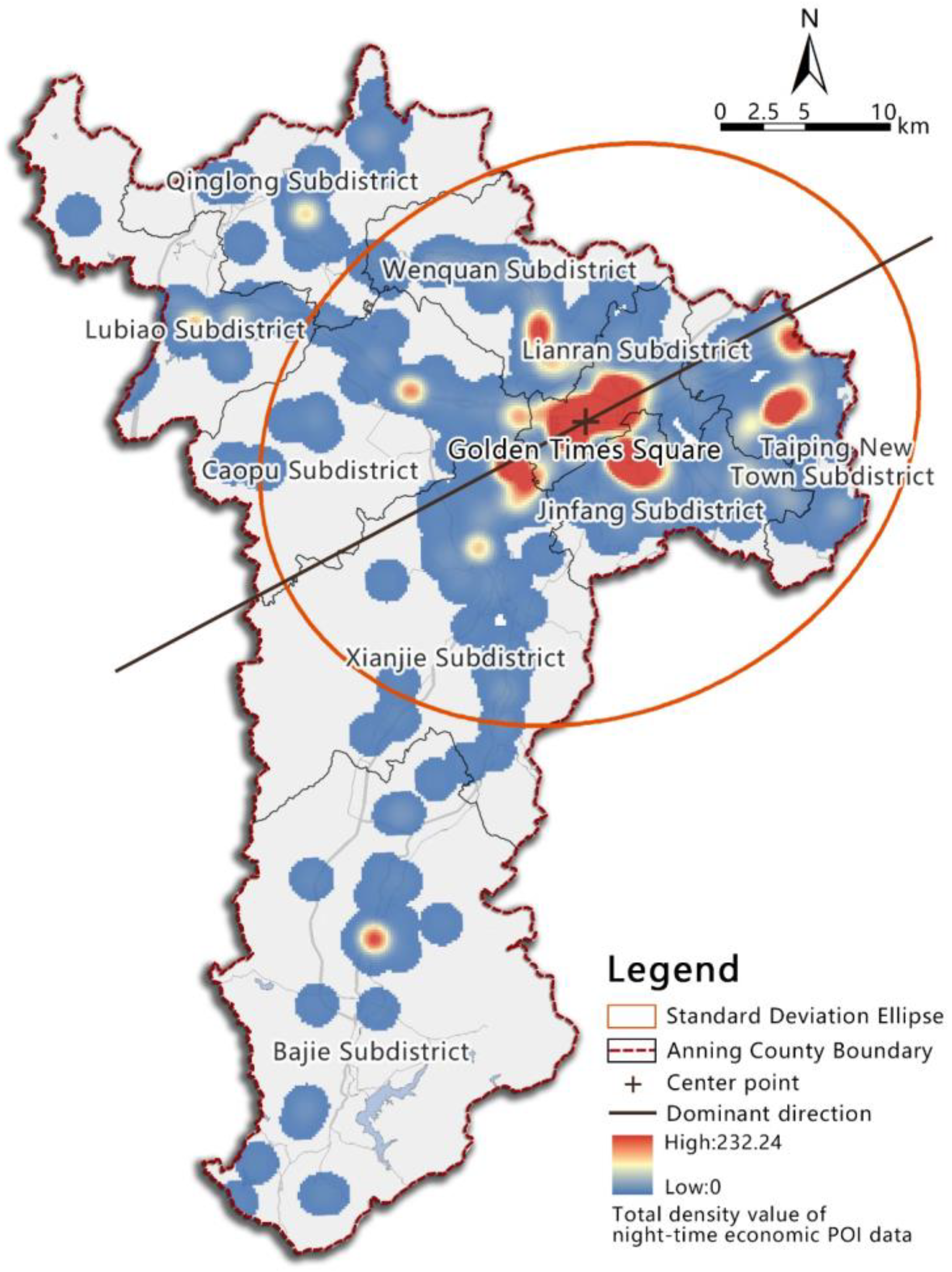
4.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Night-Time Economy in Anning County
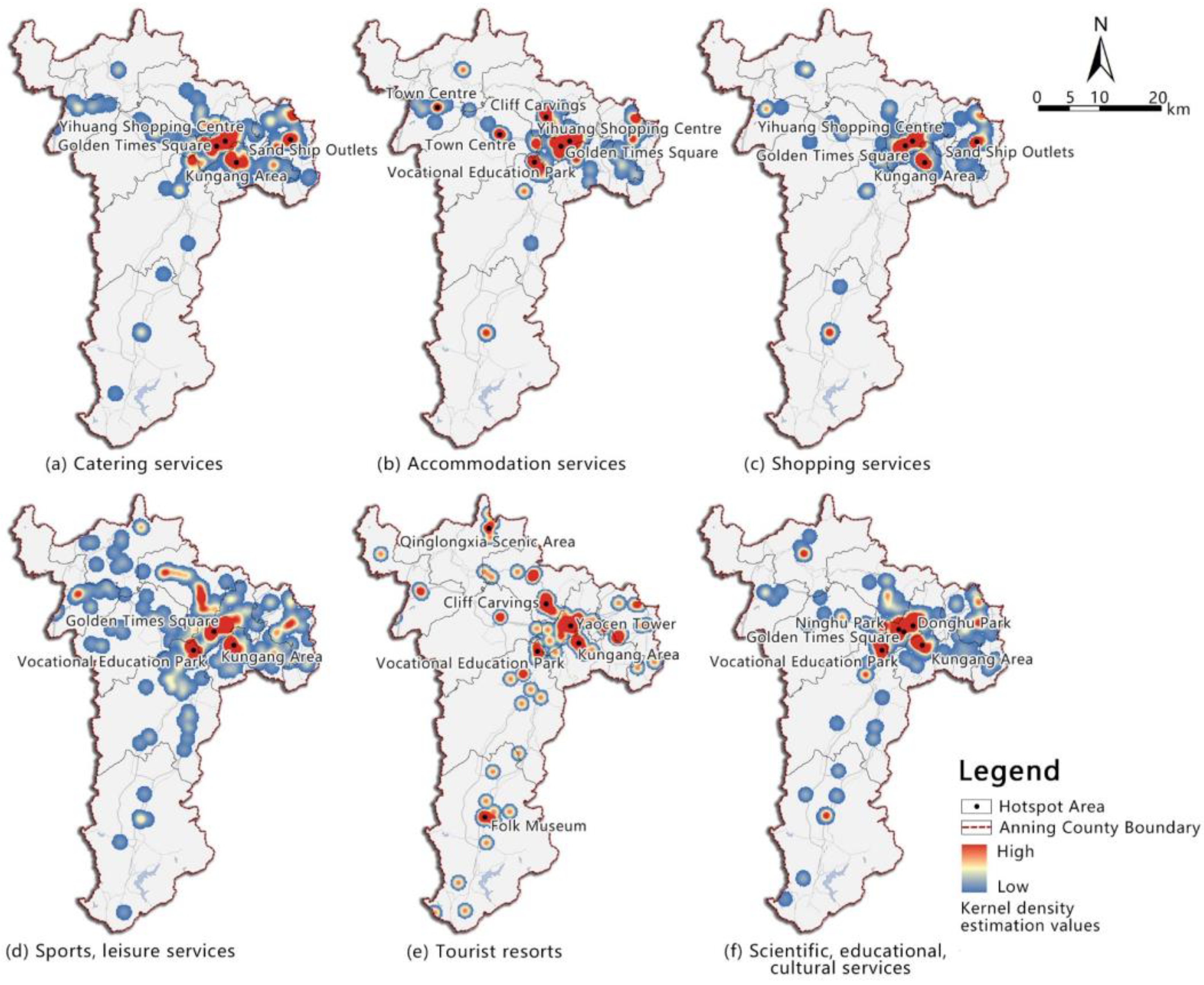
4.2. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Night-Time Economic Formats in Anning County
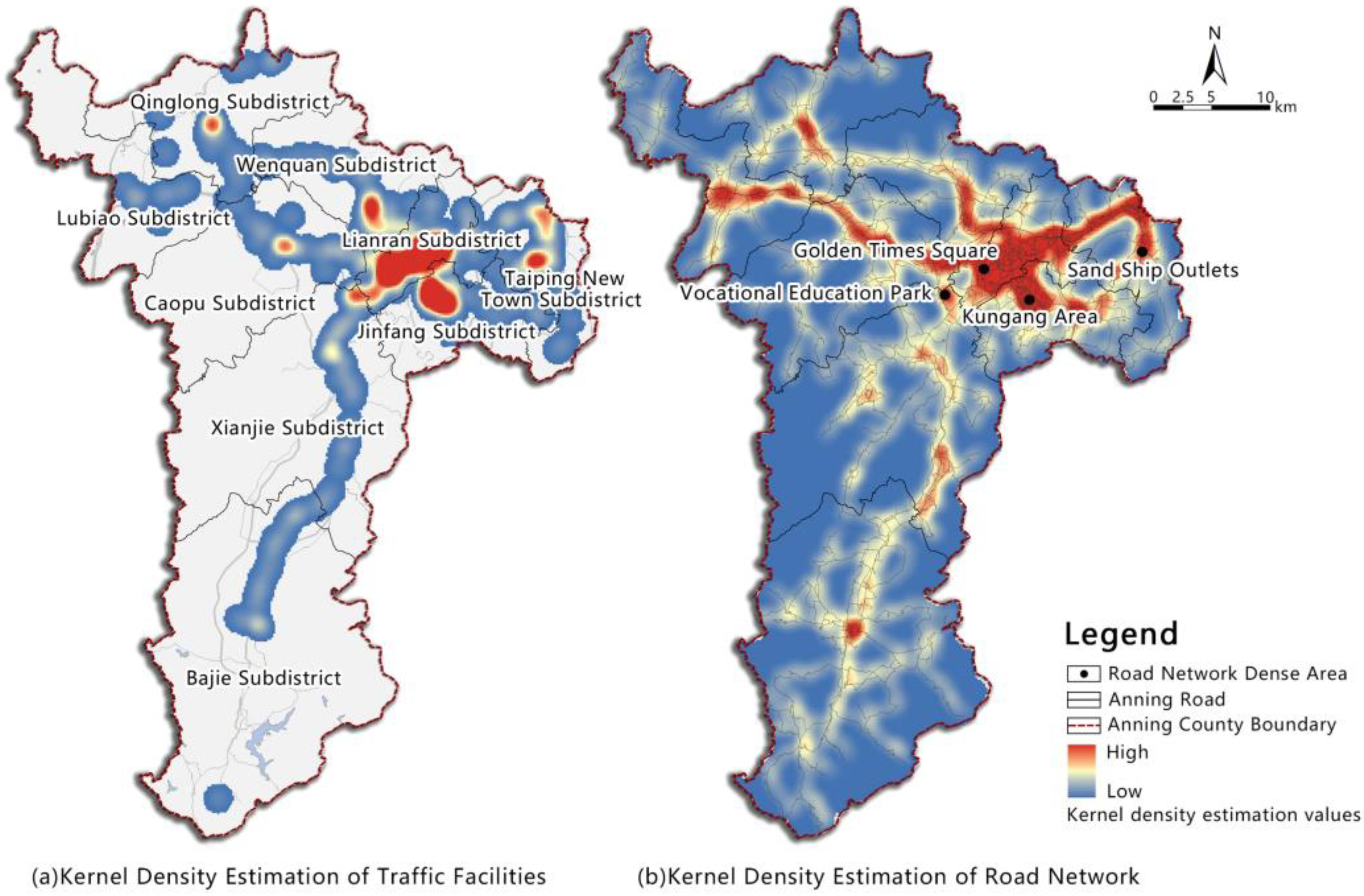
4.3. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Comprehensive Traffic in Anning County
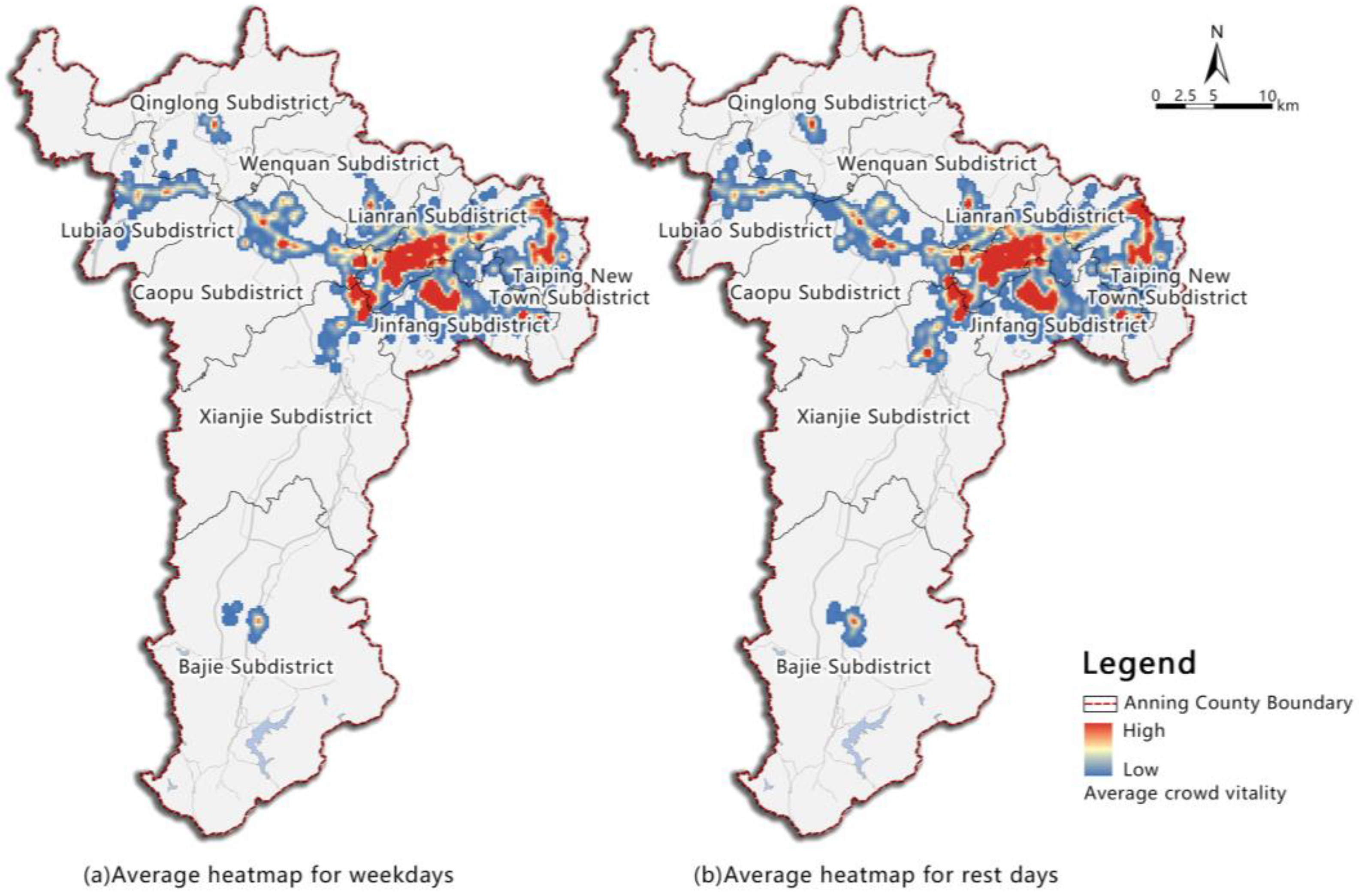
4.4. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Night-Crowd Vitality in Anning County
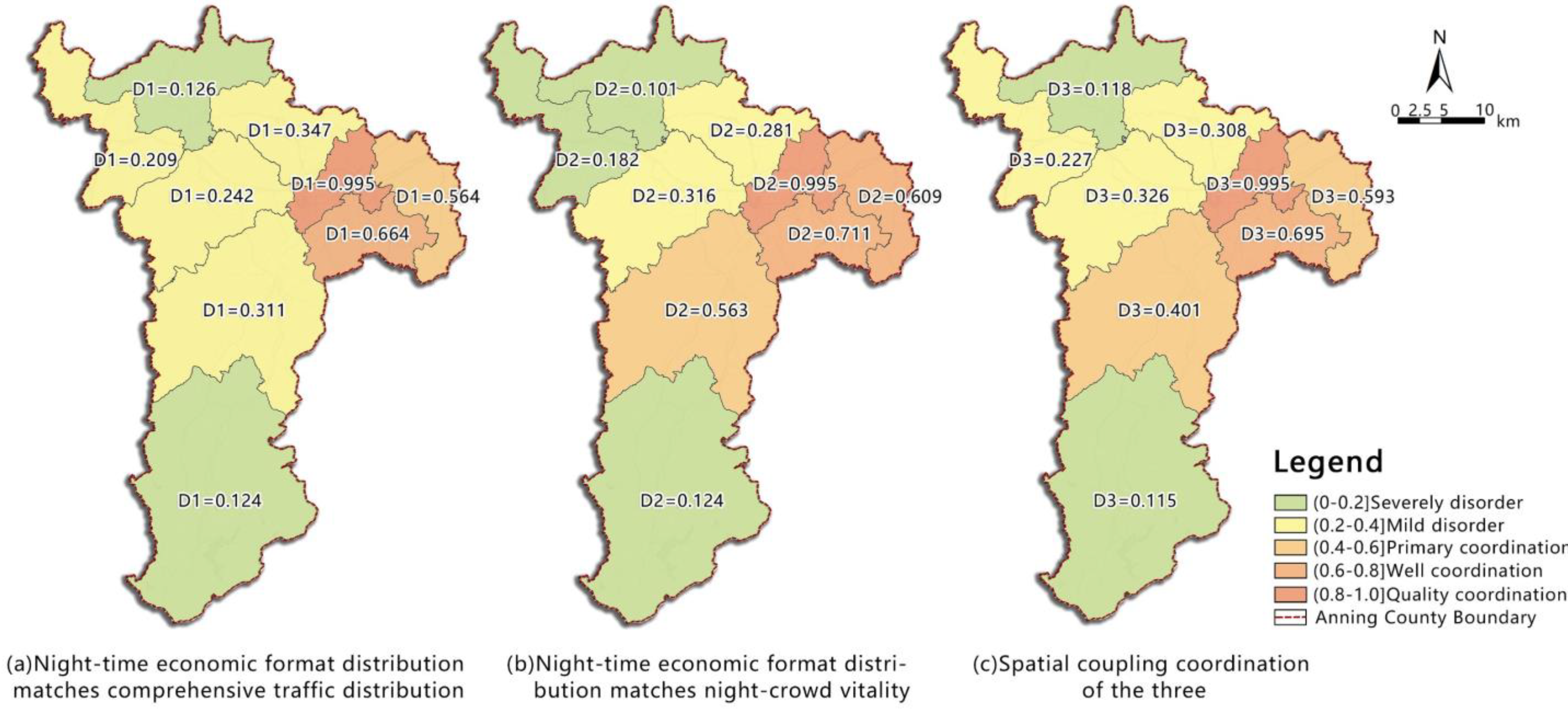
4.5. Analysis of Night-Time Economic Space Matching in Anning County
5. The Sustainable Development Strategy of the Night-Time Economy in Anning County
5.1. Determining the Night-Time Economic Development Orientation of Anning County from the Perspective of Rural Revitalization and Urban–Rural Integration
5.2. Activating Anning Night-Time Economy Vitality from the Perspective of Metropolitan Integration
5.3. Promote the Connotation of Anning Night-Time Economy from the Subdistrict Regional Characteristics
6. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaw, R. Beyond Night-Time Economy: Affective Atmospheres of the Urban Night. Geoforum 2014, 51, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashton, K.; Roderick, J.; Williams, L.P.; Green, L. Developing a Framework for Managing the Night-time Economy in Wales: A Health Impact Assessment Approach. Impact Assess. Proj. Apprais. 2018, 36, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, V.S.; Qin, Y.; Ying, T.Y.; Shen, S.J.; Lyu, G.M. Night-time Economy Vitality Index: Framework and Evidence. Tour. Econ. 2021, 1, 135481662110429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, F. Night Cultures, Night Economies. Plan. Pract. Res. 1995, 10, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, J. Cities and the Art of Cultural Planning. Plan. Pract. Res. 1990, 5, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London at Night: An Evidence Base for a 24-Hour City. 2018. Available online: https://www.london.gov.uk/business-and-economy-publications/london-night-evidence-base-24-hour-city (accessed on 23 December 2021).
- Bromley, R.; Thomas, C.; Millie, A. Exploring Safety Concerns in the Night-Time City: Revitalising the Evening Economy. Town Plan. Rev. 2000, 71, 71–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, D.; Winlow, S.; Hadfield, P.; Lister, S. Violent Hypocrisy: Governance and the Night-time Economy. Eur. J. Criminol. 2005, 2, 161–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, A.; Flint, J. Urban Safety, Anti-social Behavior and the Night-time Economy. Criminol. Crim. Justice 2009, 9, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su-Jan, Y.; Chye-Kiang, H. An (Extra) Ordinary Night out: Urban Informality, Social Sustainability and the Night-Time Economy. Urban Stud. 2013, 51, 712–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordi, N.; Emanuele, G.; Adam, E.; Martins, J.; Sequera, J. Tourism, Nightlife and Planning: Challenges and Opportunities for Community Liveability in La Barceloneta. Tour. Geogr. 2018, 20, 377–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeming, S.; Kypri, K. Costing Alcohol-Related Assault in the Night-time Economy from a Societal Perspective: The Case of Central Sydney. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2021, 40, 779–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, P.G.; Coomber, K.; de Andrade, D.; Livingston, M.; Puljević, C.; Vakidis, T.; Carah, N.; Taylor, N.; Burn, M.; Curtis, A.; et al. Queensland Alcohol-Related Violence and Night-time Economy Monitoring (QUANTEM): Rationale and Overview. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2021, 40, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, H.; Scantlebury, D.M.; Zubidat, A.E. The Loss of Ecosystem-Services Emerging from Artificial Light at Night. Chronobiol. Int. 2019, 36, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robert, G.; Nigel, W.; Philip, T. Alcohol and Personal Security in the Built Environment: Student Engagement in the Night-time Economy of Kingston upon Thames, London, UK. Lond. J. 2021, 46, 187–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.H.; Won, D.L.; Mark, E.; Jon, B. The ‘exposed’ Population, Violent Crime in Public Space and the Night-Time Economy in Manchester, UK. Eur. J. Crim. Policy Res. 2021, 27, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Nordhaus, W.D. Using Luminosity Data as A Proxy for Economic Statistics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8589–8594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henderson, J.V.; Storeygard, A.; Weil, D.N. Measuring Economic Growth from Outer Space. Am. Econ. Rev. 2012, 102, 994–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, H. On the Scale, Format and Consumers of the Night Fair during the Song Dynasty. J. Cap. Norm. Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 2, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, N.; Tian, Q. Theoretical Research and Operation Promotion Path of Night-time Economy. Enterp. Econ. 2021, 40, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, T.H.; Ren, Y.T.; Shen, L.Y.; Qian, Y. Study on Spatial Heterogeneity of Consumption Vibrancy and Its Driving Factors in Large City: A Case of Chengdu City. Urban Dev. Stud. 2020, 27, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Opinions of The General Office of the State Council on Further Stimulating the Potential of Cultural and Tourism Consumption. General Office of the State Council: Beijing, China. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2019-08/23/content_5423809.htm (accessed on 23 August 2019).
- Opinions on Accelerating the Development of Circulation and Promoting Commercial Consumption. General Office of the State Council: Beijing, China. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2019-08/27/content_5425015.htm (accessed on 27 August 2019).
- Why does China Develop Night Economy? Available online: https://m.thepaper.cn/baijiahao_4782907 (accessed on 26 October 2019).
- 2019–2022 the Development Trend and Consumption Behavior of The Night Economy Industry Report. Available online: https://www.iimedia.cn/c400/65686.html (accessed on 12 August 2021).
- Li, Q.Y.; Chen, L.L. Thoughts on the Consumption of Night Sports Boosting the Development of Night Economy. J. Chengdu Sport Univ. 2021, 47, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.L.; Zhu, S.H.; Li, Y.X. A Research on the Path of Innovative Development of Night Tourism in Suzhou: Based on Network Text Analysis and Questionnaire Survey. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Suzhou (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 38, 24–31, 107. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.M. Study on Consumption Characteristics and Upgrading Path of Urban Night-Time Food Economy in China. Consum. Econ. 2020, 36, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, D.P.; Liao, J.W.; Xu, Y. Research on the Evolution Mechanism of Night-time Economic Policies in China. Consum. Econ. 2021, 37, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.X. Research on Special Policies of Night-time Economy: Based on Content Analysis Method. Contemp. Econ. Manag. 2021, 43, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.W.; Wang, Y.F. Urban Night-time Tourism Consumption Space from the Perspective of Scene: A Study Based on the Cultural Scene of Super Wenheyou in Changsha. Wuhan Univ. J. (Philos. Soc. Sci.) 2021, 74, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.L. The Empirical Study on Night Consumption Tendency of Beijing Residents: Based on Iv-logit Regression model. Urban Probl. 2021, 2, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.P.; Qiu, Y.Q.; Xia, H.Y. Multi-level Thinking on Urban Night-time Economic Development: Taking Chengdu as An Example. Mod. Bus. 2021, 26, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Zhang, J.H. Matching Urban Leisure Service Level and Vitality in the Night-time: A Case Study of Nanjing. China Anc. City 2021, 35, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, N.N.; Shao, X.Y. Research on Coupling Coordination of Ecological Environment-Tourism Industry-Urbanization in the Yellow River Basin. Econ. Probl. 2022, 3, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.K.; Bai, Y.S.; Hong, S.M. Spatiotemporal Differentiation Characteristics and Dynamic Factors of Coupled and Coordinated Development of Urbanization and Ecological Environment: A Case Study of Sichuan Province. Urban Probl. 2021, 12, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, D. Optimizing Urban Spatial Layout and Promoting Night Economic Development—A Case Study of Zhenjiang City. Trade Fair Econ. 2021, 16, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.K.; Chen, B.; Deng, X.Z.; Fang, D.B.; Huang, H.J.; Li, H.Z.; Li, S.T.; Liu, S.Y.; Wei, H.K.; Zhang, X.B.; et al. Analysis of Research Hotspots in Management of Coordination Development of Economy and Society. J. Manag. Sci. China 2021, 24, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.F.; Ma, S.; Xiang, W.Y.; Kan, C.C.; Wu, K.; Long, Y. Classification of Shrinking Cities in China Using Baidu Big Data. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 2477–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.M.; Zhen, F.; Zhang, S.Q. Research on Spatial Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Urban Employment Based on Big data. Urban Dev. Stud. 2021, 28, 2, 48–57, 181. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.W.; Liang, Y.Q.; Cui, L.Y. Analysis of Economic Agglomeration Characteristics of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Cluster Based on NPP-VIIRS Night Light Data. J. Southwest Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 43, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.M. Apply Fringe Identification to Understand Urban Economic Development in China: In Case of Wuhan. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.H.; Ding, Z.H.; Huang, K.; Song, Y.; Dong, H.X. Spatial Distribution of Enterprise Communities and Its Implications Based on POI Data: A Case of Xi’an, China. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2021, 147, 05021028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.; Zhou, X.C.; Gong, Y.X. Car-sharing Travel Patterns in Shanghai Based on Big Data. Prog. Geogr. 2021, 40, 2035–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitor, W.; Nícollas, S.; Matheus, V.; Adriano, C.; Fernando, M.; Leonard, R. Points of Interest Recommendations: Methods, Evaluation and Future Directions. Inf. Syst. 2021, 101, 101789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Review and Prospect of the Research on Qin County System in the Last 40 years. Trends Recent Res. Hist. China 2021, 5, 16–25. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.S.; Zang, Y.Z.; Yang, Y.Y. China’s Rural Revitalization and Development: Theory, Technology and Management. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 1923–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.T.; Liu, Y.S.; Yang, Y.Y.; Jiang, N. County-rural Revitalization Spatial Differences and Model Optimization in Miyun Subdistrict of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. J. Rural Stud. 2021, 86, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2020 China Night Economic Development Report: Scene Innovation and Digital Reconstruction. Available online: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/fOsF4mnNyiHzVq8NcDKBTQ (accessed on 25 October 2020).
- Li, Z.L. Research on the Coupling Mechanism and Coordinated Development of Rural Revitalization—Rural Tourism System: A Case Study on Fenghuang County in Hunan. Geogr. Res. 2019, 38, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Ren, Y.S.; Zhu, D.C.; Cheng, J.M.; Yang, X.Z.; Yang, Z.; Yao, J.M. The Research Framework and Prospect of Rural Revitalization Led by Rural Tourism. Geogr. Res. 2019, 38, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiding Opinions of the General Office of the People’s Government of Yunnan Province on Promoting the Development at Night. Yunnan Provincial People’s Government: Yunnan, China. Available online: http://yn.gov.cn/zwgk/zfgb/2020/2020d10q/szfbgtwj/202004/t20200423_202968.html (accessed on 23 April 2020).
- Yunnan’s Economic Operation in 2021. Yunnan Provincial Bureau of Statistics: Yunnan, China. Available online: http://stats.yn.gov.cn/xxgk/gkml/zmfd/zm1/202201/t20220127_1073051.html (accessed on 23 April 2020).
- Implementation Opinions on Promoting Night Economic Development in Kunming. Kunming Municipal Bureau of Commerce: Kunming, China. Available online: http://swj.km.gov.cn/c/2020-08-15/3631414.shtml (accessed on 15 August 2020).
- Wang, L.C. Spatial-temporal Characteristics of Urban Population Aggregation Based on Baidu Heat Map in Central Areas of Wuhan City. J. Hum. Settl. West China 2018, 33, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhao, W.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, S.; Liu, C. Research on the Coupling Coordination Relationship between Urbanization and the Air Environment: A Case Study of the Area of Wuhan. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Shen, J.; He, R.; Fan, B.H.; Han, H. Dynamic Analysis of the Coupling Coordination Relationship between Urbanization and Water Resource Security and Its Obstacle Factor. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.J.; Jiao, F.C.; Ren, L.J.; Xu, X.G.; Wang, J.C.; Wang, X. Coupling Coordination Relationship between Urbanization and Atmospheric Environment Security in Jinan City. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 204, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Q.; Ye, Z.N. Research on Urban Spatial Structure Based on Baidu Heat Map: A Case Study on the Central City of Shanghai. City Plan. Rev. 2016, 40, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.L. The Theory and Practice Exploration of “Remembering Nostalgia” in the Construction of New Urbanization. Geogr. Res. 2015, 34, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, F.J.; Chen, W.X.; Zeng, Y.Y.; Li, J.F. The Nexus between Urbanization and Traffic Accessibility in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River Urban Agglomerations, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McArthur, J.; Robin, E.; Smeds, E. Socio-spatial and Temporal Dimensions of Transport Equity for London’s Night Time Economy. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2019, 121, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.D.; Xu, J.; Xu, H.; Sha, L.; Wang, X.R. Discussion of the Interactive Influence between the Night Lighting and Road Trees on Urban Roads. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2019, 35, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.Y.; Wang, Y.C. Shaping a Smart Transportation System for Sustainable Value Co-Creation. Inf. Syst. Front. 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk-Anioł, J.; Grochowicz, M.; Pawlusiński, R. All Change: How a Tourism City Responds to COVID-19: A CEE Perspective (Kraków Case Study). Sustainability 2021, 13, 7914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puttaiah, M.H.; Raverkar, A.; Avramakis, E. All Change: How COVID-19 Is Transforming Consumer Behaviour. Swiss Re Institute. 2020. Chapter 2. Available online: https://www.swissre.com/institute/research/topics-and-risk-dialogues/health-and-longevity/covid-19-and-consumer-behaviour.html (accessed on 10 December 2020).
- Da Silva Lopes, H.; Remoaldo, P.C.; Ribeiro, V.; Martín-Vide, J. Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Tourist Risk Perceptions—The Case Study of Porto. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Type of Data | Data Content | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Catering Services | Restaurants, snack bars, agritainment, etc. | 887 |
| Accommodation Services | Hotels, inns, homestays, etc. | 476 |
| Shopping services | Commercial complexes, supermarkets, convenience stores, agricultural markets, etc. | 877 |
| Sports, leisure services | Stadium, entertainment venues, theaters, leisure resorts, etc. | 540 |
| Tourist resorts | Attractions, parks, etc. | 104 |
| Scientific, educational, cultural services | Schools, museums, exhibition halls, libraries, cultural centers, etc. | 582 |
| Operating Range | Before 18:00 | 18:00–20:00 | 20:00–22:00 | After 22:00 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| County bus | 11 | 20 | 11 | 4 |
| Taiping bus | 1 | 5 | 3 | / |
| Anning to Kunming Intercity Bus | 2 | 7 | 1 | / |
| Rural bus | 3 | 1 | / | / |
| Proportion of total bus routes | 24.64% | 47.83% | 21.74% | 5.8% |
| Name of Subdistrict | D1 | D2 | D3 | Comprehensive Matching Level | Coupling Coordination Degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bajie Subdistrict | 0.124 | 0.124 | 0.115 | 1 | Severely disorder |
| Caopu Subdistrict | 0.242 | 0.316 | 0.326 | 2 | Mild disorder |
| Jinfang Subdistrict | 0.664 | 0.711 | 0.695 | 4 | Well coordination |
| Lianran Subdistrict | 0.995 | 0.995 | 0.995 | 5 | Quality coordination |
| Lubiao Subdistrict | 0.209 | 0.182 | 0.227 | 2 | Mild disorder |
| Qinglong Subdistrict | 0.126 | 0.101 | 0.118 | 1 | Severely disorder |
| Taiping New Town Subdistrict | 0.564 | 0.609 | 0.593 | 3 | Primary coordination |
| Wenquan Subdistrict | 0.347 | 0.281 | 0.308 | 2 | Mild disorder |
| Xianjie Subdistrict | 0.311 | 0.563 | 0.401 | 3 | Mild disorder |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y. Spatial Matching Analysis and Development Strategies of County Night-Time Economy: A Case of Anning County, Yunnan Province. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4891. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094891
Wang W, Liu L, Yang Y. Spatial Matching Analysis and Development Strategies of County Night-Time Economy: A Case of Anning County, Yunnan Province. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):4891. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094891
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Weiwu, Lingjun Liu, and Yuxin Yang. 2022. "Spatial Matching Analysis and Development Strategies of County Night-Time Economy: A Case of Anning County, Yunnan Province" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 4891. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094891
APA StyleWang, W., Liu, L., & Yang, Y. (2022). Spatial Matching Analysis and Development Strategies of County Night-Time Economy: A Case of Anning County, Yunnan Province. Sustainability, 14(9), 4891. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094891







