Vulnerability Assessment of Pacific Whiteleg Shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) Farms and Vendors in Davao, Philippines Using FishVool
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
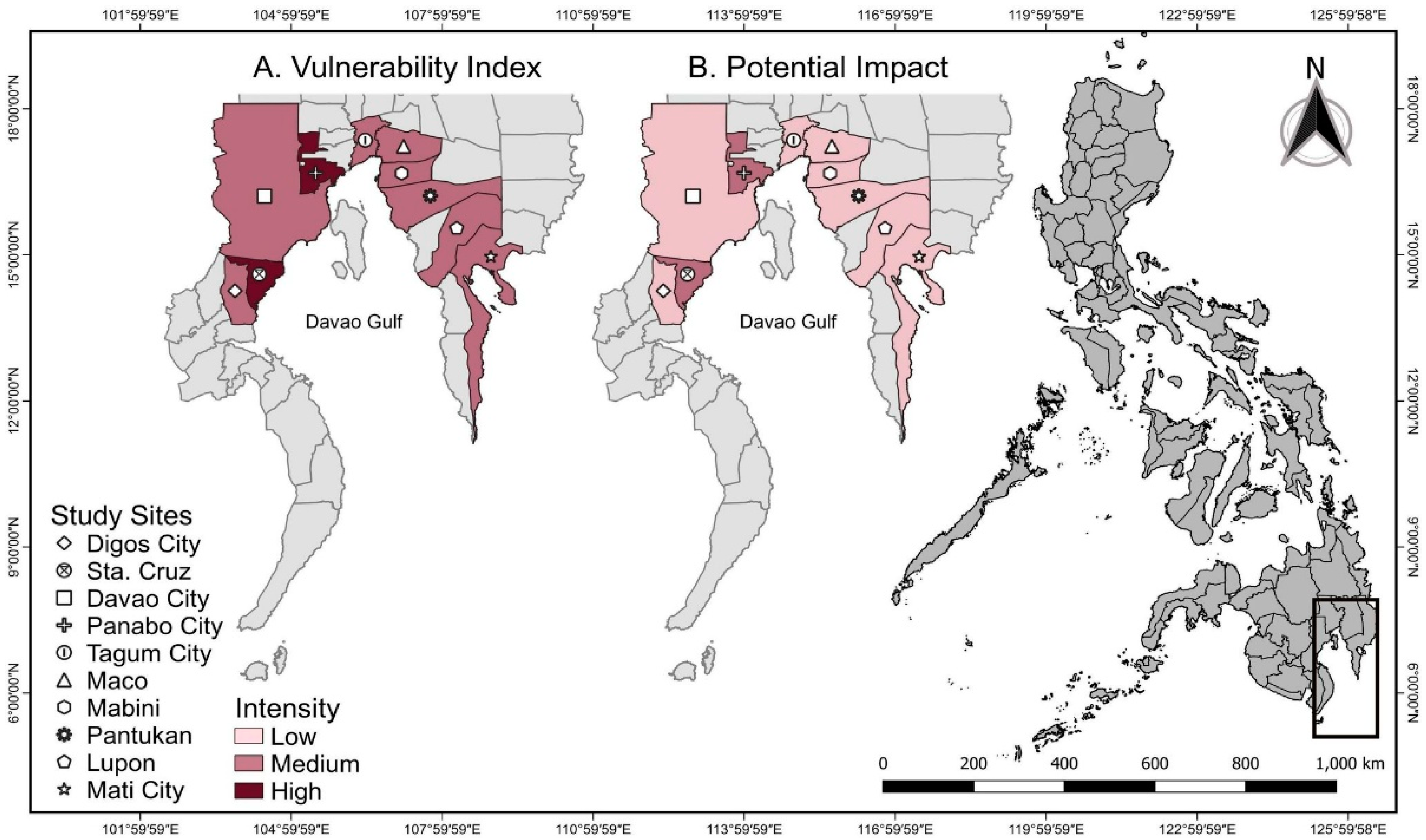
2.1. Description of Study Area
2.2. Data Collection and Analysis
2.3. Farm Vulnerability Index Criteria for Vulnerability Components
2.4. Market Vulnerability Index Criteria for Vulnerability Components
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. The Direct and Indirect Impacts of Climate Change
4.2. Local Impact of Climate Change Variabilities
4.3. Adaptation of Shrimpfish Farmers
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, N.; Diana, J.S. Coastal to inland: Expansion of prawn farming for adaptation to climate change in Bangladesh. Aquac. Rep. 2015, 2, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macusi, E.D.; Geronimo, R.C.; Santos, M.D. Vulnerability drivers for small pelagics and milkfish aquaculture value chain determined through online participatory approach. Mar. Policy 2021, 133, 104710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasinghe, J.M.P.K.; Gamage, D.G.N.D.; Jayasinghe, J.M.H.A. Combating Climate Change Impacts for Shrimp Aquaculture Through Adaptations: Sri Lankan Perspective. In Sustainable Solutions for Food Security; Sarkar, A., Sensarma, S., van Loon, G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 287–309. [Google Scholar]
- PSA. Fisheries Statistics of the Philippines 2018–2020; Philippine Statistics Authority: Quezon City, Philippines, 2020; p. 320.
- Funge-Smith, S.; Briggs, M.R.P.; Subasinghe, R.; Phillips, M. Introductions and Movement of Penaeus vannamei and Penaeus stylirostris in Asia and the Pacific; FAO Regional Office for Asia Pacific: Bangkok, Thailand, 2004; pp. 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, I.C.; Chien, Y.H. The Pacific White Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, in Asia: The World’s Most Widely Cultured Alien Crustacean. In In the Wrong Place—Alien Marine Crustaceans: Distribution, Biology and Impact; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 489–519. [Google Scholar]
- Corre, V.J. The shrimp farming industry in the Philippines. In Proceedings of the Aquaculture Workshop for SEAFDEC/AQD Training Alumni, Iloilo, Philippines, 8–11 September 1992; pp. 88–103. [Google Scholar]
- Marte, C.L. Milkfish aquaculture in the Philippines: An overview. In Milkfish Aquaculture in Asia; Liao, I.C., Leaño, E.M., Eds.; National Taiwan Ocean University: Keelung City, Taiwan, 2010; pp. 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.Y.; Primavera, J.H.; Dahdouh-Guebas, F.; Mckee, K.; Bosire, J.O.; Cannicci, S.; Diele, K.; Fromard, F.; Koedam, N.; Marchand, C.; et al. Ecological role and services of tropical mangrove ecosystems: A reassessment. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2014, 23, 726–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, O.; Pretell, K.; Ramírez, B.; Sandoval, J.; Caballero, J.L.; Dorado, G. Metagenomic Analyses of Biofilms on Whiteleg Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Effluents: Implications for Worldwide Aquaculture Bioremediation and Environmental Sustainability in the Current Trend of Climate Change and Global Warming—State of the Art and Experimental Proof of Concept. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2021, 29, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, J.V.; Marques, H.L.D.; Pereira, R.T.L.; Barreto, O.J.S.; de Paula, E.J. Cage polyculture of the Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei and the Philippines seaweed Kappaphycus alvarezii. Aquaculture 2006, 258, 412–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primavera, J.H. Overcoming the impacts of aquaculture on the coastal zone. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2006, 49, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, D.C.; Kauffman, J.B.; Murdiyarso, D.; Kurnianto, S.; Stidham, M. Mangroves among the most carbon-rich forests in the tropics. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendleton, L.; Donato, D.C.; Murray, B.C.; Crooks, S.; Jenkins, W.A. Estimating global “blue carbon” emissions from conversion and degradation of vegetated coastal ecosystems. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anticamara, J.A.A.; Go, K.T.B. Impacts of super-typhoon Yolanda on Philippine reefs and communities. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2017, 17, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, D.; Briones, R.M. Impacts of Natural Disasters on Agriculture, Food Security, and Natural Resources and Environment in the Philippines; Philippine Institute for Development Studies: Manila, Philippines, 2012.
- Islam, M.; Yasmin, R. Impact of aquaculture and contemporary environmental issues in Bangladesh. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2017, 5, 100–107. [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein, D.; Künzel, V.; Schäfer, L.; Winges, W. Global Climate Risk Index 2020: Who Suffers Most from Extreme Weather Events? Weather-Related Loss Events in 2018 and 1999 to 2018; Germanwatch: Bonn, Germany, 2020; p. 44. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Summary for policymakers. In Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability; Cambridge Univerisy Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.M.; Islam, N.; Habib, A.; Mozumder, M.M.H. Climate Change Impacts on a Tropical Fishery Ecosystem: Implications and Societal Responses. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.M.; Akber, M.A.; Ahmed, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Rahman, M.R. Climate change adaptations of shrimp farmers: A case study from southwest coastal Bangladesh. Clim. Dev. 2018, 11, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamauag, S.S.; Aliño, P.M.; Martinez, R.J.S.; Muallil, R.N.; Doctor, M.V.A.; Dizon, E.C.; Geronimo, R.C.; Panga, F.M.; Cabral, R.B. A framework for vulnerability assessment of coastal fisheries ecosystems to climate change—Tool for understanding resilience of fisheries (VA–TURF). Fish. Res. 2013, 147, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licuanan, W.R.Y.; Siringan, F.P.; Mamauag, S.S.; Samson, M.S.; Alino, P.M.; Rollon, R.N.; Sta Maria, M.Y.Y.; Quibilan, M.C.C.; Martinez, R.J.S.; España, N.B.; et al. Integrated coastal sensitivity, exposure, and adaptive capacity to climate change. In Vulnerability Assessment Tools for Coastal Ecosystems: A Guidebook; Marine Environment and Resources Foundation, Inc.; Conservation International—Philippines: Quezon City, Philippines, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jacinto, M.R.; Songcuan, A.J.G.; Yip, G.V.; Santos, M.D. Development and application of the fisheries vulnerability assessment tool (FishVool) to tuna and sardine sectors in the Philippines. Fish. Res. 2015, 161, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Chavez, P.D.; Calderon, G.J.A.; Santos, S.B.; Vera Cruz, E.M.; Santos, M.D. Vulnerability to Climate Change of “Giant Squid” (Thysanoteuthis rhombus) Fishery in Marinduque, Philippines. Philipp. J. Fish. 2021, 28, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguila, A.C.M.; Santos, M.D. Fisheries Vulnerability Assessment Tool: FISHVOOL Instruction Manual; National Fisheries Research and Development Institute (NFRDI): Quezon City, Philippines, 2015; p. 29.
- IPCC. Impacts, Adaptation & Vulnerability, Contribution of Working Group II to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; University of Cambridge: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, A.L.; Low, P.J.; Ellis, J.R.; Reynolds, J.D. Climate Change and Distribution Shifts in Marine Fishes. Science 2005, 308, 1912–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulvy, N.K.; Baum, J.K.; Clarke, S.; Compagno, L.J.V.; Cortes, E.; Domingo, A.; Fordham, S.; Fowler, S.; Francis, M.P.; Gibson, C.; et al. You can swim but you can’t hide: The global status and conservation of oceanic pelagic sharks and rays. Aquat. Conserv. 2008, 18, 459–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehodey, P.; Alheit, J.; Barange, M.; Baumgartner, T.; Beaugrand, G.; Drinkwater, K.; Fromentin, J.M.; Hare, S.R.; Ottersen, G.; Perry, R.I.; et al. Climate variability, fish, and fisheries. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 5009–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macusi, E.D.; Abreo, N.A.S.; Cuenca, G.C.; Ranara, C.T.B.; Cardona, L.T.; Andam, M.B.; Guanzon, G.C.; Katikiro, R.E.; Deepananda, K.H.M.A. The potential impacts of climate change on freshwater fish, fish culture and fishing communities. J. Nat. Stud. 2015, 14, 14–31. [Google Scholar]
- Deepananda, K.H.M.A.; Macusi, E.D. The changing climate and its implications to capture fisheries. J. Nat. Stud. 2012, 11, 71–87. [Google Scholar]
- Katikiro, R.E.; Macusi, E.D. Impacts of Climate Change on West African Fisheries and its Implications on Food Production. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2012, 15, 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- O’Reilly, C.M.; Alin, S.R.; Plisnier, P.D.; Cohen, A.S.; McKee, B.A. Climate change decreases aquatic ecosystem productivity of Lake Tanganyika, Africa. Nature 2003, 424, 766–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall-Spencer, J.M.; Rodolfo-Metalpa, R.; Martin, S.; Ransome, E.; Fine, M.; Turner, S.M.; Rowley, S.J.; Tedesco, D.; Buia, M.-C. Volcanic carbon dioxide vents show ecosystem effects of ocean acidification. Nature 2008, 454, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barbier, E.B. Climate change impacts on rural poverty in low-elevation coastal zones. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 165, A1–A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bell, J.D.; Albert, J.; Andréfouët, S.; Andrew, N.L.; Blanc, M.; Bright, P.; Brogan, D.; Campbell, B.; Govan, H.; Hampton, J.; et al. Optimising the use of nearshore fish aggregating devices for food security in the Pacific Islands. Mar. Policy 2015, 56, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosegrant, M.W.; Cline, S.A. Global food security: Challenges and policies. Science 2003, 302, 1917–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lagmay, A.M.F.; Racoma, B.A. Lessons from tropical storms Urduja and Vinta disasters in the Philippines. Disaster Prev. Manag. Int. J. 2018, 28, 154–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagmay, A.M.F.; Agaton, R.P.; Bahala, M.A.C.; Briones, J.B.R.T.; Cabacaba, K.M.C.; Caro, C.V.C.; Dasallas, L.L.; Gonzalo, L.A.L.; Ladiero, C.N.; Lapidez, J.P.; et al. Devastating storm surges of Typhoon Haiyan. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2015, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafferty, K.D.; Porter, J.W.; Ford, S.E. Are diseases increasing in the ocean? Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2004, 35, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovats, R.S.; Hajat, S.; Bouma, M.J.; Worrall, E.; Haines, A. El Nino and health. Lancet 2003, 362, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macandog, D.M.; de la Cruz, C.P.P.; Edrial, J.D.; Reblora, M.A.; Pabico, J.P.; Salvacion, A.R.; Marquez, T., Jr.; Macandog, P.B.M.; Perez, D.K.B. Eliciting Local Ecological Knowledge and Community Perception on Fishkill in Taal Lake through Participatory Approaches. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2014, 17, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vista, A.; Norris, P.; Lupi, F.; Bernsten, R. Nutrient loading and efficiency of tilapia cage culture in Taal Lake, Philippines. Philipp. Agric. Sci. 2006, 89, 48–57. [Google Scholar]
- Bagarinao, T. The decline of native fishes and fisheries and the rise of aquaculture in lakes and rivers in the Philippines. In Proceedings of the 6th Asian Fisheries Forum: Book of Abstracts, Bangkok, Thailand, 25–30 November 2001; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Macusi, E.D.; Estor, D.E.P.; Borazon, E.Q.; Clapano, M.B.; Santos, M.D. Environmental and Socioeconomic Impacts of Shrimp Farming in the Philippines: A Critical Analysis Using PRISMA. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handisyde, N.; Telfer, T.C.; Ross, L.G. Vulnerability of aquaculture-related livelihoods to changing climate at the global scale. Fish Fish. 2017, 18, 466–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayati, I.; Putri, I.A.P.; Ghani, M.W.; Situmorang, A.; Widayatun. Small-scale fishing families and their dailymultiple-stressor on climate change and COVID-19: Preliminary findings. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 739, 012047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-M.; Borazon, E.Q.; Muñoz, K.E. Critical problems associated with climate change: A systematic review and meta-analysis of Philippine fisheries research. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 49425–49433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macusi, E.D.; Macusi, E.S.; Jimenez, L.A.; Catam-isan, J.P. Climate change vulnerability and perceived impacts on small-scale fisheries in eastern Mindanao. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2020, 189, 105143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macusi, E.D.; Kezia, L.; Camaso, K.L.; Barboza, A.; Macusi, E.R. Perceived vulnerability and climate change impacts on small-scale fisheries in Davao gulf, Philippines. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 597385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnier, L.; Gascuel, D.; Alava, J.J.; Barragán, M.J.; Gaibor, N.; Hollander, F.A.; Kanstinger, P.; Niedermueller, S.; Ramírez, J.; Cheung, W.W.L. Small-Scale Fisheries in a Warming Ocean: Exploring Adaptation to Climate Change; WWF Germany: Berlin, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Binh, M.N.; Thuy, N.T.T.; Dan, T.V. Assessment of Impacts of and Adaptation to Climate Change in Fisheries and Agriculture in the Coastal Province of Thua Thien Hue, Vietnam; SEARCA: Los Baños, Philippines, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Galappaththi, E.K.; Ichien, S.T.; Hyman, A.A.; Aubrac, C.J.; Ford, J.D. Climate change adaptation in aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 2160–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Cisneros, K.; Cochrane, K.L.; Rivers, N.; Sauer, W.H.H. Assessing South Africa’s Potential to Address Climate Change Impacts and Adaptation in the Fisheries Sector. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 652955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belton, B.; Rosen, L.; Middleton, L.; Ghazali, S.; Mamun, A.-A.; Shieh, J.; Noronha, H.S.; Dhar, G.; Ilyas, M.; Price, C.; et al. COVID-19 impacts and adaptations in Asia and Africa’s aquatic food value chains. Mar. Policy 2021, 129, 104523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N. Linking prawn and shrimp farming towards a green economy in Bangladesh: Confronting climate change. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2013, 75, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kais, S.M.; Islam, M.S. Impacts of and resilience to climate change at the bottom of the shrimp commodity chain in Bangladesh: A preliminary investigation. Aquaculture 2017, 493, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monirul Islam, M.; Sallu, S.; Hubacek, K.; Paavola, J. Limits and barriers to adaptation to climate variability and change in Bangladeshi coastal fishing communities. Mar. Policy 2014, 43, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adger, W.N. Approaches to Vulnerability to Climate Change; Centre for Social and Economic Research on the Global Environment, University of East Anglia: Norwich, UK; University College London: London, UK, 1995; p. 66. [Google Scholar]
- Corbett, J. Famine and household coping strategies. World Dev. 1988, 16, 1099–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, D.; Pomeroy, R. Projected Economic Impact of Climate Change on Marine Capture Fisheries in the Philippines. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselberg, A.E.; Aakre, I.; Scholtens, J.; Overå, R.; Kolding, J.; Bank, M.S.; Atter, A.; Kjellevold, M. Fish for food and nutrition security in Ghana: Challenges and opportunities. Glob. Food Secur. 2020, 26, 100380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.M.; Lorenzen, K. Livelihood Diversification in Rural Laos. World Dev. 2016, 83, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magombeyi, M.S.; Taigbenu, A.E.; Barron, J. Rural food insecurity and poverty mappings and their linkage with water resources in the Limpopo River Basin. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2016, 92, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béné, C.; Arthur, R.; Norbury, H.; Allison, E.H.; Beveridge, M.; Bush, S.; Campling, L.; Leschen, W.; Little, D.; Squires, D.; et al. Contribution of Fisheries and Aquaculture to Food Security and Poverty Reduction: Assessing the Current Evidence. World Dev. 2016, 79, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Burman, R.R. Chapter 15—Agricultural extension reforms and institutional innovations for inclusive outreach in India. In Agricultural Extension Reforms in South Asia; Babu, S.C., Joshi, P.K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 289–315. [Google Scholar]
- Babu, S.C.; Glendenning, C.J. Chapter 6—Information needs of farmers: A systemic study based on farmer surveys. In Agricultural Extension Reforms in South Asia; Babu, S.C., Joshi, P.K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 101–139. [Google Scholar]
- Pomeroy, R.; Ferrer, A.J.; Pedrajas, J. An analysis of livelihood projects and programs for fishing communities in the Philippines. Mar. Policy 2017, 81, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Pomeroy, R. The impact of community-based fisheries management (CBFM) on equity and sustainability of small-scale coastal fisheries in the Philippines. Mar. Policy 2017, 86, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macusi, E.D.; Liguez, A.K.O.; Macusi, E.S.; Digal, L.N. Factors influencing catch and support for the implementation of the closed fishing season in Davao Gulf, Philippines. Mar. Policy 2021, 130, 104578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macusi, E.D.; Siblos, S.K.V.; Betancourt, M.E.S.; Macusi, E.S.; Calderon, M.N.; Bersaldo, M.J.I.; Digal, L.N. Impacts of COVID-19 on the catch of small-scale fishers and their families due to restriction policies in Davao Gulf, Philippines. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 770543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, S.M.; Moss, D.R.; Arce, S.M.; Lightner, D.V.; Lotz, J.M. The role of selective breeding and biosecurity in the prevention of disease in penaeid shrimp aquaculture. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 110, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; Lavilla-Pitogo, C.; Lopez, M.M.L.; Hao, B. Guidance in Development of Aquaculture Component of a National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance. Asian Fish. Sci. 2020, 33, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Components | Score | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 or 2 | 3 or 4 | 5 | ||
| Mortality rate (S1; compare your harvest 5 years ago) | Low; Very low | Medium; High | Very high | |
| Growth rate (S2; weight of harvest per unit area) | Highly increased; Increased | No change; Decreased | Highly decreased | |
| Water quality of pond (S3) | Low; Very low | Medium; High | Very high | |
| Water temperature (S4) | Very low frequency; Low frequency | Medium frequency; High frequency | Warmed compared 5 yrs ago | |
| Source of pond water (S5) | Silted; Low siltation | Neutral; No siltation | Good quality | |
| Source of fry/post-larvae (S6) | Highly abundant, Abundant | No change; Decreased | Highly decreased | |
| Change in salinity level (S7) | Very low frequency; Low frequency | Medium frequency;High frequency | Salinity has changed compared 5 yrs ago | |
| Shrimp pond exposure in the farm (E1) | Rare occurrence (0–1; 2) | intermediate occurrence (3–4; 5–6) | Frequent occurrence (>6 times a year) | |
| Household site exposure to extreme events (E2) | Rare occurrence (0–1; 2) | intermediate occurrence (3–4; 5–6) | Frequent occurrence (>6 times a year) | |
| Exposure | Community site exposure to extreme events (E3) | Rare occurrence (0–1; 2) | intermediate occurrence (3–4; 5–6) | Frequent occurrence (>6 times a year) |
| Adaptive capacity | Climate change awareness (AC1) | 1; 2 | 3; 4 | 5 |
| Access to information (AC2) | 1; 2 | 3; 4 | 5 | |
| Adaptive strategies (AC3) | 1; 2 | 3; 4 | 5 | |
| Cultural practices modification (AC4) | 1; 2 | 3; 4 | 5 | |
| Climate change support (AC5) | 1; 2 | 3; 4 | 5 | |
| Literacy (AC6) | 1; 2 | 3; 4 | 5 | |
| Potential Impact | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exposure | Sensitivity | |||
| L | M | H | ||
| L | L | L | M | |
| M | L | M | H | |
| H | M | H | H | |
| Vulnerability | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potential Impact | Adaptive Capacity | |||
| L | M | H | ||
| L | M | L | M | |
| M | H | M | L | |
| H | H | H | M | |
| Vulnerability Category | Score |
|---|---|
| Low | 0 to 2 |
| Medium | 2.1 to 4 |
| High | 4.1 to 5 |
| Vulnerability Assessment (VA) Components | Parameters | Score | Average Score | Vulnerability Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity (S) | S1: Mortality rate | 2 | 2.3 | M |
| S2: Growth | 2.9 | |||
| S3: Water quality of pond | 2.2 | |||
| S4: Water temperature | 2.1 | |||
| S5: Source of pond water | 2.5 | |||
| S6: Source of fry | 2.5 | |||
| S7: Change in salinity | 1.7 | |||
| Exposure (E) | E1: Exposure of shrimp ponds to weather disturbances/natural hazard | 1.5 | 1.4 | L |
| E2: Household site assessment | 1.3 | |||
| E3: Community site assessment | 1.3 | |||
| Adaptive Capacity (AC) | AC1: Climate change awareness | 2.5 | 2 | L |
| AC2: Source of information | 1.8 | |||
| AC3: Adaptive strategy | 2.3 | |||
| AC4: Modification of cultural practices | 1.4 | |||
| AC5: Support on climate change organization | 1.5 | |||
| AC6: Literacy | 2.7 |
| Overall Average Assessment Values | ||
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 2.3 | M |
| Exposure | 1.4 | L |
| Adaptive Capacity | 2 | L |
| Site/Market | Vulnerability Index | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | Exposure | Adaptive Capacity | |
| Pantukan | M | L | L |
| Mabini | M | L | L |
| Tagum | M | L | L |
| Maco | M | L | L |
| Lupon | M | L | L |
| Panabo | M | M | L |
| Davao | M | L | L |
| Digos | M | L | L |
| Sta cruz | M | M | L |
| Site/Market | Potential Impact | Vulnerability |
|---|---|---|
| (Sensitivity × Exposure) | (Adaptive Capacity × Potential Impact) | |
| Pantukan | L | M |
| Mabini | L | M |
| Tagum | L | M |
| Maco | L | M |
| Lupon | L | M |
| Panabo | M | H |
| Davao | L | M |
| Digos | L | M |
| Sta cruz | M | H |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Macusi, E.D.; Albarido, N.A.; Clapano, M.B.; Santos, M.D. Vulnerability Assessment of Pacific Whiteleg Shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) Farms and Vendors in Davao, Philippines Using FishVool. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4541. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14084541
Macusi ED, Albarido NA, Clapano MB, Santos MD. Vulnerability Assessment of Pacific Whiteleg Shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) Farms and Vendors in Davao, Philippines Using FishVool. Sustainability. 2022; 14(8):4541. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14084541
Chicago/Turabian StyleMacusi, Edison D., Nitcel Aymie Albarido, Misael B. Clapano, and Mudjekeewis D. Santos. 2022. "Vulnerability Assessment of Pacific Whiteleg Shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) Farms and Vendors in Davao, Philippines Using FishVool" Sustainability 14, no. 8: 4541. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14084541
APA StyleMacusi, E. D., Albarido, N. A., Clapano, M. B., & Santos, M. D. (2022). Vulnerability Assessment of Pacific Whiteleg Shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) Farms and Vendors in Davao, Philippines Using FishVool. Sustainability, 14(8), 4541. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14084541







