Seasonal Abundance and Distribution Patterns of Microplastics in the Lis River, Portugal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area—The Lis River
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Laboratory Procedures
2.3.1. Water
2.3.2. Sediment
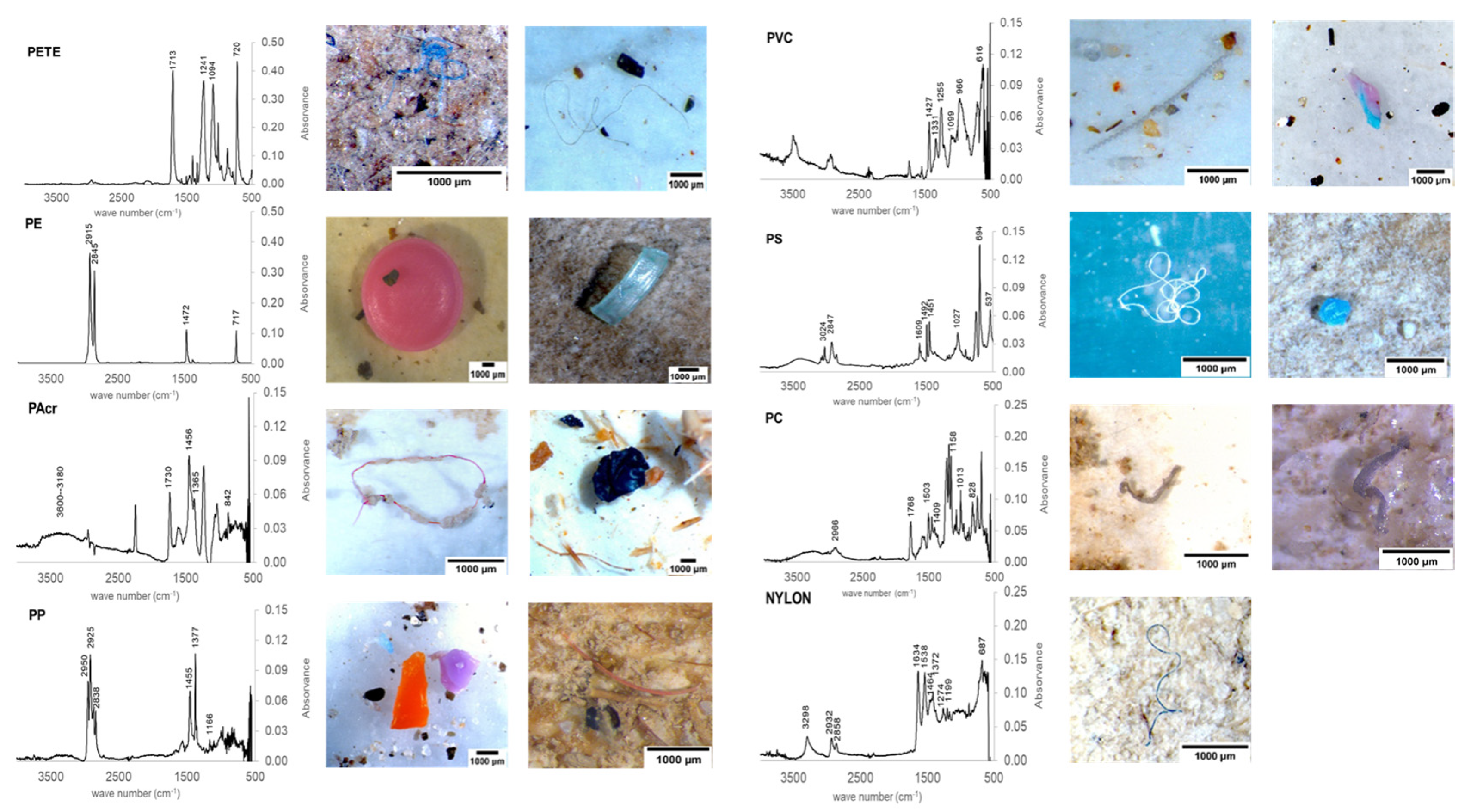
2.4. Microplastics Characterisation
2.5. Polymer Identification
2.6. Contamination Control
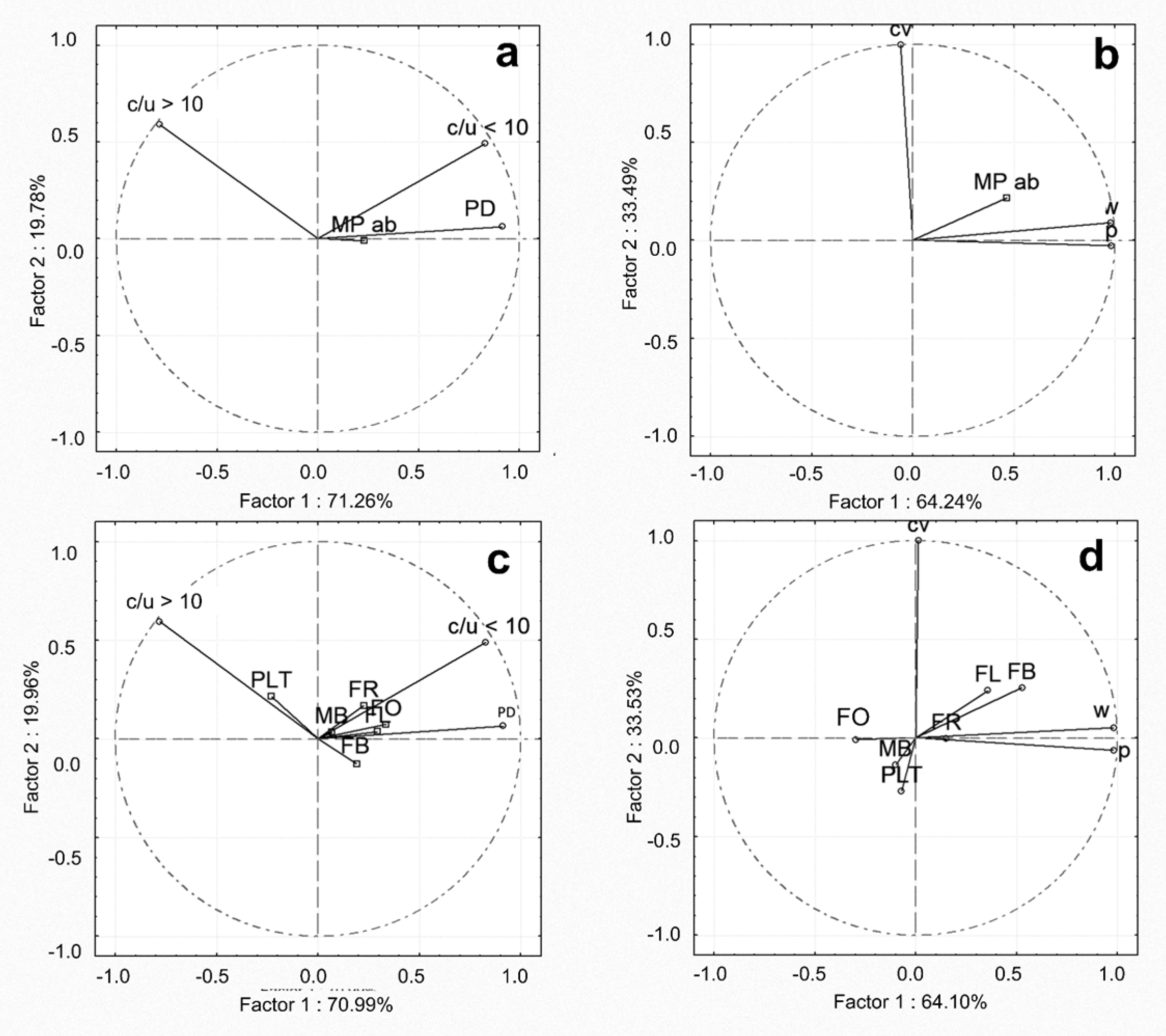
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
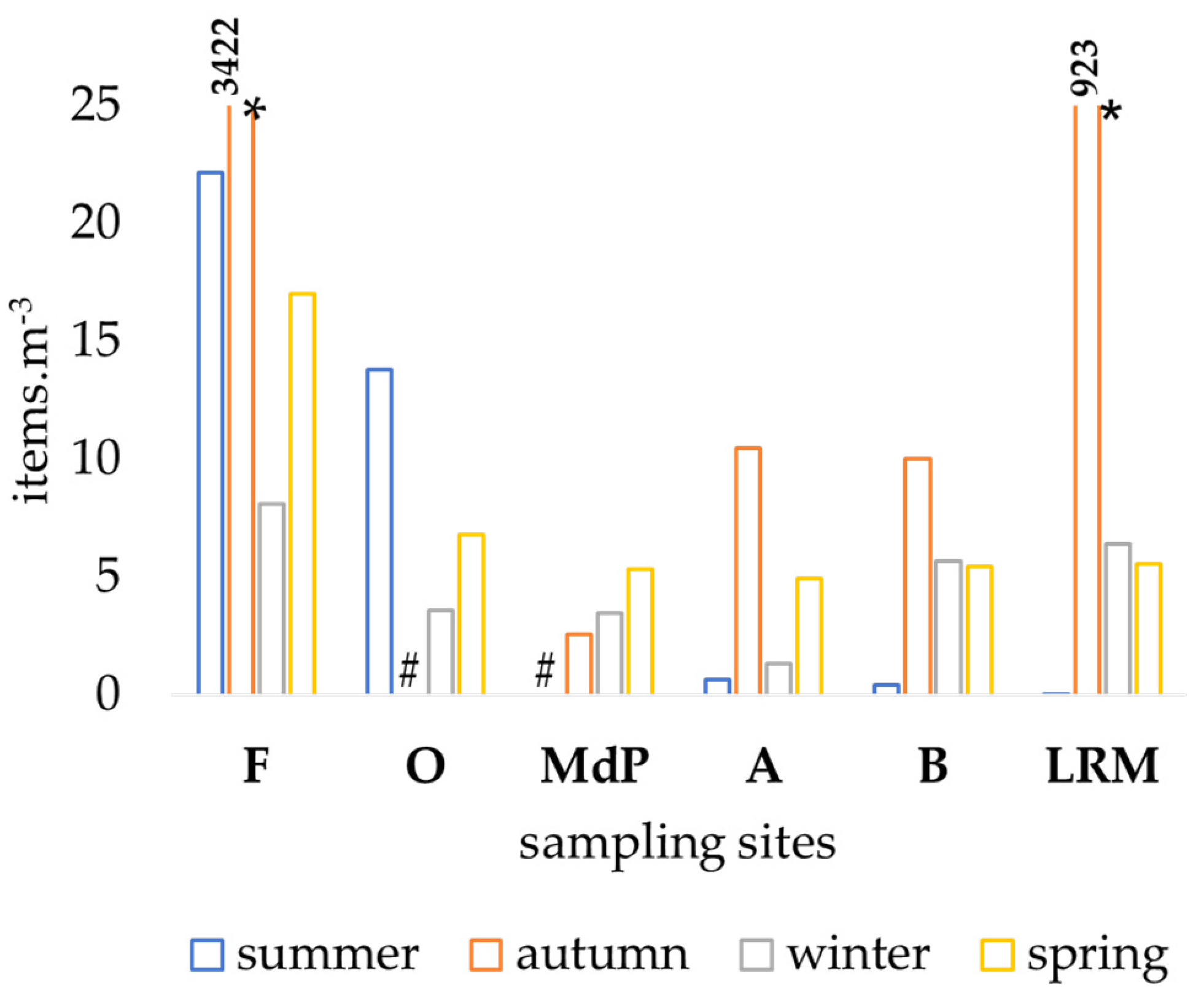
3.1. Microplastics in Water
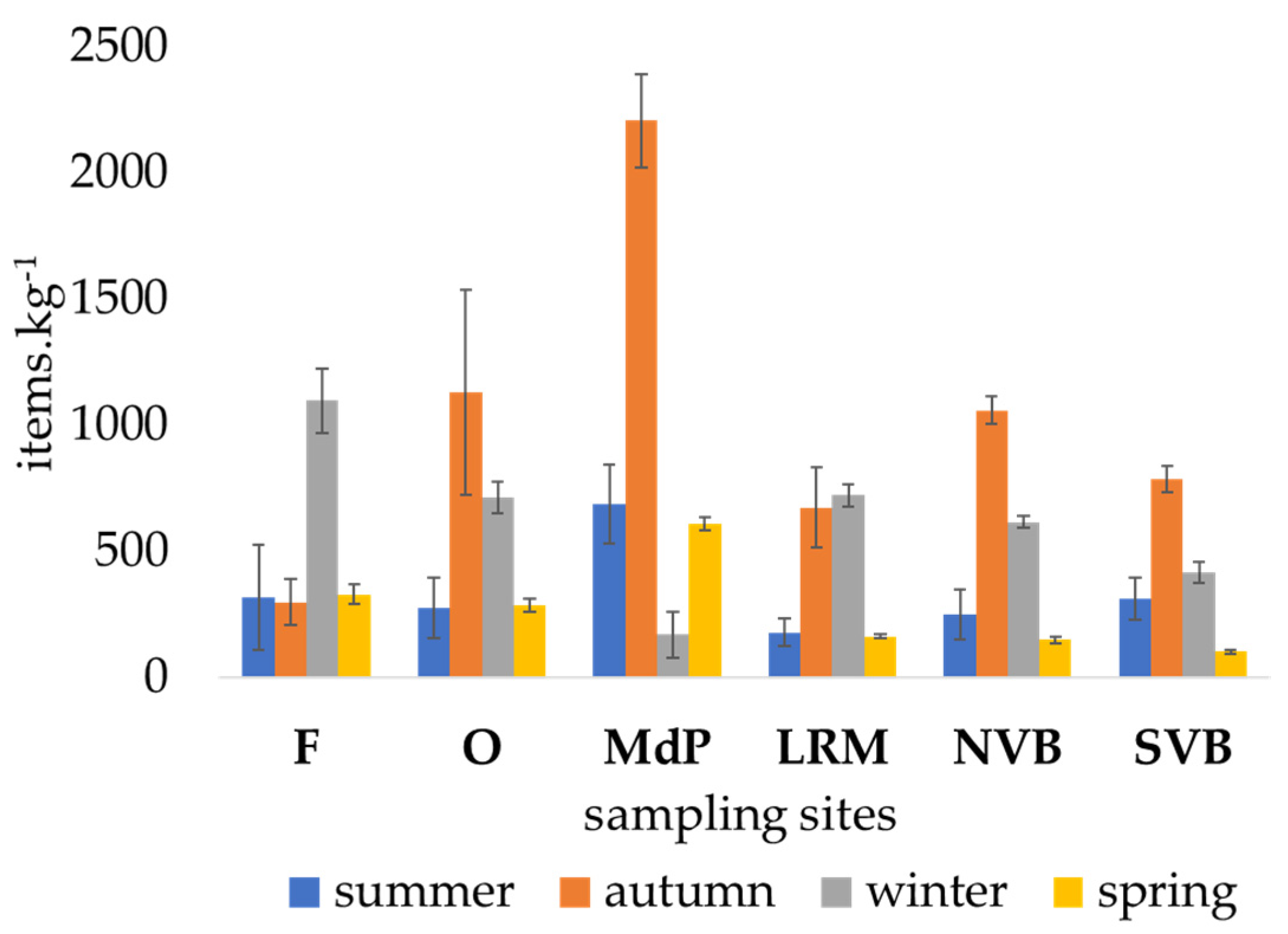
3.2. Microplastics in Sediment
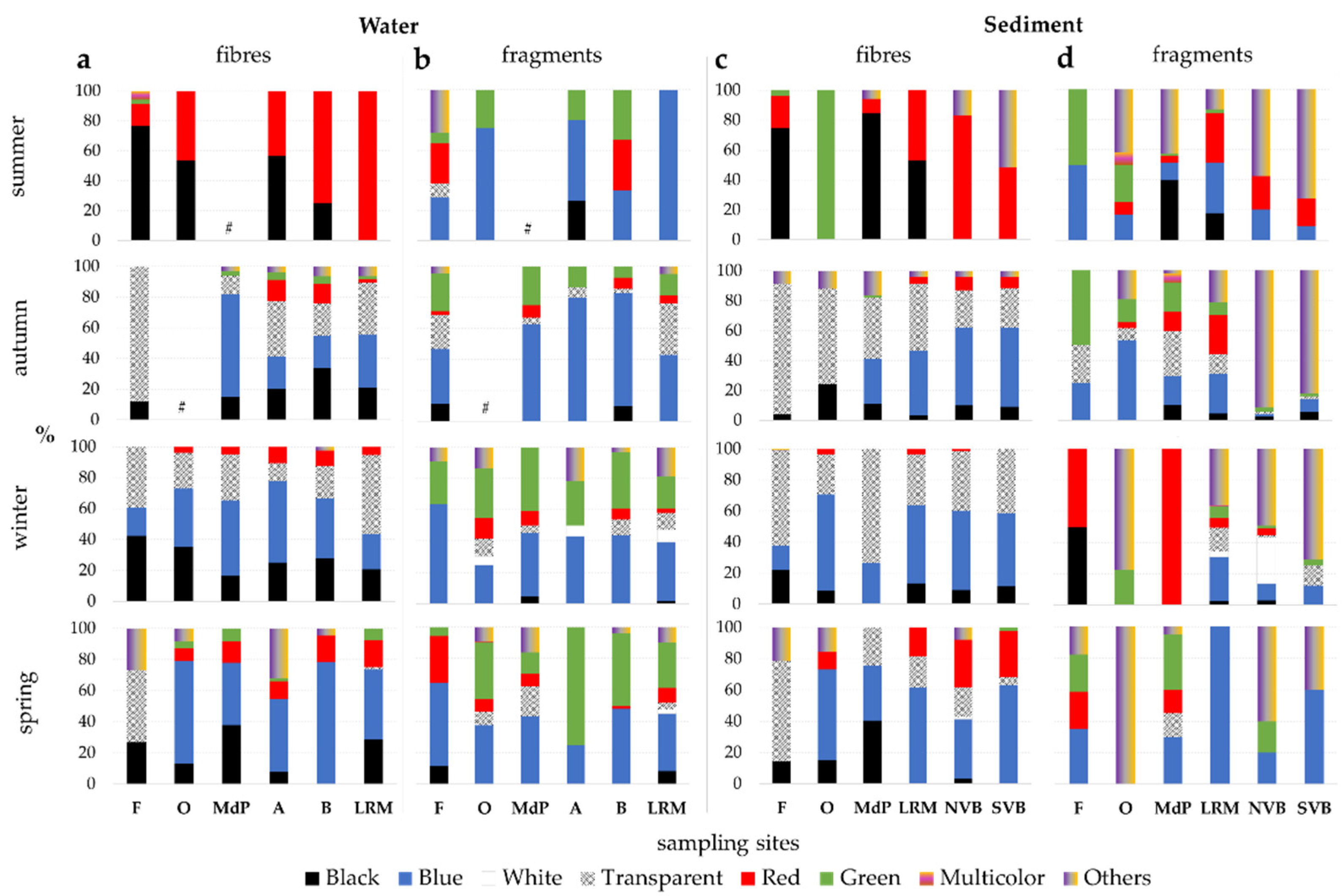
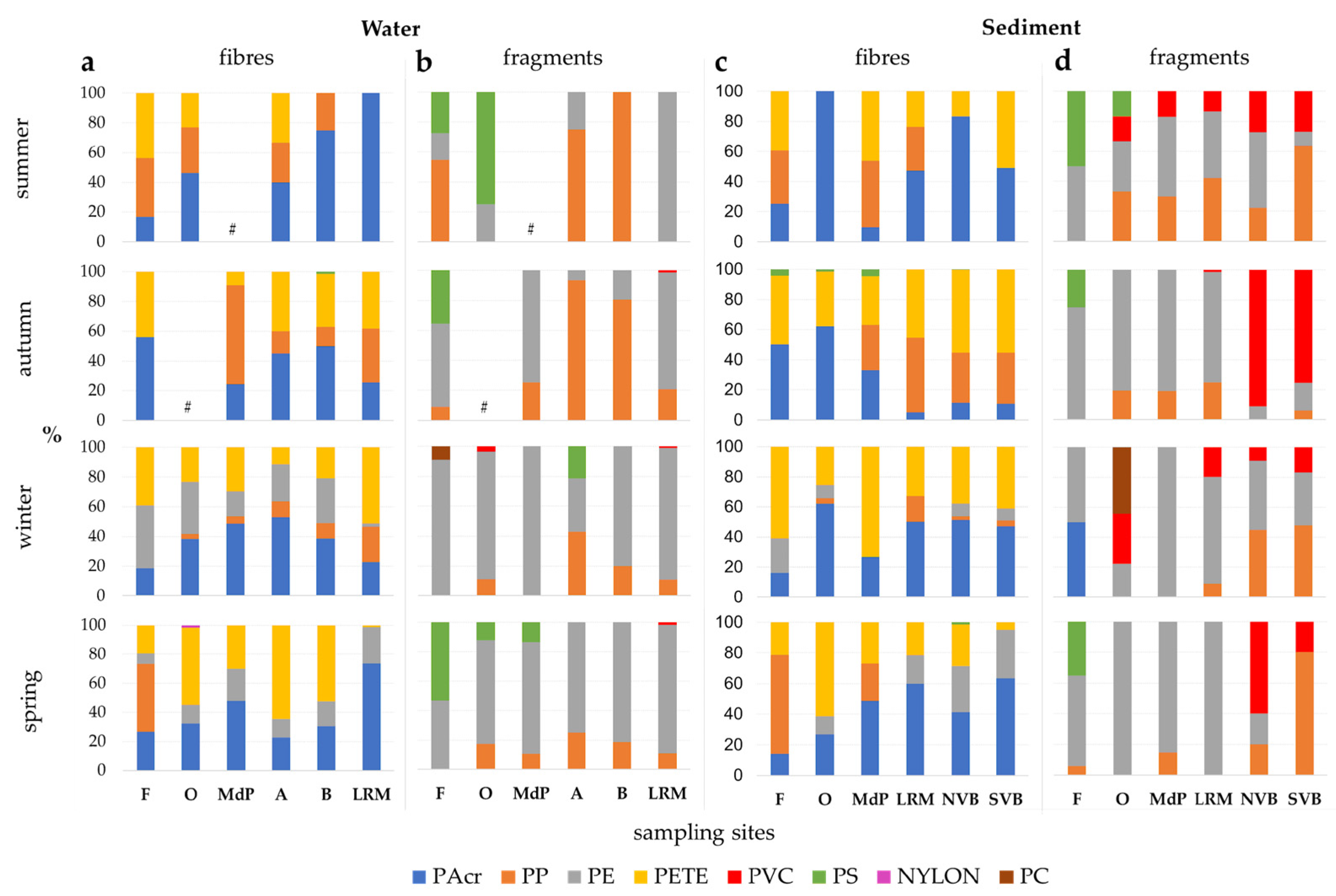
3.3. Microplastics Types
3.4. Microplastics’ Colour and Size
3.5. Microplastics’ Polymer Composition
4. Discussion
4.1. Microplastics’ Spatial and Temporal Abundance in Water and Sediment
4.2. Microplastic Types
4.3. Microplastics’ Colour, Size and Polymer Composition
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barnes, D.K.A.; Galgani, F.; Thompson, R.C.; Barlaz, M. Accumulation and Fragmentation of Plastic Debris in Global Environments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ivleva, N.P.; Wiesheu, A.C.; Niessner, R. Microplastic in Aquatic Ecosystems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 1720–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, A.A.; Walton, A.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E.; Svendsen, C. Microplastics in Freshwater and Terrestrial Environments: Evaluating the Current Understanding to Identify the Knowledge Gaps and Future Research Priorities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- PlasticsEurope. Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/plastics-the-facts-2021/ (accessed on 9 February 2022).
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, Use, and Fate of All Plastics Ever Made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frias, J.P.G.L.; Nash, R. Microplastics: Finding a Consensus on the Definition. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, S.; Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Gao, T.; Sillanpää, M. Atmospheric Microplastics: A Review on Current Status and Perspectives. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 203, 103118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, J.C.; Frias, J.G.L.; Micaelo, A.C.; Sobral, P. Resin Pellets from Beaches of the Portuguese Coast and Adsorbed Persistent Organic Pollutants. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 130, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rillig, M.C. Microplastic in Terrestrial Ecosystems and the Soil? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6453–6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issac, M.N.; Kandasubramanian, B. Effect of Microplastics in Water and Aquatic Systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 19544–19562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooi, M.; van Nes, E.H.; Scheffer, M.; Koelmans, A.A. Ups and Downs in the Ocean: Effects of Biofouling on Vertical Transport of Microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7963–7971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LITTERBASE: Online Portal for Marine Litter. Available online: https://litterbase.awi.de/interaction_graph (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- Espinosa, C.; Esteban, M.Á.; Cuesta, A. Microplastics in Aquatic Environments and Their Toxicological Implications for Fish. In Toxicology–New Aspects to this Scientific Conundrum; Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, M.; Love, D.C.; Rochman, C.M.; Neff, R.A. Microplastics in Seafood and the Implications for Human Health. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Redford, D.P.; Trulli, H.K.; Trulli, W.R. Sources of Plastic Pellets in the Aquatic Environment. Rangel. Syst. 1997, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massos, A.; Turner, A. Cadmium, Lead and Bromine in Beached Microplastics. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayaturrahman, H.; Lee, T.G. A Study on Characteristics of Microplastic in Wastewater of South Korea: Identification, Quantification, and Fate of Microplastics during Treatment Process. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the Marine Environment: A Review of the Methods Used for Identification and Quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Kross, S.M.; Armstrong, J.B.; Bogan, M.T.; Darling, E.S.; Green, S.J.; Smyth, A.R.; Veríssimo, D. Scientific Evidence Supports a Ban on Microbeads. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10759–10761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eerkes-Medrano, D.; Thompson, R.C.; Aldridge, D.C. Microplastics in Freshwater Systems: A Review of the Emerging Threats, Identification of Knowledge Gaps and Prioritisation of Research Needs. Water Res. 2015, 75, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M. A Novel Method for Preparing Microplastic Fibers. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, srep34519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altan, M. Thermoplastic Foams: Processing, Manufacturing, and Characterization. Recent Res. Polym. 2018, 6, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espí, E.; Salmerón, A.; Fontecha, A.; García, Y.; Real, A.I. Plastic Films for Agricultural Applications. J. Plast. Film. Sheeting 2006, 22, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Shi, H.; Fei, Y.; Huang, S.; Tong, Y.; Wen, D.; Luo, Y.; Barceló, D. Microplastics in Agricultural Soils on the Coastal Plain of Hangzhou Bay, East China: Multiple Sources Other than Plastic Mulching Film. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, T.; Burkhardt-Holm, P. Seasonal Microplastics Variation in Nival and Pluvial Stretches of the Rhine River–From the Swiss Catchment towards the North Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.T.; Simmons, S.L. The Degradation of Plastic Litter in Rivers: Implications for Beaches. J. Coast. Conserv. 1996, 2, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löhr, A.; Savelli, H.; Beunen, R.; Kalz, M.; Ragas, A.; van Belleghem, F. Solutions for Global Marine Litter Pollution. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2017, 28, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lebreton, L.C.M.; van der Zwet, J.; Damsteeg, J.W.; Slat, B.; Andrady, A.; Reisser, J. River Plastic Emissions to the World’s Oceans. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Carvalho, A.R.; Garcia, F.; Riem-Galliano, L.; Tudesque, L.; Albignac, M.; ter Halle, A.; Cucherousset, J. Urbanization and Hydrological Conditions Drive the Spatial and Temporal Variability of Microplastic Pollution in the Garonne River. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constant, M.; Ludwig, W.; Kerhervé, P.; Sola, J.; Charrière, B.; Sanchez-Vidal, A.; Canals, M.; Heussner, S. Microplastic Fluxes in a Large and a Small Mediterranean River Catchments: The Têt and the Rhône, Northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 136984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchcock, J.N.; Mitrovic, S.M. Microplastic Pollution in Estuaries across a Gradient of Human Impact. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; Godoy, V.; da Costa, J.P.; Calero, M.; Martín-Lara, M.A.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Microplastics and Fibers from Three Areas under Different Anthropogenic Pressures in Douro River. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.O.; Abrantes, N.; Gonçalves, F.J.M.; Nogueira, H.; Marques, J.C.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Microplastics in Water and Sediments of a Freshwater System (Antuã River, Portugal). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augspurger, C.; Karwautz, C.; Mußmann, M.; Daims, H.; Battin, T.J. Drivers of Bacterial Colonization Patterns in Stream Biofilms. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 72, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rummel, C.D.; Jahnke, A.; Gorokhova, E.; Kühnel, D.; Schmitt-Jansen, M. Impacts of Biofilm Formation on the Fate and Potential Effects of Microplastic in the Aquatic Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia, F.; de Carvalho, A.R.; Riem-Galliano, L.; Tudesque, L.; Albignac, M.; ter Halle, A.; Cucherousset, J. Stable Isotope Insights into Microplastic Contamination within Freshwater Food Webs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zou, X.; Li, B.; Yao, Y.; Zang, Z.; Li, Y.; Yu, W.; Wang, W. Preliminary Study of the Source Apportionment and Diversity of Microplastics: Taking Floating Microplastics in the South China Sea as an Example. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, F.; Gasperi, J.; Gabrielsen, G.W.; Tassin, B. Plastic Particle Ingestion by Wild Freshwater Fish: A Critical Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12974–12988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, J.; Fonseca, A.; Vilar, V.J.P.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Botelho, C.M.S. Water Quality in Lis River, Portugal. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 7125–7140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, L.J.J.; van Emmerik, T.; van der Ent, R.; Schmidt, C.; Lebreton, L. More than 1000 Rivers Account for 80% of Global Riverine Plastic Emissions into the Ocean. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eaaz5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portal Do INE. Available online: https://www.ine.pt/xportal/xmain?xpgid=ine_main&xpid=INE (accessed on 9 January 2021).
- Gago, J.; Filgueiras, A.; Pedrotti, M.L.; Caetano, M.; Frias, J. Standardised Protocol for Monitoring Microplastics in Seawater. Deliverable 4.1. JPI-Oceans BASEMANproject. 2018, p. 32. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/330931801_Standardised_protocol_for_monitoring_microplastics_in_seawater?channel=doi&linkId=5c5c2491a6fdccb608aefbf9&showFulltext=true (accessed on 14 January 2022).
- Frias, J.; Pagter, E.; Nash, R.; O’Connor, I.; Carretero, O.; Filgueiras, A.; Viñas, L.; Gago, J.; Antunes, J.; Bessa, F.; et al. Standardised Protocol for Monitoring Microplastics in Sediments. Deliverable 4.2. JPI-Oceans BASEMANproject. 2018, p. 24. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326552185_Standardised_protocol_for_monitoring_microplastics_in_sediments?channel=doi&linkId=5b572280aca27217ffb7ccb2&showFulltext=true (accessed on 14 January 2022).
- Coppock, R.L.; Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.K.; Queirós, A.M.; Galloway, T.S. A Small-Scale, Portable Method for Extracting Microplastics from Marine Sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Primpke, S.; Wirth, M.; Lorenz, C.; Gerdts, G. Reference Database Design for the Automated Analysis of Microplastic Samples Based on Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5131–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, M.R.; Horgen, F.D.; Orski, S.V.; Rodriguez, C.V.; Beers, K.L.; Balazs, G.H.; Jones, T.T.; Work, T.M.; Brignac, K.C.; Royer, S.J.; et al. Validation of ATR FT-IR to Identify Polymers of Plastic Marine Debris, Including Those Ingested by Marine Organisms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marković, G.; Marinović-Cincović, M.; Vodnik, V.; Radovanović, B.; Budinski-Simendić, J.; Veljković, O. Thermal Stability of Acrylonitrile/Chlorosulphonated Polyethylene Rubber Blend. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2009, 97, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Kobayashi, Y.; Hirata, K.; Miura, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Iwaki, M.; Oka, T.; Hama, Y. Three-Group Type Mechanism in the Curing Behavior of Polyacrylate and Blocked Toluene Diisocyanate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 83, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera. Available online: https://www.ipma.pt/en/index.html (accessed on 10 January 2021).
- He, P.; Chen, L.; Shao, L.; Zhang, H.; Lü, F. Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) Landfill: A Source of Microplastics?-Evidence of Microplastics in Landfill Leachate. Water Res. 2019, 159, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitchcock, J.N. Storm Events as Key Moments of Microplastic Contamination in Aquatic Ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, A.A.; Svendsen, C.; Williams, R.J.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E. Large Microplastic Particles in Sediments of Tributaries of the River Thames, UK–Abundance, Sources and Methods for Effective Quantification. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sekudewicz, I.; Dąbrowska, A.M.; Syczewski, M.D. Microplastic Pollution in Surface Water and Sediments in the Urban Section of the Vistula River (Poland). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nizzetto, L.; Bussi, G.; Futter, M.N.; Butterfield, D.; Whitehead, P.G. A Theoretical Assessment of Microplastic Transport in River Catchments and Their Retention by Soils and River Sediments. Environ. Sci. Processes Impacts 2016, 18, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, A.K.; Corsi, S.R.; Mason, S.A. Plastic Debris in 29 Great Lakes Tributaries: Relations to Watershed Attributes and Hydrology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10377–10385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, A.; Keckeis, H.; Lumesberger-Loisl, F.; Zens, B.; Krusch, R.; Tritthart, M.; Glas, M.; Schludermann, E. The Danube so Colourful: A Potpourri of Plastic Litter Outnumbers Fish Larvae in Europe’s Second Largest River. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 188, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schell, T.; Hurley, R.; Nizzetto, L.; Rico, A.; Vighi, M. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Microplastics in a Mediterranean River Catchment: The Importance of Wastewater as an Environmental Pathway. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Goonetilleke, A.; Ayoko, G.A.; Rintoul, L. Abundance, Distribution Patterns, and Identification of Microplastics in Brisbane River Sediments, Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.; Worch, E.; Knepper, T.P. Occurrence and Spatial Distribution of Microplastics in River Shore Sediments of the Rhine-Main Area in Germany. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6070–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonkos, L.T.; Friedel, E.A.; Perez-Reyes, A.C.; Ghosal, S.; Arthur, C.D. Microplastics in Four Estuarine Rivers in the Chesapeake Bay, U.S.A. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 14195–14202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Saad, M.; Mirande, C.; Tassin, B. Synthetic Fibers in Atmospheric Fallout: A Source of Microplastics in the Environment? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 104, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, H.; Peng, G.; Xu, P.; Li, D. Coastal Ocean Dynamics Reduce the Export of Microplastics to the Open Ocean. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balthazar-Silva, D.; Turra, A.; Moreira, F.T.; Camargo, R.M.; Oliveira, A.L.; Barbosa, L.; Gorman, D. Rainfall and Tidal Cycle Regulate Seasonal Inputs of Microplastic Pellets to Sandy Beaches. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Sánchez, L.; Grelaud, M.; Garcia-Orellana, J.; Ziveri, P. River Deltas as Hotspots of Microplastic Accumulation: The Case Study of the Ebro River (NW Mediterranean). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 1186–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhu, L.; Li, D. Microplastic in Three Urban Estuaries, China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edo, C.; González-Pleiter, M.; Leganés, F.; Fernández-Piñas, F.; Rosal, R. Fate of Microplastics in Wastewater Treatment Plants and Their Environmental Dispersion with Effluent and Sludge. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Crump, P.; Niven, S.J.; Teuten, E.; Tonkin, A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Accumulation of Microplastic on Shorelines Woldwide: Sources and Sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9175–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, F.; Hubbart, J.A. The Occurrence and Transport of Microplastics: The State of the Science. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, S.A.; Garneau, D.; Sutton, R.; Chu, Y.; Ehmann, K.; Barnes, J.; Fink, P.; Papazissimos, D.; Rogers, D.L. Microplastic Pollution Is Widely Detected in US Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluent. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfei, S.; Schito, A.M.; Zuccari, G. Biodegradable and Compostable Shopping Bags under Investigation by Ftir Spectroscopy. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horodytska, O.; Valdés, F.J.; Fullana, A. Plastic Flexible Films Waste Management–A State of Art Review. Waste Manag. 2018, 77, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhani, Z.; Lei, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhang, X.; Naidu, R.; Megharaj, M.; Fang, C. Microplastics Generated When Opening Plastic Packaging. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vox, G.; Loisi, R.V.; Blanco, I.; Mugnozza, G.S.; Schettini, E. Mapping of Agriculture Plastic Waste. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2016, 8, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Nor, N.H.M.; Hermsen, E.; Kooi, M.; Mintenig, S.M.; de France, J. Microplastics in Freshwaters and Drinking Water: Critical Review and Assessment of Data Quality. Water Res. 2019, 155, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Sharma, P.; Manna, C.; Jain, M. Abundance, Interaction, Ingestion, Ecological Concerns, and Mitigation Policies of Microplastic Pollution in Riverine Ecosystem: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Plastics and Microplastics in the Oceans: From Emerging Pollutants to Emerged Threat. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 128, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Villiers, S. Microfibre Pollution Hotspots in River Sediments Adjacent to South Africa’s Coastline. Water SA 2019, 45, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Rocher, V.; Tassin, B. Synthetic and Non-Synthetic Anthropogenic Fibers in a River under the Impact of Paris Megacity: Sampling Methodological Aspects and Flux Estimations. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nayak, R.; Kanesalingam, S.; Houshyar, S.; Wang, L.; Padhye, R.; Vijayan, A. Evaluation of Thermal, Moisture Management and Sensorial Comfort Properties of Superabsorbent Polyacrylate Fabrics for the next-to-Skin Layer in Firefighters’ Protective Clothing. Text. Res. J. 2017, 88, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghsiahi, H.; Wang, K.; Selviah, D.R. Optical Loss and Crosstalk in Multimode Photolithographically Fabricated Polyacrylate Polymer Waveguide Crossings. Integr. Opt. Devices Mater. Technol. XVIII 2014, 8988, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Faassen, A.; Borm, P.J.A. Composition and Health Hazards of Water-Based Construction Paints: Results from a Survey in the Netherlands. Environ. Health Perspect. 1991, 92, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, V.D.; Patil, A.J.; Kandasubramanian, B. Polycarbonate Nanocomposites for High Impact Applications. In Handbook of Consumer Nanoproducts; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2021; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkanorachaki, K.; Kiparissis, S.; Kalogerakis, G.C.; Yiantzi, E.; Psillakis, E.; Kalogerakis, N. Plastic Pellets, Meso- and Microplastics on the Coastline of Northern Crete: Distribution and Organic Pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.; Wallerstein, C.; Arnold, R. Identification, Origin and Characteristics of Bio-Bead Microplastics from Beaches in Western Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cózar, A.; Echevarría, F.; González-Gordillo, J.I.; Irigoien, X.; Úbeda, B.; Hernández-León, S.; Palma, Á.T.; Navarro, S.; García-de-Lomas, J.; Ruiz, A.; et al. Plastic Debris in the Open Ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10239–10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isobe, A.; Uchida, K.; Tokai, T.; Iwasaki, S. East Asian Seas: A Hot Spot of Pelagic Microplastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvim, C.B.; Mendoza-Roca, J.A.; Bes-Piá, A. Wastewater Treatment Plant as Microplastics Release Source–Quantification and Identification Techniques. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 255, 109739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, K.; Clum, A.; Deepe, J.; Lane, H.; Beckingham, B. Wastewater Treatment Plants as a Source of Microplastics to an Urban Estuary: Removal Efficiencies and Loading per Capita over One Year. Water Res. X 2019, 3, 100030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estahbanati, S.; Fahrenfeld, N.L. Influence of Wastewater Treatment Plant Discharges on Microplastic Concentrations in Surface Water. Chemosphere 2016, 162, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
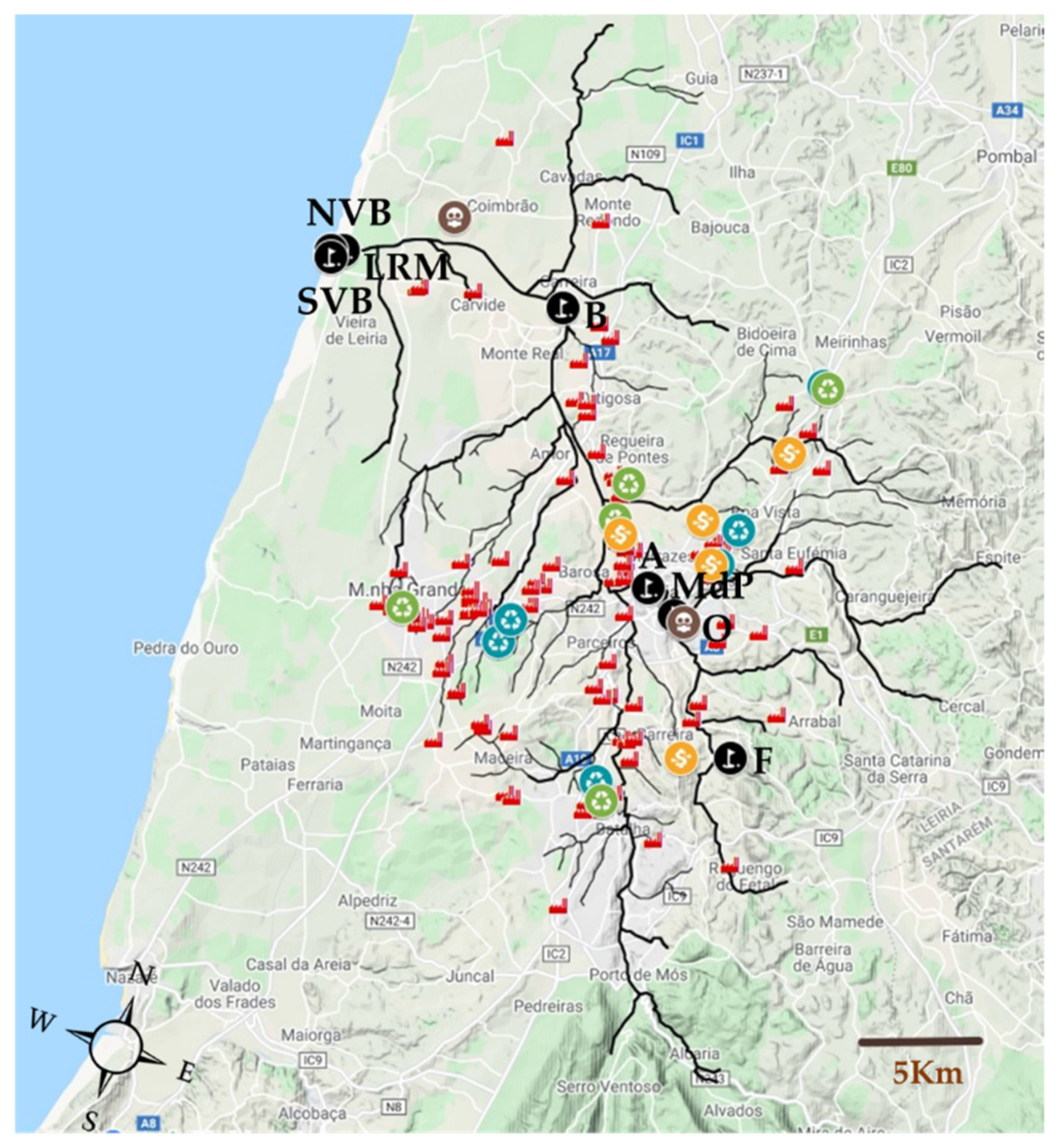
 (Fontes—F, Olhalvas—O, Moinho de Papel—MdP, Arrabalde—A, Bóia—B, Lis River mouth—LRM, North Vieira Beach—NVB and South Vieira Beach—SVB) and potential contributors of MP to the Lis River (plastic products manufacturers
(Fontes—F, Olhalvas—O, Moinho de Papel—MdP, Arrabalde—A, Bóia—B, Lis River mouth—LRM, North Vieira Beach—NVB and South Vieira Beach—SVB) and potential contributors of MP to the Lis River (plastic products manufacturers  and suppliers
and suppliers  , recycling units
, recycling units  , solid waste management
, solid waste management  and wastewater treatment plant—WWTP
and wastewater treatment plant—WWTP  ).
).
 (Fontes—F, Olhalvas—O, Moinho de Papel—MdP, Arrabalde—A, Bóia—B, Lis River mouth—LRM, North Vieira Beach—NVB and South Vieira Beach—SVB) and potential contributors of MP to the Lis River (plastic products manufacturers
(Fontes—F, Olhalvas—O, Moinho de Papel—MdP, Arrabalde—A, Bóia—B, Lis River mouth—LRM, North Vieira Beach—NVB and South Vieira Beach—SVB) and potential contributors of MP to the Lis River (plastic products manufacturers  and suppliers
and suppliers  , recycling units
, recycling units  , solid waste management
, solid waste management  and wastewater treatment plant—WWTP
and wastewater treatment plant—WWTP  ).
).

| Sites | Coordinates | Population Density (hab.km−2) | Characterisation and Potential Contributors | No of Potential Contributors < 10 km from Site | No of Potential Contributors > 10 km from Site | Type of Sample |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fontes (F) | 39°41′07.7″ N 8°46′15.9″ W | 179.3 | Closest to headwaters; Local village; Family farms; Washing clothes in the river; No plastic units upstream | 0 | 0 | water and sediment |
| Olhalvas (O) | 39°44′17.0″ N 8°47′44.3″ W | 566.6 | Next to WWTP (1); Plastic manufacturers (9); Plastic suppliers (1) | 11 | 0 | water and sediment |
| Moinho de Papel (MdP) | 39°44′25.9″ N 8°47′58.7″ W | 224.6 | Urban zone; Plastic manufacturers (9); Plastic suppliers (1); Solid waste management (1); WWTP (1) | 11 | 1 | water and sediment |
| Arrabalde (A) | 39°45′04.5″ N 8°48′44.4″ W | 1177.6 | Urban zone; Plastic manufacturers (10); Plastic suppliers (1); Solid waste management (1); WWTP (1) | 11 | 2 | water |
| Bóia (B) | 39°51′43.8″ N 8°51′45.8″ W | 210.5 | Intensive agriculture zone; Plastic manufacturers (82); Plastic suppliers (6); Recycling units (4); Solid waste management (6); WWTP (1) | 6 | 93 | water |
| Lis River mouth (LRM) | 39°52′49.6″ N 8°57′47.9″ W | 137.5 | River mouth; Pine forest of Leiria; Plastic manufacturers (87); Plastic suppliers (6); Recycling units (4); Solid waste management (6); WWTP (2) | 4 | 101 | water and sediment |
| North Vieira Beach (NVB) | 39°52′52.9″ N 8°58′11.4″ W | 137.5 | Beach; River’s disemboguement; Plastic manufacturers (87); Plastic suppliers (6); Recycling units (4); Solid waste management (6); WWTP (2) | 4 | 101 | sediment |
| South Vieira Beach (SVB) | 39°52′41.2″ N 8°58′14.3″ W | 137.5 | Beach; River’s disemboguement; Plastic manufacturers (87); Plastic suppliers (6); Recycling units (4); Solid waste management (6); WWTP (2) | 4 | 101 | sediment |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sá, B.; Pais, J.; Antunes, J.; Pequeno, J.; Pires, A.; Sobral, P. Seasonal Abundance and Distribution Patterns of Microplastics in the Lis River, Portugal. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14042255
Sá B, Pais J, Antunes J, Pequeno J, Pires A, Sobral P. Seasonal Abundance and Distribution Patterns of Microplastics in the Lis River, Portugal. Sustainability. 2022; 14(4):2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14042255
Chicago/Turabian StyleSá, Bárbara, Joana Pais, Joana Antunes, João Pequeno, Ana Pires, and Paula Sobral. 2022. "Seasonal Abundance and Distribution Patterns of Microplastics in the Lis River, Portugal" Sustainability 14, no. 4: 2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14042255
APA StyleSá, B., Pais, J., Antunes, J., Pequeno, J., Pires, A., & Sobral, P. (2022). Seasonal Abundance and Distribution Patterns of Microplastics in the Lis River, Portugal. Sustainability, 14(4), 2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14042255








