A Modified Multi-Level Inverter System for Grid-Tied DES Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
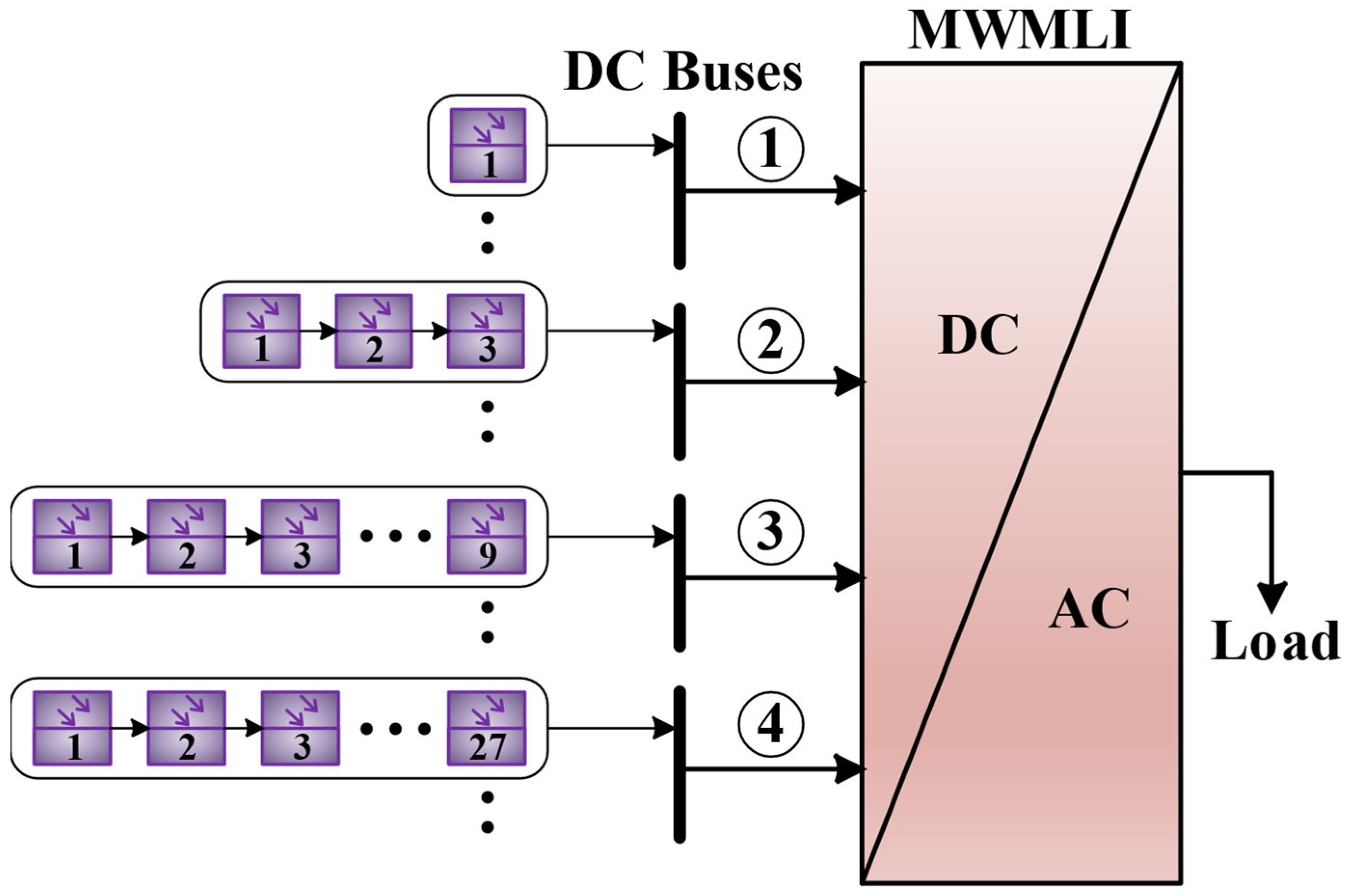
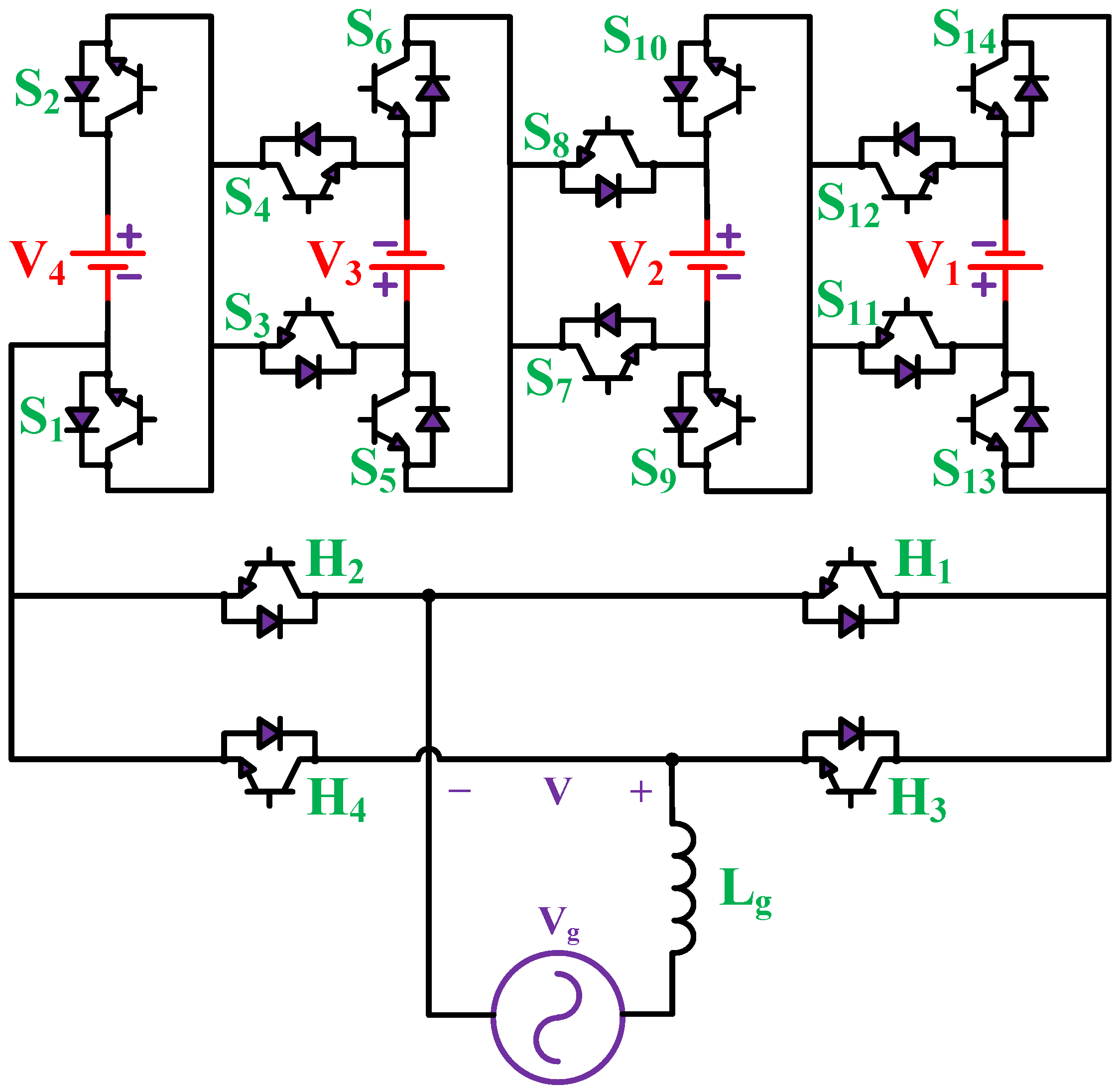
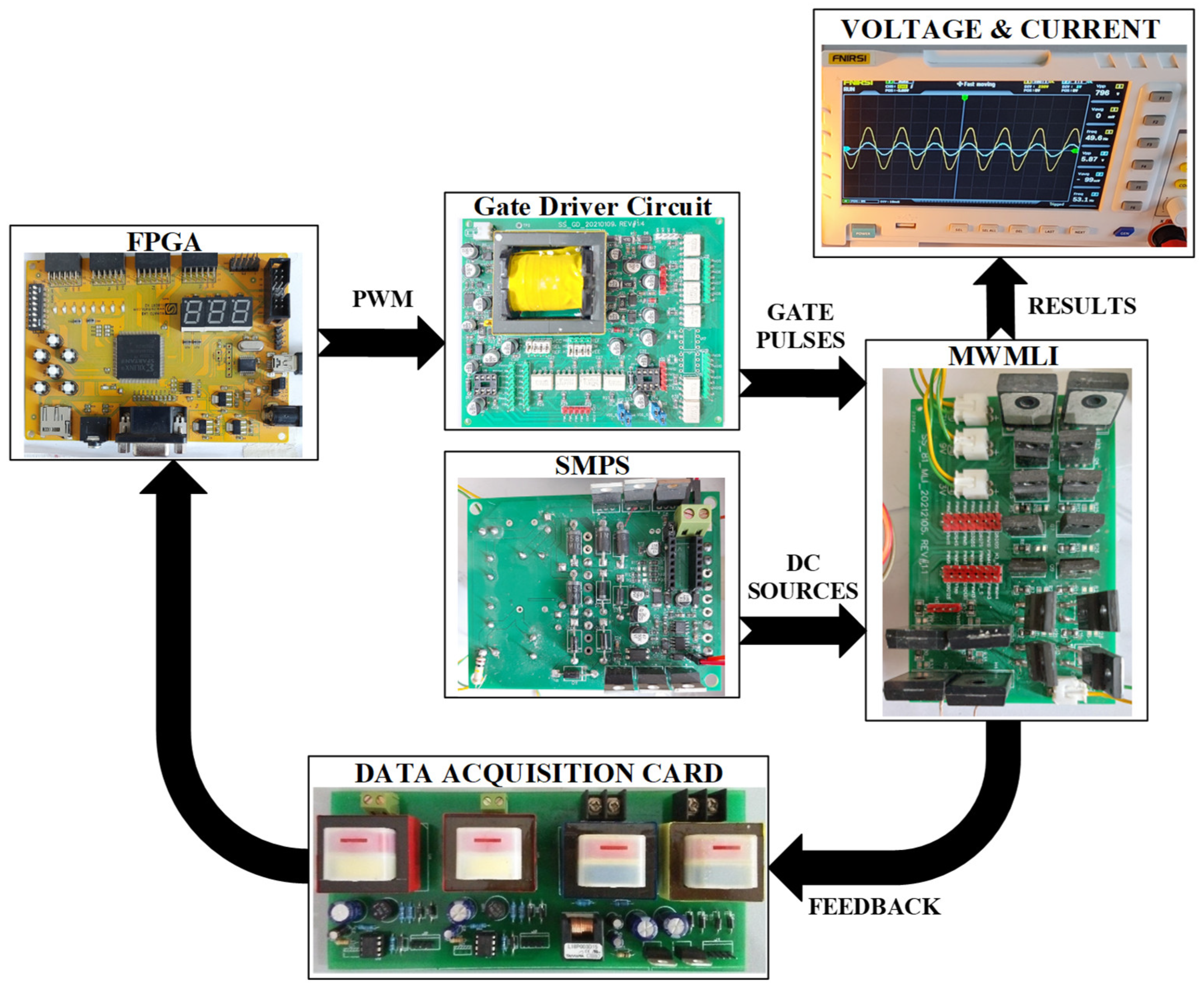
2. Proposed MWMLI Topology
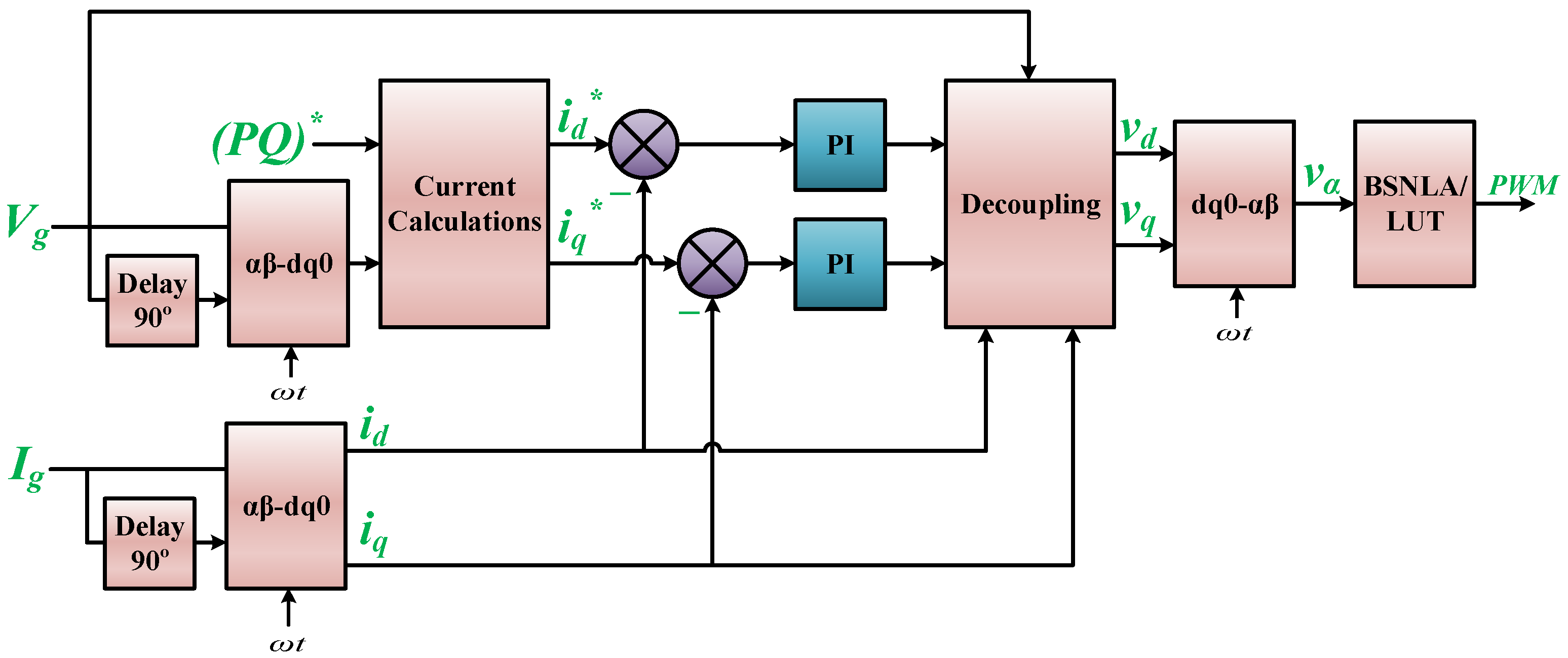
3. Controller Implementation
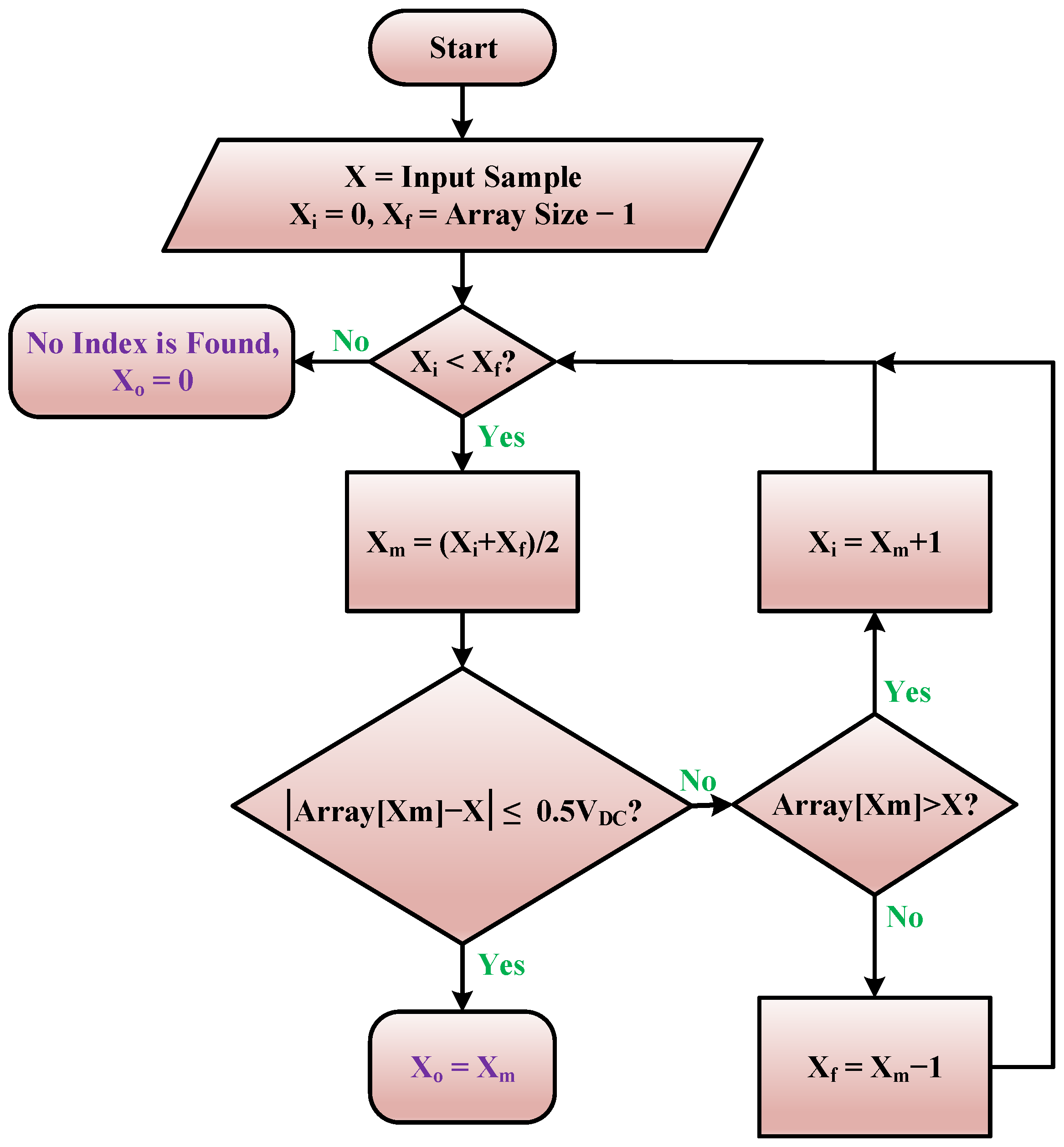
Binary Search Nearest Level Algorithm
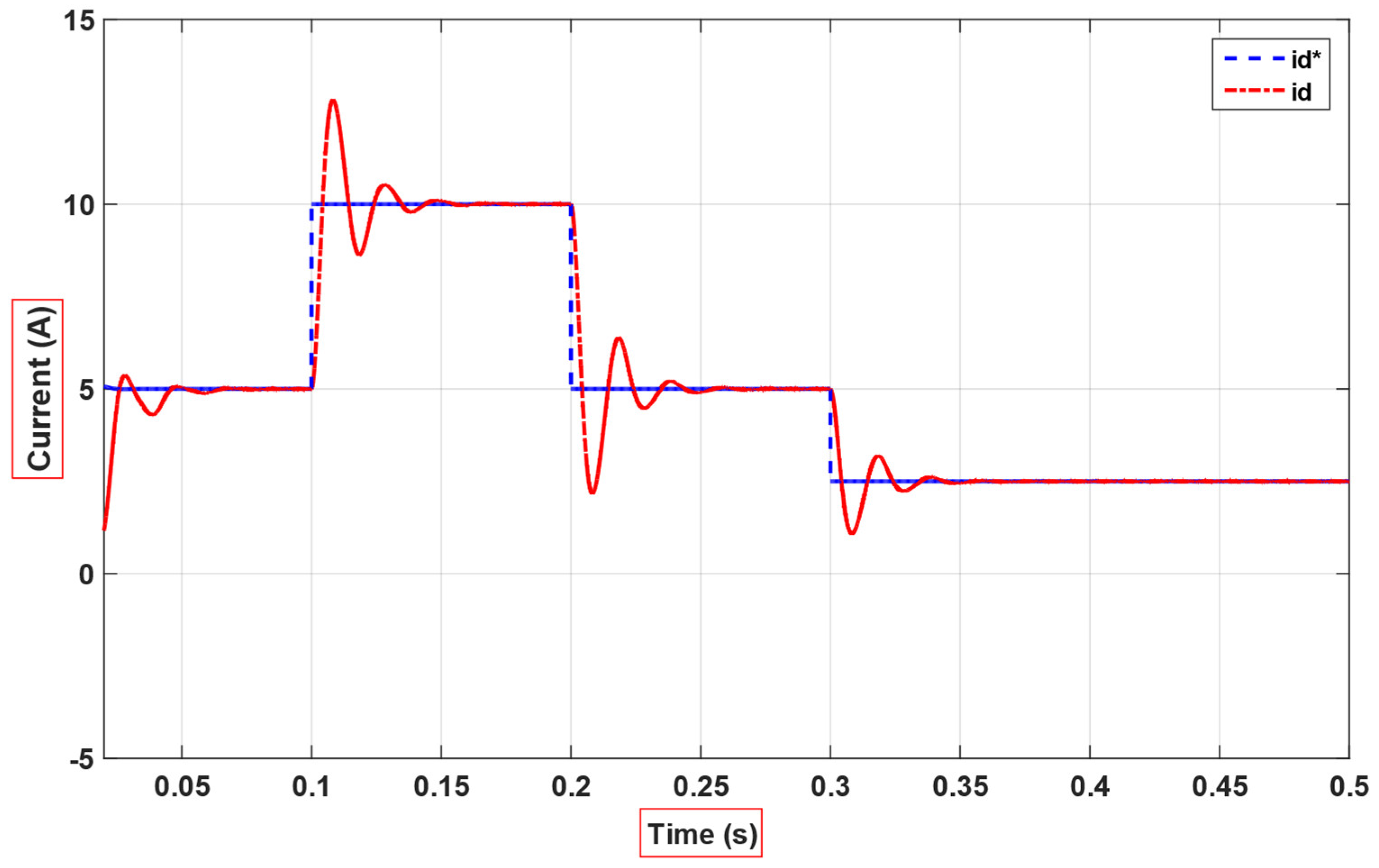
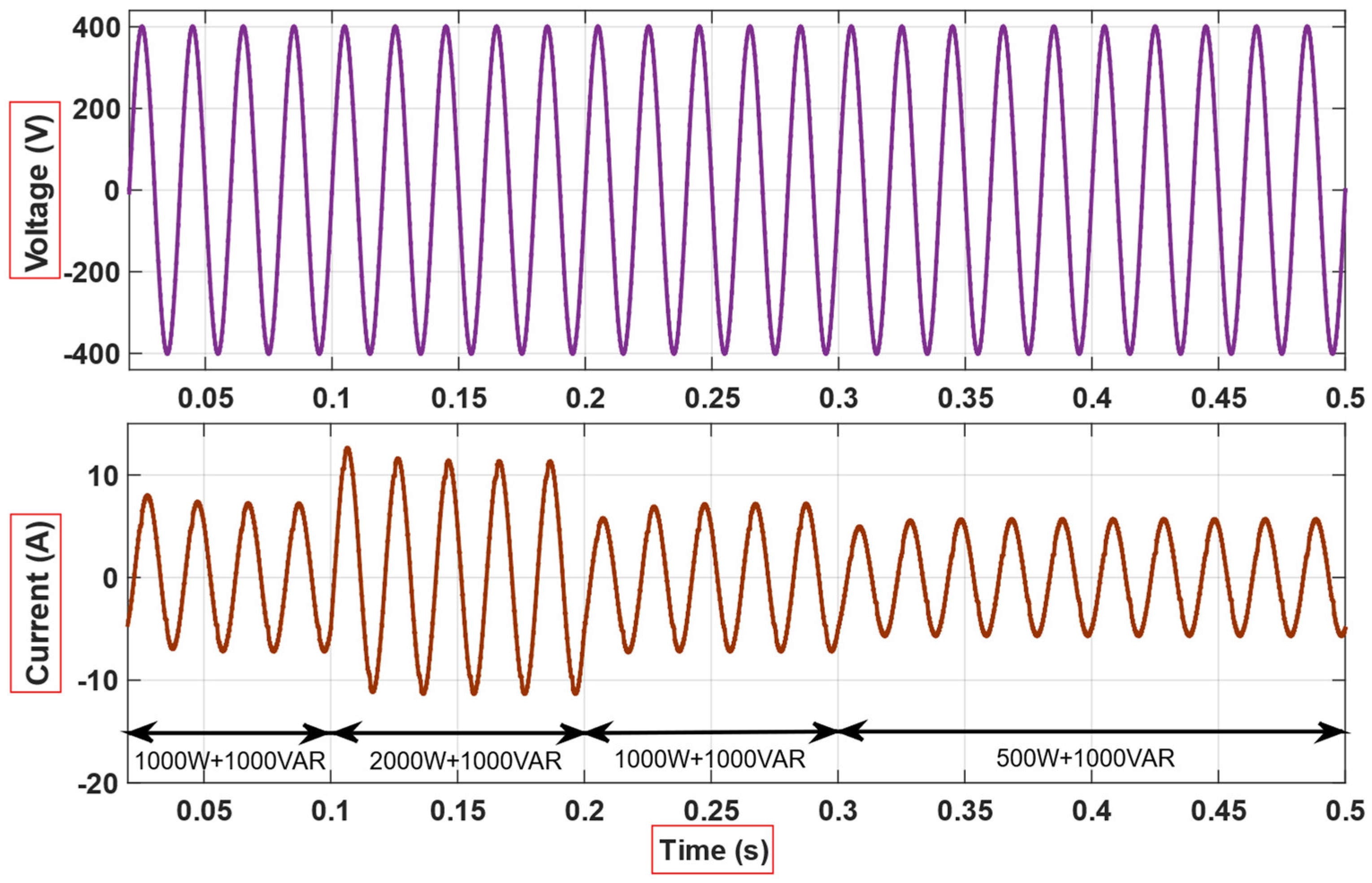
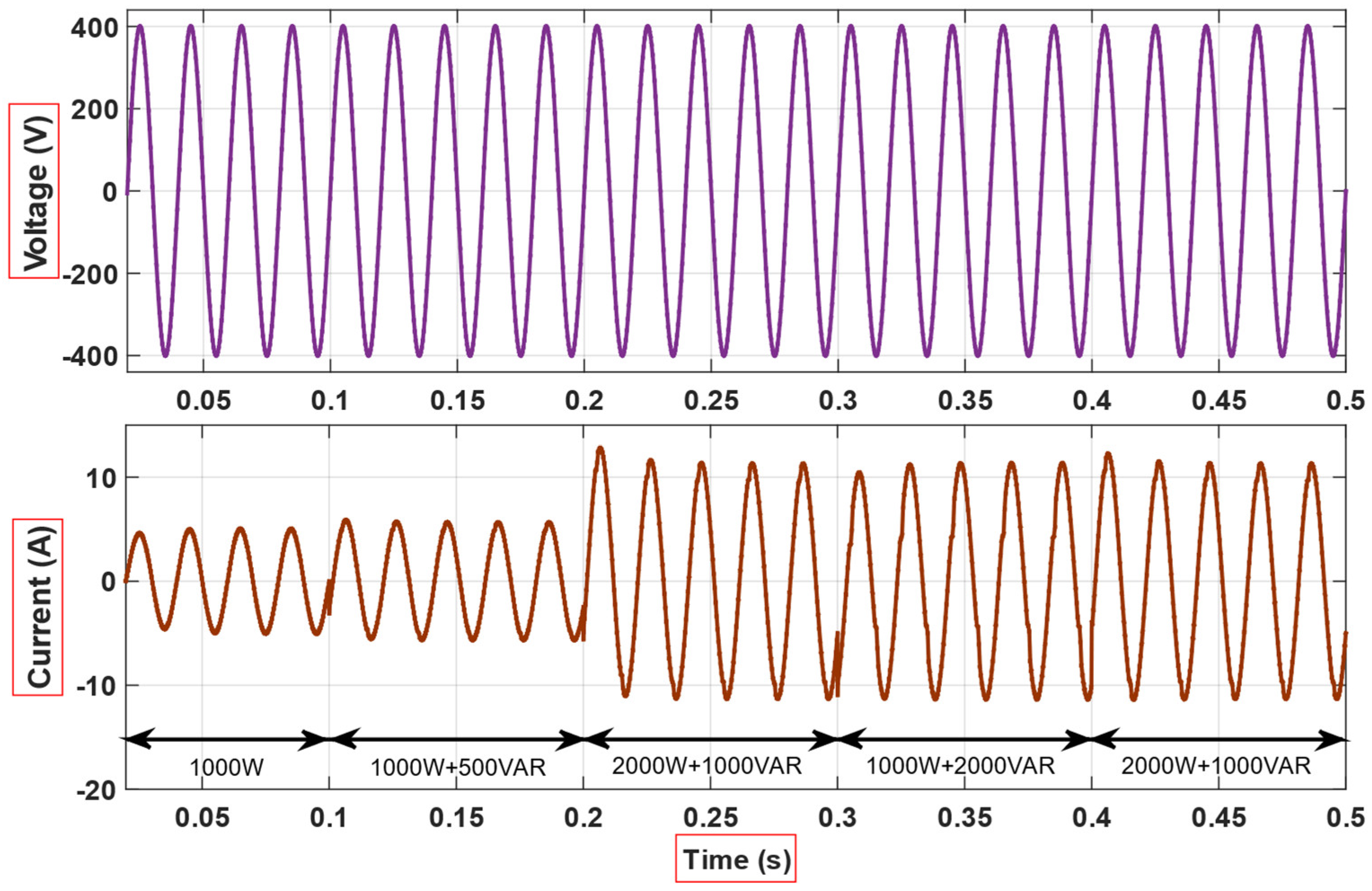
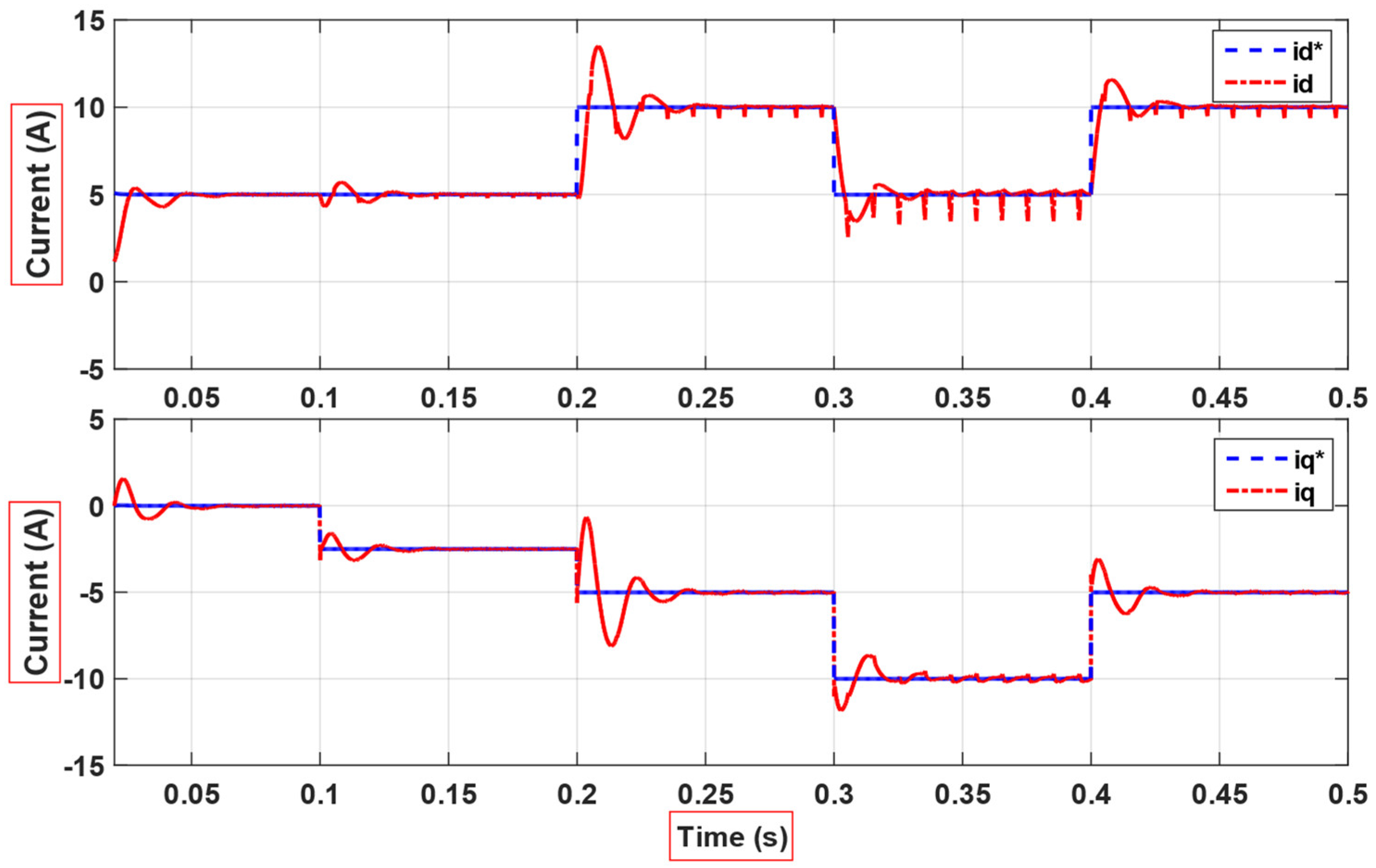
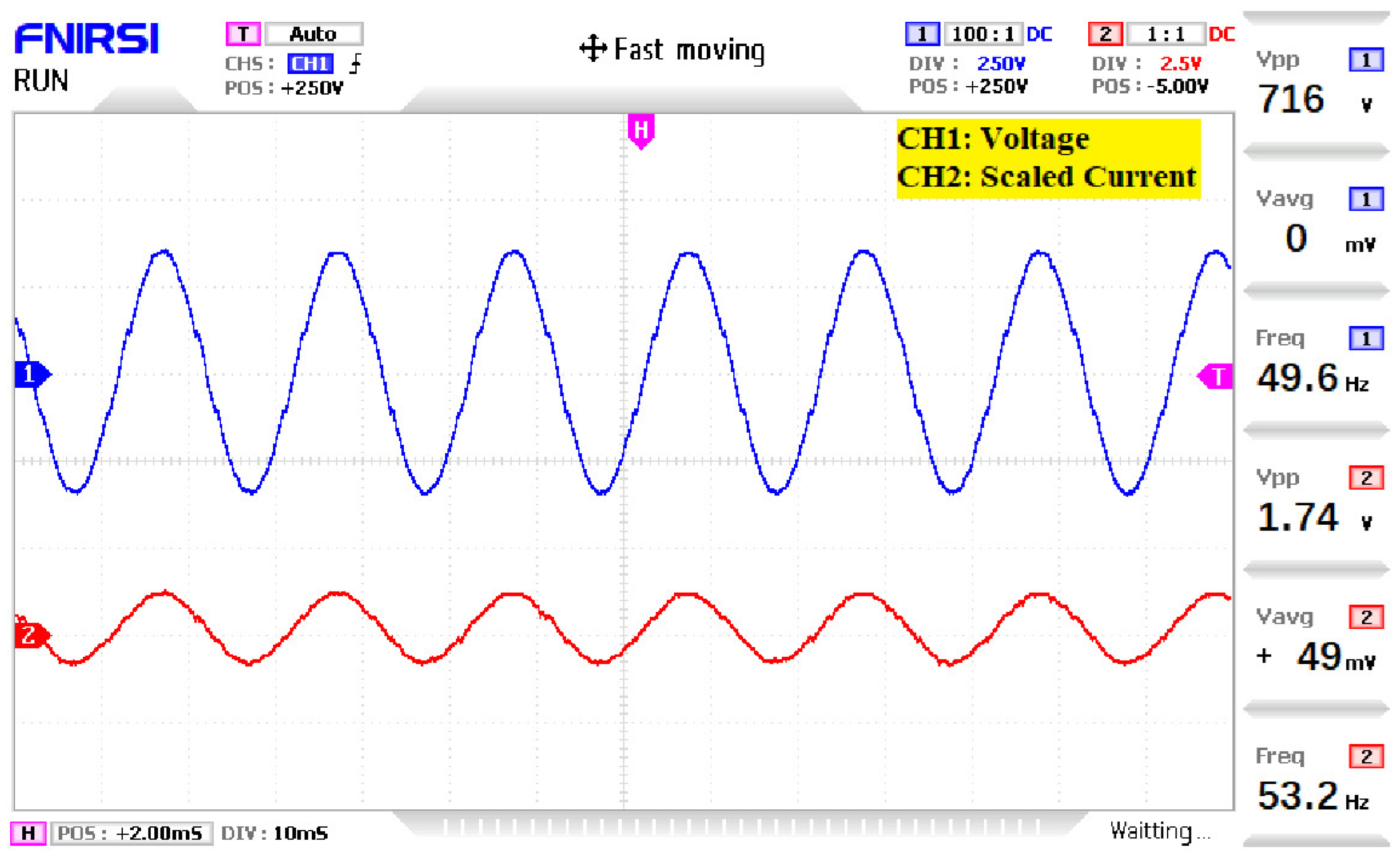
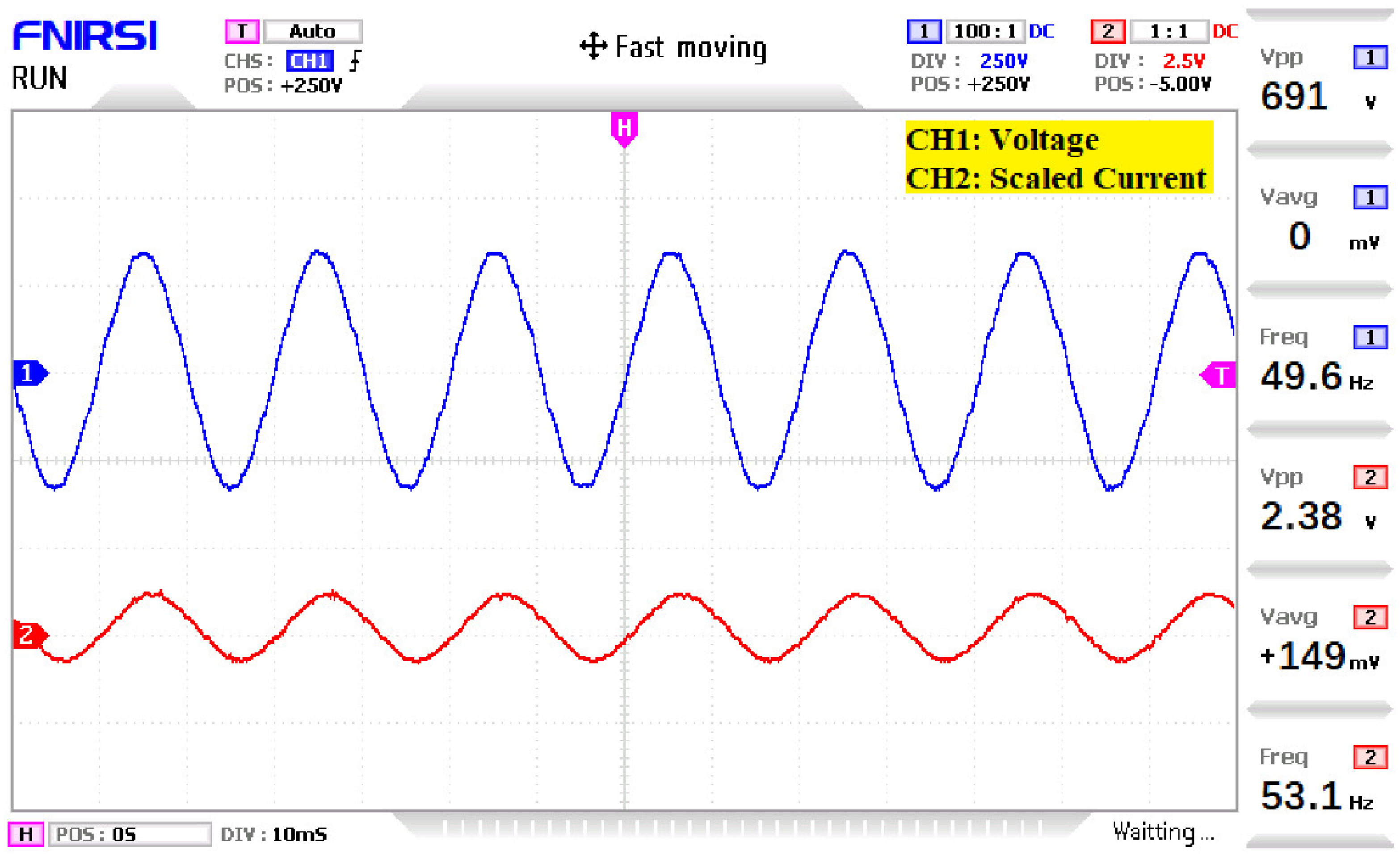
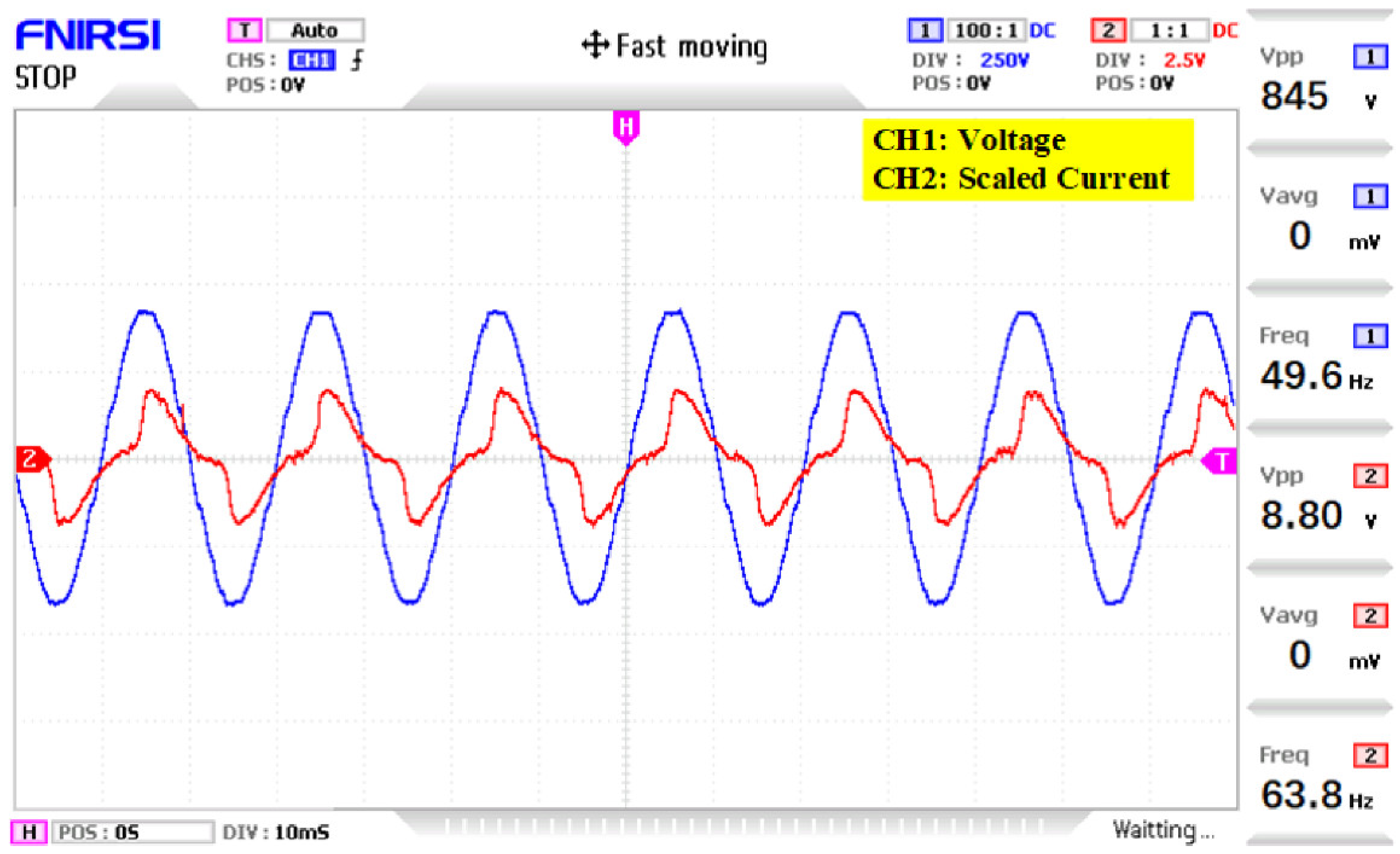
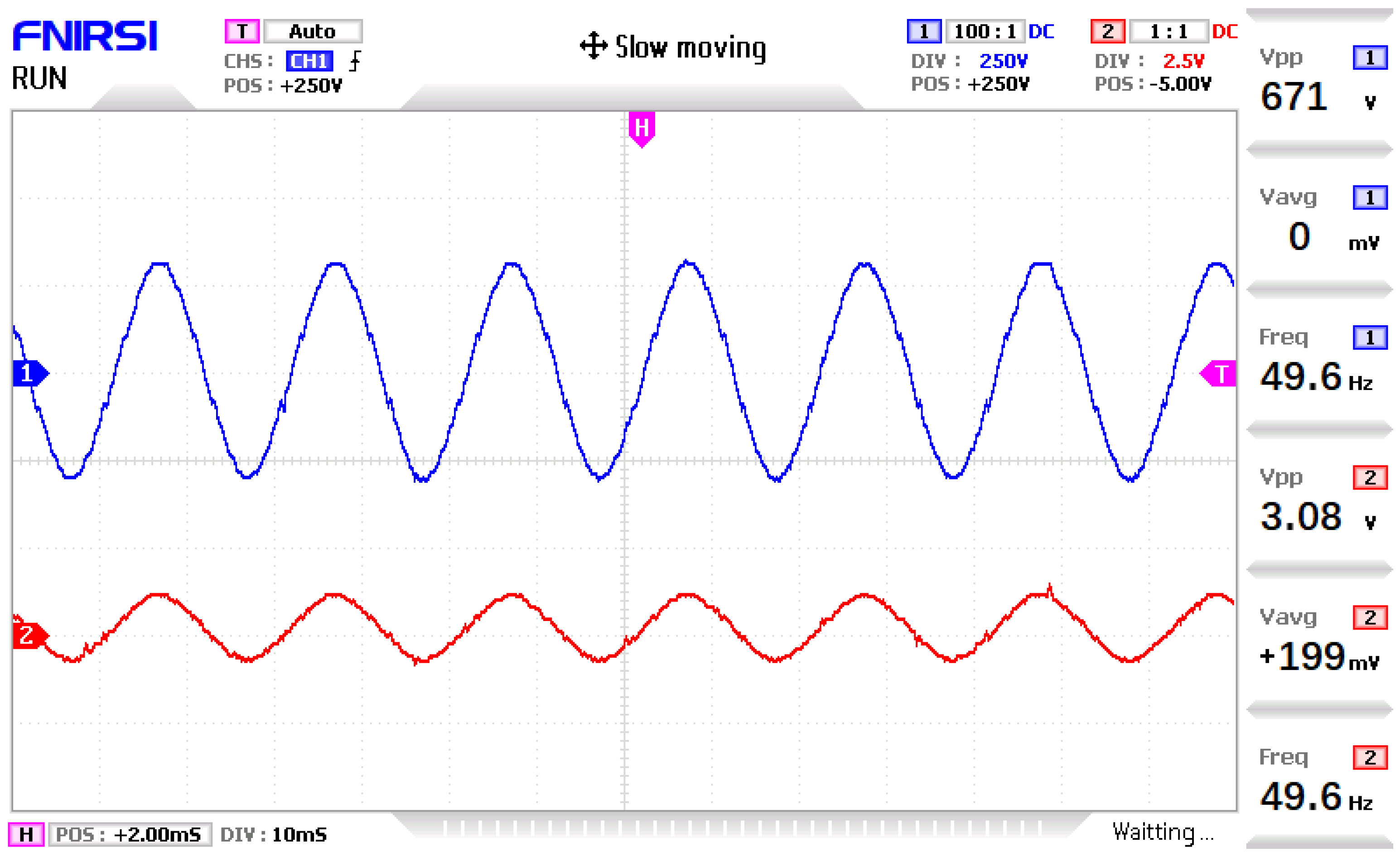
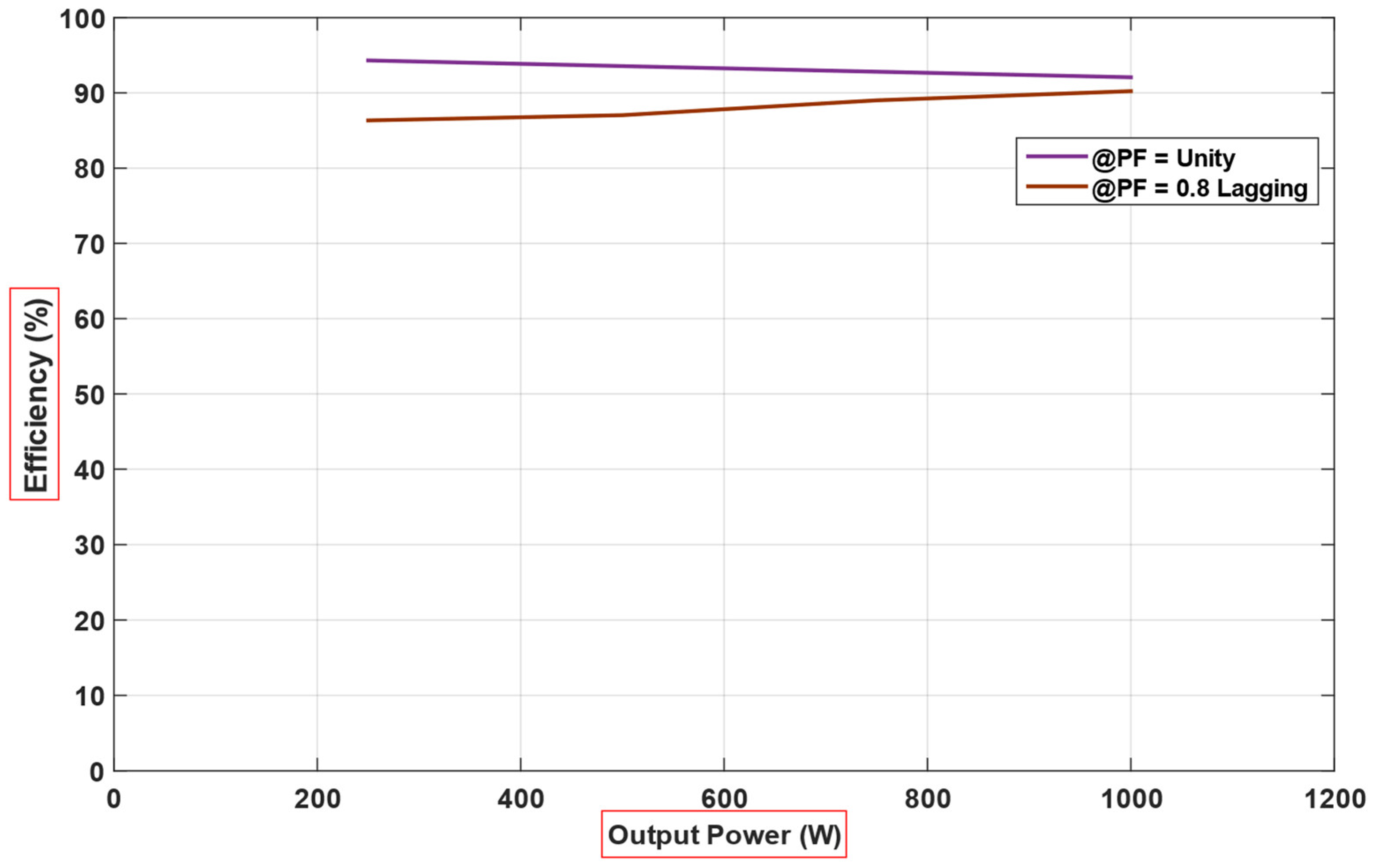
4. Simulation and Experimental Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raveendhra, D.; Pathak, M.K. Three-phase capacitor clamped boost inverter. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2019, 7, 1999–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Barbi, I. Fundamentals of a new diode clamping multilevel inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2000, 15, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, M.S.; Gharehpetian, G.B.; Mahdavi, Z.; Keyhani, A. Eighteen-Step Inverter: A low-loss three-phase inverter for low-cost standalone applications. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasu, R.; Chattopadhyay, S.K.; Chakraborty, C. Asymmetric cascaded H-bridge multilevel inverter with single dc source per phase. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 5398–5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmian, S.Y.; Barakati, S.M. A new asymmetric multilevel inverter with reduced number of components. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 8, 4333–4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Raghuram, M.; Pilli, N.K.; Singh, S.K.; Pan, X.; Xiong, X. A generalized switched inductor cell modular multilevel inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind Appl. 2020, 56, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.; Lim, C.S.; Siwakoti, Y.P.; Lee, K.B. Dual T-type five-level cascaded multilevel inverter with double voltage boosting gain. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 9522–9529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, O.A.; Wang, H. Five-level one-capacitor boost multilevel inverter. IET Power Electron. 2020, 13, 2245–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.S.M.; Almakhles, D.J.; Ibrahim, S.A.A.; Alyami, S.; Selvam, S.; Bhaskar, M.S. A generalized multilevel inverter topology with reduction of total standing voltage. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 168941–168950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataramanaiah, J.; Suresh, Y.; Panda, A.K. A review on symmetric, asymmetric, hybrid and single dc sources based multilevel inverter topologies. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 788–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, E.; Alilu, S.; Laali, S. A new general topology for cascaded multilevel inverters with reduced number of components based on developed H-bridge. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 3932–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.D.; Mekhilef, S.; Shah, N.M.; Memon, M.A. Optimal design of a new cascaded multilevel inverter topology with reduced switch count. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 24498–24510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.D.; Mekhilef, S.; Shah Ali, J.S.M.; Meraj, M.; Iqbal, A. A new single phase single switched-capacitor based nine-level boost inverter topology with reduced switch count and voltage stress. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 174178–174188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, B.; Majumdar, S.; Jana, K.C. Reduction in controlled power switches for a single-phase novel multilevel inverter. Int. J. Electron. 2019, 106, 1200–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, B.; Majumdar, S.; Jana, K.C. Reduction of power electronic devices in a single-phase generalized multilevel inverter. J. Circuits Sys. Comp. 2020, 29, 2050093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanamjayulu, C.; Devalraju, P.; Sanjeevikumar, P.; Pandav, M.K.; Jens, H.B.; Frede, B. Design and implementation of seventeen level inverter with reduced components. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 16746–16760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadaei, E.; Sheikholeslami, A.; Gholamian, S.A.; Adabi, J. A square T-type (ST-type) module for asymmetrical multilevel inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadaei, E.; Kaviani, M.; Bertilsson, K. A 13-levels module (K-type) with two dc sources for multilevel inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 5186–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodaparast, A.; Adabi, J.; Rezanejad, M. A step-up switched-capacitor multilevel inverter based on 5-level t-type modules. IET Power Electron. 2019, 12, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanamjayulu, C.; Arunkumar, G.; Pandian, B.J.; Kumar, C.V.R.; Kumar, M.P.; Jerin, A.R.A.; Venugopal, P. Real-time implementation of a 31-level asymmetrical cascaded multilevel inverter for dynamic loads. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 51254–51266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sid-Ali, A.; Kamal, M.; Abderrezzak, C.; Bruno, F. Multilevel inverter topology for renewable energy grid integration. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 8855–8866. [Google Scholar]
- Mahfuz-Ur-Rahman, A.M.; Islam, M.R.; Muttaqi, K.M.; Sutanto, D. Model predictive control for a new magnetic linked multilevel inverter to integrate solar photovoltaic systems with the power grids. IEEE Trans. Ind Appl. 2020, 56, 7145–7155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Saqib, M.A.; Kashif, S.A.R. Modified W-type configuration for a single-phase reduced parts count 81-level inverter. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pigazo, A.; Moreno, V.M.; EstEbanez, E.J. A recursive park transformation to improve the performance of synchronous reference frame controllers in shunt active power filters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 2065–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flah, A.; Khan, I.A.; Agarwal, A.; Sbita, L.; Marcelo, G. Simoes Field-oriented control strategy for double-stator single-rotor and double-rotor single-stator permanent magnet machine: Design and operation. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 90, 106953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sr. No. | S1 | S3 | S5 | S7 | S9 | S11 | S13 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | VDC |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2VDC |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3VDC |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4VDC |
| 6 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 5VDC |
| 7 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6VDC |
| 8 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 7VDC |
| 9 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 8VDC |
| 10 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 9VDC |
| 11 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 10VDC |
| 12 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 11VDC |
| 13 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 12VDC |
| 14 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 13VDC |
| 15 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 14VDC |
| 16 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 15VDC |
| 17 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 16VDC |
| 18 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 17VDC |
| 19 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 18VDC |
| 20 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 19VDC |
| 21 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 20VDC |
| 22 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 21VDC |
| 23 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 22VDC |
| 24 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 23VDC |
| 25 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 24VDC |
| 26 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 25VDC |
| 27 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 26VDC |
| 28 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 27VDC |
| 29 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 28VDC |
| 30 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 29VDC |
| 31 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 30VDC |
| 32 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 31VDC |
| 33 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 32VDC |
| 34 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 33VDC |
| 35 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 34VDC |
| 36 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 35VDC |
| 37 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 36VDC |
| 38 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 37VDC |
| 39 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 38VDC |
| 40 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 39VDC |
| 41 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 40VDC |
| Parameter | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Inductance (Lg) | 1 | mH |
| Grid frequency (f) | 50 | Hz |
| Lowest DC voltage (VDC) | 10 | V |
| Value of Kp | 100 | - |
| Value of Ki | 8000 | - |
| Grid voltage amplitude (Vg) | 400 | Vpeak |
| Parameter | Quantity/Value |
|---|---|
| IRFP450 | 6 |
| R6015ENX | 8 |
| UCC28700DBVR | 2 |
| IRF3205 | 12 |
| CSD19534Q5A | 2 |
| T750342424 | 2 |
| TLP250 | 16 |
| KNF6450A | 4 |
| IR2103 | 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, S.; Saqib, M.A.; Kashif, S.A.R.; Hashmi, K.; Aymen, F.; AboRas, K.M.; Jasińska, L.; Leonowicz, Z. A Modified Multi-Level Inverter System for Grid-Tied DES Applications. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16545. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416545
Ahmed S, Saqib MA, Kashif SAR, Hashmi K, Aymen F, AboRas KM, Jasińska L, Leonowicz Z. A Modified Multi-Level Inverter System for Grid-Tied DES Applications. Sustainability. 2022; 14(24):16545. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416545
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Sajjad, Muhammad Asghar Saqib, Syed Abdul Rahman Kashif, Khurram Hashmi, Flah Aymen, Kareem M. AboRas, Laura Jasińska, and Zbigniew Leonowicz. 2022. "A Modified Multi-Level Inverter System for Grid-Tied DES Applications" Sustainability 14, no. 24: 16545. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416545
APA StyleAhmed, S., Saqib, M. A., Kashif, S. A. R., Hashmi, K., Aymen, F., AboRas, K. M., Jasińska, L., & Leonowicz, Z. (2022). A Modified Multi-Level Inverter System for Grid-Tied DES Applications. Sustainability, 14(24), 16545. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416545










