Abstract
Urban living labs (ULLs) are progressive forms of interventions that aim to fulfil the sustainability ambitions of cities and communities. They provide opportunities to translate new ideas into practice. The increasing interest among researchers, practitioners, and policy makers in understanding sustainability transitions (ST) has brought new forms of experimentation through which cities and communities can be governed. Recently, there has been increasing attention towards the concept of circular economy (CE). This term promises the creation of distinct city systems in which material flows can be managed efficiently. In this article, we explore how ULLs can become pathways of sustainability transition towards innovative city systems from a circular economy perspective. By adopting a series of systematic analyses, i.e., multiple correspondence analysis and content analysis, we demonstrate the main pathways of circular economy-oriented innovative city systems that have been used in the literature. As a result of this work, we identify the main pathways, namely knowledge production, policy making, co-creation, geographical embeddedness, urban transitions, networks of cooperation among institutions, culture change, and collaborative engagement.
1. Introduction
With the increasing complexities and societal challenges brought by climate change, mobility, and air pollution, cities have become places for experimentation in which a series of innovations and practices has emerged to respond to their sustainability goals [1,2,3,4]. Small-scale incremental changes have become a part of a reasoning whereby small differences can lead to wider changes at city level and beyond [5,6]. Urban living labs are at the heart of these discussions, as they offer “a forum for innovation, applied to the development of new products, systems, services and process, employing working methods to integrate people into the entire development process as users and co-creators, to explore, examine, experiment, test and evaluate new ideas, scenarios, processes, systems, concepts and creative solutions in complex and real contexts” [7] (p. 13). They act as vehicles for exploring the changing dynamics of urban challenges, in which experimentation is used to inform urban practice [4].
Recently, there has been increasing interest in the concept of circular economy, and how it can stimulate changes by adopting ULL practices as part of the sustainability transition [8,9,10]. A series of funding and competitive tender opportunities have been advertised at EU level, which aim to explore how circular economy can support the transition towards a sustainable, regenerative, and inclusive economy across regions of Europe at local and regional levels (see Horizon 2022 calls on Circular Cities: This destination and its topics target climate-neutral circular and bioeconomy transitions, covering safe integrated circular solutions at territorial and sectoral levels; for more details see: https://ec.europa.eu/info/funding-tenders/opportunities/portal/screen/opportunities/topic-details/horizon-cl6-2022-circbio-01-01, accessed on 27 February 2022). They promote a sociotechnical system change associated with the concept of CE as part of sustainability transitions in cities [11]. The concept is an essential part of a regenerative system in which resource input and waste emission and energy leakage are mitigated by slowing, closing, and narrowing material and energy loops [12]. This regenerative system can be achieved through durable design, maintenance, repair, reuse, remanufacturing, refurbishing, and recycling.
However, there is limited literature on how urban living labs can become pathways of sustainability transition towards innovative city systems from a circular economy perspective [13,14,15,16,17]. In fact, city systems are searching for new ways of solving or tackling those major challenges to achieve sustainable transformations. More research is needed, due to the complexities of those challenges and the way in which new sets of knowledge are being incorporated, to foster circular economy in cities.
Based on this context, our research question addresses how urban living labs can become pathways for sustainability transition from a circular economy perspective. This paper explores the set of criteria needed for this transition. It offers a systematic review of the literature, with the application of multiple correspondence analysis and content analysis. The sections that follow present the theoretical background, the methodology used to perform the extensive literature review—including the quantitative bibliometric analysis and a qualitative content analysis of the texts retrieved—and the results of this analysis, before drawing some further conclusions.
2. Theoretical Framework
The theoretical framework of this work comprises three intertwined concepts: Urban Living Labs, Sustainability Transitions, and Circular Economy (CE). We take the premises that ULLs can work as sustainable transitions to introduce innovation or to promote changes in city systems from a CE perspective. Therefore, it is necessary to conceptualize these three concepts as follows.
2.1. Sustainability Transitions
Sustainability transitions are understood as multilevel, multiphase processes of structural change during which the dominant social structures (regimes) come under pressure from external changes in society and from endogenous innovations [18,19]. Research on sustainability transitions focuses on significant transformations in established economic sectors, such as energy, food, transport, or mobility, associated with and triggered by sustainability challenges, This is an area of study that has expanded, diversified, and deepened since 2010 [20,21,22]. This research focuses on four theoretical frameworks: the multilevel perspective, technological innovation system approach, strategic niche management, and transition management [23]. These theoretical frameworks use a systemic perspective to capture coevolutionary complexity and critical phenomena such as path-dependency, emergence, and nonlinear dynamics; they also highlight the changes in systems based on technologies, institutional structures, business models, organizations, and policies.
Sustainability transitions (ST) are of special interest within the main sustainability challenges because they have different dimensions: social, technological, and ecological [24]. Sustainability problems are viewed and defined differently by different stakeholders and interest groups [23]. Such problems exceed the challenges of technoscientific problems in many ways. They are highly complex, imposing extraordinary demands on policy makers, managers, and researchers [25].
To accelerate transformative change, ST approaches emphasize the importance of purposive experimentation, often in the context of sociotechnical niches [17,26]. Additionally, the sociotechnical-transition perspective builds on several earlier concepts, many of which are rooted in evolutionary theorizing of technological change and innovation systems [20]. Therefore, transition-studies perspectives provide a great deal of insight into how new approaches, such as ULLs, can be formed as a process through which transition management is deployed and governed [7]. In this sense, we understand that to introduce innovation, or to promote changes in cities, ULLs can produce a variety of pathways through which sustainable transitions toward circular cities can became a reality.
2.2. Urban Living Labs
Urban living labs are forms of urban experimentation that promote sustainability transitions [1,16]. ULLs offer opportunities to foster sustainability in cities, via testing and learning in real time [27,28]. They provide settings for applying the development of new products and services, systems, and processes, using methods to integrate people in the entire process as users and co-creators [29]. The European network of living labs (Enoll) defines ULLs as a user-centered open innovation ecosystem based on a systematic user co-creation approach, integrating research and innovation processes in real-life communities and settings [30].
Von Wirth [17] argues that ULLs represent sites in cities that allow stakeholders to design, test, and learn from sociotechnical innovations in real-time. Urban living labs seek to deliver innovative and transformative improvements across the urban environment, from buildings to green spaces, transport to energy systems, local food to sustainable forms of consumption. They work within and across the urban sociotechnical and socioecological system to mobilize change [7]. Urban living labs provide an environment that brings different actors together to contribute to sustainable development. They may address pressing urban problems, such as building design, green infrastructure, or low-carbon technologies.
ULLs can be a form of transformation arena; a multiactor governance instrument that is characterized by a normative focus on achieving sustainability goals that are determined by the participants themselves, through their interactions [21,31]. Urban living labs allow complementary sets of projects to offer holistic solutions to tackle unsustainable issues. Indeed, ULLs emphasize sustainability through continuous learning and development, and they can take significant responsibility for economic, social, and ecological effects. ULLs allow experimentation based on real-life conditions through which they can work as sustainable transitions to introduce innovation or to promote changes in city systems. This way, we depart from the idea that ULLs themselves produce pathways such as knowledge, policy drivers, etc., that will mediate transitions to city transformations based on circular economy values.
2.3. Circular Economy
The circular economy is a primary agenda of many agencies and academic institutions in European countries, and it is a promising concept for industries, society, and policy development [9,32]. Its challenges are to deal with all materials through a process of dematerialization, material substitution, and reuse of materials at the end of their life cycle [10]. The CE principles aim to shift the focus away from products and processes and towards durable design, maintenance, repair, reuse, remanufacturing, refurbishing, and recycling [12,33,34]. Furthermore, a more sustainable and inclusive built environment is one that will meet future demands [32].
As a renewal system, circular economy envelops resource input and minimizes waste emission and energy leakage by slowing, closing, and narrowing material and energy loops. It also acts as a driver of urban sustainability transitions [8,10,11,34]. As a result, CE is becoming a new sustainability paradigm, with strategies to reduce waste generation through better resource management that have been gaining prominence in policy and planning agendas in numerous cities and regions [12,35].
Implementing CE principles also promotes sustainable urban growth, reducing possible negative environmental impacts and stimulating social inclusion [9]. The circular economy is also increasingly being used as the overarching strategy of city systems and international plans to foster sustainable transformations and support the development of a green economy [8]. Another concept is the circular city; a city that practices CE principles to close resource loops, in partnership with the city’s stakeholders, in order to realize its vision of a future-proof city [11]. Hence, the transition towards a CE works inside and outside of complex systems. The relationships and support between socioeconomic and environmental dynamics are crucial. Several aspects are necessary for innovation in the city system, such as establishing a co-creation process, different governance approaches, the development of spatial decisions, and the way we educate urban planners and designers [32].
It is from this perspective that we acknowledge ULLs as mechanisms that can be part of the innovative city system through tools, policies, methodologies, and strategies that can produce sustainability transformation through knowledge and/or solutions based on CE principles. Therefore, sustainability transition, urban living labs, and circular economy can play a significant role together in city system transformation. In this research, the assumption is that according to the literature, ULLs can become pathways for sustainability transition towards innovative city systems from a circular economy perspective. In other words, urban living labs, when adopting CE values, may produce/develop a variety of pathways through their insights/experimentations to support/turn them into sustainable transitions towards innovative city systems.
2.4. Pathways for Sustainability Transition towards Innovative City Systems
According to the literature, ULLs are new kinds of experimentation and knowledge that contribute to the societal and environmental problems faced by the future of local innovation [4]. In this sense, ULLs are forums for the production of pathways that act as transitions to a more innovative city system.
Knowledge production is identified as a pathway to foster transitions in city systems based on ULL experimentations. For instance, the transference of knowledge is understood as a vehicle for collaboratively enacting transformative knowledge [17]. In this way, ULLs foster knowledge among actors and how they develop sustainable practices to face urban challenges in the city system [7,17,36,37,38]. Through the dissemination of the knowledge generated, ULLs play a central role in rebuilding sustainable pathways for dealing with challenges facing the city system [39]. Greer [10] states that the ULLs offer a change in the market, meeting the widespread demand for knowledge and innovation to meet the requirements of competitive tenders. UULs can foster reflexivity for theory and practice, to better understand how theorizations and the application of circular economy could be advanced in support of urban sustainability transitions [8]. In other words, “transition learning consists of monitoring, evaluation, and reflexive activities aimed at understanding the present state and the dynamics in a system and the possible pathways from present to future situations” [40] (p. 24).
Policy making is also a pathway that can promote transformation or innovation in city systems. The results of ULL experimentations become references for establishing a transformative agenda. Policies can become key mechanisms of the transition-management process, with focus on generating a sharing sense of ownership and desirable sustainable future [21]. Thus, it helps stakeholders to integrate it with their agendas and practices. Policy instruments in the 2030 Agenda for sustainable development goals relate to goal 11 for sustainable cities and communities. This goal adopts the transition of cities toward more sustainable models, which is also advocated in the main policy framework [2]. Thus, ULLs are a fruitful tool that can be used to trigger innovative policies and practices relating to the reuse of materials and the integration of material that directs the transition towards a CE in a city system [36,41,42,43]. ULLs include policy instruments, incentives, consultation deployed, forms of learning, measurement, and accountability for determining the levels of adoption of sustainability in the urban ecosystems [7,37].
Co-creation is another pathway that emerges from ULLs as a sustainable transition to change a city system. For Sovacool [22], co-creation approaches may be pathways that can differ meaningfully across three different domains: timing, scope, and level of collaboration. Puerari [31] identified in ULLs, there are different types of co-creation approaches that connect with the explicit dynamics of participation, facilitation, and organization. They always involve each stakeholder in defining and creating strategies with the goal of improving quality of life for the population. It helps overcome situations of institutional lock-in [9,32,37]. ULLs facilitate urban sustainability transitions because they connect a sense of change (transformation) with a sense of place by co-creating new narratives of place, co-producing knowledge on new practices and new relations between people and place [16]. Co-creation practices in ULLs take place in different forms, including fluid forms of engagement that are not necessarily settled ‘a priori’ [31]. Generally, in ULLs, the innovation process is assured thanks to co-creation activities [44]. By co-creation, unusual and new ideas can be developed, acknowledging the presence and the coworking of several stakeholders at the same time, in the same place.
Geographical embeddedness is another ULL pathway for sustainable transitions in systems. Geography for quality of life plays an important role in ULLs through spatial challenges related to the need for circular regeneration of territories as an innovative process that can eventually lead to healthier cities and a better quality of life [33]. Ribeiro [38] states that ULLs embody a territorial focus on finding locally sustainable solutions to address wicked problems that tend to be global. This is why cities are used as laboratories. In short, ULLs are geographically embedded and context-driven environments in which user-centered research and development activities are conducted in order to experiment and learn based on stakeholders embedded in a specific innovative city system from a CE.
Urban transitions are reconfiguration processes for unpacking the competing, coexisting, and complementary interactions between multiple experimental processes that generate new place-based configurations [45]. They are also a pathway for the innovating of city systems. ULLs try out visions of an urban future that coordinate various actors through the reconstruction of urban infrastructures and at the same time, offer opportunities to tackle environmental problems with testable solutions in specific locations [46]. This vision guides the collaboration activities in an innovative city system, and may be aligned with sustainability issues. From this perspective, innovative city systems are considered central to ecological, societal, and economic sustainability transition, where it is implemented [47]. All things considered, the mechanism of ULLs is critical in terms of understanding their role in governing urban development and contributing to environmental transformation [7].
Networks of cooperation among institutions are enabling conditions, supporting the identification of operative tools and envisioning decision-making processes [33], and these networks are characterized as ULL pathways for change. For instance, problem solving arenas (lock-in situations) in ULLs are suitable spaces and transition arenas for collaborative forms of urban governance. Connections among actors can be established and the boundaries between sectors, interests, and contexts are subject to further exploration [45]. The ULL approach draws heavily on transdisciplinary and sustainability science in framing an approach that co-produces two interlinked strands of knowledge of relevance to both society and science [48]. ULLs are designed to bring together multiple actors seeking novel solutions to various challenges and fostering learning to apply innovative city systems [16]. Von Wirth [17] states that it is a key indicator in the ULLs because it supports the dissemination of innovations and know-how developed within ULLs to a broader context. Additionally, the value network of an urban living lab ecosystem generates value through dynamic exchanges between various stakeholders, and these exchanges can be mapped as different value flows [37,49].
Connecting niche and regime actors helps to influence and empower civil society, in order to shape sustainability in their environments and contribute to sustainable transition (ST) [21]. Niches provide a good context for experiments with sustainable practices in ULLs. At the same time, adaptation to this specific and deviant context makes it difficult to scale up experiments to the dominant regime [17]. In this context, according to Ampe [26], minimizing the regime-to-niche activities leads roles played by incumbents in niches being overlooked. Accordingly, the ‘diachronic and systemic focus’ of the multilevel perspective observes how established actors are enrolled in niche networks and practices to increase their impact.
Culture change is another pathway that plays a key factor in determining sustainability adoption levels in an innovative city system [37]. This pathway has to do with the concept of ULLs to become transformative and social practice. ULLs become transformative when governance structure, leadership, and power distribution are significant factors, in addition to having user involvement [27]. The authors conceptualize the transformative potential of ULLs for sustainability as their ability to initiate and catalyze change processes by advancing sustainable innovations that address socioeconomic and environmental challenges in city systems. Transformative ULLs focused on CE should be based on unconventional procedures, to break down the existing routines and enable urban actors to design, test, and learn from sociotechnical innovations in real-time [36]. From ULLs, various opportunities might emerge that accelerate sustainability and environmental transitions within innovative city systems [37]. ULLs also serve as both a living testbed and a catalyst for a broader transition to becoming an innovative city system from a circular economy perspective [2]. Social practices then consist of elements that are integrated when practices are enacted, and these practices emerge, persist, and disappear as connections between defining characteristics are made and broken [50]. Indeed, the social-practice perspective can analyze the process and its interrelationship with ULLs. As we observe, ULLs are used to explore, test, and apply social practices and consumption patterns in city systems [29,51]. Likewise, these practices are human activities and how these activities are habitually performed concerning different elements and embedded in society and shaped by culture and meanings, materials and technologies, institutions, and infrastructures [17,22]. Overall, forms of urban experimentation, such as ULLs, from a transitions perspective, are about placemaking in city systems and challenging the dominant discourses and practices in their context [16]. Thus, the legacy lies not in technology uptake or a growing sociotechnical niche, but in stakeholders’ social relations and stories [52]. To conclude, ULLs are a particular governance project that provides and conceptualize their role in culture change [7].
Collaborative engagement in ULL environments produces different responses, contexts, and categories, such as product-related, process-oriented, and service-proactive innovation [9]. It is considered as another pathway and it refers to different forms of user participation, connections between actors, and funding and resources. Different forms of user participation are a critical characteristic and are highly relevant for the design, testing, and development of innovative solutions, addressing sustainability challenges in city systems [6,27,28,37,51]. Additionally, user involvement in ULLs faces a variety of engagement challenges that are actively involved in generating and transferring knowledge, developing services and strategies [7,9,21,29,35,37,39]. Connections between actors include actions taken to facilitate the dissemination of CE and settings that create a favorable environment [10]. ULLs are encouraged to join forces in order to better understand the complexity of their urban challenges, increase the quality of life at city-system scale, and tackle varying urban challenges. In summary, actor competence is a key aspect of transition arenas for understanding the complexity of the problem of city systems [21]. Collaboration between actors connects urban districts, to create transformation processes for sustainable development in city systems [53]. Funding and resources are important tools for sustainable city promotion, and municipalities govern ULLs by providing direct financial support to actors [49]. ULLs may be strategic resources for cities to attract capital [41]. For instance, they have attracted the attention of European funding programs [6,51]. They can also seek external funding through municipalities [49]. ULLs promote resources and economic value flows (funding) between actors to promote sustainable practices in the city systems [37]. With the introduction of the CE to solve urban challenges, this became a way of “rebuilding capital,” whether financial, manufactured, human, social, or natural, in innovative city systems [8].
In summary, knowledge production, policy making, co-creation, geographical embeddedness, urban transitions, networks of cooperation among institutions, culture change, and collaborative engagement are pathways that work as sustainable potential transitions to achieve changes toward an innovative city system. A systematic literature review was carried out for this research. The section that follows gives details of the methodological conceptual design used for the literature review.
3. Methodology
This study conducted a systematic literature review, in order to analyze how urban living labs can become pathways for sustainability transitions to innovative city system from a circular economy perspective. The research design was divided into two steps: selection of relevant papers, and definition of data analysis (multiple correspondence analysis, and content analysis coding process).
3.1. Selection of the Papers
Three search strings—urban living labs, sustainability transitions, and circular economy in cities—were applied to the Web of Science® and Scopus® databases to find papers on these topics. First, we applied four combinations of search strings to search for papers: (1) urban living lab* AND sustainab* transition*; (2) urban living lab* AND circular economy; (3) sustainab* transition* AND circular economy AND cit*; and (4) urban living lab* AND sustainab* transition* and circular economy. Table 1 shows the selected articles. Although we started the search in 2020, we only completed the final selection of articles on 10 October 2021.

Table 1.
Papers selection from Web of Science and Scopus.
Table 1 summarizes the paper-selection process. Based on these criteria, we selected 41 articles for this study (see Appendix A for an overview).
3.2. Definition of Data Analysis
The data analyses to address how urban living labs can become pathways for sustainability transition towards innovative city systems from a circular economy perspective included multiple correspondence analysis and content analysis. Details of these procedures are described below.
3.2.1. Multiple Correspondence Analysis
Multiple correspondence analysis (MCA) is an exploratory multivariate technique for graphical and numerical analysis without any restrictive assumption [54]. Aria [54] states that MCA performs a homogeneity analysis of an indicator matrix to obtain a low-dimensional Euclidean representation of the original data. In co-word analysis, MCA is applied to a Document × per Word matrix A. Variables are keywords, and the individuals observed are the papers. The keywords are plotted on a two-dimensional map [CS <- conceptual Structure (M, field = “ID,” minDegree = 5, k.max = 5, stemming = FALSE), labelsize = 5]. We followed the method of Aria [55]. The bibliometrix R-package enables the use of the conceptual structure function to perform MCA, in order to examine the relationship between keywords papers and identify clusters of documents that express common concepts. Keywords represent active variables in the model.
The aim of the co-word analysis is to map the conceptual structure of a framework using the word co-occurrences in a bibliographic collection. The analysis can be performed through dimensionality reduction techniques such as a multiple correspondence analysis. We performed our MCA using also a set of illustrative variables, i.e., papers’ publication period to analyze the field evolution. Assuming that the most-cited papers are more representative of the structure of the field, we performed MCA considering the weight (citations per year) assigned to the papers. The output was a map, according to number of factorial axes selected (5 clusters). Given the different approaches used for the selection of factors in the literature (prefixed number between 2 and 4; eigenvalue method; screen test), we finally agreed on the choice of the first factorial plan (Axis 1 and Axis 2). The results are interpreted based on the relative positions of the points and their distribution among the dimensions; the more similar the words are in the distribution, the closer they are represented in the map [54].
3.2.2. Content Analysis Coding Process
Content analysis is a set of techniques of communication analysis (oral, written, visual, etc.) that aims to obtain, using systematic procedures, the content of the indicator messages, allowing the inference of knowledge related to the conditions of production and reception of these messages [56]. We coded all the papers through four stages. First, we read the articles. Then, we identified the thematic trends (categories) from the titles, keywords, abstracts, discussion, and conclusions. Thirdly, we selected the context unit that represented the thematic trends. Finally, we created a Microsoft excel file in which we included: Categories (recurrent themes), Register unit, Authors, and Findings and conclusion. This file became our matrix analysis, which was used to address our research problem.
4. Results
4.1. Multiple Correspondence Analysis: Exploring Expanded Concepts
Figure 1 and Figure 2 present the multiple correspondence analysis of the abstracts (N-grams: Unigram; Number of term:100; N cluster: 8). We show a conceptual structure of the field and clustering to identify clusters of documents that express common concepts. The proximity between keywords corresponds to shared substance: keywords are close to each other because a large proportion of articles treat them together; they are distant from each other when only a small fraction of articles discusses these keywords together. For instance, in the case of the laboratories domain (blue cluster), twenty-two articles contributed to the construction of the related factor. For the same token, the map indicates an immediate correlation with the categories found through the content analysis.
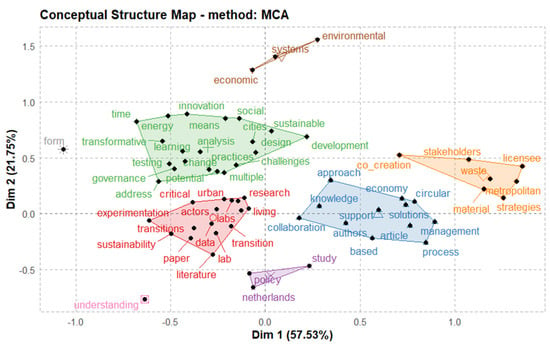
Figure 1.
MCA of ULLs, ST and CE.
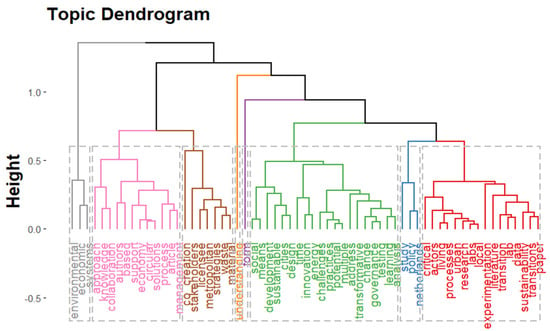
Figure 2.
MCA of ULL, ST and CE.
The green cluster represents the innovation domain; the red cluster characterizes the sustainable development domain. The blue cluster characterizes the policy domain. The grey cluster represents the environmental domain; the pink cluster represents the knowledge domain; the brown cluster represents the co-creation domain. The orange cluster represents the actor domain. The red cluster represents the urban transitions domain. Finally, the purple does not specify any domain, but indicates some factors that have no immediate connections with these research subjects. These domains contributed to the identification of the categories of the content analysis.
4.2. Content Analysis: Pathways for Sustainability Transitions to Innovative City System from a Circular Economy Perspective
Figure 3 represents the pathways identified from the content analysis of the articles. We identified eight categories that can become pathways for sustainability transitions to innovative city system from a circular economy perspective. They are: knowledge production, policy making (governance), co-creation, geographical embeddedness, urban transitions, network of cooperation among institutions, culture change, and collaborative engagement.
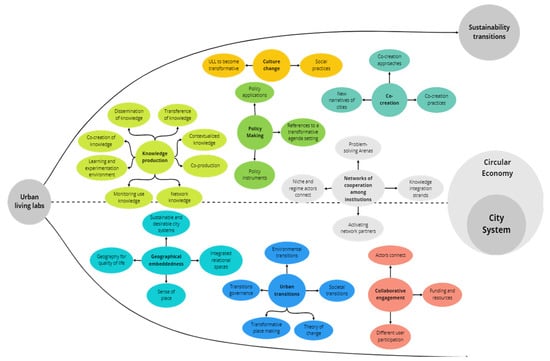
Figure 3.
Pathways and indicators from the matrix of content analysis of the selected articles.
Knowledge production, which enables knowledge transfer, acts as a vehicle for collaboration, collaborative environments, and open innovation ecosystems. It promotes the dissemination of knowledge through the sharing, fostering, and spread of knowledge. Furthermore, it involves societal actors that bring innovative solutions through the co-creation of knowledge. It also provides learning and experimentation environments through learning by doing, enhancing city-to-city learning, and promoting transitions toward a CE. In addition, it monitors the use of knowledge, transforms learning, and helps to design innovative solutions in this transition learning. It promotes a network of knowledge that constructs epistemic practices to accelerate innovation in city systems. In this way, it promotes contextualized knowledge, which can be adopted and shared by communities and citizens as a process and systemic tool. Through its experimentation in real-life processes by co-production, it helps catalyze change and generate new practices and relations in the process of urban transformation. In summary, this evidence contributes to the circular economy governance perspective.
Policy making permits references to a transformative-agenda setting through the mechanism of transition management and co-benefits of adaptation of urban competitiveness. Moreover, it is a policy instrument that triggers innovative policies, and the adoption of levels of the urban ecosystem through sustainable development goals. Therefore, policy applications are a fertile ground in planned experimentation, to test CE initiatives in the urban context.
Co-creation is another pathway whose approaches are about the dynamics of participation by timing, scope, and level of collaboration, always involving stakeholders. Thus, new narratives of cities contribute to transforming cities, thinking of alternatives to urban futures, and changing societal systems. Co-creation practices involve the coworking of stakeholders in complex systems through innovative processes.
Geographical embeddedness allows the geography for quality of life, and places the circular regeneration system in an urban environment. This leads to the integration of relational spaces through bounded sites for experimentation design, and the implementation of sustainable place-based solutions. Additionally, a sustainable and desirable city system brings circular economy imaginaries and governance capacities to test out solutions for urban sustainability and generate city-to-city learning. The places of co-creation, where meanings, beliefs, symbols, values, and feelings come together, create a symbolic locality of change to construct a sense of place. Furthermore, an innovative city system generates interconnection dynamics in an open system, ground for resources, and potential synergies, which are aspects of urban living labs.
Urban transitions, as a pathway, integrate the environmental transitions to growing up the human–nature relationship, and disseminate CE principles through governance in urban development. In addition, social transitions help catalyze changes in the city system to shape governance through a development mechanism that accelerates learning. Transition governance allows the ULL form of governance to bring innovation, on different scales, across multiple sectors and involving multiple actors, to bring strategies for friendly futures. Thus, transformative place making enables innovative experiments through testing and developing things to improve and redesign city systems in a new place-based configuration. Finally, the theory of change, focused on sustainability, leads to new practices, in a systemic shift toward a circular economy.
Networks of cooperation among institutions define specific enabling conditions to solve problems through collaborative forms of urban governance, involving the public sector to protect and enhance ecosystem services as regional strategies for CE. In addition, knowledge integration strands help to co-produce knowledge for society and science that promotes economic growth and improves social cohesion. Thus, activating network partners as an urban change agent encourages the dissemination of innovation and know-how as value through dynamic exchange. Finally, the niche and regime actors connect, allowing the empowerment of the civil society toward sustainability transitions to overlock the roles and enroll in niche networks.
Cultural change as a determinant that allows ULLs to become transformative, bringing the user involvement that enables the ULLs to initiate and catalyze processes of change and function as living testbeds, and as catalysts for a broader transition. Social practices also help to analyze the process and its interrelations between the ULLs and the human activities embedded in society, their social relations, and their stories.
Collaborative engagement allows for the participation of different users, which is essential for critical assessment of innovative solutions addressing sustainability challenges, and for generating governance in transition toward circular economy. Connections between actors also help disseminate the circular economy through improved quality of life, as they join forces to understand urban challenges. Funding and resources are important financial support tools for seeking, developing, and generating funding programs and rebuilding capital.
In summary, knowledge production, policy making, co-creation, geographical embeddedness, urban transitions, networks of cooperation among institutions, culture change, and collaborative engagement are the pathways found in this literature review study, based on content analysis, as having the potential to achieve changes toward an innovative city system.
5. Discussion
To address the research question, we characterize how urban living labs could become pathways for sustainability transitions to innovative city systems from a circular economy perspective. Urban living labs arise from innovative city systems to tackle the regime and transform the spaces through strategies and solutions toward circular economy. Therefore, ULLs have the potential to produce knowledge through experimentation, which in turn, supports sustainable sociotechnical configuration. It also affects the urban governance to formulate trigger innovative policies to encourage city-system transformations. The co-creation development process of ULLs can enable stakeholder engagement and building strategies, associated with knowledge generation, that contribute to urban sustainability transitions.
Knowledge production paves the way for a series of stages that lead city-system in-novation, through activities such as the transfer, dissemination, and co-creation of knowledge. Knowledge transfer provides a vehicle for collaboratively enacting transformative knowledge that can build more accessible contexts for knowledge transfer to a more open innovation ecosystem. Thus, ULLs produce transferability of results as well as scientific and societal learning and transformation. ULLs can also provide a strategic platform for the dissemination of knowledge, based on a shared knowledge on CE principles among actors. Hence, ULLs foster knowledge among actors and how they develop sustainable practices in urban challenges in the city system, favoring innovation. Through the dissemination of the generated knowledge, ULLs play a central role in building sustainable pathways to face city-system challenges. ULLs also develop innovative solutions among citizens, practitioners, decision makers, and researchers based on the co-creation of knowledge. Co-creation of knowledge is a fundamental way to solve urban challenges in a real-life context, and is becoming a new learning arena in ULL experimentations. It involves societal actors in initiating and conducting the experiments and learning about what the system should be and how to the desired transformation can be attained.
Urban living labs are seen as spaces for facilitating experimentation on sustainability solutions, where various urban actors can design, experiment, and learn from sociotechnical innovations. ULLs work as learning environments to enhance city-to-city learning and to improve the governance capacities needed to accelerate effective and efficient transitions towards innovative city systems based on the principles of circular economy. The experimentation within ULLs provides new knowledge, produced under laboratory conditions, that is generally valid and may be transferable to other settings, where it can be improved on through further analysis and activity.
Sustainability transitions in urban contexts focus on the relation of human nature to diffuse and generate changes in city systems. Indeed, ULLs bring learning, innovation, and strategies to create and improve sustainable urban scenarios, leading new practices in a systemic shift toward circular cities. Circular economy views support transitions through the operationalization in contemporary urban governance for sustainability and low-carbon cities. Based on circular economy principles, it is possible to create new solutions through collaborative citizen engagement, involving real situations. These processes of transformation also generate culture changes in society that will affect everyday social practices.
This new configuration includes network cooperation among academic, public, and private sectors, which can enhance niche experimentation in the form of circular transitions as developed within the ULLs. Accordingly, their impact of experimentation requires an understanding of their geographical embeddedness as a sociospatial context.
In summary, it focuses on their various forms of coexistence, within a framework of coopetition in particular. In their planning and development practices, cities need to constantly navigate between various collaborative and competitive orientations in order to promote sustainable and collaborative urban development, while also remaining competitive [57].
6. Conclusions
Urban living labs are new kinds of experimentation and knowledge that contribute to the social and environmental problems arising from transformation. To address the research question, we characterize how urban living labs could become pathways for sustainability transitions to innovative city systems from a circular economy perspective. We applied multiple correspondence analysis and content analysis, through which we triangulated this discussion.
The pathways found in the literature review, i.e.,: knowledge production, policy making, co-creation, geographical embeddedness, urban transitions, networks of cooperation among institutions, culture change, and collaborative engagement, were evidenced through the two technical approaches applied and mentioned above.
For instance, the pathways found based in the content analysis are also supported by the evidence found in the MCA. There were similarities between some of the concepts, such as co-creation, urban experimentation, stakeholder, experiments, local government, governance, technologies, real world, city futures and systemic change, knowledge transfer, managing transition, spatial planning, territories, and urban planning. It is clear that the pathways found in the literature review are significant STs to introduce innovations in a city system supported by CE principles, such as regeneration, sharing, optimization, looping, virtualization and exchange [11].
Although not the specific subject of this research, it is important to mention that smart cities and social innovation are valuable themes for future research. Thus, an urban living lab is a space in which many actors come together to co-create, develop and test products and services. The urban living lab is also partially responsible for promoting the sustainable city system, facilitating sustainability transitions to an innovative city system, from a circular economy perspective.
Innovative city systems need to go circular, and ULLs are niche innovations that help change the system. Moreover, future research could build on these findings, with universities, for instance, becoming important actors in the knowledge production of ULLs.
Monitoring and evaluation methods can also help to explore system dynamics into the stage of designing innovative sustainability solutions. As such, transition learning processes consist of monitoring, assessment, and analytical activities aimed at understanding the current state and the dynamics in a system, and the viable pathways from current to future contexts. In this perspective, the knowledge produced in the ULLs is extremely contextualized. These experiments in sustainability transitions need to recognize the messiness, complexity, and politics of transitions, and experimentation is necessary.
In policymaking, ULLs can act as tools for transformative innovation policy. In the pathways of collaborative engagement, the ULL is developed as a sustainable entity, generating new resources and funding through new business models. The products, services, social connections, and/or knowledge produced within the ULLs need to be adopted and shared by communities and citizens, by turning on ambivalent role of contextualized knowledge and the implications for sustainability transitions.
These ULL pathways will probably generate a new ontological circular city-system concept that could contribute to constructing future investigations that can be empirically applied, and that can advance the field of ST studies and urban experimentations focused on urban living labs. They may also have future implications in other contexts. They will probably affect social practices and city applications in the field, provoking changes and innovation in the current regime. ULLs will generate new scientific approaches regarding city-system development that could benefit the economy and businesses in the city.
To conclude, it is important to note some of the limitations of this research. Given that this is a systematic literature review, ethnography research in real ULLs is important, to understand how the pathways identified in this literature review could be identified in real contexts. It is also important for ULLs to promote ecological interventions associated with urban transitions, such as nature-based solutions in city systems, which we also consider a limitation found in this study. Another limitation of this research relates to the political implications (power, stakeholders, incumbents, regime, etc.) associated with the discourses of circular economy and the sustainable development agenda on ULLs.
Author Contributions
Supervision, A.A. and A.E.; Writing—original draft, D.H.F.A.; Writing—review & editing, A.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Papers used in the final sample of this study.
Table A1.
Papers used in the final sample of this study.
| Source | Title | Journal | Pathways | Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [2] | Assessing Integrated Circular Actions as Nexus Solutions Across Different Urban Challenges: Evidence Toward a City-Sensitive Circular Economy. | Green Energy and Technology | Collaborative engagement | Different user participation |
| Funding and resources | ||||
| Culture change | ULLs to become transformative. | |||
| Geographical embeddedness | Geography for quality of life | |||
| Integrated relational spaces | ||||
| Sustainable and desirable city system | ||||
| Policy making | Policy instruments | |||
| Urban transitions | Theory of change | |||
| Transformative place making | ||||
| [6] | Urban living laboratories: Conducting the experimental city? | European Urban and Regional Studies | Collaborative engagement | Different user participation |
| Funding and resources | ||||
| Culture change | Social practices | |||
| ULLs to become transformative. | ||||
| Geographical embeddedness | Geography for quality of life | |||
| Knowledge production | Dissemination of knowledge | |||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Activating network partners | |||
| Problem-solving arenas (lock-in situations) | ||||
| Policy making | Policy instruments | |||
| Urban transitions | Societal transitions | |||
| Theory of change | ||||
| Transformative place making | ||||
| Transition governance | ||||
| [7] | Urban living labs: governing urban sustainability transitions. | Environmental Sustainability | Collaborative engagement | Actors connect |
| Different user participation | ||||
| Culture change | ULLs to become transformative. | |||
| Geographical embeddedness | Sustainable and desirable city system | |||
| Knowledge production | Co-creation of knowledge | |||
| Contextualized knowledge | ||||
| Dissemination of knowledge | ||||
| Learning and experimentation environments | ||||
| Network knowledge | ||||
| Policy making | Policy instruments | |||
| References to a transformative agenda setting | ||||
| Urban transitions | Environmental transitions | |||
| Societal transitions | ||||
| Theory of change | ||||
| Transformative place making | ||||
| Transition governance | ||||
| [8] | Exploring circular economy imaginaries in European cities: A research agenda for the governance of urban sustainability transitions. | Journal of Cleaner Production | Collaborative engagement | Actors connect |
| Funding and resources | ||||
| Culture change | ULLs to become transformative. | |||
| Geographical embeddedness | Sustainable and desirable city system | |||
| Knowledge production | Co-production | |||
| Dissemination of knowledge | ||||
| Network knowledge | ||||
| Policy making | Policy applications | |||
| Policy instruments | ||||
| References to a transformative agenda setting | ||||
| Urban transitions | Societal transitions | |||
| Transformative place making | ||||
| Transition governance | ||||
| [9] | Managing the transition towards circular metabolism: Living labs as a co-creation approach. | Urban Planning | Co-creation | Co-creation approaches |
| Co-creation practices | ||||
| New narratives of cities | ||||
| Collaborative engagement | Actors connect | |||
| Participation of different users | ||||
| Culture change | Social practices | |||
| Geographical embeddedness | Geography for quality of life | |||
| Integrated relational spaces | ||||
| Knowledge production | Co-creation of knowledge | |||
| Contextualized knowledge | ||||
| Co-production | ||||
| Dissemination of knowledge | ||||
| Learning and experimentation environments | ||||
| Network knowledge | ||||
| Transfer of knowledge | ||||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Niche and regime actors connect | |||
| Problem-solving arenas (lock-in situations) | ||||
| Policy making | Policy applications | |||
| Urban transitions | Environmental transitions | |||
| Transition governance | ||||
| [10] | The dissemination of circular services: Transforming the Dutch catering sector. | Journal of Cleaner Production | Co-creation | Co-creation practices |
| Collaborative engagement | Actors connect | |||
| Funding and resources | ||||
| Geographical embeddedness | Integrated relational spaces | |||
| Knowledge production | Co-production | |||
| Dissemination of knowledge | ||||
| Learning and experimentation environments | ||||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Niche and regime actors connect | |||
| Urban transitions | Environmental transitions | |||
| Theory of change | ||||
| Transition governance | ||||
| [16] | Sense of place and experimentation in urban sustainability transitions: the Resilience Lab in Carnisse, Rotterdam, The Netherlands. | Sustainability Science | Co-creation | Co-creation approaches |
| New narratives of cities | ||||
| Collaborative engagement | Actors connect | |||
| Culture change | Social practices | |||
| Geographical embeddedness | Integrated relational spaces | |||
| Sense of place | ||||
| Sustainable and desirable city system | ||||
| Knowledge production | Co-creation of knowledge | |||
| Dissemination of knowledge | ||||
| Learning and experimentation environments | ||||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Activating network partners | |||
| Niche and regime actors connect | ||||
| Policy making | Policy applications | |||
| References to a transformative agenda setting | ||||
| Urban transitions | Societal transitions | |||
| Theory of change | ||||
| Transformative place making | ||||
| [17] | Impacts of urban living labs on sustainability transitions: mechanisms and strategies for systemic change through experimentation. | European Planning Studies | Co-creation | New narratives of cities |
| Collaborative engagement | Actors connect | |||
| Culture change | Social practices | |||
| ULLs to become transformative. | ||||
| Geographical embeddedness | Integrated relational spaces | |||
| Sense of place | ||||
| Knowledge production | Co-creation of knowledge | |||
| Contextualized knowledge | ||||
| Dissemination of knowledge | ||||
| Learning and experimentation environments | ||||
| Network knowledge | ||||
| Transferring knowledge | ||||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Activating network partners | |||
| Niche and regime actors connect | ||||
| Policy making | Policy applications | |||
| Urban transitions | Environmental transitions | |||
| Transformative place making | ||||
| Transition governance | ||||
| [19] | The challenges of water, waste and climate change in cities. | Environment, Development and Sustainability | Geographical embeddedness | Geography for quality of life |
| Sustainable and desirable city system | ||||
| Knowledge production | Dissemination of knowledge | |||
| Learning and experimentation environments | ||||
| Policy making | Policy applications | |||
| References to a transformative agenda setting | ||||
| Urban transitions | Societal transitions | |||
| [21] | Direct impacts of an urban living lab from the participants’ perspective: Livewell Yarra. | Sustainability | Collaborative engagement | Actors connect |
| Different user participation | ||||
| Culture change | ULLs to become transformative. | |||
| Knowledge production | Co-creation of knowledge | |||
| Dissemination of knowledge | ||||
| Learning and experimentation environments | ||||
| Network knowledge | ||||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Niche and regime actors connect | |||
| Policy making | References to a transformative agenda setting | |||
| Urban transitions | Environmental transitions | |||
| Transition governance | ||||
| [22] | Sociotechnical agendas: Reviewing future directions for energy and climate research. | Energy Research & Social Science | Co-creation | Co-creation approaches |
| Culture change | Social practices | |||
| Geographical embeddedness | Innovative system | |||
| Knowledge production | Co-creation of knowledge | |||
| Learning and experimentation environments | ||||
| Network knowledge | ||||
| Policy making | References to a transformative agenda setting | |||
| Urban transitions | Societal transitions | |||
| Theory of change | ||||
| [26] | Incumbents’ enabling role in niche-innovation: Power dynamics in a wastewater project. | Environmental Innovation and Societal Transitions | Networks of cooperation among institutions | Niche and regime actors connect |
| Problem-solving arenas (lock-in situations) | ||||
| Urban transitions | Transition governance | |||
| [27] | Urban living labs and the role of users in co-creation. | GAIA-Ecological Perspectives for Science and Society | Co-creation | Co-creation approaches |
| Co-creation practices | ||||
| Collaborative engagement | Actors connect | |||
| Different user participation | ||||
| Culture change | ULLs to become transformative. | |||
| Knowledge production | Monitoring use of knowledge | |||
| Urban transitions | Societal transitions | |||
| Transformative place making | ||||
| [28] | Municipalities as enablers in urban experimentation. | Journal of Environmental Policy & Planning | Collaborative engagement | Actors connect |
| Different user participation | ||||
| Knowledge production | Co-creation of knowledge | |||
| Monitoring use of knowledge | ||||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Activating network partners | |||
| Niche and regime actors connect | ||||
| Policy making | Policy instruments | |||
| Urban transitions | Transformative place making | |||
| [29] | Jointly Experimenting for Transformation? Shaping Real-World Laboratories by Comparing Them. | GAIA-Ecological Perspectives For Science and Society | Co-creation | Co-creation approaches |
| New narratives of cities | ||||
| Collaborative engagement | Actors connect | |||
| Different user participation | ||||
| Culture change | Social practices | |||
| ULLs to become transformative. | ||||
| Geographical embeddedness | Sustainable and desirable city system | |||
| Knowledge production | Contextualized knowledge | |||
| Dissemination of knowledge | ||||
| Learning and experimentation environments | ||||
| Monitoring use of knowledge | ||||
| Network knowledge | ||||
| Transferring knowledge | ||||
| Policy making | Policy applications | |||
| References to a transformative agenda setting | ||||
| Urban transitions | Environmental transitions | |||
| Societal transitions | ||||
| Theory of change | ||||
| [31] | Co-creation dynamics in Urban Living Labs. | Sustainability | Co-creation | Co-creation approaches |
| Co-creation practices | ||||
| Collaborative engagement | Actors connect | |||
| Geographical embeddedness | Integrated relational spaces | |||
| Sense of place | ||||
| Knowledge production | Co-creation of knowledge | |||
| Dissemination of knowledge | ||||
| Learning and experimentation environments | ||||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Niche and regime actors connect | |||
| Problem-solving arenas (lock-in situations) | ||||
| Policy making | Policy instruments | |||
| References to a transformative agenda setting | ||||
| [32] | Facilitating circular economy in urban planning. | In Urban Planning | Co-creation | Co-creation approaches |
| [33] | Beyond wastescapes: Towards circular landscapes. addressing the spatial dimension of circularity through the regeneration of wastescapes. | Sustainability | Co-creation | Co-creation approaches |
| New narratives of cities | ||||
| Collaborative engagement | Actors connect | |||
| Different user participation | ||||
| Culture change | ULLs becoming transformative. | |||
| Geographical embeddedness | Geography for quality of life | |||
| Sense of place | ||||
| Sustainable and desirable city system | ||||
| Knowledge production | Transferring knowledge | |||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Problem-solving arenas (lock-in situations) | |||
| Policy making | Policy applications | |||
| References to a transformative agenda setting | ||||
| Urban transitions | Environmental transitions | |||
| Societal transitions | ||||
| [34] | A Geodesign Decision Support Environment for Integrating Management of Resource Flows in Spatial Planning | Urban Planning | Co-creation | Co-creation approaches |
| Collaborative engagement | Different user participation | |||
| Geographical embeddedness | Integrated relational spaces | |||
| Knowledge production | Co-creation of knowledge | |||
| Co-production | ||||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Knowledge-integration strands | |||
| Urban transitions | Environmental transitions | |||
| Theory of change | ||||
| [35] | Transferring Circular Economy Solutions across Differentiated Territories: Understanding and Overcoming the Barriers for Knowledge Transfer. | Urban Planning | Culture change | Social practices |
| Geographical embeddedness | Innovative system | |||
| Integrated relational spaces | ||||
| Sustainable and desirable city system | ||||
| Knowledge production | Co-creation of knowledge | |||
| Co-production | ||||
| Learning and experimentation environments | ||||
| Network knowledge | ||||
| Transferring knowledge | ||||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Activating network partners | |||
| Problem-solving arenas (lock-in situations) | ||||
| Policy making | Policy applications | |||
| References to a transformative agenda setting | ||||
| Urban transitions | Environmental transitions | |||
| [36] | Transformative urban living labs: Towards a circular economy in Amsterdam and Turin. | Sustainability | Collaborative engagement | Actors connect |
| Culture change | ULLs to become transformative. | |||
| Geographical embeddedness | Integrated relational spaces | |||
| Knowledge production | Co-production | |||
| Dissemination of knowledge | ||||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Problem-solving arenas (lock-in situations) | |||
| Policy making | Policy instruments | |||
| References to a transformative agenda setting | ||||
| Urban transitions | Transformative place making | |||
| Transition governance | ||||
| [37] | Urban living lab as a circular economy ecosystem: Advancing environmental sustainability through economic value, material, and knowledge flows. | Sustainability | Co-creation | Co-creation approaches |
| Co-creation practices | ||||
| Collaborative engagement | Actors connect | |||
| Different user participation | ||||
| Funding and resources | ||||
| Culture change | Social practices | |||
| ULLs to become transformative. | ||||
| Geographical embeddedness | Innovative system | |||
| Integrated relational spaces | ||||
| Knowledge production | Dissemination of knowledge | |||
| Learning and experimentation environments | ||||
| Network knowledge | ||||
| Transferring knowledge | ||||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Activating network partners | |||
| Policy making | Policy instruments | |||
| Urban transitions | Environmental transitions | |||
| Theory of change | ||||
| Transformative place making | ||||
| Transition governance | ||||
| [38] | Urban food forestry networks and Urban Living Labs articulations. | Journal of Urbanism | Co-creation | Co-creation approaches |
| Culture change | ULLs to become transformative. | |||
| Geographical embeddedness | Geography for quality of life | |||
| Sustainable and desirable city system | ||||
| Knowledge production | Dissemination of knowledge | |||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Activating network partners | |||
| Problem-solving arenas (lock-in situations) | ||||
| Urban transitions | Transformative place making | |||
| Transition governance | ||||
| [39] | From Real-World Labs to Urban Experiments: German and International Debates. | Raumforschung und Raumordnung/Spatial Research and Planning | Collaborative engagement | Different user participation |
| Knowledge production | Dissemination of knowledge | |||
| Learning and experimentation environments | ||||
| Monitoring use of knowledge | ||||
| Transferring knowledge | ||||
| Urban transitions | Transformative place making | |||
| [40] | Circling the Square: Governance of the Circular Economy Transition in the Amsterdam Metropolitan Area. | European Spatial Research and Policy | Collaborative engagement | Actors connect |
| Different user participation | ||||
| Funding and resources | ||||
| Culture change | Social practices | |||
| Knowledge production | Monitoring use of knowledge | |||
| Transferring knowledge | ||||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Niche and regime actors connect | |||
| Policy making | Policy applications | |||
| References to a transformative agenda setting | ||||
| Urban transitions | Theory of change | |||
| Transition governance | ||||
| [41] | Urban living labs for the smart grid: Experimentation, governmentality and urban energy transitions | In Urban Living Labs: Experimenting with City Futures | Collaborative engagement | Actors connect |
| Funding and resources | ||||
| Culture change | Social practices | |||
| Ulls to become transformative. | ||||
| Geographical embeddedness | Sustainable and desirable city system | |||
| Knowledge production | Co-creation of knowledge | |||
| Contextualized knowledge | ||||
| Dissemination of knowledge | ||||
| Learning and experimentation environments | ||||
| Transferring knowledge | ||||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Activating network partners | |||
| Knowledge integration strands | ||||
| Problem-solving arenas (lock-in situations) | ||||
| Policy making | Policy instruments | |||
| References to a transformative agenda setting | ||||
| Urban transitions | Environmental transitions | |||
| Societal transitions | ||||
| Theory of change | ||||
| Transformative place making | ||||
| Transition governance | ||||
| [42] | Greening Regional Cities: The Role of Government in Sustainability Transitions. | Sustainable development research in the Asia-Pacific region In: World Sustainability Series | Collaborative engagement | Actors connect |
| Funding and resources | ||||
| Geographical embeddedness | Innovative system | |||
| Knowledge production | Dissemination of knowledge | |||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Niche and regime actors connect | |||
| Policy making | Policy instruments | |||
| Urban transitions | Transition governance | |||
| [43] | Creating a national urban research and development platform for advancing urban experimentation. | Sustainability | Culture change | ULLs to become transformative. |
| Geographical embeddedness | Integrated relational spaces | |||
| Sustainable and desirable city system | ||||
| Knowledge production | Co-creation of knowledge | |||
| Learning and experimentation environments | ||||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Niche and regime actors connect | |||
| Policy making | Policy instruments | |||
| Urban transitions | Environmental transitions | |||
| Societal transitions | ||||
| Theory of change | ||||
| Transformative place making | ||||
| [45] | Unpacking the formation of favourable environments for urban experimentation: The case of the bristol energy scene. | Sustainability | Collaborative engagement | Actors connect |
| Geographical embeddedness | Integrated relational spaces | |||
| Sense of place | ||||
| Knowledge production | Learning and experimentation environments | |||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Activating network partners | |||
| Knowledge integration strands | ||||
| Niche and regime actors connect | ||||
| Problem-solving arenas (lock-in situations) | ||||
| Policy making | References to a transformative agenda setting | |||
| Urban transitions | Transformative place making | |||
| Transition governance | ||||
| [47] | Towards territorial product-service systems: A framework linking resources, networks and value creation. | Sustainable Production and Consumption | Collaborative engagement | Actors connect |
| Funding and resources | ||||
| Geographical embeddedness | Geography for quality of life | |||
| Innovative system | ||||
| Integrated relational spaces | ||||
| Sustainable and desirable city system | ||||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Activating network partners | |||
| Niche and regime actors connect | ||||
| Urban transitions | Environmental transitions | |||
| Societal transitions | ||||
| [48] | Sustainability-oriented labs in real-world contexts: An exploratory review. | Journal of Cleaner Production | Co-creation | Co-creation approaches |
| New narratives of cities | ||||
| Collaborative engagement | Actors connect | |||
| Funding and resources | ||||
| Culture change | Social practices | |||
| ULLs to become transformative. | ||||
| Geographical embeddedness | Integrated relational spaces | |||
| Knowledge production | Learning and experimentation environments | |||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Activating network partners | |||
| Knowledge integration strands | ||||
| Problem-solving arenas (lock-in situations) | ||||
| Policy making | Policy instruments | |||
| References to a transformative agenda setting | ||||
| Urban transitions | Environmental transitions | |||
| Societal transitions | ||||
| Theory of change | ||||
| Transformative place making | ||||
| Transition governance | ||||
| [49] | Experimental governance: the role of municipalities in urban living labs. | European Planning Studies | Collaborative engagement | Actors connect |
| Funding and resources | ||||
| Culture change | ULLs to become transformative. | |||
| Geographical embeddedness | Integrated relational spaces | |||
| Knowledge production | Learning and experimentation environments | |||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Activating network partners | |||
| Niche and regime actors connect | ||||
| Policy making | Policy instruments | |||
| Urban transitions | Transition governance | |||
| [51] | Urban living labs for sustainability and low carbon cities in Europe: Towards a research agenda. | Journal of Cleaner Production | Co-creation | New narratives of cities |
| Collaborative engagement | Actors connect | |||
| Different user participation | ||||
| Funding and resources | ||||
| Culture change | Social practices | |||
| Geographical embeddedness | Geography for quality of life | |||
| Integrated relational spaces | ||||
| Sense of place | ||||
| Knowledge production | Co-creation of knowledge | |||
| Co-production | ||||
| Dissemination of knowledge | ||||
| Learning and experimentation environments | ||||
| Network knowledge | ||||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Knowledge integration strands | |||
| Problem-solving arenas (lock-in situations) | ||||
| Policy making | Policy applications | |||
| References to a transformative agenda setting | ||||
| Urban transitions | Transformative place making | |||
| Transition governance | ||||
| [52] | Housing Industry Transitions: An Urban Living Lab in Melbourne, Australia. | Urban Policy and Research | Co-creation | New narratives of cities |
| Culture change | Social practices | |||
| ULLs to become transformative. | ||||
| Knowledge production | Dissemination of knowledge | |||
| Learning and experimentation environments | ||||
| Network knowledge | ||||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Niche and regime actors connect | |||
| Policy making | Policy applications | |||
| Urban transitions | Societal transitions | |||
| Theory of change | ||||
| Transformative place making | ||||
| [53] | Strengthening local economy—an example of higher education institutions’ engagement in “co-creation for sustainability.” | Region | Co-creation | Co-creation approaches |
| Collaborative engagement | Actors connect | |||
| Culture change | ULLs to become transformative. | |||
| Geographical embeddedness | Integrated relational spaces | |||
| Knowledge production | Co-creation of knowledge | |||
| Co-production | ||||
| Dissemination of knowledge | ||||
| Monitoring use of knowledge | ||||
| Urban transitions | Theory of change | |||
| Transformative place making | ||||
| [57] | Agency in circular city ecosystems—A rationalities perspective. | Sustainability | Collaborative engagement | Actors connect |
| Different user participation | ||||
| Geographical embeddedness | Integrated relational spaces | |||
| Sustainable and desirable city system | ||||
| Knowledge production | Co-creation of knowledge | |||
| Urban transitions | Theory of change | |||
| [58] | Embedding higher education into a Real-World Lab: A process-oriented analysis of Six Transdisciplinary Project Courses. | Sustainability | Co-creation | New narratives of cities |
| Collaborative engagement | Actors connect | |||
| Culture change | Social practices | |||
| Geographical embeddedness | Integrated relational spaces | |||
| Sustainable and desirable city system | ||||
| Knowledge production | Dissemination of knowledge | |||
| Learning and experimentation environments | ||||
| Transferring knowledge | ||||
| Urban transitions | Environmental transitions | |||
| Societal transitions | ||||
| [59] | Evaluating evolving experiments: the case of local government action to implement ecological sustainable design. | Journal of Environmental Planning and Management. | Knowledge production | Contextualized knowledge |
| Learning and experimentation environments | ||||
| Monitoring use of knowledge | ||||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Activating network partners | |||
| Niche and regime actors connect | ||||
| Urban transitions | Societal transitions | |||
| Theory of change | ||||
| Transformative place making | ||||
| [60] | Navigating between adaptation and transformation: How intermediaries support businesses in sustainability transitions. | Journal of Cleaner Production | Culture change | Social practices |
| Geographical embeddedness | Integrated relational spaces | |||
| Knowledge production | Dissemination of knowledge | |||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Activating network partners | |||
| Niche and regime actors connect | ||||
| Problem-solving arenas (lock-in situations) | ||||
| Policy making | Policy applications | |||
| Policy instruments | ||||
| Urban transitions | Societal transitions | |||
| Transformative place making | ||||
| Transition governance | ||||
| [46] | Thinking critically about smart city experimentation: entrepreneurialism and responsibilization in urban living labs. | Local Environment. | Co-creation | Co-creation approaches |
| Collaborative engagement | Actors connect | |||
| Culture change | Social practices | |||
| ULLs to become transformative. | ||||
| Geographical embeddedness | Sustainable and desirable city system | |||
| Knowledge production | Co-creation of knowledge | |||
| Dissemination of knowledge | ||||
| Monitoring use of knowledge | ||||
| Networks of cooperation among institutions | Niche and regime actors connect | |||
| Problem-solving arenas (lock-in situations) | ||||
| Policy making | Policy applications | |||
| References to a transformative agenda setting | ||||
| Urban transitions | Environmental transitions | |||
| [61] | Public agency in changing industrial circular economy ecosystems: Roles, modes and structures. | Sustainability | Co-creation | Co-creation practices |
| Urban transitions | Societal transitions | |||
| Theory of change |
References
- Fuenfschilling, L.; Frantzeskaki, N.; Coenen, L. Urban experimentation & sustainability transitions. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2018, 27, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreucci, M.B.; Croci, E. Assessing Integrated Circular Actions as Nexus Solutions Across Different Urban Challenges: Evidence Toward a City-Sensitive Circular Economy. In Smart and Sustainable Planning for Cities and Regions, Proceedings of the International conference on Smart and Sustainable Planning for Cities and Regions, Bolzano, Italy, 9–13 December 2019; Green Energy and Technology book series; Bisello, A., Vettorato, D., Haarstad, H., Borsboom-van Beurden, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronéer, D.; Ståhlbröst, A.; Habibipour, A. Urban Living Labs: Towards an Integrated Understanding of Their Key Components. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2019, 9, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy, A.; van Bueren, E. Challenges of Urban Living Labs towards the Future of Local Innovation. Urban Plan. 2020, 5, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geels, I.F.W. The Dynamics of Transitions in Socio-Technical Systems: A Multi-Level Analysis of the Transition Pathway from Horse-Drawn Carriages to Automobiles (1860–1930). Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2005, 17, 445–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulkeley, H.; Marvin, S.; Palgan, Y.V.; McCormick, K.; Breitfuss-Loidl, M.; Mai, L.; von Wirth, T.; Frantzeskaki, N. Urban Living Laboratories: Conducting the Experimental City? Eur. Urban Reg. Stud. 2019, 26, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulkeley, H.; Coenen, L.; Frantzeskaki, N.; Hartmann, C.; Kronsell, A.; Mai, L.; Marvin, S.; McCormick, K.; van Steenbergen, F.; Voytenko Palgan, Y. Urban Living Labs: Governing Urban Sustainability Transitions. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2017, 22, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratini, C.F.; Georg, S.; Jørgensen, M.S. Exploring Circular Economy Imaginaries in European Cities: A Research Agenda for the Governance of Urban Sustainability Transitions. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 974–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amenta, L.; Attademo, A.; Remøy, H.; Berruti, G.; Cerreta, M.; Formato, E.; Palestino, M.F.; Russo, M. Managing the Transition towards Circular Metabolism: Living Labs as a Co-Creation Approach. Urban Plan. 2019, 4, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, R.; von Wirth, T.; Loorbach, D. The Diffusion of Circular Services: Transforming the Dutch Catering Sector. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 121906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendeville, S.; Cherim, E.; Bocken, N. Circular Cities: Mapping Six Cities in Transition. Environ. Innov. Soc. Transit. 2018, 26, 171–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissdoerfer, M.; Savaget, P.; Bocken, N.M.P.; Hultink, E.J. The Circular Economy—A New Sustainability Paradigm? J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coenen, L.; Benneworth, P.; Truffer, B. Toward a Spatial Perspective on Sustainability Transitions. Res. Policy 2012, 41, 968–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binz, C.; Truffer, B.; Coenen, L. Why Space Matters in Technological Innovation Systems—Mapping Global Knowledge Dynamics of Membrane Bioreactor Technology. Res. Policy 2014, 43, 138–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengers, F.; Raven, R. Toward a Spatial Perspective on Niche Development: The Case of Bus Rapid Transit. Environ. Innov. Soc. Transit. 2015, 17, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantzeskaki, N.; van Steenbergen, F.; Stedman, R.C. Sense of Place and Experimentation in Urban Sustainability Transitions: The Resilience Lab in Carnisse, Rotterdam, The Netherlands. Sustain. Sci. 2018, 13, 1045–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Wirth, T.; Fuenfschilling, L.; Frantzeskaki, N.; Coenen, L. Impacts of Urban Living Labs on Sustainability Transitions: Mechanisms and Strategies for Systemic Change through Experimentation. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2019, 27, 229–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loorbach, D. Transition Management for Sustainable Development: A Prescriptive, Complexity-Based Governance Framework. Governance 2010, 23, 161–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koop, S.H.A.; van Leeuwen, C.J. The Challenges of Water, Waste and Climate Change in Cities. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2017, 19, 385–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markard, J. Sustainability Transitions: Exploring the Emerging Field and Its Relations to Management Studies. Acad. Manag. Proc. 2017, 2017, 14100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, D.; Salter, R. Direct Impacts of an Urban Living Lab from the Participants’ Perspective: Livewell Yarra. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovacool, B.K.; Hess, D.J.; Amir, S.; Geels, F.W.; Hirsh, R.; Medina, L.R.; Miller, C.; Palavicino, C.A.; Phadke, R.; Ryghaug, M.; et al. Sociotechnical Agendas: Reviewing Future Directions for Energy and Climate Research. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2020, 70, 101617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, J.; Geels, F.W.; Kern, F.; Markard, J.; Onsongo, E.; Wieczorek, A.; Alkemade, F.; Avelino, F.; Bergek, A.; Boons, F.; et al. An Agenda for Sustainability Transitions Research: State of the Art and Future Directions. Environ. Innov. Soc. Transit. 2019, 31, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loorbach, D.; Frantzeskaki, N.; Avelino, F. Sustainability Transitions Research: Transforming Science and Practice for Societal Change. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2017, 42, 599–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markard, J.; Raven, R.; Truffer, B. Sustainability Transitions: An Emerging Field of Research and Its Prospects. Res. Policy 2012, 41, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampe, K.; Paredis, E.; Asveld, L.; Osseweijer, P.; Block, T. Incumbents’ Enabling Role in Niche-Innovation: Power Dynamics in a Wastewater Project. Environ. Innov. Soc. Transit. 2021, 39, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menny, M.; Voytenko Palgan, Y.; McCormick, K. Urban Living Labs and the Role of Users in Co-Creation. GAIA 2018, 27, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar-Landgren, D.; Kronsell, A.; Palgan, Y.V.; von Wirth, T. Municipalities as Enablers in Urban Experimentation. J. Environ. Policy Plan. 2019, 21, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäpke, N.; Stelzer, F.; Caniglia, G.; Bergmann, M.; Wanner, M.; Singer-Brodowski, M.; Loorbach, D.; Olsson, P.; Baedeker, C.; Lang, D.J. Jointly Experimenting for Transformation? Shaping Real-World Laboratories by Comparing Them. GAIA Ecol. Perspect. Sci. Soc. 2018, 27, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Leminen, S.; Westerlund, M. A Systematic Review of Living Lab Literature. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 213, 976–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puerari, E.; de Koning, J.I.J.C.; von Wirth, T.; Karré, P.M.; Mulder, I.J.; Loorbach, D.A. Co-Creation Dynamics in Urban Living Labs. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remøy, H.; Wandl, A.; Ceric, D.; van Timmeren, A. Facilitating Circular Economy in Urban Planning. Urban Plan. 2019, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amenta, L.; van Timmeren, A. Beyond Wastescapes: Towards Circular Landscapes. Addressing the Spatial Dimension of Circularity through the Regeneration of Wastescapes. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowski, M.; Varjú, V.; Amenta, L. Transferring Circular Economy Solutions across Differentiated Territories: Understanding and Overcoming the Barriers for Knowledge Transfer. Urban Plan. 2019, 4, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciniegas, G.; Šileryté, R.; Dąbrowski, M.; Wandl, A.; Dukai, B.; Bohnet, M.; Gutsche, J.-M. A Geodesign Decision Support Environment for Integrating Management of Resource Flows in Spatial Planning. Urban Plan. 2019, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuomo, F.; Ravazzi, S.; Savini, F.; Bertolini, L. Transformative Urban Living Labs: Towards a Circular Economy in Amsterdam and Turin. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engez, A.; Leminen, S.; Aarikka-Stenroos, L. Urban Living Lab as a Circular Economy Ecosystem: Advancing Environmental Sustainability through Economic Value, Material, and Knowledge Flows. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, B.; Lewis, N. Urban Food Forestry Networks and Urban Living Labs Articulations. J. Urban. 2021, 14, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, K.; Haupt, W. From Real-World Labs to Urban Experiments: German and International Debates. Raumforsch. Raumordn./Spat. Res. Plan. 2021, 79, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heurkens, E.; Dąbrowski, M. Circling the Square: Governance of the Circular Economy Transition in the Amsterdam Metropolitan Area. Eur. Spat. Res. Policy 2021, 27, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenda, A.M. Urban Living Labs for the Smart Grid. In Urban Living Labs Experimenting with City Futures; Taylor & Francis: Milton Park, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.; Sharpe, S.; Giurco, D. Greening Regional Cities: The Role of Government in Sustainability Transitions; World Sustainability Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland; Institute for Sustainable Futures, University of Technology Sydney: Ultimo, NSW, Australia, 2018; pp. 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Newton, P.; Frantzeskaki, N. Creating a National Urban Research and Development Platform for Advancing Urban Experimentation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, K.; van Bueren, E. The Defining Characteristics of Urban Living Labs. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2017, 7, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrens, J.; Johnstone, P.; Schot, J. Unpacking the Formation of Favourable Environments for Urban Experimentation: The Case of the Bristol Energy Scene. Sustainability 2018, 10, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenda, A.M. Thinking Critically about Smart City Experimentation: Entrepreneurialism and Responsibilization in Urban Living Labs. Local Environ. 2019, 24, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgadillo, E.; Reyes, T.; Baumgartner, R.J. Towards Territorial Product-Service Systems: A Framework Linking Resources, Networks and Value Creation. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 28, 1297–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrory, G.; Schapke, N.; Holmen, J.; Holmberg, J. Sustainability-Oriented Labs in Real-World Contexts: An Exploratory Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronsell, A.; Mukhtar-Landgren, D. Experimental Governance: The Role of Municipalities in Urban Living Labs. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2018, 26, 988–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shove, E.; Pantzar, M.; Watson, M. The Dynamics of Social Practice: Everyday Life and How It Changes; SAGE Publications Inc.: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voytenko, Y.; McCormick, K.; Evans, J.; Schliwa, G. Urban Living Labs for Sustainability and Low Carbon Cities in Europe: Towards a Research Agenda. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 123, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.; Horne, R.; Doyon, A. Housing Industry Transitions: An Urban Living Lab in Melbourne, Australia. Urban Policy Res. 2020, 38, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogedain, A.; Hamm, R. Strengthening Local Economy—An Example of Higher Education Institutions’ Engagement in “Co-Creation for Sustainability”. Region 2020, 7, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuccurullo, C.; Aria, M.; Sarto, F. Foundations and Trends in Performance Management. A Twenty-Five Years Bibliometric Analysis in Business and Public Administration Domains. Scientometrics 2016, 108, 595–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. Bibliometrix: An R-Tool for Comprehensive Science Mapping Analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardin, L. Análise Do Conteúdo; Edições: Lisboa, Portugal, 2011; Volume 70, pp. 99–120. [Google Scholar]
- Hirvensalo, A.; Teerikangas, S.; Reynolds, N.-S.; Kalliomäki, H.; Mäntysalo, R.; Mattila, H.; Granqvist, K. Agency in Circular City Ecosystems—A Rationalities Perspective. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beecroft, R. Embedding Higher Education into a Real-World Lab: A Process-Oriented Analysis of Six Transdisciplinary Project Courses. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyon, A.; Moore, T.; Moloney, S.; Hurley, J. Evaluating Evolving Experiments: The Case of Local Government Action to Implement Ecological Sustainable Design. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2020, 63, 2042–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundurpi, A.; Westman, L.; Luederitz, C.; Burch, S.; Mercado, A. Navigating between Adaptation and Transformation: How Intermediaries Support Businesses in Sustainability Transitions. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 125366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uusikartano, J.; Väyrynen, H.; Aarikka-Stenroos, L. Public Agency in Changing Industrial Circular Economy Ecosystems: Roles, Modes and Structures. Sustainability 2020, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).