Abstract
Given the current huge generation of solid waste worldwide, alternative and innovative methodologies for incorporating these materials should be encouraged elsewhere. In this context, the objective of this research is to evaluate the use of glass waste as a substitute for sand as raw material in ceramics. Formulations containing from 0% to 20% of glass waste were produced, thus replacing natural sand. Extruded and calcined specimens were produced at temperatures of 800, 900 and 1000 °C. The characterization results demonstrated the compatibility and their potential for the glass waste for improving the properties of ceramics. Results of density, water absorption and flexural strength improved when 20% of glass waste was added due to the porosity reduction, provided by the formation of a liquid phase and then by a sintering, promoted by the glass waste. This resulted in coherent properties with ceramic applications in the form of tiles and blocks, at a calcining temperature of 800 °C. On the contrary, results without glass did not reach the necessary parameters even at 1000 °C. In conclusion, the feasibility of using glass waste has been proven, which, in addition to improving the material’s properties, provides economy benefits for the ceramic industry, with the calcination process at milder temperatures.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the generation of industrial solid waste has increased exponentially around the world. This increase has as main reasons the population increase and the consequent increase in waste production [1]; urbanization processes, generating an increase in the number of inhabitants in large cities and the generation of waste [2]; the industrialization process [3]; and the increase in inappropriate places for the final disposal of waste, through dumps [1,2], which further aggravates this environmental problem.
Given this, the need to find ways to reuse waste is increasingly urgent. An alternative, which will be studied in this work, is the reuse of these wastes in the red ceramic industry, due to the diversity of functions that wastes can play in these types of materials [4]. It is known that the clays used for the production of ceramic artifacts are essentially plastic in nature, which enables, for example, use of waste that introduces non-plastic elements into the clayey mass to control this property [5,6]. As an example, the work of Moreira et al. (2008) [7] evaluated the use of ornamental rock waste in ceramics, proving the technological feasibility and economic advantages obtained with the use of this waste. Similar results were obtained by Amaral et al. (2019) [8]. In this research, the authors evaluated the use of ornamental rock residue in ceramic materials produced by uniaxial pressing. The authors’ objective was to evaluate the possibility of applying this waste in paving blocks. The results obtained highlight the feasibility of using waste in the proposed application.
Another possibility is the use of waste that helps to reduce the energy expenditure of the material in the calcination stage. This action can be direct through the supply of energy through exothermic reactions, or indirect through the reduction of the melting temperature of the ceramic material. The work by Delaqua et al. (2020) [9] evaluated the use of powdered cigarette waste in red ceramics with satisfactory results in the evaluated properties and proving the energy gain of the ceramic material during burning. Another relevant work with similar characteristics was developed by Delaqua et al. (2020) [10], where the authors evaluated the use of macrophyte biomass in ceramic materials, with positive conclusions.
A waste of great importance from an industrial point of view is glass waste. Only in Brazil, all products made with glass correspond on average to 3% of urban waste, and about 47% of glass packaging is recycled annually in the country, totaling 470 thousand tons per year [11]. Moreover, in general, this waste is 100% recyclable, that is, it can be indefinitely recycled [12]. However, when this waste is wrongly disposed of, it can be harmful, for reasons such that it is not biodegradable, and in most cases, it has a high cutting power [13]. In this article, the use of wastes from the manufacturing process of tempered glass as a melting element in red ceramics was studied, with the waste being removed from the initial manufacturing stage, that is, from the cutting of flat glass.
Other relevant information on glass waste, especially its application in ceramics, is highlighted by Silva et al. (2017) [14]. In this research, the authors developed a literature review on the use of glass waste in ceramic materials, highlighting several advantages obtained with the use of waste. An advantage is that the use of glass waste can reduce the environmental impact of the ceramic industry. Another issue addressed is the diversity of glass waste, which can be obtained from different sources. This information highlights the importance of conducting research with this material.
Another point that deserves to be highlighted is the need to use a typical ternary composition containing clay (30–60% by weight%), feldspar (15–40% by weight%) and quartz (5–30% by weight%) to produce ceramic materials [15,16]. This composition was studied such as in Luo et al. (2021) [17], where the authors evaluated the effect of replacing quartz and clay with fly ash to produce ceramics. In this study, the authors proved the need to use the typical ternary composition to obtain ceramic materials with adequate properties [18]. Thus, it is expected that the use of glass waste will contribute to the ternary composition, adding feldspar to the mix and providing adequate technological properties.
The main innovations of this work are to propose the use of glass waste to replace the sand used as a substitute for clayey masses. Although there are other published works with glass wastes [14,19], the analysis of new methodologies that enable the real application of the waste in ceramic materials is necessary.
2. Materials and Methods
The materials used in the research were commercial clayey mass, composed of two clays typical of the region used by the industries of Campos dos Goytacazes, RJ, Brazil. The mass is predominantly kaolinitic and has been used in other studies [5,8,9]. Moreover, natural quartz sand and glass waste were used in the formulation’s soda–calcium plan. The waste was obtained from a company located in Rio das Ostras, RJ, Brazil.
The raw materials used in the research were characterized by X-ray fluorescence (XRF), using an S2 POLAR equipment, from BRUKER supplier. In addition, they were characterized through physical particle size tests, using the procedure of NBR 7181 [20], and through scanning electron microscopy (SEM) using a Shimadzu SSX-550 Superscan equipment. The samples used in SEM were prepared in advance using sanding and polishing. The samples were tested immediately after the metallization process, not requiring a conditioning step.
The formulations were produced using 60% clay 1, 20% clay 2 and 20% natural sand, as shown in Table 1. In addition, it was proposed to replace 0–20% glass waste, as a substitute for natural sand.

Table 1.
Formulations used for production of red ceramics.
The formulations defined in Table 1 were initially evaluated for linear and optical dilatometry using a Netzsch brand DIL 402 pc equipment with a heating rate of 5 °C/min and a maximum temperature of 1050 °C. The rate used in this assay can vary in the range of 3–5 °C/min (slow burning), as the dilatometry results are close and do not affect the discussion of the results [21,22]. The masses of approximately 2 g were previously sieved in a sieve with 42 μm opening and prepared with 8% moisture, for subsequent compaction in a cylindrical shape with a force of 2 tons, with an application time of 5 s. In the formulations before firing, plasticity tests were also carried out, through the Atterberg limits defined by NBR 6459 [23] and NBR 7180 [24]. In this way, it was possible to obtain the prognosis of extrusion.
Afterward, the specimens were produced by extrusion, using a prismatic geometry of 15 × 25 × 115 mm. These specimens were evaluated for linear shrinkage by drying and dry density before the calcination process. The firing was carried out in a laboratory Muffle furnace by Maitec model FL 1300, at 800, 900 and 1000 °C. In the burning, a heating rate of 3 °C/min was used until reaching the burning temperature, with a plateau of 240 min. Cooling was by natural convection. After firing, density after firing, linear retraction after firing, water absorption, and flexural strength, were all tested. The procedure was adapted from NBR 15310 [25] and NBR 15270 [26]. Finally, microstructural analysis was performed using SEM.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Raw Materials
Table 2 presents the XRF results of the raw materials. It is observed that the chemical composition of clays is predominantly based on SiO2 and Al2O3, which is typical of clay minerals. The presence of Fe2O3 is important, as it offers the reddish after-firing color typical of ceramic artifacts [27]. The presence of TiO2 helps in the surface hardness of the material, which can improve its mechanical properties, but it makes the material more fragile [28,29]. It can also act as a coloring oxide, clearing the ceramic piece after firing. The presence of K2O, MgO, Na2O and CaO is important because these alkaline and earthy alkaline elements act in the formation of the liquid phase, which is the main sintering mechanism of ceramic materials [6,30]. The loss of ignition, above 10%, is problematic because it is an indication of the presence of organic matter that can increase the material’s shrinkage and porosity, hence the importance of using corrective materials such as sand and glass waste. The use of two types of clay is justified to minimize dependence on a single deposit and to make the material less heterogeneous.

Table 2.
Chemical composition by XRF of raw materials.
The chemical composition of natural sand is predominantly based on SiO2, which is compatible with its mineralogical composition based on quartz. The glass waste, however, has predominantly SiO2 in its composition, which is typical of glass. This material is probably in an amorphous form, contributing to the reduction of the material’s porosity. There is also a high content of Na2O (6.86%) and CaO (15.54%). These components aid in the formation of a liquid phase and improve strength, as they reduce the porosity of the material. The high content of CaO can cause bleaching in ceramic pieces, producing other static patterns for the pieces [31,32].
Figure 1 presents the results of the granulometry of the raw materials, while Figure 2 presents the SEM of the glass waste. It is easy to observe that the particle size of glass waste is close to the particle size of natural sand, which is another result that indicates the feasibility of using glass waste as a substitute for sand in ceramic materials. Regarding the morphology of the waste, an irregular pattern can be seen in Figure 2, due to the amorphism of the material, and particles with a high specific surface area, which is important to increase the resistance of the ceramic materials after firing.
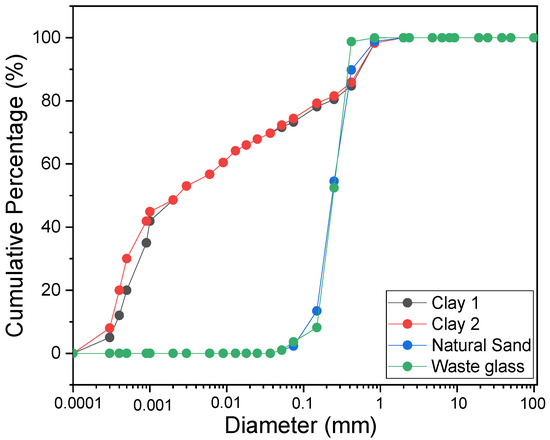
Figure 1.
Granulometry of raw materials.

Figure 2.
SEM of the glass waste.
3.2. Characterization of Ceramic Masses before Firing
Figure 3 presents the results of the dilatometry of the ceramic masses, revealing that the use of glass waste promotes the formation of larger amounts of liquid phase than natural sand, due to the presence of amorphous silica. Around 600 °C, the first relevant event occurs, which is when the glass enters to a softening point, showing a high reduction in its viscosity [33,34]. This is also evident by the optical dilatometry shown in Figure 3. The ceramic mass with 0% glass waste, and which has only natural sand, suffers an adverse event at this same temperature due to the allotropic transformation of the quartz, which can cause defects in ceramic materials [35]. The use of an amorphous material that can fulfill the same roles as natural sand is an advantage in this regard.
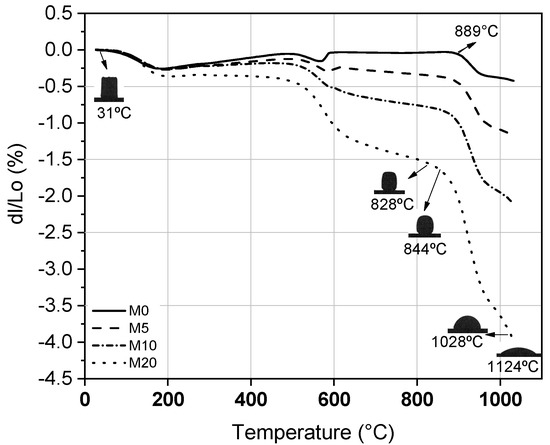
Figure 3.
Dilatometry results.
Another important event takes place between 800 and 1000 °C, where the glass fusion occurs. These temperatures promote greater formation of the liquid phase, which can help the ceramic properties due to the reduction of porosity [33]. The excess of this phase can be harmful, due to the high shrinkage that can cause excessive defects in the manufacturing stage [36]. Thus, it is necessary to evaluate the results obtained after firing, especially for the mass containing 20% of glass waste, to verify that the retraction obtained was not too excessive. This will be discussed further later in this text.
Figure 4 presents the extrusion prognostic results. It is observed that all the studied ceramic masses are within the acceptable extrusion region. This point is important for using the glass waste in place of the natural sand because problems during the extrusion step will impact the properties of the ceramic material before and after firing [8]. This indicates that the behavior of the waste is non-plastic, compatible with natural sand, which also behaves this way.
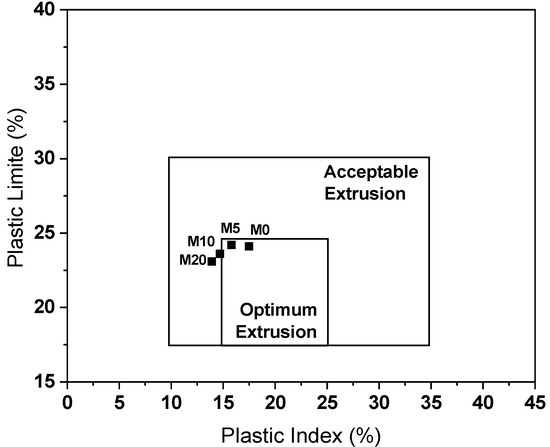
Figure 4.
Extrusion prognosis.
Figure 5 shows the results of apparent density during the drying and linear drying. Note that the apparent density of the specimens increased with the use of the glass protector. This characteristic is because the greater the density, the greater the mass of the material occupying the same volume. This information can help to reduce the porosity of ceramic pieces after firing [37]. Regarding linear drying, note that glass reduces shrinkage. This is also positive due to the formation of particles, which will probably increase after the retraction of ceramic pieces and the firing due to the liquid phase. The reduction in drying shrinkage can compensate the high shrinkage after firing [38].

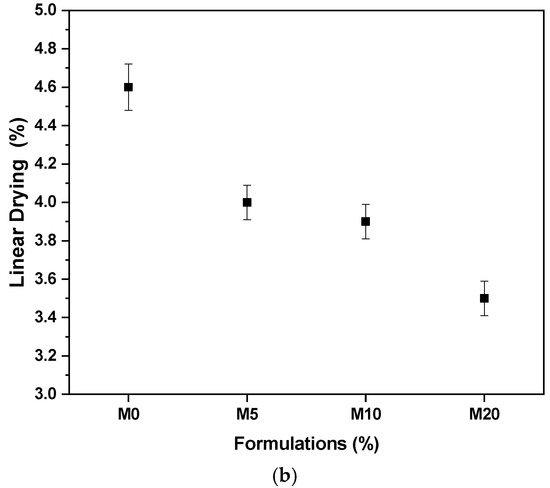
Figure 5.
Results of (a) apparent drying density; (b) linear drying.
3.3. Characterization of Ceramic Masses after Firing
Figure 6 shows the post-fire density and post-fire linear shrinkage results. It is observed that as the calcination temperature increases, the apparent density of the ceramic material increases, as does the linear shrinkage. This behavior is the pattern of this type of material and has already been reported by other authors [7,39]. However, the glass waste promoted an increase in the densification of the ceramic material, which is directly related to the formation of a liquid phase and greater sintering of resistant phases in the material. A negative characteristic is that the use of the waste promoted an increase in the firing shrinkage, which was already expected based on the other results. Compositions 10% and 20% show shrinkage above 4% at a firing temperature of 1000 °C. This can be a problem during the manufacture of ceramic parts due to defects in the developed products. The other retraction values, however, are within the standards established by other authors, such as Girondi et al. (2020) [9], Delaqua et al. (2020b) [10], and Delaqua, et al. (2022) [22].
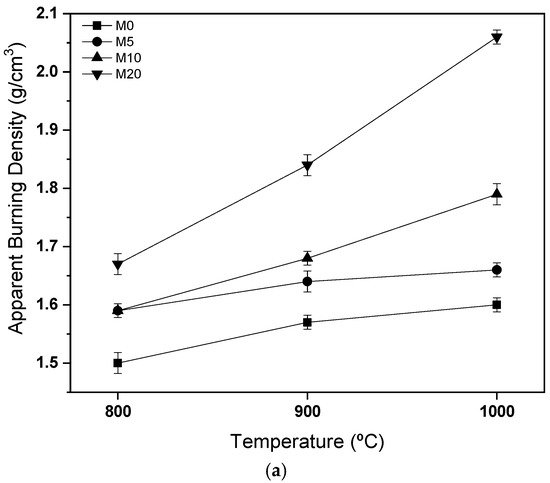

Figure 6.
Results of (a) apparent burning density; (b) linear shrinkage.
Figure 7 presents the water absorption results, in which the mass containing only natural sand (0%) does not meet the limits for tiles, since at all temperatures, it presents water absorption greater than 20%. The masses containing glass waste, especially the one with 20% of the material, meet the water absorption requirements for both tiles and blocks, already in the calcination at 800 °C [7]. This is a great advantage because it provides savings in the manufacture of ceramics. The reduction of water absorption is related to the reduction of porosity and to the formation of liquid phase. As observed in Figure 3, from 600 °C onward, the glass already reaches its softening point, and therefore, it already has a functional liquid phase mechanism. At 1100 °C, glass still meets its operating point, updated, even more with the interconnection mechanisms of the materials [13,33]. These results do not prove the feasibility of using the glass waste, as they are used to use this material.
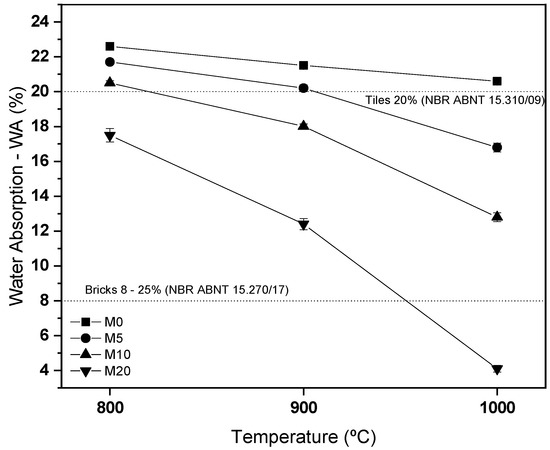
Figure 7.
Water absorption results.
Figure 8 presents the flexural strength results. It is observed that the 20% composition meets the requirements of blocks and tiles already at a temperature of 800 °C, proving the savings highlighted in Figure 7. That is, it does not make much sense to propose calcination at higher temperatures if in this calcination range the composition of 20% already meets the requirements for water absorption and flexural strength, promoting savings in the firing stage. The same results are not possible without the use of glass waste, since the 0% composition does not meet the 6.5 MPa limit for tiles nor at the highest calcination temperature [8,10]. The results obtained are consistent with those highlighted by other authors and can be attributed to the formation of a liquid phase, as previously discussed [32].
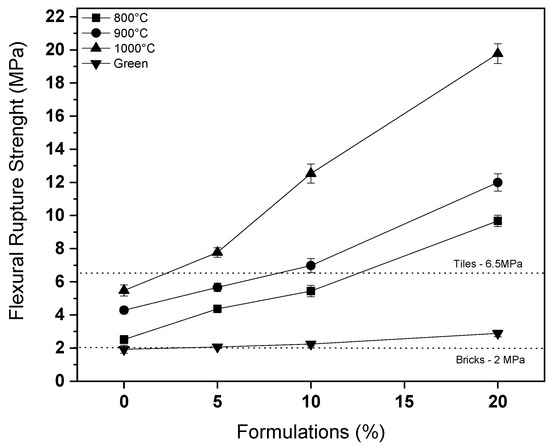
Figure 8.
Flexural rupture strength results.
Based on the discussion of the results, the effect of glass waste on ceramic materials is clear. It is observed that the role of natural sand is to act as a source of quartz for ceramic materials. In ceramic materials, quartz has the function of controlling shrinkage and reducing defects in the material. Quartz replacement, therefore, should be limited so as not to exacerbate these problems. However, the use of glass waste contributes feldspar to the ceramic material. This component, as highlighted in the introduction, contributes to the typical ternary composition of ceramic materials, containing clay, feldspar, and quartz [15,16]. The presence of glass waste contributes to a decrease in the firing temperature and an increase in the apparent density, resulting in a reduction in porosity and an increase in flexural rupture strength. Conversely, glass waste causes defects in ceramic materials, which is why its content should be limited to 20%, as proven in this research. At 1000 °C, the introduction of 20% of the glass waste caused an increase in flexural rupture strength from approximately 5 to almost 20 MPa. Conversely, it caused an increase in linear shrinkage from 2.5% to approximately 7.0%, which leads to an increase in material defects, as will be discussed below. Figure 9 shows a picture of the 20% specimens calcined at 1000 °C, where the formation of defects in the material, which, although they did not affect the strength gain, make the material of low aesthetic value. Therefore, the use of lower temperatures is more advantageous, since at 800 °C, it is possible to obtain values compatible with the main applications of ceramic materials.
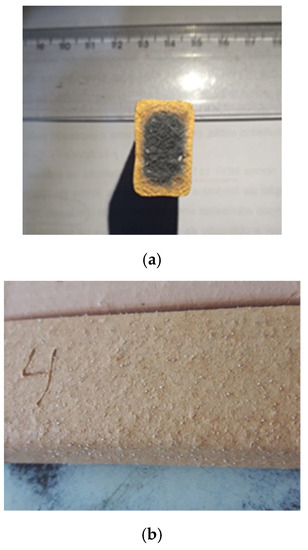
Figure 9.
Macroscopic analysis of the 20% composition: (a) inner surface; (b) external surface.
Figure 9a shows a typical defect of ceramics produced with clays containing high levels of Fe2O3 called black heart. This defect is essentially due to the high iron content present in the clay, which occurred in all compositions calcined at 1000 °C in this research. It is observed that the thermal effect is a catalyst for the black heart. Thus, an essential action to reduce these defects is to use lower calcination temperatures [40]. It can be seen from the results presented above that the use of glass waste makes it possible to reduce the calcination temperature without affecting the properties evaluated. Thus, an efficient action to reduce these defects is the use of glass waste to improve sintering in ceramic materials.
The formation of surface defects, highlighted in Figure 9b, is related to the high linear shrinkage values of this composition, shown in Figure 6b, and to the sintering mechanism promoted by glass waste. This sintering mechanism is potentiated at a temperature of 1000 °C, because as illustrated in Figure 3, at this temperature range, the glass waste melts, causing the surface defects observed in the material [4].
Figure 10 presents the SEM results of the ceramic masses. Figure 10a,b shows the difference between the 0% and 20% compositions calcined at 800 °C, where in Figure 10b, the presence of a more compact and dense structure is visible. This can be attributed to the sintering promoted by the glass waste. Figure 10c,d shows the effects of calcination at 1000 °C in the 0% and 20% formulations, where the formation of a glassy phase in the 20% composition is clear. This is directly related to the use of glass, which promotes the formation of a liquid phase and reduces the porosity of the material. This happens due to the melting process of the glass waste, observed in Figure 3. In this temperature range, the glass becomes liquid, densifying the matrix and filling the pores not accessible by the sand that the glass waste replaces. Thus, the mechanism involved is liquid phase diffusion, which fills the accessible pores of the ceramic material and contributes to the flexural rupture strength [33]. The images are compatible with the results obtained by Figure 7 and Figure 8.
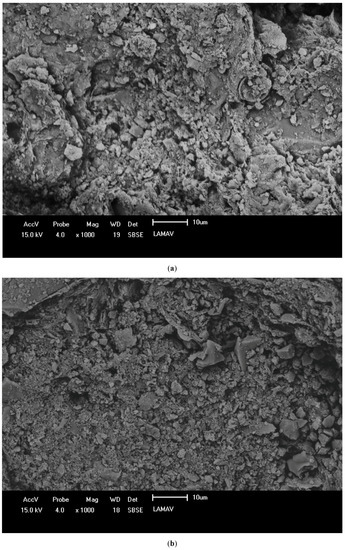

Figure 10.
SEM of specimens: (a) 0% composition calcined at 800 °C; (b) 20% composition calcined at 800 °C; (c) 0% composition calcined at 1000 °C; (d) 20% composition calcined at 1000 °C.
4. Conclusions
Based on the results obtained, the following conclusions were summarized:
- The characterization of the glass waste shows the material’s compatibility with natural sand, enabling its use, in addition to indicating a potential for improving flexural rupture strength, due to the alkali levels, which increases the sintering of the ceramic.
- The masses containing glass waste did not present problems in the extrusion prognosis, in addition to improving the densification of the ceramic material after drying and after firing.
- After firing, the use of 20% glass waste promoted the sintering of the ceramic mass, due to the formation of a liquid phase, reducing porosity and improving the properties of water absorption and flexural strength. There were problems with burn retraction, but within tolerated limits.
- The masses containing 20% of glass waste obtained parameters compatible with industrial applications at a calcination temperature of 800 °C, while the composition containing only natural sand did not present the same behavior even at temperatures of 1000 °C. This indicates the feasibility of using glass waste.
As perspectives for future work, the following stand out: (i) evaluate the influence of the granulometry of the glass waste on the properties of red ceramics; (ii) evaluate the effect of using 15% and 25% of glass waste as a substitute for sand; (iii) carry out durability and degradation tests on the red ceramic containing glass waste.
Author Contributions
Methodology, C.V., G.D. and J.M.; formal analysis G.D. and J.M.; resources S.M. and C.V.; formal analysis, H.C. and F.V.J.; writing—original draft preparation, G.D., J.M. and M.M.; writing—review and editing, C.V., G.D., M.M. and H.C.; supervision, C.V.; project administration, C.V.; funding acquisition, C.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro: E-26/200.847/2021 and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico: 301634/2018.1.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank FAPERJ and CNPQ as well as NewTemper for the waste and the Laboratory of Advanced Materials—LAMAV/UENF for the support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Parthan, S.R.; Milke, M.W.; Wilson, D.C.; Cocks, J.H. Cost Estimation for Solid Waste Management in Industrialising Regions—Precedents, Problems and Prospects. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mrayyan, B.; Hamdi, M.R. Management Approaches to Integrated Solid Waste in Industrialized Zones in Jordan: A Case of Zarqa City. Waste Manag. 2006, 26, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Wang, R.; Yan, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y. A Pilot Ecological Engineering Project for Municipal Solid Waste Reduction, Disinfection, Regeneration and Industrialization in Guanghan City, China. Ecol. Eng. 1998, 11, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondi, M.; Raimondo, M.; Zanelli, C. Clays and Bodies for Ceramic Tiles: Reappraisal and Technological Classification. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 96, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; Roy, K. Cerâmica sustentável derivada de resíduos sólidos: Uma revisão. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2020, 8, 984–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, L.; Toledo, R.; Machado, F.; Holanda, J.N.F.; Vargas, H.; Fariajr, R. Thermal characterisation of red clay from the Northern Region of Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil using an open photoacoustic cell, in relation to structural changes on firing. Appl. Clay Sci. 2008, 42, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, J.; Manhães, J.P.; Holanda, J.N. Processing of red ceramic using ornamental rock powder waste. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 196, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, L.F.; Carvalho, J.P.R.G.d.; da Silva, B.M.; Delaqua, G.C.G.; Monteiro, S.N.; Vieira, C.M.F. Development of Ceramic Paver with Ornamental Rock Waste. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girondi, G.D.; Marvila, M.M.; de Azevedo, A.R.G.; de Souza, C.C.; Souza, D.; de Brito, J.; Vieira, C.M.F. Recycling Potential of Powdered Cigarette Waste in the Development of Ceramic Materials. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2020, 22, 1672–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girondi Delaqua, G.C.; Marvila, M.T.; Souza, D.; Sanchez Rodriguez, R.J.; Colorado, H.A.; Fontes Vieira, C.M. Evaluation of the Application of Macrophyte Biomass Salvinia Auriculata Aublet in Red Ceramics. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 275, 111253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, C.M.F.; Morais, A.S.C.; Monteiro, S.N.; Delaqua, G.C.G. Teste Industrial de Cerâmica Vermelha Incorporada Com Resíduo de Vidro de Lâmpada Fluorescente. Cerâmica 2016, 62, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, B.; Zhang, S. A Review of Glass Ceramic Foams Prepared from Solid Wastes: Processing, Heavy-Metal Solidification and Volatilization, Applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Guo, Y.; Fang, J. Effect of MgO Addition on Crystallization, Microstructure and Properties of Glass-Ceramics Prepared from Solid Wastes. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 881, 159821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.V.; de Brito, J.; Lye, C.Q.; Dhir, R.K. The Role of Glass Waste in the Production of Ceramic-Based Products and Other Applications: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 167, 346–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zheng, S.; Ma, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, X. Ceramic Tiles Derived from Coal Fly Ash: Preparation and Mechanical Characterization. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 11953–11966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, R.R.; Neto, H.G.M.; Santana, L.N.L.; Lira, H.L.; Ferreira, H.S.; Neves, G.A. Optimization of Wastes Content in Ceramic Tiles Using Statistical Design of Mixture Experiments. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 28, 3027–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Chu, P.K.; Qi, T. Substitution of Quartz and Clay with Fly Ash in the Production of Architectural Ceramics: A Mechanistic Study. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 12514–12525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasui, S.; Kim, G.; Nam, J.; van Riessen, A.; Hadzima-Nyarko, M. Effects of Waste Glass as a Sand Replacement on the Strength and Durability of Fly Ash/GGBS Based Alkali Activated Mortar. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 21175–21196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, C.; Pan, L.; Lu, H.; Sun, H.; Hu, X. Preparation of Double-Layer Glass-Ceramic/Ceramic Tile from Bauxite Tailings and Red Mud. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 29, 1887–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NBR 7181; Solo-Análise Granulométrica. Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas-ABNT: São Paulo, Brasil, 2016.
- de Strieder, M.C.; Ratusznei, F.; Pereira, M.; Montedo, O.R.K. Laser-Assisted Glass-Based Sealing of Polished Porcelain Stoneware Tile Surface to Increase Stain Resistance. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 3478–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girondi Delaqua, G.C.; Ferreira, M.d.N.; Amaral, L.F.; Sánchez Rodríguez, R.J.; Atem de Carvalho, E.; Fontes Vieira, C.M. Incorporation of Sludge from Effluent Treatment Plant of an Industrial Laundry into Heavy Clay Ceramics. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 47, 103451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NBR 6459:2016; Solo—Determinação Do Limite de Liquidez. Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas-ABNT: São Paulo, Brasil, 2016.
- NBR 7180:2016; Solo—Determinação Do Limite de Plasticidade. Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas-ABNT: São Paulo, Brasil, 2016.
- NBR 15310; Componentes Cerâmicos—Telhas—Terminologia, Requisitos e Métodos de Ensaio. ABNT: São Paulo, Brasil, 2005.
- NBR 15270-1; Componentes Cerâmicos—Blocos e Tijolos Para Alvenaria Parte 1: Requisitos. ABNT: São Paulo, Brasil, 2017.
- Gencel, O.; Sutcu, M.; Erdogmus, E.; Koc, V.; Cay, V.V.; Gok, M.S. Properties of Bricks with Waste Ferrochromium Slag and Zeolite. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 59, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülen, Ş.M.; Çöpoğlu, N.; Yılmaz, Y.B.; Karaahmet, O.; Cengiz, T.; Gökdemir, H.; Çiçek, B. TiO2-Based Glass-Ceramic Coatings: An Innovative Approach to Architectural Panel Applications. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, M.; Birol, B.; Kaya, F. Investigation of Photocatalytic Properties of TiO2 Nanoparticle Coating on Fly Ash and Red Mud Based Porous Ceramic Substrate. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 24270–24280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conconi, M.S.; Morosi, M.; Maggi, J.; Zalba, P.E.; Cravero, F.; Rendtorff, N.M. Thermal Behavior (TG-DTA-TMA), Sintering and Properties of a Kaolinitic Clay from Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. Cerâmica 2019, 65, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, F.; Jordan, M.M.; Montero, M.A. Ceramic behaviour of clays in Central Chile. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 157, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondi, M.; Guarini, G.; Raimondo, M.; Zanelli, C. Recycling PC and TV Waste Glass in Clay Bricks and Roof Tiles. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karamanov, A.; Dzhantov, B.; Paganelli, M.; Sighinolfi, D. Glass Transition Temperature and Activation Energy of Sintering by Optical Dilatometry. Thermochim. Acta 2013, 553, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoeini, M.; Hesaraki, S.; Kolahi, A. Effect of BaO Substitution for CaO on the Structural and Thermal Properties of SiO2–B2O3–Al2O3–CaO–Na2O–P2O5 Bioactive Glass System Used for Implant Coating Applications. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 31666–31680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes Vieira, C.M.; Monteiro, S.N. Firing Behavior of the Clay Fraction of a Natural Kaolinitic Clay: Are They Different? Mater. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assías, S.G.; Pabón, F.; Cala, N.; Delvasto, P. Incorporation of Fluorescent Lamp Waste into Red-Clay Bricks: Defect Formation, Physical and Mechanical. Properties. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 1621–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliche-Quesada, D.; Martínez-Martínez, S.; Pérez-Villarejo, L.; Iglesias-Godino, F.J.; Martínez-García, C.; Corpas-Iglesias, F.A. Valorization of Biodiesel Production Residues in Making Porous Clay Brick. Fuel Proces. Technol. 2012, 103, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oummadi, S.; Nait-Ali, B.; Alzina, A.; Paya, M.-C.; Gaillard, J.-M.; Smith, D.S. Optical Method for Evaluation of Shrinkage in Two Dimensions during Drying of Ceramic Green Bodies. Open Ceram. 2020, 2, 100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagonbé, B.P.; Tsozué, D.; Nzeukou, A.N.; Ngos, S. Mineralogical, physico-chemical and ceramic properties of clay materials from Sekandé and Gashiga (North, Cameroon) and their suitability in earthenware production. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzo, F.; Guarino, V.; Ciotola, A.; Verde, M.; de Bonis, A.; Capaldi, C.; Morra, V. An Archaeometric Investigation in a Consumption Context: Exotic, Imitation and Traditional Ceramic Productions from the Forum of Cumae (Southern Italy). J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2021, 35, 102768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).