A Bibliometric Review on Artificial Intelligence for Smart Buildings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Scientometric Analysis by Citespace
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Research Methods
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Analysis of the Publications
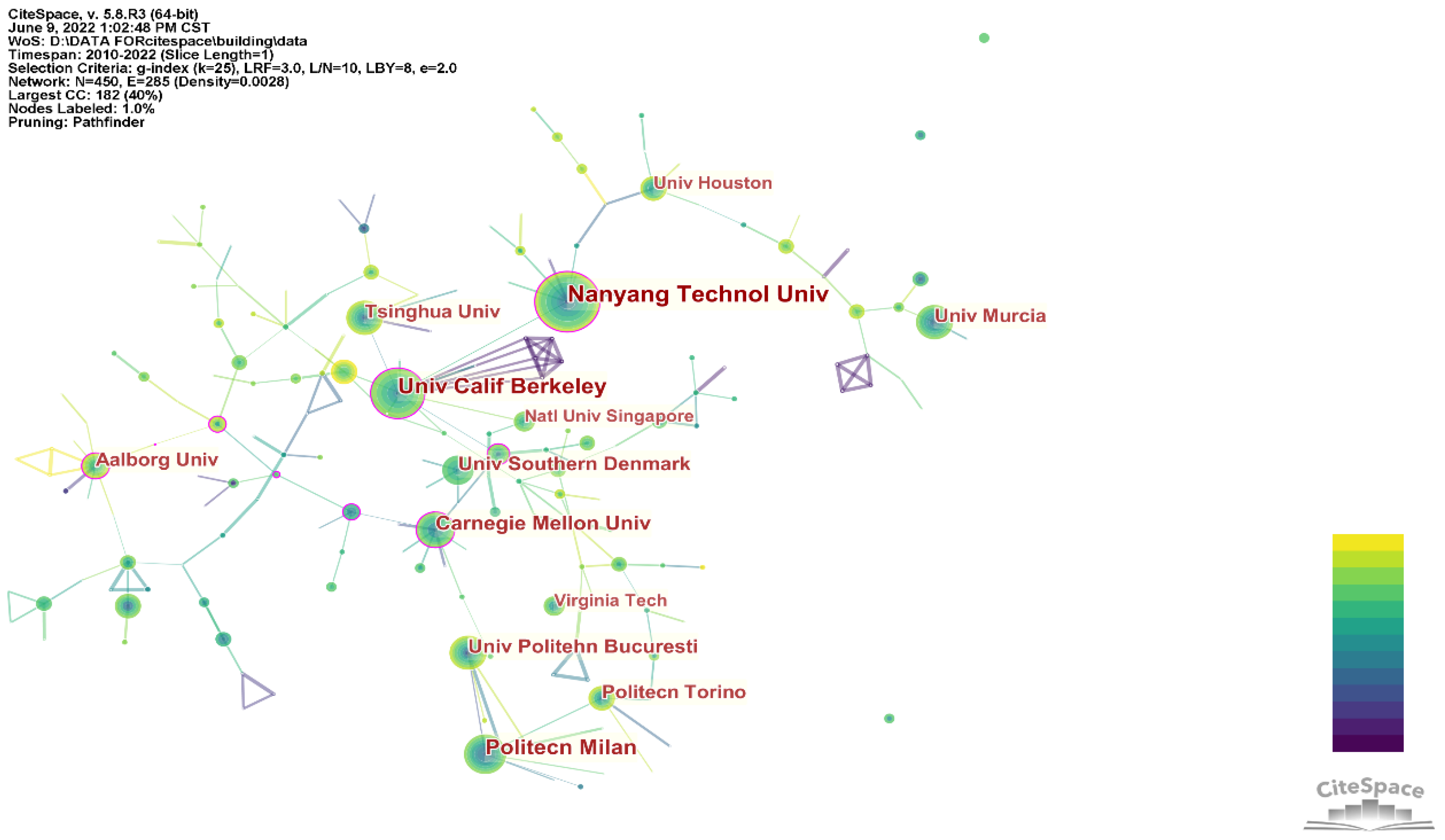
3.2. Nations and Institutions
3.3. Co-Citation Network
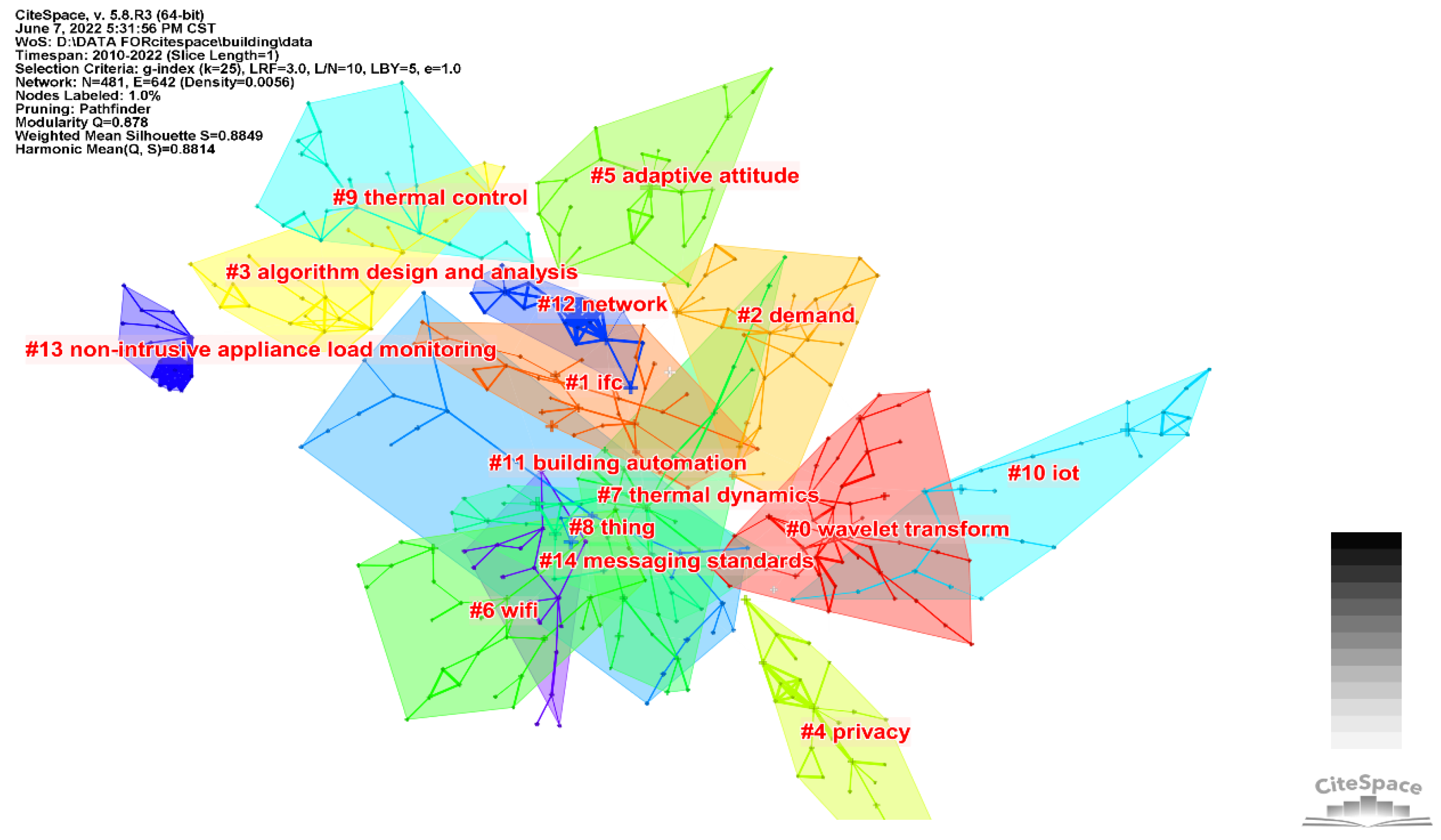
3.4. Keyword Co-Occurrence and Cluster Analysis
3.4.1. Co-Occurrence of Keywords
3.4.2. Clustering of the Keywords
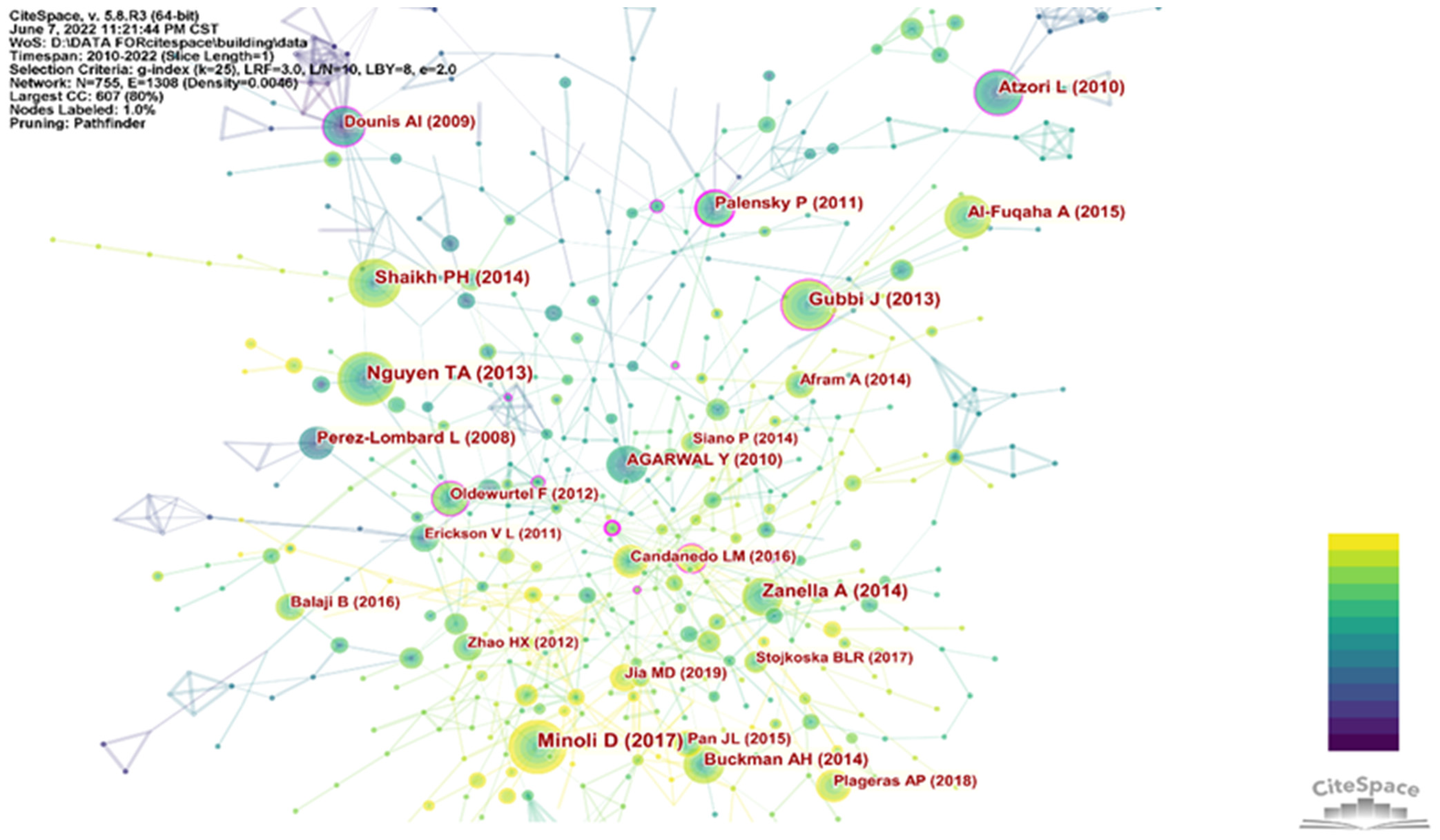
3.5. Literature Co-Citation, Clustering, and Burst Word Detection
3.5.1. Literature Co-Citation
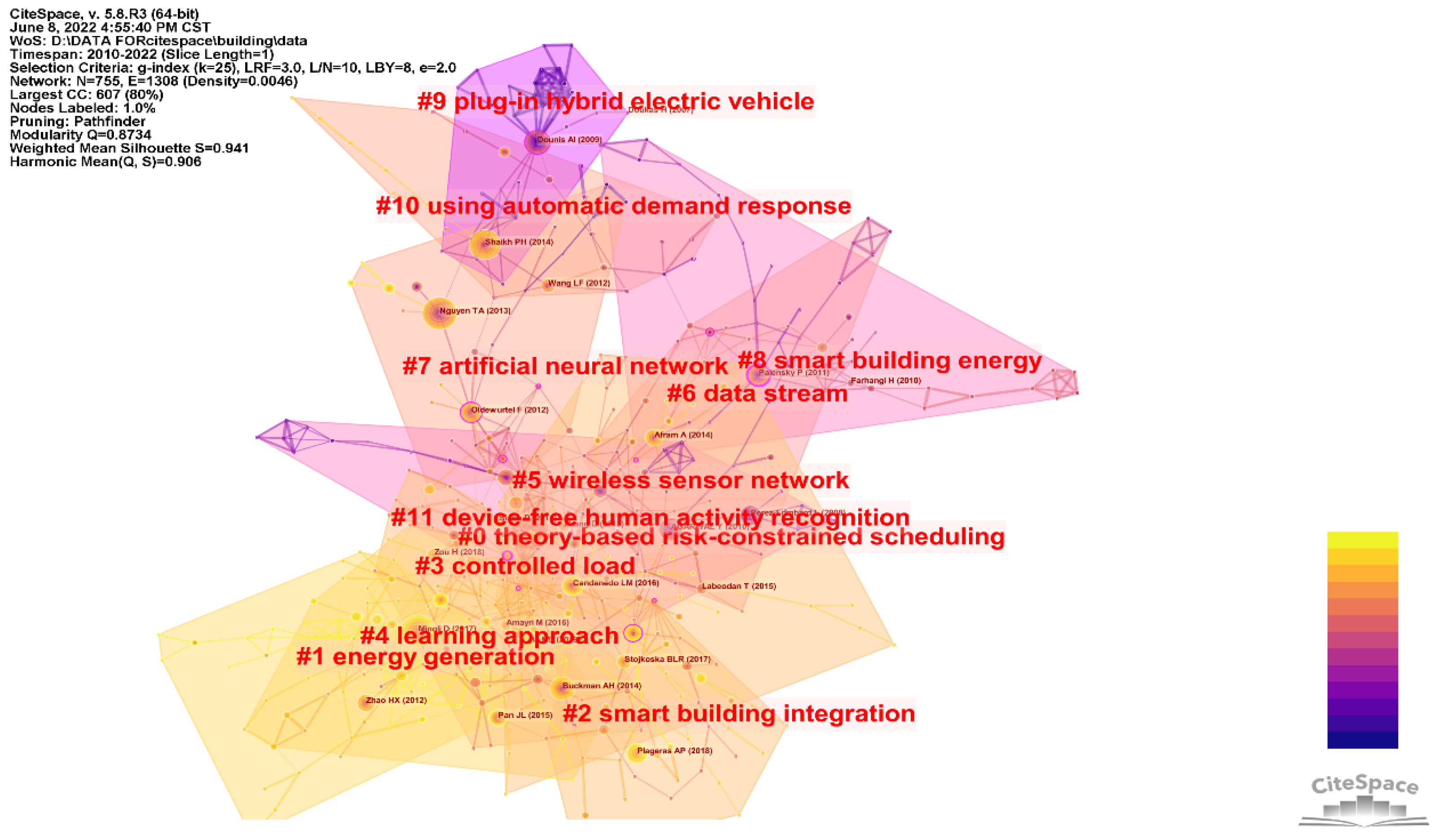
3.5.2. Subject Clustering
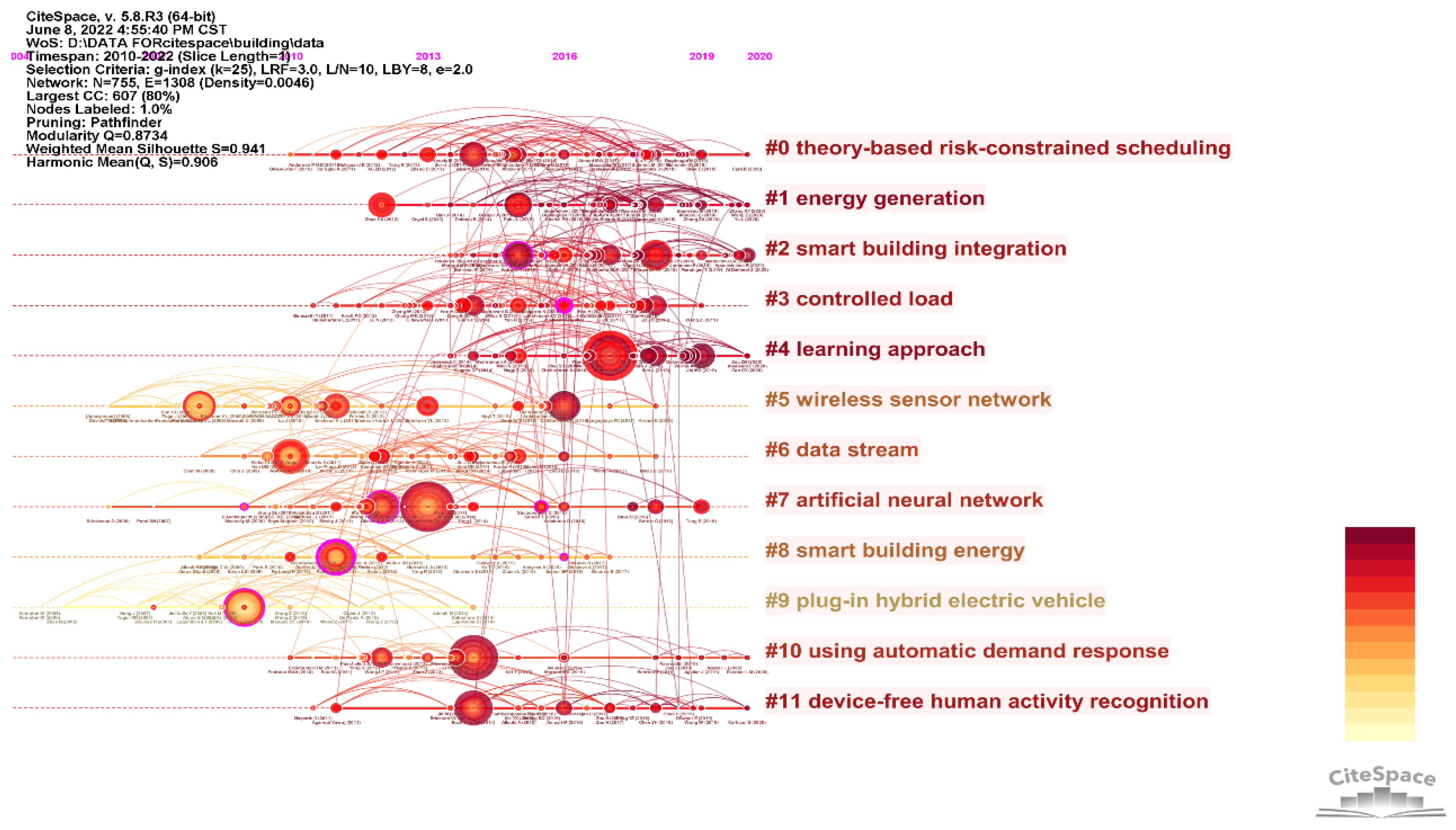
3.6. Burst Detection and Analysis
4. Key Applications in Smart Buildings with AI
4.1. The Most Cited References and Their Topics
4.2. Advanced Technologies Associated with Smart Buildings
4.2.1. The Internet of Things (IOT)
4.2.2. Energy Prediction under Data-Driven Technologies
4.2.3. Performance Optimization
4.2.4. Information Fusion and Optimal Route Planning
4.2.5. Building Maintenance and Management
4.2.6. Building Energy Management Technology
4.2.7. Challenges and Future Trends
5. Conclusions
- (1)
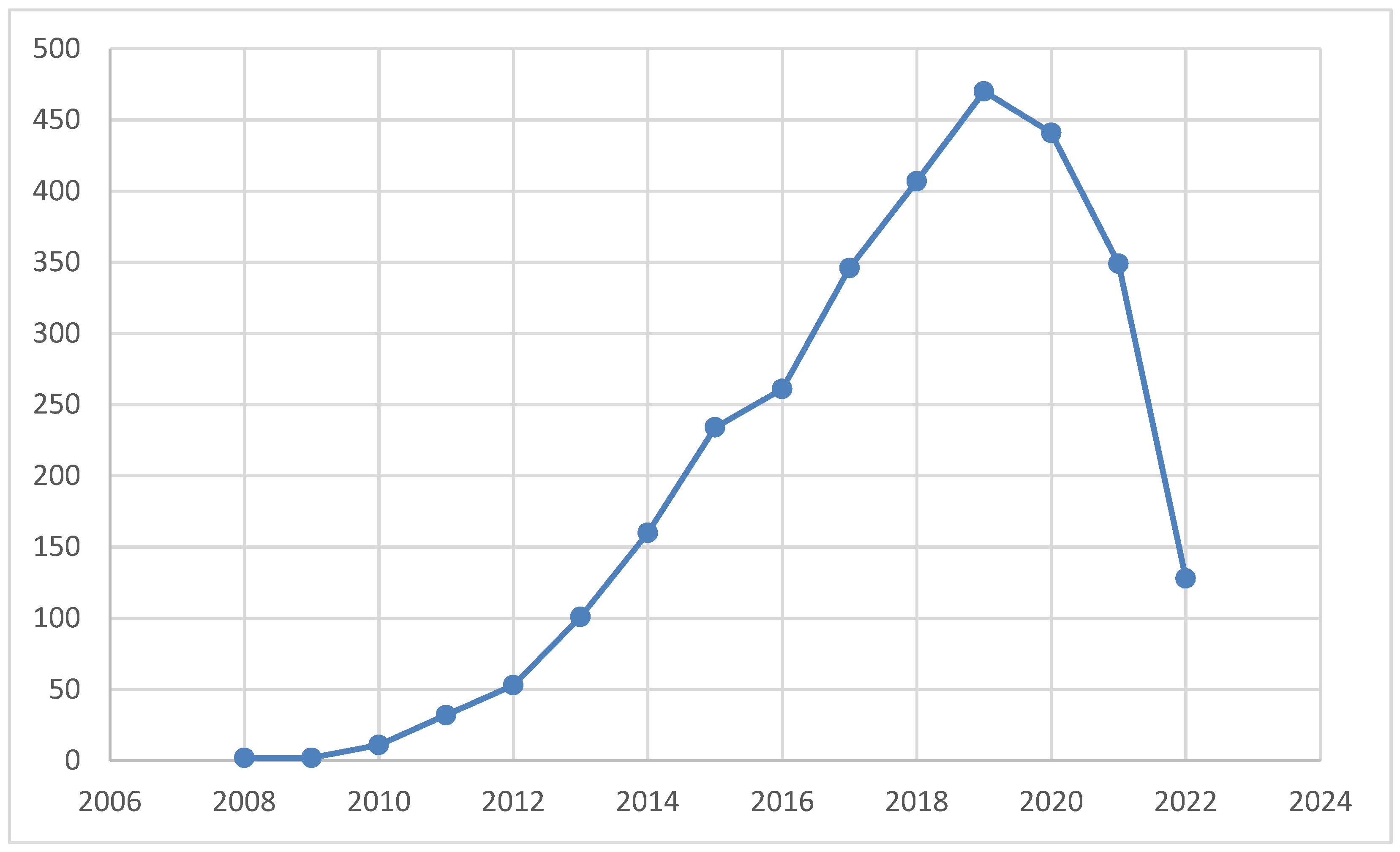
- The number of research and published articles in this field is huge. From 2008 to 2019, the number of 2019 articles has been growing. However, the number of research articles has been declining in the past two years, indicating that the research interests has been receding.
- (2)
- China and the US have the most articles. However, neither the US nor China have connections with other countries, indicating little cooperation between these two countries and others. By contrast, European countries have pretty close cooperation amongst themselves.
- (3)
- By clustering analysis of literature themes and keywords, it is found that the current research interests mainly focus on theory-based risk constraint scheduling, energy power generation, integrated intelligent building, load control, wireless sensor network, etc.
- (4)
- The literature cited and co-citation analysis have found the following main research issues: preliminary research focus on HVAC control technology, Internet technology, efficient energy management in building environment, commercial building automation, industrial plant management. Moreover, great attention has been given to the technologies such as IOT, data-driven-based building energy prediction, and advanced building energy management.
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- AbuGrain, M.Y.; Alibaba, H.Z. Optimizing Existing Multistory Building Designs towards Net-Zero Energy. Sustainability 2017, 9, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.P.C.; Darko, A.; Ameyaw, E.E. Strategies for Promoting Green Building Technologies Adoption in the Construction Industry—An International Study. Sustainability 2017, 9, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinopoulos, G.; Serasidou, A.; Antoniadou, P.; Papadopoulos, A.M. Building Integrated Shading and Building Applied Photovoltaic System Assessment in the Energy Performance and Thermal Comfort of Office Buildings. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, S.; Srinivasan, R.S.; Kibert, C.J.; Steiner, R.L.; Demirezen, E. AI-Based Campus Energy Use Prediction for Assessing the Effects of Climate Change. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H. Visualized Co-Simulation of Adaptive Human Behavior and Dynamic Building Performance: An Agent-Based Model (ABM) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) Approach for Smart Architectural Design. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.A.; Aiello, M. Energy intelligent buildings based on user activity: A survey. Energy Build. 2013, 56, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaneh, H.; Malehmirchegini, L.; Bejan, A.; Afolabi, T.; Mulumba, A.; Daka, P.P. Artificial Intelligence Evolution in Smart Buildings for Energy Efficiency. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M. Research on AI-Smart Building. J. Inf. Technol. Civ. Eng. Archit. 2018, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Wu, Z.; Fu, B. Key Technologies for Driving Innovative Application of Intelligent Building. Build. Electr. 2019, 10, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Minoli, D.; Sohraby, K.; Occhiogrosso, B. IoT Considerations, Requirements, and Architectures for Smart Buildings—Energy Optimization and Next-Generation Building Management Systems. IEEE Int. Things J. 2017, 4, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, P.H.; Nor, N.B.M.; Nallagownden, P.; Elamvazuthi, I.; Ibrahim, T. A review on optimized control systems for building energy and comfort management of smart sustainable buildings. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 34, 409–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, A.; Bui, N.; Castellani, A.; Vangelista, L.; Zorzi, M. Internet of things for smart cities. IEEE Internet Things J. 2014, 1, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, A.M.U.; Chun, D.; Zeeshan; Han, H.; Jeon, G.; Chen, K. A review of the applications of artificial intelligence and big data to buildings for energy-efficiency and a comfortable indoor living environment. Energy Build. 2019, 202, 109383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, C.S.; Costa, C.; Pina, A.; Santos, M.Y.; Ferrão, P. An urban building database (UBD) supporting a smart city information system. Energy Build. 2018, 158, 244–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, A.; Liu, S.; Yu, Y. Comparative study of data driven methods in building electricity use prediction. Energy Build. 2019, 194, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valinejadshoubi, M.; Moselhi, O.; Bagchi, A.; Salem, A. Development of an IoT and BIM-based automated alert system for thermal comfort monitoring in buildings. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 66, 102602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apanaviciene, R.; Vanagas, A.; Fokaides, P.A. Smart Building Integration into a Smart City (SBISC): Development of a New Evaluation Framework. Energies 2020, 13, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffarianhoseini, A.; Berardi, U.; AlWaer, H.; Chang, S.; Halawa, E.; Ghaffarianhoseini, A.; Clements-Croome, D. What is an intelligent building? Analysis of recent interpretations from an international perspective. Archit. Sci. Rev. 2016, 59, 338–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albino, V.; Berardi, U.; Dangelico, R.M. Smart cities: Definitions, dimensions, performance, and initiatives. J. Urban Technol. 2015, 22, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2006, 57, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, X. Research on the Literature of Green Building Based on the Web of Science: A Scientometric Analysis in CiteSpace (2002–2018). Sustainability 2019, 11, 3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Chan, F.T.S.; Zhu, F.; Wang, X.; Yang, J. A Visualization Review of Cloud Computing Algorithms in the Last Decade. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Chan, F.T.; Zhu, F.; Wang, X.; Yang, J. Ten Years of Sustainability (2009 to 2018): A Bibliometric Overview. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1655. [Google Scholar]
- Dounis, A.I.; Caraiscos, C. Advanced control systems engineering for energy and comfort management in a building environment—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 1246–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G. The Internet of Things: A Survey. Comput. Netw. 2010, 54, 2787–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palensky, P.; Dietrich, D. Demand Side Management: Demand Response, Intelligent Energy Systems, and Smart Loads. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2011, 7, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fuqaha, A.; Guizani, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Aledhari, M.; Ayyash, M. Internet of Things: A Survey on Enabling Technologies, Protocols, and Applications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 17, 2347–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbi, J.; Buyya, R.; Marusic, S.; Palaniswami, M. Internet of Things (IoT): A Vision, Architectural Elements, and Future Directions. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2013, 29, 1645–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afram, A.; Janabi-Sharifi, F. Theory and applications of HVAC control systems—A review of model predictive control (MPC). Build. Environ. 2014, 72, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Lombard, L.; Ortiz, J.; Pout, C. A review on buildings energy consumption information. Energy Build. 2008, 40, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siano, P. Demand response and smart grids—A survey. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 30, 461–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, Y.; Balaji, B.; Gupta, R.; Lyles, J.; Weng, T. Occupancy-driven energy management for smart building automation. In Proceedings of the 2nd ACM Workshop on Embedded Sensing Systems for Energy-Efficiency in Buildings (BuildSys’10), Zurich, Switzerland, 3–5 November 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dewurtel, F.; Parisio, A.; Jones, C.N.; Gyalistras, D.; Gwerderd, M.; Stauche, V.; Lehmannf, B.; Moraria, M. Use of model predictive control and weather forecasts for energy efficient building climate control. Energy Build. 2012, 45, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, V.L.; Carreira-Perpiñán, M.Á.; Cerpa, A.E. OBSERVE: Occupancy-based system for efficient reduction of HVAC energy. In Proceedings of the 10th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, Chicago, IL, USA, 12–14 April 2011; pp. 258–269. [Google Scholar]
- Candanedo, L.M.; Feldheim, V. Accurate occupancy detection of an office room from light, temperature, humidity and CO2 measurements using statistical learning models. Energy Build. 2016, 112, 28–39. [Google Scholar]
- Balaji, B. Some remarks on quantum physics, stochastic processes, and nonlinear filtering theory. In Proceedings of the SPIE-The International Society for Optical Engineering, Signal Processing, Sensor/Information Fusion, and Target Recognition XXV, Baltimore, MD, USA, 17–21 April 2016; Volume 9842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.X.; Magoulès, F. A review on the prediction of building energy consumption. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 3586–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojkoska, B.; Trivodaliev, K.V. A review of internet of things for smart home: Challenges and solutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140 Pt 3, 1454–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Komeily, A.; Wang, Y.; Srinivasan, R.S. Adopting internet of things for the development of smart buildings: A review of enabling technologies and applications. Autom. Constr. 2019, 101, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Jain, R.; Paul, S.; Vu, T.; Saifullah, A.; Sha, M. An Internet of Things Framework for Smart Energy in Buildings: Designs, Prototype, and Experiments. IEEE Int. Things J. 2015, 2, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckman, A.H.; Mayfield, M.; Beck, S.B.M. What is a smart building? Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 2014, 3, 92–109. [Google Scholar]
- Plageras, A.P.; Psannis, K.E.; Stergiou, C.; Wang, H.; Gupta, B.B. Efficient IoT-based sensor BIG Data collection–processing and analysis in smart buildings. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 82, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labeodan, T.; Zeiler, W.; Boxem, G.; Zhao, Y. Occupancy measurement in commercial office buildings for demand-driven control applications—A survey and detection system evaluation. Energy Build. 2015, 93, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Sookoor, T.; Srinivasan, V.; Gao, G.; Holben, B.; Stankovic, J.; Field, E.; Whitehouse, K. The smart thermostat: Using occupancy sensors to save energy in homes. In Proceedings of the 8th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, Zürich, Switzerland, 3–5 November 2010; pp. 211–224. [Google Scholar]
- Serale, G.; Fiorentini, M.; Capozzoli, A.; Bernardini, D.; Bemporad, A. Model predictive control (MPC) for enhancing building and HVAC system energy efficiency: Problem formulation, applications and opportunities. Energies 2018, 11, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amasyali, K.; El-Gohary, N.M. A Review of Data-Driven Building Energy Consumption Prediction Studies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 1192–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T.M.; Boudreau, M.-C.; Helsen, L.; Henze, G.; Mohammadpour, J.; Noonan, D.; Patteeuw, D.; Pless, S.; Watson, R.T. Ten questions concerning integrating smart buildings into the smart grid. Build. Environ. 2016, 108, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Q. Deep reinforcement learning for building HVAC control. In Proceedings of the 54th Annual Design Automation Conference 2017, Austin, TX, USA, 18–22 June 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, J.; Rezgui, Y.; Kwan, A.; Piriou, S. A zone-level, building energy optimisation combining an artificial neural network, a genetic algorithm, and model predictive control. Energy 2018, 151, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali Saraji, M.; Streimikiene, D.; Kyriakopoulos, G.L. Fermatean fuzzy CRITIC-COPRAS method for evaluating the challenges to industry 4.0 adoption for a sustainable digital transformation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, R.; Cavone, G.; Pippia, T.; De Schutter, B.; Dotoli, M. Robust Optimal Control for Demand Side Management of Multi-Carrier Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2022, 19, 1338–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, H.; Jadid, S. Optimal energy management for multi-microgrid considering demand response programs: A stochastic multi-objective framework. Energy 2020, 195, 116992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarabaggio, P.; Carli, R.; Dotoli, M. Noncooperative Equilibrium Seeking in Distributed Energy Systems Under AC Power Flow Nonlinear Constraints. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yea, Z.; Kimb, M.K. Predicting Electricity Consumption in a Building Using an Optimized Back-propagation and Levenberg–Marquardt Back-propagation Neural Network: Case Study of a Shopping Mall in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 42, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, B.; Xu, C.; Mahapatra, R.P.; Selvaraj, P. Understanding the Cyber-Physical System in International Stadiums for Security in the Network from Cyber-Attacks and Adversaries using AI. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, B.I. Research on Path-Finding Behavior of Display Space Based on Visual Domain Method- Take Dalian Urban Planning Exhibition Center as An Example. Master’s Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 15 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.-L. Constructing intelligent living-space controlling system with blue-tooth and speech-recognition microprocessor. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 9308–9318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, A.; Ugaji, M.; Yamabe, Y. A building structural-performance monitoring system using RFID tag with sensors. In Proceedings of the EG-ICE 2010—17th International Workshop on Intelligent Computing in Engineering, Nottingham, UK, 30 June–2 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Simma, K.; Mammoli, C.J.A.; Bogus, S.M. Real-Time Occupancy Estimation Using WiFi Network to Optimize HVAC Operation. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 155, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, S.; Larijani, H.; Curtis, K.; Wixted, A.; Amini, A. Empirical Propagation Performance Evaluation of LoRa for Indoor Environment. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Informatics INDIN, Emden, Germany, 24–26 July 2017; pp. 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Miao, Y.M.; Hao, Y.X.; Hwang, K. Narrow Band Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 20557–20577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 13757-2; Communication Systems for Meters and Remote Reading of Meters, Part 2, Physical and Link Layer. CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 2004; pp. 1–32, ISBN: 0580449599.
- Wang, Y.M. The internet of things smart home system design based on ZigBee/GPRS technology. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 263, 2849–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.M.; Lim, J.H. Smart Home Energy Management System using IEEE 802.15.4 and ZigBee. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2010, 56, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Srinivasan, R.S. A review of artificial intelligence based building energy use prediction: Contrasting the capabilities of single and ensemble prediction models. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 75, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merabet, G.H.; Essaaidi, M.; Ben Haddou, M.; Qolomany, B.; Qadir, J.; Anan, M.; Al-Fuqaha, A.; Abid, M.R.; Benhaddou, D. Intelligent building control systems for thermal comfort and energy-efficiency: A systematic review of artificial intelligence-assisted techniques. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 144, 110969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.Y.; Zhang, S.; Stone, P. The PETLON Algorithm to Plan Efficiently for Task-Level-Optimal Navigation. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2020, 69, 471–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Wang, J.; Qi, C.; Min, C.; Sundén, B. Medium-term heat load prediction for an existing residential building based on a wireless on-off control system. Energy 2018, 152, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Li, B.; Lei, Y.; Liu, M. Analysis of a Residential Building Energy Consumption Demand Model. Energies 2011, 4, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusiak, A.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z. A data-driven approach for steam load prediction in buildings. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S.; Yuen, R.; Lee, E. An intelligent approach to assessing the effect of building occupancy on building cooling load prediction. Build. Environ. 2011, 46, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Moayedi, H.; Bahiraei, M.; Lyu, Z. Employing artificial bee colony and particle swarm techniques for optimizing a neural network in prediction of heating and cooling loads of residential buildings. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 120082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Srikumar, V.; Smith, A.D. Predicting electricity consumption for commercial and residential buildings using deep recurrent neural networks. Appl. Energy 2018, 212, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Wang, J.; Gang, W.; Li, S. Assessment of deep recurrent neural network-based strategies for short-term building energy predictions. Appl. Energy 2019, 236, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potočnik, P.; Šilc, J.; Papa, G. A comparison of models for forecasting the residential natural gas demand of an urban area. Energy 2018, 167, 511–522. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Meng, Q.; Cai, J.; Yoshino, H.; Mochida, A. Applying support vector machine to predict hourly cooling load in the building. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 2249–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.S.; Hassan, M.Y.; Abdullah, M.P.; Rahman, H.A.; Hussin, F.; Abdullah, H.; Saidur, R. A review on applications of ANN and SVM for building electrical energy consumption forecasting. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Fang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, X.; Ji, Y. Using Long Short-Term Memory Networks to Predict Energy Consumption of Air-conditioning Systems. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 55, 102000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.Y.; Cho, S.B. Predicting Residential Energy Consumption using CNN-LSTM Neural Networks. Energy 2019, 182, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedi, J.; Toshniwal, D. Deep learning framework to forecast electricity demand. Appl. Energy 2019, 238, 1312–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zi, X.H.; Liang, L.Q.; Fan, Z.B.; Yan, J.W.; Pan, D.M. Forecasting performance comparison of two hybrid machine learning models. J. Build. Eng. 2019, 21, 64–73. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, R.K.; Smith, K.M.; Culligan, P.J.; Taylor, J.E. Forecasting energy consumption of multi-family residential buildings using support vector regression: Investigating the impact of temporal and spatial monitoring granularity on performance accuracy. Appl. Energy 2014, 123, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, P.; Chu, Y.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Ni, L.; Bao, Y.; Wang, K. Short-term electrical load forecasting using the Support Vector Regression (SVR) model to calculate the demand response baseline for office buildings. Appl. Energy 2017, 195, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrooz, F.; Mariun, N.; Marhaban, M.; Mohd Radzi, M.; Ramli, A. Review of control techniques for HVAC systems—Nonlinearity approaches based on fuzzy cognitive maps. Energies 2018, 11, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnier, L.; Haghighat, F. Multiobjective optimization of building design using TRNSYS simulations, genetic algorithm, and Artificial Neural Network. Build Environ. 2010, 45, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Li, B.; Jia, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, D. Application of multi-objective genetic algorithm to optimize energy efficiency and thermal comfort in building design. Energy Build. 2015, 88, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collotta, M.; Messineo, A.; Nicolosi, G.; Pau, G. A dynamic fuzzy controller to meet thermal comfort by using neural network forecasted parameters as the input. Energies 2014, 7, 4727–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgarm, N.; Sajadi, B.; Kowsary, F.; Delgarm, S. Multi-objective optimization of the building energy performance: A simulation-based approach by means of particle swarm optimization (PSO). Appl. Energy 2016, 170, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H. A Feature Selection-Based Predictive-Learning Framework for Optimal Actuator Control in Smart Homes. Actuators 2021, 10, 84. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, M.; Vallée, J.C.; Shtrepi, L.; Astolfi, A.; Fabrizio, E. A thermal and acoustic co-simulation method for the multi-domain optimization of nearly zero energy buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 40, 102699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonban, M.S.; Romeral, L.; Akbarimajd, A.; Ali, Z.; Ghazimirsaeid, S.S.; Marzband, M.; Putrus, G. Autonomous energy management system with self-healing capabilities for green buildings (microgrids). J. Build. Eng. 2020, 34, 101604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, M.; Liu, X.; Howe, J. Multi-agent Gaussian Adaptive Resonance Theory Map for building energy control and thermal comfort management of UCLan’s WestLakes Samuel Lindow Building. Energy Build. 2014, 80, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, M.; Stables, M.; Liu, X.; Howe, J. Intelligent multi-agent system for building heat distribution control with combined gas boilers and ground source heat pump. Energy Build. 2013, 62, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Davidsson, P.; Boman, M. Distributed monitoring and control of office buildings by embedded agents. Inf. Sci. 2005, 171, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Peng, Y.; Lu, D. Survey of multisensor data fusion models. J. Tsinghua Univ. (Sci. Tech.) 1996, 36, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, L.A. Sensor and Data Fusion Concepts and Applications; SPIE Optical Engineering Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Llinas, J.; Hall, D.L. An introduction to multi-sensor data fusion. In Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (Cat. No.98CH36187) (ISCAS ’98), Beijing, China, 31 May–3 June 1998; Volume 6, pp. 537–540. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Guam, X.; Wang, G. Survey on the Progress and Prospect of Multi-sensor Information Fusion. J. Astronaut. 2005, 26, 524–530. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Jiang, C.; Zhou, S.; Tan, H.; Liu, Y. Trajectory Planning Based on Real-Time Octree Map for Indoor Unknown Environment Exploration. Electron. Opt. Control 2021, 28, 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Matos, R.; Rodrigues, H.; Costa, A.; Rodrigues, F. Building Condition Indicators Analysis for BIM-FM Integration. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2022, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahramani, Z. Probabilistic machine learning and artificial intelligence. Nature 2015, 521, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paral, A.; Roy, D.; Samanta, K. A deep learning-based approach for condition assessment of semi-rigid joint of steel frame. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 34, 101946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Burton, H.; Huang, H. Machine Learning applications for building structural design and performance assessment: State-of-art review. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 33, 101816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.-J.; Choi, W.; Suh, G.; Mahmoudkhani, S.; Büyüköztürk, O. Autonomous Structural Visual Inspection Using Region-Based Deep Learning for Detecting Multiple Damage Types. Comput. Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2017, 33, 731–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Mosalam, K.M. Deep Transfer Learning for Image-Based Structural Damage Recognition. Comput. Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2018, 33, 748–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osco, L.; Junior, J.; Ramos, A.; Furuya, D.; Santana, D.; Teodoro, L.; Gonçalves, W.; Baio, F.; Pistori, H.; Junior, C.; et al. Leaf Nitrogen Concentration and Plant Height Prediction for Maize Using UAV-Based Multispectral Imagery and Machine Learning Techniques. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borin, P.; Cavazzini, F. Condition assessment of rc bridges. Integrating machine learning, photogrammetry and bim. In International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Proceedings of the 27th CIPA International Symposium “Documenting the Past for a Better Future”, Ávila, Spain, 1–5 September 2019; International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing: Hannover, Germany, 2019; Volume XLII-2/W15. [Google Scholar]


| Order | Concerns | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Annual publication amount |
|
| 2 | Key nations/institutions and their research networks |
|
| 3 | Most cited authors |
|
| 4 | Keywords |
|
| 5 | Publications |
|
| 6 | Advanced technologies in AI-smart buildings |
|
| No. | Country | Number of Investigations/Articles | Betweeniess Centrality |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | USA | 651 | 0.06 |
| 2 | People Republic of China | 332 | 0.03 |
| 3 | Italy | 246 | 0.29 |
| 4 | France | 203 | 0.03 |
| 5 | India | 174 | 0 |
| 6 | Spain | 154 | 0.36 |
| 7 | UK | 124 | 0.16 |
| 8 | Germany | 120 | 0.34 |
| No. | Country | Institution | Publication Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Singapore | Nanyang Technological University | 62 |
| 2 | America | UC, Berkeley | 54 |
| 3 | Italy | Milan University of Technology | 43 |
| 4 | America | Carnegie Mellon University | 37 |
| 5 | Denmark | The University of Southern Denmark | 8 |
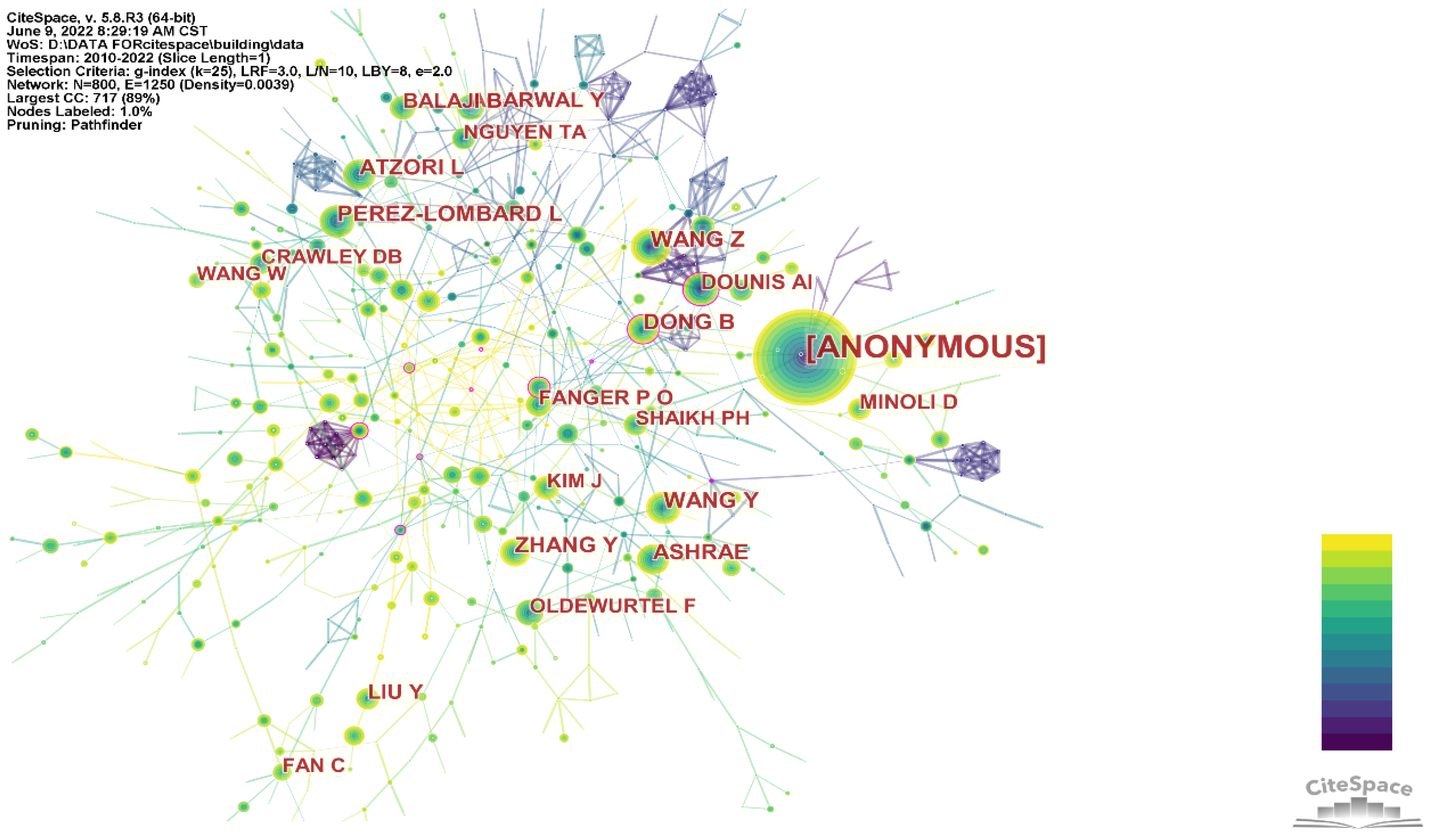
| No. | Author | Frequency | Betweeniess Centrality |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [Anonymous] | 791 | 0.04 |
| 2 | Wang, Z. | 101 | 0.03 |
| 3 | Dong, B. | 87 | 0.19 |
| 4 | Chen, X. J. | 70 | 0.16 |
| 5 | Ma, Y. D. | 64 | 0.10 |
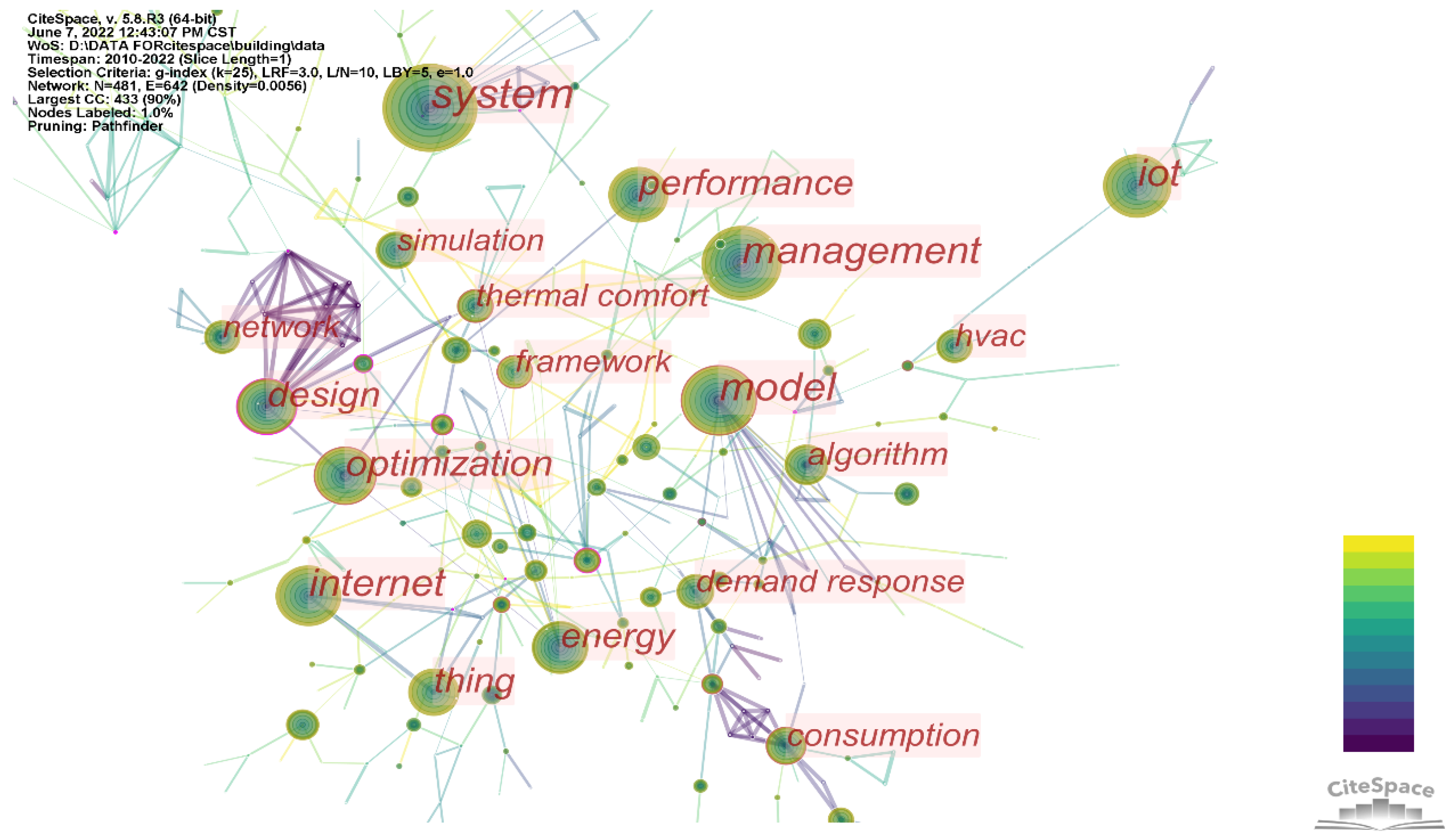
| Rank | Frequency | Betweenness Centrality | Keyword |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 317 | 0.06 | System |
| 2 | 206 | 0.17 | Model |
| 3 | 181 | 0.1 | Internet |
| 4 | 176 | 0.06 | Internet of things |
| 5 | 168 | 0 | Management |
| 6 | 143 | 0.12 | Optimization |
| 7 | 117 | 0.33 | Design |
| 8 | 103 | 0.08 | Energy |
| 9 | 95 | 0.08 | Demand response |
| 10 | 72 | 0.14 | Consumption |
| 11 | 63 | 0.12 | Framework |
| 12 | 62 | 0.17 | Thermal comfort |
| 13 | 43 | 0.23 | Efficiency |
| 14 | 39 | 0.26 | Strategy |
| 15 | 33 | 0.27 | Demand Side management |
| Cluster Number and Name | Author | Year | Frequency | DOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #0 theory-based risk-constrained scheduling | Afram A. [29] | 2014 | 24 | 10.1016/j.buildenv.2013.11.016 |
| #1 energy generation | Pan J.L. [40] | 2015 | 25 | 10.1109/JIOT.2015.2413397 |
| #2 smart building integration | Plageras A.P. [42] | 2018 | 26 | 10.1016/j.future.2017.09.082 |
| #3 controlled load | Siano P. [31] | 2014 | 21 | 10.1016/j.rser.2013.10.022 |
| #4 learning approach | Minoli D. [10] | 2017 | 70 | 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2647881 |
| #5 wireless sensor network | Candanedo L.M. [35] | 2016 | 26 | 10.1016/j.enbuild.2015.11.071 |
| #6 data stream | Labeodan T. [43] | 2015 | 29 | 10.1016/j.enbuild.2015.02.028 |
| #7 artificial neural network | Nguyen T.A. [6] | 2013 | 57 | 10.1016/j.enbuild.2012.09.005 |
| #8 smart building energy | Palensky P. [26] | 2011 | 34 | 10.1109/TII.2011.2158841 |
| #9 plug-in hybrid electric vehicle | Dounis A.I. [24] | 2009 | 32 | 10.1016/j.rser.2008.09.015 |
| #10 using automatic demand response | Shaikh P.H. [11] | 2014 | 48 | 10.1016/j.rser.2014.03.027 |
| #11 device-free human activity recognition | Buckman A.H. [41] | 2014 | 36 | 10.1108/SASBE-01-2014-0003 |
| Rank | Author(s) | Year | DOI | Strength | Duration | Scope (2010–2022) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dounis A.I. et al. [24] | 2009 | 10.1016/j.rser.2008.09.015 | 11.97 | 2011–2017 |  |
| 2 | Atzori L. et al. [25] | 2010 | 10.1016/j.comnet.2010.05.010 | 12.23 | 2013–2018 |  |
| 3 | Palensky P. et al. [26] | 2011 | 10.1109/TII.2011.2158841 | 10.46 | 2013–2017 |  |
| 4 | Perez-Lombard L. et al. [30] | 2008 | 10.1016/j.enbuild.2007.03.007 | 16.74 | 2014–2016 |  |
| 5 | Lu J. [44] | 2010 | 10.1145/1869983.1870005 | 11.69 | 2014–2018 |  |
| 6 | Minoli D. et al. [10] | 2017 | 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2647881 | 7.68 | 2020–2022 |  |
| 7 | Plageras A.P. et al. [42] | 2018 | 10.1016/j.future.2017.09.082 | 5.4 | 2020–2022 |  |
| 8 | Serale G. et al. [45] | 2018 | 10.3390/en11030631 | 5.32 | 2020–2022 |  |
| 9 | Amasyali K. et al. [46] | 2018 | 10.1016/j.rser.2017.04.095 | 5.23 | 2020–2022 |  |
| 10 | Lawrence T.M. et al. [47] | 2016 | 10.1016/j.buildenv.2016.08.022 | 4.94 | 2020–2022 |  |
| 11 | Wei T.S. [48] | 2017 | 10.1145/3061639.3062224 | 4.56 | 2020–2022 |  |
| 12 | Reynolds J. et al. [49] | 2018 | 10.1016/j.energy.2018.03.113 | 4.56 | 2020–2022 |  |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, J. A Bibliometric Review on Artificial Intelligence for Smart Buildings. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10230. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610230
Luo J. A Bibliometric Review on Artificial Intelligence for Smart Buildings. Sustainability. 2022; 14(16):10230. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610230
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Jiaxi. 2022. "A Bibliometric Review on Artificial Intelligence for Smart Buildings" Sustainability 14, no. 16: 10230. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610230
APA StyleLuo, J. (2022). A Bibliometric Review on Artificial Intelligence for Smart Buildings. Sustainability, 14(16), 10230. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610230





