Challenges in Micro and Small Food Enterprises during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Ecuador
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- What biosafety practices did the MSEs apply?
- Which areas and processes were successful in mitigating the COVID-19 pandemic crisis?
- How did the adoption of biosafety practices support operational efficiency in the COVID-19 pandemic context?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Foundation Stage
2.2. Pre-Field Stage
2.3. Field Stage
- General business profile (54 questions);
- General information on COVID-19 (36 questions);
- Interview about biosafety activities in their production processes.
2.4. Reporting Stage
3. Results
3.1. Qualitative Analysis
3.2. Quantitative Analysis
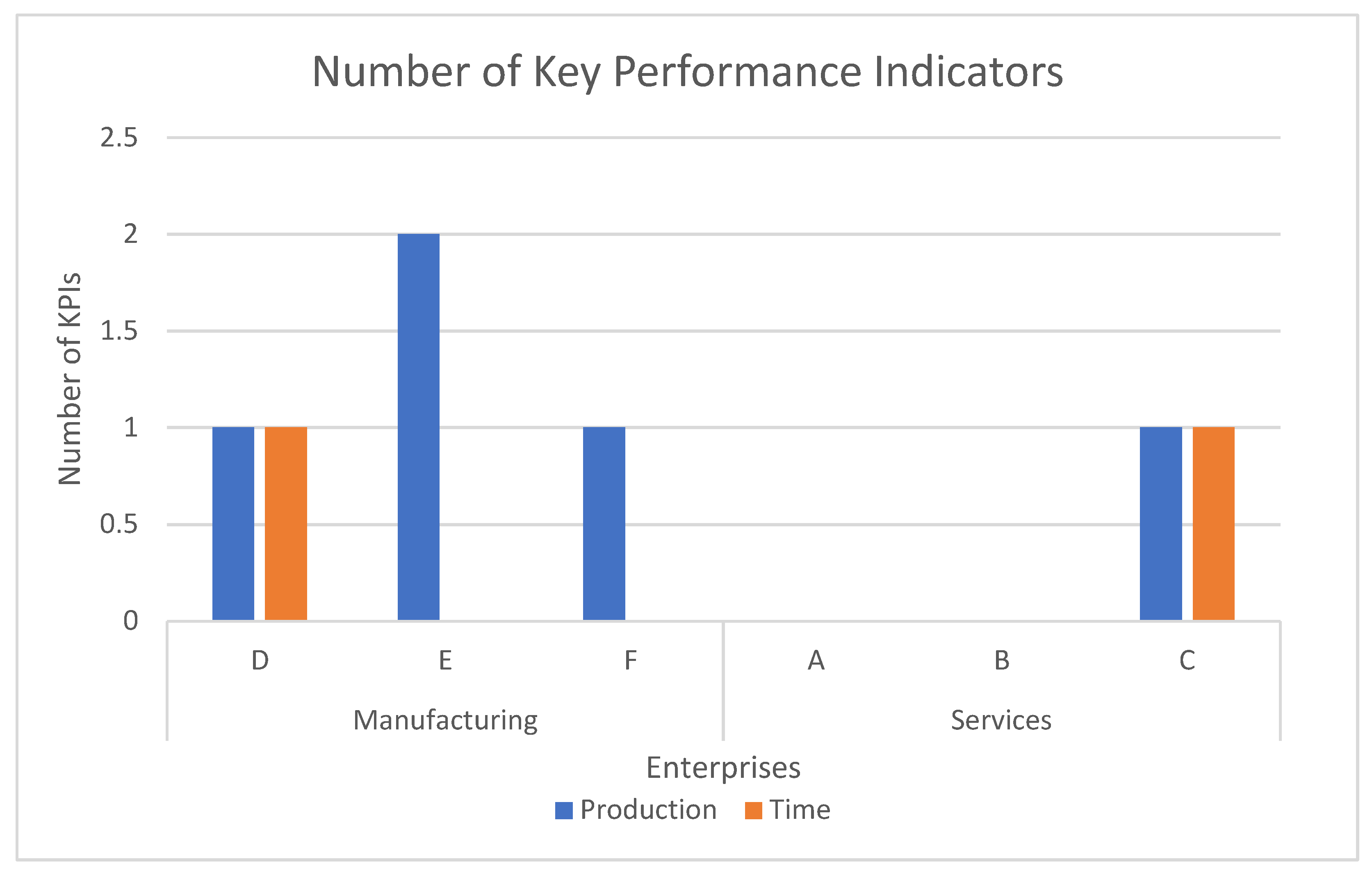
3.2.1. Non-Value-Added Activities
3.2.2. Availability Rate
3.2.3. Idle Time
3.2.4. Performance Rate
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Health and Safety Questionnaire
| General Profile | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Code | Code Digitalization | Question | Answer | |||||
| Manager Profile | ||||||||
| MA1 | MP1 | Full name of the decision-maker interviewed | ||||||
| MA2 | MP2 | Gender of the interviewee | ||||||
| MA3 | MP3 | Age of the interviewee | ||||||
| MA4 | MP4 | Phone number of the interviewee | ||||||
| MA5 | MP5 | Email address of the interviewee | ||||||
| MA6 | MP6 | Last academic degree obtained | ||||||
| MA7 | MP7 | Job title of the interviewee | ||||||
| MA8 | MP8 | For how long has the interviewee been working for the company? | ||||||
| MA9 | MP9 | How many hours per week does the interviewee dedicate to the company? | ||||||
| Company Profile | ||||||||
| CO1 | CP1 | Name of the company | ||||||
| CO2 | CP2 | When was the company established? | ||||||
| CO3 | CP3 | Sector | ||||||
| CO4 | CP4 | Subsector | ||||||
| CO5 | CP5 | Is the company a family business? | Further comments | |||||
| CO6 | CP6 | Number of permanent workers at this moment | ||||||
| CO7 | CP7 | Number of temporary employees at this moment | ||||||
| CO8 | How has the number of employees changed as a consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic? | |||||||
| CO9 | CP8 | What is the weekly work schedule of the company? | ||||||
| CO10 | CP9 | Does the company purchase when it is out of stock, on a periodic basis, or when a minimum threshold is attained? | Further comments | |||||
| CO11 | CP11 | What is the company’s production strategy? | Further comments | |||||
| CO12 | CP12 | Who is the company’s main customer? | Further comments | |||||
| CO13 | CP13 | How does the product make it to market? | Further comments | |||||
| CO14 | CP14 | In which markets does the company sell its products? (mark all that apply) | Local (city) | Regional (nationwide) | International (exports) | |||
| CO15 | CP15 | How many direct competitors does the company have? | ||||||
| CO16 | CP16 | What is the current differentiation strategy for the company (how do you try to beat your competitors)? | Product | Service | Distribution channel | Relationship | Reputation | Price |
| CO17 | CP17 | How do the customers pay for their purchases? | Credit | Upfront | Barter | Other | ||
| CO18 | CP20 | How have the incomes of your company changed in the last 6 months? | Further comments | |||||
| CO19 | CP21 | How have the costs of your company changed in the last 6 months? | Further comments | |||||
| CO20 | Which were the main changes in the company as a result of the pandemic? | |||||||
| CO21 | CP22 | What is your company’s main strength? | ||||||
| CO22 | CP23 | What is your company’s biggest weakness? | ||||||
| CO23 | CP24 | Which of the following indicators do you consider crucial to measure your company’s performance? | Productivity | Customer satisfaction | Quality | Utilization rate | Fill rate | Further comments |
| CO24 | CP25 | Which of the following indicators do you measure at least once a month? | Productivity | Customer satisfaction | Quality | Utilization rate | Fill rate | Further comments |
| Company Information | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| # | Type | Options | Questions |
| 1 | Open | - | What was the line of business in 2019? |
| 2 | Open | - | What is the line of business now? |
| 3 | Time | - | When is the time of entry? |
| 4 | Time | - | When is the departure time? |
| 5 | Multiple choice | 1, 2, 3, 4 | What is the number of daily shifts that have been established? |
| 6 | Multiple choice | 4 hours, 6 hours, 10 hours, 12 hours | How many hours does each shift have? |
| 7 | Category | Yes/No | Is the company certified Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)? |
| 8 | Date | - | What date was the certification obtained? |
| 9 | Category | Yes/No, N/A | Do you measure any indicators related to quality or productivity at least once a month? (Produced units, production times, accepted products, rejected products, standardized weight...) Put N/A if measured previously |
| 10 | Open | - | Which indicators? |
| 11 | Category | Yes/No, N/A | Has there been any change in your number of customers between 2019 and 2020? N/A if you do not know |
| 12 | Category | Yes/No | Has the number of customers decreased in 2020 from 2019? |
| 13 | Single choice | - | By what percentage has the number of customers decreased? |
| 14 | Category | Yes/No | Has the number of customers increased in 2020 from 2019? |
| 15 | Single choice | - | By what percentage has the number of customers increased? |
| 16 | Category | Yes/No, N/A | Has there been any change in the number of units produced of the best-selling product in 2020 from 2019? |
| 17 | Category | Yes/No | Has there been any decrease in the number of units produced of the best-selling product in 2020 from 2019? |
| 18 | Numeric | - | By what percentage has the number of units produced decreased? |
| 19 | Category | Yes/No | Has there been any increase in the number of units produced of the best-selling product in 2020 from 2019? |
| 20 | Numeric | - | By what percentage has it increased? |
| 21 | Open | - | Observations |
| General Information Related with COVID-19 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| # | Type | Options | Questions |
| 1 | Category | Yes/No | Has there been any biosafety protocol created for preventing the spread of COVID-19 in accordance with the standards established by the Health Authority? |
| 2 | Category | Always, sometimes, never | Have the biosecurity measures and actions established in the protocol to prevent the spread of COVID-19 been disseminated/disseminated weekly? |
| 3 | Category | Yes/No, N/A | Do you have ongoing communication campaigns to make staff aware of COVID-19 prevention measures? |
| 4 | Category | Yes/No | Has signage been implemented to reinforce COVID-19 prevention measures? |
| 5 | Category | Yes/No | Does your company have its own occupational health personnel or other staff members responsible for identifying and monitoring COVID-19 cases? |
| 6 | Category | Yes/No | Is the person in charge trained to attend and follow up on cases of COVID-19? |
| 7 | Category | Yes/No | Have any employees belonging to vulnerable groups been identified and registered? (Over 60 years old, disabled, those with lung conditions or chronic diseases, pregnant women. and those in charge of older adults with chronic diseases) |
| 8 | Category | Yes/No | Has a teleworking system been implemented? |
| 9 | Open | - | In what areas have teleworking been implemented? |
| 10 | Category | Yes/ No | Is there a contingency plan in place in the event that a positive case is identified within the company? |
| 11 | Open | - | What does the contingency plan entail? (For example, operations suspended, shifts increased). Explain in as much detail as possible |
| 12 | Category | Yes/No | Has a mobilization plan been established for company personnel to avoid contagion when using public transport? |
| 13 | Open | - | What does the mobilization plan entail? Explain in as much detail as possible |
| 14 | Category | Yes/No | Is it mandatory to have a negative COVID-19 test (rapid test or PCR) to enter the workplace? |
| 15 | Category | Yes/No | Have workers had rapid testing? |
| 16 | Category | Yes/No, N/A | Has the company covered the costs of these tests? N/A is partially or don’t know |
| 17 | Single choice | Every week, every 15 days, every month | How often are the tests done? |
| 18 | Single choice | Only once, every week, every 15 days, every month | How often should the employee take the tests and present them at the company? |
| 19 | Category | Yes/No | Is the monitoring of symptoms associated with COVID-19 carried out daily at the entrance to the premises? |
| 20 | Category | Yes/No, N/A | Does the company have thermometers or laser temperature sensors in place at the entrance(s) to the premises? |
| 21 | Category | Yes/No | Does the company have contagion prevention kits? (Gel, antiseptic alcohol, masks, other face covering) |
| 22 | Numeric | - | What is the percentage of additional costs necessitated by supplies related to the COVID-19 pandemic (cleaning)? |
| 23 | Category | Yes/No | Does the company have open and ventilated communal spaces? |
| 24 | Open | - | What activities are permitted in the communal spaces? |
| 25 | Category | Yes/No | Do you have a collective dining area? |
| 26 | Category | Yes/No, N/A | Do you share dishes and kitchen utensils? |
| 27 | Multiple choice | Reception, production, handling of finished product | Select the areas in which antiseptic/antibacterial gel are provided. (Select all that apply) |
| 28 | Multiple choice | Reception, production, handling of finished product | Select in which areas you have material / supplies for cleaning and disinfection of surfaces. (Select all that apply) |
| 29 | Single choice | Yes/No, Sometimes | Are cleaners, sanitizers, and other toxic chemicals kept away from food? |
| 30 | Single choice | All, some, none | Are all the cleaning and disinfection product containers correctly labelled? |
| 31 | Single choice | All, some, none | When handling cleaning products, do you follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for usage and usage volumes as specified on the product label? |
| 32 | Category | Yes/No, Sometimes | Are the cleaning staff trained in how to prepare the chemicals for cleaning and disinfection? |
| 33 | Category | Always, sometimes, never | Do you allocate part of your daily schedule to carrying out biosecurity activities? |
| 34 | Category | Always, sometimes, never | The workday includes stops/breaks to carry out biosecurity activities |
| 35 | Numeric | - | How long does it take on average to carry out activities related to biosecurity? |
| 33 | Single choice | Always, sometimes, never | Is waste classification carried out? (Separation of biological waste from regular waste). |
| 34 | Single choice | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or more | What is the weekly frequency of waste disposal? |
| 35 | Category | Yes/No | Has training related to cross-contamination been carried out? |
| 36 | Open | - | Observations |
| Reception and Storage | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| # | Type | Options | Questions |
| 1 | Category | Yes/No | Do you have a reception and storage process? N/A if a physical space is not needed or completely isolated from production |
| 2 | Checkbox | Mask, Gloves, Goggles, Face shield, Rubber boots, Suit, Apron, Hairnet | What types of personal protective equipment is used in the reception and storage area? |
| 3 | Category | Yes/No | Is there a policy that prohibits the use of watch, rings, earrings, bracelets, belt, etc. in the reception and storage area? |
| 4 | Category | Yes/No | Is compliance with this policy verified? |
| 5 | Category | Yes/No | Is there a policy that requires nails to be kept clean, short, and unpainted in the reception and storage area? |
| 6 | Category | Yes/No | Is compliance with this policy verified? |
| 7 | Category | Yes/No | Has the number of people who work in the reception and storage area decreased? |
| 8 | Numeric | - | If so, by what percentage? |
| 9 | Category | Yes/No | Is a distance of two meters between workers in reception and storage area kept? |
| 10 | Single choice | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 o more | How often is cleaning carried out in the reception and storage area? |
| 11 | Category | Yes/No | In cleaning and sanitizing procedures, is there a combination of physical and chemical methods for surface cleaning, scrubbing, brushing, and sanitizing? |
| 12 | Category | Yes/No | Are antiseptics used to remove microorganisms from hands (soaps, alcohol, quaternary ammonium compounds, iodine compounds, hypochlorite) in the reception and storage area? |
| 13 | single choice | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or more | What is the policy for daily hand washing frequency in the reception and storage area? |
| 14 | Category | Yes/No | Is compliance with policy verified? |
| 15 | single choice | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or more | What is the policy regarding how often disposable gloves are to be changed in the reception and storage area? |
| 16 | Category | Yes/No | Is compliance with policy verified? |
| 17 | Category | Yes/No, N/A | Are the characteristics that correspond to each type of product, such as smell, color, flavor, aroma, and texture, verified? |
| 18 | Category | Yes/No | Is the expiration date of all products verified when they are received? |
| 19 | Single choice | Reject and return to the supplier, reject and throw them away, fix the container, try to recover the product, content | What is done when a product is delivered with damaged and/or defective packaging? |
| 20 | Category | Yes/No | Is food stored immediately in appropriate places and at the temperature conditions required for each one? |
| 21 | Single choice | Always, sometimes, never | Is contact with the floor avoided during reception and storage of food (at least 15 cm of separation)? |
| 22 | Single choice | Always, sometimes, never | Is the product stored in accordance with the manufacturer’s specifications? e.g. if the product requires to be frozen, should it be stored at freezing temperatures? |
| 23 | Single choice | Always, sometimes, never | Is bulk food stored in closed, contamination-free containers? |
| 24 | Single choice | Always, sometimes, never | Are products stored away from exposed or unprotected drains, far from walls and ceiling? |
| 25 | Open | - | Observations |
| Productive Process | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| # | Type | Options | Questions |
| 1 | Open | - | Do you have a production process established? |
| 2 | Checkbox | Mask, Gloves, Goggles, Face shield, Rubber boots, Suit, Apron, Hairnet | What personal protective equipment is used in the production area? |
| 3 | Category | Yes/No | Is there a policy that prohibits the use of watches, rings, earrings, bracelets, belt in the production area? |
| 4 | Category | Yes/No | Is compliance with this policy verified? |
| 5 | Category | Yes/No | Is there a policy that requires nails to be kept clean, short, and unpolish in the production area? |
| 6 | Category | Yes/No | Is compliance with this policy verified? |
| 7 | Category | Yes/No | Has the number of people who work in the production area decreased? |
| 8 | Numeric | - | If so, by what percentage? |
| 9 | Category | Yes/No | Is a distance of two meters kept between workers in the production area? |
| 10 | Single choice | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or more | How many times per day daily is the production area cleaned? |
| 11 | Category | Yes/No | In your cleaning and sanitizing procedures, is there a combination of physical and chemical methods for surface cleaning, scrubbing, brushing, and sanitizing? |
| 12 | Category | Yes/No | Are antiseptics used to remove microorganisms from hands (soaps, alcohol, quaternary ammonium compounds, iodine compounds, hypochlorite) in the production area? |
| 13 | Single choice | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 o more | What is the policy for daily handwashing frequency in the production area? |
| 15 | Single choice | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or more | What is the policy for daily change of disposable gloves in the production area? |
| 16 | Category | Yes/No | Is compliance with this policy verified? |
| 17 | Open | - | Observations |
| Handling the Finished Product | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| # | Type | Options | Questions |
| 1 | Open | - | Is a finished product handling process in place? |
| 2 | Checkbox | Mask, Gloves, Goggles, Face shield, Rubber boots, Suit, Apron, Hairnet | What types of personal protective equipment are used in the finished product handling area? |
| 3 | Category | Yes/No | Is there a policy that prohibits the use of watches, rings, earrings, bracelets, belts, etc. in the finished product handling area? |
| 4 | Category | Yes/No | Is compliance with this policy verified? |
| 5 | Category | Yes/No | Is there a policy that requires keeping nails clean and short, without polish in the finished product handling area? |
| 6 | Category | Yes/No | Is compliance with this policy verified? |
| 7 | Category | Yes/No | Has the number of people working in the finished product handling area decreased? |
| 8 | Numeric | - | If so, by what percentage? |
| 9 | Category | Yes/No | Is a distance of at least 2 metres kept between workers in the finished product handling area? |
| 10 | Single choice | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or more | How many times per day is the finished product handling area cleaned? |
| 11 | Category | Yes/No | In cleaning and sanitizing procedures, is there a combination of physical and chemical methods for surface cleaning, scrubbing, brushing, and sanitizing? |
| 12 | Category | Yes/No | Are antiseptics used to remove microorganisms from hands (soaps, alcohol, quaternary ammonium compounds, iodine compounds, hypochlorite) in the finished product handling area? |
| 13 | Single choice | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or more | What is the policy for the daily frequency of changing disposable gloves in the finished product handling area? |
| 14 | Category | yes/ No | Is compliance with this policy verified? |
| 15 | Single choice | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or more | What is the policy for the daily frequency of changing disposable gloves in the finished product handling area? |
| 16 | Category | Yes/No | Is compliance with this policy verified? |
| 17 | Open | - | Observations |
| Delivery | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| # | Type | Options | Questions |
| 1 | Open | - | Is a delivery process established? |
| 2 | Category | Yes/No | Does the company have its own home delivery service (company vehicle) for its products? |
| 3 | Checkbox | Mask, Gloves, Goggles, Face shield, Rubber boots, Suit, Apron, Hairnet | What types of personal protective equipment are used in the delivery area? |
| 4 | Category | Yes/No | Is there a policy that prohibits the use of watches, rings, earrings, bracelets, belts, etc. in the delivery area? |
| 5 | Category | Yes/No | Is compliance with this policy verified? |
| 6 | Category | Yes/No | Is there a policy that requires keeping nails clean and short, without polish in the delivery area? |
| 7 | Category | Yes/No | Is compliance with this policy verified? |
| 8 | Category | Yes/No | Has the number of people working in the delivery area decreased? |
| 9 | Numeric | - | If so, by what percentage? |
| 10 | Category | Yes/No | Is a distance of at least 2 metres kept between workers in the delivery area? |
| 11 | Single choice | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or more | How many times per day is the delivery area cleaned? |
| 12 | Category | Yes/No | Is the vehicle disinfected before loading the product? |
| 13 | Category | Yes/No | Is the vehicle ventilated? (Without using air conditioner.) |
| 14 | Category | Yes/No | In your cleaning and sanitizing procedures, is there a combination of physical and chemical methods for surface cleaning, scrubbing, brushing, and sanitizing? |
| 15 | Category | Yes/No | Are antiseptics used to eliminate microorganisms from hands (soaps, alcohol, quaternary ammonium compounds, iodine compounds, hypochlorite) in the delivery handling area? |
| 16 | Single choice | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or more | What is the policy for daily hand washing frequency in the finished product handling area? |
| 17 | Category | yes/ No | Is compliance with this policy verified? |
| 18 | Single choice | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or more | What is the daily policy for changing disposable gloves in the delivery area? |
| 19 | Category | Yes/No | Is compliance with this policy verified? |
| 20 | Category | Yes/No | Is food transported in closed, covered or completely sealed containers? |
| 21 | Category | Yes/No | Is the transportation of food along with cleaning products or toxic substances prohibited/avoided? |
| 22 | Open | - | Observations |
References
- Comisión Económica Para América Latina y el Caribe [CEPAL]. Sectores y empresas frente a la COVID-19: Emergencia y reactivación. Inf. Espec. COVID-19 2020, 4, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- International Labor Organization [ILO]. Panorama Temático Laboral. Pequeñas empresas, grandes brechas. Presente Y Futuro Protección Soc. En América Lat. Y El Caribe 2015, 4, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Diéguez Castrillón, M.I. Formación en la industria alimentaria: Su importancia para la competitividad de las empresas. Cienc. Y Tecnol. Aliment. 2000, 2, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development & Food and Drug Organization [OCDE/FAO]. Perspectivas Agrícolas 2019–2028; OECD Publishing: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios Cruz, M.; Santos, E.; Velázquez Cervantes, M.A.; León Juárez, M. COVID-19, a worldwide public health emergency. COVID-19, una emergencia de salud pública mundial. Rev. Clin. Esp. 2020, 221, 55–61, Advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruinen de Bruin, Y.; Lequarre, A.S.; McCourt, J.; Clevestig, P.; Pigazzani, F.; Zare Jeddi, M.; Goulart, M. Initial impacts of global risk mitigation measures taken during the combatting of the COVID-19 pandemic. Saf. Sci. 2020, 128, 104773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, T.; Nayak, A.U.S. County-level analysis to determine if social distancing slowed the spread of COVID-19. Rev. Panam. Salud Publica Pan Am. J. Public Health 2020, 44, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, A.E.; Coulborn, R.M.; Perez, V.; Larson, E.L. Effect of hand hygiene on infectious disease risk in the community setting: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Public Health 2008, 98, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Castrillón, F.J.; Toro-Montoya, A.I. SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19: El virus, la enfermedad y la pandemia. Med. Y Lab. 2020, 24, 183–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.B.; Jagadeesan, P. COVID-19 from Food Safety and Biosecurity Perspective. Open Food Sci. J. 2020, 12, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabeil, N.F.; Pazim, K.H.; Langgat, J. The impact of COVID-19 pandemic crisis on micro-enterprises: Entrepreneurs’ perspective on business continuity and recovery strategy. J. Econ. Bus. 2020, 3, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indriastuti, M.; Fuad, K. Impact of COVID-19 on digital transformation and sustainability in small and medium enterprises (smes): A conceptual framework. In Conference on Complex, Intelligent, and Software Intensive Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 471–476. [Google Scholar]
- Nordhagen, S.; Igbeka, U.; Rowlands, H.; Shine, R.S.; Heneghan, E.; Tench, J. COVID-19 and small enterprises in the food supply chain: Early impacts and implications for longer-term food system resilience in low-and middle-income countries. World Dev. 2021, 141, 105405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, M.; Liu, J.; Ren, W. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on micro, small, and medium-sized Enterprises operating in Pakistan. Res. Glob. 2020, 2, 100018. [Google Scholar]
- Programa de las Naciones Unidas para el Desarrollo [PNUD]. Las Implicaciones Socio-Económicas de la Pandemia por COVID-19: Ideas Para la Acción en Políticas Públicas; United Nations Development Programme|One United Nations Plaza: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 1–309. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.; Rocha, A.; Cowling, M. Financing entrepreneurship in times of crisis: Exploring the impact of COVID-19 on the market for entrepreneurial finance in the United Kingdom. Int. Small Bus. J. Res. Entrep. 2020, 38, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Censos [INEC]. Mercado laboral: Encuesta Nacional de Empleo, Desempleo y Subempleo (ENEMDU). Obs. Económico 2021, 45, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods, 3rd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, Y.; Rashid, A.; Warraich, M.A.; Sabir, S.S.; Waseem, A. Case study method: A step-by-step guide for business researchers. Int. J. Qual. Methods 2019, 18, 1609406919862424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Producción. Protocolo de Bioseguridad Para el Sector Industrial y Comercial-COVID-19; Ministerio de Producción, Comercio Exterior, Inversiones y Pesca: Guayaquil, Ecuador, 2020; Available online: https://www.produccion.gob.ec/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/DOC_CORONA.pdf (accessed on 26 September 2021).
- Agencia Nacional de Regulación; Control y Vigilancia Sanitaria. Protocolo que Deben Cumplir los Establecimientos de Alimentación Colectiva y Para Quienes Preparen y Entreguen Alimentos; Agencia Nacional de Regulación, Control y Vigilancia Sanitaria: Guayaquil, Ecuador, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Censos. Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Censos, Anexo No. 7: Clasificación Uniforme de Actividades Económicas CIIU-4.0; Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Censos: Quito, Ecuador, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Perecman, E.; Curran, S.R. A Handbook for Social Sciences Field Research: Essay & Bibliographic Sources on Research Design and Methods; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Denzin, N.K.; Lincoln, Y.S. Collecting and Interpreting Qualitative Materials; Writing: A method of inquiry; Sage: London, UK, 1998; Chapter 12; ISBN 076191434X/9780761914341. [Google Scholar]
- Dunford, R.; Su, Q.; Tamang, E. The Pareto Principle; The Plymouth Student Scientist: Plymouth, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, P.; Kumar Sharma, R. A hybrid framework based on SIPOC and Six Sigma DMAIC for improving process dimensions in supply chain network. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2014, 31, 522–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrina, U.; Firdaus, A. The Selection of Productivity Key Performance Indicators for Car Manufacturing Companies Using Integrated Performance Measurement System. Sinergi 2018, 22, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwa, N.R.; Sangwan, K.S. Development of an integrated performance measurement framework for lean organizations. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2018, 29, 41–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, T.; Raut, N. Waste elimination by lean manufacturing. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2017, 4, 168–170. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, V.C.; Leitner, U. Lean tools and lean transformation process in health care. Int. J. Manag. Sci. Eng. Manag. 2010, 5, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krygier, N.; Solarin, A.; Orozova-Bekkevold, I. A Drilling Company’s Perspective on Non-Productive Time NPT Due to Well Stability Issues. In Proceedings of the SPE Norway Subsurface Conference, Bergen, Norway, 2–3 November 2020; OnePetro: Bergen, Norway, 2020. [Google Scholar]
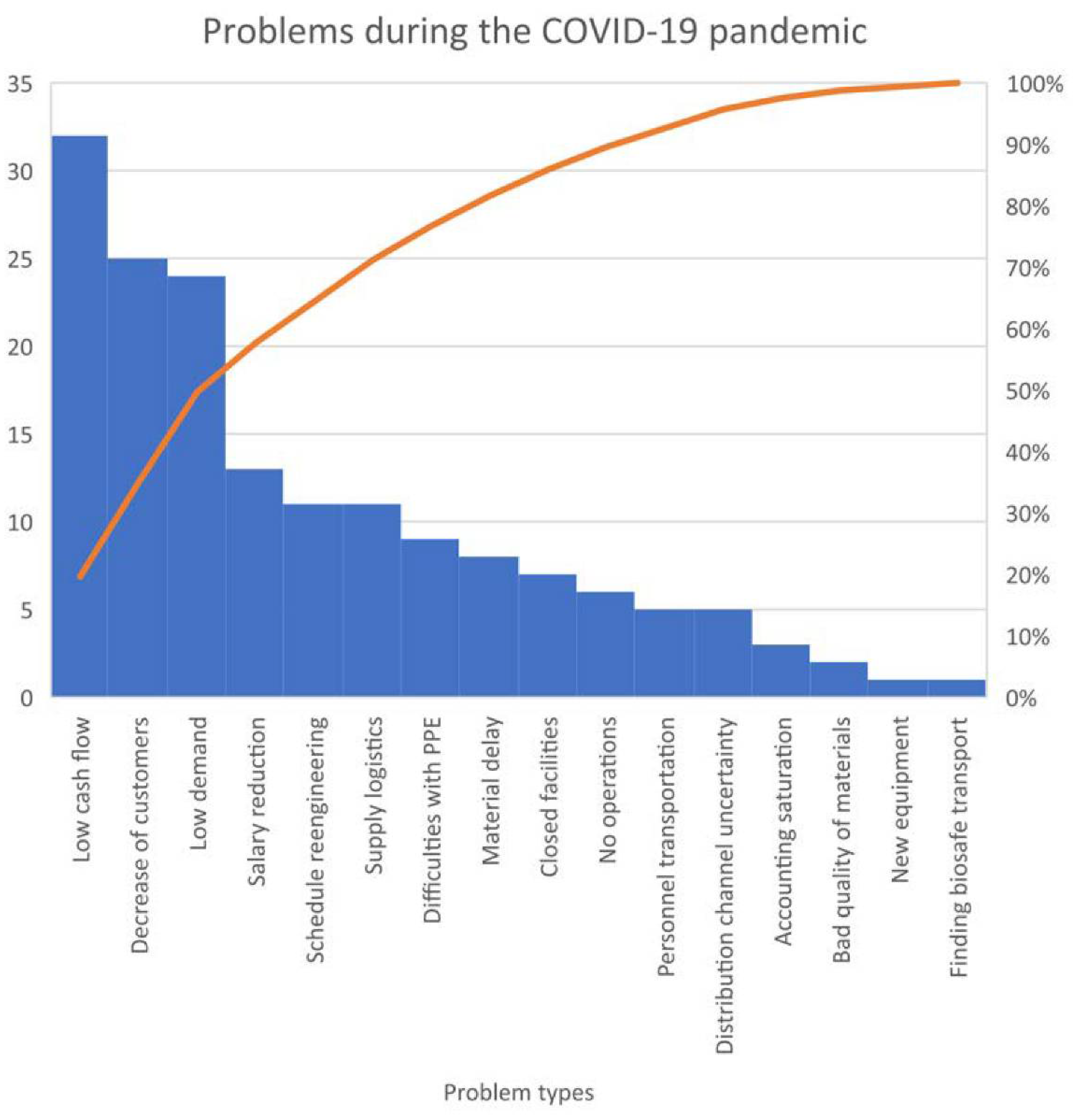
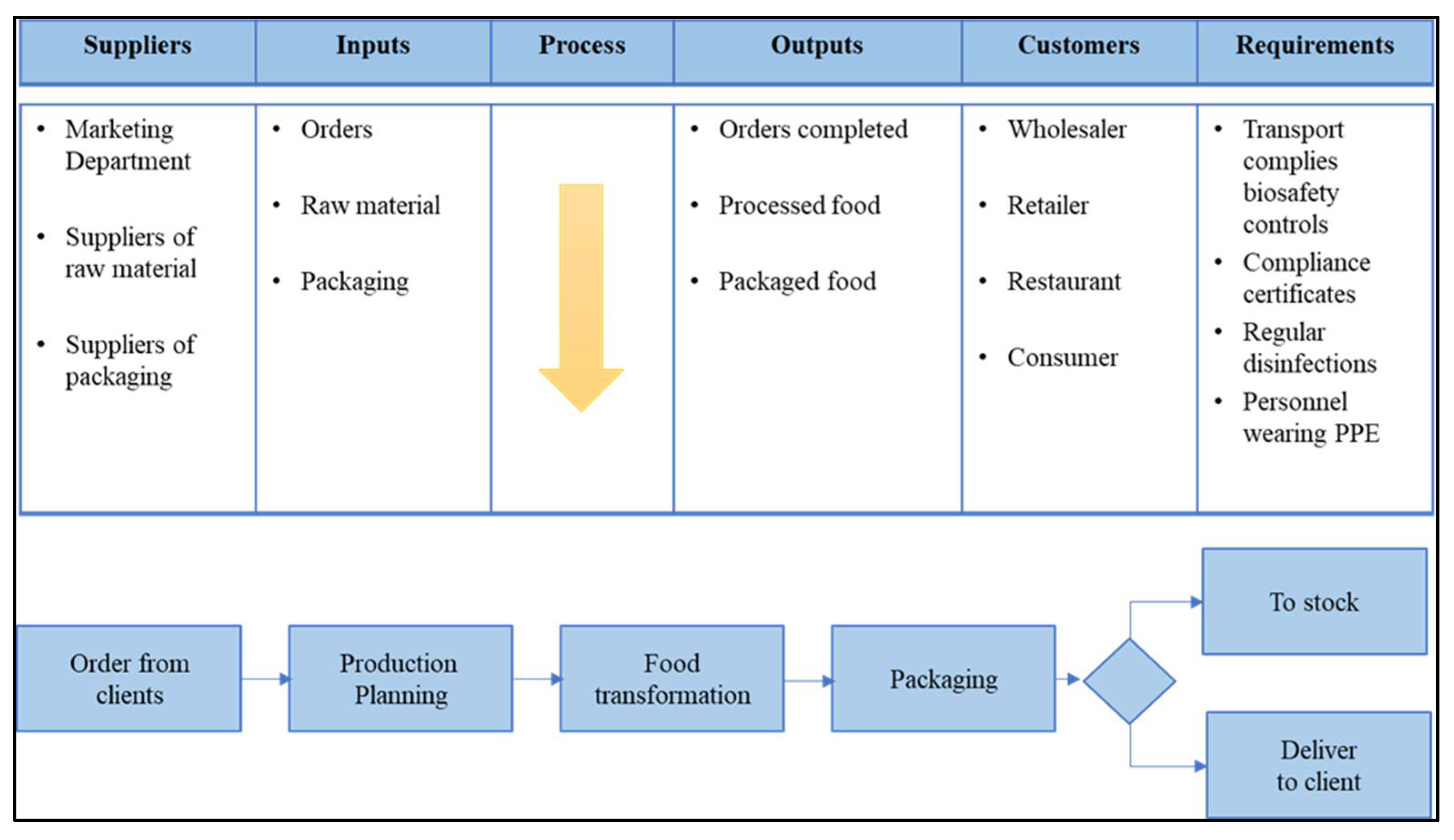
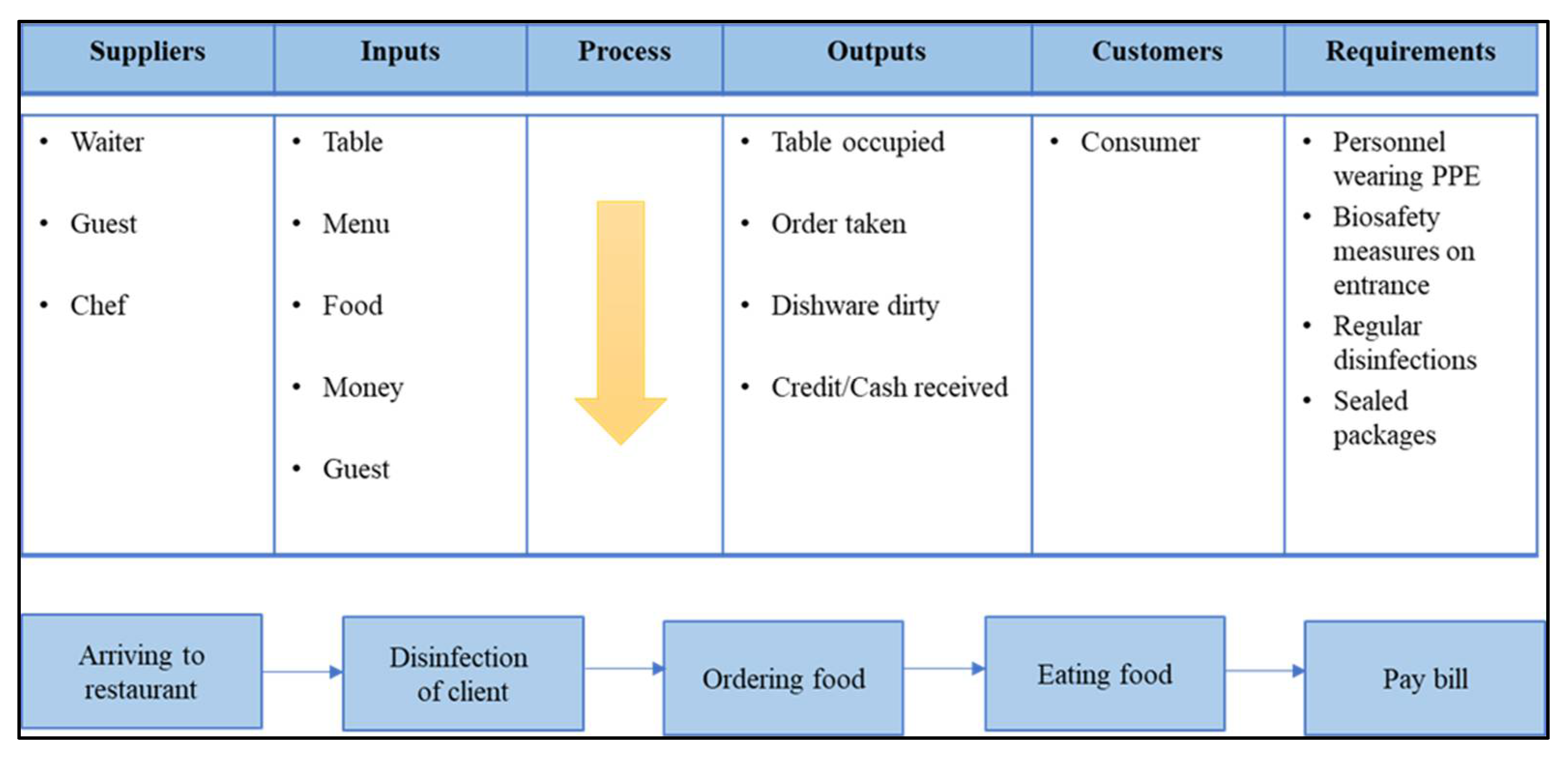
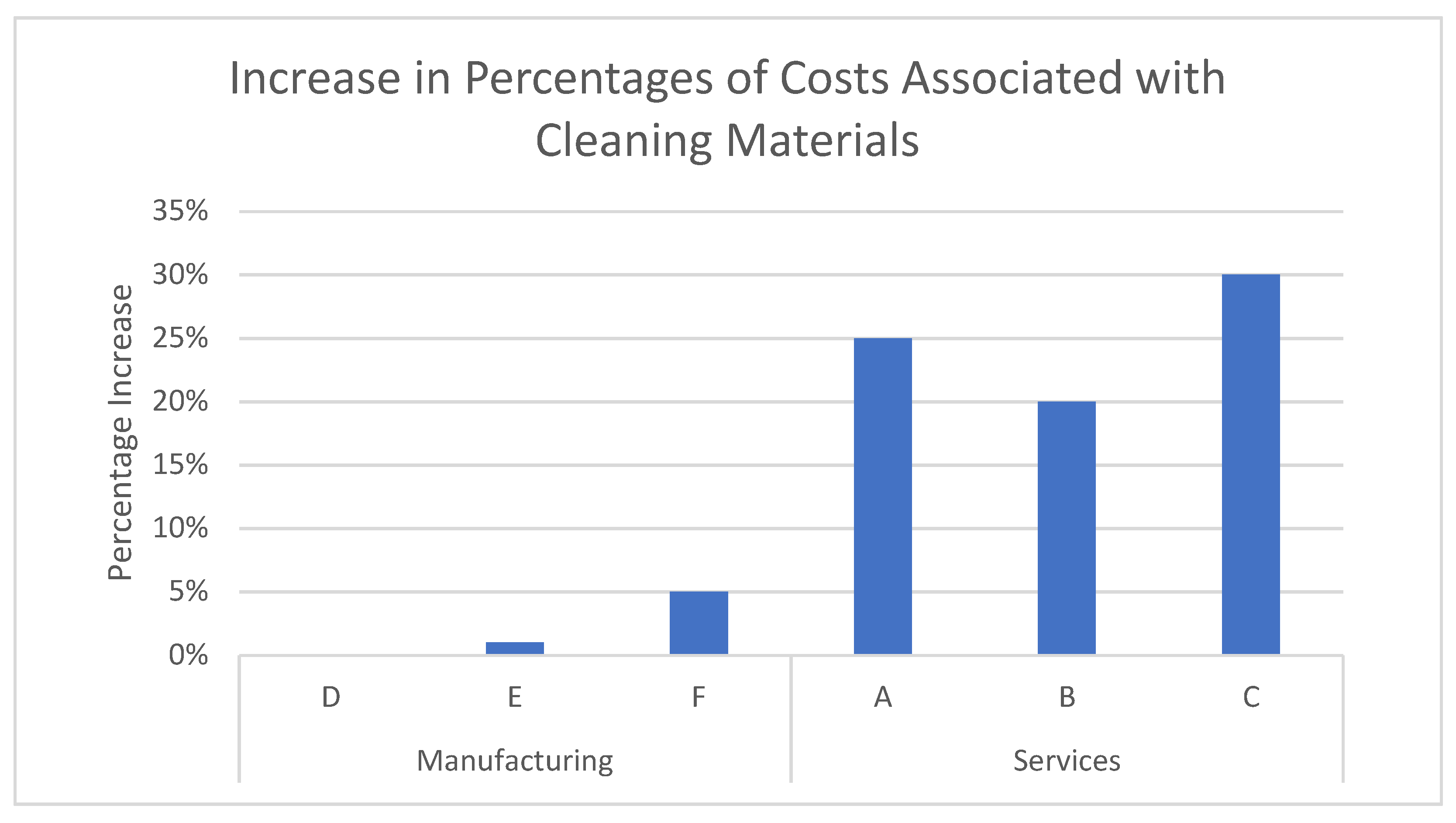
| KPI | Formula | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Availability rate | ||
| Idle time | ||
| Performance rate | Actual output = Units produced—Defects Theoretical output = Units produced |
| Enterprise | Size | Type | N° Employees | Time in Operation | Manufacturing Practice Certification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Micro | Services—Restaurant | 2 | 8 years | No |
| B | Micro | Services—Restaurant | 3 | 25 years | No |
| C | Micro | Services—Restaurant | 3 | 6 years | No |
| D | Micro | Manufacturing—Fruit Pulp | 8 | 20 years | No |
| E | Small | Manufacturing—Granola Bars and Cookies | 11 | 20 years | Yes |
| F | Small | Manufacturing—Dairy Products | 10 | 10 years | No |
| Services | Manufacturing | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COVID-19 Biosafety Protocols | A | B | C | Total | D | E | F | Total |
| Written biosafety protocol | ✓ | ✓ | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | 2 | ||
| Own occupational health personnel or party responsible for COVID-19 cases | 0 | 0 | ||||||
| Symptoms controlled at the entrance | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 3 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 3 |
| Mobility plan to prevent contagion | ✓ | 1 | ✓ | 1 | ||||
| Contingency plan if a case is reported on-site | ✓ | ✓ | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 3 | |
| Ongoing communication campaigns | ✓ | ✓ | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 3 | |
| Signage to reinforce COVID-19 prevention protocols | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 3 | ✓ | ✓ | 2 | |
| Services | Manufacturing | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units Produced | A | B | C | D | E | F |
| No change | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Decrease | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Planned Downtime | Unplanned Downtime Related to COVID-19 |
|---|---|
| Wearing PPE or clothing | Symptoms controlled at the company’s entrance |
| Performing disinfection activities | Increased frequency of disinfection activities |
| Handwashing breaks | Increased frequency of handwashing breaks to three times |
| Changing disposable gloves | Increased changes of disposable gloves |
| Lunch break | Symptoms monitored during labor hours |
| Planned Downtime | Unplanned Downtime Related to COVID-19 |
|---|---|
| Performing disinfection activities | Symptoms controlled at the company’s entrance Increasing the frequency of disinfection activities from two to three times |
| Handwashing breaks | Increased frequency of handwashing breaks from three to five times |
| Changing disposable gloves | Increased changes of disposable gloves from one to two times |
| Lunch break | Symptoms monitored during labor hours |
| Manufacturing Companies | Service Companies |
|---|---|
| Non-value-added activities | Non-value-added activities |
| Availability rate | Availability rate |
| Idle time | Idle time |
| Performance rate |
| Manufacturer | Percentage | Service | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 3.70% | S1 | 9.39% |
| M2 | 2.96% | S2 | 6.85% |
| M3 | 1.95% | S3 | 4.76% |
| Manufacturer | Percentage | Service | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 6.40% | S1 | 7.28% |
| M2 | 5.00% | S2 | 8.33% |
| M3 | 2.50% | S3 | 5.45% |
| Manufacturer | Percentage | Service | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 4.30% | S1 | 7.28% |
| M2 | 5.00% | S2 | 7.71% |
| M3 | 2.50% | S3 | 5.45% |
| Manufacturer | Percentage |
|---|---|
| M1 | 4.00% |
| M2 | 3.00% |
| M3 | 3.00% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orellana-Rojas, C.; Chávez-Campuzano, C.; Herrera-Cervantes, A.; Guevara, Y.; Romero, Y.; Moyano, M.; Rentería-Ramos, R.; Chong, M. Challenges in Micro and Small Food Enterprises during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Ecuador. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9576. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159576
Orellana-Rojas C, Chávez-Campuzano C, Herrera-Cervantes A, Guevara Y, Romero Y, Moyano M, Rentería-Ramos R, Chong M. Challenges in Micro and Small Food Enterprises during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Ecuador. Sustainability. 2022; 14(15):9576. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159576
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrellana-Rojas, Clara, Carolina Chávez-Campuzano, Andrea Herrera-Cervantes, Yndira Guevara, Yereth Romero, Mariana Moyano, Rafael Rentería-Ramos, and Mario Chong. 2022. "Challenges in Micro and Small Food Enterprises during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Ecuador" Sustainability 14, no. 15: 9576. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159576
APA StyleOrellana-Rojas, C., Chávez-Campuzano, C., Herrera-Cervantes, A., Guevara, Y., Romero, Y., Moyano, M., Rentería-Ramos, R., & Chong, M. (2022). Challenges in Micro and Small Food Enterprises during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Ecuador. Sustainability, 14(15), 9576. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159576






