3.3. Research Object
The main purpose of this research is to explore the relationship between leadership style and the effectiveness of vocational high school teachers in the daytime and nighttime departments under the influence of the school situation. This research includes public and private industrial high schools, agricultural industrial high schools, commercial vocational high schools, and vocational high schools, as the research mother group, and so the research object is all teachers who work in the daytime and nighttime departments at vocational high schools. In order to bring the data closer to the facts, we adopt stratified proportional sampling to divide Taiwan into four regions: northern, central, southern, and eastern. The stratified proportional sampling is carried out according to the number of vocational high schools to improve sample representativeness.
The statistical method of this study adopts HLM. Because the research structure of this study is divided into two levels, the first level is for teachers, and the second one is for schools [
24]. in the linear analysis of levels, the sample number of the highest level should be at least 30 to meet the minimum requirements of HLM. The sample number of the second school level is at least 30. Therefore, this research requires at least 30 vocational high schools, and there must be at least 30 teachers at each school, which means at least 900 teachers make up the research sample to meet the HLM statistical threshold requirements. After that, the study distributed 1085 questionnaires in total, which are composed of 35 copies each at 31 vocational high schools. Finally, we collected a total of 30 school questionnaires. After excluding invalid questionnaires, 920 questionnaires were compiled, achieving a questionnaire response rate of 84.7%.
3.4. Research Hypothesis
Supporting leadership refers to the characteristics of being friendly, close, and caring for members of the organization. There is a relationship of mutual trust and respect between the leader and the members of the organization [
25]. The leader cares about the lives of the members of the organization through mutual trust. To increase the work efficiency of the members of the organization [
26], their leadership styles will affect the design of teachers’ teaching strategies.
Hypothesis 1a: There is a positive correlation between multiple teaching strategies supporting leadership and teacher effectiveness.
Hypothesis 1b: There is a positive impact between class management supporting leadership and teacher effectiveness.
Teachers’ supportive leadership style is affected by environmental factors in the teaching strategies and class management of teacher effectiveness [
27].
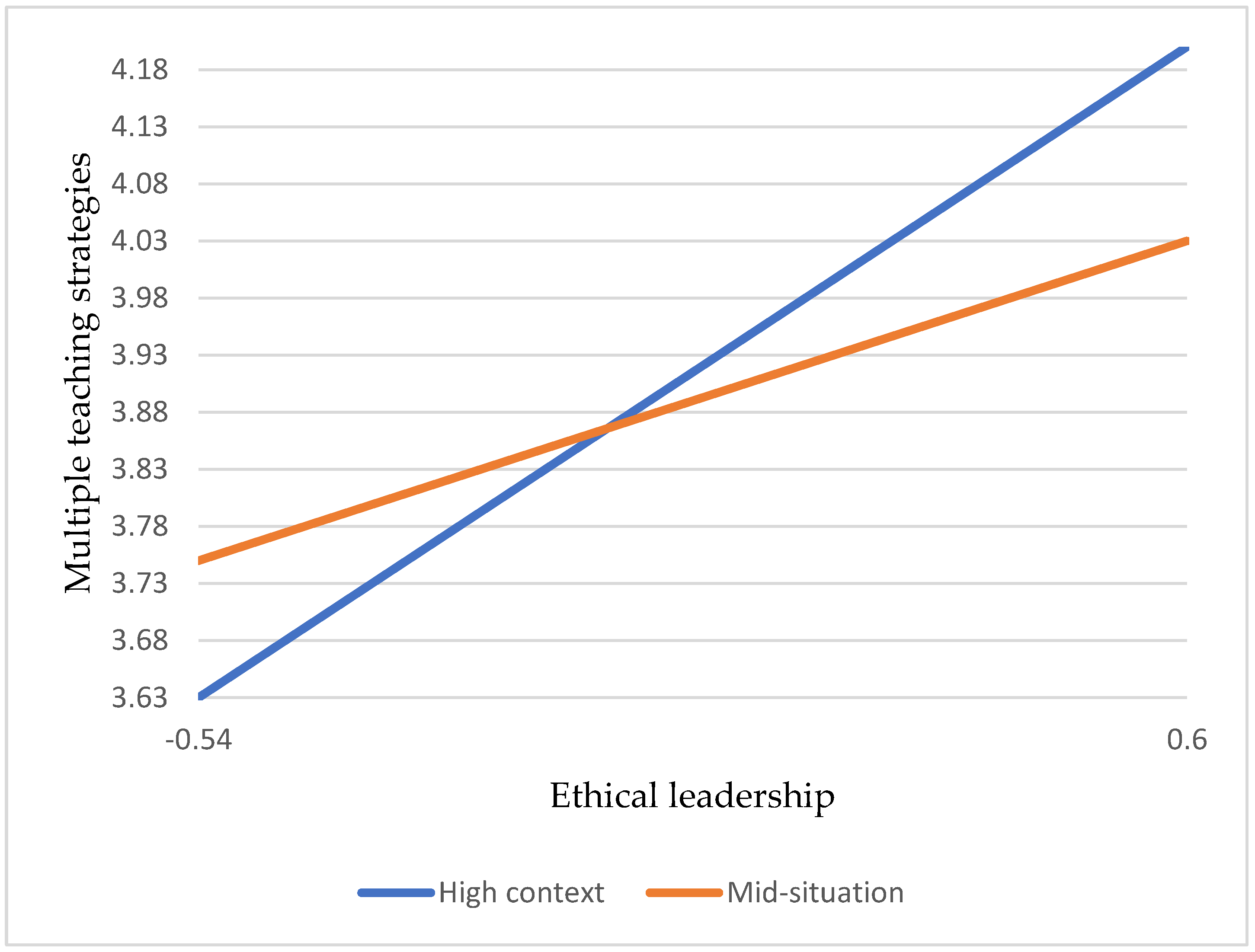
Hypothesis 5a: Compared with lower school situations, vocational high school teachers support multiple teaching strategies in that leadership positively impacts their effectiveness in high school situations.
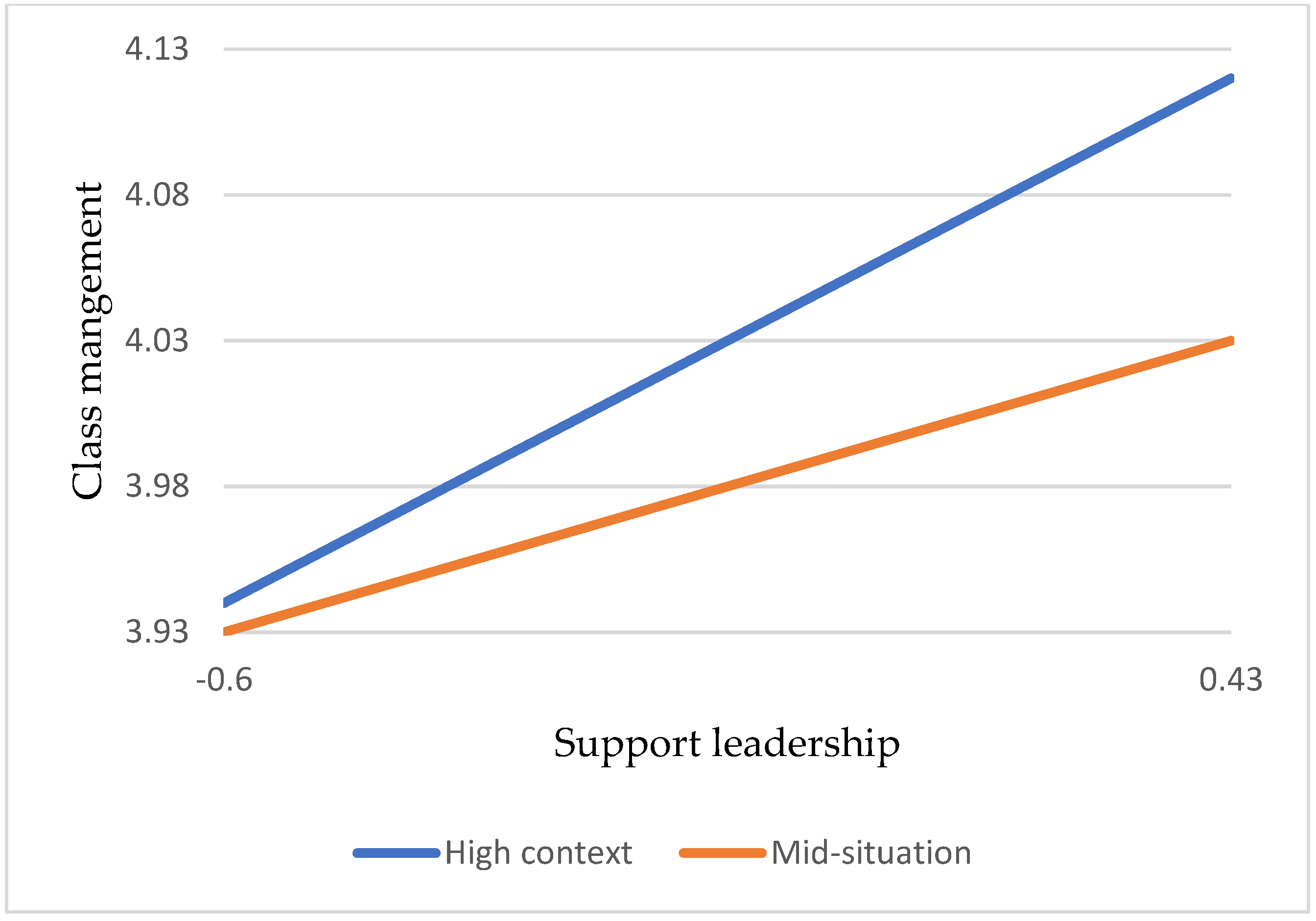
Hypothesis 5b: Compared with lower school situations, vocational high school teachers support class management in that leadership positively impacts their effectiveness in high school situations.
Many foreign scholars have studied the effectiveness of charismatic leadership. For example, Shamir, House, and Arthur (1993) examined the influence of charismatic leaders on their subordinates through motivational theory and found that charismatic leaders can be evoked by their vision [
28].
Motivation and needs of members enable members to improve their performance behavior [
29].
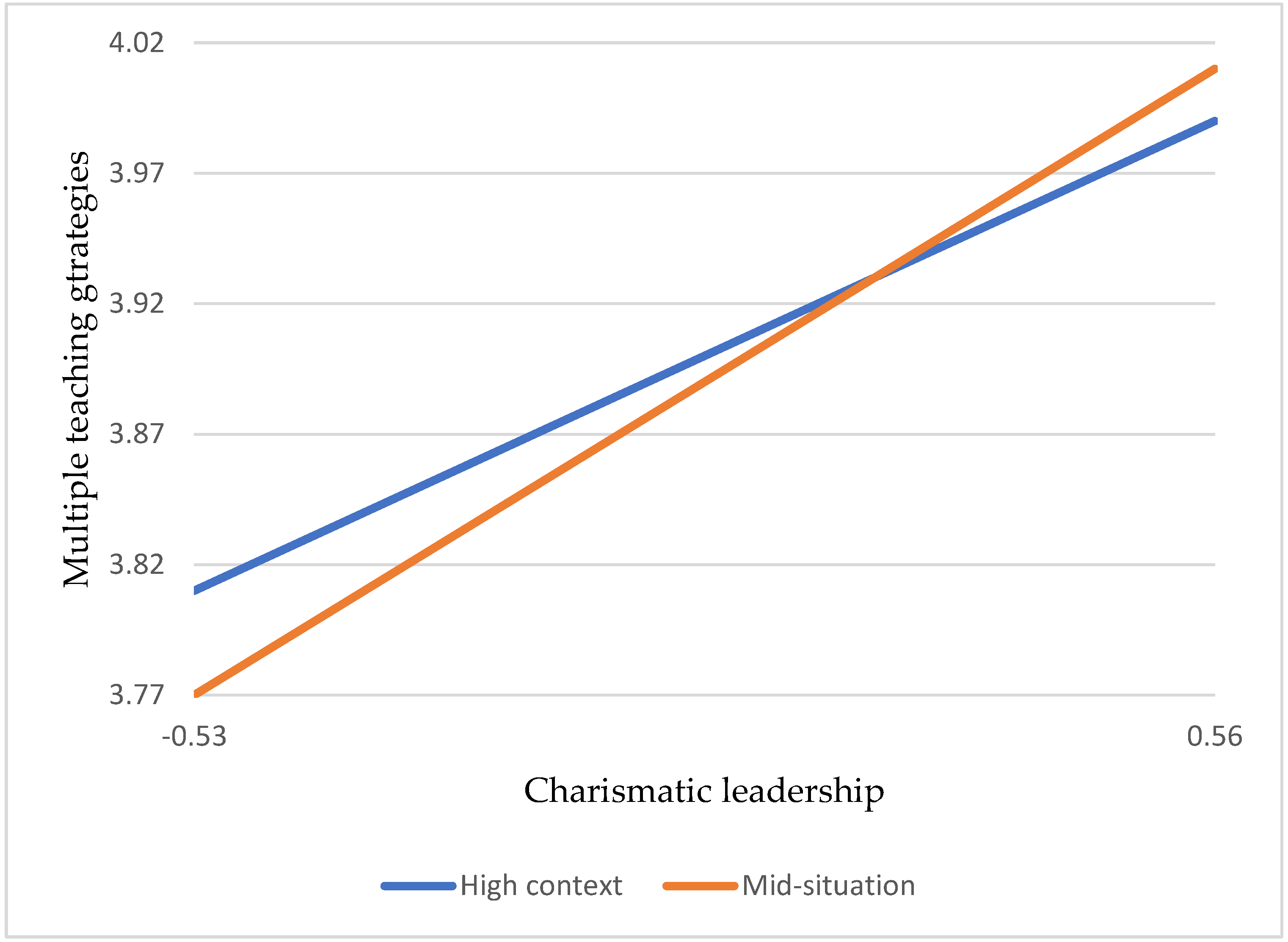
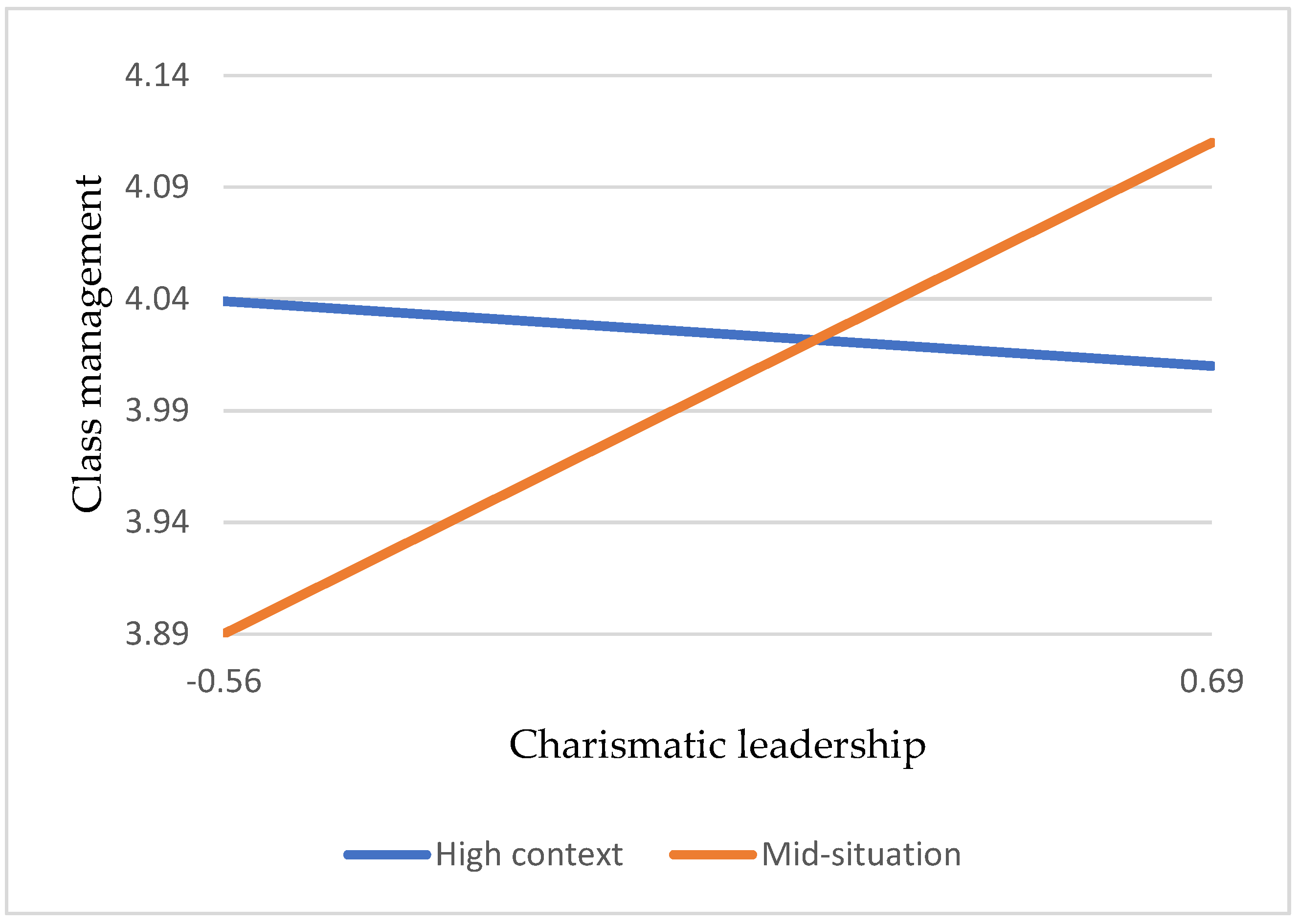
Hypothesis 2a: Charismatic leadership positively correlates with multiple teaching strategies for teacher effectiveness.
Hypothesis 2b: Charismatic leadership positively correlates with class management of teacher effectiveness.
School situations have an impact on a teacher’s charismatic leadership style and teacher effectiveness [
30]. Thus, the following hypotheses are proposed.
Hypothesis 6a: Compared to lower school situations, vocational high school teachers’ charismatic leadership positively influences multiple teaching strategies of teacher effectiveness in high school situations.
Hypothesis 6b: Compared to lower school situations, vocational high school teachers’ charismatic leadership positively affects the class management of a teacher’s effectiveness in high school situations.
Using the principles of ethical leadership on campus to plan something and implement it carefully can further enhance the school’s effectiveness and cause a positive impact on class management [
31]. This study concludes that moral leadership has a positive effect on teacher effectiveness, and so the hypothesis goes as follows.
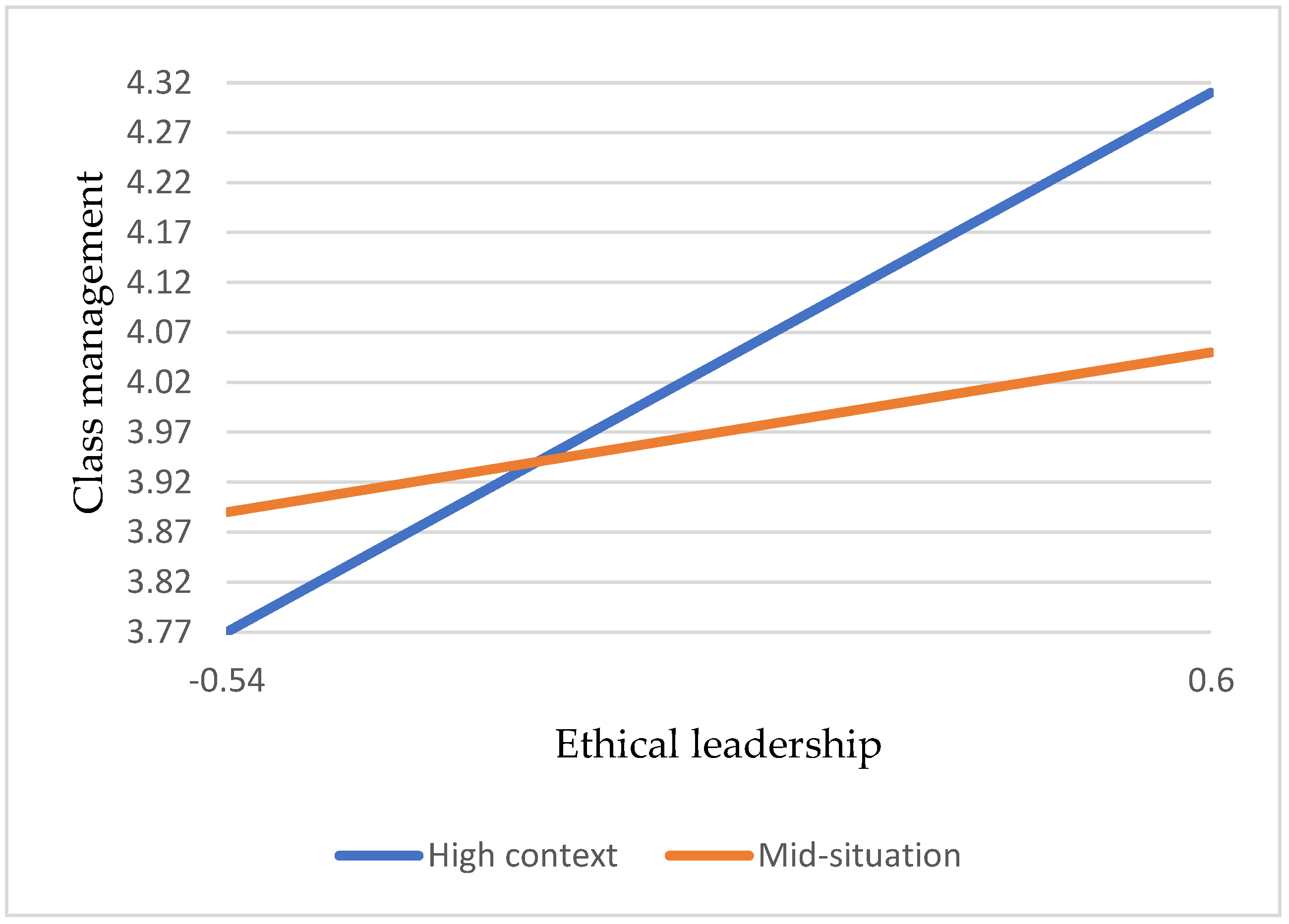
Hypothesis 3a: There is a positive correlation between ethical leadership and multiple teaching strategies for teacher effectiveness.
Hypothesis 3b: There is a positive correlation between ethical leadership and class management of teacher effectiveness.
When teachers have a moral leadership style, they have a positive impact on the effectiveness of multiple teaching strategies and class management. However, the two may be affected by context and other related factors [
32].
Hypothesis 7a: Compared to lower school situations, vocational high school teachers’ moral leadership positively affects the multiple teaching strategies of teacher effectiveness in high school situations.
Hypothesis 7b: Compared to lower school situations, vocational high school teachers’ moral leadership positively affects the class management of the teacher’s effectiveness in high school situations.
Task-oriented leadership can condense the centripetal force of organization members and the mode of strategies used. It thus impacts the effectiveness of the organization team [
33].
Hypothesis 4a: Task-oriented leadership positively correlates with multiple teaching strategies for teacher effectiveness.
Hypothesis 4b: Task-oriented leadership positively correlates with class management of teacher effectiveness.
Task-oriented leadership, therefore, has an influential relationship between the multiple teaching strategies of teacher effectiveness and class management. However, the situation will have an impact on both of them [
34].
Hypothesis 8a: Compared to lower school situations, vocational high school teachers’ task-oriented leadership positively affects the multiple teaching strategies of teacher effectiveness in high school situations.
Hypothesis 8b: Compared to lower school situations, vocational high school teachers’ task-oriented leadership positively affects the class management of teacher effectiveness in high school situations.
This study uses HLM as the statistical method. In order to match up with HLM, this research puts leadership style and teacher effectiveness as the first level and the situational variables as the second level and then adds the control variables for daytime and nighttime departments. The research’s hypothetical architecture diagram is shown in
Figure 1.
3.5. Research Tool
This work explores leadership styles—focusing on ethical leadership, charismatic leadership, supportive leadership, and task-oriented leadership—and explores and analyzes the inquiry through literature [
35]. Therefore, the ‘relationship-oriented’ dimension is subdivided into ‘charismatic leadership’ and ‘supportive leadership’, and the ‘work-oriented dimension’ is divided into ‘moral leadership’ and ‘task-based leadership’. Referenced are searched and discussed based on the four leadership styles and translated with the original meanings kept. Then, they are modified according to the research purpose and they complete the five-point leadership style scale.
The situational variables in Fiedle’s contingency theory are based on the five-point Leader–Subordinate Relationship Scale (LMR), the three-point Work Structure Scale (TS), and the three-point Authority Scale (PP). The scales are combined and analyzed to calculate the situations of high, medium, and low controls [
36]. Therefore, regarding the measurement of contextual variables, this study mainly refers to the three scales of the Fiedler Contingency Theory to measure the situation: Leader and Subordinate Relationship Scale (LMR), Work Structure Scale (TS), and Power Scale (PP). According to the purpose of this research, translation and semantic modification are carried out to complete the context scale.
Questions about the preparation of the Leader–Subordinate Relationship Scale (LMR), the Work Structure Scale (TS), and the Authority Scale (PP) are in the situational scale of this study.
Based on the scales of Woolfolk Hoy [
37]. Cronbach’s values in this study are all greater than 0.7. Therefore, they have a relatively high reliability, as shown in Ta Tschannen-Moran, and Woolfolk Hoy, this research divides teacher effectiveness into two dimensions according to its study purpose: “multiple teaching strategies” and “class management” [
38,
39].
Snijders and Bosker indicated in class linear analysis that the number of samples in the highest class must be at least. Therefore, in order to meet the minimum sample requirements of HLM, 900 teachers in total at 30 vocational high schools are required. In this study, questionnaires were collected from 30 schools, and after excluding invalid questionnaires and incomplete ones, we acquired a total of 920 valid questionnaires.
The basic background information of valid samples was analyzed by statistical methods such as frequency distribution (N) and percentage (%). Among the 920 formal samples, there is a total of 813 teachers in the daytime department, accounting for 88.4% of the effective sample, while the number of teachers in the nighttime department is 107, accounting for 11.6% of the effective sample. There are 643 male teachers, accounting for 69.9% of the effective sample, and there are 277 female teachers, accounting for 30.1% of the effective sample. From the above analyses, the sample survey results of this study found that the respondents lean heavily more on male teachers. Among the 30 schools sampled in this study, 21 industrial senior high schools accounted for 70%, 3 commercial high schools accounted for 10%, and 6 commercial and industrial high schools accounted for 20%. There are 28 public schools and 2 private schools. In total, questionnaires from 30 schools were collected in this study, composed of 6 in the north accounting for 20%, 12 in the central region accounting for 40%, and 12 in the southern region accounting for 40%.
Reliability is verified using Cronbach’s value [
40]. It has been pointed out that the generally acceptable value of Cronbach’s value is between 0.6 and 0.7. The Cronbach’s values in this study are all greater than 0.7. Therefore, they have a relatively high reliability, as shown in
Table 1.
This study uses the principal component method in factor analysis to extract the main factor, and the factors whose characteristic value is greater than 1 are selected. The factor rotation axis method (Varimax) is used to perform the rotation axis of a factor, and the items with a factor loading greater than 0.5 are retained. Before factor analysis, the KMO and Bartlett spherical test analysis data were used to determine whether factor analysis can be performed. Therefore, this study first calculates the KMO value to determine whether the factor analysis is suitable. Kaiser also stated that the larger the KMO value is, the more suitable it is for factor analysis. On the contrary, when the KMO value is less than 0.5, it is not suitable for factor analysis [
41].
An analysis of the returned formal questionnaire finds that the KMO values of the four dimensions of the leadership style scale are all greater than 0.8, which is greater than the threshold value of 0.6 recommended by Kaiser, and so it is suitable for factor analysis. The
p-value of Bartlett’s sphere test is less than 0.001, reaching the significant standard, and so it is suitable for factor analysis, as shown in
Table 2.
After KMO and Bartlett’s sphere test analysis, factor analysis and aggregate validity analysis are performed. The cumulative explanatory variation of each aspect is greater than 50%, and the load of each factor is at least greater than 0.5. In addition, the CR values of these two dimensions are both higher than 0.8, which meets the standard of greater than 0.6, and the average variance extraction (AVE) is higher than the standard of 0.5. The results are shown in
Table 3.
According to the results of the returned formal questionnaire analysis, the KMO values of the three dimensions of the situational scale are all greater than 0.7, which is higher than the threshold value of 0.6 recommended by Kaiser, and so it is suitable for factor analysis. The
p-value of Bartlett’s sphere test is less than 0.001, reaching a significant standard, and so it is suitable for factor analysis, as shown in
Table 4.
After the KMO and Bartlett’s sphere test analyses, factor analysis and aggregate validity analysis are performed, and the cumulative explanatory variance of each aspect is greater than 50%. The load of each factor is higher than 0.5. In addition, the CR values of the three potential variables are higher than 0.8, which meets the standard of greater than 0.6, and the average variance extraction (AVE) is also higher than the standard of 0.5. The details are listed in the table.
According to the results of the returned formal questionnaire analysis, the KMO values of the two dimensions of the situational scale are both greater than 0.6, which is higher than the threshold value of 0.6 recommended by Kaiser, and so it is suitable for factor analysis. The
p-value of Bartlett’s sphere test is less than 0.001, reaching the significant standard, and so it is suitable for factor analysis, as shown in
Table 5.
After the KMO and Bartlett sphere test analyses, factor analysis and convergent validity analysis are performed, and the cumulative explanatory variation of each aspect is greater than 60%. The load of this factor is higher than 0.5. In addition, the CR values are all higher than 0.8, which meets the standard of greater than 0.6, and the average variance extraction (AVE) is also higher than the standard of 0.5. The results are shown in
Table 6.