Secured Protocol with Collaborative IoT-Enabled Sustainable Communication Using Artificial Intelligence Technique
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- i.
- In the distributed processing of IoT systems, the proposed protocol provides a collaborative intelligence for the multi-path selection technique. Additionally, it offers more effective distributed services for networked devices and increases resource utilization.
- ii.
- The collaborative information is updated using a multi-parametric function that balances the contributions of each metric and improves the reception of IoT data over the inherently unreliable network.
- iii.
- Furthermore, to strengthen the trustworthiness of sustainable systems, security methods are applied to multi-stages.
- iv.
- Extensive tests demonstrate the significant improvement of the proposed protocol for routing and security analysis.
2. Related Work
Problem Identification
3. Proposed Secured Protocol with Collaborative Intelligence
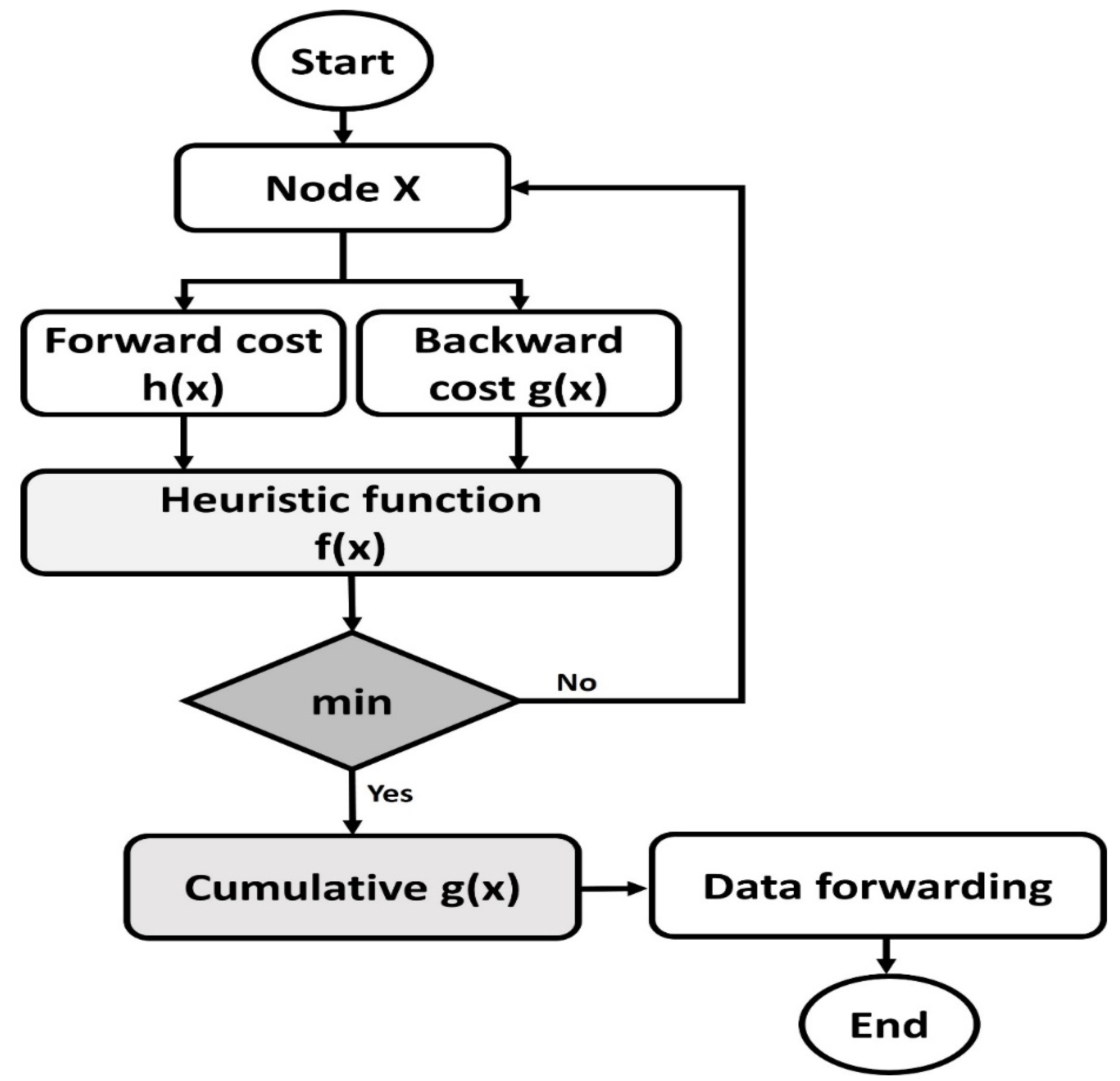
3.1. Routing Phase with Collaborative Intelligence
3.2. Security Phase with Authentication and Trustworthiness
4. Performance Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akpakwu, G.A.; Silva, B.J.; Hancke, G.P.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M. A Survey on 5G Networks for the Internet of Things: Communication Technologies and Challenges. IEEE Access 2017, 6, 3619–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Singh, A.K. Applications of Internet of Things (IoT) in Green Computing. In Intelligence of Things: AI-IoT Based Critical-Applications and Innovations; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedeoglu, V.; Jurdak, R.; Dorri, A.; Lunardi, R.; Michelin, R.; Zorzo, A.; Kanhere, S. Blockchain Technologies for IoT. In Advanced Applications of Blockchain Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 55–89. [Google Scholar]
- Teli, S.R.; Zvanovec, S.; Ghassemlooy, Z. Optical Internet of Things Within 5G: Applications and challenges. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Internet of Things and Intelligence System (IOTAIS), Bali, Indonesia, 1–3 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, T.; Cai, Z.; Hua, L. 5G-Oriented IoT Coverage Enhancement and Physical Education Resource Management. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2021, 80, 103346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, S.; Khedr, A.M.; Al Aghbari, Z.; Agrawal, D.P. Opportunistically Exploiting Internet of Things for Wireless Sensor Network Routing in Smart Cities. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2018, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piran, M.J.; Verma, S.; Menon, V.G.; Suh, D.Y. Energy-efficient transmission range optimization model for wsn-based internet of things. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 67, 2989–3007. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, B.B.; Dhanalakshmi, R. Recent advancements and challenges of Internet of Things in smart agriculture: A survey. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2022, 126, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Abbas, N.; Nasir, M.; Haseeb, K.; Saba, T.; Rehman, A.; Mehmood, Z. Steganography-assisted secure localization of smart devices in internet of multimedia things (IoMT). Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 17045–17065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Haque, A.; Blaabjerg, F. Machine learning in wireless sensor networks for smart cities: A survey. Electronics 2021, 10, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseeb, K.; Almogren, A.; Ud Din, I.; Islam, N.; Altameem, A. SASC: Secure and Authentication-Based Sensor Cloud Architecture for Intelligent Internet of Things. Sensors 2020, 20, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseeb, K.; Jan, Z.; Alzahrani, F.A.; Jeon, G. A Secure Mobile Wireless Sensor Networks based Protocol for Smart Data Gathering with Cloud. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 97, 107584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Chaurasiya, V.K. A strategy for elimination of data redundancy in internet of things (IoT) based wireless sensor network (wsn). IEEE Syst. J. 2018, 13, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Jing, X.; Yan, Z.; Yang, L.T. A survey on data fusion in internet of things: Towards secure and privacy-preserving fusion. Inf. Fusion 2019, 51, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Jha, V.K. A review on recent trends in query processing and optimization in big data. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2022, 124, 633–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murshed, M.G.S.; Murphy, C.; Hou, D.; Khan, N.; Ananthanarayanan, G.; Hussain, F. Machine learning at the network edge: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021, 54, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, N.; Altamimi, M.; Haseeb, K.; Siraj, M. Secure and Sustainable Predictive Framework for IoT-Based Multimedia Services Using Machine Learning. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, G.; Cabral, B.; Pereira, V.; Bernardino, J. Computation offloading in Edge Computing environments using Artificial Intelligence techniques. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2020, 95, 103840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djedouboum, A.C.; Ari, A.A.A.; Gueroui, A.M.; Mohamadou, A.; Aliouat, Z. Big data collection in large-scale wireless sensor networks. Sensors 2018, 18, 4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shahraki, A.; Taherkordi, A.; Haugen, Ø.; Eliassen, F. Clustering objectives in wireless sensor networks: A survey and research direction analysis. Comput. Netw. 2020, 180, 107376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseeb, K.; Islam, N.; Saba, T.; Rehman, A.; Mehmood, Z. LSDAR: A Light-weight Structure based Data Aggregation Routing Protocol with Secure Internet of Things Integrated Next-generation Sensor Networks. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 54, 101995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, I.; Kumar, A.; Bansal, M. A review on lightweight cryptography algorithms for data security and authentication in IoTs. In Proceedings of the 2017 4th International Conference on Signal Processing, Computing and Control (ISPCC), Solan, India, 21–23 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, A.; Engineer, M. A Survey of Lightweight Cryptographic Algorithms for IoT-Based Applications. In Smart Innovations in Communication and Computational Sciences; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampayo, S.L.; Montavont, J.; Noël, T. REFLOOD: Reactive routing protocol for wake-up radio in IoT. Ad Hoc Netw. 2021, 121, 102578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanth, A.; Jayachitra, S. A novel multi-objective optimization strategy for enhancing quality of service in IoT-enabled WSN applications. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 2020, 13, 1905–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibri, S.E. The IoT for smart sustainable cities of the future: An analytical framework for sensor-based big data applications for environmental sustainability. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 38, 230–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Chanak, P.; Bhattacharya, M. Energy-efficient intelligent routing scheme for IoT-enabled WSNs. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 11440–11449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diène, B.; Rodrigues, J.J.; Diallo, O.; Ndoye, E.H.M.; Korotaev, V.V. Data management techniques for Internet of Things. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 138, 106564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Wan, X.; Gan, P. A double-blockchain solution for agricultural sampled data security in Internet of Things network. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 117, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seema, B.; Yao, N.; Carie, A.; Shah, S.B.H. Efficient data transfer in clustered IoT network with cooperative member nodes. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 34241–34251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, T.; Haseeb, K.; Din, I.U.; Almogren, A.; Altameem, A.; Fati, S.M. EGCIR: Energy-Aware Graph Clustering and Intelligent Routing Using Supervised System in Wireless Sensor Networks. Energies 2020, 13, 4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, T.M.; Samal, U.C.; Mohapatra, S.K. Energy-efficient modified LEACH protocol for IoT application. IET Wirel. Sens. Syst. 2018, 8, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Khan, J.Y.; Ngo, D.T. A distributed energy-harvesting-aware routing algorithm for heterogeneous IoT networks. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2018, 2, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniata, M.; Reda, H.T.; Chilamkurti, N.; Abuadbba, A. Energy-efficient hybrid routing protocol for IoT communication systems in 5G and beyond. Sensors 2021, 21, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, O.J.; Yuvaraj, T.; Paul, J.K.; Nguyen, H.H.; Gundepudi, K.; Shukla, M.K. Improving Energy Efficiency and QoS of LPWANs for IoT Using Q-Learning Based Data Routing. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2021, 8, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, T.U.; Asim, M.; Baker, T.; Hassan, J.; Tariq, N. CTrust-RPL: A control layer-based trust mechanism for supporting secure routing in routing protocol for low power and lossy networks-based Internet of Things applications. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2021, 32, e4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, D.; Likhachev, M.; Stentz, A. A guide to heuristic-based path planning. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Planning under Uncertainty for Autonomous Systems, International Conference on Automated Planning and Scheduling (ICAPS), Monterey, CA, USA, 5–10 June 2005; pp. 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Allouche, D.; Givry, S.d.; Katsirelos, G.; Schiex, T.; Zytnicki, M. Anytime hybrid best-first search with tree decomposition for weighted CSP. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming, Cork, Ireland, 31 August 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Attack | Proposed Procedure |
|---|---|
| Malicious packets | Nodes’ unique identities |
| Compromised nodes | Computation of trust value |
| Privacy | Data encryption using lightweight xor operations |
| Authentication | Gateway extracts the node’s identity and compares it with the actual value |
| Untrusted nodes | Verification based on the unique identity and shared secret key |
| Data integrity | Data hashing |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of nodes | 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 |
| Deployment | Random |
| Sink node | 3 |
| Network dimension | 300 m × 300 m |
| Transmission range | 3 m |
| Packet size | 64 bytes |
| Initial energy | 2 J |
| Time intervals | 1500 s |
| Simulations run | 15 |
| Gateways | 2–10 |
| Malicious devices | 10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, N.; Haseeb, K.; Ali, M.; Jeon, G. Secured Protocol with Collaborative IoT-Enabled Sustainable Communication Using Artificial Intelligence Technique. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8919. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148919
Islam N, Haseeb K, Ali M, Jeon G. Secured Protocol with Collaborative IoT-Enabled Sustainable Communication Using Artificial Intelligence Technique. Sustainability. 2022; 14(14):8919. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148919
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Naveed, Khalid Haseeb, Muhammad Ali, and Gwanggil Jeon. 2022. "Secured Protocol with Collaborative IoT-Enabled Sustainable Communication Using Artificial Intelligence Technique" Sustainability 14, no. 14: 8919. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148919
APA StyleIslam, N., Haseeb, K., Ali, M., & Jeon, G. (2022). Secured Protocol with Collaborative IoT-Enabled Sustainable Communication Using Artificial Intelligence Technique. Sustainability, 14(14), 8919. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148919








