An Environmentally Friendly Solution for Waste Facial Masks Recycled in Construction Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
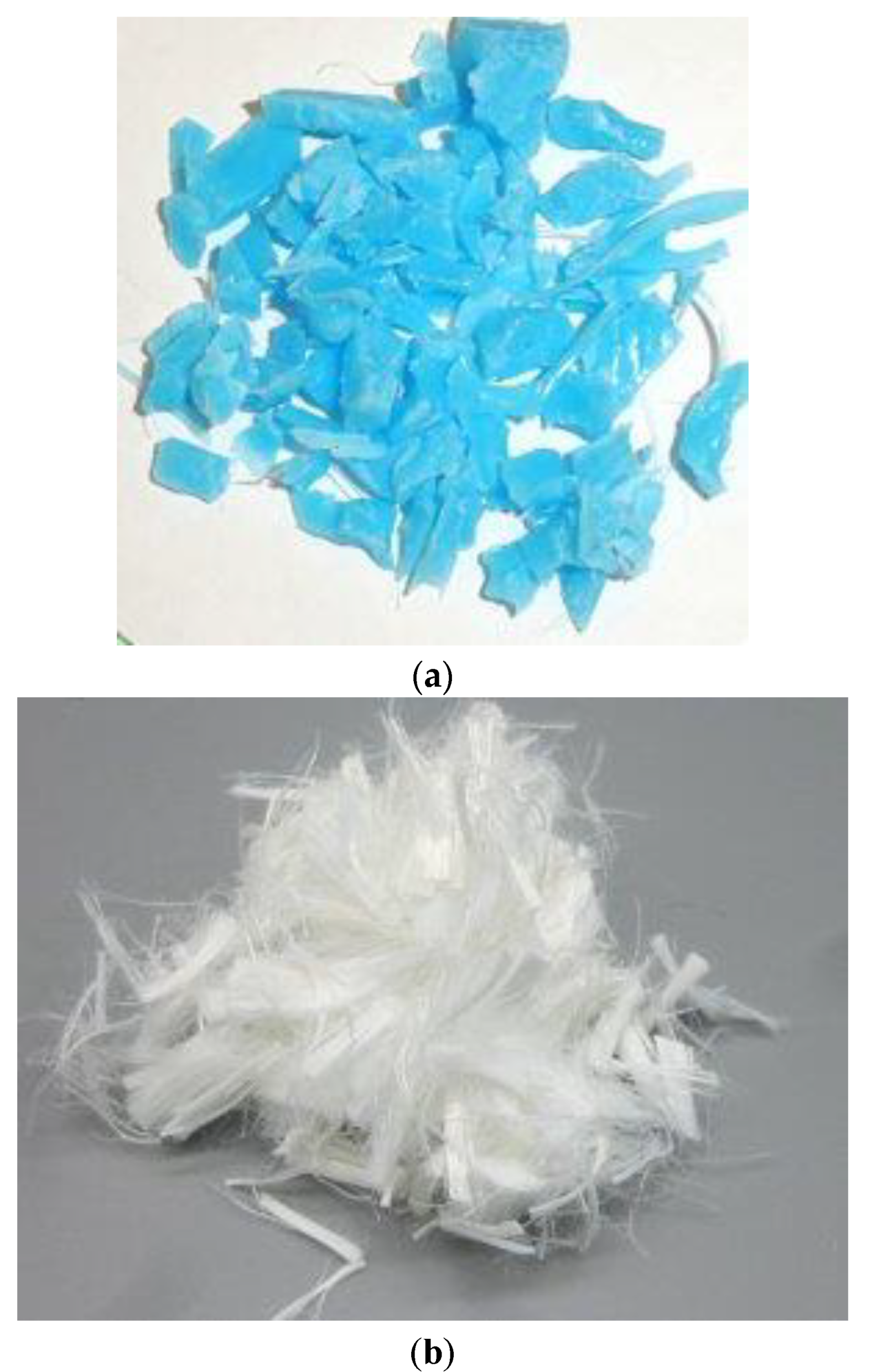
2.1. Preparing of Fibereed and Shredded Masks
2.2. Preparation of Sample Concretes
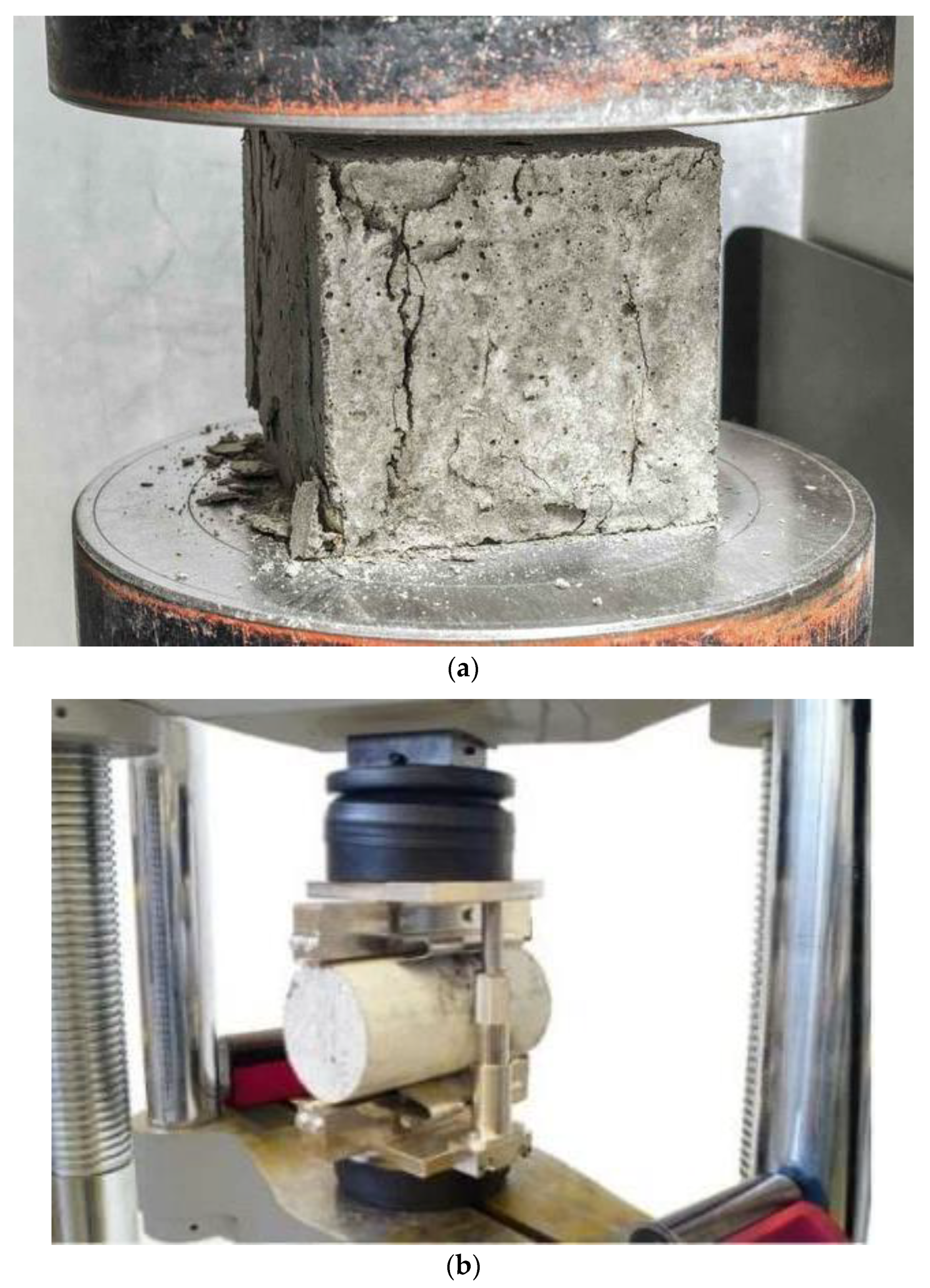
2.3. Compressive and Tensile Strength Tests
2.4. Detection of Thermal Properties
2.5. Durability Tests
3. Results and Discussion
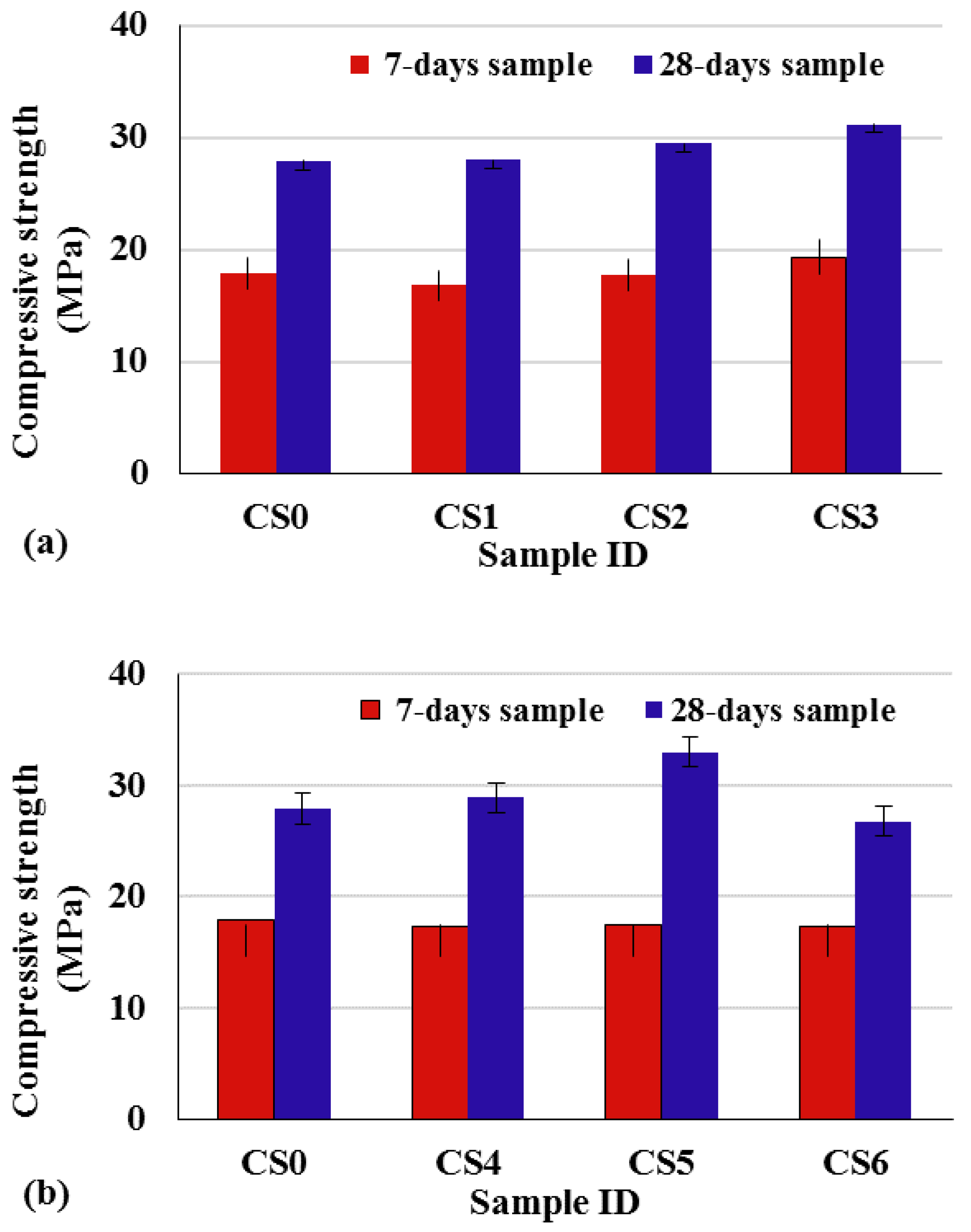
3.1. The Effect of Waste Masks on Compressive Strength
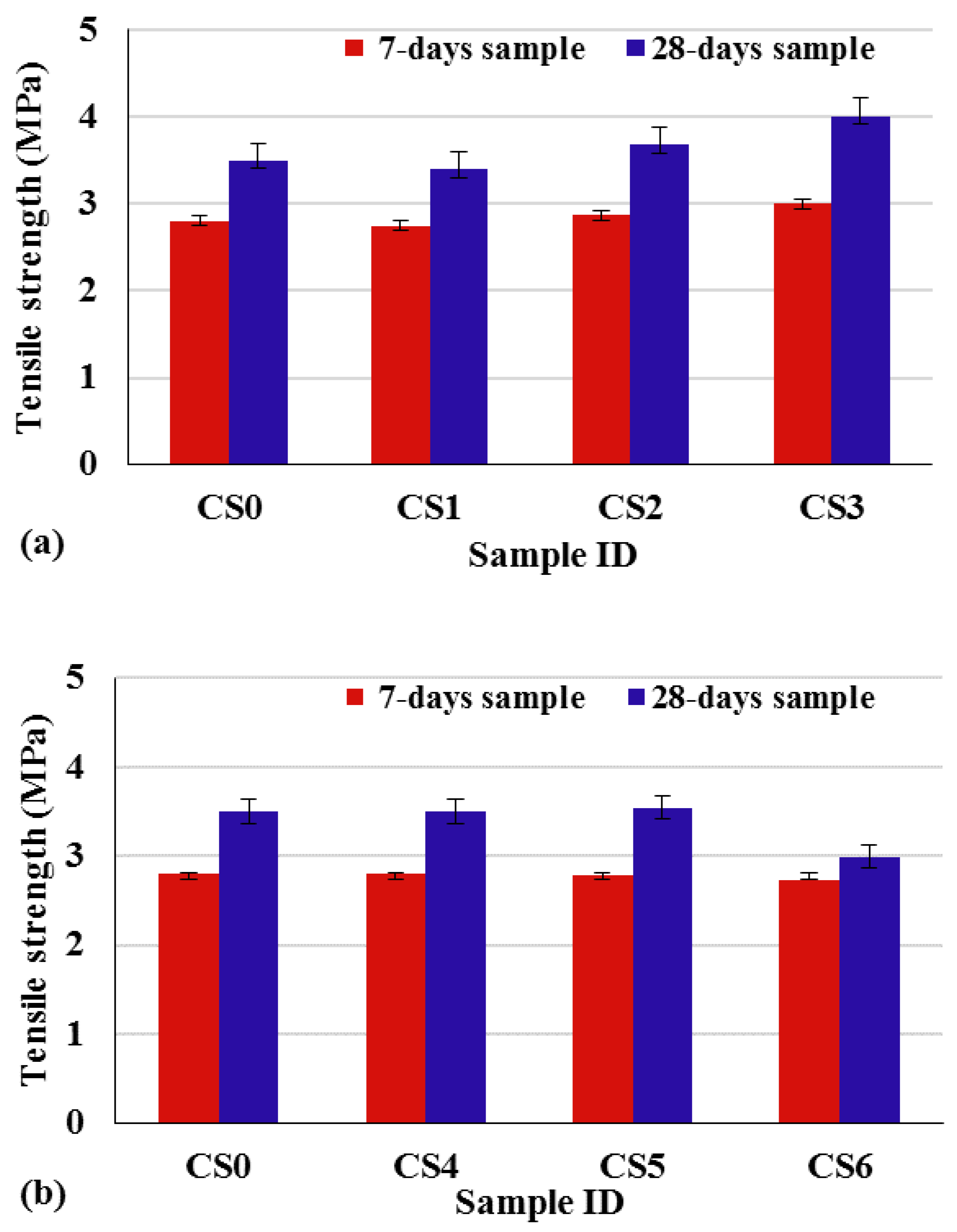
3.2. The Effect of Waste Masks on Tensile Strength
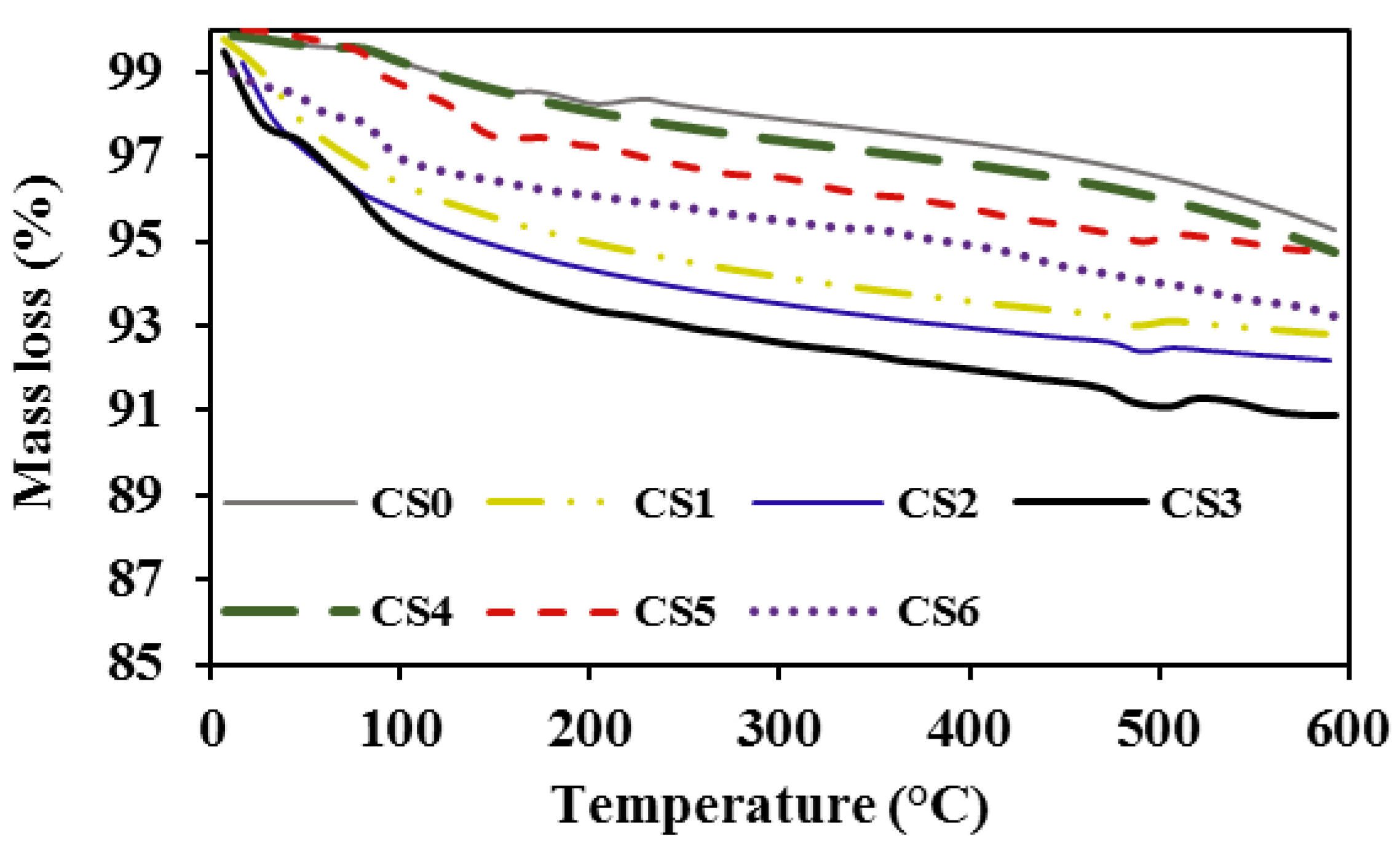
3.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.4. Microstructure of the Concrete
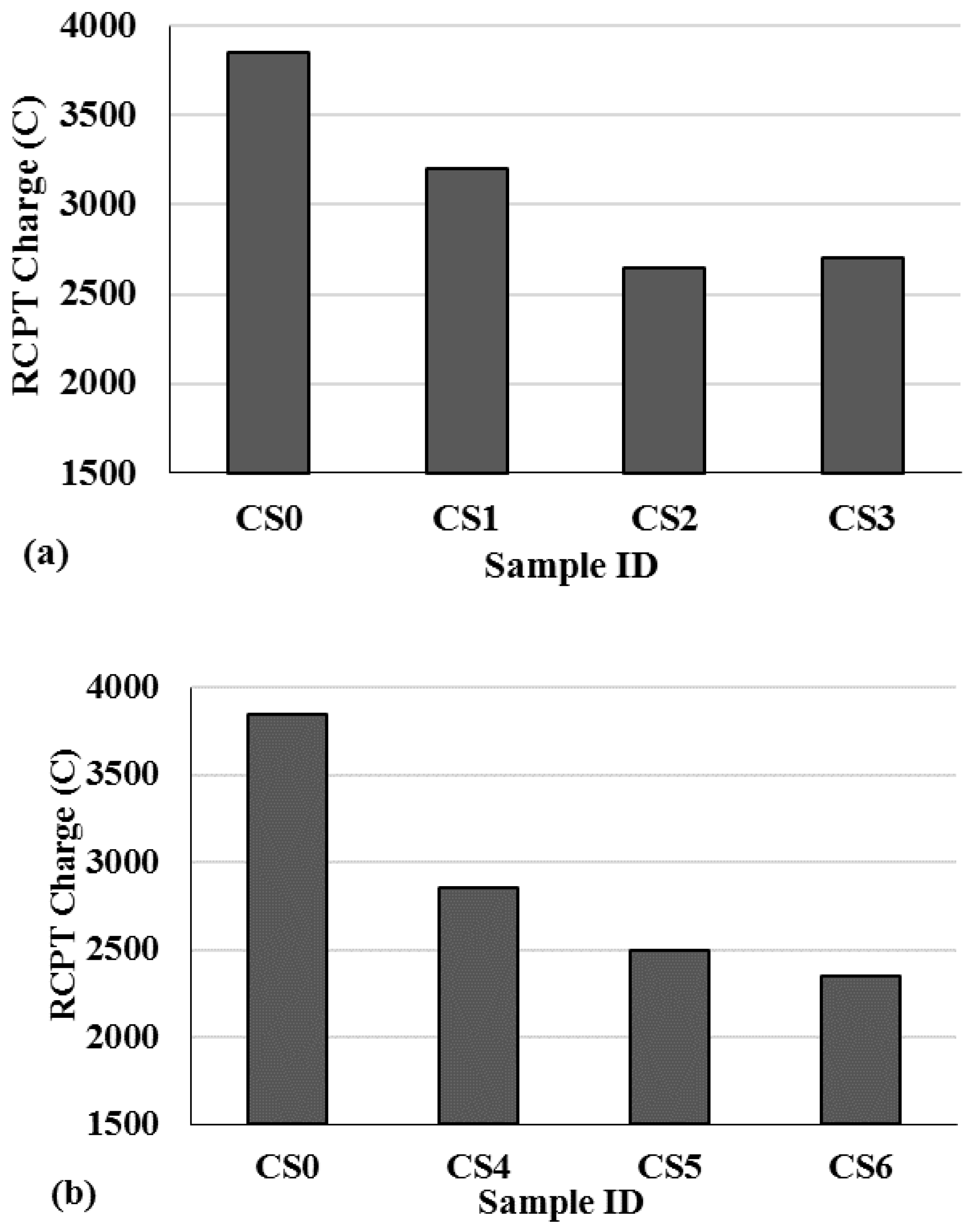
3.5. RCPT Test Result
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El Haj Assad, M.; Ahmadi, M.H.; Sadeghzadeh, M.; Yassin, A.; Issakhov, A. Renewable hybrid energy systems using geothermal energy: Hybrid solar thermal–geothermal power plant. Int. J. Low Carbon Technol. 2021, 16, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, M.; Ghasempour, R.; Ahmadi, M.H.; Chitsaz, A.; Ghazanfari Holagh, S. Exergetic, exergo-economic, and exergo-environmental analyses of a trigeneration system driven by biomass and natural gas. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2021, 147, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, O.; Shafii, M.B.; Rezaee Shirin-Abadi, A.; Heydarian, R.; Ahmadi, M.H. The impacts of utilizing nano-encapsulated PCM along with RGO nanosheets in a pulsating heat pipe, a comparative study. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 19481–19499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadhosseini, H.; Alyousef, R.; Md. Tahir, M. Towards Sustainable Concrete Composites through Waste Valorisation of Plastic Food Trays as Low-Cost Fibrous Materials. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonoli, A.; Zanni, S.; Serrano-Bernardo, F. Sustainability in building and construction within the framework of circular cities and european new green deal. The contribution of concrete recycling. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugarte, M.; Martinez-Arguelles, G.; Torres, J. Experimental evaluation of modified sulfur concrete for achieving sustainability in industry applications. Sustainability 2018, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alrshoudi, F.; Mohammadhosseini, H.; Tahir, M.M.; Alyousef, R.; Alghamdi, H.; Alharbi, Y.R.; Alsaif, A. Sustainable use of waste polypropylene fibers and palm oil fuel ash in the production of novel prepacked aggregate fiber-reinforced concrete. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangelo, F.; Navarro, T.G.; Farina, I.; Petrillo, A. Comparative LCA of concrete with recycled aggregates: A circular economy mindset in Europe. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2020, 25, 1790–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajerani, A.; Suter, D.; Jeffrey-Bailey, T.; Song, T.; Arulrajah, A.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Law, D. Recycling waste materials in geopolymer concrete. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2019, 21, 493–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, D.; Yu, R.; Shui, Z.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, C.; Zhou, F.; Ding, M.; Tong, X.; He, Y. A novel development of green ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) based on appropriate application of recycled cementitious material. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Singh, A.; Xiao, J.; Hou, S. Combined use of recycled powder and recycled coarse aggregate derived from construction and demolition waste in self-compacting concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 254, 119323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, E.R.; Camões, A.; Branco, F.; Aguiar, J.; Fangueiro, R. Recycling of biomass and coal fly ash as cement replacement material and its effect on hydration and carbonation of concrete. Waste Manag. 2019, 94, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrounias, P.; Giannakopoulou, P.P.; Rogkala, A.; Lampropoulou, P.; Tsikouras, B.; Rigopoulos, I.; Hatzipanagiotou, K. Petrographic and mechanical characteristics of concrete produced by different type of recycled materials. Geosciences 2019, 9, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacob-Vaillancourt, C.; Sorelli, L. Characterization of concrete composites with recycled plastic aggregates from postconsumer material streams. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 182, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Zollinger, D.; Grasley, Z. Economic input-output life cycle assessment of concrete pavement containing recycled concrete aggregate. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadinia, A.; Wong, Y.C.; Arulrajah, A.; Horpibulsuk, S. Strength evaluation of utilizing recycled plastic waste and recycled crushed glass in concrete footpaths. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 197, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.; Da Silva, P.; De Brito, J. Self-compacting concrete with recycled aggregates—A literature review. J. Build. Eng. 2019, 22, 349–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, K.; Gupta, N. Application of domestic & industrial waste materials in concrete: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 2926–2931. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, T.; Xiao, J.; Zou, S.; Wang, Y. Hardened properties of layered 3D printed concrete with recycled sand. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 113, 103724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Liu, Q.; Xia, B.; Singh, A.; Lv, Z.; Song, W. Natural gravel-recycled aggregate concrete applied in rural highway pavement: Material properties and life cycle assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 130219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Ma, Z.; Wu, H.; Wang, W. The utilization of eco-friendly recycled powder from concrete and brick waste in new concrete: A critical review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 114, 103807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wu, P.; Schartup, A.T.; Zhang, Y. Plastic waste release caused by COVID-19 and its fate in the global ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2111530118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T.; Mohajerani, A.; Giustozzi, F. Recycling of waste materials for asphalt concrete and bitumen: A review. Materials 2020, 13, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awoyera, P.O.; Adesina, A.; Gobinath, R. Role of recycling fine materials as filler for improving performance of concrete-a review. Aust. J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 17, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, M.S.; Shubbar, A.A.; Abed, Z.A.-A.R.; Ibrahim, M.S. Properties of eco-friendly cement mortar contained recycled materials from different sources. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 31, 101444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, J. A review of life cycle assessment of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 209, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Ling, T.-C.; Mo, K.H. Recycling of wastes for value-added applications in concrete blocks: An overview. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 138, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małek, M.; Jackowski, M.; Łasica, W.; Kadela, M. Characteristics of recycled polypropylene fibers as an addition to concrete fabrication based on portland cement. Materials 2020, 13, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sutar, S.; Kumar, M.H. Strength Behaviour of Glass Fiber Reinforced Concrete. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2021, 8, 2206–2211. [Google Scholar]
- Pakravan, H.; Latifi, M.; Jamshidi, M. Hybrid short fiber reinforcement system in concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 142, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, A.J. Size and shape effect of specimen on the compressive strength of HPLWFC reinforced with glass fibres. J. King Saud Univ. Eng. Sci. 2017, 29, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noushini, A.; Hastings, M.; Castel, A.; Aslani, F. Mechanical and flexural performance of synthetic fibre reinforced geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 186, 454–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Dai, X.-B.; Gao, J.-X.; Wang, P. Effect of nano-SiO2 particles on fracture properties of concrete composite containing fly ash. Curr. Sci. 2015, 2015, 2035–2043. [Google Scholar]
- Nuaklong, P.; Boonchoo, N.; Jongvivatsakul, P.; Charinpanitkul, T.; Sukontasukkul, P. Hybrid effect of carbon nanotubes and polypropylene fibers on mechanical properties and fire resistance of cement mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 275, 122189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; Ding, T.; Xiao, J. Life cycle assessment of concrete structures with reuse and recycling strategies: A novel framework and case study. Waste Manag. 2020, 105, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.-J.; Iizuka, A.; Shibata, E. Chemical recycling and use of various types of concrete waste: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Feng, W.; Chen, Z.; Nong, Y.; Guan, S.; Sun, J. Fracture behavior of a sustainable material: Recycled concrete with waste crumb rubber subjected to elevated temperatures. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 318, 128553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.W.; Soomro, M.; Evangelista, A.C.J. A review of recycled aggregate in concrete applications (2000–2017). Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 172, 272–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, A.; Sarmah, A.K. Construction and demolition waste generation and properties of recycled aggregate concrete: A global perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 186, 262–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yan, L.; Fu, Q.; Kasal, B. A comprehensive review on recycled aggregate and recycled aggregate concrete. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 171, 105565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toghroli, A.; Shariati, M.; Sajedi, F.; Ibrahim, Z.; Koting, S.; Mohamad, E.T.; Khorami, M. A review on pavement porous concrete using recycled waste materials. Smart Struct. Syst. 2018, 22, 433–440. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, V.W.; Butera, A.; Le, K.N.; Li, W. Utilising CO2 technologies for recycled aggregate concrete: A critical review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 250, 118903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayeh, B.A.; Alyousef, R.; Alabduljabbar, H.; Alaskar, A. Recycling of rice husk waste for a sustainable concrete: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Shi, C.; Guan, X.; Zhu, J.; Ding, Y.; Ling, T.-C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y. Durability of recycled aggregate concrete—A review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 89, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Li, W.; Dong, W.; Tam, V.W.Y.; Yu, T. Durability deterioration of concrete under marine environment from material to structure: A critical review. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 35, 102074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S. Effect of fiber reinforcement and distribution on unconfined compressive strength of fiber-reinforced cemented sand. Geotext. Geomembr. 2009, 27, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbaba, M.; Asefi, E.; Sadaghian, H.; Mirmiran, A. Effect of age on the compressive strength of ultra-high-performance fiber-reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 175, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

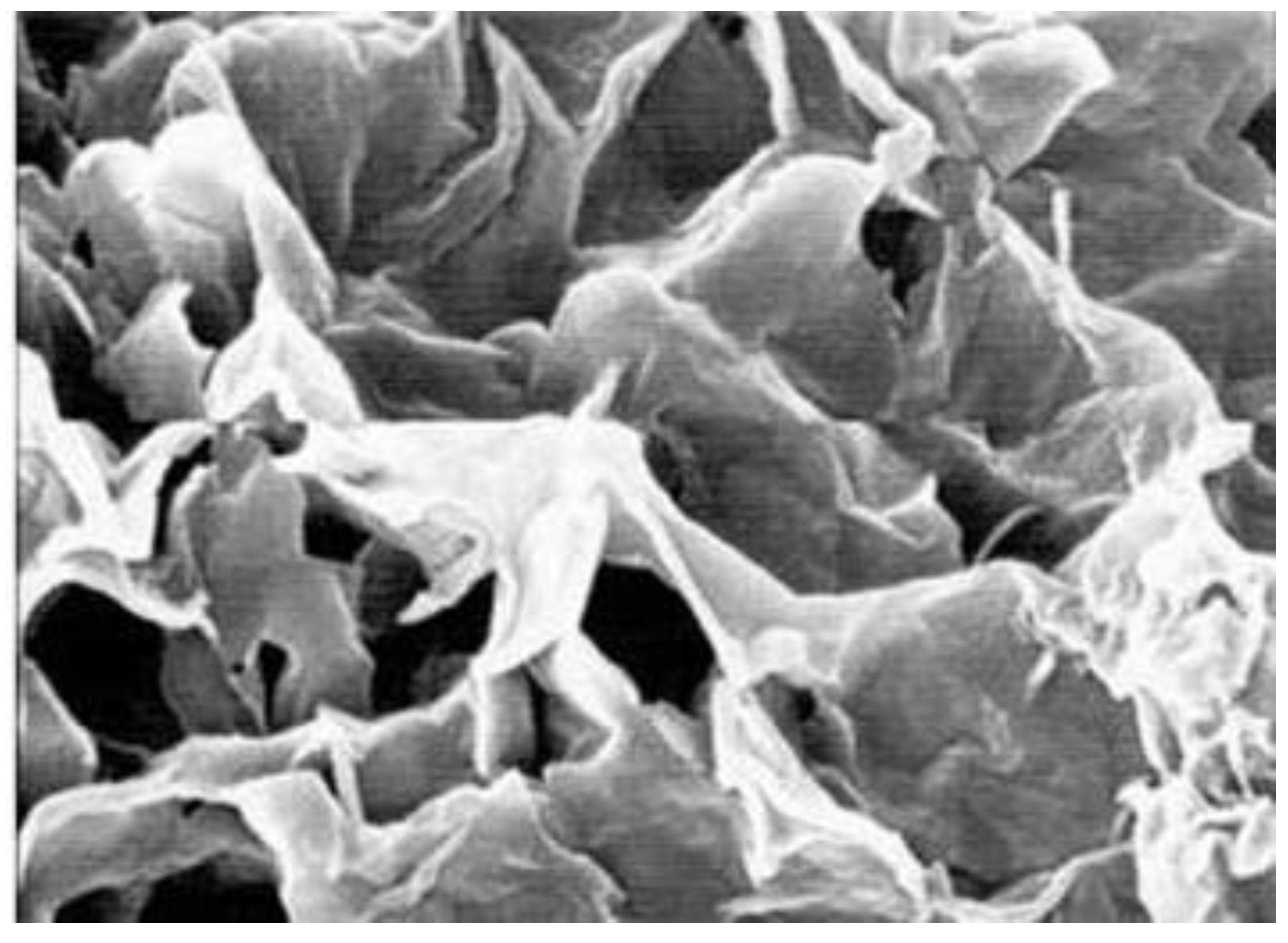
| Element | Weight (%) |
|---|---|
| Mg | 2.94 |
| Al | 9.99 |
| Ca | 25.85 |
| Si | 59.11 |
| K | 2.11 |
| Mixture ID | Fiber (% Vol) | Cement (kg/m3) | Water (kg/m3) | Superplasticizer (kg/m3) | Coarse Aggregate (kg/m3) | Fine Aggregate (kg/m3) | W/C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS0 | -- | 350 | 182 | 5.25 | 857 | 859 | 0.5 |
| CS1 | 1 (Fibered) | 350 | 182 | 5.25 | 857 | 859 | 0.5 |
| CS2 | 1.5 (Fibered) | 350 | 182 | 5.25 | 857 | 859 | 0.5 |
| CS3 | 2 (Fibered) | 350 | 182 | 5.25 | 857 | 859 | 0.5 |
| CS4 | 0.75 (shredded) | 350 | 182 | 5.25 | 857 | 859 | 0.5 |
| CS5 | 1 (shredded) | 350 | 182 | 5.25 | 857 | 859 | 0.5 |
| CS6 | 1.5 (shredded) | 350 | 182 | 5.25 | 857 | 859 | 0.5 |
| Fiber (% Vol) | Compressive Strength (Mpa) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present Study | Małek et al. [28] | |||||||
| 7 Days | SD | 28 Days | SD | 7 Days | SD | 28 Days | SD | |
| -- | 17.2 | 1.12 | 27.3 | 0.65 | 18.3 | 0.76 | 27.9 | 0.15 |
| 1% | 16.7 | 0.81 | 28 | 0.96 | 17.3 | 0.29 | 28.2 | 2.16 |
| Sample ID | Sample Age | Compressive Strength Increase (%) |
|---|---|---|
| CS1 | 7-days | −6.14 |
| 28-days | 0.36 | |
| CS2 | 7-days | −1.12 |
| 28-days | 5.73 | |
| CS3 | 7-days | 7.82 |
| 28-days | 11.70 | |
| CS4 | 7-days | −3.19 |
| 28-days | 3.58 | |
| CS5 | 7-days | −2.79 |
| 28-days | 18.28 | |
| CS6 | 7-days | −3.46 |
| 28-days | −3.94 |
| Sample ID | Sample Age | Tensile Strength Increase (%) |
|---|---|---|
| CS1 | 7 days | −1.78 |
| 28 days | −2.85 | |
| CS2 | 7 days | 2.50 |
| 28 days | 5.14 | |
| CS3 | 7 days | 7.14 |
| 28 days | 14.57 | |
| CS4 | 7 days | 0.36 |
| 28 days | 0.00 | |
| CS5 | 7 days | −0.36 |
| 28 days | 1.14 | |
| CS6 | 7 days | −2.50 |
| 28 days | −14.57 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, M.; Opulencia, M.J.C.; Chandra, T.; Chandra, S.; Muda, I.; Dias, R.; Chetthamrongchai, P.; Jalil, A.T. An Environmentally Friendly Solution for Waste Facial Masks Recycled in Construction Materials. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8739. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148739
Ali M, Opulencia MJC, Chandra T, Chandra S, Muda I, Dias R, Chetthamrongchai P, Jalil AT. An Environmentally Friendly Solution for Waste Facial Masks Recycled in Construction Materials. Sustainability. 2022; 14(14):8739. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148739
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Madad, Maria Jade Catalan Opulencia, Teddy Chandra, Stefani Chandra, Iskandar Muda, Rui Dias, Paitoon Chetthamrongchai, and Abduladheem Turki Jalil. 2022. "An Environmentally Friendly Solution for Waste Facial Masks Recycled in Construction Materials" Sustainability 14, no. 14: 8739. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148739
APA StyleAli, M., Opulencia, M. J. C., Chandra, T., Chandra, S., Muda, I., Dias, R., Chetthamrongchai, P., & Jalil, A. T. (2022). An Environmentally Friendly Solution for Waste Facial Masks Recycled in Construction Materials. Sustainability, 14(14), 8739. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148739








