Implementation of a 3D Coupled Hydrodynamic–Biogeochemical Model in Kuwait Bay
Abstract
:1. Introduction
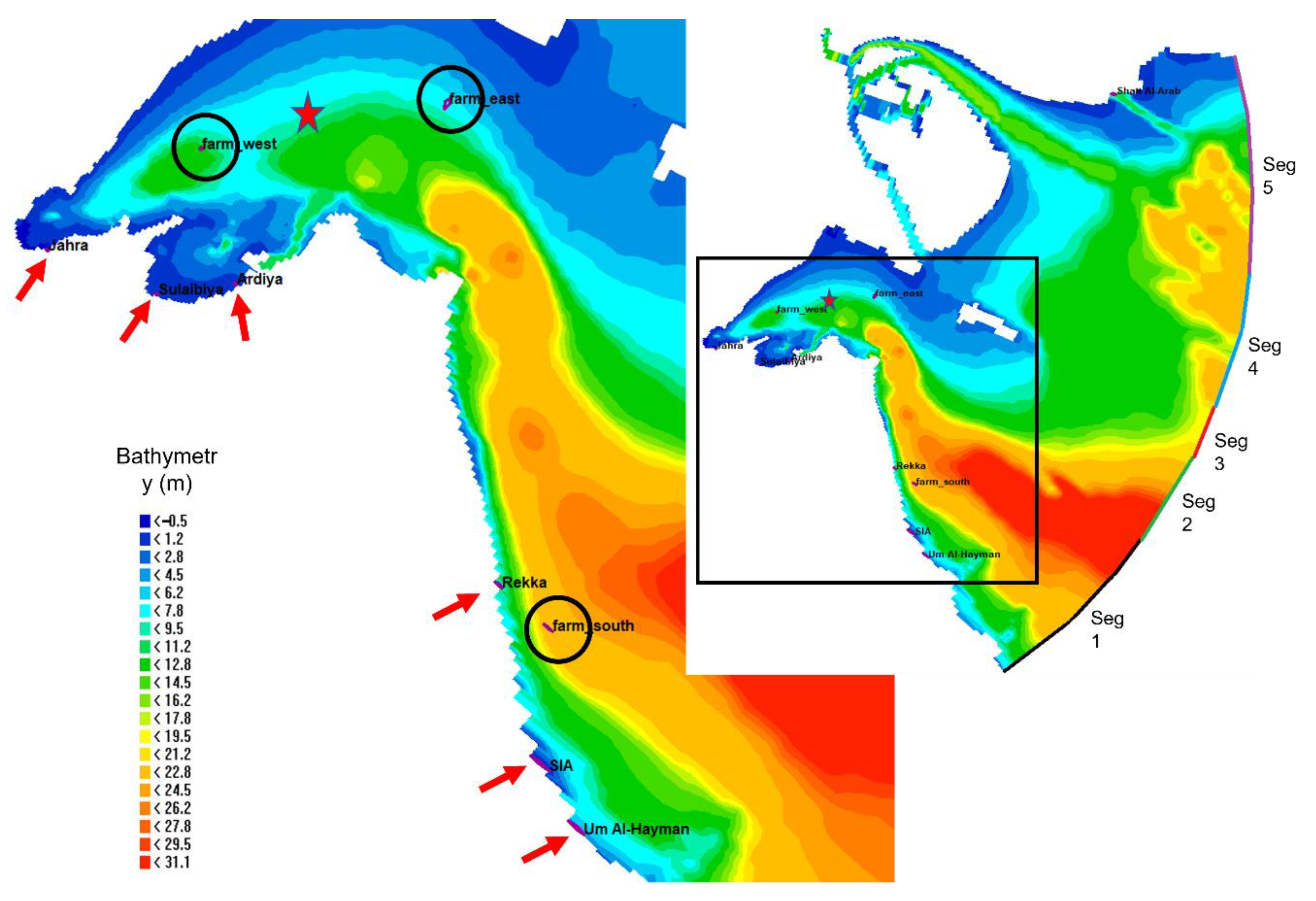
2. Description of the Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Available Datasets
3.2. Hydrodynamic Model Setup
Model Calibration
3.3. Biogeochemical Model Setup
3.4. Modelling Finfish Farms
4. Results
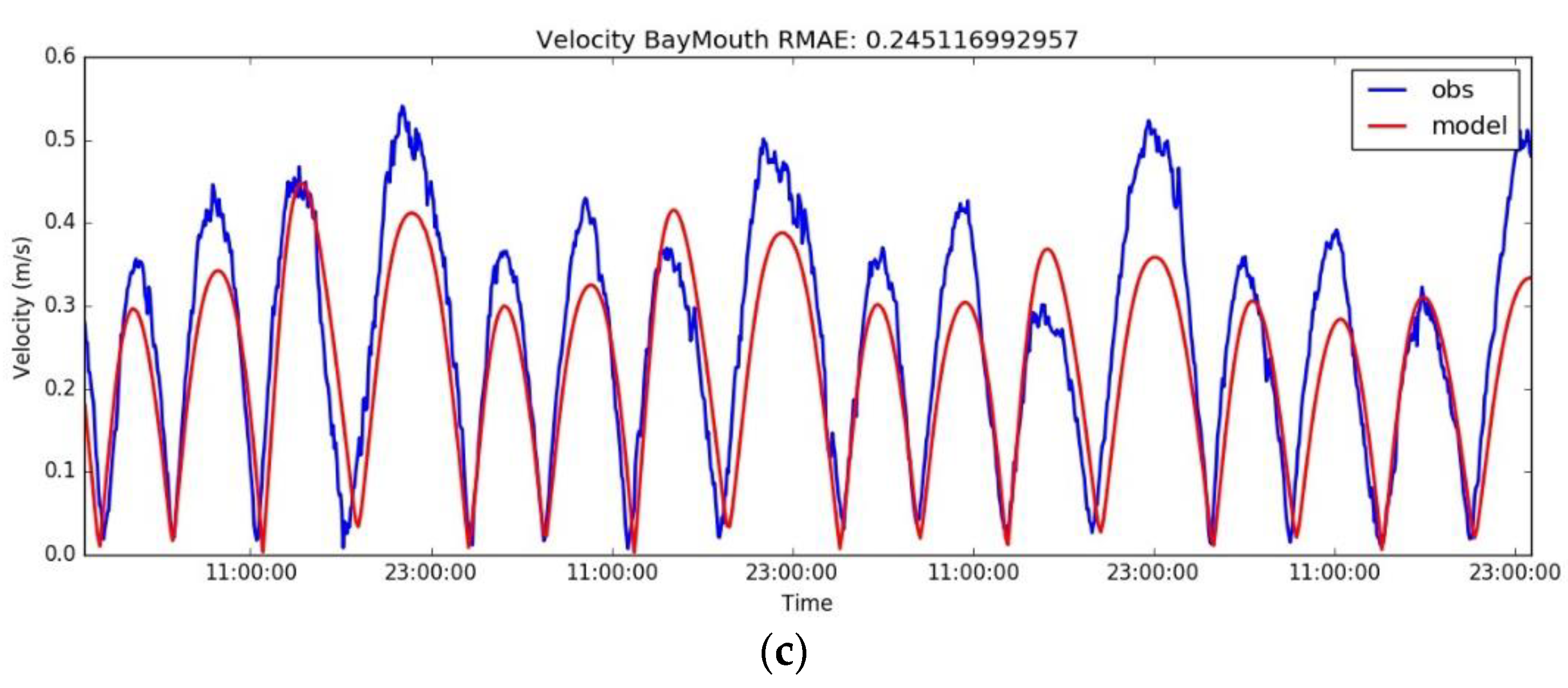
4.1. Hydrodynamic Model Validation
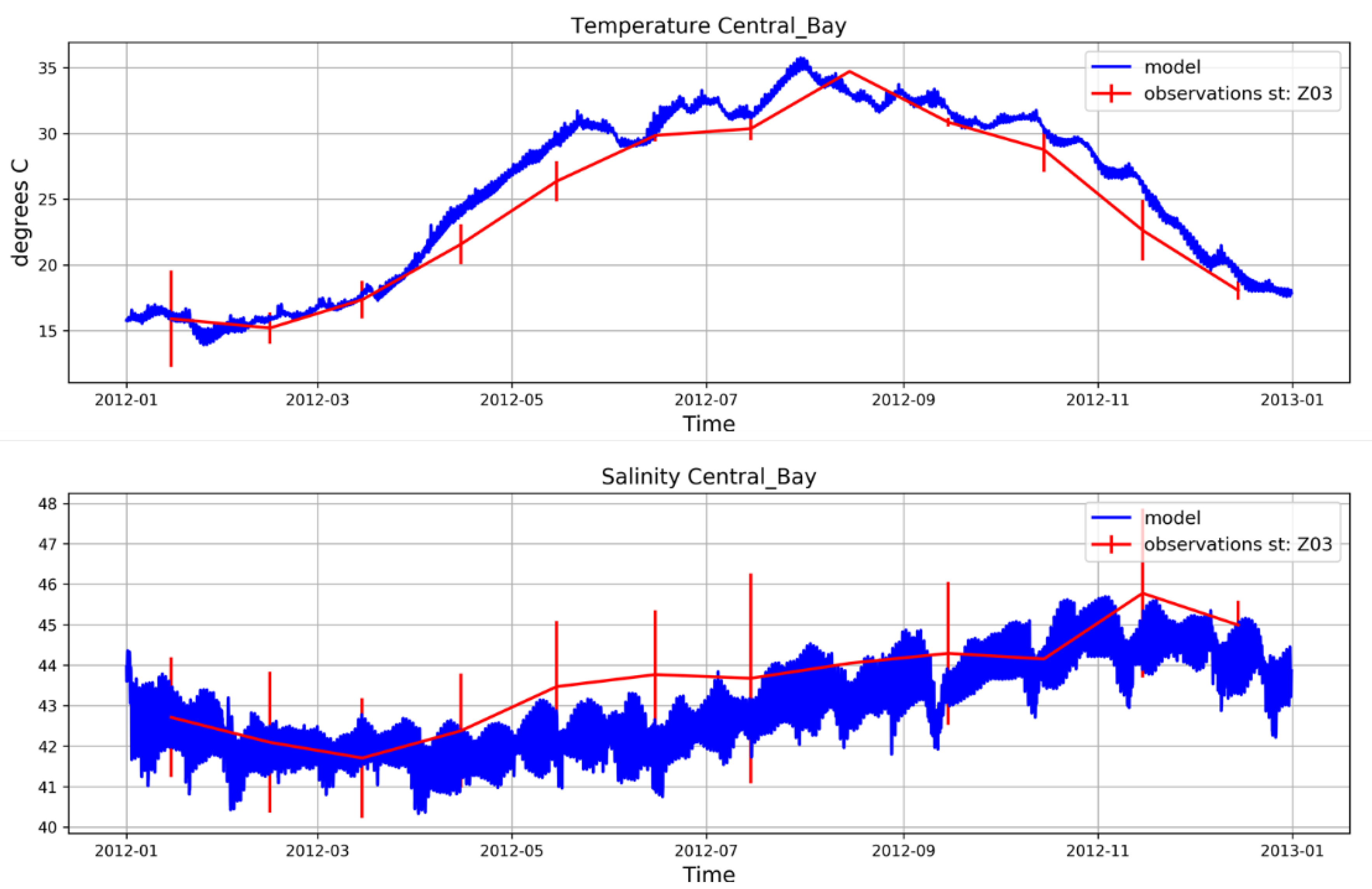
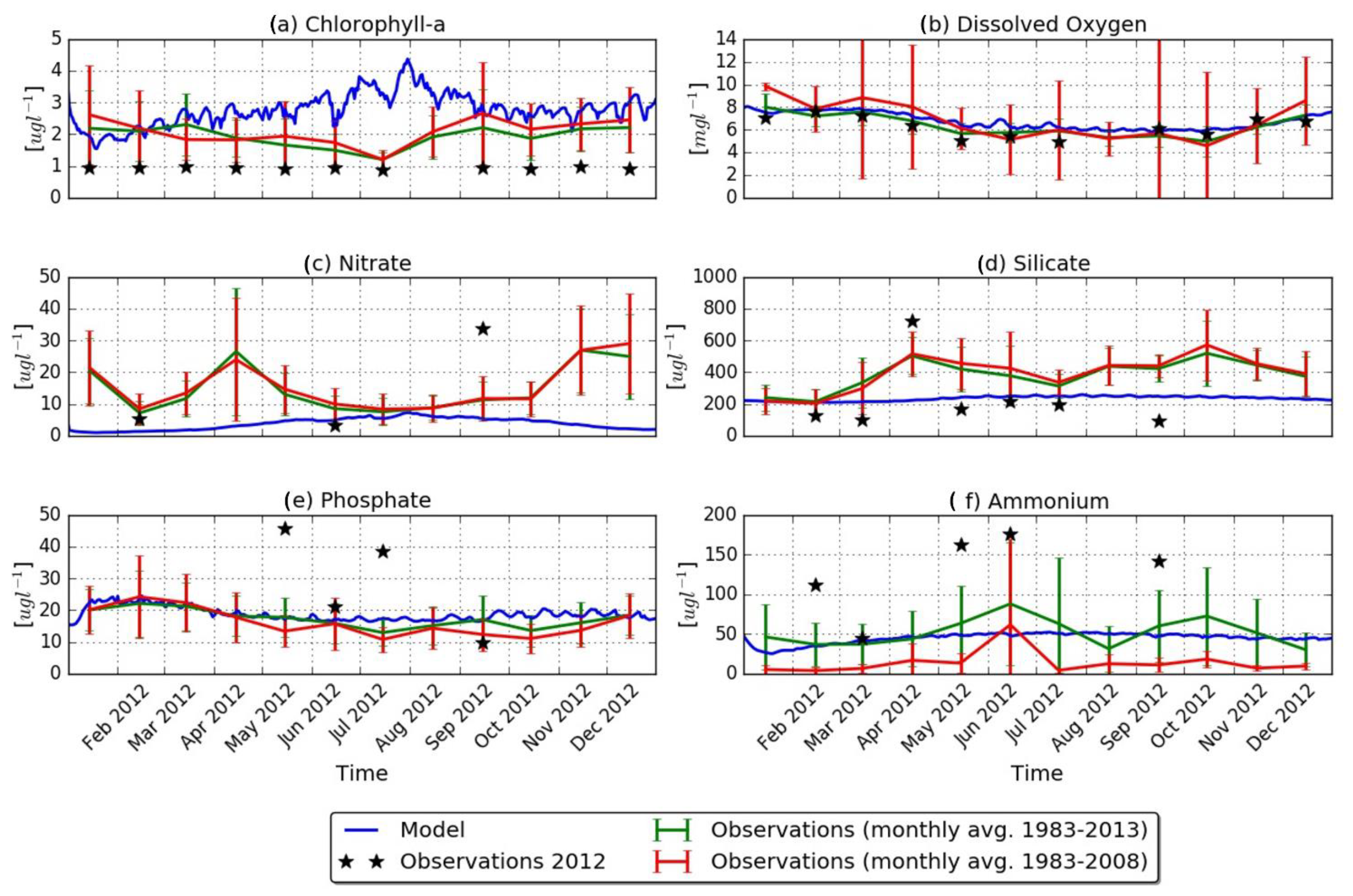
4.2. Biogeochemical Model Validation
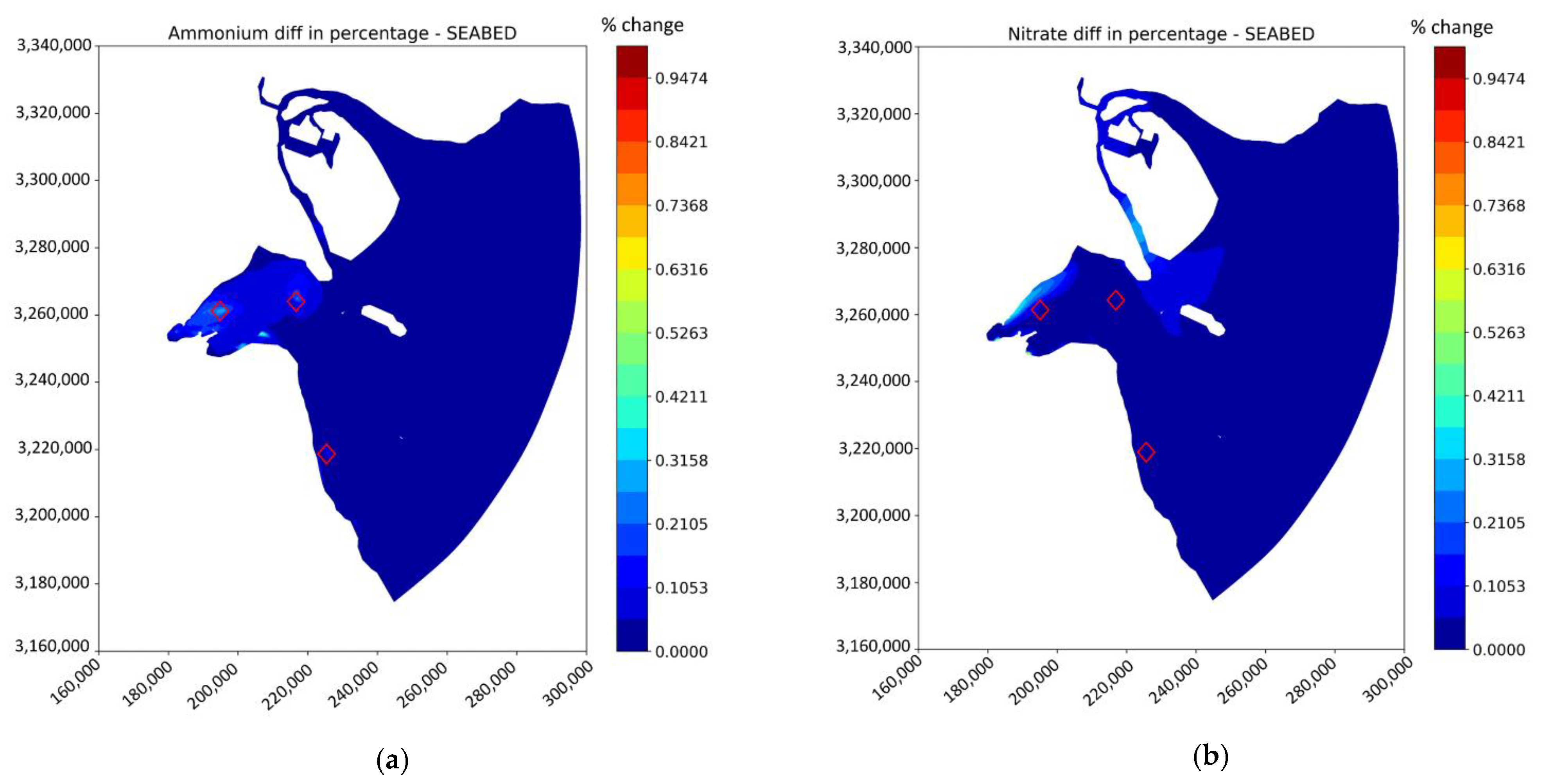
4.3. The Effect of Finfish Farms
5. Discussion
5.1. Biogeochemical Model Results
5.2. Finfish Farms Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food security: The challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Béné, C.; Barange, M.; Subasinghe, R.; Pinstrup-Andersen, P.; Merino, G.; Hemre, G.I.; Williams, M. Feeding 9 billion by 2050—Putting fish back on the menu. Food Secur. 2015, 7, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thilsted, S.H.; Thorne-Lyman, A.; Webb, P.; Bogard, J.R.; Subasinghe, R.; Phillips, M.J.; Allison, E.H. Sustaining healthy diets: The role of capture fisheries and aquaculture for improving nutrition in the post-2015 era. Food Policy 2016, 61, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Price, C.; Black, K.D.; Hargrave, B.T.; Morris, J.A. Marine cage culture and the environment: Effects on water quality and primary production. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2014, 6, 151–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murad, H. State of Kuwait: National Review on Marine Cage Aquaculture. FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Report No. 892 FIMA/R892 (En). 2009. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-i0723e.pdf (accessed on 5 February 2018).
- Alosairi, Y.; Alsulaiman, N. Hydro-environmental processes governing the formation of hypoxic parcels in an inverse estuarine water body: Model validation and discussion. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 144, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. 2019. Available online: http://www.fao.org/fishery/countrysector/naso_kuwait/en (accessed on 15 December 2019).
- Pokavanich, T.; Alosairi, Y. Summer flushing characteristics of Kuwait Bay. J. Coast. Res. 2014, 30, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, M. Physical oceanography of the Gulf, Strait of Hormuz, and the Gulf of Oman: Results from the Mt. Mitchell Expedition. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1993, 27, 35–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alosairi, Y.; Pokavanich, T. Residence and transport time scales associated with Shatt Al-Arab discharges under various hydrological conditions estimated using a numerical model. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 118, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Said, T.; Al-Ghunaim, A.; Subba Rao, D.V.; Al-Yamani, F.; Al-Rifaie, K.; Al-Baz, A. Salinity-driven decadal changes in phytoplankton community in the NW Arabian Gulf of Kuwait. Env. Monit Assess 2017, 189, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alajmi, H.M. Effect of Physical, Chemical and Biological Treatment on the Removal of Five Pharmaceuticals from Domestic Wastewater in Laboratory-Scale Reactors and a Full-Scale Plant. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Newcastle, Newcastle, Australia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pokavanich, T.; Polikarpov, I.; Lennox, A.; Al-Hulail, F.; Al-Said, T.; Al-Enezi, E.; Al-Yamani, F.; Stokozov, N.; Shuhaibar, B. Comprehensive investigation of summer hydrodynamic and water quality characteristics of desertic shallow water body: Kuwait Bay. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Coastal Dynamics, Arcachon, France, 23–26 June 2013; pp. 1253–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Alosairi, Y.; Pokavanich, T.; Alsulaiman, N. Three-dimensional hydrodynamic modelling study of reverse estuarine circulation: Kuwait Bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Yamani, F.; Subba Rao, D.; Mharzi, A.; Ismail, W.; Al-Rifaie, K. Primary production off Kuwait, an arid zone environment, Arabian Gulf. Int. J. Ocean. Oceanogr. 2006, 1, 67–85. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Yamani, F. Importance of the freshwater influx from the Shatt-AlArab River on the Gulf marine environment. In Protecting the Gulf’s Marine Ecosystems from Pollution; Abuzinada, A.H., Barth, H.-J., Krupp, F., Böer, B., Al Abdessalaam, T.Z., Eds.; Birkhäuser Verlag: Basel, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Subba Rao, D.; Al-Yamani, F. Phytoplankton ecology in the waters between Shatt-Al-Arab and Straits of Hormuz-the Arabian Gulf. Plankton Biol. Ecol. 1998, 45, 101–116. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, M.J.; Breckels, M.; Graves, C.A.; Barry, J.; Capuzzo, E.; Huerta, F.P.; Al Ajmi, F.; Al-Hussain, M.M.; LeQuesne, W.J.F.; Lyons, B.P. Seasonal and Temporal Drivers Influencing Phytoplankton Community in Kuwait Marine Waters: Documenting a Changing Landscape in the Gulf. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devlin, M.; Massoud, M.; Hamid, S.; Al-Zaidan, A.; Al-Sarawi, H.; Al-Enezi, M.; Al-Ghofran, L.; Smith, A.; Barry, J.; Stentiford, G.; et al. Changes in the water quality conditions of Kuwait’s marine waters: Long term impacts of nutrient enrichment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deltares. Delft3D-FLOW. Hydro-Morphodynamics User Manual; Version 3.15; Deltares: Delft, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bacon, J.; Phillips, R. Rehabilitaion of Impacted Marine Areas in Kuwait. In Cefas Interim Report: Numerical Modelling of Kuwait Bay 2014; Cefas: Suffolk, UK, 2014; not publicly available. [Google Scholar]
- Todd Navigation. Admiralty Chart—2884 Mina’ Az Zawr to Al Basrah & Bushehr,2014. AC2884 UKHO. Available online: https://www.toddchart.com/Products/Admiralty-Chart-2884-Mina-Az-Zawr-To-Al-Basrah-and-Bushehr/AC2884 (accessed on 20 July 2016).
- Zuo, H.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Mogensen, K. The new eddy-permitting ORAP5 ocean reanalysis: Description, evaluation and uncertainties in climate signals. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 49, 791–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.; Trenberth, K.E. Estimates of freshwater discharge from continents: Latitudinal and seasonal variations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2002, 3, 660–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kampf, J.; Sadrinasab, M. The circulation of the Persian Gulf: A numerical study. Ocean Sci. 2006, 2, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alosairi, Y.; Pokavanich, T. Seasonal circulation assessments of the Northern Arabian/Persian Gulf. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 116, 270–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhakeem, A.; Elshorbagy, W.; Bleninger, T. Long-term hydrodynamic modeling of the Arabian Gulf. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 94, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijn, L.C.; Walstra, D.J.R.; Grasmeijer, B.; Sutherland, J.; Pan, S.; Sierra, J.P. Simulation of nearshore hydrodynamics and morphodynamics on the time scale of storms and seasons using process-based profile models. In The Behaviour of a Straight Sandy Coast on the Time Scale of Storms and Seasons: Process Knowledge and Guidelines for Coastal Management; EC MAST Project, MAS3-CT97-0086 COAST3D–EGMOND; Van Rijn, L.C., Ruessink, B.G., Mulder, J.P.M., Eds.; Vliz.be: Ostend, Belgium, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Deltares. D-Water Quality. In Versatile Water Quality Modelling in Delta Shell User Manual; Version 1.1; Deltares: Delft, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pokavanich, T.; Alosairi, Y.; Reimer De Graaff Morelissen, R.; Verbruggen, W.; Al-Rifaie, K.; Altaf, T.; Al-Said, T. Three-dimensional Arabian Gulf hydro-environmental modeling using Delft3D. In Proceedings of the 36th IAHR World Congress 2015, The Hague, The Netherlands, 28 June—3 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environment-Iraq. The Marshes-Shatt al-Arab-Gulf System; Status Report; Volume 1. Marine Science Centre 2011–University of Basra. Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/handle/20.500.11822/8849 (accessed on 6 September 2017).
- Hassam, W. The nitrogen and phosphate forms in water of Shatt Al-Arab River in Basra/Iraq. Marsh Bull. 2013, 8, 182–192. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Muzaini, S. Management of land-based sources of marine pollution. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2013, 16, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleisa, E.; Alshayji, K. Analysis on Reclamation and Reuse of Wastewater in Kuwait. J. Eng. Res. 2019, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Irrigation in the Middle East Region in Figures: AQUASTAT Survey, 2008 Water Report 34. Available online: http://www.fao.org/docrep/012/i0936e/i0936e00.htm (accessed on 15 October 2017).
- Dubber, D.; Gray, N.F. Replacement of chemical oxygen demand (COD) with total organic carbon (TOC) for monitoring wastewater treatment performance to minimize disposal of toxic analytical waste. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2010, 45, 1595–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Song, X.; Yuan, M.; Donga, D. The Factors Affecting Relationship between COD and TOC of Typical Papermaking Wastewater. In Advances in Computer Science, Intelligent System and Environment. Advances in Intelligent and Soft Computing; Jin, D., Lin, S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 105. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.; Feng, L.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Y.; Loiselle, S.A. Variability of particulate organic carbon in inland waters observed from MODIS Aqua imagery. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 084011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S. Nitrogen and phosphorus budget in coastal and marine cage aquaculture and impacts of effluent loading on ecosystem: Review and analysis towards model development. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G.K.; Liutkus, M.; Robinson, S.M.C.; Chopin, T.R.; Blair, T.; Lander, T.; Mullen, J.; Page, F.; Moccia, R.D. A review of the biophysical properties of salmonid faeces: Implications for aquaculture waste dispersal models and integrated multi-trophic aquaculture. Aquac. Res. 2009, 40, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Olsen, L.M.; Reitan, K.I.; Olsen, Y. Discharge of nutrient wastes from salmon farms: Environmental effects, and potential for integrated multi-trophic aquaculture. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2012, 2, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouwman, A.F.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Overbeek, C.C.; Bureau, D.P.; Pawlowski, M.; Glibert, P.M. Hindcasts and future projections of global inland and coastal nitrogen and phosphorus loads due to finfish aquaculture. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2013, 21, 112–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Andresen, K.; Handå, A.; Jensen, B.; Reitan, K.I.; Olsen, Y. Chemical composition and release rate of waste discharge from an Atlantic salmon farm with an evaluation of IMTA feasibility. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2013, 4, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pokavanich, T.; Alosairi, Y. Measurement of seasonal variability of hydro-environmental characteristics of Kuwait Bay. Arab J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Extinction Coefficient (m2/mg C) | Nitrogen/Carbon Ratio | Silicon/Carbon Ratio | Mortality (day−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default|Used | Default|Used | Default|Used | Default|Used | |
| Diatoms-E | 0.24|0.0192 | 0.255|0.204 | 0.447|0.00894 | 0.07|0.07 |
| Diatoms-N | 0.21|0.0168 | 0.07|0.056 | 0.283|0.00566 | 0.08|0.08 |
| Diatoms-P | 0.21|0.0168 | 0.105|0.084 | 0.152|0.00304 | 0.08|0.08 |
| Flagellates-E | 0.25|0.02 | 0.2|0.16 | 0|0 | 0.07|0.28 |
| Flagellates-N | 0.225|0.018 | 0.078|0.0624 | 0|0 | 0.08|0.32 |
| Flagellates-P | 0.225|0.018 | 0.113|0.0904 | 0|0 | 0.08|0.32 |
| Nutrient | Concentration (g/m3) |
|---|---|
| DO | 6 |
| NH4 | 0.09 |
| NO3 | 0.0075 |
| PO4 | 0.02 |
| Si | 0.2 |
| Opal-Si | 0.1 |
| POC and DON | 0.4 |
| PON | 0.06 |
| POP | 0.006 |
| DOC | 5 |
| DOP | 0.04 |
| Shatt Al-Arab River | SIA | Jahra | Rekka | Um Al-Hayman | Sulaibiya | Ardiya | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow rate | 60 | 0.7 | 0.25 | 0.65 | 0.018 | 1.61 | 0.97 |
| DO | 6 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| NO3 | 0.01691 | 0.3835 | 4.198 | 4.198 | 4.198 | 4.198 | 4.198 |
| PO4 | 0.00293 | 18.32 | 8.1425 | 8.1425 | 8.1425 | 8.1425 | 8.1425 |
| SiO2 | 0.04447 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| NH4 | 0.002 | 0.928 | 0.2695 | 0.2695 | 0.2695 | 0.2695 | 0.2695 |
| Opal-Si | 0.001 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| POC | 40 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| PON | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| POP | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| DOC | 500 | 158.42 | 49.1775 | 49.1775 | 49.1775 | 49.1775 | 49.1775 |
| DON | 40 | 13.06 | 4.87 | 4.87 | 4.87 | 4.87 | 4.87 |
| DOP | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Water Depth (m) | Cell Area (m2) | Cell Volume (m3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Farm_west | 11.8 | 7.6621 × 104 | 45,091 |
| Farm_east | 7.3 | 5.6295 × 105 | 206,039 |
| Farm_south | 22.3 | 1.8478 × 105 | 205,660 |
| Waste Input (kg per Tonne of Fish Production) | Annual Input Assuming 127 Tonnes/Year Production (Tonnes y−1) | |
|---|---|---|
| PON | 21 | 2.67 |
| DIN 1 (as ammonium) | 73 | 9.27 |
| DON | 1 | 0.13 |
| POP | 9 | 1.14 |
| DIP 2 (as phosphate) | 7 | 0.89 |
| DOP | 0 | 0.00 |
| POC | 210 | 26.67 |
| DOC | 7 | 0.89 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Araújo, M.A.V.C.; García-García, L.; Aldridge, J. Implementation of a 3D Coupled Hydrodynamic–Biogeochemical Model in Kuwait Bay. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8715. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148715
Araújo MAVC, García-García L, Aldridge J. Implementation of a 3D Coupled Hydrodynamic–Biogeochemical Model in Kuwait Bay. Sustainability. 2022; 14(14):8715. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148715
Chicago/Turabian StyleAraújo, Maria Amélia V. C., Luz García-García, and John Aldridge. 2022. "Implementation of a 3D Coupled Hydrodynamic–Biogeochemical Model in Kuwait Bay" Sustainability 14, no. 14: 8715. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148715
APA StyleAraújo, M. A. V. C., García-García, L., & Aldridge, J. (2022). Implementation of a 3D Coupled Hydrodynamic–Biogeochemical Model in Kuwait Bay. Sustainability, 14(14), 8715. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148715







