Framework for Sustainable Wireless Sensor Network Based Environmental Monitoring
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A comprehensive literature review with respect to the sustainable wireless sensor network-based environment monitoring.
- Proposing an environmental monitoring methodology and a framework typically for WSN applications using IEEE 802.15.4 to optimize the available resource in the network.
- Conducting real testbed experimentations to evaluate the sustainability of the WSN-based environmental monitoring design.
2. Literature Studies
2.1. Background
2.2. Related Work
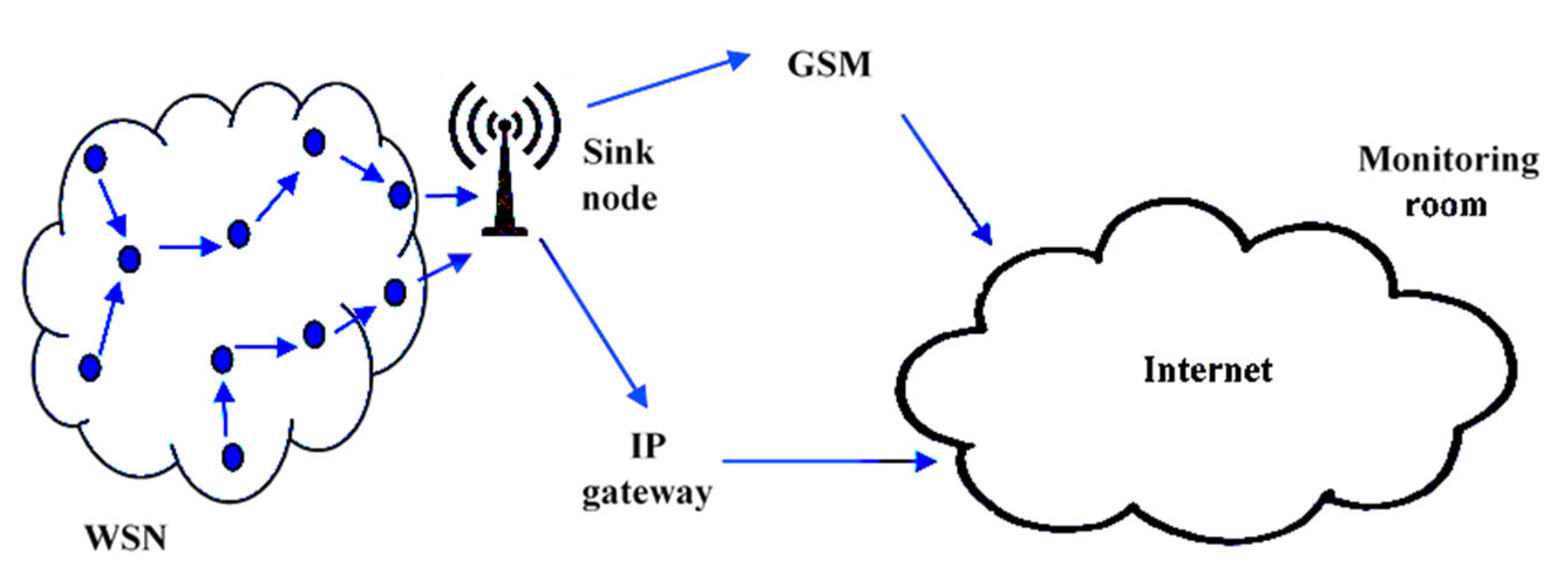
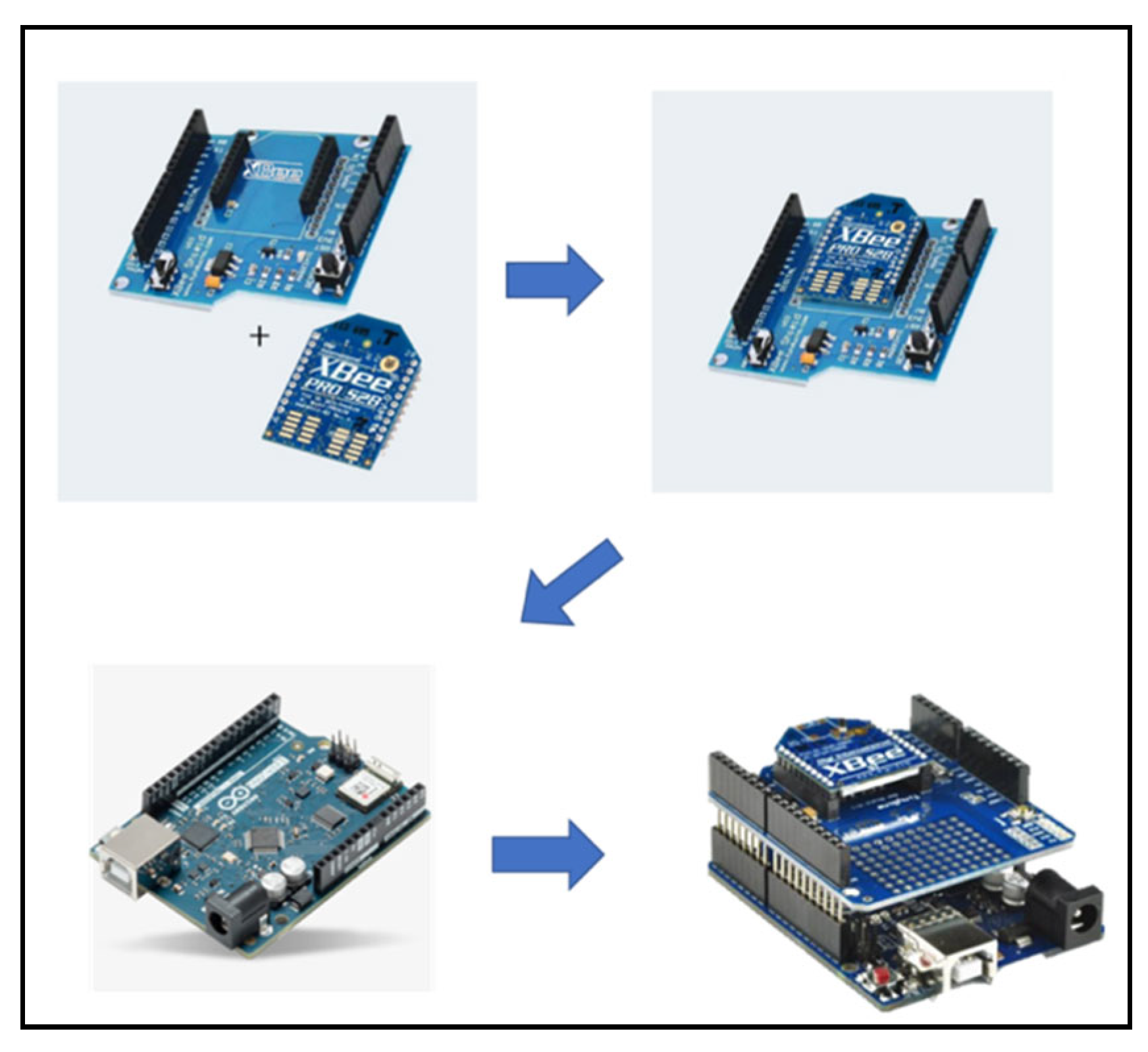
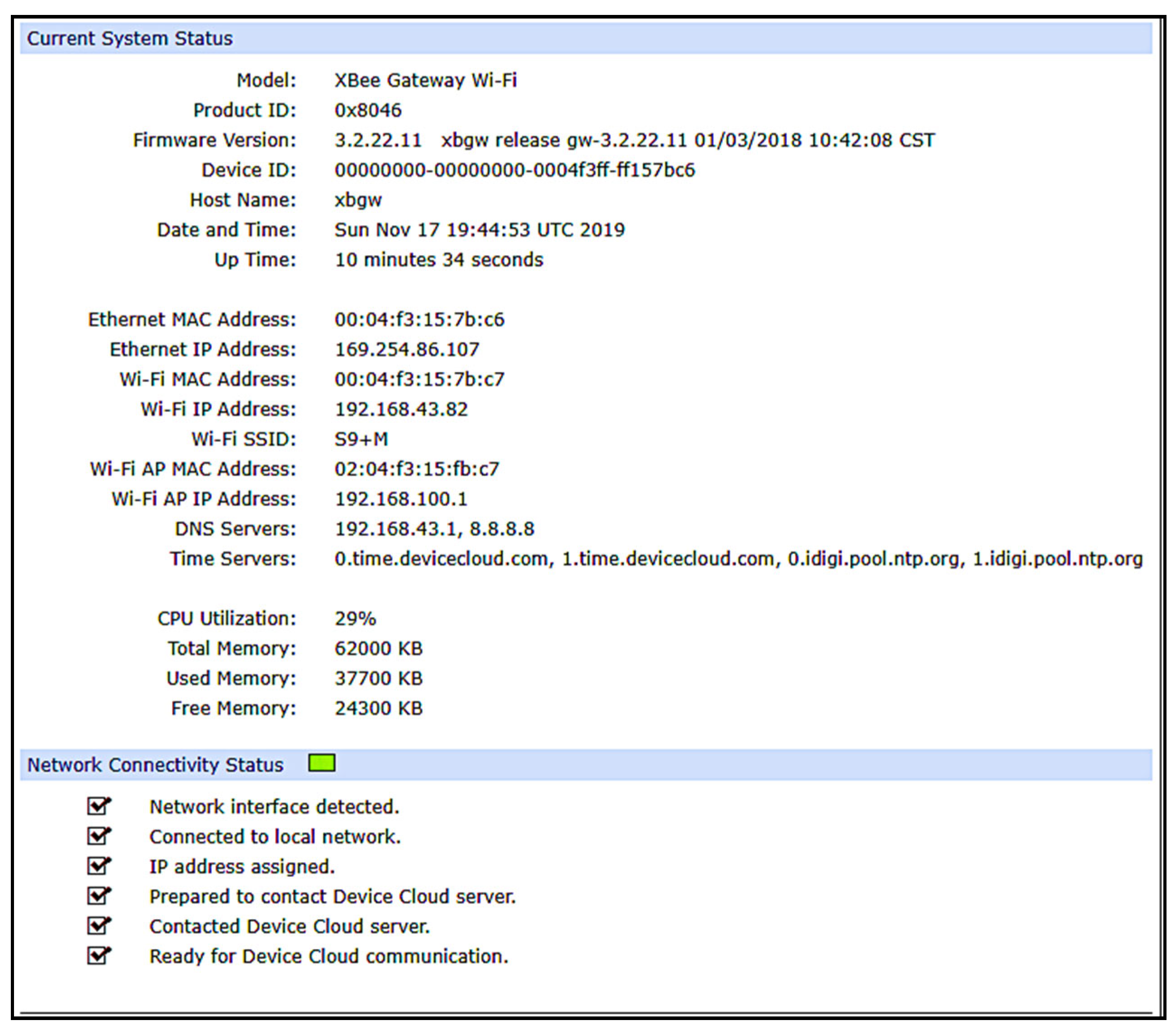
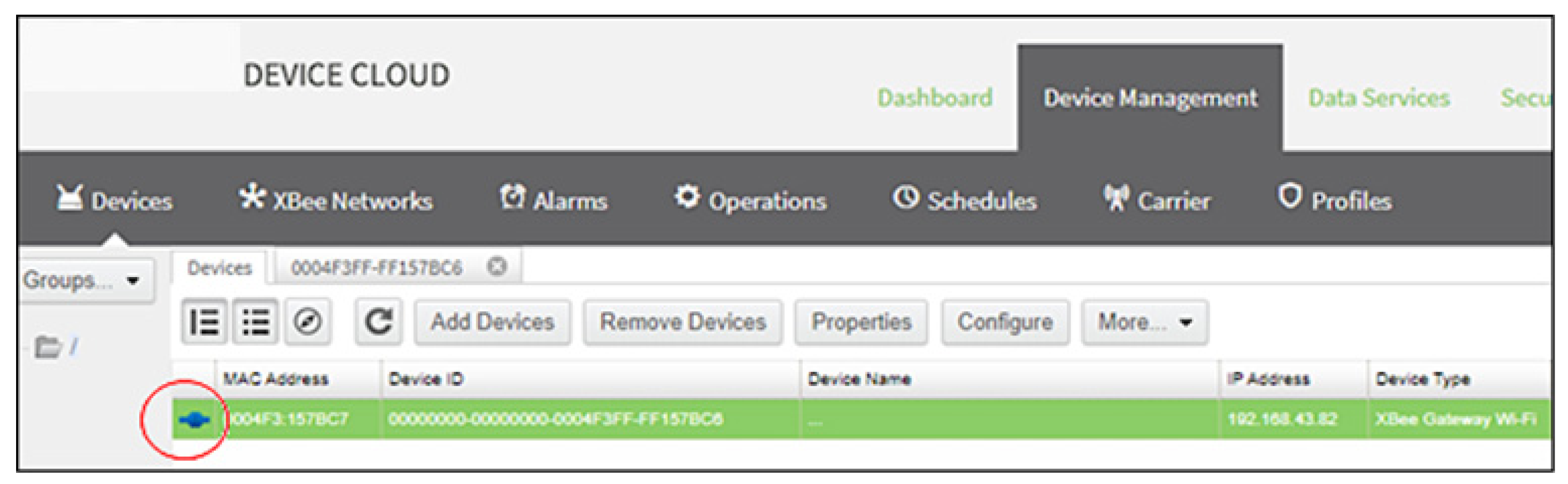
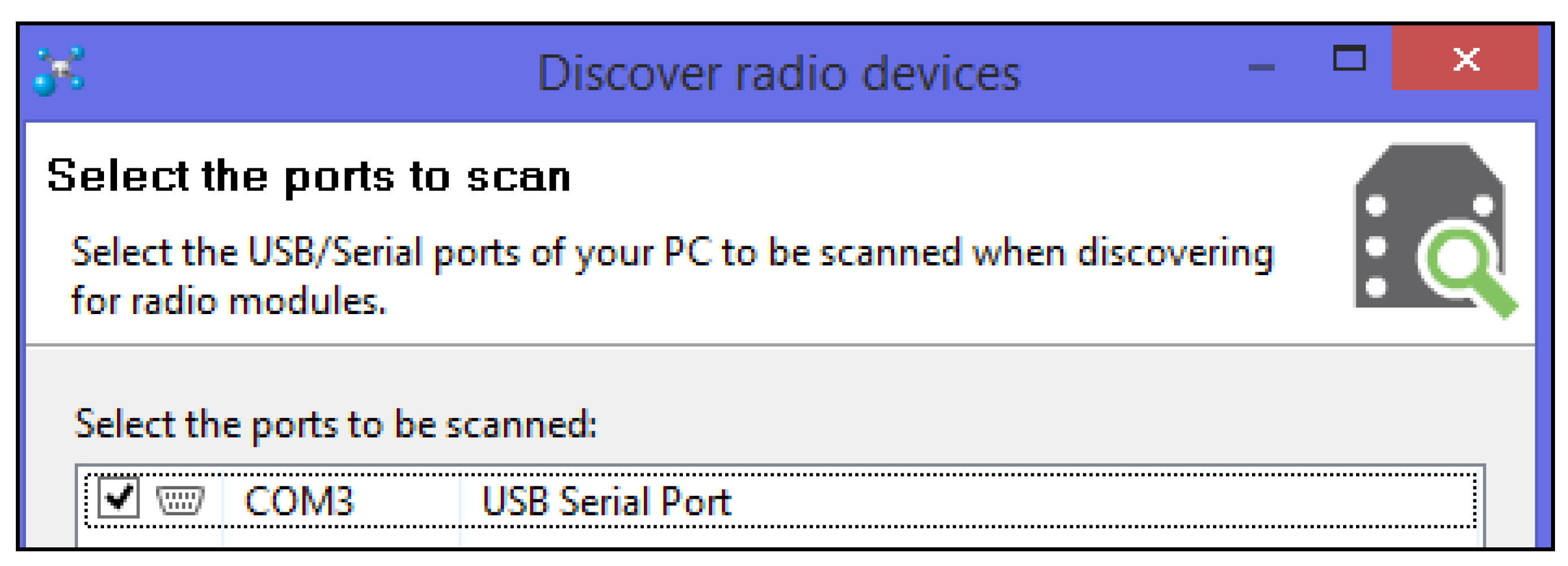
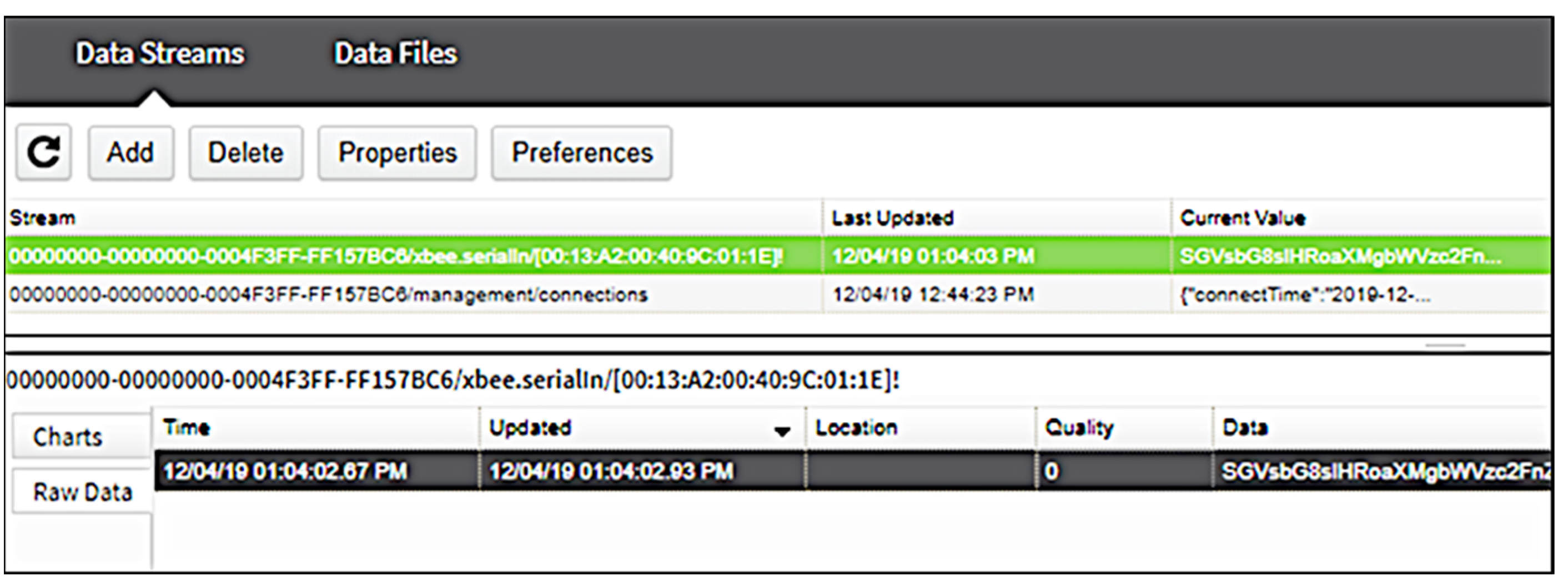
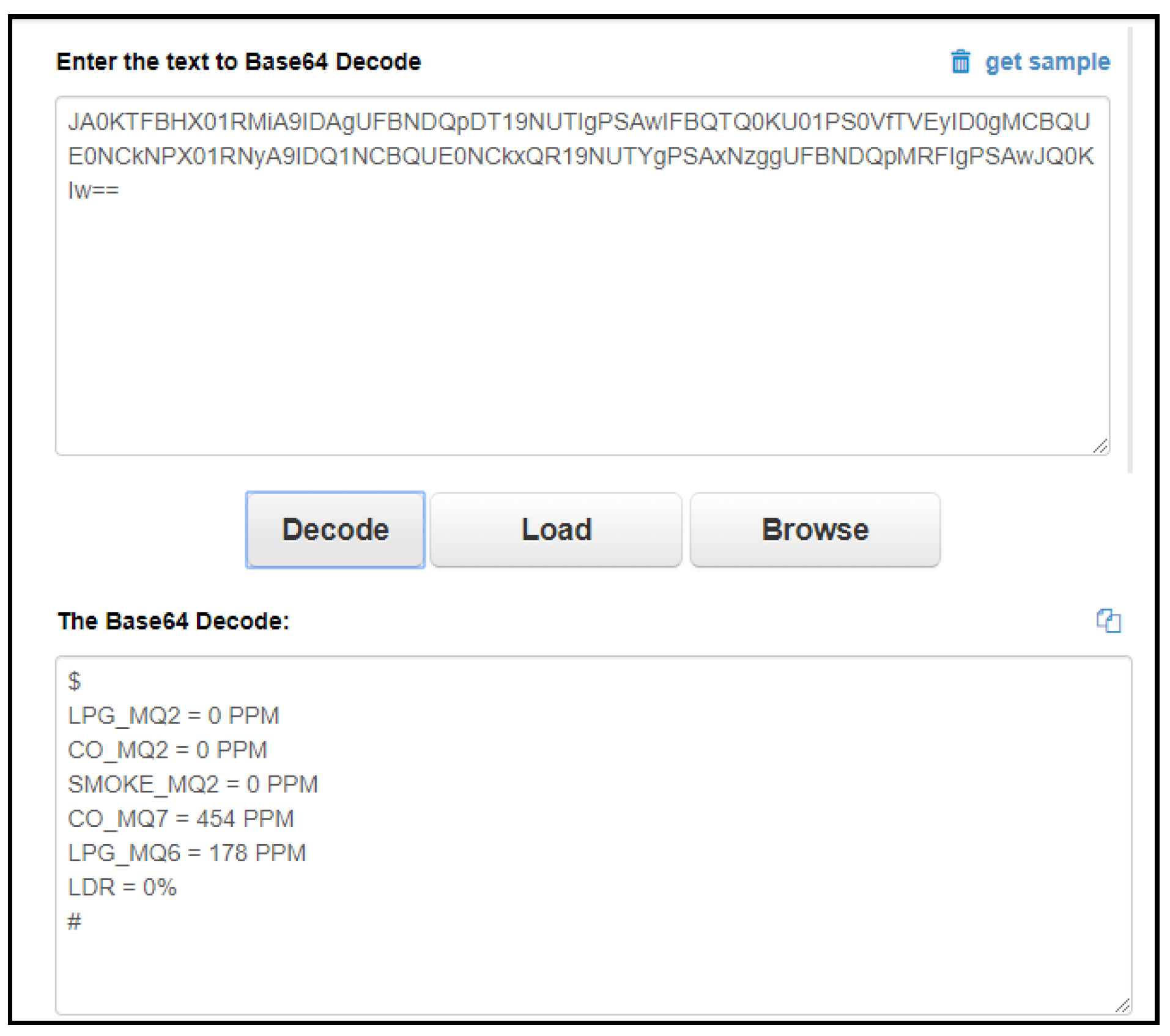
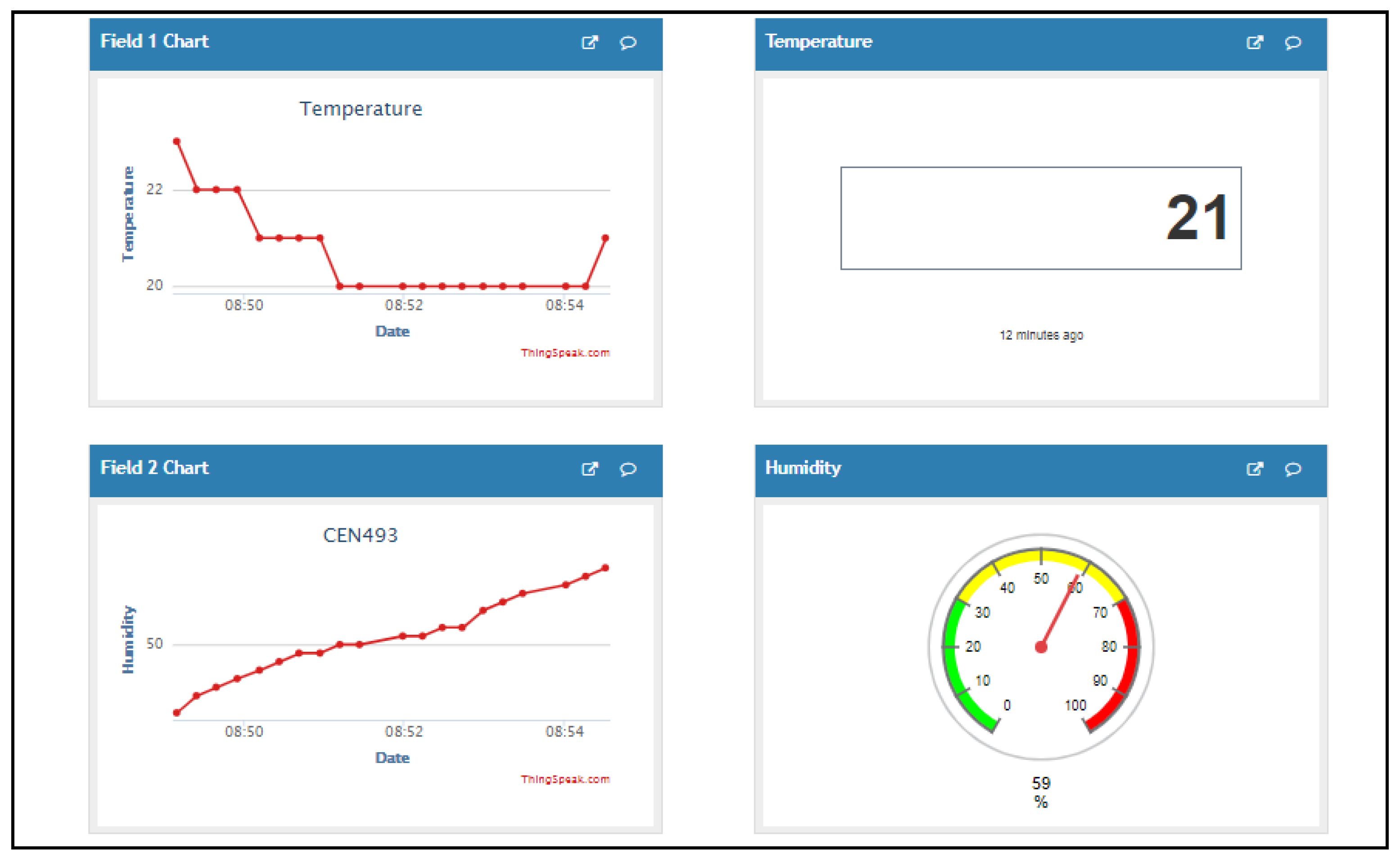
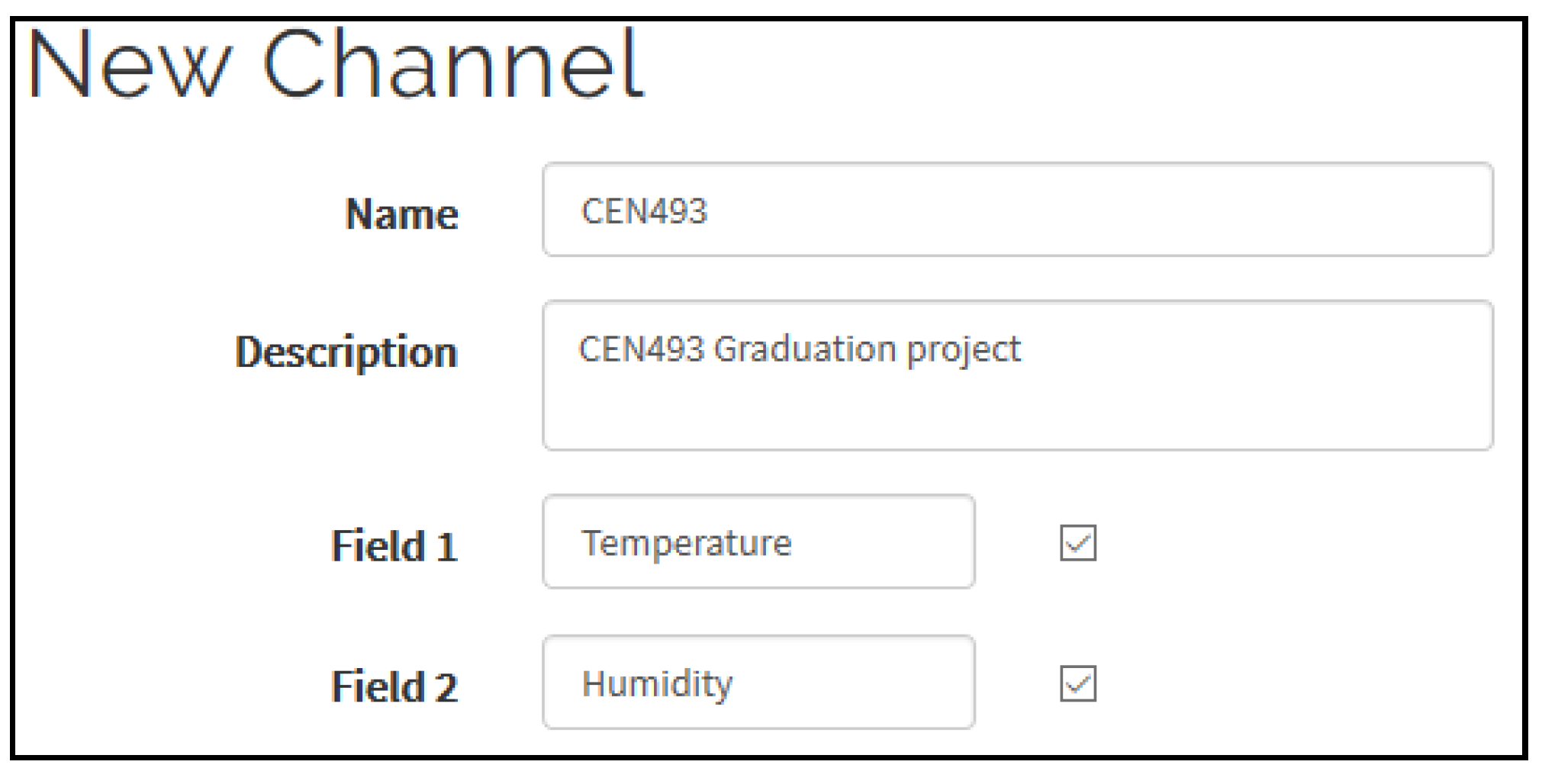
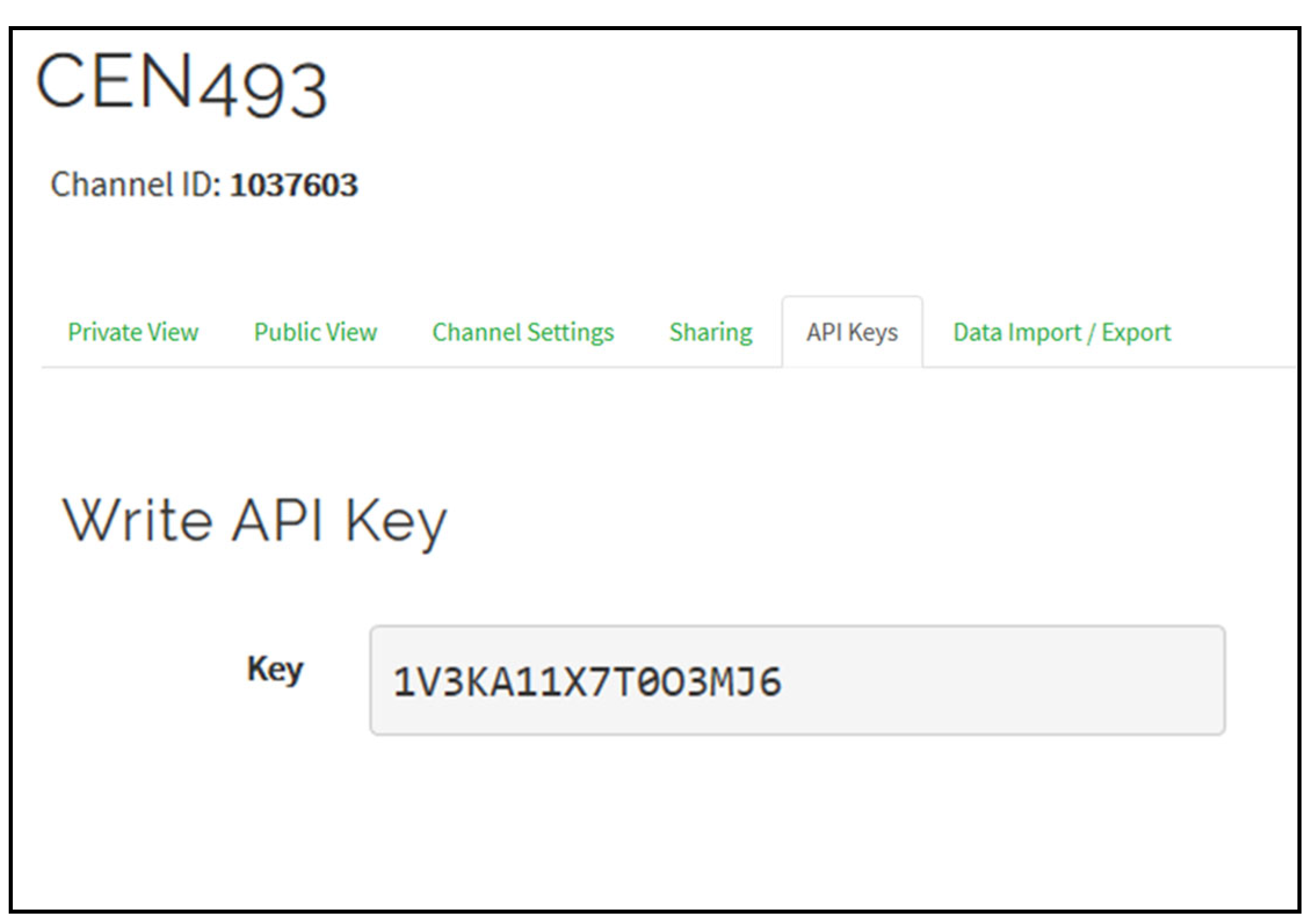
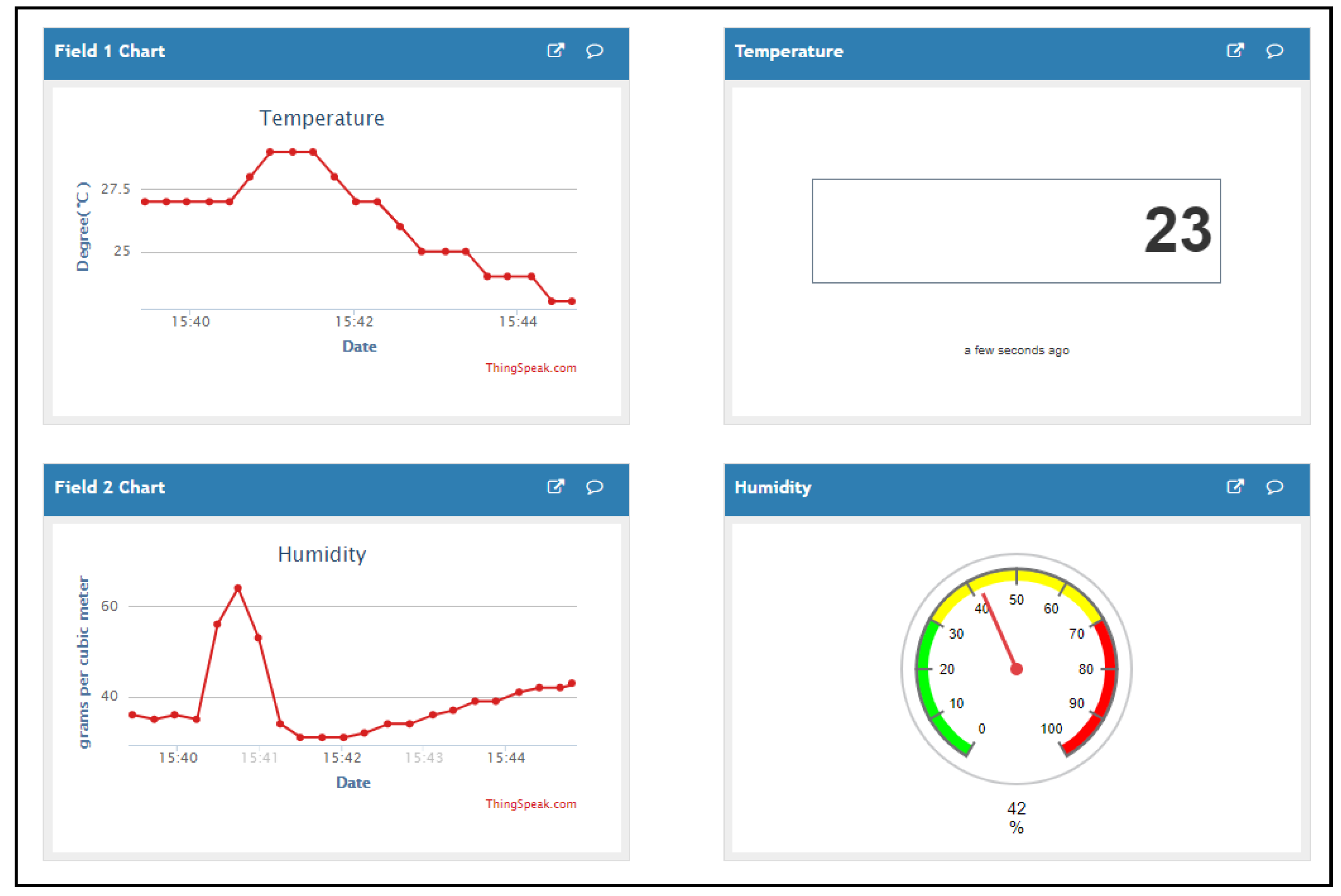
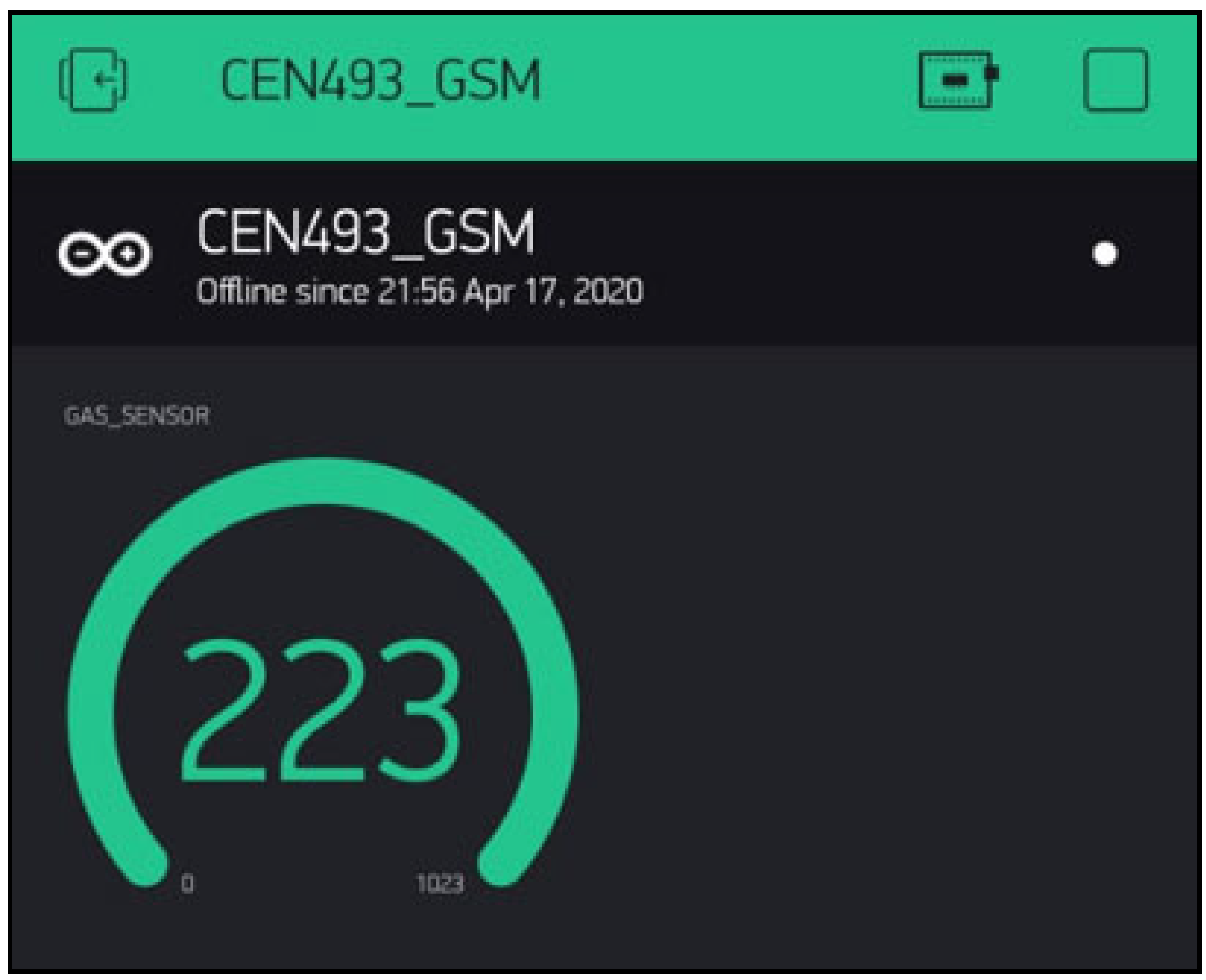
3. Methodology, Implementation and Results
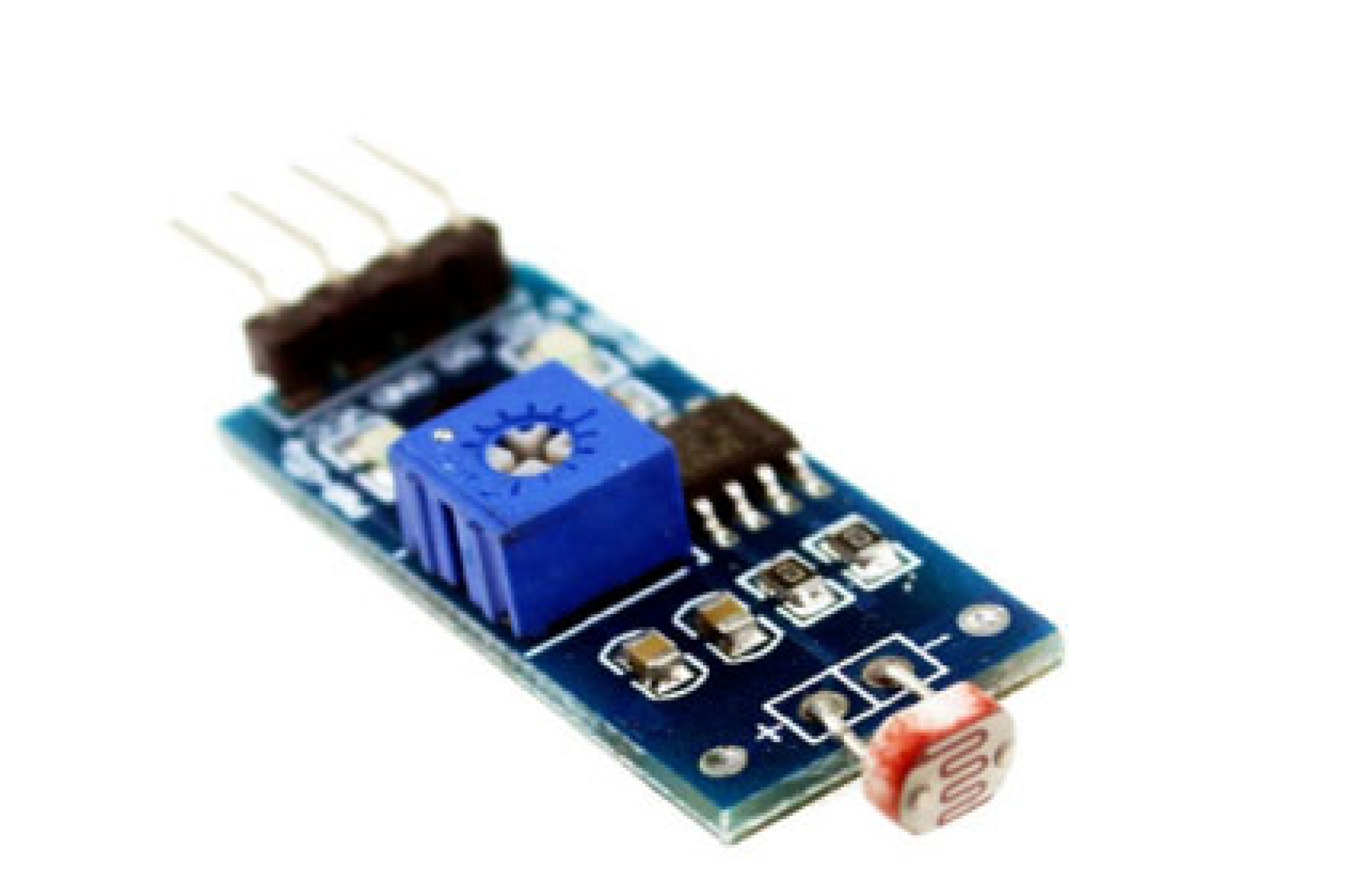
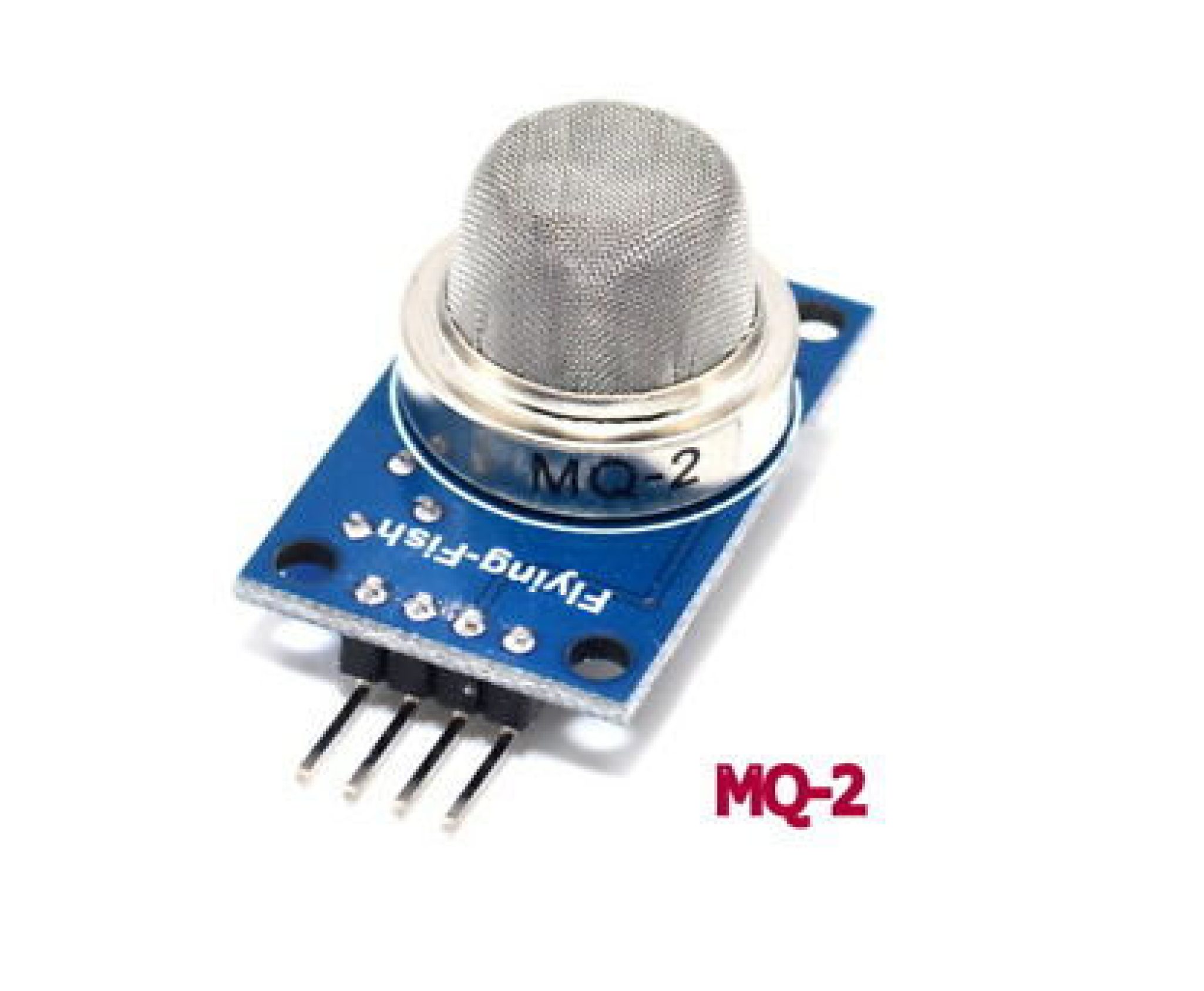
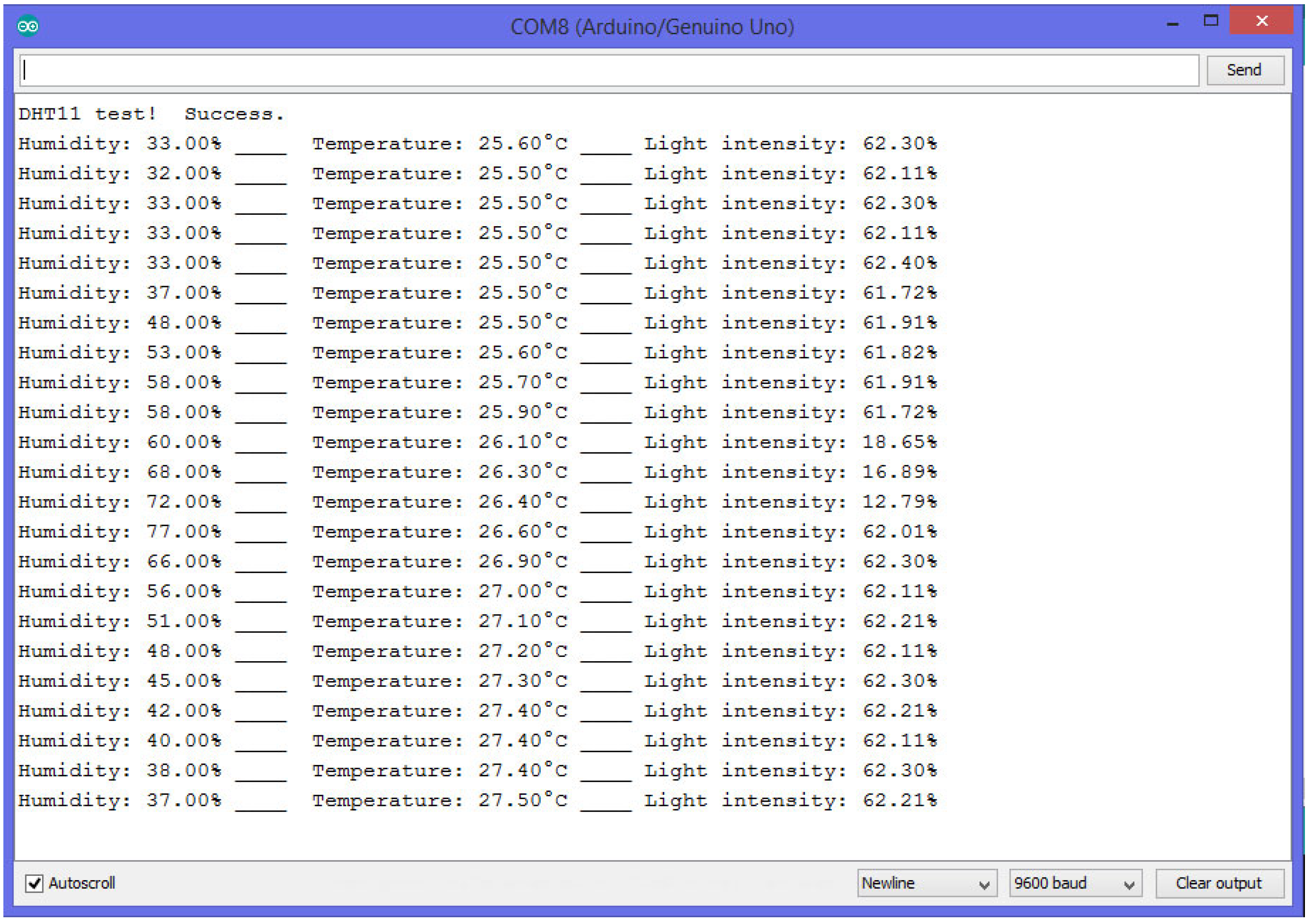
Sensors
- Pros:
- ○
- Easy to use.
- ○
- No coding required.
- ○
- No wires required.
- Cons:
- ○
- Limited to the board’s Rx and Tx.
- ○
- Fixed serial pins and cannot be changed.
- ○
- Extra component, which costs.
- Pros:
- ○
- Can be configured to use any GPIO as Tx, Rx.
- ○
- No shield required (saves cost).
- ○
- Does not block the board Tx, Rx, which the uploaded code goes through.
- Cons:
- ○
- Must download Serial Software Library to configure GPIOs.
- ○
- Requires knowledge in coding.
- ○
- If wires are damaged, connection will be lost.
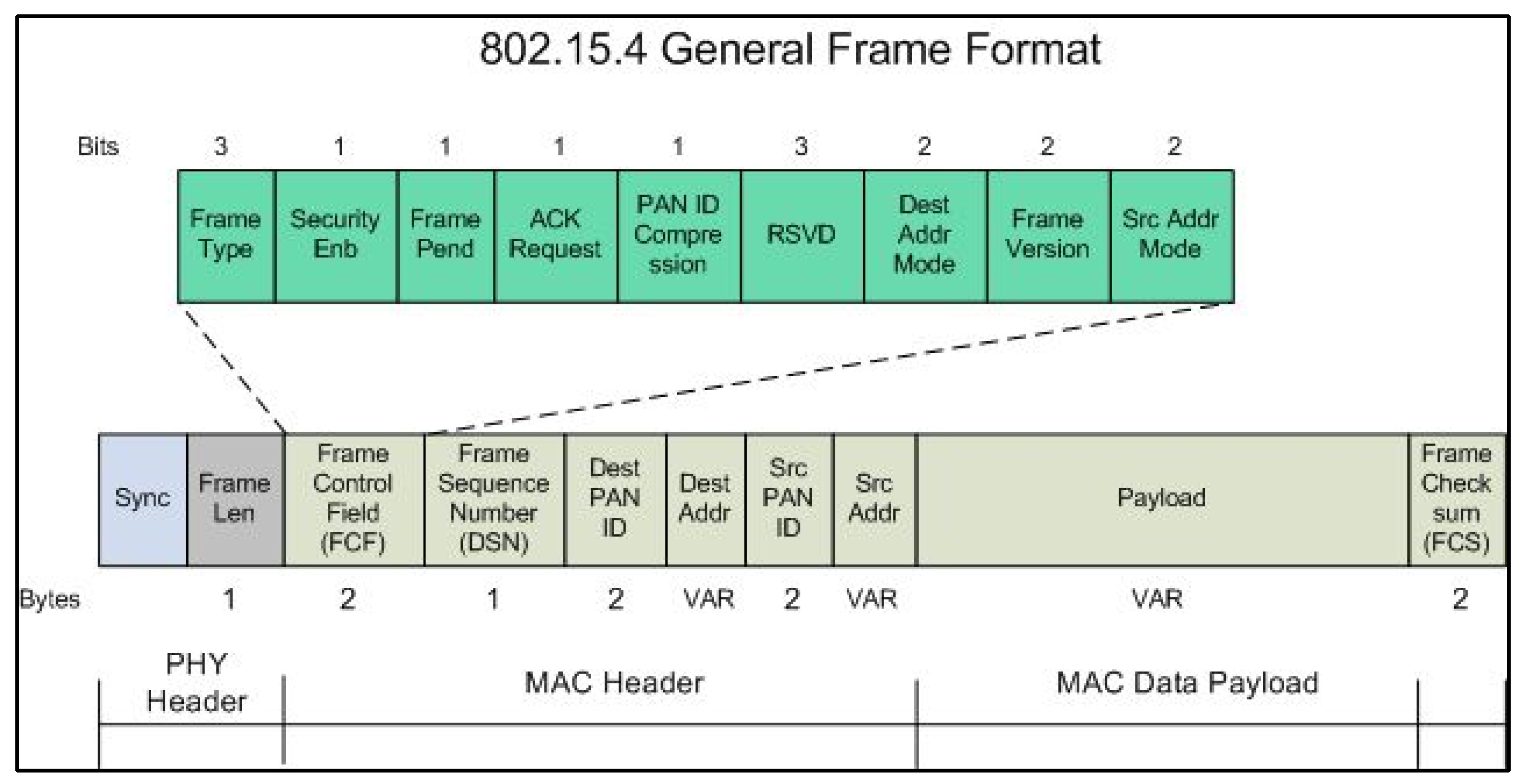
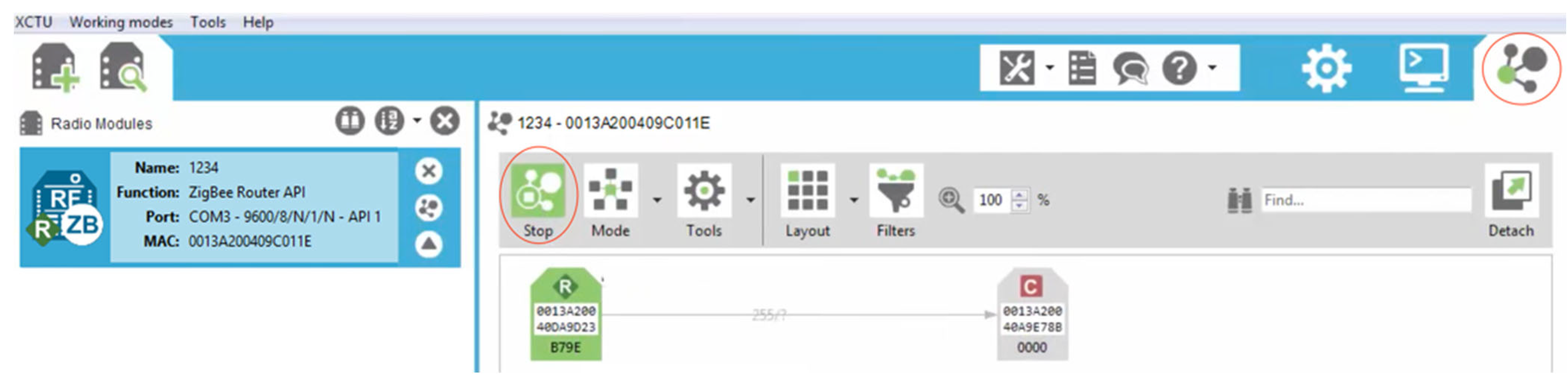
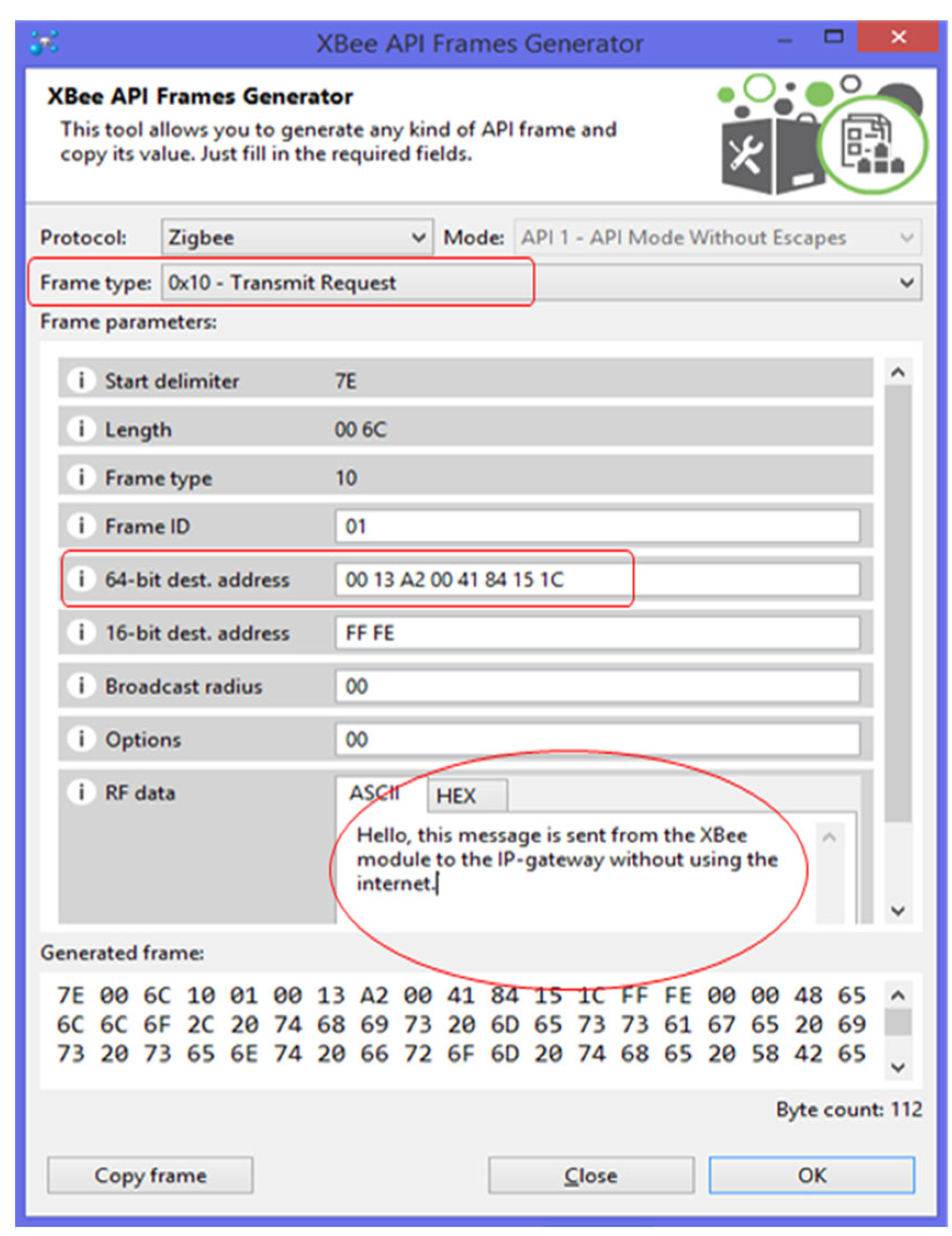
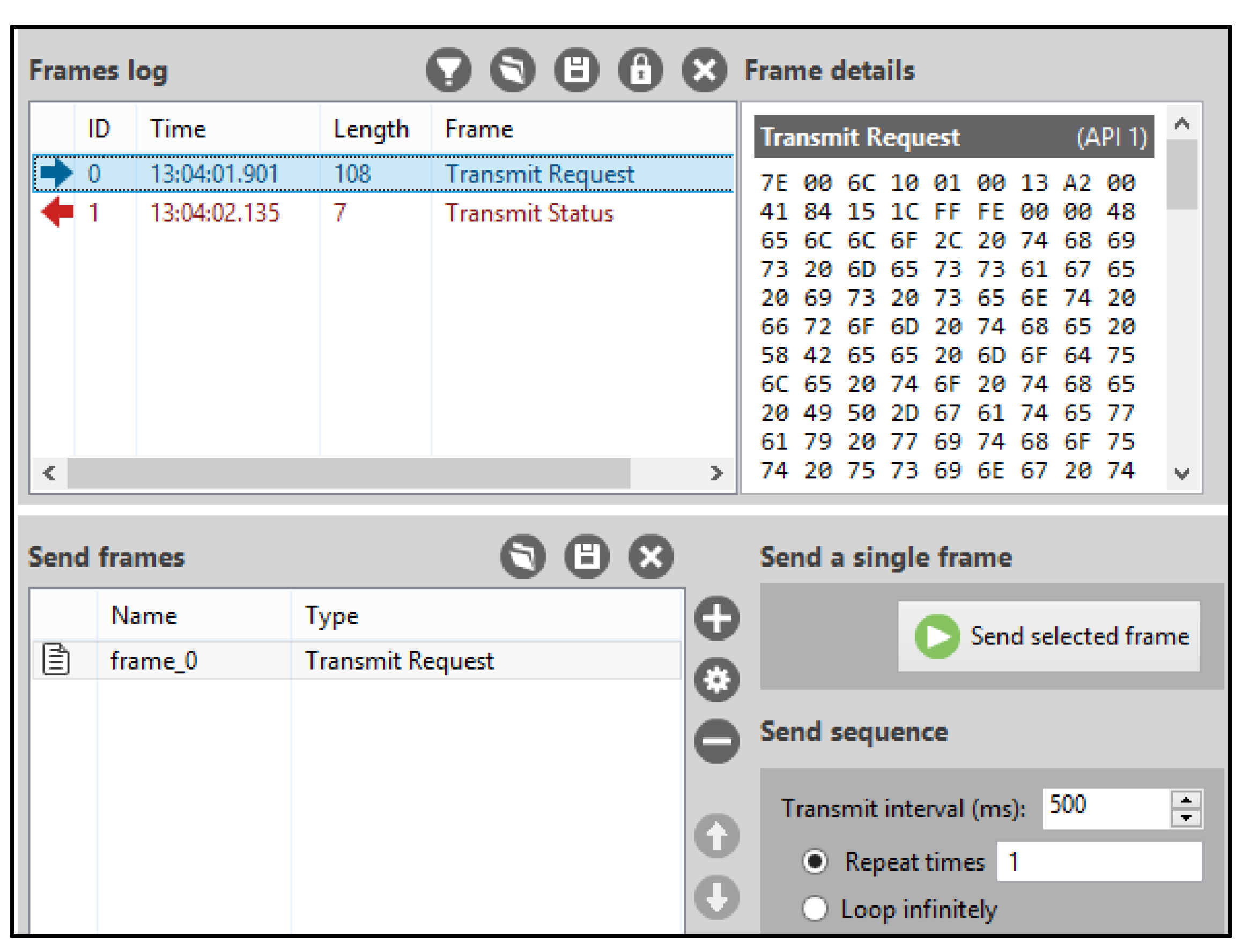
- The Frame type must be “Transmit Request”.
- The “64-bit dest. address” is the IP-gateway MAC address.
- The “RF data” is the message to be transmitted.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

Appendix B
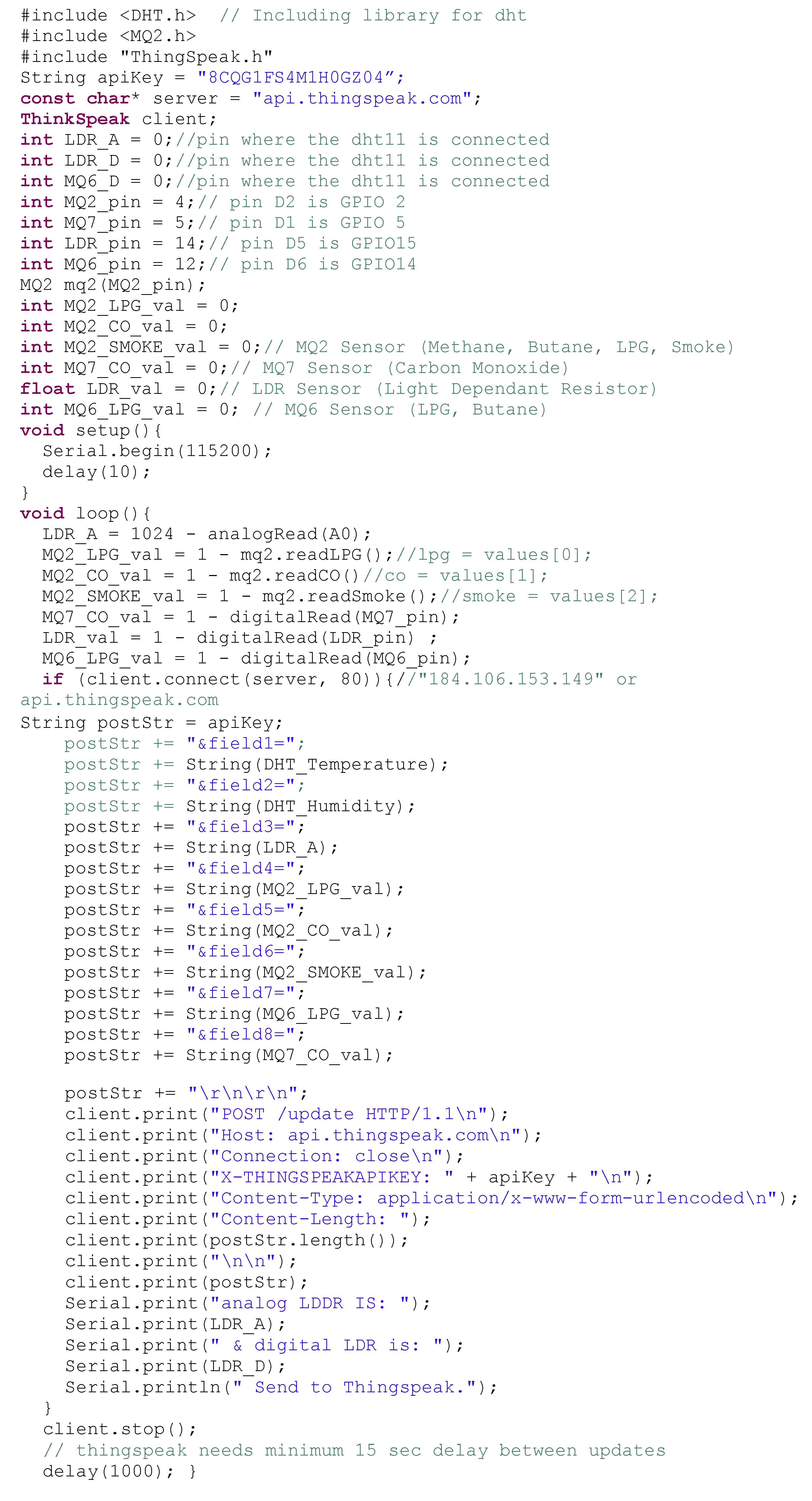
Appendix C
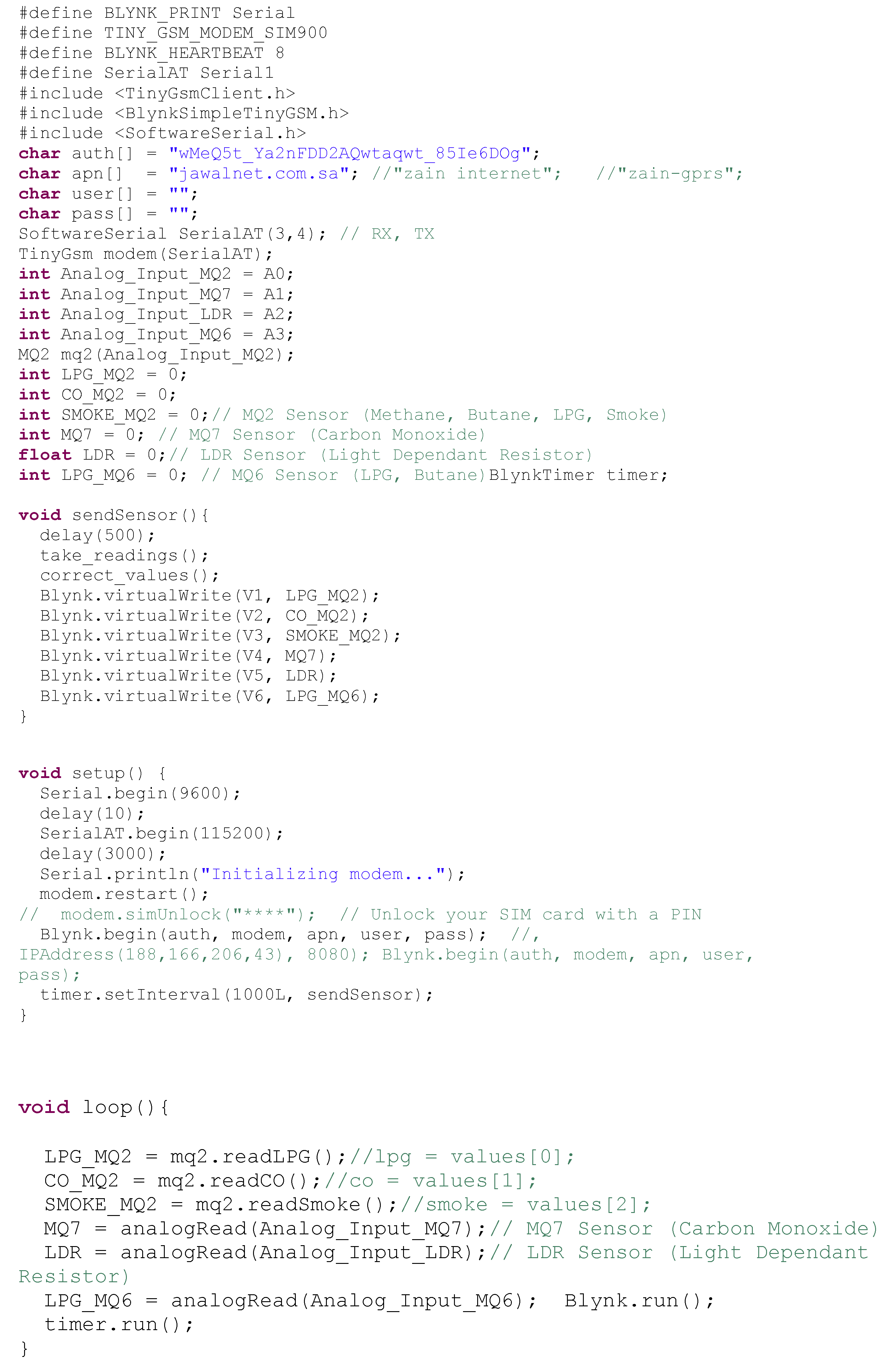
References
- Razooqi, Y.S.; Al-Asfoor, M. Intelligent Routing to Enhance Energy Consumption in Wireless Sensor Network: A Survey. In Mobile Computing and Sustainable Informatics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 283–300. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, K.; Fisal, N.; Al-Muhtadi, J. Empirical Studies of Bio-Inspired Self-Organized Secure Autonomous Routing Protocol. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 2232–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, K.; Derhab, A.; Al-Muhtadi, J.; Shahzad, B.; Orgun, M.A. Secure transfer of environmental data to enhance human decision accuracy. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 51, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Kaur, R.; Singh, D. Energy harvesting in wireless sensor networks: A taxonomic survey. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 118–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Kim, T. Smartphone-Based Data Collection System for Repetitive Concrete Temperature Monitoring in High-Rise Building Construction. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yaseen, M.; Saleem, K.; Orgun, M.A.; Derhab, A.; Abbas, H.; Al-Muhtadi, J.; Iqbal, W.; Rashid, I. Secure sensors data acquisition and communication protection in eHealthcare: Review on the state of the art. Telemat. Inform. 2018, 35, 702–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Muhtadi, J.; Qiang, M.; Zeb, K.; Chaudhry, J.; Saleem, K.; Derhab, A.; Orgun, M.A.; Shankaran, R.; Imran, M.; Pasha, M. A critical analysis of mobility management related issues of wireless sensor networks in cyber physical systems. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 16363–16376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazunga, F.; Nechibvute, A. Ultra-low power techniques in energy harvesting wireless sensor networks: Recent advances and issues. Sci. Afr. 2021, 11, e00720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, N. Arduino Applied; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, J.; Rodrigues, J.J.; Casal, J.; Saleem, K.; Denisov, V. Intelligent personal assistants based on internet of things approaches. IEEE Syst. J. 2016, 12, 1793–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ardao, J.C.; Rodrí guez-Rubio, R.F.; Suárez-González, A.; Rodrí guez-Pérez, M.; Sousa-Vieira, M.E. Current trends on green wireless sensor networks. Sensors 2021, 21, 4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunus, F.; Ismail, N.N.; Ariffin, S.S.; Shahidan, A.; Yusof, S.S.; Fisal, N.; Saleem, K.; Ahmed, A. Proposed Technique for Transport Protocol in Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) for Multimedia Application. J. Teknol. 2012, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, G.; Saini, J.; Dutta, M.; Singh, P.K.; Hong, W.-C. Indoor Air Quality Monitoring Systems for Enhanced Living Environments: A Review toward Sustainable Smart Cities. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, M.; Habib, S.; Javed, A.R.; Rizwan, M.; Srivastava, G.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Lin, J.C.-W. Applications of wireless sensor networks and internet of things frameworks in the industry revolution 4.0: A systematic literature review. Sensors 2022, 22, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkama, L.; Bouallouche-Medjkoune, L. IEEE 802.15. 4 historical revolution versions: A survey. Computing 2021, 103, 99–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-S.; Kim, K.-I.; Shah, B.; Ullah, S.; Kim, K. An extended IEEE 802.15. 6 for thermal-aware resource management. Ad Hoc Netw. 2022, 131, 102856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassein, M.B.; Al Nassan, H.; Mardini, W.; Khamayseh, Y. An Optimal (BO, SO) Values for Different Arrival Rates IEEE 802.15. 4/LR-WPAN. In Proceedings of the 2021 12th International Conference on Information and Communication Systems (ICICS), Valencia, Spain, 24–26 May 2021; pp. 392–398. [Google Scholar]
- Jabri, I.; Mansour, K.; Al-Oqily, I.; Ezzedine, T. Enhanced characterization and modeling of A-MPDU aggregation for IEEE 802.11 n WLANs. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2022, 33, e4384. [Google Scholar]
- Farooqi, M.R.; Iqbal, N.; Singh, N.K.; Affan, M.; Raza, K. Wireless sensor networks towards convenient infrastructure in the healthcare industry: A systematic study. In Sensors for Health Monitoring; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 31–46. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, J.; Lu, C.; Srivastava, M.B.; Stankovic, J.A.; Terzis, A.; Welsh, M. Wireless sensor networks for healthcare. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 1947–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aminian, M.; Naji, H.R. A hospital healthcare monitoring system using wireless sensor networks. J. Health Med. Inform. 2013, 4, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuna, G.; Gungor, V. Energy harvesting and battery technologies for powering wireless sensor networks. In Industrial Wireless Sensor Networks; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, J.J.; Gawanmeh, A.; Saleem, K.; Parvin, S. Smart Devices, Applications, and Protocols for the IoT; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, K.; Alabduljabbar, G.M.; Alrowais, N.; Al-Muhtadi, J.; Imran, M.; Rodrigues, J.J. Bio-inspired network security for 5G-enabled IoT applications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 229152–229160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Farha, F.; Li, R.; Psychoula, I.; Chen, L.; Ning, H. Security and privacy issues of physical objects in the IoT: Challenges and opportunities. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2021, 7, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, J.; Rehman, A.U.; Othman, M.T.B.; Ahmad, M.; Tariq, H.B.; Khalid, M.A.; Moosa, M.A.R.; Shafiq, M.; Hamam, H. Deployment of Wireless Sensor Network and IoT Platform to Implement an Intelligent Animal Monitoring System. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, J.; Kiresova, S.; Vince, T.; Kovac, D.; Jacko, P.; Beres, M.; Hrabovský, P. Weather Station IoT Educational Model Using Cloud Services. J. Univers. Comput. Sci. 2020, 26, 1495–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbellini, S.; Di Francia, E.; Grassini, S.; Iannucci, L.; Lombardo, L.; Parvis, M. Cloud based sensor network for environmental monitoring. Measurement 2018, 118, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, B.; Wang, S.; Lu, W.; Neupane, R.L.; Dunn, D.; Ren, Y.; Su, Q.; Calyam, P. Flexible IoT security middleware for end-to-end cloud−fog communication. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 87, 688–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. Cloud Internet of Things for the Smart Environment of a Smart City. Master’s Thesis, California State University, San Bernardino, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Arroyo, P.; Herrero, J.L.; Suárez, J.I.; Lozano, J. Wireless sensor network combined with cloud computing for air quality monitoring. Sensors 2019, 19, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prasad, B.; Manjunatha, R. Internet of Things Based Monitoring System for Oil Tanks. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Mobile Networks and Wireless Communications (ICMNWC), Tumkur, Karnataka, India, 3–4 December 2021; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Banara, S.; Singh, T.; Chauhan, A. IoT Based Weather Monitoring System for Smart Cities: A Comprehensive Review. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference for Advancement in Technology (ICONAT), Goa, India, 21–22 January 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
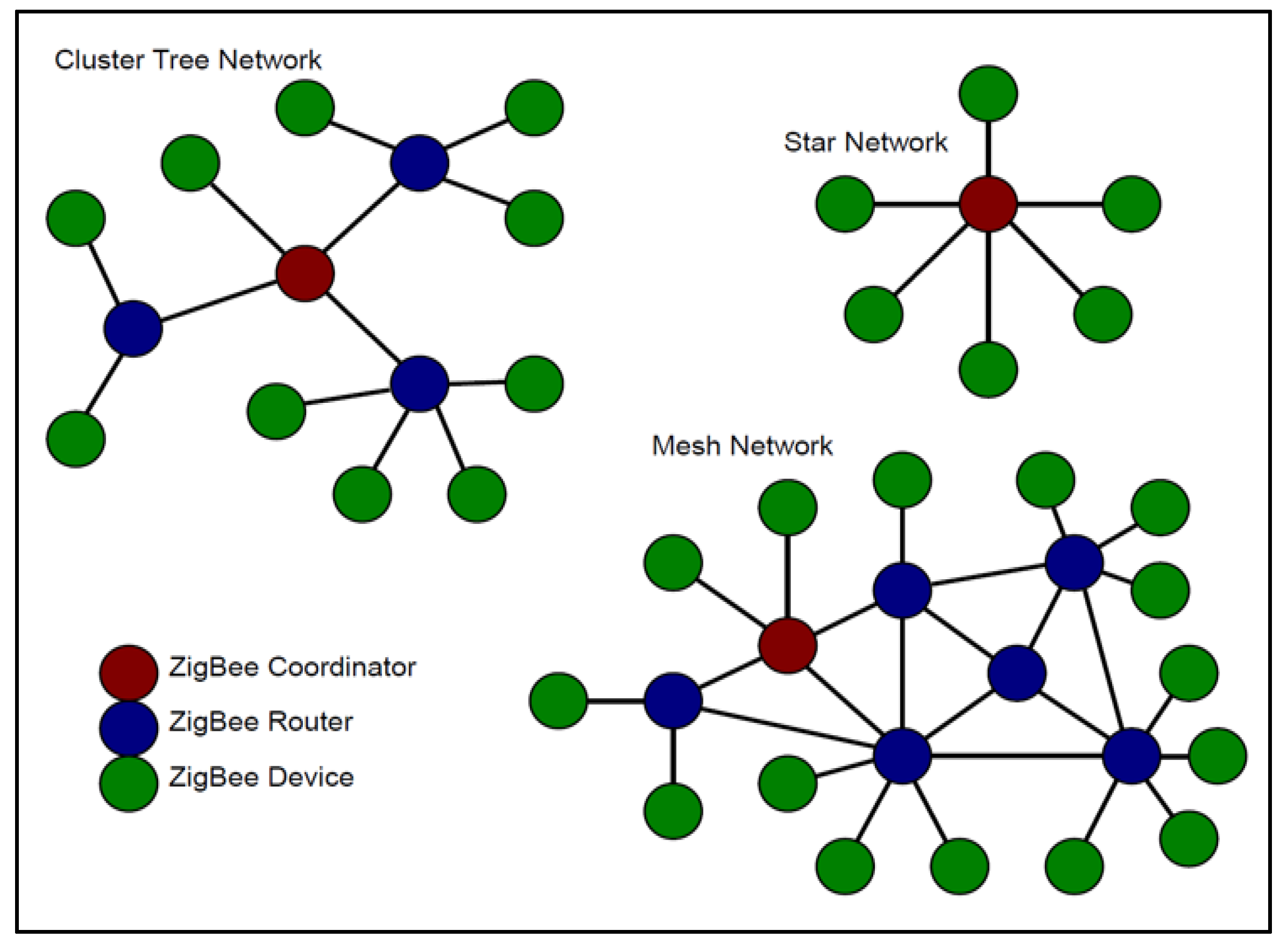
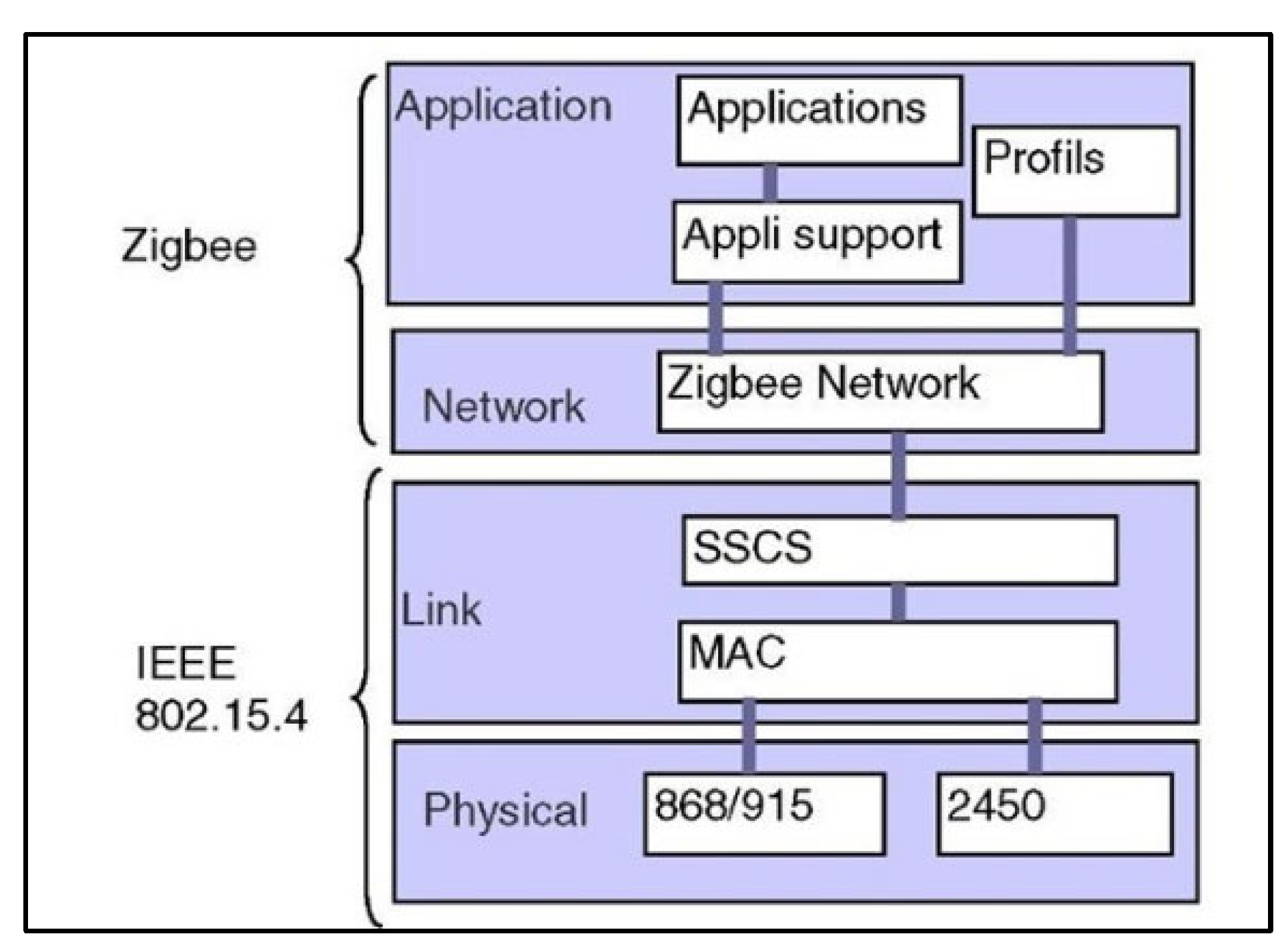












Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouni, R.; Saleem, K. Framework for Sustainable Wireless Sensor Network Based Environmental Monitoring. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8356. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148356
Ouni R, Saleem K. Framework for Sustainable Wireless Sensor Network Based Environmental Monitoring. Sustainability. 2022; 14(14):8356. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148356
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuni, Ridha, and Kashif Saleem. 2022. "Framework for Sustainable Wireless Sensor Network Based Environmental Monitoring" Sustainability 14, no. 14: 8356. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148356
APA StyleOuni, R., & Saleem, K. (2022). Framework for Sustainable Wireless Sensor Network Based Environmental Monitoring. Sustainability, 14(14), 8356. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148356






