Effects of pH Adjustment on the Release of Carbon Source of Particulate Organic Matter (POM) in Domestic Sewage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. POM Collection and Operation
2.2. Conventional Indicator Analysis
2.3. Microbial Community Structure
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Variation Characteristics of SCOD, NH4+-N, PO43−-P, and pH
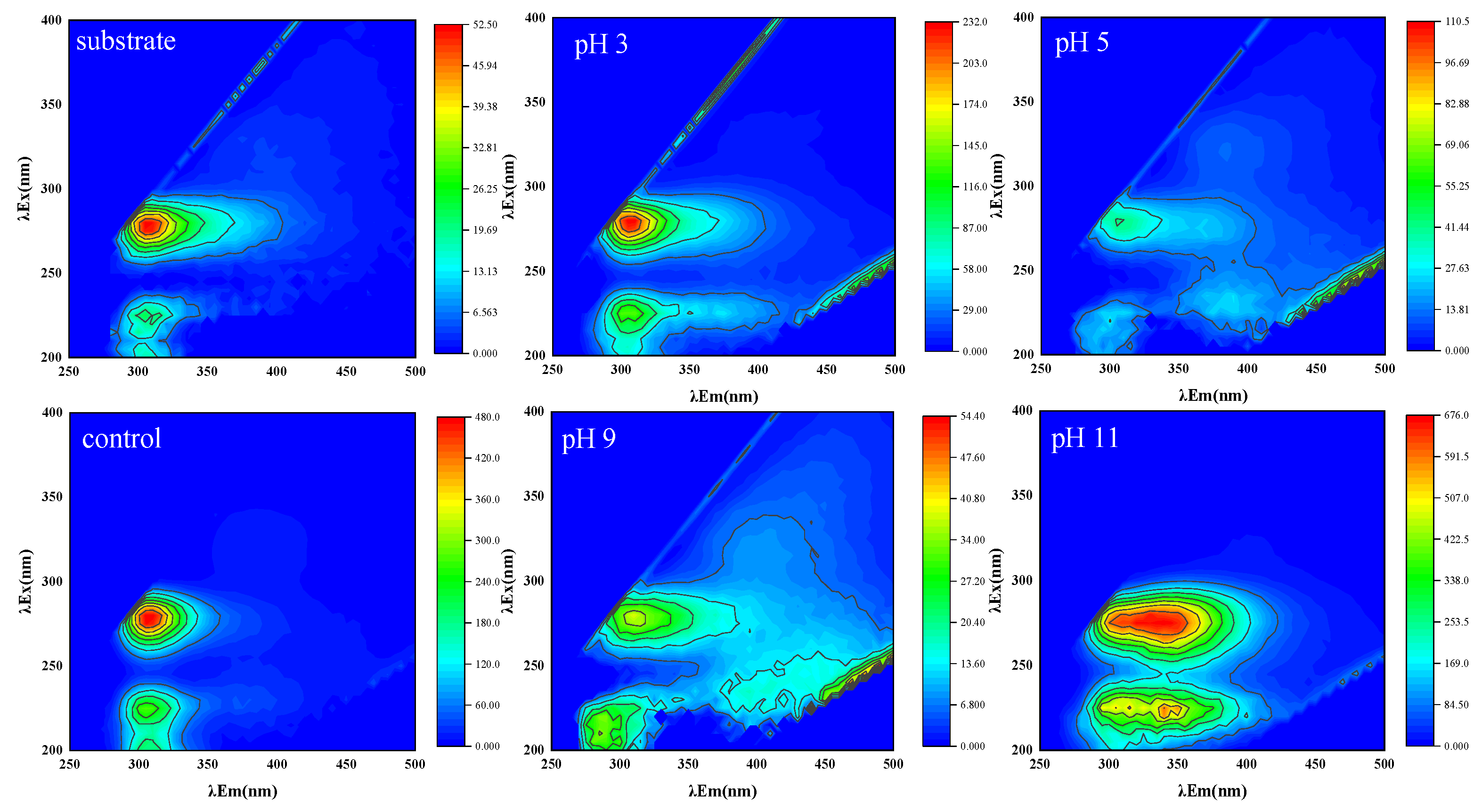
3.2. Variation of Protein, Polysaccharide and Fluorescent Substance Components
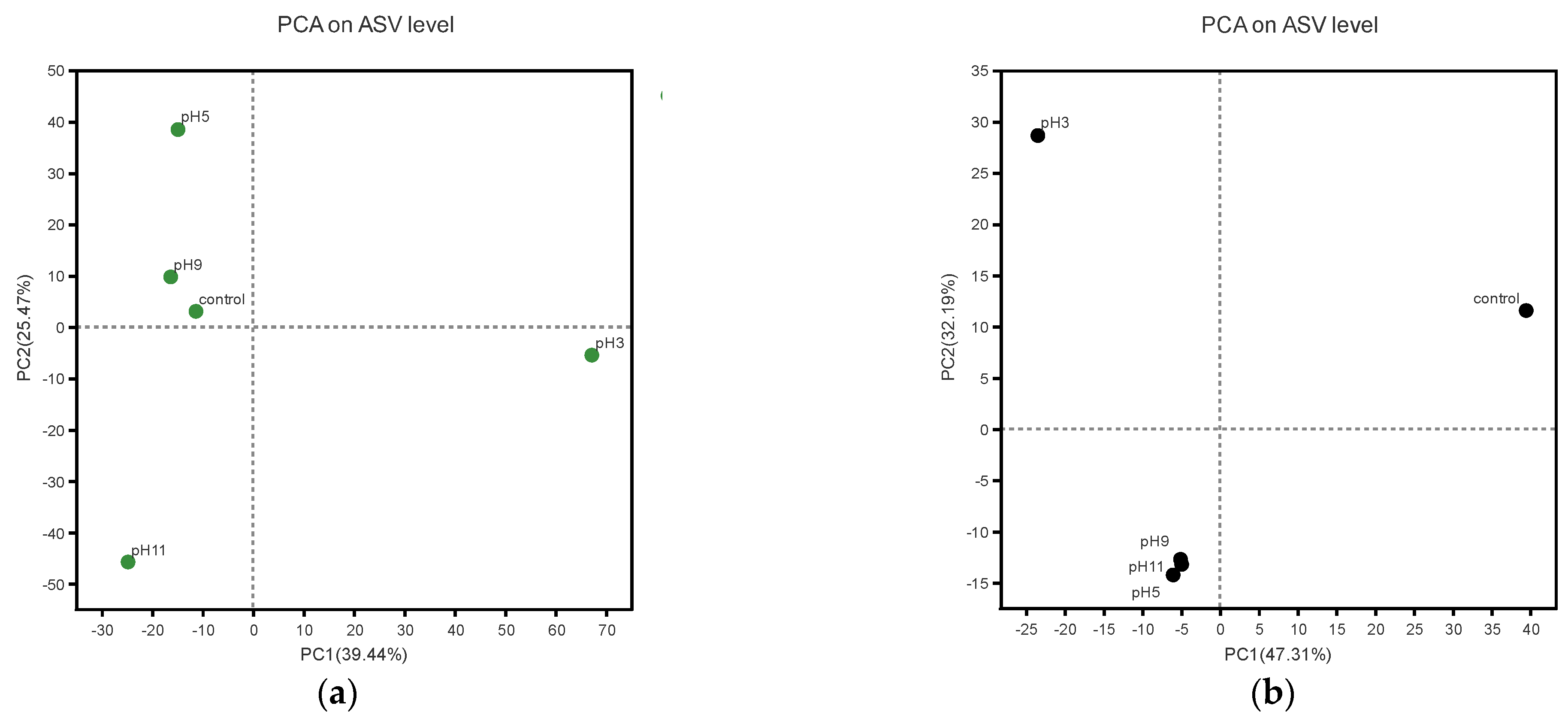
3.3. Effects of pH Adjustment on the Microbial Community Structure
3.3.1. Alpha Diversity Analysis
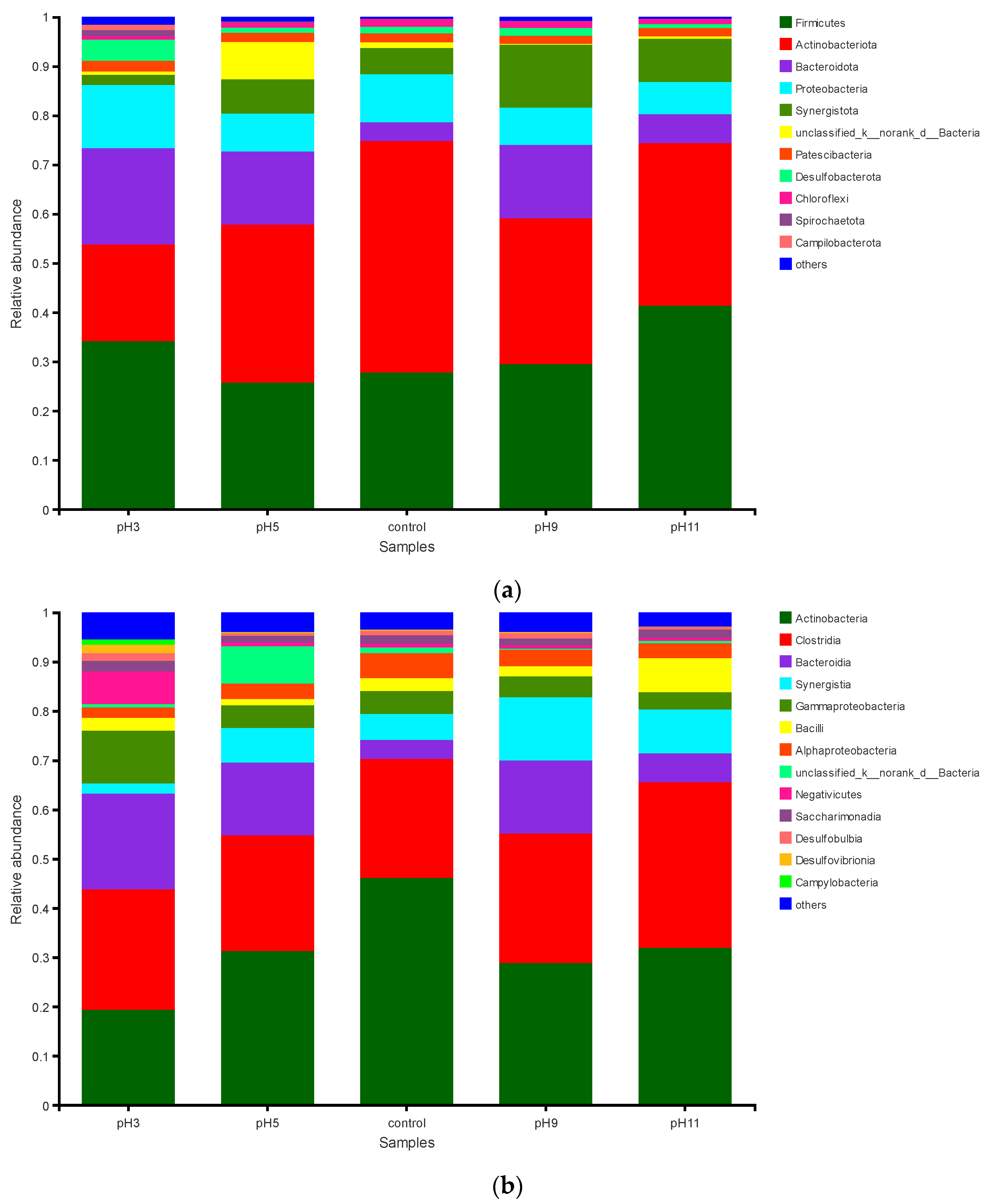
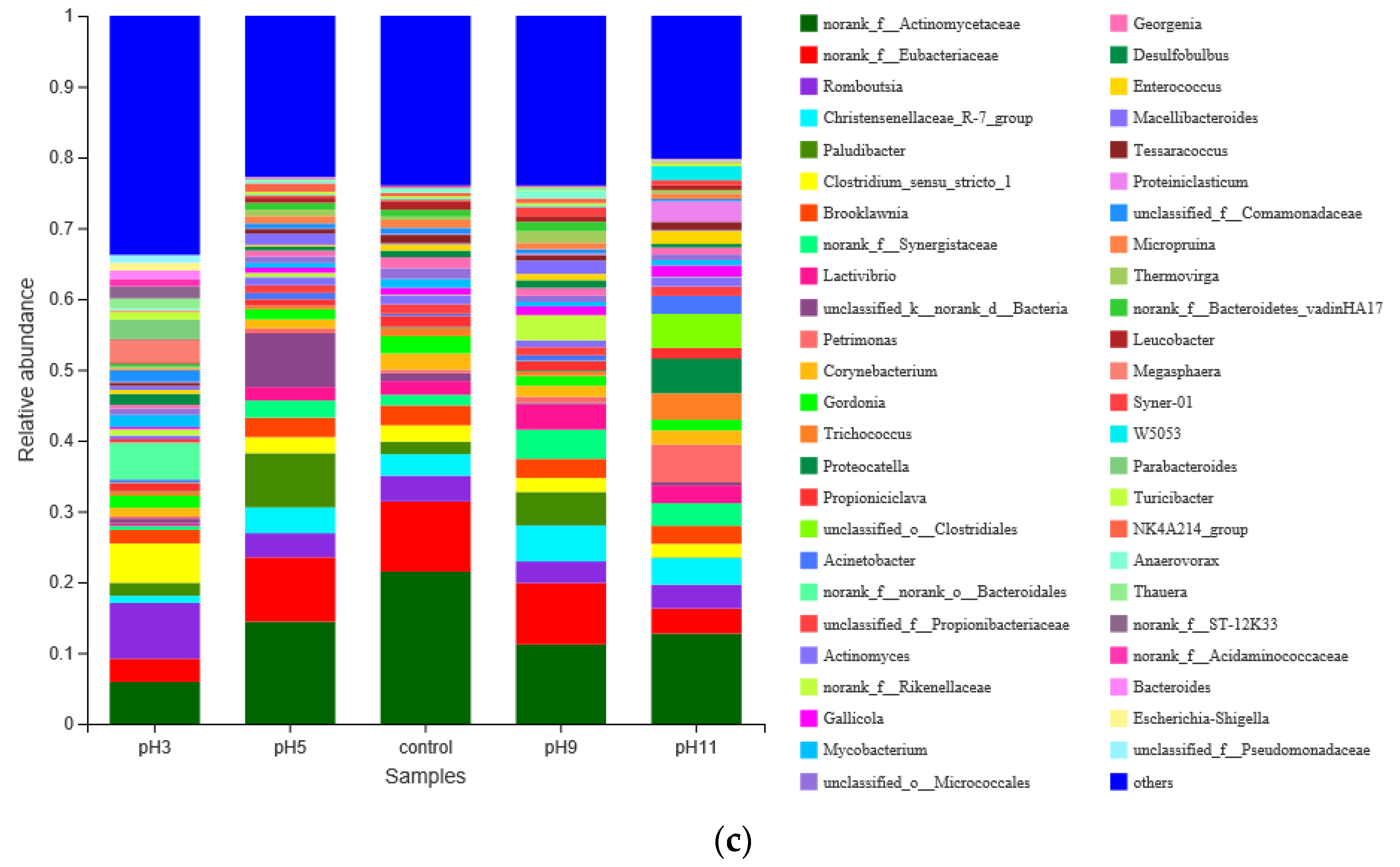
3.3.2. Effects of pH Adjustment on the Bacterial Community Structure
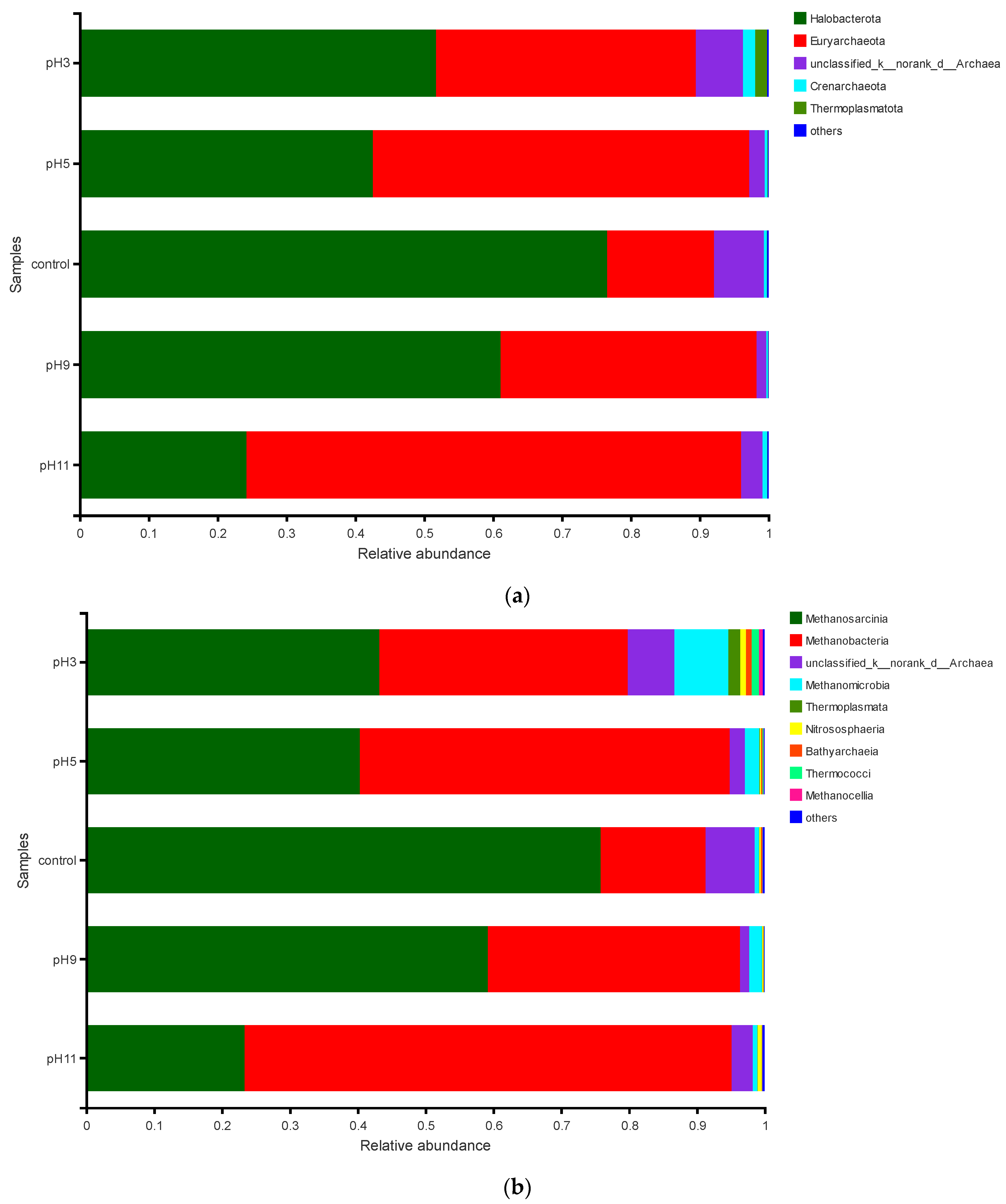
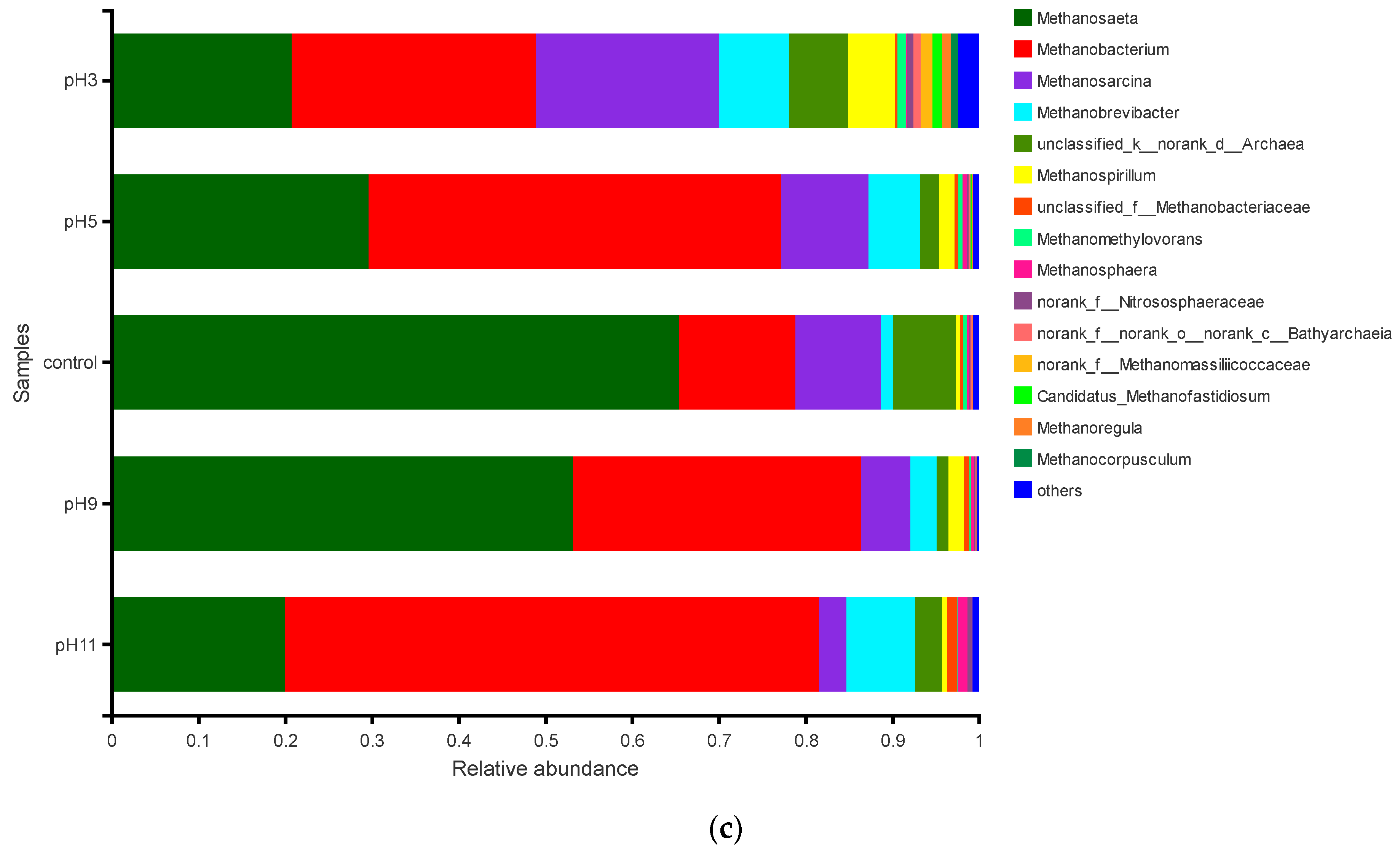
3.3.3. Effects of pH Adjustment on the Archaeal Community Structure
3.4. Pathway of Carbon Source Release
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Zhou, A.; Yue, X.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, X. Acceleration of the particulate organic matter hydrolysis by start-up stage recovery and its original microbial mechanism. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2021, 15, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Ngo, H.; Yang, L. A new activated primary tank developed for recovering carbon source and its application. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sophonsiri, C.; Morgenroth, E. Chemical composition associated with different particle size fractions in municipal, industrial, and agricultural wastewaters. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jin, P.; Zhao, H.; Meng, L. Classification of contaminants and treatability evaluation of domestic wastewater. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2007, 1, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, Q.; Luo, F.; Sun, W.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Regulation of anaerobic fermentation for producing short-chain fatty acids from primary sludge in WWTPs by different alkalis. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeleveld, P.J.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Experience with guidelines for wastewater characterisation in The Netherlands. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 45, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhon, D.; Okutman, D.; Insel, G. Characterisation and biodegradation of settleable organic matter for domestic wastewater. Water SA 2002, 28, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, L.; Du, R.; Peng, Y.; Li, Y. Successful establishment of partial denitrification by introducing hydrolytic acidification of slowly biodegradable organic matter. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315, 123887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, K.; Drewes, J.E. Alternative approach to estimate the hydrolysis rate constant of particulate material from batch data. Appl. Energy 2014, 120, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Fu, B. Improved volatile fatty acids anaerobic production from waste activated sludge by pH regulation: Alkaline or neutral pH? Waste Manag. 2016, 48, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, S.; Sarkar, O.; Swamy, Y.V.; Venkata, M. Acidogenic fermentation of food waste for volatile fatty acid production with co-generation of biohydrogen. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 182, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zhou, A.; Yue, X.; Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J. Initial-alkaline motivated fermentation of fine-sieving fractions and its effect on properties of cellulosic components. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maspolim, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, C.; Xiao, K.; Ng, W. The effect of pH on solubilization of organic matter and microbial community structures in sludge fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 190, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Yang, D.; Xu, K.; Li, K.; Ren, H. Bacterial survival strategies in sludge alkaline fermentation for volatile fatty acids production: Study on the physiological properties, temporal evolution and spatial distribution of bacterial community. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 340, 125701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Butler, D. Stepwise pH control to promote synergy of chemical and biological processes for augmenting short-chain fatty acid production from anaerobic sludge fermentation. Water Res. 2019, 155, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walter, W.G. APHA Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1961, 51, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of Sugars and Related Substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.T.; Guo, Y.; Bonnot, C.; Varrault, G.; Benedetti, M.; Parlanti, E. Characterisation of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in the Seine River catchment (France) by excitation-emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence spectroscopy combined with PARAFAC and PCA analyses. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference, Vienna, Austria, 27 April–2 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yuan, H.; Zhou, Q.; Gu, G. Hydrolysis and acidification of waste activated sludge at different pHs. Water Res. 2007, 41, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsiris, N.; Kouzeli-Katsiri, A. Bound water content of biological sludges in relation to filtration and dewatering. Water Res. 1987, 21, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellezuome, D.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, R. Mitigation of ammonia inhibition in anaerobic digestion of nitrogen-rich substrates for biogas production by ammonia stripping: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 157, 112043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilian, A.; Bancuta, O.; Bancuta, I.; Popesu, I.; Gheboianu, A.; Anase, N.; Tuican, M.; Zaharia, M. Extraction of heavy metals and phosphorus from sewage sludge with elimination of antibiotics and biological risks. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 437, 135298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; An, H.; Xie, T.; Xu, Q.; Deng, Y.; Zeng, G. Effect of initial pH on short chain fatty acid production during the anaerobic fermentation of membrane bioreactor sludge enhanced by alkyl polyglcoside. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 104, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Wang, J. Changes in microbial community structure during dark fermentative hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 25542–25550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, H.; Li, X.; Zuo, X. Oyster shells improve anaerobic dark fermentation performances of food waste: Hydrogen production, acidification performances, and microbial community characteristics. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 335, 125268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Geng, H.; Chen, R.; Liu, R.; Dai, X. Enhancing methanogenic fermentation of waste activated sludge via isoelectric-point pretreatment: Insights from interfacial thermodynamics, electron transfer and microbial community. Water Res. 2021, 197, 117072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ban, Q.; Li, J.; Wan, C. Functional bacterial and archaeal dynamics dictated by pH stress during sugar refinery wastewater in a UASB. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, H. High rejection rate of polysaccharides by microfiltration benefits Christensenella minuta and acetic acid production in an anaerobic membrane bioreactor for sludge fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, S.; Matsuura, N.; Honda, R.; Yamamoto-Ikemoto, R. Enhancement of methane production and phosphorus recovery with a novel pre-treatment of excess sludge using waste plaster board. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 255, 109844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, T. Characterization of Thauera-dominated hydrogen-oxidizing autotrophic denitrifying microbial communities by using high-throughput sequencing. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 128, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lv, C.; Tong, J.; Liu, I.; Lu, J.; Yu, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Wei, Y. Optimization and microbial community analysis of anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and sewage sludge based on microwave pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Wang, J. Enhancing biohydrogen production from disintegrated sewage sludge by combined sodium citrate-thermal pretreatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilajeliu-Pons, A.; Baneras, L.; Puig, S.; Molognoni, D.; Vila-Rovira, A.; Hernandez-Del, A.; Balaguer, M.D.; Colprim, J. External Resistances Applied to MFC Affect Core Microbiome and Swine Manure Treatment Efficiencies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e164044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, N.; Cai, G.; Pan, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Zhu, G. pH and hydraulic retention time regulation for anaerobic fermentation: Focus on volatile fatty acids production/distribution, microbial community succession and interactive correlation. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowski, A.; Tindall, B.J.; Bardin, V.; Blanchet, D.; Jeanthon, C. Petrimonas sulfuriphila gen. nov., sp. nov., a mesophilic fermentative bacterium isolated from a biodegraded oil reservoir. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55 Pt 3, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragán-Trinidad, M.; Carrillo-Reyes, J.; Buitrón, G. Hydrolysis of microalgal biomass using ruminal microorganisms as a pretreatment to increase methane recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; Cui, Z. A comparison and evaluation of the effects of biochar on the anaerobic digestion of excess and anaerobic sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Song, L.; Dong, X. Proteiniclasticum ruminis gen. nov., sp. nov., a strictly anaerobic proteolytic bacterium isolated from yak rumen. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 2221–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, F.; Ma, W.; Wang, P.; Zhao, G.; Lu, X. Influence of Temperature on Biogas Production Efficiency and Microbial Community in a Two-Phase Anaerobic Digestion System. Water 2019, 11, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Y. Ferroferric oxide triggered possible direct interspecies electron transfer between Syntrophomonas and Methanosaeta to enhance waste activated sludge anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Park, J.; Shin, W.; Tian, D.; Jun, H. Microbial communities change in an anaerobic digestion after application of microbial electrolysis cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 234, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Yang, H.; Zheng, D.; Pu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, L. Methanogenic activity and microbial communities characteristics in dry and wet anaerobic digestion sludges from swine manure. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 152, 107390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Sun, C.; Li, Y.; Peng, H.; Zhang, Y. Upgrading current method of anaerobic co-digestion of waste activated sludge for high-efficiency methanogenesis: Establishing direct interspecies electron transfer via ethanol-type fermentation. Renew. Energy 2020, 148, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Wu, P.; Ding, P.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, M.; Liu, H. Algae biochar enhanced methanogenesis by enriching specific methanogens at low inoculation ratio during sludge anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 338, 125493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonanzi, B.; Gallipoli, A.; Gianico, A.; Montecchio, D.; Pagliaccia, P.; Rossetti, S.; Braguglia, C.M. Elucidating the key factors in semicontinuous anaerobic digestion of urban biowaste: The crucial role of sludge addition in process stability, microbial community enrichment and methane production. Renew. Energy 2021, 179, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
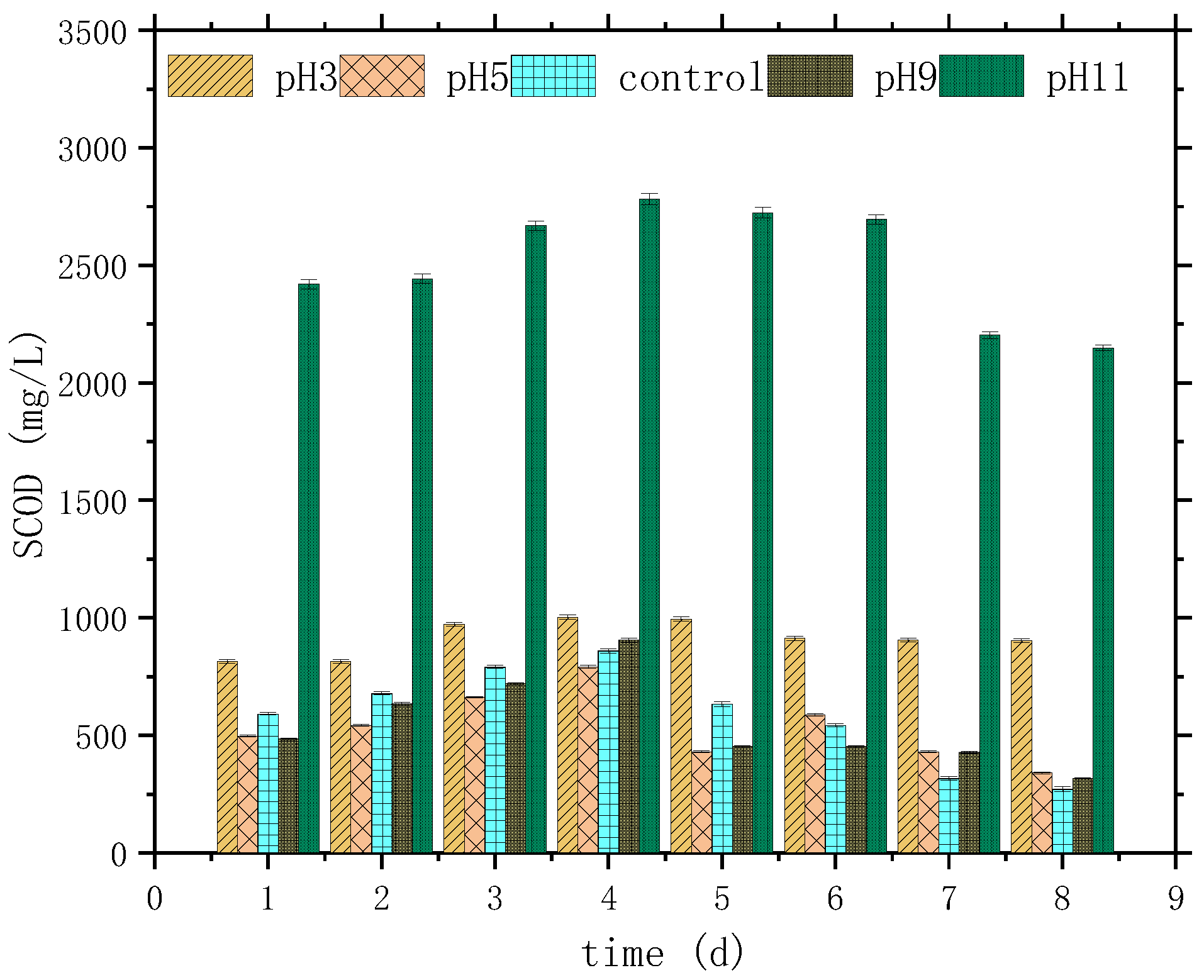
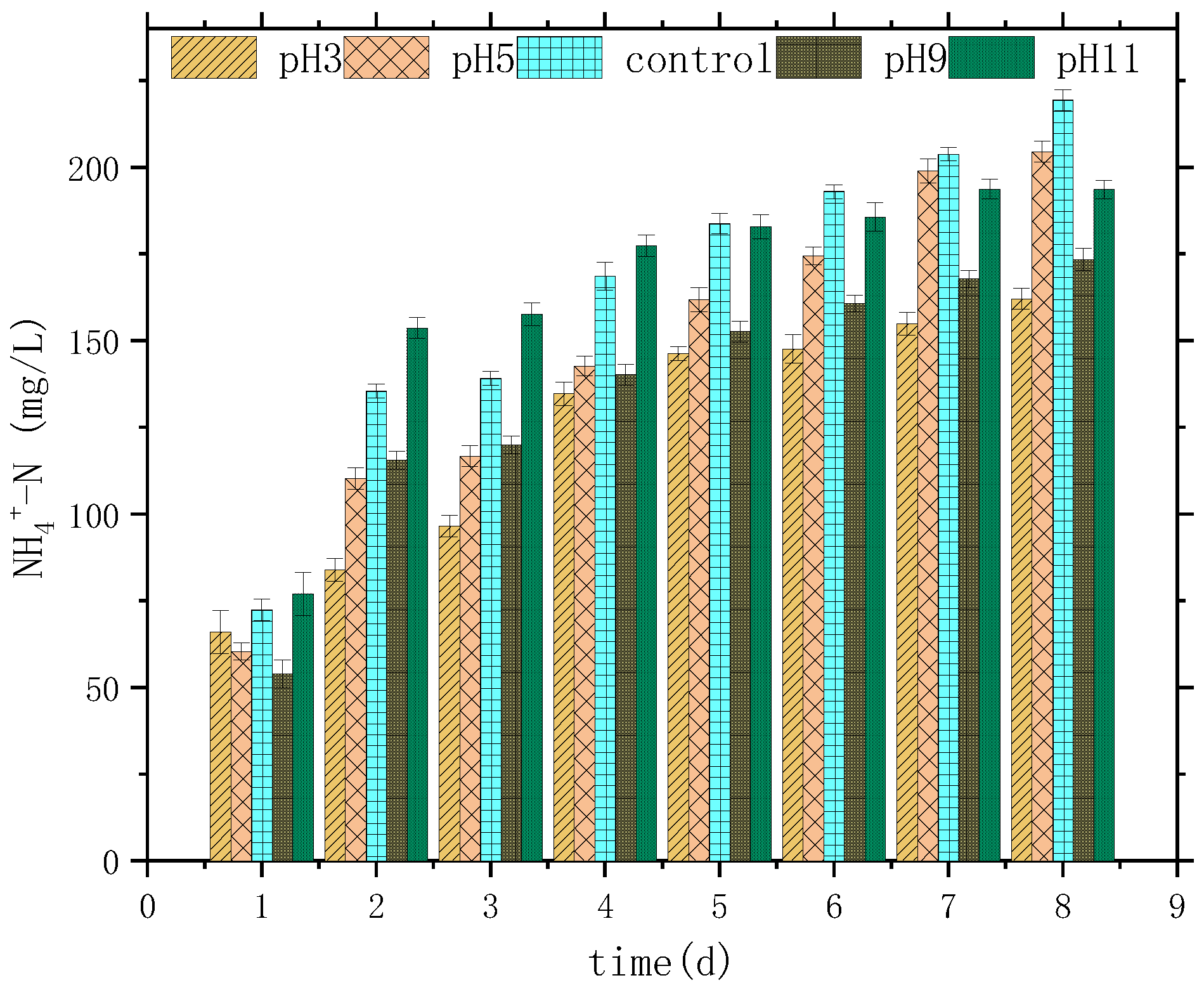
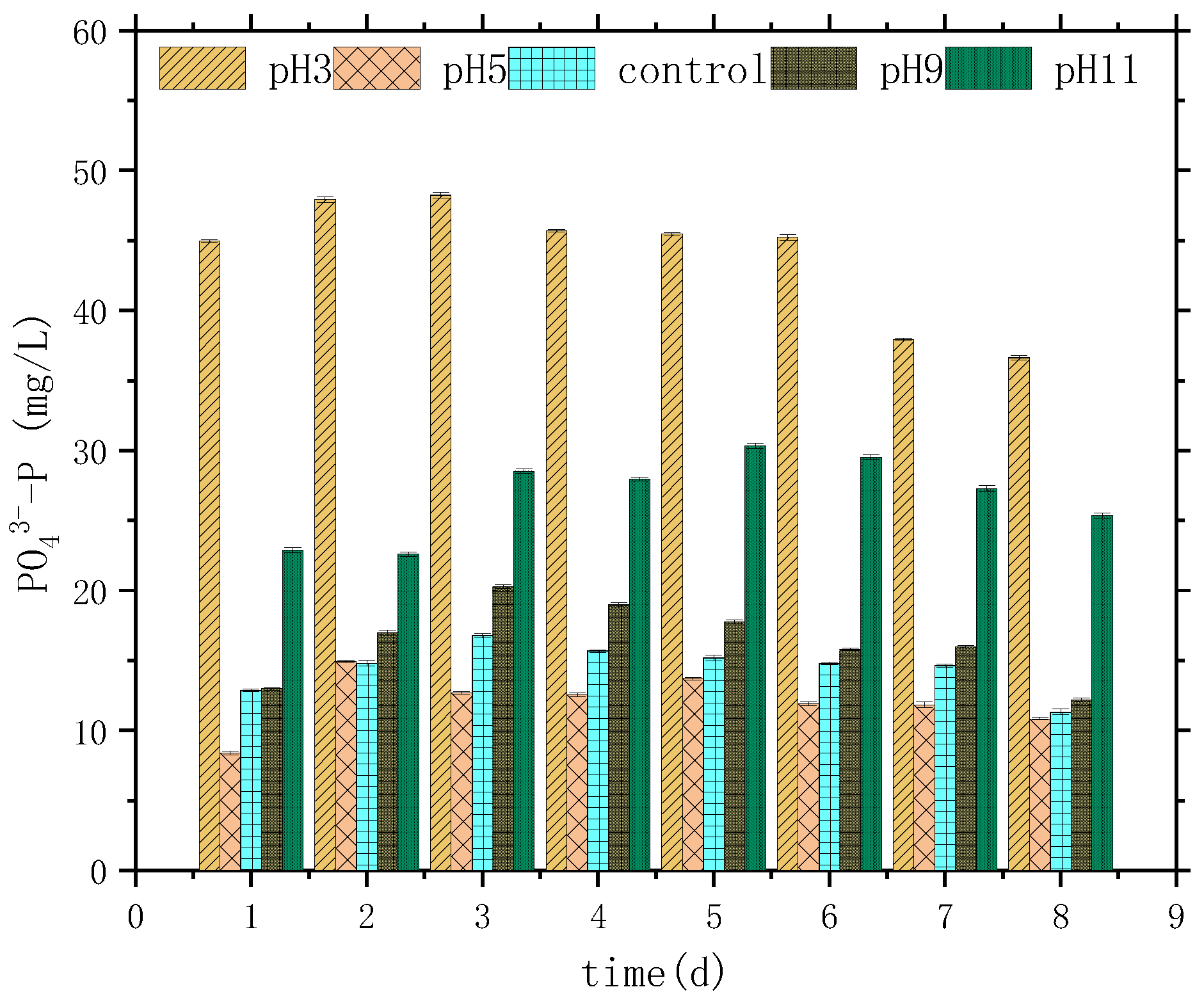
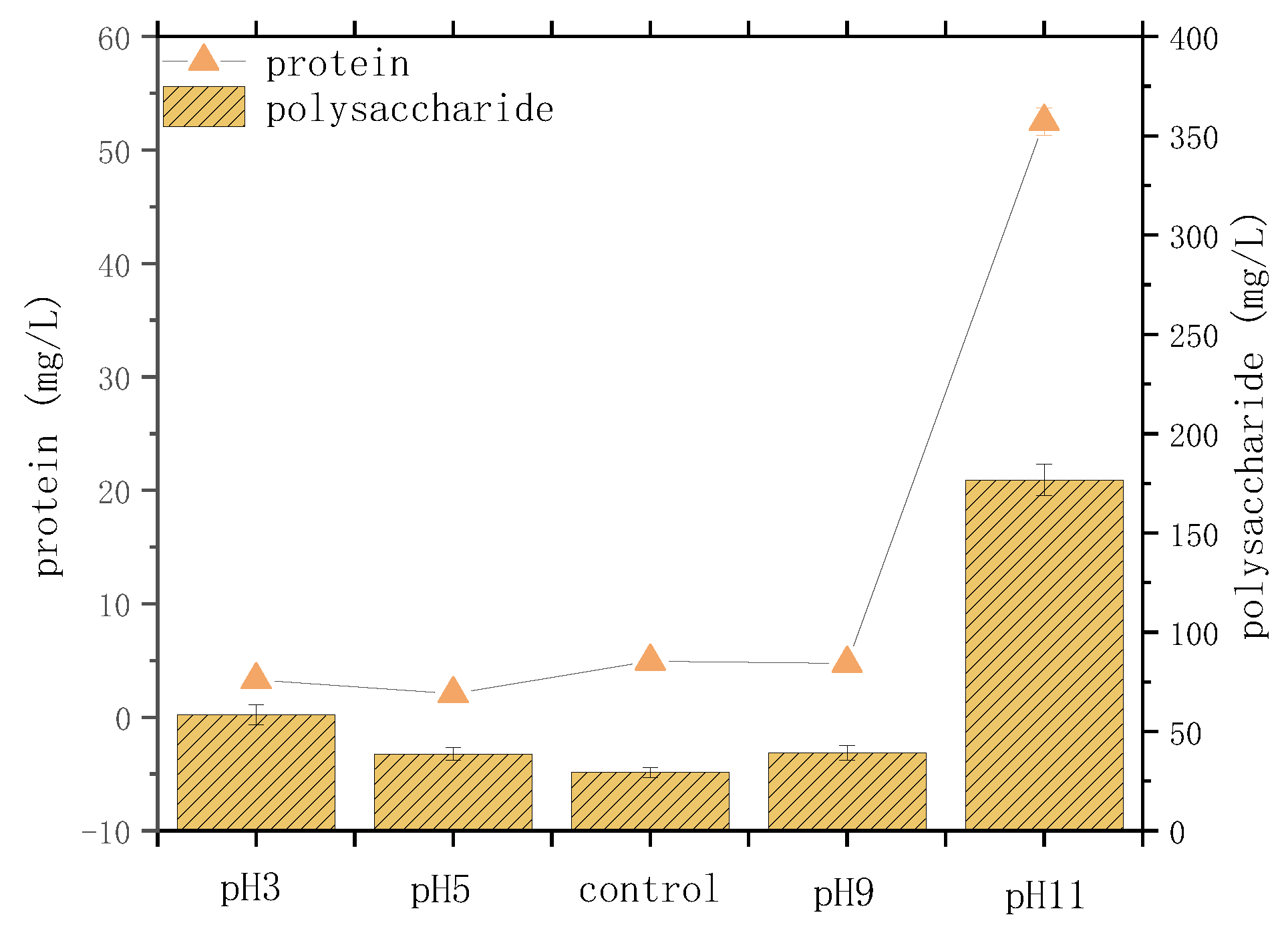


| Parameter | SCOD mg/L | NH4+-N mg/L | TP mg/L | PO43−-P mg/L | SS g/L | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration | 450 ± 3 | 66.5 ± 0.2 | 53.5 ± 2 | 7.8 ± 0.1 | 38.5 ± 1 | 7.08 ± 0.01 |
| Sample | Chao | Coverage | ASV | Shannon | Simpson |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 3 | 1715 | 1 | 1715 | 5.798 | 0.012 |
| pH 5 | 1505 | 1 | 1505 | 5.238 | 0.021 |
| control | 932 | 1 | 932 | 5.135 | 0.023 |
| pH 9 | 1356 | 1 | 1356 | 5.422 | 0.015 |
| pH 11 | 1338 | 1 | 1338 | 5.160 | 0.016 |
| Sample | Chao | Coverage | ASV | Shannon | Simpson |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 3 | 479 | 1 | 479 | 3.72 | 0.059 |
| pH 5 | 271 | 1 | 271 | 2.62 | 0.177 |
| control | 606 | 1 | 606 | 2.28 | 0.318 |
| pH 9 | 171 | 1 | 171 | 2.24 | 0.226 |
| pH 11 | 166 | 1 | 166 | 2.24 | 0.276 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, L.; Hao, J.; Lai, H.; Li, G. Effects of pH Adjustment on the Release of Carbon Source of Particulate Organic Matter (POM) in Domestic Sewage. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7746. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137746
Zhu L, Hao J, Lai H, Li G. Effects of pH Adjustment on the Release of Carbon Source of Particulate Organic Matter (POM) in Domestic Sewage. Sustainability. 2022; 14(13):7746. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137746
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Lei, Jiahou Hao, Houwei Lai, and Guibai Li. 2022. "Effects of pH Adjustment on the Release of Carbon Source of Particulate Organic Matter (POM) in Domestic Sewage" Sustainability 14, no. 13: 7746. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137746
APA StyleZhu, L., Hao, J., Lai, H., & Li, G. (2022). Effects of pH Adjustment on the Release of Carbon Source of Particulate Organic Matter (POM) in Domestic Sewage. Sustainability, 14(13), 7746. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137746






