Abstract
Integrated fixed-film activated sludge technology (IFAS) has a great advantage in improving nitrogen removal performance and increasing treatment capacity of municipal wastewater treatment plants with limited land for upgrading and reconstruction. This research aims at investigating the enhancing effects of polyethylene (PE) carrier and nitrifying bacteria PE (NBPE) carrier on nitrogen removal efficiency of an anoxic/aerobic (A/O) system from municipal wastewater and revealing temporal changes in microbial community evolution. A pilot-scale A/O system and a pilot-scale IFAS system were operated for nearly 200 days, respectively. Traditional PE and NBPE carriers were added to the IFAS system at different operating phases. Results showed that the treatment capacity of the IFAS system was enhanced by almost 50% and 100% by coupling the PE carrier and NBPE carrier, respectively. For the PE carrier, nitrifying bacteria abundance was maintained at 7.05%. In contrast, the nitrifying bacteria on the NBPE carrier was enriched from 6.66% to 23.17%, which could improve the nitrogen removal and treating capacity of the IFAS system. Finally, the ammonia efficiency of the IFAS system with NBPE carrier reached 73.0 ± 7.9% under 400% influent shock load and hydraulic retention time of 1.8 h. The study supplies a suitable nitrifying bacteria enrichment method that can be used to help enhance the nitrogen removal performance of municipal wastewater treatment plants. The study’s results advance the understanding of this enrichment method that effectively improves nitrogen removal and anti-resistance shock-load capacity.
1. Introduction
Rapid urbanization, exponential growth of household consumption and stringent discharge standards in developing countries pose a huge challenge for preventing and controlling water pollution [1]. Many municipal wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) in China suffer from insufficient nitrogen removal performance of the biochemical tank [2,3]. The poor nitrogen removal efficiency of activated sludge (AS) often has an adverse impact on the effluent stability of the WWTPs [4,5]. Meanwhile, this is a common phenomenon for the WWTPs of China, which have not reserved enough land for upgrading and expansion [6]. The above problems have led to the great need for robust and resilient wastewater treatment processes.
Biological nitrogen removal (BNR) has an incomparable advantage in the palliation of the eutrophication of a water body due to its economy and feasibility [7]. In traditional BNR systems, the nitrification process is the rate-limiting biochemical reaction and nitrifying bacteria activity can be restricted by temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen (DO), hydraulic retention time (HRT), solid retention time (SRT), toxic compounds and other operational parameters [8]. It can be inferred that nitrifying bacteria are sensitive and susceptible to BNR processes. In order to solve the above problem, many feasible technologies for enhancing the nitrogen removal performance of BNR processes were divided into two types based on different solved directions: (1) process optimization, Modified University of Cape Town (MUCT) process [9], alternating aerobic-anoxic (AAA) process [10], partial nitrification and denitrification (PND) process [7] and Anammox process [11] were developed to improve the nitrogen removal performance of BNR systems; (2) bioaugmentation technology, such as aerobic granular sludge (AGS) technology [12], moving bed biofilm reactor technology (MBBR) [13] and membrane bioreactor (MBR) technology [14] were proved as the most effective way to enlarge biomass of BNR systems, enhance nitrogen removal and reduce reactor volume. It is worth mentioning that AGS and MBBR technologies were identified as saving land area and energy demand for treating municipal and industrial wastewater [12].
During the last decade, integrated fixed-film activated sludge (IFAS), which coupled MBBR technology and conventional BNR processes, has been recognized as a cost-effective technology to enhance nitrogen removal, improve process stability and increase the treatment capacity of the WWTPs [15,16,17]. The main advantage of IFAS processes is the co-existed of both quick-growth suspended and slow-growth attached microorganisms in the same reactor configuration [18,19]. Thus, the application of a suspended carrier in the BNR process allows having biomass with a longer SRT in the biofilm for enhancing nitrification and a shorter SRT in the suspended biomass for the biodegradation of organic substances. This maintains a higher biomass concentration compared to traditional BNR processes [20]. The IFAS process has successfully been applied to different BNR systems for treating municipal and industrial wastewater, such as the A2O process [21], SBR process [22] and A/O process [23]. Actually, the IFAS process has become a feasible and reliable technology for building a new municipal WWTP and upgrading overloaded WWTPs [24].
Despite the aforementioned advantages of IFAS systems, there were limited studies investigating the possibility of enriching nitrifying bacteria on a suspended carrier by culturing it with anaerobic digestion liquor. In order to shorten the recovery time of nitrification activity in WWTPs, some studies have investigated the feasibility of enhancing nitrogen removal in a pilot-scale A2O system by adding nitrifiers cultured from anaerobic digestion liquor [25]. However, the bioaugmentation effect of nitrifiers gradually disappeared with the long-term operation of BNR systems [26,27].
In addition, in the treatment system of waste-activated sludge, the ammonium concentration of anaerobic digestion liquor, which inevitably increased the ammonium load of the aerobic treatment system, ranged from 500–2000 mg/L [28,29,30]. Anaerobic digestion liquor was used to enrich nitrifying bacteria by adding suspended carriers; it was not only beneficial for reducing the ammonium load of the mainstream wastewater treatment process, but also increased the biomass of nitrifying bacteria in the aerobic tank by bioaugmentation [31,32,33]. Free ammonia (FA), produced from the supernatant of an anaerobic digester, was an inhibitor for AS in the mainstream of WWTPs [34]. Ammonium was the substrate for nitrifying bacteria, which was insensitive to FA with an inhibition threshold of 10–150 mg NH3-N/L [35]. The economical treatment of sludge digester liquor was still a challenging problem for the operation of sludge treatment [36]. At present, there are three major side-stream biological treatment technologies for anaerobic digestion liquor: (1) SHARON process [37], (2) CANON process [38] and DEMON process [39]. IFAS process coupling with a nitrifying bacteria carrier, which was cultured from anaerobic digestion liquor in a side-stream system, might be a promising solution to enhancing nitrogen removal of municipal WWTPs.
Due to the inhibitory effect of FA derived from anaerobic digestion liquor on biomass, there were some advanced nitrogen removal processes that could exploit anaerobic digestion liquor to enhance autotrophic nitrogen removal [34,40]. Up to now, limited studies have reported solutions for solving nitrifier loss by attaching the nitrifier to a suspended carrier with ammonia-rich wastewater or anaerobic digestion liquor [41].
In this work, two pilot-scale systems (the A/O system and the IFAS system) were used to treat municipal wastewater in order to explore the feasibility of enhancing the nitrogen removal performance of WWTPs by enriching nitrifying bacteria on the PE carriers with synthetic anaerobic digestion liquor. The A/O system was the control system, which was a not-filled PE carrier or nitrifying bacteria PE (NBPE) carrier. The IFAS system was operated to improve the nitrogen removal performance by adding fresh PE carrier and NBPE carrier in two phases, respectively. NBPE carrier was cultured by synthetic anaerobic digestion liquor. The differences in nitrogen removal performance and the evolution of microbial population structure between the two pilot-scale systems are discussed. Finally, a novel side-stream biological treatment process for enhancing treatment capability and nitrification of WWTPs is proposed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Operational Procedures of A/O and IFAS Systems
Two pilot-scale systems of A/O and IFAS, which were made of carbon steel and plexiglass, were used for treating domestic wastewater, as shown in Figure 1. The A/O and IFAS systems have the same sizes of anoxic tank, aerobic tank and secondary setter, whose working volumes were 1.5 m3, 1.5 m3 and 1.0 m3, respectively. The above two systems both adopted single sludge reflux in this study, in which the sludge reflex ratio (R) from the bottom of the setter tank was transferred into the start of the anoxic tank by a peristaltic pump (Baoding, China). A pilot-scale sequencing batch biofilm reactor (SBBR) system with a 2.0 m3 working volume was used to enrich the NBPE carrier by treating the synthetic anaerobic digestion liquor, as shown in Figure 2.
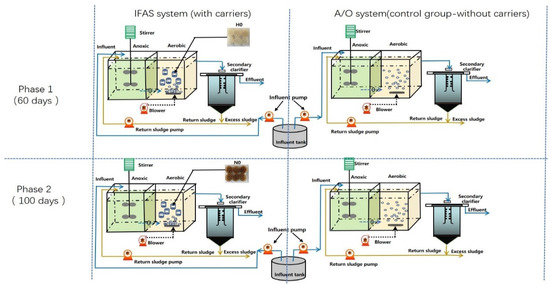
Figure 1.
Experimental procedure used for pilot-scale IFAS and A/O system in this study. H0 and N0 represent fresh PE carrier and NBPE carrier added into the aerobic tank of IFAS system.
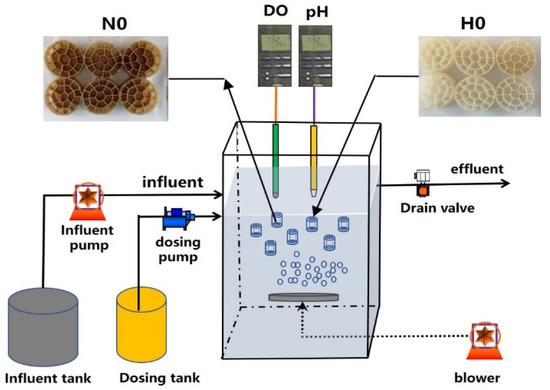
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of pilot-scale SBBR reactor for enriching the nitrifying bacteria PE carriers in this study. H0 represents fresh PE carriers added into the SBBR reactor, N0 represents enriched PE carriers produced from SBBR reactor, which were added into IFAS system.
The IFAS and A/O systems were both operated for more than 200 days, which could be divided into three periods: phase 0 (40 days), phase 1 (60 days) and phase 2 (100 days). Phase 0 was a start-up domestication period of 40 days for IFAS and A/O systems before phase 1. In the aerobic tank of A/O and IFAS systems, the aeration quantity was controlled at 6.0–8.0 m3/h by the air flowmeter during the whole operation. Phase 1 and phase 2 were divided into four operational periods. The operational parameters of the IFAS and A/O systems in the start-up period (phase 0) were almost the same as the operational parameters in phase 1. The influent, sludge reflux ratio and mixed liquid volatile suspend solid (MLVSS) in phase 0 were 5–10 m3/d, 50–200% and 5535 ± 305 mg/L. The solid retention time (SRT) of IFAS and A/O systems was 40–60 days calculated by Mt/Mw at phase 0, while Mt (15.9~17.1 kgVSS) and Mw (0.27–0.43 kgVSS/g) referred to the total sludge measured in the bioreactors and discharged excess sludge from the secondary setter. The excess sludges of IFAS and A/O systems were discharged manually at a fixed time every day during the experiment. The excess sludge in phases 1 and 2 was discharged according to the above method. Table 1 shows the detailed operational parameters of the IFAS and A/O systems during the whole operation.

Table 1.
Operation conditions of IFAS and A/O systems.
The pilot-scale SBBR system was operated for almost 100 days by treating synthetic anaerobic digestion liquor with an ammonium concentration of 100–1000 mg/L. The SBBR process was operated for 3 cycles per day; each cycle was operated for 8 h, which included influent 0.5 h, aeration 6.5 h, settlement 0.5 h and drainage 0.5 h. During the aeration period, the DO and pH in the SBBR system were controlled at 2.0–6.0 mg/L and 6.5–8.5, respectively. The pH in the SBBR reactor was automatically controlled with a PLC controller by adding 5 mol/L NaOH during the aeration period. The SRT and HRT of the SBBR system were 35 days and 36 h, respectively. The fill ratio and PE carrier packing ratio of the SBBR system were 20% and 35%, respectively. The type of carrier was K3 (Qingdao, China), which was made with a hydrophobic polyethylene resin hollow cylinder, and has a bulk specific surface area (SSA) of 500 m2/m3. The detailed influent characteristic of the synthetic anaerobic digestion liquor during the experiment is shown in Table S2.
2.2. Seeding Sludge and Real Municipal Wastewater
Seeding sludge was taken from a municipal WWTP, which was located in Kunming city of Yunnan Province, China. The municipal wastewater in this study was pumped from the aerated grit chamber of the above municipal WWTP. During the operation period of the SBBR system, the 100–1000 mg/L NH4+-N synthetic wastewater was dosed in the SBBR system in order to obtain the NBPE carriers with a high abundance of nitrifying bacteria. NH4+-N, TN, NO3−-N, NO2−-N and COD in the influent of municipal wastewater were 10.8–22.8 mgN/L, 18.9–27.6 mgN/L, 0.1–1.1 mgN/L, 0–0.2 mgN/L and 88.1–205.7 mg/L, respectively. The detailed influent characteristics of municipal wastewater during the experiment are shown in Table S1.
2.3. Analytical Methods
Mixed liquor samples were fetched 3–5 times from A/O and IFAS systems every week during the whole experiment, and all samples were analyzed after purifying with a 0.45 μm filter paper. The NH4+-N, NO3−-N, NO2−-N, TN, COD, MLSS and MLVSS concentrations of each sample were analyzed with standard methods [42]. The DO, pH and temperature were monitored using online oxygen and pH probes (E+H company, Gerlingen, Germany). The VSS of biofilm attached to the PE and NBPE carriers were achieved as follows: eight representative carriers were fetched from the aerobic tank of the IFAS system, diluted in 100 mL of deionized water, sonicated in an ultrasonic cell crusher (Ningbo, China) for 6–10 h until the biomass was vibrated from the PE carriers. Once the biomass was separated from PE carriers, the VSS of biofilm was measured according to the determination of MLSS and assessed through the total number of carriers in a liter of the reactor [18,43].
2.4. Sludge Samples Collection and DNA Extraction
In order to highlight the shift of microbial communities in A/O and IFAS systems during the whole experiment, seeding sludge and AS samples were collected from the aerobic tank of A/O and IFAS systems on day 60 (phase 1) and day 160 (phase 2) for high-throughput 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing. Meanwhile, the biofilm samples were firstly shaken off from the normal PE carriers and NBPE carriers by an ultrasonic cell crusher, then centrifuged 3 times in a 2 mL centrifuge tube with ultrapure water. Finally, two biofilm samples, which were collected from the aerobic tank of the IFAS system on day 60 (phase 1) and day 160 (phase 2), were detected with high-throughput 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing. After sampling, the E.Z.N.ATM Mag-Bind soil DNA Kit (OMEGA, Madison, WI, USA) was adopted to extract DNA following the manufacturer’s instructions. Before the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, the total community genomic DNA concentration of all sludge samples was analyzed by a fluorimeter (Qubit® 3.0, Thermo Fisher, Walham, MA, USA) to inject accurate DNA concentration for the PCR procedure.
2.5. PCR Amplification and 16S rRNA Sequencing
In the PCR amplification, the primers 341F and 805R were applied to amplify the variable regions V3 and V4 of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene [44]. The 16S rRNA V3–V4 amplicon was amplified using KAPA HiFi Hot Start Ready Mix (2×) (TaKaRa Bio Inc., Shiga, Japan). The PCR procedure was performed in a thermal instrument (Applied Biosystems 9700, Walham, MA, USA) adopting the following program: 1 cycle of denaturing at 95 °C for 3 min, first 5 cycles of denaturing at 95 °C for 30 s, annealing at 45 °C for 30 s, elongation at 72 °C for 30 s, then 20 cycles of denaturing at 95 °C for 30 s, annealing at 55 °C for 30 s, elongation at 72 °C for 30 s and a final extension at 72 °C for 5 min. The PCR products were checked using electrophoresis in 1% (w/v) agarose gels in TBE buffer (Tris, boric acid, EDTA) stained with ethidium bromide (EB) and visualized under UV light. Sequencing was performed using the Illumina MiSeq system (Illumina MiSeq, New York, NY, USA), according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.6. High-Throughput Sequence Processing
After high-throughput sequencing, the effective sequences of each sample were submitted to the Ribosomal Database Project Classifier again to identify bacterial sequences. Species richness and diversity statistics, including coverage, chao1, ace, Simpson and shannonever, were also calculated using mothur. The modified pipeline is described on the mothur website. Sequencing of amplicons from all samples was carried out by Sangon Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The compiled sequences of AS and biofilm samples were compared with the rRNA gene sequences in the GenBank using the NCBI BLAST program [45]. The sequences of sludge samples were grouped into different operational taxonomic units (OTUs) with 95% identity thresholds.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Operational Parameters of IFAS and A/O Systems
Table 1 shows the average values for each operational parameter of the IFAS and A/O systems in the whole experimental period, which was divided into three phases. During the start-up period (phase 0 = 40 days), the MLVSS of the IFAS and A/O systems decreased from 5500 mg/L to 4050~4100 mg/L. Meanwhile, the biofilm VSS of the IFAS system increased from 0 mg/L to 1650 mg/L. The excess sludge was discharged manually in order to maintain the optimal operation of the IFAS and A/O systems. In phase 0, the SVI of the IFAS system was very high (223 ± 16 mL/g), producing several sedimentation problems in the secondary settling tank and increasing the effluent SS concentration. This phenomenon of the IFAS system was due to the addition of the PE carriers that disrupted the activated sludge flocs. Afterward, the sedimentation problem was solved at the end of phase 0 when the SVI decreased to 120 mL/g owing to the restoration of the activated sludge flocs and the gradual decrease of the MLVSS concentration and SRT (from 60 to 40 days); similar results were reported by Kim et al. [46]. Subsequently, during the experimental period (phase 1 and phase 2), the IFAS system was operated at a constant MLVSS (4050 ± 255~4250 ± 375 mg/L), constant VSS of biofilm (1650 ± 125~1575 ± 155 mg/L), constant R (100%), constant C/N ratio (6.6 ± 1.0~7.7 ± 0.9) and SRT (15 ± 1.6~25 ± 5.0 days), correspondingly. The A/O system was operated at similar operational parameters (R, C/N ratio and SRT), except for the concentration of MLVSS (4100 ± 125~3825 ± 325 mg/L). It was interesting to observe that the VSS of biofilm in phase 1 was slightly higher than in phase 2; the main reason might be ascribed to the difference in microbial community structure between normal PE carrier and NBPE carrier. The biofilm in the NBPE carrier in phase 2, which had a high abundance of nitrifiers (more than 20%), had a slower growth rate compared with the biofilm of the PE carrier in phase 1 with a small abundance of nitrifiers (less than 7%). Owning to the following reasons: (a) sludge production of both suspended-growth and attached-growth biomass at phase 2 (16–18 °C) was lower than sludge production at phase 1 (18~23 °C); (b) long SRT would improve the nitrification and nitrogen removal performance of IFAS and A/O system. Therefore, the SRT values of the IFAS and A/O systems increased from 15 ± 1.6 days in phase 1 to 25 ± 5.0 days in phase 2.
It is worth mentioning that the MLVSS (4250 ± 375 mg/L) of the IFAS system was higher than the MLVSS concentration (3825 ± 325 mg/L) of the A/O system in phase 2; this phenomenon did not comply with traditional findings [47], which indicate that the MLVSS of the IFAS system was less than in the conventional AS system due to the growth of biofilm on the carrier that would assimilate a part of the substrates. In fact, it could be ascribed that the average SVI (132 ± 13) of the IFAS system was higher than the SVI (105 ± 9) of the A/O system in phase 2, which indicated that the settling property of the suspended sludge in the IFAS system was lower than that in the A/O system. Due to the discharge volume of excess sludge being fixed and adjusted every week, however, the MLVSS of excess sludge in the second clarifier was changed every day. Therefore, the method of discharging excess sludge and the fluctuations of the sludge settling properties in this study produced the difference in MLVSS in the IFAS and A/O systems at phase 2.
In order to compare the performance difference between IFAS and A/O systems, the pilot-scale systems were overloaded at phases 1 and 2, and operated at a peak hydraulic influent flowrate (10~40 m3/d and 1.8~7.2 h of HRT) instead of the design average hydraulic flowrate (10 m3/d) and design HRT (7.2 h), see Table 1.
3.2. Long-Term Performances of IFAS and A/O Systems
Variation profiles of nitrogen and COD concentration of the process during the whole operation of IFAS and A/O systems are shown in Figure 3.
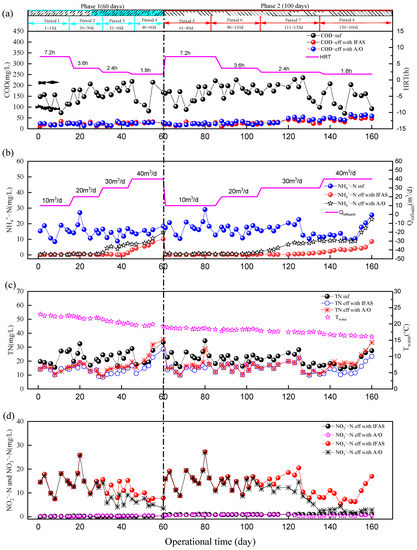
Figure 3.
Variations of the influent and effluent water qualities during long−term operation. (a) COD, (b) NH4+−N, (c) TN and (d) NO3−−N and NO2−−N concentrations of IFAS and A/O systems during operational time.
In phase 1 (period 1: 1–15 d), the influent quantity (Qinfluent) and HRT of the IFAS and A/O systems were 10 m3/d and 7.2 h (HRTaerobic/HRTanoxic = 1:1) under conditions of Sludge reflux ratio (R) = 100% and system’s water temperature (Twater) = 22.5 °C. NH4 +-N, TN and COD in the effluent of the IFAS system were 0.2 ± 0.1 mgN/L, 13.9 ± 1.8 mgN/L and 22.3 ± 7.2 mg/L, respectively, with NH4+-N, TN removal efficiency and COD efficiency of 98.6 ± 0.7%, 35.1 ± 12.8% and 79.3 ± 12.4%. As the control group, the A/O system had similar performances of nitrogen and COD. NH4+-N, TN and COD in the effluent of the A/O system were 0.3 ± 0.2 mgN/L, 14.2 ± 2.0 mgN/L and 21.6 ± 3.5 mg/L, respectively, with NH4+-N, TN removal efficiency and COD efficiency of 97.7 ± 1.1%, 33.2 ± 14.5% and 81.1 ± 5.0%.
When the Qinfluent of the IFAS and A/O systems increased from 20 m3/d to 30 m3/d in phase 1 (period 3: 31–45 d), the ammonia removal rate of the IFAS system was 94.8 ± 7.2%, higher than 61.5 ± 12.9% of the A/O system’s ammonia removal rate. Although the nitrification performance of the above two systems displayed an obvious difference, the nitrogen and COD removal performances of the above two systems were similar (see Table 2).

Table 2.
Nitrogen and COD removal performances of two pilot-scale systems during experiment.
In order to investigate the impact of extreme influent shock load on the above two systems, the Qinfluent in phase 1 (period 4: 46–60 d) was increased to 40 m3/d; meanwhile, the HRT of the above two systems decreased to 1.8 h under the condition of R = 100% and Twater = 18.5 °C. The nitrogen and COD removal capacity of the above two systems decreased rapidly. NH4+-N, TN and COD in the effluent of the IFAS system were 6.9 ± 2.4 mgN/L, 18.2 ± 4.1 mgN/L and 29.1 ± 3.2 mg/L, respectively, with the NH4+-N, TN and COD removal efficiency of 56.1 ± 10.4%, 20.7 ± 9.5% and 76.6 ± 9.9%. Correspondingly, the A/O system had worse polluted substance removal performance than IFAS’s removal performance. NH4+-N, TIN and COD in the effluent of the A/O system were 9.6 ± 3.1 mgN/L, 25.4 ± 8.1 mgN/L and 27.9 ± 2.3 mg/L, respectively, with NH4+-N, TN removal efficiency and COD efficiency of 38.7 ± 12.1%, −8.5 ± 13.3% and 77.8 ± 7.9%. The A/O system’s nitrogen removal performance broke down rapidly on the 51st day. Meanwhile, the IFAS system’s nitrogen removal effect was more stable than the A/O system’s treatment performance, whose nitrogen and COD removal rates decreased slower than the A/O system’s treatment performance. Therefore, the IFAS system with normal PE carriers had stronger shock resistance than the A/O system. When the shock load of the influent quantity (Qinfluent = 30 m3/d) was 200% higher than the design discharge (Qinfluent = 10 m3/d), the effluent quality of the IFAS system was normal, but the A/O system’s effluent started to bankrupt.
In order to improve the shock resistance of the IFAS system, the PE carriers were replaced with NBPE carriers, which were cultured almost 100 days in the SBBR system (Figure 2) in advance by treating simulated anaerobic digestion supernatant with NH4-N = 100–1000 mg/L. It is worth mentioning that there was a transitional period (7 days) for the IFAS and A/O systems before phase 2, whose treatment performance of nitrogen and COD were returned to normal status. The transitional period’s operational data are not shown in Figure 3.
In phase 2 (period 5: 61–85 d), the Qinfluent and HRT of the IFAS and A/O systems were 10 m3/d and 7.2 h (HRTaerobic/HRTanoxic = 1:1) under conditions of R = 100% and Twater = 17.8 °C. NH4+-N, TN and COD in the effluent of IFAS system were 0.2 ± 0.2 mgN/L, 14.3 ± 2.2 mgN/L and 22.3 ± 5.1 mg/L, respectively, with NH4+-N, TN and COD removal efficiency of 98.7 ± 1.0%, 37.6 ± 7.7% and 84.5 ± 7.1%. Compared with the control group, the A/O system had similar performances of nitrogen and COD. NH4+-N, TN and COD in the effluent of the A/O system were 0.6 ± 0.2 mgN/L, 16.3 ± 4.7 mgN/L and 21.6 ± 3.4 mg/L, respectively, with NH4+-N, TN and COD removal efficiency of 96.4 ± 1.2%, 30.9 ± 6.9% and 85.4 ± 3.4%. The TN in the effluent of the A/O system was a little higher than the water standard. There were similar nitrogen and COD removal performances of IFAS and A/O systems in phase 2 (period 6: 86–110 d), which is shown in Table 2.
When the Qinfluent of the IFAS and A/O systems increased 30 m3/d in phase 2 (period 7: 110–135 d), the ammonia removal rate of the IFAS system was 95.3 ± 3.8%, higher than 55.1 ± 23.2% of A/O system’s ammonia removal rate.
In phase 2 (period 8: 136–160 d), the operational conditions were the same as the operational condition of phase 1 (period 4: 46–60 d), except Twater = 16.5 °C. NH4+-N, TN and COD in the effluent of the IFAS system were 3.9 ± 1.9 mgN/L, 14.3 ± 4.3 mgN/L and 45.1 ± 7.2 mg/L, respectively, with NH4+-N, TN and COD removal efficiency of 73.0 ± 7.9%, 25.5 ± 5.6% and 66.1 ± 8.5%. The A/O system’s nitrogen removal performance broke down on the 142nd day. The NH4+-N, TN and COD in the effluent the of A/O system were 11.8 ± 4.9 mgN/L, 20.6 ± 6.1 mgN/L and 53.6 ± 9.2 mg/L, respectively, with NH4+-N, TN and COD removal efficiency of 18.9 ± 8.8%, −7.6 ± 15.7% and 59.3 ± 11.6%.
Therefore, When the shock load of influent quantity (Qinfluent = 40 m3/d) was 300% higher than the design treatment capacity (Qinfluent = 10 m3/d), the effluent quality of the IFAS system with NBPE carriers operated normally, but the A/O system’s effluent started to crash. The IFAS system with NBPE carriers had stronger shock resistance than the A/O system and IFAS with normal PE carriers at phase 1. As reported, the IFAS process can accomplish enhanced biological nitrogen removal and fast removal efficiency owing to the robustness of the biofilm, which enables the IFAS to operate under long SRT [48]. IFAS achieves year-round nitrification and fast removal efficiency thanks to the nitrifiers attached to the carrier [49]. Thus, the constructive merits of both attached and suspended growth systems were coupled in the IFAS process [50]. In this work, the IFAS system not only enhanced nitrogen removal, but also increased the treatment capacity of the A/O system, see Table 3.

Table 3.
The treatment capacity difference between IFAS and A/O systems.
3.3. Enhancing Nitrogen Removal Mechanism of IFAS Process
The mechanism and design of the IFAS process have been widely investigated for enhancing nitrogen removal in the conventional activated sludge (CAS) process by treating municipal wastewater [17,24]. A good balance in organics and nutrients removal has been reported by the IFAS system [51]. Nitrogen removal of the BNR system was affected by various parameters, especially the bacterial community of the biomass [52]. Due to the low C/N ratio of municipal wastewater in this study, the nitrification rate in the IFAS floc was higher than the rate in the A/O system under a shock load of 300–400% in phase 2. It is attributed to the seeding effect that enhances the floc capture of the fragment of the biofilm rich with nitrifier [22], which further enhances nitrification [53]. It explained the good ammonia removal efficiency of the IFAS system under extremely low HRT (1.8 h). Due to the low C/N ratio of 7.7 and sludge reflux ratio of 100%, the nitrification and denitrification rates of the IFAS system were 73% and 25.5% in period 8 of phase 2. However, the nitrification rate (18.9%) and denitrification rate (−7.6%) of the A/O system indicated that the control system’s nitrogen removal function was disappeared. It could be inferred that the IFAS system was superior to the A/O system in nitrogen removal under an influent shock load of 400% and a low HRT of 1.8 h. The NBPE carrier, which has a high abundance of nitrifiers, applied in the IFAS system presented an anoxic environment for improving denitrification and thus reducing the effluent nitrate concentration [54]. Moreover, the A/O system with a high MLVSS of 3850 mg/L at phase 2, without the contribution of biofilm in NBPE carrier, only achieved 59.3% COD removal and reduced nitrogen removal performance. It could be inferred that the biofilm in the IFAS system at period 8 of phase 2 contributed to 71.4% of nitrification and almost complete conversion of ammonium [51]. Nitrogen mass balance showed that the simultaneous nitrification and denitrification (SND) on the biofilm contributed to the majority of total nitrogen removal (25.2%) of the IFAS system in period 8 of phase 2; the anoxic denitrification (DN) was negligible with 0.3%, see Figure 4. Meanwhile, COD mass balance displayed that SND of biofilm and heterotrophic respiration (HR) of AS and biofilm contributed to the majority of total COD removal (40.6%) of the IFAS system. Although the IFAS system was not applied for phosphorus removal, it had a certain capacity for enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR), which consumed 27.6% COD.
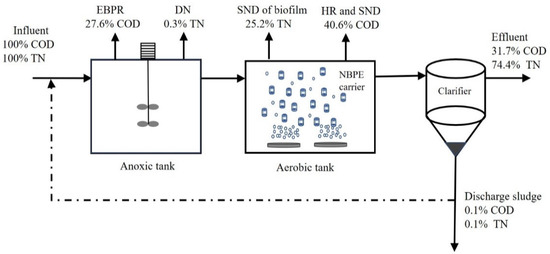
Figure 4.
Nitrogen and COD mass balances in IFAS systems at period 8 of phase 2.
3.4. Changing Trends of Community Diversity between IFAS and A/O Systems
The coverage curves of AS and biofilm samples from the aerobic tanks of IFAS and A/O systems were almost 95%, indicating that the microbial diversity was well described by the obtained sequence libraries [55], as shown in Figure 5a. The difference in sludge community diversity in the aerobic tanks of the two systems was further investigated. As shown in Figure 5a, the Shannon diversity index value of inoculated sludge was 6.7. During phase 1, the Shannon diversity index was next to 6.4; meanwhile, there were slight differences in the AS samples between these two systems in phase 2. The Shannon diversity index was 6.6, which was close to the inoculated sludge. However, the biofilm community diversity in the IFAS system was 6.3, owning to the biofilm in the IFAS system being cultured in the SBBR system over the 100 days, which had the highest abundance of nitrifying bacteria. The biofilm of the NBPE carrier had a simpler community structure compared with AS samples in the A/O system [56].
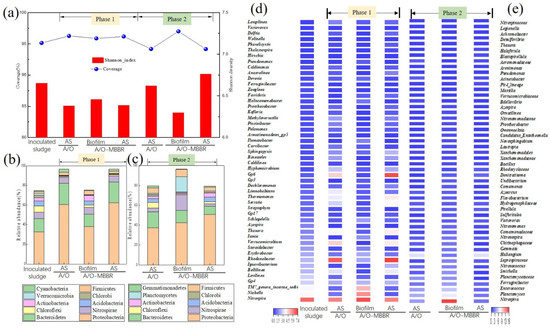
Figure 5.
Changes in the biofilm and activated sludge (AS) diversity and community structure of IFAS and A/O systems during phases 1 and 2. (a) reveal the observed coverage and Shannon diversity index of biofilm and AS in IFAS and A/O systems (b,c) show the microbial community composition of bacterial phyla in the biofilm and AS samples of IFAS and A/O systems at phases 1 and 2 (>0.1%), and (d,e) show the microbial community composition of bacterial genera in the biofilm and AS samples of IFAS and A/O systems at phase 1 and 2 (top 50).
3.5. Taxonomic Compositional Changes in IFAS and A/O Systems
Figure 5b–e revealed the taxonomic compositional changes at the phylum and genus levels. In phase 1, Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes and Nitrospirae were detected as the three major phyla for IFAS and A/O systems, accounting for 57.57–89.76% of the total abundance of each sample (Figure 5b). This result was not consistent with a former study for the IFAS process by adding polyurethane foam (PUF) carrier media [57]. AS samples in the aerobic tanks of IFAS and A/O systems demonstrated a similar community structure; however, the biofilm community structure in the IFAS system was different from the community structure of AS samples, which were collected from the IFAS and A/O systems. When the relative abundances of Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes and Nitrospirae from the IFAS system biofilm were 38.06%, 12.49% and 7.02%, the abundances of the same phyla in AS samples from the above two systems were 60.38–60.53%, 21.06–21.61% and 6.10–6.32%, respectively. Among the other seven dominant phyla, Cyanobacteria abundance (0.61%) in biofilm was lower than the abundance of AS (2.09–3.37%) of these two systems; the abundances of the remaining six phyla belonging to biofilm in the IFAS system (Firmicutes 4.14%, Chloroflexi 2.43%, Acidobacteria 4.03%, Actinobacteria 5.80%, Chlorobi 0.31% and Verrucomicrobia 0.42%) were higher than the abundances of six phyla existing in AS samples of these two systems (Firmicutes 2.31–2.92%, Chloroflexi 0.81–1.01%, Acidobacteria 0.29–0.40%, Actinobacteria 0.55–0.62%, Chlorobi 0.19–0.20% and Verrucomicrobia 0.21–0.28%). Considering that Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes and Nitrospirae phyla were closely related to the conversion of NO3−-N and NO2−-N [58], it was not surprising to detect Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes and Nitrospirae as the three most abundant phyla attached on PE carriers.
In phase 2, the biofilm community structure in the IFAS system was different from the AS samples community structure in IFAS and A/O systems (Figure 5c). However, AS in the aerobic tanks of IFAS and A/O systems revealed a similar community structure. Proteobacteria (42.55%), Nitrospirae (15.70%) and Planctomycetes (15.45%) were detected as the three major phyla for biofilm in the IFAS system. Meanwhile, Proteobacteria (37.48–50.71%), Bacteroidetes (8.44–15.92%) and Firmicutes (4.09–5.49%) were the three major phyla for AS samples in IFAS and A/O systems. The other phyla in biofilm were Bacteroidetes (12.40%), Firmicutes (7.49%), Actinobacteria (1.21%), Chloroflexi (0.99%), Gemmatimonadetes (0.26%), Acidobacteria (0.19%) and Chlorobi (0.16%), meanwhile, the remaining phyla abundance in the AS samples of the above two systems were Nitrospirae (2.33–3.76%), Planctomycetes (1.22–1.29%), Actinobacteria (2.48–4.33%), Chloroflexi (1.94–5.85%), Gemmatimonadetes (0.80–1.87%), Acidobacteria (3.73–4.73%) and Chlorobi (0.62–1.59%). Owning to the biofilm attached to PE carriers in the IFAS in phase 2, it was enriched by a pilot-scale SBBR system; the community structure was sharply different from the AS samples in the IFAS and A/O systems.
More details on the variations of the microbial community at the genus level were depicted by the heatmap, as shown in Figure 5d, e. In phase 1, similar community structures of AS samples for IFAS and A/O systems were also raised at the genera level; however, the biofilm community structure in the IFAS system was different from AS samples from the above two systems. The dominant three major genera in biofilm from the IFAS system were Nitrospira (7.02%), Niabella (5.87%) and TM7-genera-incertae-sedis (5.13%). These genera were all related to nitrogen removal function [59,60]. Meanwhile, the three major dominant genera of AS samples from the above two systems were nitrifying bacteria Nitrospira (5.98–6.18%), facultative denitrifying bacteria Rhodanobacter (6.68–7.42%) and heterotrophic bacteria GP6 (4.48–6.99%).
Similarly, in phase 2, the community structure of biofilm from the IFAS system was different from the other AS samples from the IFAS and A/O systems, as shown in Figure 5e. Nitrospira (15.66%), Planctomyces (7.27%) and Enterococcus (5.34%) were the three dominant genera in the biofilm of the IFAS system; meanwhile, the three major genera of the AS samples for the above two systems were Haliangium (6.41–6.78%), Planctomyces (2.17–4.36%) and Nitrospira (2.33–3.76%), which were nitrifying bacteria, heterotrophic denitrifying bacteria and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria, respectively. It was clear that the biofilm attached to the NBPE carrier from the IFAS system had a higher abundance of nitrogen-removing bacteria than the bacteria abundance of AS samples from IFAS and A/O systems. It is worth mentioning that nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB: Nitrospira) abundances in AS and biofilm samples were apparently higher than ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB: Nitrosomonas) abundances of corresponding samples in phase 1 and phase 2. The ratio imbalance of nitrifiers (AOB and NOB) did not comply with the good nitrification performance of the IFAS and A/O systems, which were not the PNA process in this study either [44]. The main reason was likely that Nitrospira could be recognized as novelty complete ammonia oxidizers [61,62].
3.6. Succession of Nitrogen Removal Genera in IFAS and A/O Systems
A total of 28 genera of potential nitrifiers (e.g., Nitrosomonas and Nitrospira), denitrifiers (e.g., Thauera, Dechloromonas, Iamia and so on) and heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification bacteria (e.g., Niabella, Hyphomicrobium and so on) were detectable (>0.01%) [63], as shown in Figure 6a. Twenty-four of them were found in the inoculated sludge, and at the same time, they were also present in the activated sludge of the IFAS and A/O systems, some genera (e.g., Nitrosospira, Nitrosococcus, Azonexus and so on) disappeared in the biofilm of the IFAS system at phase 1 or phase 2 [64,65].
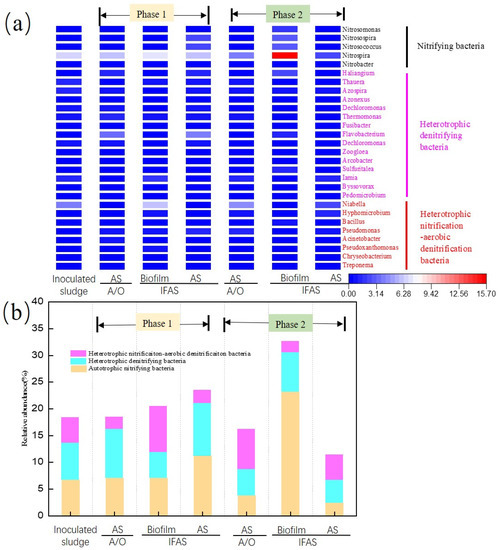
Figure 6.
Nitrogen removal genera in biofilm and AS of IFAS and A/O systems at phase 1 and phase 2. (a) The relative abundance of 28 nitrogen genera in all samples (>0.01%). (b) The trends in abundance of genera involved in nitrification and denitrification.
In phase 1, three genera related to ammonia removal had similar changing trends in AS between the IFAS and A/O systems, but it was different between the biofilm and AS in the above two systems, as shown in Figure 6a. The ammonia oxidizing bacteria (AOB) in biofilm, including Nitrosomonas, Nitrosospira and Nitrosococcus, did not change compared with inoculated sludge, but the AOB was increased from 0.01% to 1.68% and 0.36% in AS of the IFAS and A/O systems, respectively. Two genera related to nitrite removal did not show clearly changing trends in biofilm and AS samples from the above two systems. Nitrobacter was maintained with an average abundance of 0.01%, which was negligible. Nitrospira was the dominant genera in the nitrifying bacteria, whose abundances in biofilm and AS of the IFAS system were 7.02% and 6.18%, respectively. Meanwhile, Nitrospira in AS of the A/O system was 5.98%, which had a slight decline compared with inoculated sludge (6.66%).
Owing to the PE carriers taken from the aerobic tank of the IFAS system, the community structure of the denitrifiers was different from AS samples from IFAS and A/O systems in phase 1. The denitrifiers were divided into two groups: heterotrophic denitrifying bacteria (HDB) and heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification bacteria (HNAD). For HDB members, the three dominant genera in AS samples were Flavobacterium (3.36–4.06%), Haliangium (1.16–1.23%) and Thermomonas (0.93–1.42%). In contrast, the three dominant genera in the biofilm were Iamia (1.59%), Thauera (0.66%) and Thermomonas (0.60%). Moreover, compared to inoculated sludge, the dominant HDB genus changed from Thauera to Flavobacterium and Iamia for AS and biofilm samples in phase 1 [66]. For HNAD members, compared with inoculated sludge, the dominant HNAD genus changed from Niabella (3.81%) to Pseudomonas (0.7–1.26%) in AS samples from IFAS and A/O systems; however, the HNAD dominant genus Niabella in the biofilm was enriched from 3.81% to 5.87%, compared with inoculated sludge. Thus, it can be inferred that the biofilm attached to the carriers was useful for enriching HNAD bacteria.
In phase 2, five genera related to ammonia removal in AS samples showed a similar structure, but the abundance of nitrifying bacteria in AS samples decreased to 2.33–3.76%. Meanwhile, the nitrifying bacteria in the biofilm of the IFAS system dramatically increased from 7.05% to 23.17%, which was cultured in the SBBR reactor for about 100 days before adding it into the aerobic tank of the IFAS system. Nitrobacter in biofilm was maintained at low abundance (0.01%); the remaining four nitrifying bacteria genera, Nitrosomonas, Nitrosospira, Nitrosococcus and Nitrospira, were increased to 1.7%, 2.9%, 2.9% and 15.66%, respectively. Meanwhile, denitrifiers in AS samples of IFAS and A/O systems showed a similar trend at the genera level. The major three dominant genera of HDB in the AS samples were Azospira (0.68–0.96%), Thermomonas (0.45–0.78%) and Iamia (1.16–1.27%), correspondingly, Haliangium, Sulfuritalea and Flavobacterium were the major three dominant genera of HDB in the biofilm at phase 2. The dominant genera of the AS samples from the above two systems in phase 2 changed from Pseudomonas to Niabella compared with the AS samples in phase 1.
Meanwhile, the dominant genera of HNAD in the biofilm in phase 2 was Bacillus. The biofilm communities formed on NBPE carriers play a key role in the removal of nitrogenous contaminants. HDB and HNAD bacteria did not show a significant increase in the biofilm at phase 2, indicating that denitrifiers are more dependent on the anoxic environment, which was suitable to enrich denitrifiers.
In Figure 6b, temporal trends in the cumulative abundance of nitrifying bacteria and denitrifying bacteria (HDB and HNAD) were further explored. Before adding PE carriers, the abundances of nitrifying bacteria, HDB and HNAD bacteria in the inoculated sludge were 6.69%, 7.02% and 4.68%, respectively. For AS samples in phase 1, the abundance of nitrifiers and HDB increased slightly, while the abundance of HNAD declined. Correspondingly, for biofilm in phase 1, the abundance of nitrifiers and HNAD increased to 7.05% and 8.53%, but the abundance of HDB declined to 4.91%. The above changes indicated the low-speed enrichment of nitrifying bacteria attached to the carriers at phase 1. For AS samples in phase 2, the abundance of nitrifying bacteria and HDB declined slightly compared with AS samples in phase 1, owing to the temperature being decreased from 21 °C to 16 °C. It is worth mentioning that the abundance of nitrifying bacteria in phase 2 was maintained at 23.17% at day 160, which was enriched in the SBBR reactor before being added to the aerobic tank of IFAS. It was easy to infer that the community structure of the biofilm on the NBPE carriers was reliable during the phase 2 stage.
3.7. Potential Application of the NBPE Carriers in A/O Wastewater Treatment Plants
Nitrogen removal performance is the key factor in the operation of municipal WWTPs [67]. As shown in Figure 3, good nitrogen removal of the IFAS system was achieved in phase 2 under the shock load of 200–400% without the addition of an external carbon source. The average effluent NH4+-N and TN of the IFAS system were 3.9 and 14.3 mg/L under the shock load of 400% and HRT of 1.8 h. Although the nitrogen removal efficiency of this work was lower than the nitrogen removal performance of conventional pre-denitrification BNR processes (55.4–93.6%, Table 4), the IFAS process was operated with the R of 100% and HRT of 1.8 h at a steady period, which are stringent operational conditions for the conventional BNR processes listed in Table 4. The lower R and shorter HRT of the IFAS system indicated a smaller demand for energy [7,68]. The main reason for achieving reliable nitrogen removal in this study was possibly the contribution of biofilm on the NBPE carrier under the condition of 400% shock load [69]. Therefore, the IFAS process coupled with the NBPE carrier might be a promising solution for the new construction and upgrading of WWTPs, especially for the districts with low C/N ratio municipal wastewater.

Table 4.
Comparison of this work with other IFAS processes treating municipal wastewater.
Based on the results of this study, a novel side-stream operation strategy for enhancing nitrogen removal in the mainstream of WWTPs was proposed. This strategy involves recirculating a portion of the activated sludge through a sideline nitrifying bacteria enrichment tank [33], where the biofilm attached to the NBPE carriers is subjected to treatment with digesting liquor in an aerobic SBR (see Figure 7). In traditional WWTPs, the sludge digesting liquor contains a significant amount of ammonium at a concentration of about 500–2000 mg/L, with temperature and pH up to 30 °C and 8.1–8.4, respectively [28]. The high pH and high ammonium concentration can enrich nitrifying bacteria in the PE carriers. If the supernatant of the anaerobic digester was treated in a side-stream system, the nitrogen loading to the mainstream BNR system was solved and WWTPs could be operated more economically and effectively. Therefore, the sludge digesting liquor could be used as an easily available nitrogen resource for this novel strategy in WWTPs.
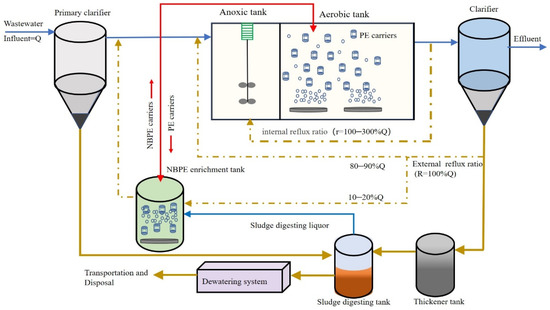
Figure 7.
Schematic diagram for applying NBPE carrier in WWTPs to enhance nitrogen removal in the mainstream.
4. Conclusions
A pilot-scale IFAS system coupled with PE and NBPE carriers was first explored for long-term (200 days) nitrogen removal from municipal wastewater. Stable nitrification was realized in an IFAS system with an ammonia removal rate of 73.0–98.7% under the condition of 200–400% shock load. Meanwhile, the nitrifying bacteria abundance of NBPE carriers was maintained at 23.17% compared with 6.69% of nitrifying bacteria in the inoculated sludge. A high ammonia removal efficiency of 95.3 ± 3.8% was acquired at a 300% shock load, with the influent COD and NH4+-N of 179.2 ± 44 mg/L and 16.1 ± 4.1 mg/L, respectively. The IFAS system coupled with NBPE carriers provides good resistance to shock loading in domestic wastewater treatment with an HRT of 1.8 h. The biofilm on the NBPE carrier of the IFAS system under a shock load of 400% contributed to 71.4% of nitrification and almost complete conversion of ammonium. The IFAS system displayed better removal efficiency for organics and nitrogen compared to the A/O system. The results of this study highlight the possibility of operating IFAS processes under low HRT and could meet the stringent effluent standard. These novel methods, as an effective side-stream treatment process of sludge digesting liquor, can greatly improve the nitrogen removal performance and treatment capacity of WWTPs under the condition of shock load.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su14127193/s1, Table S1. Characteristics of domestic wastewater for IFAS and A/O systems; Table S2. Characteristics of synthetic sludge digesting liquor for SBBR system; Table S3. Richness and diversity of AS and biofilm samples in IFAS and A/O system; Figure S1. Curves of NH4+-N, NO3−-N, NO2−-N, pH, DO and temperature with time in a dynamic cycle of the SBBR system; Figure S2. Photos of fresh PE carriers, normal PE carriers and NBPE carriers.
Author Contributions
S.G. contributed to the conceptualization, methodology development, data curation and analyses, visualization and original manuscript drafting. L.L. contributed to methodology development, resource allocation, data curation and analyses and reviewing the manuscript. X.Z. contributed to data curation and analyses and reviewing the manuscript. J.Q. contributed to funding acquisition and reviewing the manuscript. Z.Z. contributed to the conceptualization, project administration and reviewing the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Jiangxi Provincial Technological Innovation Guidance Program (No. 2021BDH81029) and the Research and Development Program of Power China Zhongnan Engineering Corporation limited (No. YF-A-2020-46).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| IFAS | Integrated fixed-film activated sludge technology |
| A/O | Anoxic/aerobic process |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| PUF | Polyurethane foam |
| NBPE | Nitrifying bacteria polyethylene carrier |
| AS | Activated sludge |
| HDB | Heterotrophic denitrifying bacteria |
| HNAD | Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification bacteria |
| AOB | Ammonia oxidizing bacteria |
| NOB | Nitrite oxidizing bacteria |
| HRT | Hydraulic retention time |
| WWTPs | Wastewater treatment plants |
| DO | Dissolved oxygen |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| OTU | Operational taxonomic units |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| DTC | Designed treatment capacity |
| FA | Free ammonia |
| R | Sludge reflux ratio |
| RT | Total recycle ratio of system, including R and nitrifying recycle ratio |
| EBPR | Enhanced biological phosphorus removal |
| SND | Simultaneous nitrification and denitrification |
| HR | Heterotrophic respiration |
| HD | Heterotrophic denitrification |
References
- Di Biase, A.; Kowalski, M.S.; Devlin, T.R.; Oleszkiewicz, J.A. Moving bed biofilm reactor technology in municipal wastewater treatment: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 247, 849–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.H.; Yang, W.N.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.S.; Jin, P.K.; Dzakpasu, M.; Yang, S.J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.C.; Ao, D. Current status of urban wastewater treatment plants in China. Environ. Int. 2016, 92–93, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.B.; Shao, Y.T.; Wang, H.C.; Liu, G.H.; Qi, L.; Xu, X.L.; Liu, S. Current operation state of wastewater treatment plants in urban China. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.Y.; Wang, X.M.; Liu, H.Q.; Yu, H.Q.; Li, W.W. Optimizing operation of municipal wastewater treatment plants in China: The remaining barriers and future implications. Environ. Int. 2019, 129, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Chiu, Y.H.; Liu, F.P. Measuring the Performance of Wastewater Treatment in China. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, S.Y.; Shin, J.; Ryu, J. Expand, relocate, or underground? Social acceptance of upgrading wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 45618–45628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, B.; Li, X. A continuous plug-flow anaerobic/aerobic/anoxic/aerobic (AOAO) process treating low COD/TIN domestic sewage: Realization of partial nitrification and extremely advanced nitrogen removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 145387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; Park, H.; Cho, K.H.; Park, J.M. Long term assessment of factors affecting nitrifying bacteria communities and N-removal in a full-scale biological process treating high strength hazardous wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 134, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiopoulou, E.; Aivasidis, A. A modified UCT method for biological nutrient removal: Configuration and performance. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulazzaky, M.A.; Abdullah, N.H.; Mohd Yusoff, A.R.; Paul, E. Conditioning the alternating aerobic–anoxic process to enhance the removal of inorganic nitrogen pollution from a municipal wastewater in France. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 100, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gu, W.; Liu, Y.; Liang, P.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X. Challenges, solutions and prospects of mainstream anammox-based process for municipal wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulazzaky, M.A.; Nuid, M.; Aris, A.; Muda, K. Mass transfer kinetics of biosorption of nitrogenous matter from palm oil mill effluent by aerobic granules in sequencing batch reactor. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 2151–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zheng, L.; Ye, C.; Zhou, Z.; Ni, B.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H. Unveiling organic loading shock-resistant mechanism in a pilot-scale moving bed biofilm reactor-assisted dual-anaerobic-anoxic/oxic system for effective municipal wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.M.; Jiang, S.F.; Zhang, Z.H.; Ye, Q.Q.; Zhang, Y.C.; Zhou, J.H.; Hong, Q.K.; Yu, J.M.; Wang, H.Y. Impact of static biocarriers on the microbial community, nitrogen removal and membrane fouling in submerged membrane bioreactor at different COD:N ratios. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.L.; Zhao, Y.X.; Yang, K.C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.G.; Ji, M. Application oriented bioaugmentation processes: Mechanism, performance improvement and scale-up. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuarrie, J.P.; Boltz, J.P. Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor Technology: Process Applications, Design, and Performance. Water Environ. Res. 2011, 83, 560–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, S.; Bilad, M.R.; Man, Z.; Wibisono, Y.; Jaafar, J.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Khan, A.L.; Aslam, M. Recent progress in integrated fixed-film activated sludge process for wastewater treatment: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 268, 110718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo-Altamirano, M.J.; Maza-Márquez, P.; Pérez, S.; Rodelas, B.; Pozo, C.; Osorio, F. Fate of pharmaceutically active compounds in a pilot-scale A2O integrated fixed-film activated sludge (IFAS) process treating municipal wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Diaz, J.C.; Monteoliva-Garcia, A.; Martin-Pascual, J.; Munio, M.M.; Garcia-Mesa, J.J.; Poyatos, J.M. Moving bed biofilm reactor as an alternative wastewater treatment process for nutrient removal and recovery in the circular economy model. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299, 122631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, E.; Mehrabani Zeinabad, A.; Borghei, S.M.; Torresi, E.; Muñoz Sierra, J. Optimising nutrient removal of a hybrid five-stage Bardenpho and moving bed biofilm reactor process using response surface methodology. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Peng, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Zhao, W.; Zeng, W. Optimization denitrifying phosphorus removal at different hydraulic retention times in a novel anaerobic anoxic oxic-biological contact oxidation process. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 106, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Mohammed, A.; Liu, Y. Wastewater ammonia removal using an integrated fixed-film activated sludge-sequencing batch biofilm reactor (IFAS-SBR): Comparison of suspended flocs and attached biofilm. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 116, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, M.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Peng, Y. Integrated fixed-biofilm activated sludge reactor as a powerful tool to enrich anammox biofilm and granular sludge. Chemosphere 2015, 140, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyva-Díaz, J.C.; Martín-Pascual, J.; Poyatos, J.M. Moving bed biofilm reactor to treat wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 881–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, L.; Peng, D.; Wei, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Yu, L. Nitrogen removal from an AAO pilot plant with nitrifier bioaugmentation after seasonal deterioration. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 52, 5136–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, L.Y.; Wan, Q.; Wang, Z.F.; Wang, B.B.; Zhang, X.Y.; Hou, Y.P. Effect of long-term bioaugmentation on nitrogen removal and microbial ecology for an A(2)O pilot-scale plant operated in low SRT. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 55, 1567–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuda, A.; Zieminski, K. Challenges in Treatment of Digestate Liquid Fraction from Biogas Plant. Performance of Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Activity in Activated Sludge Process. Energies 2021, 14, 7321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aponte-Morales, V.E.; Payne, K.A.; Cunningham, J.A.; Ergas, S.J. Bioregeneration of Chabazite During Nitrification of Centrate from Anaerobically Digested Livestock Waste: Experimental and Modeling Studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4090–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fux, C.; Velten, S.; Carozzi, V.; Solley, D.; Keller, J. Efficient and stable nitritation and denitritation of ammonium-rich sludge dewatering liquor using an SBR with continuous loading. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2765–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.L.; Duan, H.R.; Wei, W.; Ni, B.J.; Laloo, A.; Yuan, Z.G. Achieving Stable Mainstream Nitrogen Removal via the Nitrite Pathway by Sludge Treatment Using Free Ammonia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9800–9807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, S.Y.; Stenstrom, M.K. Bioaugmentation to Improve Nitrification in Activated Sludge Treatment. Water Environ. Res. 2010, 82, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenstrom, F.; Jansen, J.L. Impact on nitrifiers of full-scale bioaugmentation. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 3079–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.F.; Peng, D.C.; Pan, R.L. Shifts in Nitrification Kinetics and Microbial Community during Bioaugmentation of Activated Sludge with Nitrifiers Enriched on Sludge Reject Water. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 691894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.W.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.S.; Peng, L.; Wang, D.B.; Ni, B.J. The roles of free ammonia (FA) in biological wastewater treatment processes: A review. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthonisen, A.C.; Loehr, R.C.; Prakasam, T.B.S.; Srinath, E.G. Inhibition of nitrification by ammonia and nitrous-acid. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1976, 48, 835–852. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Shen, M.; Li, J.; Huang, S.; Li, Z.; Yan, Z.; Peng, Y. Cooperation between partial-nitrification, complete ammonia oxidation (comammox), and anaerobic ammonia oxidation (anammox) in sludge digestion liquid for nitrogen removal. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, S.; Gilbert, E.M.; Vlaeminck, S.E.; Joss, A.; Horn, H.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Full-scale partial nitritation/anammox experiences—An application survey. Water Res. 2014, 55, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Padin, J.R.; Pozo, M.J.; Jarpa, M.; Figueroa, M.; Franco, A.; Mosquera-Corral, A.; Campos, J.L.; Mendez, R. Treatment of anaerobic sludge digester effluents by the CANON process in an air pulsing SBR. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wett, B. Development and implementation of a robust deammonification process. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 56, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, G.; Zhou, L.; Yu, H.; Yang, F. Start-up of a full-scale SNAD-MBBR process for treating sludge digester liquor. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 343, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raper, E.; Stephenson, T.; Anderson, D.R.; Fisher, R.; Soares, A. Industrial wastewater treatment through bioaugmentation. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 118, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Monteoliva-García, A.; Martín-Pascual, J.; Muñío, M.M.; Poyatos, J.M. Effects of carrier addition on water quality and pharmaceutical removal capacity of a membrane bioreactor—Advanced oxidation process combined treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, T.; Peng, Z.; Jiang, K.; Niu, N.; Wang, J.; Liu, A. Nitrogen removal characteristics of biofilms in each area of a full-scale AAO oxidation ditch process. Chemosphere 2022, 302, 134871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pylro, V.S.; Roesch, L.F.W.; Morais, D.K.; Clark, I.M.; Hirsch, P.R.; Tótola, M.R. Data analysis for 16S microbial profiling from different benchtop sequencing platforms. J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 107, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-s.; Gellner, J.W.; Boltz, J.P.; Freudenberg, R.G.; Gunsch, C.K.; Schuler, A.J. Effects of integrated fixed film activated sludge media on activated sludge settling in biological nutrient removal systems. Water Res. 2010, 44, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regmi, P.; Thomas, W.; Schafran, G.; Bott, C.; Rutherford, B.; Waltrip, D. Nitrogen removal assessment through nitrification rates and media biofilm accumulation in an IFAS process demonstration study. Water Res. 2011, 45, 6699–6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, X.; Chen, S. Enhancing nitrogen removal efficiency and reducing nitrate liquor recirculation ratio by improving simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in integrated fixed-film activated sludge (IFAS) process. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 73, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Schuler, A.J.; Gunsch, C.K.; Pei, R.; Gellner, J.; Boltz, J.P.; Freudenberg, R.G.; Dodson, R. Comparison of Conventional and Integrated Fixed-Film Activated Sludge Systems: Attached- and Suspended-Growth Functions and Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction Measurements. Water Environ. Res. 2011, 83, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Díaz, J.C.; Martín-Pascual, J.; Muñío, M.M.; González-López, J.; Hontoria, E.; Poyatos, J.M. Comparative kinetics of hybrid and pure moving bed reactor-membrane bioreactors. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 70, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, G.; Capodici, M.; Cosenza, A.; Cina, P.; Di Trapani, D.; Puglia, A.M.; Ekama, G.A. Bacterial community structure and removal performances in IFAS-MBRs: A pilot plant case study. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 198, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Li, J.; Wang, R. Nitrogen removal performance and microbial community structure dynamics response to carbon nitrogen ratio in a compact suspended carrier biofilm reactor. Ecol. Eng. 2008, 32, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Trapani, D.; Christensson, M.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G.; Ødegaard, H. Performance of a hybrid activated sludge/biofilm process for wastewater treatment in a cold climate region: Influence of operating conditions. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 77, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergine, P.; Salerno, C.; Berardi, G.; Pollice, A. Sludge cake and biofilm formation as valuable tools in wastewater treatment by coupling Integrated Fixed-film Activated Sludge (IFAS) with Self Forming Dynamic Membrane BioReactors (SFD-MBR). Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 268, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Z.; Wang, Q.; She, Z.; Gao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, L.; Jin, C. Nitrogen removal pathway and dynamics of microbial community with the increase of salinity in simultaneous nitrification and denitrification process. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Yang, H.; Zhang, F.; Su, Y.; Wang, S.L. Activated sludge under free ammonia treatment using gel immobilization technology for long-term partial nitrification with different initial biomass. Process Biochem. 2020, 99, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Zheng, H.; Chu, L.; Zhang, C.; Chen, H.; Kong, X.; Xing, X.-H. Effects of packing rates of cubic-shaped polyurethane foam carriers on the microbial community and the removal of organics and nitrogen in moving bed biofilm reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 117, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.P.; Ye, J.Y.; Xiang, H.W.; Jiang, J.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Li, Y.Y. Enhanced nitrogen removal from low C/N wastewater using biodegradable and inert carriers: Performance and microbial shift. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 300, 122658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, J.; Ma, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, B.; Peng, Y. Improving municipal wastewater nitrogen and phosphorous removal by feeding sludge fermentation products to sequencing batch reactor (SBR). Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 222, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xing, D.; Ren, N. p-Nitrophenol degradation and microbial community structure in biocathode bioelectrochemical system. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 89821–89826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daims, H.; Lebedeva, E.V.; Pjevac, P.; Han, P.; Herbold, C.; Albertsen, M.; Jehmlich, N.; Palatinszky, M.; Vierheilig, J.; Bulaev, A.; et al. Complete nitrification by Nitrospira bacteria. Nature 2015, 528, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kessel, M.A.H.J.; Speth, D.R.; Albertsen, M.; Nielsen, P.H.; Op den Camp, H.J.M.; Kartal, B.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Lucker, S. Complete nitrification by a single microorganism. Nature 2015, 528, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cao, G.; Feng, N.; Pan, Y. Bioaugmentation of two-stage aerobic sequencing batch reactor with mixed strains for high nitrate nitrogen wastewater treatment. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 28, 3103–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, F.; Xia, Y.; Guo, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, T. Taxonomic relatedness shapes bacterial assembly in activated sludge of globally distributed wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2421–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretti, P.; Choubert, J.M.; Canler, J.P.; Petrimaux, O.; Buffiere, P.; Lessard, P. Understanding the contribution of biofilm in an integrated fixed-film-activated sludge system (IFAS) designed for nitrogen removal. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 71, 1500–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIlroy, S.J.; Starnawska, A.; Starnawski, P.; Saunders, A.M.; Nierychlo, M.; Nielsen, P.H.; Nielsen, J.L. Identification of active denitrifiers in full-scale nutrient removal wastewater treatment systems. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, K.; Qiang, J.; Pang, H.; Yuan, Y.; An, Y.; Zhou, C.; Ye, J.; Wu, Z. Mainstream nitrogen separation and side-stream removal to reduce discharge and footprint of wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javid, A.H.; Hassani, A.H.; Ghanbari, B.; Yaghmaeian, K. Feasibility of Utilizing Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor to Upgrade and Retrofit Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2013, 7, 963–972. [Google Scholar]
- Germain, E.; Bancroft, L.; Dawson, A.; Hinrichs, C.; Fricker, L.; Pearce, P. Evaluation of hybrid processes for nitrification by comparing MBBR/AS and IFAS configurations. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 55, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Trapani, D.; Mannina, G.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Comparison between hybrid moving bed biofilm reactor and activated sludge system: A pilot plant experiment. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).