Abstract
The engineering properties of particulate materials are the collective manifestation of interactions among their constituent particles and are structures within which particles adopt their spatial arrangement. For the first time in the literature, this paper employs an extended concept of ‘fractals’ to show that materials constituting particles of a certain size can be rationalized in three universal fractals. Within each fractal, materials build repeatable, reproducible, and predictable traits, and exhibit the stress-strain behaviors of nondifferentiable, self-similar trajectories. We present experimental evidence for such repeatable traits by subjecting six different particulate materials to static undrained isotropic, static undrained anisotropic, and cyclic undrained isotropic stresses. This paper shows that universal fractals are associated with fractal structures; herein, we explore the matters that influence their spatial arrangement. Within the context of sustainable design, ways of engineering natural particulate systems to improve a product’s physical and hydromechanical properties are already well established. In this review, a novel extended concept of fractals is introduced to inform the biomimetic design of particulate systems, to show how biomimicry can benefit in preserving general behavioral traits, and how biomimicry can offer predicated forms, thereby enhancing the design efficiency. To pursue such an ideal, processes that lead to the engineering of natural materials should not compromise their loyalty to the parent universal fractal.
1. Introduction
It has been intuitively established that the behavior of particulate materials varies within and depends on their constituent elements. These include the skeleton (i.e., frame particles), binders (i.e., the fines fraction, capillary fluid, and charged compounds), void spaces, and the structure (or form) that contains the three components.
1.1. Forms and Behavioral Traits
The principal aim of this contribution is to establish the significance and rationalize the main typologies of structures (forms) in natural particulate matter, to relax their randomness and sort them into certain ‘universal fractal’ ranges, and to identify the behavioral traits of ‘universal fractals’ and find ways to imitate them. Identifying such behavioral traits can help to predict the behaviors of natural and engineered materials at the macroscale. This approach is broadly known as biomimicry and is discussed at length in the following sections.
A recent work [1] sets out the significance of the size and shape of the skeleton and binders (i.e., particles), raising the question of whether the imitation of the resulting structures has any interest or value in a geomorphological context. They correlated the random shape of loessic depression landscapes with the random shape of the soil particles constructing the landscape. Loess is a porous, particulate material made from predominantly silt-sized particles. It was transported by winds, typically from glacial sources, and deposited by the air on land, thickening and becoming lightly cemented over time. Under this cumulative weight, loess can structurally collapse on wetting and form closed depression landscapes, the likes of which are reported across the globe and include features in the Titel Plateau in Siberia [2], Timaru in New Zealand [3], the Meerdaal Forest in Belgium [4], Norfolk in eastern England [5], Gansu Province in China [6] and the Lorraine Plain in northeastern France [7]. Fagg et al. [1] used the Zingg particle-shape system to determine a mean random shape for loess particles. They referred to a simple Monte Carlo analysis conducted in an earlier work [8] that simulated the formation and collapse of metastable loessic random structures. Land depressions are the product of such a structural collapse; on that basis, Fagg et al. [1] extended the Zingg system to determine a mean random shape of closed depressions in loessic landscapes across select areas in southern Romania and associated these shapes to that of loess particles. Interestingly, Fagg et al. [1] proposed a Zingg III with a 2:1 side ratio that is common between land depressions and their constituent soil particles. The work of Fagg et al. [1] is a manifestation of how an awareness of the size and shape of particles, voids, and the resulting structures can explain the behavioral traits of materials in general.
The impacts of structure on behavioral traits extend to non-geological disciplines. Zuriguel et al. [9] studied the effect of bulk grain structure on the outlets of silos that discharge materials. They studied the arch structures that cause jamming during discharge by gravity and block the granular flow. Zuriguel et al. [10] rethought the design of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells (PEFCs) by imitating the fractal geometry of the upper airway tree of the human lung and its hierarchical network. They imitated the structure of the lung’s natural fluid distribution system (i.e., the respiratory organs) to overcome mass transport issues in PEFCs. Fractal geometry, branching, and the mechanical functions of trees were discussed by the authors of [11] and extended to architectural forms in the construction sector. Tang and Marangoni [12] used fractal scaling models to link the mechanical properties and microstructure of fat in food. Similar contributions include the effect of structure on the properties of seeds, flours, starches, and legumes [13], barley [14], ceramics [15], and proteins [16]. A good, recently published study that contains several more examples of structures having an impact on behavior is by West [17]; the problems of scale, fractals, and forms are exhaustively discussed across a handful of disciplines.
1.2. Biomimicry, Sustainability, and Design
The principal aim of this manuscript is to identify and reduce the randomness of natural structures in the context of granular materials. This will be achieved by organizing natural forms (i.e., structures) in ‘universal fractals’ and building an awareness of their implications on the behavior of granular materials in general. Associating fractal forms with behavior allows designers to have an appreciation of granular materials’ properties. Designers can imitate certain fractal forms to manipulate the behavior of materials in general. It also allows practitioners to predict ‘forms’ at larger or smaller scales.
1.2.1. Fractals for Relaxing Randomness
Particulate matters vary in size, shape, and crystalline integrity. Despite their inherent variability, they have a tendency to break. Firstly, of relevance for engineered granular materials is their long-term behavior and how sustainable their design and subsequent existence would be [18]. Secondly, the ‘tendency-to-break’ factor could be used to make provision for associating certain particle-size ranges (i.e., universal ‘fractals’) with certain behavioral traits. Both directions lend a stimulus to the particle breakage phenomenon.
In the food industry, in dairy powders, breakage during processing, transportation, and storage leads to the crystallization of lactose and a decrease in flowability. Breakage can also destabilize milk proteins and negatively impact their solubility, emulsifying, and foaming properties [19]. Similar challenges extend to the beverage industry. The dissolution of instant powders (e.g., coffee) in water is associated with the sorting and particle size distribution of agglomerates [20]. Both phenomena are highly dependent on particle comminution, drivers, and mechanisms. In the pharmacological industry, and for powdered drugs in particular, the physical properties—including crystal shape, sorting, texture, form, and size—of an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) have a direct influence on their dissolution rate in the gut and, thereby, on their overall bio-performance [21]. However, the properties of APIs are highly variable. The question that follows is as to whether and how an awareness of particle size, associated with the chance to survive (or the chance to break), has any value in terms of design efficiency and sustainability. Particle breakage under controlled laboratory conditions can provide an answer. The controlled crushing of particles yields fragments of finer solids and voids that are repeatable in structure (i.e., aspect ratio, shape, and sorting) and structure-dependent hydromechanical properties. These are ‘fractals’ that repeat at different scales, rationalizing the inherent randomness and, thereby, enhancing the design efficiency.
1.2.2. Imitation of Fractals
Biomimicry is the imitation (mimesis) of life (bios). Biomimetic engineering, from an Aristotelian viewpoint, involves studying and abstracting four imitable traits from nature: forms, materials, generative processes, and functions [22]. These four traits are discussed at length in Section 4 of this paper. ‘Form’, in the context of particulate matters, is the micro-structure. The imitation of forms in creating engineered systems does not necessarily need the imitation of matters, processes, or functions. This highlights the significance of form. Abstraction of form can occur at two levels; that is, the abstraction of natural forms and the abstraction of abstraction. Section 3 will show that natural forms can be rationalized in four universal fractals. By utilizing abstraction of form, one can imitate these natural fractals. In Section 3, universal fractals are shown to exhibit universal functions. Imitating functions would be an abstraction of abstraction. The present research concerns the abstraction of natural forms.
On a broader scale, a form can be a macro-structure. A prime example of fractal elements is the Eiffel Tower, from an architectural point of view. In building the Eiffel Tower, very few large, thick, and heavy beams are used. Instead, the tower is predominantly made up of carefully oriented thin, slender, and light beams ‘in a self-similar kind of way’ with three levels of hierarchy (Figure 1e), creating a self-supporting meshwork of linear elements that repeat themselves in the same form at different scales. While the scale changes, the general traits are preserved across all levels. A second example of abstracted forms is the Shinkansen 500-series high-speed train in Japan (Figure 1d), which imitates several forms found in birds. Owls inspired the design of the pantograph—that is, the rig that connects the train to the electrical wires above. The design was modeled after owl feathers, reducing noise by using the same curvature and shape (Figure 1a). The Adélie penguin, whose smooth body allows it to swim underwater and slide effortlessly, inspired the pantograph’s supporting shaft, which was redesigned for lower wind resistance (Figure 1b). The kingfisher is a bird that dives to catch its prey. The unique shape of its beak allows it to enter the water with barely a splash (Figure 1c). That form inspired the design of the bullet-shaped tip of the Shinkansen 500 (Figure 1d).
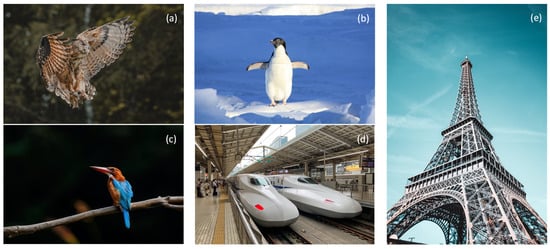
Figure 1.
Examples of imitating form (i.e., structure) in the sustainable design of engineered systems: (a) owl feathers, imitated in the design of the pantograph wing of a Shinkasen 500 series train; (b) Adélie penguin body form, imitated in the design of the pantograph base of a Shinkasen 500 series train; (c) the beak of the kingfisher, imitated to design the general form of the Shinkasen 500 series train; (d) Shinkasen 500 series trains; (e) the hierarchy of fractal elements in the Eiffel Tower (all images have Pexels Licenses).
1.3. Forms and Behavioral Traits: A Particulate Matters Perspective
Structure is defined here as the packing quality of, and mutual relationship between, particles that constitute a particulate matter. Once determined, structure can inform the design of particulate materials, the types, shapes, sorting, size, and relative abundance of inclusions, and ways of their placement in the natural medium. Through such an informed design, the general physio-mechanical behavioral traits of engineered materials can be predicted. This makes the design efficient, less resource-demanding, and more reliable.
In the next sections, an extended concept of ‘fractals’ will be introduced to enhance the efficiency of a design. The paper will show that despite inherent variations among particulate materials and how they respond to stress, matters containing certain predominant mode sizes exhibit stress-strain behaviors of nondifferentiable, self-similar trajectories.
2. Materials and Methods
The foundation for the ideas developed and discussed herein stems from experiments exclusively performed as part of this paper and the research conducted by the authors in recent years, also the extended double porosity and fractality concepts developed by the authors. The fractality concept was developed through the controlled crushing of ten quartz sand sizes (63 μm to 2 mm), including vein sand and sand with crystallin cleavage planes. Materials were collected from Golden Beach (Cyprus), Besparmak Mountain (Cyprus), Western Cape (South Africa), Bedfordshire (2 grades from England), Urmia (Iran), Firoozkooh (3 grades from Iran), and Craig Rofft (Wales)—see [23,24]. Materials were ground to a broad range of silt-sized powder (<63 μm) using a range of mills, including a Retsch RM200 mortar mill and a high-energy Siebtechnik disc mill. The intact and ground material samples were then subjected to grading. For each batch, a dry sieving method was used for >63 μm particles. A laser diffraction sensor HELOS/KR, gravity disperser GRADIS/L, and dosing unit VIBRI/L were utilized for grading the particles <63 μm. From the myriad particle and mode size distribution diagrams, pronounced and gap size ranges were identified and analyzed to attain universal favored and unfavored particle sizes—see also Figure 2a.
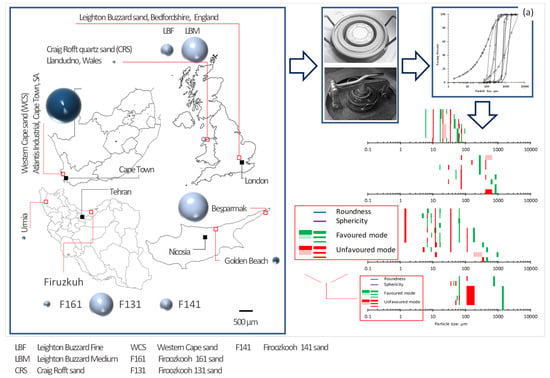
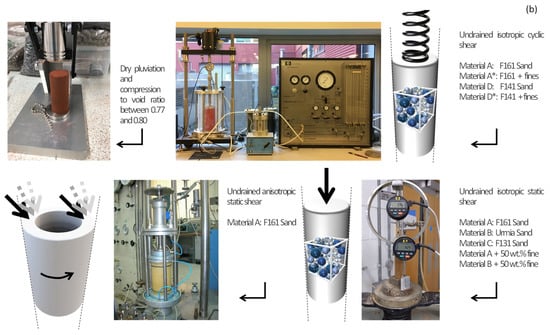
Figure 2.
Methods illustrated: (a) ten predominantly quartz-based particulate matter samples were collected, crushed into a range of grades, and analyzed by sieving and laser diffraction spectroscopy to determine the universal fractals; (b) mechanical testing on eight testing powders: specimen preparation, undrained isotropic and anisotropic static shearing, and undrained isotropic cyclic shearing.
Three testing programs were conducted on six selected materials. All materials were chemically inert, rigid, and sized from 2 μm to 2 mm in equivalent diameter—that is, various combinations of intact sands and mixtures of intact and ground sands. In the three testing programs, undrained compressive triaxial tests were exclusively conducted for the purposes of this research. The materials and methods associated with these tests are discussed in Section 2.1. The data associated with the undrained isotropic cyclic triaxial and undrained anisotropic static triaxial tests are imported from [25,26]. Figure 2b illustrates a graphical summary of the mechanical testing program.
2.1. Experiment Method
The test specimens used were all sized 36 mm in diameter, 80 mm in height, and compacted to a high void ratio of 0.77 to 0.80 via dry pluviation. Quartz powder was rained down through the air into latex-membrane-lined split-molds placed on the pedestal of a triaxial apparatus (Bishop, cyclic, and hollow-cylinder torsion (HCTA)). A negative 15 kPa pressure was applied to split-molds to assist in the removal of their contents. The triaxial cell was then filled with de-aired water and the cell pressure was gradually increased to 50 kPa. Cell pressure was increased gradually to target cell pressure while a mixture of CO2 gas and de-aired water was flushed into the specimen from the bottom. Specimens were deemed fully saturated when they reached a B-Skempton value of 0.96. Further experimental particulars are discussed alongside the results for the convenience of readers.
3. Fractals at Particle Level
3.1. Universal Fractals for Dry Crystalline Solid Particles
It is tempting to define brackets of ‘fractal size’ for particles. Three levels of ‘fractal size brackets’ are proposed here: particles (of a certain size) that never break, that almost certainly break, and that almost certainly heal and re-aggregate, following breakage. It is even more tempting to have these ‘fractal size’ brackets as the universal level for any particulate matter, regardless of their crystalline quality and chemical composition.
Reference is made to two pivotal studies here, in the development of a universal model for fractal sizes.
Assadi-Langroudi et al. [23] referred to a series of interrupted grinding experiments—using a high-energy Siebtechnik agate disc mill—on dry-clean crystalline quartz powders. The parent material had a pronounced mode size of 500 µm (0.5 mm), , , and . Particle breakdown was found to occur at the entire range of applied stresses and was attributed to so-called ‘Moss defects’, which are essentially sets of internal defective planes of weakness.
In pharmacological disciplines, Moss defects are known as crystal lattice defects [27]. The term ‘Moss defects’ comes from the field of geology, and they are named for the author of [28]; these are eutectic features, the legacy of tensile stresses originated from the transition of displacive β-quartz to α-quartz during cooling. Arguably, defect planes are self-forming and control particle size, texture, shape, and sorting, giving to the particle assembly a degree of inherent anisotropy. For all levels of applied grinding energy, Assadi-Langroudi et al. [23] referred to visible defect planes (microfractures), a unique maximum particle size, a fractal dimension of between 1.70 to 2.51, a distinctive 8:5:2 size ratio—that is, a Zingg class 3, as defined in [29]—and certain favored and unfavored mode sizes for particles that are intrinsically breakable and non-breakable. Through the comminution process—note that particulate matters of any type go through comminution through their lifetime—certain particle sizes continuously gain and lose population. This is a quality of self-healing. At the macro level, these particles break into finer ones, before self-healing and re-aggregating to form ‘welded’ coagulates of the original size. Assadi-Langroudi and Theron [24] quantified these ‘fractal sizes’ as 5, 7, 12, 316, and 610 µm of particles (also 440 µm and 720 µm, as reported by [30]); as 68 µm in particles generated from aeolian collision, thermolysis, and chemical degradation; and as 20 and 75 µm in particles generated from cyclic freeze-thaw processes and low-energy abrasion. These were ‘inherently breakable’ particles, the first of the three ‘universal fractals’. Assadi-Langroudi and Theron [24] showed that particles sized 10–17 µm, 45–47 µm, and 56–58 µm are ‘inherently unbreakable’, regardless of their type and origin. These particles survive the energies applied to them in the erosive environment and have a roundness, R, of 0.25 ± 0.02. On the other side of the spectrum, particles sized 30–34 µm and 106–193 µm are ‘inherently breakable’, and there is a universal shortage of these sizes. Inherently breakable particles have a sphericity, S, of 0.68 ± 0.03. In the interests of simplicity, the term ‘universal fractals’ is used henceforth where reference is made to powders constituting particles with a mean size within those ranges of the three ‘fractal sizes’.
3.1.1. Steady-State Traits
The storage and transportation of powders change the stress environment and may lead to the material’s softening or hardening with strain.
Material may partially flow. This occurs when the deviatoric stress increases to a peak and the material undergoes contraction. At peak deviatoric stress, particles lose their interparticle support, leading to excessive deformation and, thereby, failure. Upon failure, the deviatoric stress decreases with further straining until the material reaches the steady state, generally referred to as the quasi-steady state (). The marks a transition from contractive to dilative behavior. The can be found in data, where is the mean normal stress and is a function of effective major and minor principal stresses, , and is the effective deviatoric stress or the difference between major and minor principal stresses, . The occurs when reaches the minimum value. Further strain leads to an increase in deviatoric stress () toward the ultimate steady state (). Partial flow is common in saturated, medium-dense materials.
Conversely, material may never flow. Upon and during loading, the deviatoric stress increases with the strain as the material contracts. The effective mean normal stress rate () initially increases, then decreases to a minimum. This coincides with the transition from contractive to dilative behavior, which is broadly known as phase transformation (). Further straining leads to an increase in deviatoric stress () toward the ultimate steady state (). Seeing no flow is common in saturated, dense materials.
Establishing whether a powdered material partially flows or hardens with strain is central to quality control and the sustainability of design. This step, however, needs substantial testing resources. In fact, determining particle size distribution is straightforward. Once determined, it is tempting to use the mean particle size as an index of stress-strain behavior. Three stressing scenarios are discussed: isotropic static stresses, anisotropic static stresses, and isotropic cyclic stresses. Undrained triaxial shearing simulates the static compression environment, as occurs during the storage of bulk granular materials. In the civil engineering context, this simple experiment provides data for the design of conventional foundations, backfills, and slopes. Undrained hollow-cylinder torsional triaxial (HCTA) shearing simulates confined static anisotropic stress environments, where various combinations of compressive and torsional stresses are applied to materials. This benefits the design of sustainably engineered granular materials with strong levels of inherent anisotropy, as well as multi-modal and composite materials, along with any granular material that would be subjected to out-of-plane stresses. Undrained triaxial cyclic shearing simulates confined cyclic compression environments, as happens during the transportation of bulk granular materials, and when bulk granular materials are subjected to some form of transitional loading at high frequency (e.g., traffic loading for rail-track subgrades).
3.1.2. Loading Scenarios
- Scenario 1: Isotropic static stresses
Ghadr and Assadi-Langroudi [31] explored the steady states for two loosely compacted powders, here referred to as A and B. Material A was sized 0.3 mm, putting it in the ‘self-healing’ bracket. Material B was sized 0.15 mm, putting it in the ‘inherently breakable’ bracket, with particles that were relatively rounder and more spherical in shape. A third powder, material C, was adopted as a reference, with a mean size belonging to none of the universal fractal ranges. The mean particle size for material C was 0.92 mm, the largest and the most angular of all the samples. The three materials were loosely compacted to achieve a high void ratio of 0.77 to 0.80—that is, the volume of voids to the space occupied by solids when saturated, consolidated, confined, and sheared under undrained conditions.
Figure 3a presents the variation of with —known as the stress path—for materials A, B, and C. The diagram implies that irrespective of particle size and the initial effective mean principal stress, a non-flow (NF) deformation with strain hardening (HS) governs the behavior of unimodal particulate materials. Powders that do not belong to any universal fractal range develop greater strength at phase transformation ()—this is the onset of flow and instability, with greater mean stress at phase transformation (), and the least post-peak softening. On the other side of the spectrum are those powders with ‘inherently breakable’ particles. These develop the greatest post-peak softening behavior and have the least strength at phase transformation ().
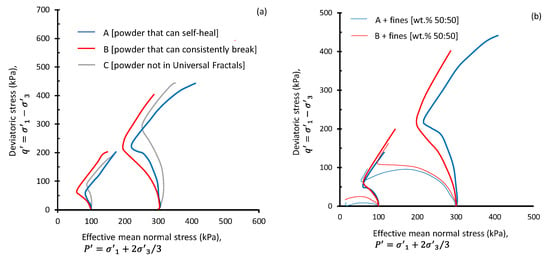
Figure 3.
Stress path on the plane: (a) three powders compressed to an identical loose state: Powder A, constituting particles fitting the ‘self-healing’ universal fractal, Powder B, constituting particles fitting the ‘inherently breakable’ universal fractal model, Powder C, constituting particles fitting none of the universal fractals; (b) Powders A and B, mixed with 50 wt % of the 2–63 μm fines fraction.
The mechanisms leading to flow become more complex for powders constituting particles of more than one pronounced mode size. This may be the state of any particulate material following aging or breakdown. This may also happen in a bimodal material, such as powdered drugs that constitute two or more active pharmaceutical ingredients, coffee beans, seeds, etc. To simulate bimodal materials in the laboratory, and via a new set of experiments developed exclusively for this study, a subset of Powders A and B were dried and ground in a benchtop Retsch RM200 mortar mill. Grinding consisted of applying 100 impacts per minute to 70 g batches of dried powder, at 50 Hz frequency, over 6-min grinding periods with no cooling-time interruption. Gravity sedimentation was then employed to separate the sub-2 μm and >63 μm fractions from the ground material. The output screened fines were then dried in an oven for 24 h up to 105 °C, then cooled and mixed with the parent material (i.e., Powders A and B) in a 1:1 weight ratio. The mixtures were saturated in distilled water, statically compressed to a high 0.77 to 0.80 void ratio, isotopically consolidated, and then sheared under undrained conditions. Figure 3b presents the variation of with for materials A and B, each mixed at 50% by weight of fines. The non-flow behavior previously seen in Powders A and B changed to partial flow and strain softening for all materials. It was established in Figure 3a that powders with ‘inherently breakable’ particles develop the least strength at the phase transformation (). In Figure 3b and when mixed with fines, powders with ‘inherently breakable’ particles develop the maximum deviatoric stress at the phase transformation stage.
- Scenario 2: Anisotropic static stresses
The crystal lattice defects that cause universal fractals induce a quality of inherent anisotropy in particulate matters. That, combined with the anisotropic nature of stresses during storage and transportation, requires one to ascertain the true effect of anisotropy on particulate matters, as well as for each universal fractal.
Reference here is made to an earlier work [25] where Powder A was subjected to undrained anisotropic shearing, using a hollow cylinder torsional apparatus (HCTA). Figure 4 plots the stress path for Powder A when subjected to compression (), compression and strong torsion (), compression and moderate torsion (), and compression (); here, is the angle of the maximum principal stress, with respect to the long axis of samples, and is the intermediate principal stress ratio—. In Figure 4, and upon subjecting Powder A to torsion, the non-flow strain hardening response changes to flow with strain softening. The nonflow response remains valid for a gentler (lower than 60°) direction of principal stress. While it is quite evident that the increased from 0 to 1 leads to weaker and softer material behavior, it is rather interesting to see the independence of deviatoric stress at phase transformation from that material’s inherent anisotropy. To this end, the concept of universal fractals appears to be extendable to materials with inherent anisotropy and to materials subjected to anisotropic loading.
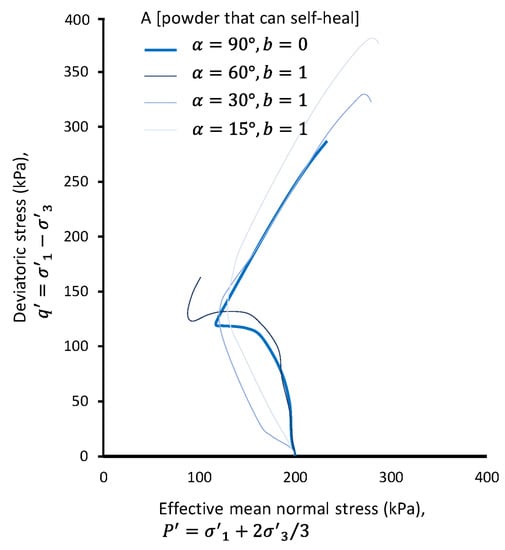
Figure 4.
Stress path on the plane for Powder A, containing particles fitting the ‘self-healing’ universal fractal that are subjected to compression, along with various levels of simultaneous compression–torsion.
- Scenario 3: Isotropic cyclic stresses
The cyclic loading of saturated powders may trigger sudden softening and flow, leading to a state of viscosity. To put the idea of reproducible stress-strain traits for powders with particles sized within one universal fractal to the test, a subset of the data reported in recent work by the authors of [26] are revisited here. Experimental data on four loosely compacted particulate materials are analyzed here in the context of fractals. Of the four material types, two powders are in the ‘self-healing’ universal fractal size bracket, and two belong to none of the universal fractal size brackets but are of exactly the same chemical composition.
Materials in the ‘self-healing’ Universal Fractal class were Powder A—introduced earlier—and the slightly coarser Powder A*, both having a similar shape. Materials of similar chemical compositions, but mean sizes, that do not fit any of the universal fractals were Powders D and D*. All materials were loosely compacted, saturated, consolidated, and subjected to a harmonically varying cyclic deviatoric stress, at a low 0.05 Hz frequency and a cyclic stress ratio () of 0.15, where .
Figure 5a illustrates the stress–strain hysteresis loops for test powders A and A*. The strain increases with the loading cycles for both powders, more noticeably in A* compared to A. The gain in strain in both powders, however, is gentle, indicative of a quality of brittleness and relatively low strength. This behavior is consistent with the low effective deviatoric stress at the phase transformation state for powders in the self-healing universal fractal range (see Figure 3a). In Figure 5b, strain increases with the loading cycles at a much greater pace than that seen in Figure 5a. Materials D and D* have a quality of softness and tend to flow, but at greater levels of strain. This behavior is consistent with the high effective deviatoric stress at the phase transformation state for Powder C in Figure 3a.
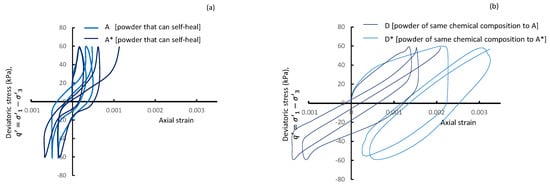
Figure 5.
Stress–strain hysteresis loops for (a) test powders A and A* with a capability to self-heal. (b) Test powders D and D* have a similar chemical composition to A and A*, respectively, but the mean sizes do not fit any universal fractal bracket.
The simple take-home message from this section would be that particulate materials belonging to universal fractals build repeatable, reproducible, and predictable traits in an erosive environment, one that applies various types of stresses to the material, including isotropic and anisotropic static stresses and isotropic cyclic stresses.
3.2. Universal Fractals for Granular Materials at Large
The fractality concept discussed in Section 3.1 was restricted to crystalline solids and did not include amorphous particulate matters. For granular materials that are large (i.e., a mix of solids with various minerals of various crystalline qualities), their hydromechanical properties, such as air-entry value, the threshold of collapsibility, and static flow potential, are associated with structure. In an earlier work [32], we showed that the hydraulic hysteresis that typically appears in soil–water characteristics curves is probably controlled by pore spaces of a certain size in soils. In that study [32], a series of suction-controlled oedometer experiments were conducted on a synthetic geo-material and the findings were paired with real-time measurements of the changing structure. The geomaterial constituted an open assemblage of crystalline solids (quartz, sesquioxides, and phyllosilicates) as well as amorphous matter. Three ‘fractals’ were proposed for the void spaces. The abundance of these fractal voids, the extent of sub-63 μm particles that reside in them at any one time, and the structures that emerge from them (see Section 3.3) were then associated with the hydromechanical properties. A brief summary of the experimental campaign and how and what fractals came from this are outlined here.
The test specimens contained 70 wt % of non-plastic crystallin-defect quartz silt (with a pronounced mode size of 10–20 μm, a maximum size of 63 μm, and a minimum size of 2 μm), from 10 wt % kalolinite clay (plastic and sub-2 μm in size) and 20 wt % of precipitated calcium carbonate. The test specimens were dry and had an extremely high porosity of 65%. K0-wetting resulted in the disappearance of sub-5 μm-sized particles (and associated 0.001 with 0.25 μm-sized pores), indicating the aggregation and formation of larger ped units. Wetting led to a gentler reduction in the abundance of 5- to 20-μm-sized particles (and associated 0.3 to 1.5 μm- and 8 to 19 μm-sized pores). Both particle size ranges shown here fall into the self-healing universal fractal bracket. The formation of larger aggregates led to a decrease in trans-assemblage pore spaces, as manifested by the drop of maximum pore size from 76 μm to 42 μm. Almost similar structural changes were seen upon the application of varying levels of effective deviator stress, followed by wetting; that is, a sharp reduction in particles sized <1 μm and particles sized 20 to 30 μm. Axial K0-loading of the dry samples led to a forced compression of 0.8 to 20 μm-sized particles (and the disappearance of the associated 0.25 to 2 μm-sized pores, as did the 0.001 to 0.25 μm-sized pores). These particle sizes also fall within the bracket of self-healing particles. The emergence of 2 to 20 μm in pore size is indicative of denser aggregates.
In summary, fractal particle sizes are associated with fractal pore sizes. Fractality occurs in both crystalline solids and composites containing amorphous solid phases. Notable ‘self-healing’ particle sizes include 5, 7, 12, 20, 68, 75, 316, 440, 610 and 720 µm. Notable ‘self-healing’ pore sizes include 0.001 to 0.25 μm, 0.3 to 1.5 μm, and 2 to 20 μm. ‘Inherently breakable’ particle-size fractals include 30–34 µm and 106–193 µm. ‘Inherently unbreakable’ particle-size fractals include 10–17 µm, 45–47 µm, and 56–58 µm.
3.3. Universal Fractal Structures
Voids surround the particles to form structures. Assadi-Langroudi and Ng’ambi [33] revisited the structure paradigms and popularized the notions of ‘packing qualities’ in non-overlapping monodispersed clean and rigid spherical particles. Particulate materials under stress move from an initial, very loose state to denser states. This transition marks a suite of ‘packing qualities’. For particulate materials with a mean size fitting one of the universal fractals, their transitioning packing qualities can also be rationalized into ‘fractal structures’.
3.3.1. Packing Qualities
In a three-dimensional Euclidean space, the most open packing form is the simple cubic (SC) scenario, where particle assemblages have six square sides (A-face). The SC forms a void ratio of 0.91, where each unit cell accommodates 8 spherical particles at the coordinates 000, 001, 010, 100, 110, 101, 011, and 111. In this scenario, SC is also referred to as 600 packing—that is, 6 As, 0 Bs, and 0 Cs, where A-faces are square, C-faces are rhombohedral, and B-faces are between a square and a rhombohedron. The closest possible packing scenario is the rhombohedral cubic close packing (CCP) scenario, where aggregates have two A-faces and four C-faces—also referred to as 204 packing. The CCP forms a void ratio of 0.35. Between SC and CCP is a whole world of packing scenarios. These can be summarized in eight of the packing qualities, with the nomenclature of 042, 402, 240, 024, 222, 060, and 204 and 006. Simple packings 006 and 204, however, bear similar void ratios, although they have different average acute face angles (see [34]).
In Figure 6a, the various ‘fractal packings’ are demarcated for the transition from 600 to 204 (or 006). The terms ‘fractional density’ and ‘packing density’ are used interchangeably. Marked in Figure 6a is the plethora of packing qualities through which a particulate material can travel during its service life. Assadi-Langroudi and Ng’ambi [33] rationalized this spectrum by defining three fractal structures: for void ratios above 0.6, a random loose packing (RLP) structure governs the structure. This changes to random close packing (RCP) for void ratios between 0.5 and 0.6. The close packing (CP) structure occurs at void ratios below 0.5.
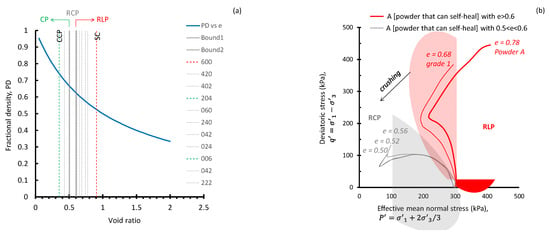
Figure 6.
The association of universal fractals at particle and structure levels: (a) the transition of particulate structures from simple cubic (SC) to cubic close packing (CCP) through nine simple packing states; (b) undifferentiable stress paths in the RLP and RCP universal fractal structures.
3.3.2. Fractals at Particle and Structure Levels
Fractal structures can be found in any powdered material. To explore these fractal structures, and in a suite of experiments designed and conducted exclusively for this contribution, Powder A—representing particles with a mean size in the self-heal universal fractal bracket—was crushed using a benchtop Retsch RM200 mortar mill into four grades. The ground material was then compressed to achieve a high void ratio of 0.77 to 0.80, then saturated, consolidated, and subjected to undrained shearing.
In Figure 6b, Powder A and ‘grade 1’ share a similarly pronounced mode size that brings them into the ‘self-heal’ universal fractal range. Grades 2 to 4 have pronounced mode sizes that do not fit any of the universal fractals. The initial void ratio of Powder A and grade 1 is 0.78 and 0.68, respectively. These are the void ratio values ahead of undrained loading. Both void ratio values are greater than 0.6; hence, they bring Powder A and ‘grade 1’ into the random loose packing (RLP) universal fractal structure range. To this end, particles that belong to one of the three universal fractals form packings that belong to one of the three main universal fractal structures. In Figure 6b, grades 3, 4, and 5 attained void ratio values of between 0.5 and 0.56, which are within the range of universal random close packing (RCP). The stress paths for the three grades almost converge and show fundamental differences from parent Powder A and grade 1. Observations here lend further evidence to the association of fractals at particle and structure levels.
4. Discussion: Fractals and Biomimetic Design
Biomimetic innovations, at a theoretical level, involve observing, studying, and abstracting traits from natural systems. Matters that can be imitated from nature are plenty and include forms, structures, organizations, processes, mechanisms, functions, behaviors, constructions, and systems. As a group, these are referred to as ‘imitable traits’.
Aristotle put forward the doctrine of four causes—which means that everything is caused by four different things. This causality led to the Aristotelian typology of imitable traits [35]. On this basis, there are four different traits that can be imitated from natural systems: matters, generative processes, functions, and forms.
‘Matter’, in the Aristotelian worldview, is that from which something is made or composed. ‘Generative processes’ are either ‘producing’, or ‘effecting’. ‘Producing’ processes involve bringing things into being (e.g., the aggregation of self-healing particles). ‘Effecting’ processes involve bringing about specific effects (e.g., the continuous crushing of particles in the erosive environment). ‘Functions’ are what something does (e.g., steady states). ‘Form’ is those characteristics that shape the matter at large. An example of forms for particulate matter is particle size, or how the particles pack together to form particle assemblies.
A viable typology of traits needs to be economical to ensure that there are as few traits as possible, comprehensive, to include all the basic traits, and coherent, so that all the different traits fit together as do the pieces of a jigsaw, without overlapping.
For particulate materials, in Section 3, it was established that particles with a certain mean size that fits certain universal fractals build repeatable, reproducible, and predictable traits. They exhibit certain of the stress-strain behaviors of nondifferentiable, self-similar trajectories. It was further established that particles in a universal fractal will move through a number of basic packing qualities (from a total of nine) while remaining in one of the three universal fractal structures. Movement between universal fractal structures would result in a consequent movement between particle-level universal fractals and vice versa. In other words, engineering intervention can improve the physicomechanical properties of particulate materials but does not necessarily change the ‘forms’ of the stress-strain response, as long as the intervention does not lead to the movement of parent material from one universal fractal to another.
5. Conclusions
By appropriating the fractality concept, this paper illustrated how the general behavioral forms of engineered particulate matter can be predicted and retained while improving functions through predictable generative processes.
Particles in nature are plentiful and diverse. However, they fit one of the three main universal fractals. Within each universal fractal, particles build repeatable, reproducible, and predictable traits, including stress-strain behavior, flow, and steady states. These traits are nondifferentiable. The structures within which these particles are placed have the capability to self-form nondifferentiable traits. In other words, matter influences the environment—as defined by fabric, structure, and texture—just as the environment influences matter.
Fractality occurs in both crystalline solids and composites containing amorphous solid phases. Notable ‘self-healing’ particle sizes include 5, 7, 12, 20, 68, 75, 316, 440, 610, and 720 µm. Notable ‘self-healing’ pore sizes include 0.001 to 0.25 μm, 0.3 to 1.5 μm, and 2 to 20 μm. ‘Inherently breakable’ particle size fractals include 30–34 µm and 106–193 µm. ‘Inherently unbreakable’ particle-size fractals include 10–17 µm, 45–47 µm, and 56–58 µm.
Granular materials with a pronounced mode size that is within the ‘inherently breakable’ fractal range develop the least strength at phase transformation . This is valid for both clean granular materials and composites (where the granular material is mixed with finer fractions) in any confinement conditions and in both compressive and torsional environments.
The strength at phase transformation is higher in clean granular materials that are sized in the ‘self-healing’ range. The behavior is that of non-flow; the material exhibits brittle failure, followed by strain-hardening.
The strength at phase transformation is greatest in clean granular materials that are not sized in the ranges of any of the universal fractals. These materials show strain hardening under undrained static compression, which changes to strain-softening under undrained cyclic compression.
All loose clean granular materials, irrespective of their size, develop non-flow strain hardening under undrained static compression; over time, and upon the progressive particle crushing and formation of a second, pronounced finer mode size, these materials develop post-failure softening that can lead to partial or total flow.
Engineering interventions include adding specifically sized elements to parent particles or rearranging particles to achieve an ‘intended’ packing quality. This paper presented evidence showing that as long as interventions do not yield a transition between universal fractals, their functions can be improved and forms can be preserved, thereby improving the design efficiency, enhancing certainties, and minimizing the resources needed for design.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.A. and A.A.-L.; methodology, S.G. and A.A.-L.; validation, H.A., A.A.-L.; formal analysis, A.A.-L. and S.G.; investigation, S.G. and A.A.-L.; resources, S.G.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.-L.; writing—review and editing, H.A., S.G. and A.A.-L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fagg, R.; Smalley, I. ‘Hardcastle Hollows’ in loess landforms: Closed depressions in aeolian landscapes—In a geoheritage context. Open Geosci. 2018, 10, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeeden, C.; Hark, M.; Hambach, U.; Markovic, S.; Zöller, L. Depressions on the Titel loess plateau: Form, pattern, genesis. Geogr. Pannonica 2007, 11, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hardcastle, J. Origin of the loess deposit of the Timaru plateau. Trans. N. Z. Inst. 1889, 22, 406–414. [Google Scholar]
- Vanwalleghem, T.; Poesen, J.; Vitse, I.; Bork, H.R.; Dotterweich, M.; Schmidtchen, G.; Deckers, J.; Lang, A.; Mauz, B. Origin and evolution of closed depressions in central Belgium, European loess belt. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2007, 32, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, H.C. Some reflections on the origin of hollows in Norfolk compared with those in the Paris region. Rev. Géomorphologie Dyn. 1961, 12, 110–117. [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire, E.; Wang, J.T.; Meng, X.M. The environment: Geology, geomorphology, climate and land use. In Landslides in the Thick Loess Terrain of Northwest China; Derbyshire, E., Meng, X., Dijkstra, T.A., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 1999; pp. 22–46. [Google Scholar]
- Etienne, D.; Ruffaldi, P.; Goepp, S.; Ritz, F.; Georges-Leroy, M.; Pollier, B.; Dambrine, E. The origin of closed depressions in Northeastern France: A new assessment. Geomorphology 2011, 126, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibben, S. A microstructural model for collapsing soils. Ph.D. Thesis, Nottingham Trent University, Nottingham, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zuriguel, I.; Garcimartín, A.; Maza, D.; Pugnaloni, L.A.; Pastor, J.M. Jamming during the discharge of granular matter from a silo. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 71, 051303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trogadas, P.; Cho, J.I.S.; Neville, T.P.; Marquis, J.; Wu, B.; Brett, D.J.L.; Coppens, M.-O. A lung-inspired approach to scalable and robust fuel cell design. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rian, I.; Sassone, M. Tree-inspired dendriforms and fractal-like branching structures in architecture: A brief historical overview. Front. Arch. Res. 2014, 3, 298–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, D.; Marangoni, A.G. Microstructure and fractal analysis of fat crystal networks. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2006, 83, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, T.; Baik, B.-K.; Czuchajowska, Z. Microstructure of Seeds, Flours, and Starches of Legumes. Cereal Chem. 1997, 74, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.; Knoblauch, M.; Ullrich, S.; Baik, B.-K. Microstructure of hard and soft kernels of barley. J. Cereal Sci. 2011, 54, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.E.; Rainforth, M. Ceramic Microstructures: Property Control by Processing, 1st ed.; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1994; p. 602. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, V.J.; Gunning, A.P. Microscopy, microstructure and displacement of proteins from interfaces: Implications for food quality and digestion. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, G. Scale: The Universal Laws of Life and Death in Organisms, Cities and Companies; Orion Publishing Co.: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhry, Q.; Watkins, R.; Castle, L. Knowns, Unknowns, and Unknown Unknowns. In Nanotechnologies in Food; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2010; pp. 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.E.; Scher, J.; Desobry-Banon, S.; Desobry, S. Milk powders ageing: Effect on physical and functional proper-ties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2004, 44, 297–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiarkina, I.; Sang, C.; Depree, N.; Prince-Pike, A.; Yu, W.; Wilson, D.; Young, B.R. The significance of powder breakdown during conveying within industrial milk powder plants. Adv. Powder Technol. 2016, 27, 2363–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Variankaval, N.; Cote, A.S.; Doherty, M.F. From form to function: Crystallization of active pharmaceutical ingredi-ents. AIChE J. 2008, 54, 1682–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assadi-Langroudi, A.; O’Kelly, B.C.; Barreto, D.; Cotecchia, F.; Dicks, H.; Ekinci, A.; Garcia, F.E.; Harbottle, M.; Tagarelli, V.; Jefferson, I.; et al. Recent Advances in Nature-Inspired Solutions for Ground Engineering (NiSE). Int. J. Geosynth. Ground Eng. 2021, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langroudi, A.A.; Jefferson, I.; O’Hara-Dhand, K.; Smalley, I. Micromechanics of quartz sand breakage in a fractal context. Geomorphology 2014, 211, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assadi Langroudi, A.; Theron, E. Gaps in particulate matters: Formation, mechanisms, implications. In Proceedings of the 17th African Regional Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Cape Town, South Africa, 6–10 October 2019; pp. 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Ghadr, S.; Bahadori, H.; Assadi-Langroudi, A. Anisotropy in Sand–Fibre Composites and Undrained Stress–Strain Implications. Int. J. Geosynth. Ground Eng. 2019, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadr, S.; Samadzadeh, A.; Bahadori, H.; O’Kelly, B.C.; Assadi-Langroudi, A. Liquefaction Resistance of Silty Sand with Ground Rubber Additive. Int. J. Géoméch. 2021, 21, 04021076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasenack, N.; Müller, B.W. Micron-Size Drug Particles: Common and Novel Micronization Techniques. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2004, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, A.J. Origin, shaping and significance of quartz sand grains. J. Geol. Soc. Aust. 1966, 13, 97–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalley, I.J. Formation of Quartz Sand. Nature 1966, 211, 476–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blatt, H. Original Characteristics of Clastic Quartz Grains. J. Sediment. Res. 1967, 37, 401–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadr, S.; Assadi-Langroudi, A. Effect of Grain Size and Shape on Undrained Behaviour of Sands. Int. J. Geosynth. Ground Eng. 2019, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assadi-Langroudi, A.; Jefferson, I. Collapsibility in calcareous clayey loess: A factor of stress-hydraulic history. Int. J. Geomate 2013, 5, 620–627. [Google Scholar]
- Assadi-Langroudi, A.; Ng’Ambi, S.; Smalley, I. Loess as a collapsible soil: Some basic particle packing aspects. Quat. Int. 2018, 469, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, T.; Smalley, I.; Rogers, C. Particle packing in loess deposits and the problem of structure collapse and hydroconsolidation. Eng. Geol. 1995, 40, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicks, H. The philosophy of biomimicry. Philos. Technol. 2016, 29, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).