Evaluation of Regional Carrying Capacity under Economic-Social-Resource-Environment Complex System: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Framework
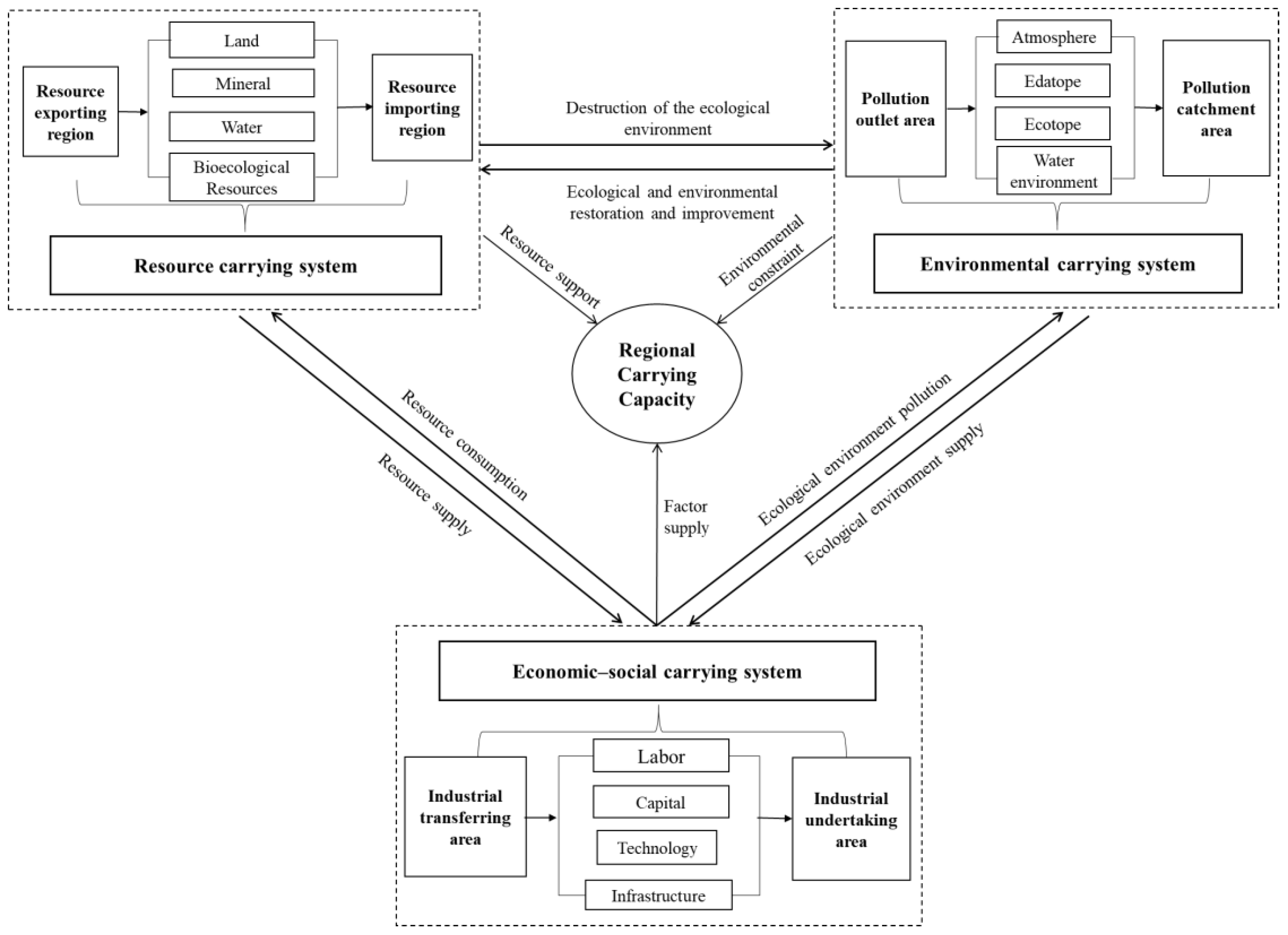
2.1. Regional Carrying Capacity
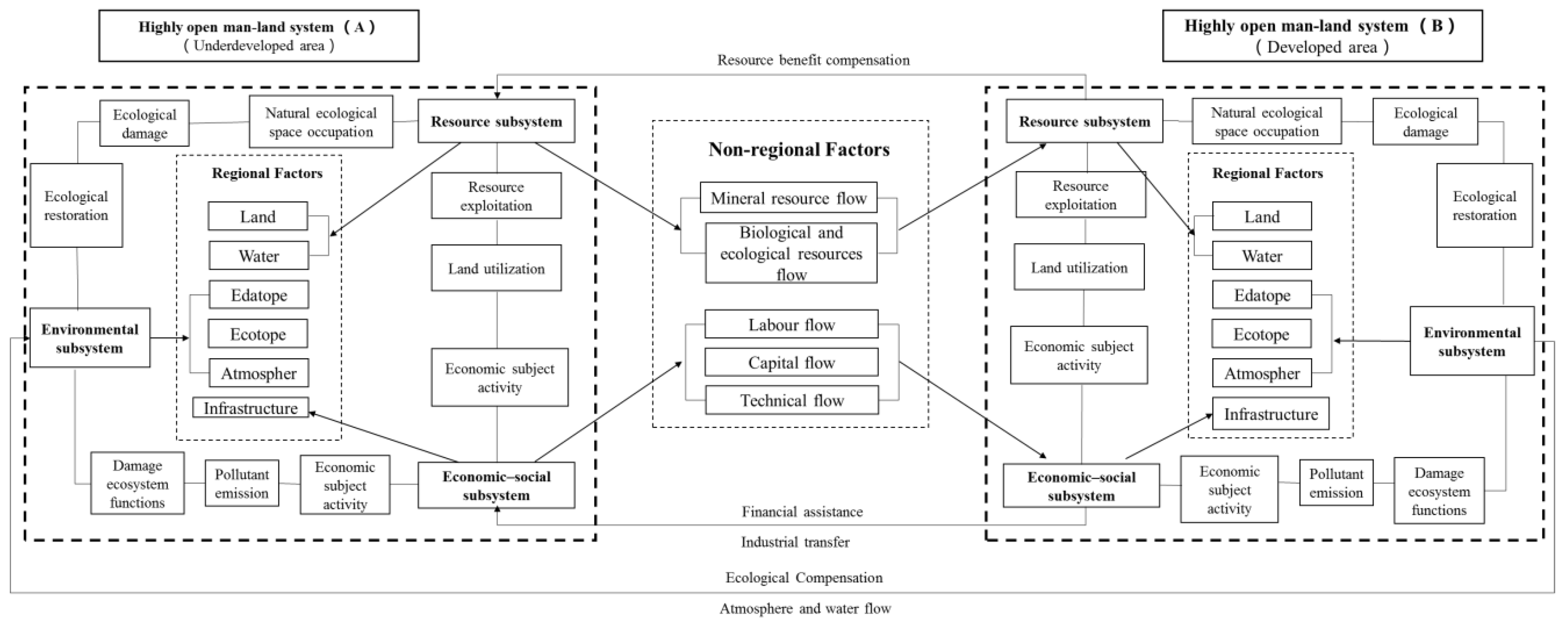
2.2. Factor Flow and Regional Carrying Capacity
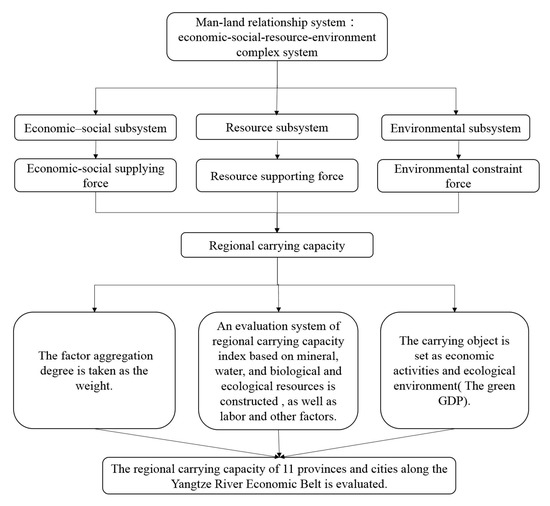
2.3. Regional Carrying Capacity Evaluation Framework
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Evaluation Model
3.1.1. Weight
3.1.2. Regional Carrying Capacity Index
3.1.3. Regional Carrying Capacity Object
3.2. Data Collection
3.3. Criteria for Judging Regional Carrying Status
4. Results and Discussion
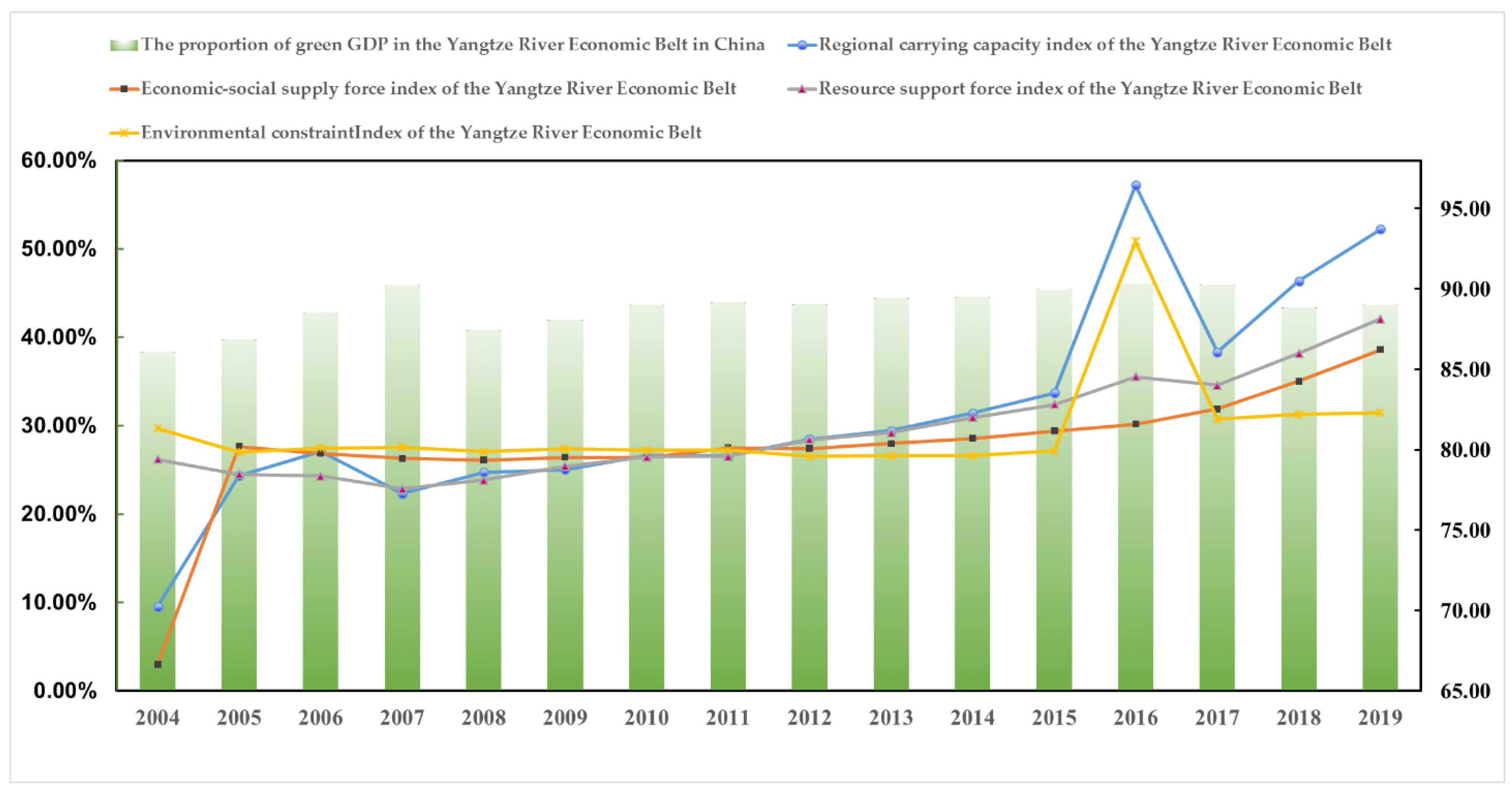
4.1. Evaluation Results of Regional Carrying Capacity
4.2. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Carrying Capacity in the Yangtze River Economic Belt
4.2.1. Distribution of Regional Carrying Capacity
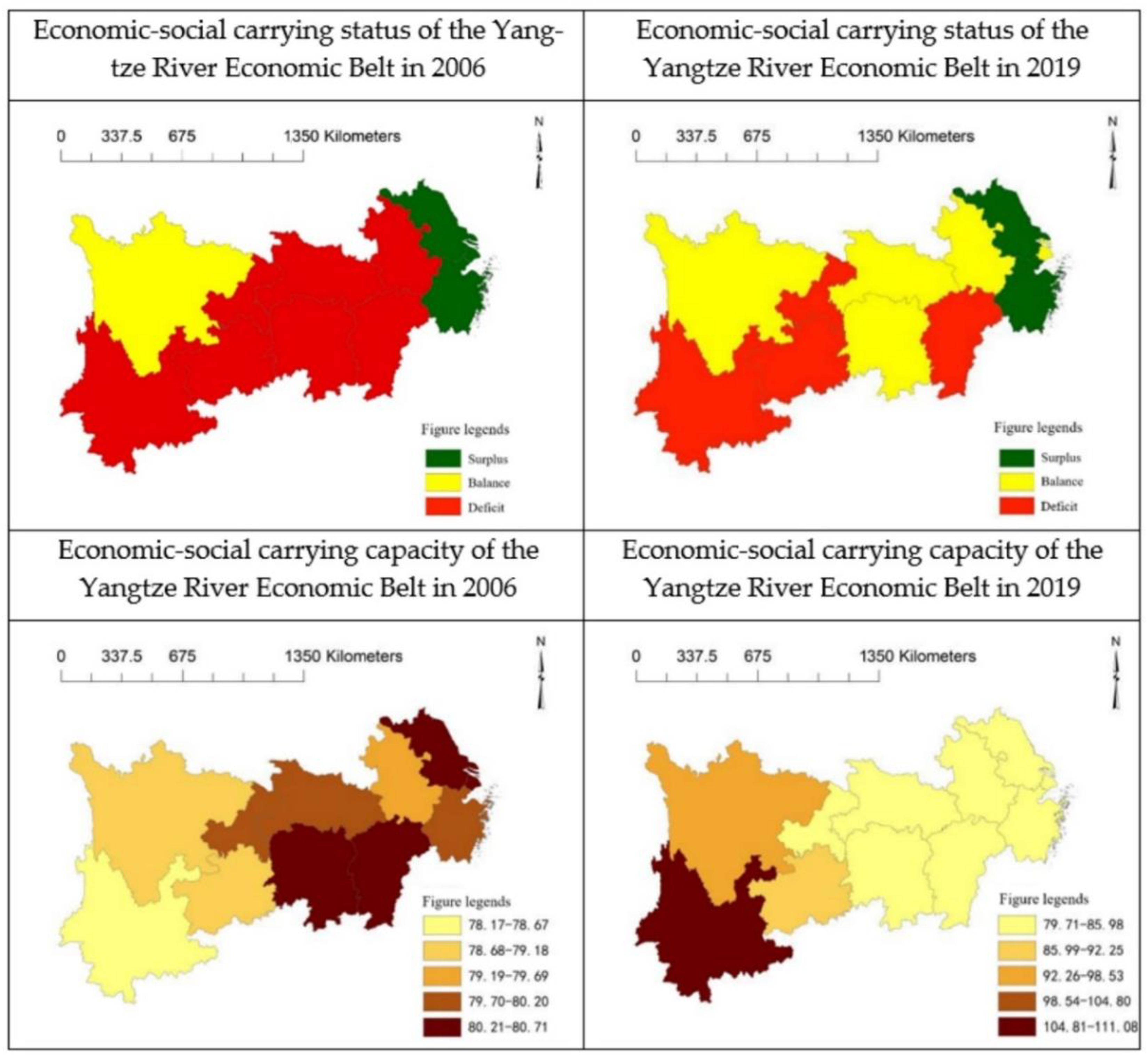
4.2.2. Distribution of the Economic-Social Supplying Force
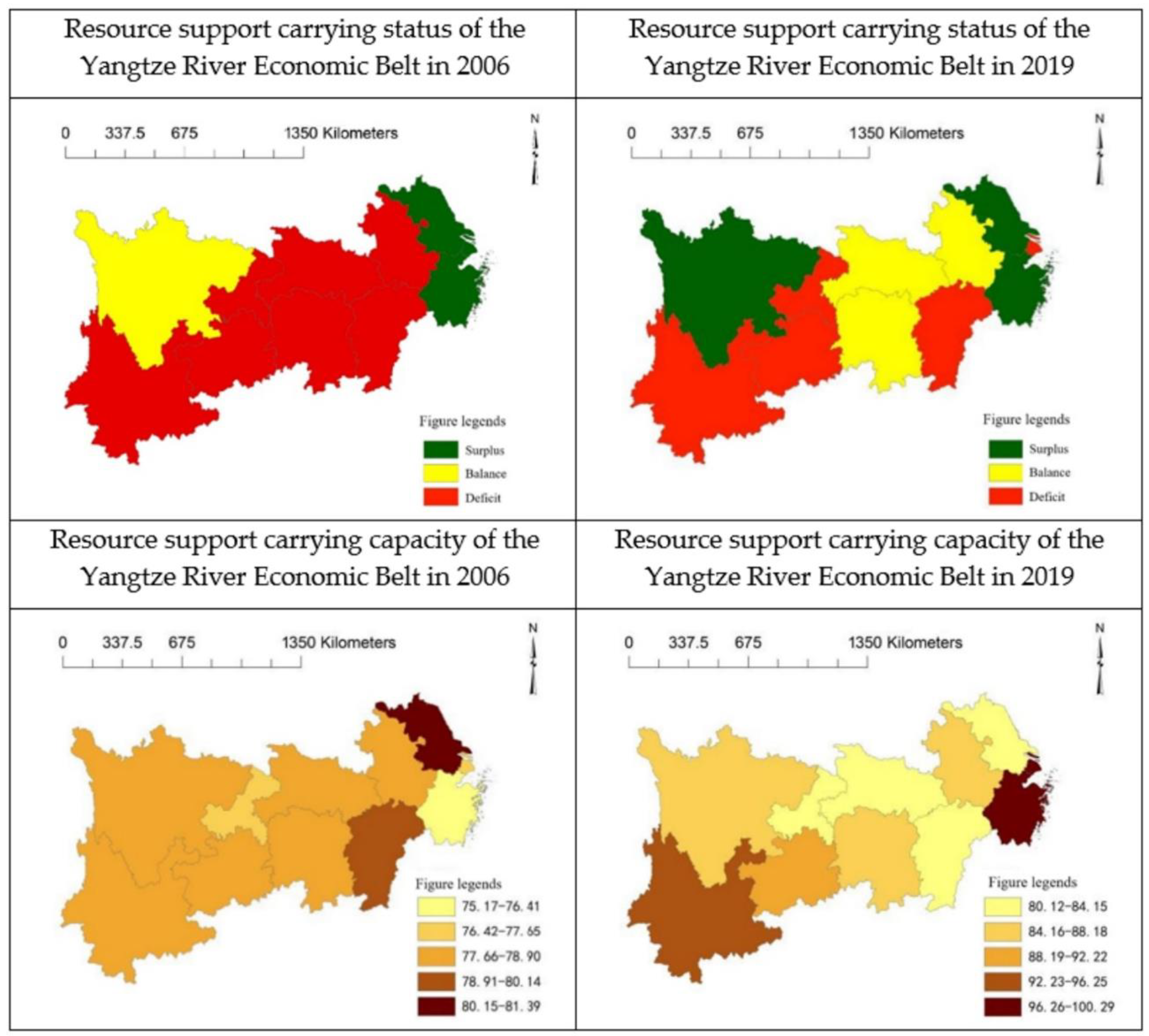
4.2.3. Distribution of the Resource Supporting Force
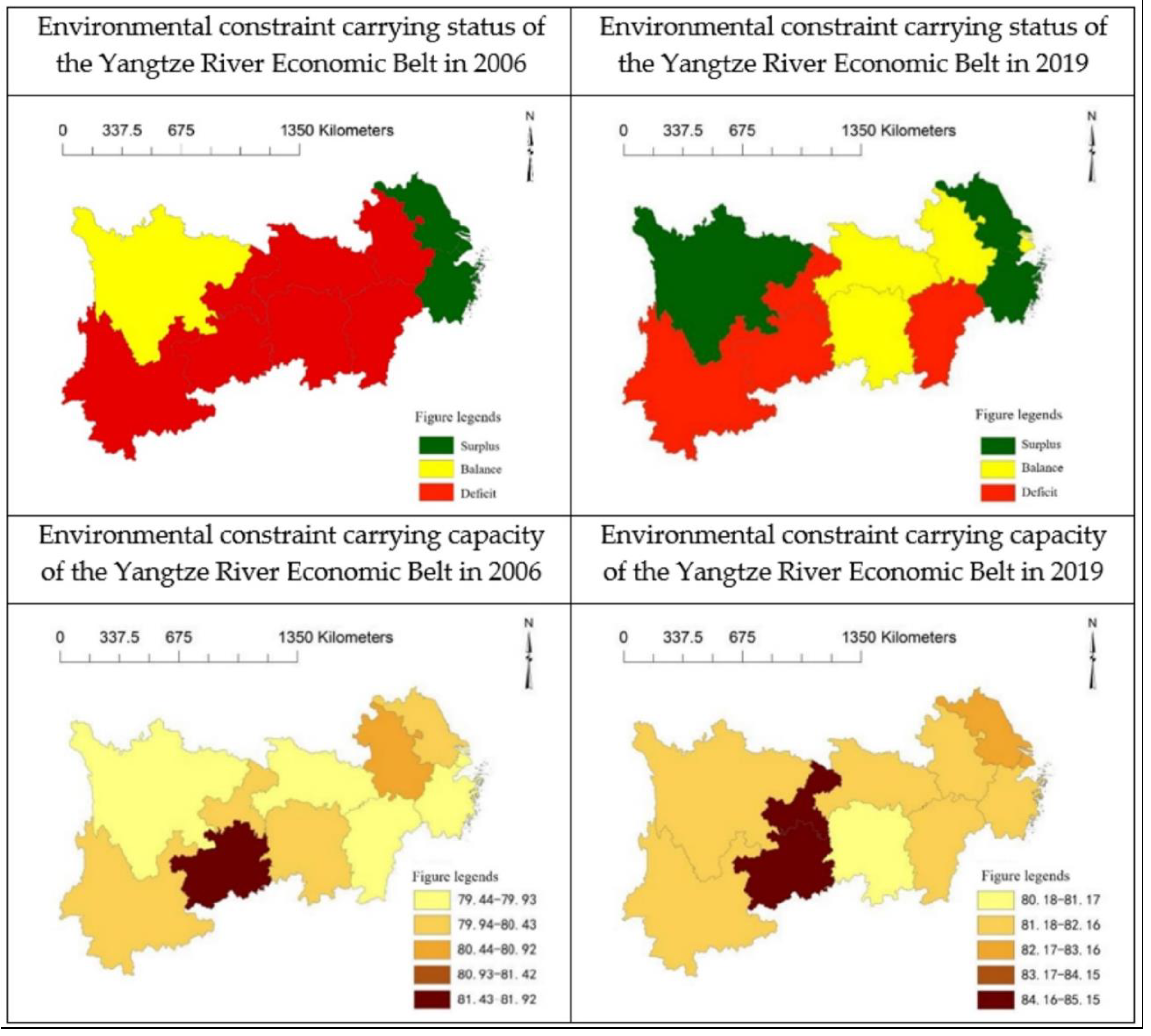
4.2.4. Distribution of the Environmental Constraint Force
5. Conclusions and Policy Recommendation
- The factor concentration is caused by the factor flow in and among the subsystems of economy, society, resources, and environment in the man-land relationship regional system. Effective aggregation can improve resource utilization efficiency, thus realizing the positive externality and enhancing the carrying capacity;
- Regional carrying capacity is a comprehensive status formed by the interaction of the economy, society, resources, and environment under the open perspective of the man-land system. The supporting force of the resource subsystem has become the most critical factor affecting the carrying capacity of the Yangtze River economic belt. The carrying status of economic-social subsystems, resources, and the environment are highly consistent with the regional carrying status, indicating that the economic-social subsystem also constitutes a part of the regional carrying capacity and has a significant impact on the regional carrying capacity. This verifies the theory proposed in this paper, in which the economic-social subsystem is a part of the regional carrying system;
- The functions of different systems should be treated separately to find out the main factors restricting regional carrying capacity in different periods. The influence of factor flow and material exchange on regional carrying capacity should be emphasized from the perspective of multi-system and multi-factor integration. In particular, economic development and technological progress help improve the efficiency of resource exploitation and utilization and the maximum capacity of the environment to make up for the lack of regional resource and environmental carrying capacity. The regions along the Yangtze River Economic Belt present a relatively balanced regional development trend of carrying capacity, economic-social supplying force, resource supporting force, and environmental constraint force from the eastern part to the central part to the western part.
- The evaluation system of regional carrying capacity formed in this study can be well applied to the evaluation of regional sustainable development and the monitoring of regional carrying capacity in urban spatial planning and can better track the changes in regional resources and the environment. It is suggested that the central government and local governments should apply this system to establish a regional bearing capacity evaluation database;
- The variation of factor flow and the difference in regional factor endowment should be paid attention to in the evaluation of regional carrying capacity in both developed and less developed regions. Green and low-carbon sustainable development should be based on regional differences in resource and environmental endowment and economic and social development status. China’s planning for regional development should be based on the current situation of regional carrying capacity. For example, the Yangtze River Economic Belt should play the role of a growth pole;
- China should continue to carry out ecological civilization construction and carry out ecological protection and restoration projects. According to the evaluation results of carrying capacity, China’s ecological protection and restoration effects are obvious. Financial investment in ecological protection and restoration and ecological compensation should be continuously increased to reduce environmental pollution and improve regional carrying capacity.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Kim, J.D. Impact of urbanization on energy demand: An empirical study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China. Energy Policy 2020, 139, 111354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.H.; Du, X.Y.; Ren, Y.T.; Shen, L.Y.; Cheng, G.Y.; Wang, J.H. Sustainable urban development: An examination of literature evolution on urban carrying capacity in the Chinese context. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.Y.; Shu, T.H.; Liao, X.; Yang, N.; Ren, Y.T.; Zhu, M.C.; Cheng, G.Y.; Wang, J.H. A new method to evaluate urban resources environment carrying capacity from the load-and-carrier perspective. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 154, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhiming, F.; Tong, S.; Yanzhao, Y.; Huimin, Y. The progress of resources and environment carrying capacity: From single-factor carrying capacity research to comprehensive research. J. Resour. Ecol. 2018, 9, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearnside, P.M. Estimation of human carrying capacity in rainforest areas. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1990, 5, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrow, K.; Bolin, B.; Costanza, R.; Dasgupta, P.; Folke, C.; Holling, C.S.; Jansson, B.-O.; Levin, S.; Mäler, K.-G.; Perrings, C.J.E.; et al. Economic growth, carrying capacity, and the environment. Ecol. Econ. 1995, 15, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.J.P. Environment, Carrying capacity reconsidered. Popul Environ. 1999, 21, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Feng, Z.M.; Yang, Y.Z.; Lin, Y.M.; Wu, Y.Y. Research on Land Resource Carrying Capacity: Progress and Prospects. J. Resour. Ecol. 2018, 9, 331–340. [Google Scholar]
- Graymore, M.L.M.; Sipe, N.G.; Rickson, R.E. Sustaining Human Carrying Capacity: A tool for regional sustainability assessment. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, G.P.; Xu, M.D.; Wang, F.; Zuo, C. The Comprehensive Evaluation Model of Resources and Environmental Carrying Capability. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2014, 16, 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.Q.; Lu, B.B.; Zheng, J.H. Analysis and Prediction of Land Resources’ Carrying Capacity in 31 Provinces of China from 2008 to 2016. Sustainability 2021, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.W.; Wu, J.Q.; Zang, C.F. A comprehensive evaluation of the eco-carrying capacity and green economy in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 281, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Hu, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, D.; Liu, J.J.N.H. Research on comprehensive carrying capacity of Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region based on state-space method. Nat. Hazards 2016, 84, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatai Adedoyin, F.; Agboola, P.O.; Ozturk, I.; Bekun, F.V.; Agboola, M.O. Environmental consequences of economic complexities in the EU amidst a booming tourism industry: Accounting for the role of brexit and other crisis events. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 305, 127117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Elshkaki, A.; Zhong, S.; Shen, L. Study on Relative Carrying Capacity of Land Resources and Its Zoning in 31 Provinces of China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Shen, L.; Wei, X.; Wang, J.; Cheng, G. A guiding index framework for examining urban carrying capacity. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, T. Index system of urban resource and environment carrying capacity based on ecological civilization. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2018, 68, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Shi, W.; Fu, Y. Quantitative evaluation and optimized utilization of water resources-water environment carrying capacity based on nature-based solutions. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Shi, Y.; Wan, K. Integrated evaluation of the carrying capacities of mineral resource-based cities considering synergy between subsystems. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wei, X.; Guo, Q. A three-dimensional evaluation model for regional carrying capacity of ecological environment to social economic development: Model development and a case study in China. Ecol. Ind. 2018, 89, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, M.; Dawes, L.; Grace, P. Scalar considerations in carrying capacity assessment: An Australian example. Popul. Env. 2015, 36, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dan-lin, Y.; Han-ying, M. Regional carrying capacity: Case studies of Bohai Rim area. J. Geogr. Sci. 2002, 12, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, H. Comprehensive evaluation of regional resources and environmental carrying capacity using a PS-DR-DP theoretical model. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, M. The carrying capacity imperative: Assessing regional carrying capacity methodologies for sustainable land-use planning. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Deng, H. Comprehensive evaluation for sustainable development based on relative resource carrying capacity—A case study of Guiyang, Southwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 20090–20103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Wang, J.; He, K.J.A.G. Analysis on the urban land resources carrying capacity during urbanization—A case study of Chinese YRD. Appl. Geogr. 2020, 116, 102170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.Y.; Zhou, K.; Chen, D.; Fan, J. Evaluation and analysis of provincial differences in resources and environment carrying capacity in China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Fang, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L. Conjugate evaluation of sustainable carrying capacity of urban agglomeration and multi-scenario policy regulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Du, Q.; Zou, P.X.W.; Lu, C.; Li, Y. A method for incorporating heterogeneity in measuring the economic carrying capacity of urban infrastructures. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 332, 130058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.X.; Shen, L.Y.; Liu, Z.; Luo, L.Y.; Wang, J.H.; Chen, Y. Comparative analysis on the evolution of ecological carrying capacity between provinces during urbanization process in China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Shu, T.; Shen, L.; Liao, X.; Yang, N.; He, H. Economic perspective-based analysis on urban infrastructures carrying capacity—A China study. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2020, 83, 106381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, L.J.; Huang, X.J. The interdisciplinary study and integration of disciplines for geography and resources science. J. Nat. Resour. 2020, 35, 1830–1838. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Wang, C.; Ye, Y.; Wen, B. An Improved Method for Evaluating Regional Resource Carrying Capacities: A Case Study of the Tarim River Basin in Arid China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 2415–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.L.; Li, C.J.; Liu, S.Q.; Zhou, K. Land carrying capacity in rural settlements of three gorges reservoir based on the system dynamic model. Nat. Resour. Model. 2018, 31, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, R.; Appenzeller, T. Beyond reductionism—Introduction. Science 1999, 284, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.C.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Y.L. The Paradigm Transformation of Geography from the Perspective of Complexity Sciences. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2010, 65, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.Y.; Zang, C.F.; Zhang, J.M. Economic and resource and environmental carrying capacity trade-off analysis in the Haihe River basin in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D.M.; Godschalk, D.R.; Axler, N. The Carrying Capacity Concept as a Planning Tool; American Society of Planning Officials: Chicago, IL, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, K.R.; Fan, J. The Formation Mechanism of Regional Function: An Analysis Based on the Theory of Man-Earth Areal System. Econ. Geogr. 2018, 38, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Lu, W.X.; Zhao, Y.; Song, W.B. Development tendency analysis and evaluation of the water ecological carrying capacity in the Siping area of Jilin Province in China based on system dynamics and analytic hierarchy process. Ecol. Model. 2014, 275, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.D. Theoretical studies of man-land system as the core of geographical science. Geogr. Res. 2002, 21, 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Guo, Z.Y.; Wu, J.P.; Ye, S.F. Constructing an assessment indices system to analyze integrated regional carrying capacity in the coastal zones—A case in Nantong. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2014, 93, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.H.; Zeng, Q. Is the green technological progress bias of mariculture suitable for its factor endowment?—Empirical results from 10 coastal provinces and cities in China. Mar. Pol. 2021, 124, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Zheng, B.H.; Khu, S.T. Validation of the hypothesis on carrying capacity limits using the water environment carrying capacity. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanaswamy, V.; Scott, J.A.; Ness, J.N.; Lochhead, M. Resource flow and product chain analysis as practical tools to promote cleaner production initiatives. J. Clean. Prod. 2003, 11, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, G.; Verdiani, G.; Dal Sasso, S. Evaluation of carrying capacity and territorial environmental sustainability. J. Agric. Eng. 2012, 43, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giljum, S. Trade, materials flows, and economic development in the South: The example of Chile. J. Ind. Ecol. 2004, 8, 241–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Cheng, J.H.; Zhu, Y.L.; Xiong, W.W. Research on diversity of mineral resources carrying capacity in Chinese mining cities. Resour. Policy 2016, 47, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.; Jeong, Y.; Lee, D.; Lee, W.; Choi, H. Determining development density using the Urban Carrying Capacity Assessment System. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2005, 73, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.N.; Li, J.S.; Lu, B.B.; Luo, M.H.; Li, L.Z. Exploring the Spatial Pattern and Influencing Factors of Land Carrying Capacity in Wuhan. Sustainability 2019, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, D.Q. Spatial agglomeration and driving factors of environmental pollution: A spatial analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.D.; Yu, X.G. Carrying capacity of resources and problems of sustainable development in yangtze basin. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Val. 2002, 11, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.R.; Wu, T.; Zhang, Y. The spatial-temporal variation and convergence of green innovation efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 26868–26881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Li, H. Resources, Environment and Green Development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt; Nanjing University Press: Nanjing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Zhang, Q.W.; Zhang, A.P.; Hussain, H.A.; Liu, X.R.; Yang, Z.L. Spatiotemporal characteristics of the bearing capacity of cropland based on manure nitrogen and phosphorus load in mainland China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.J.; Jin, Y.Z.; Guo-Liang, X.U.; Chang-Yan, W.U. Conception of Sub-Line of Hu Huangyong Population Line and Patterns of Future Population Carrying in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2017, 26, 1937–1944. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.H.; Huang, X.J.; Chen, W.L. Threshold Effect of High-Tech Industrial Scale on Green Development-Evidence from Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sustainability 2019, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Peng, B.H.; Wei, G.; Elahi, E. Comprehensive Evaluation and Spatial Difference Analysis of Regional Ecological Carrying Capacity: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Urban Agglomeration. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Sun, C. Comprehensive carrying capacity, economic growth and the sustainable development of urban areas: A case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, N.; Zhou, W. The DPSIRM—Grey cloud clustering method for evaluating the water environment carrying capacity of Yangtze River economic Belt. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Cheng, G.; Du, X.; Meng, C.; Ren, Y.; Wang, J. Can urban agglomeration bring “1 + 1 > 2Effect”? A perspective of land resource carrying capacity. Land Use Policy 2022, 117, 106094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Guan, X.; Lu, S.; Qin, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D. Examining the spatiotemporal change of forest resource carrying capacity of the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 21213–21230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Ma, X. Identifying resource and environmental carrying capacity in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China: The perspectives of spatial differences and sustainable development. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 14775–14798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Wang, C.; Han, L.; Wu, S.; Lou, L.; Xu, B.; Liu, Y. Resources and Environmental Pressure, Carrying Capacity, And Governance: A Case Study of Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tian, Y.; Huang, K.; Yi, T. Spatial-temporal differentiation of the coupling coordinated development of regional energy-economy-ecology system: A case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 124, 107394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, H.; Liang, D.; Chen, Y.; Tian, P.; Xia, J.; Wang, H.; Lei, X. Ecological sustainability and its driving factor of urban agglomerations in the Yangtze River Economic Belt based on three-dimensional ecological footprint analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 330, 129802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, M.; Yang, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, M. Decoupling water environment pressures from economic growth in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Target Layer | Criterion Layer | Factor Layer | Indicator Layer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regional carrying subject | Economic-social subsystem | Labor | Index of number employed |
| Capital | Fixed investments | ||
| Technology | R&D spending; Full-time equivalent of R&D personnel | ||
| Infrastructure | Railway, inner channel, and highway mileage; Urban green area | ||
| Resource subsystem | Minerals | Solid mineral production (coal, iron ore, etc.); Oil and gas mineral production (crude oil, natural gas) | |
| Land | Urban construction land area; Effective irrigated area of cultivated land; | ||
| Water | Total water resources | ||
| Bioecological resources | Live wood stock; Food production | ||
| Environmental subsystem | Water environment | Total chemical oxygen demand emission; Total ammonia nitrogen emissions | |
| Edatope | Pesticide usage; Production of general industrial solid waste | ||
| Atmosphere | Total sulfur dioxide emission; Total nitrogen oxide emissions | ||
| Ecotope | Forest coverage | ||
| Regional carrying object | Economic-social activities | Green GDP | GDP; Loss of value of natural resources; Environmental pollution loss value; Positive returns on resources and environment |
| Year | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regional Unit Carrying Capacity | The Yangtze River Economic Belt | 736.61 | 778.73 | 969.6 | 1304.34 | 1318.46 | 1537.3 | 1840.65 | 2225.71 | 2488.86 | 2751.5 | 2992.78 | 3207.7 | 3089.4 | 3927.57 | 4020.18 | 4432.64 |
| The country | 813.54 | 822.85 | 965.74 | 1192.99 | 1365.93 | 1533 | 1775.23 | 2118.84 | 2378.7 | 2583.39 | 2822.14 | 2975.2 | 2857.37 | 3499.65 | 3759.04 | 4112.71 | |
| The difference rate | 10.44% | 5.67% | −0.40% | −8.54% | 3.60% | −0.28% | −3.55% | −4.80% | −4.43% | −6.11% | −5.70% | −7.25% | −7.51% | −10.90% | −6.50% | −7.22% | |
| Carrying status | Deficit | Deficit | Balance | Surplus | Deficit | Balance | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | |
| Unit Carrying Capacity of Economic-social Subsystem | The Yangtze River Economic Belt | 776.3 | 761.14 | 970.88 | 1268.49 | 1306 | 1522.69 | 1843.36 | 2212.07 | 2507.06 | 2779.13 | 3051.49 | 3301.24 | 3652.2 | 4096.47 | 4317.65 | 4818.39 |
| The country | 831.68 | 809.16 | 956.22 | 1165.23 | 1347.9 | 1524.36 | 1769.22 | 2109.26 | 2391.96 | 2609.21 | 2845.07 | 3020.7 | 3280.85 | 3692.74 | 4157.27 | 4601.49 | |
| The difference rate | 7.13% | 6.31% | −1.51% | −8.14% | 3.21% | 0.11% | −4.02% | −4.65% | −4.59% | −6.11% | −6.76% | −8.50% | −10.17% | −9.86% | −3.71% | −4.50% | |
| Carrying status | Deficit | Deficit | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Balance | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | |
| Unit Carrying Capacity of Resource Subsystem | The Yangtze River Economic Belt | 651.72 | 777.95 | 988.57 | 1299.16 | 1326.9 | 1533.34 | 1842.44 | 2226.68 | 2489.9 | 2756.13 | 3002.96 | 3235.91 | 3524.89 | 4024.52 | 4230.33 | 4713.56 |
| The country | 708.42 | 817.28 | 966.92 | 1182.84 | 1360.51 | 1528.2 | 1763.87 | 2109.83 | 2366.84 | 2579.74 | 2820.53 | 3009.5 | 3268.75 | 3735.99 | 4094.54 | 4562.51 | |
| The difference rate | 8.70% | 5.06% | −2.19% | −8.95% | 2.53% | −0.33% | −4.26% | −5.25% | −4.94% | −6.40% | −6.07% | −7.00% | −7.27% | −7.17% | −3.21% | −3.20% | |
| Carrying status | Deficit | Deficit | Surplus | Surplus | Deficit | Balance | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | |
| Unit Carrying Capacity of Environmental Subsystem | The Yangtze River Economic Belt | 636.16 | 764.27 | 966.81 | 1257.39 | 1297.31 | 1512.67 | 1832.81 | 2215.55 | 2521.97 | 2805.21 | 3093.11 | 3352.47 | 3205.78 | 4127.48 | 4425.59 | 5046.89 |
| The country | 693.04 | 809 | 951.38 | 1151.82 | 1334.06 | 1506.99 | 1760.68 | 2125.13 | 2427.71 | 2661.11 | 2941.21 | 3129.24 | 3006.59 | 3732.43 | 4220.76 | 4785.72 | |
| The difference rate | 8.94% | 5.85% | −1.60% | −8.40% | 2.83% | −0.38% | −3.94% | −4.08% | −3.74% | −5.14% | −4.91% | −6.66% | −6.21% | −9.57% | −4.63% | −5.17% | |
| Carrying status | Deficit | Deficit | Surplus | Surplus | Deficit | Balance | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | Surplus | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Ou, G.; Elshkaki, A.; Liu, R. Evaluation of Regional Carrying Capacity under Economic-Social-Resource-Environment Complex System: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7117. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127117
Zhang Z, Ou G, Elshkaki A, Liu R. Evaluation of Regional Carrying Capacity under Economic-Social-Resource-Environment Complex System: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sustainability. 2022; 14(12):7117. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127117
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhimin, Guoli Ou, Ayman Elshkaki, and Ruilin Liu. 2022. "Evaluation of Regional Carrying Capacity under Economic-Social-Resource-Environment Complex System: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt" Sustainability 14, no. 12: 7117. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127117
APA StyleZhang, Z., Ou, G., Elshkaki, A., & Liu, R. (2022). Evaluation of Regional Carrying Capacity under Economic-Social-Resource-Environment Complex System: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sustainability, 14(12), 7117. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127117