Combining Numerical Simulation and Deep Learning for Landslide Displacement Prediction: An Attempt to Expand the Deep Learning Dataset
Abstract
:1. Introduction
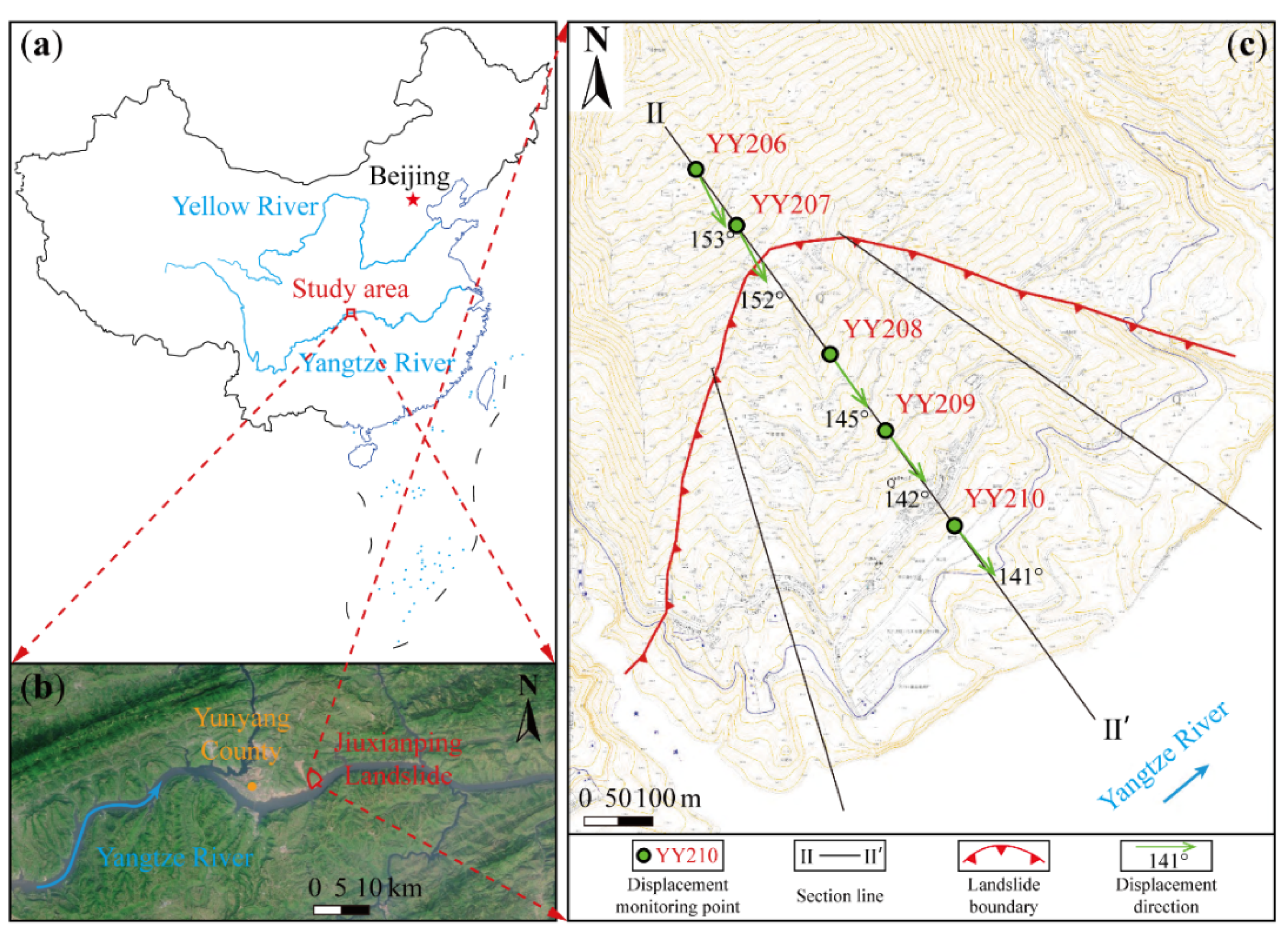
2. Jiuxianping Landslide
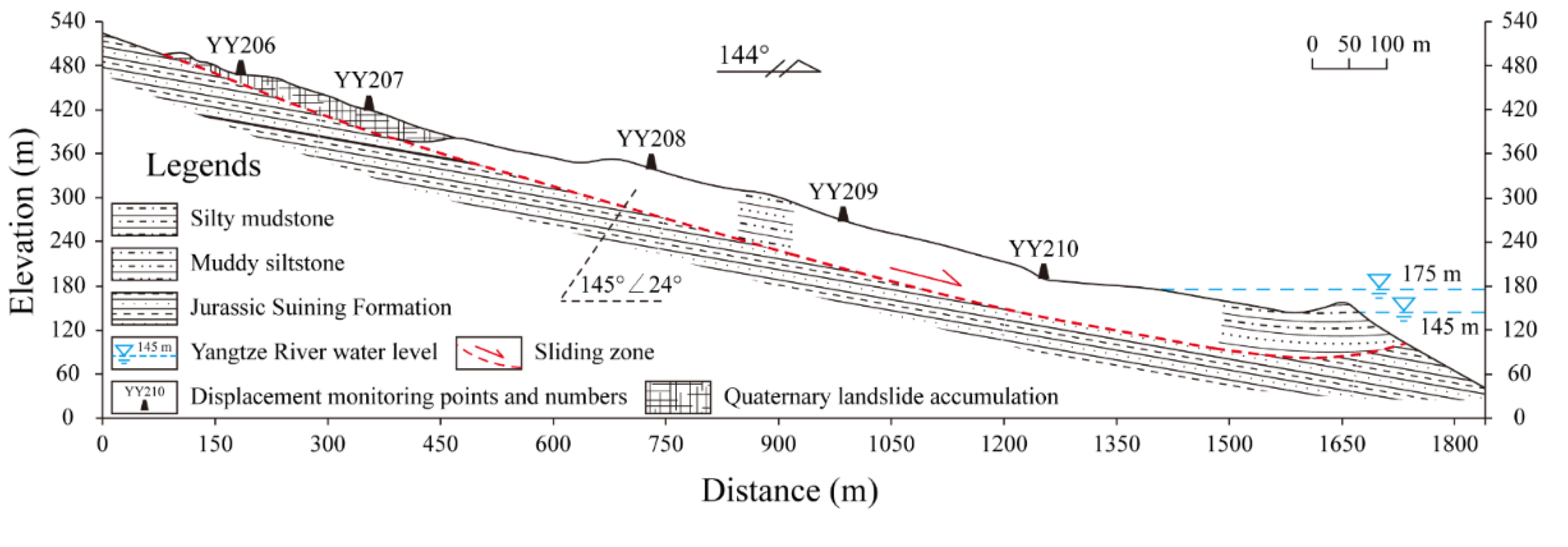
2.1. Regional Background and Geological Structure
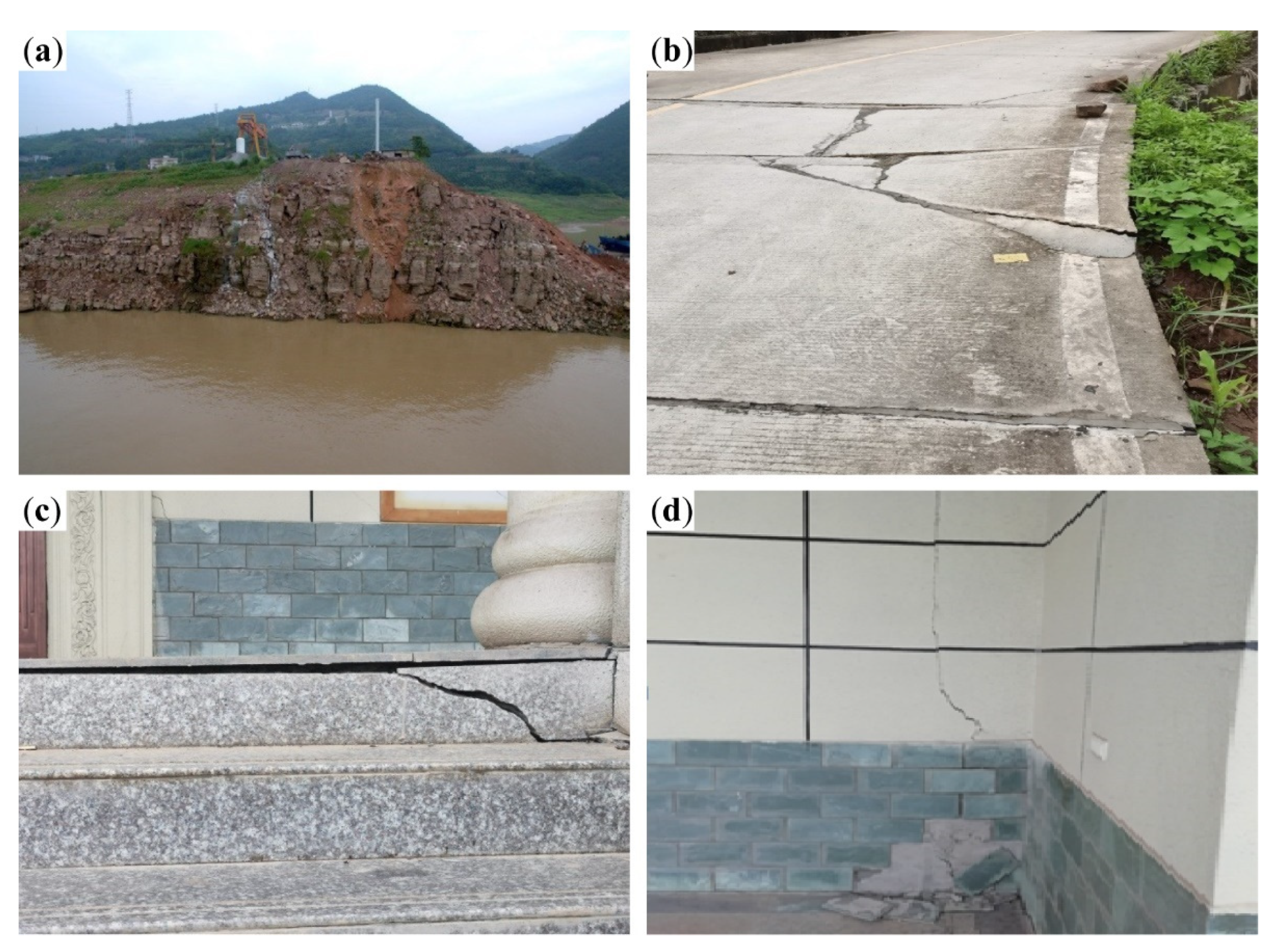
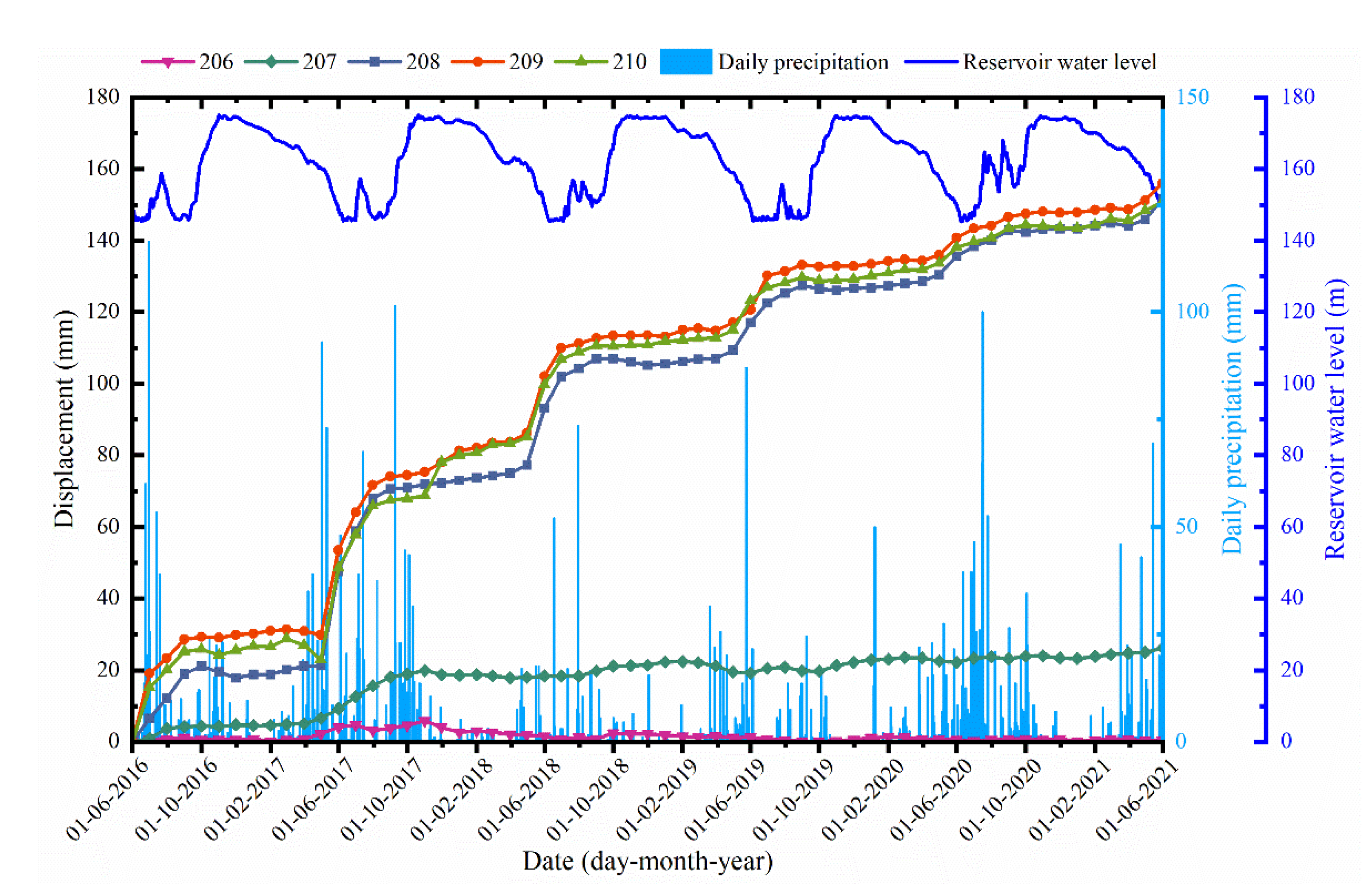
2.2. Monitoring Results
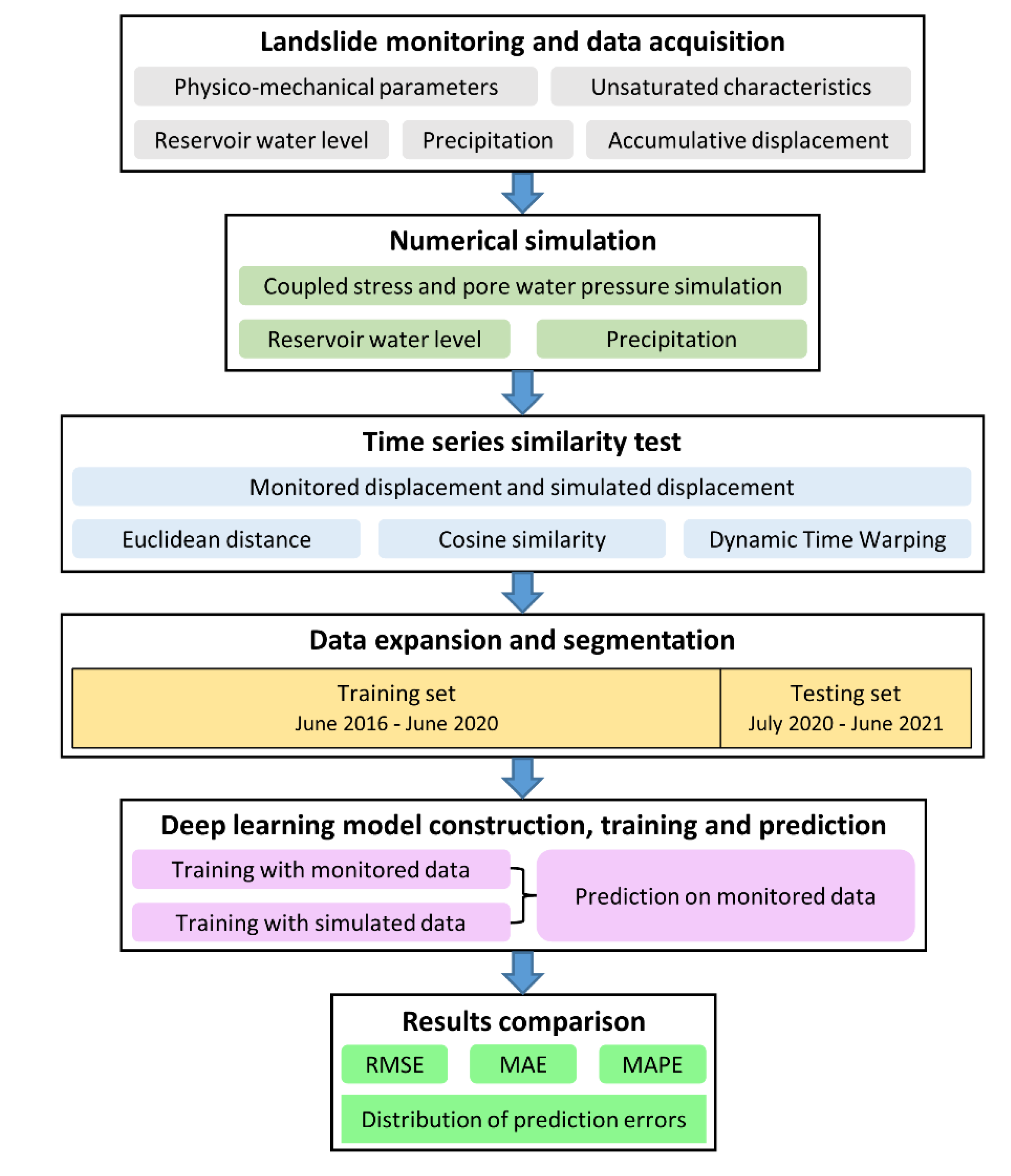
3. Coupled Numerical Simulation Schemes
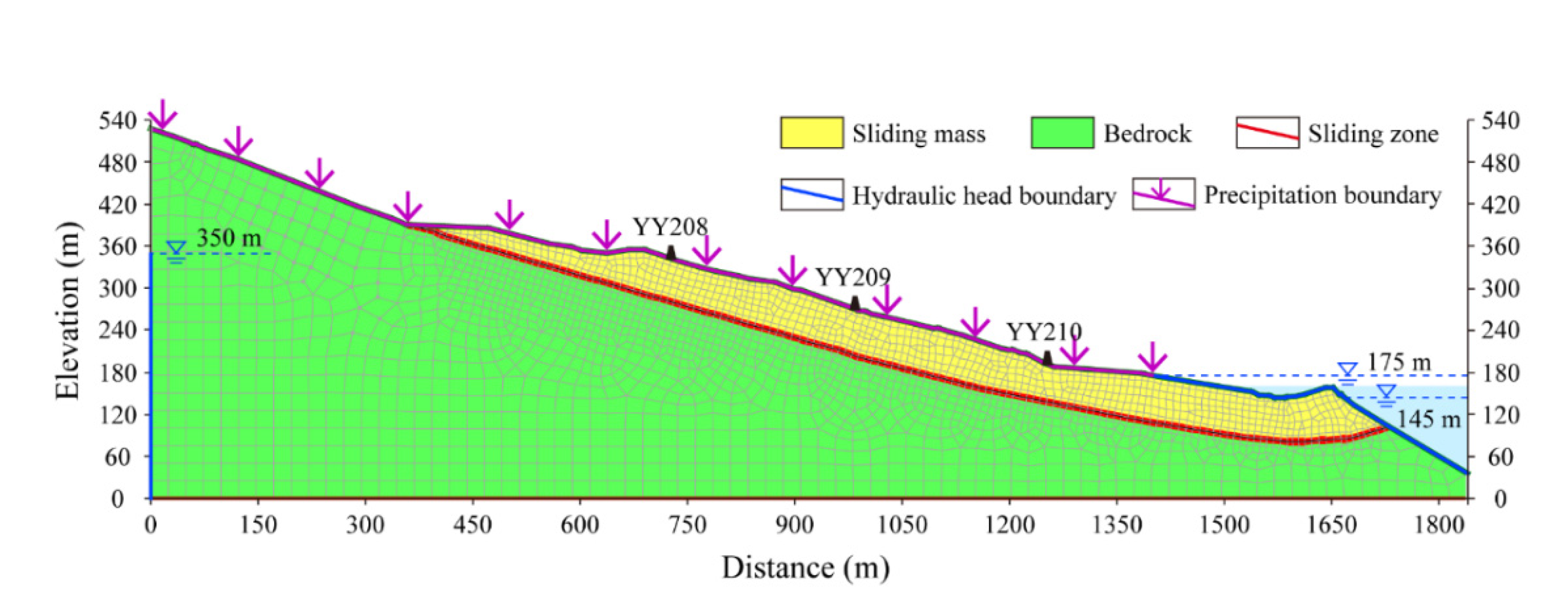
3.1. Numerical Model
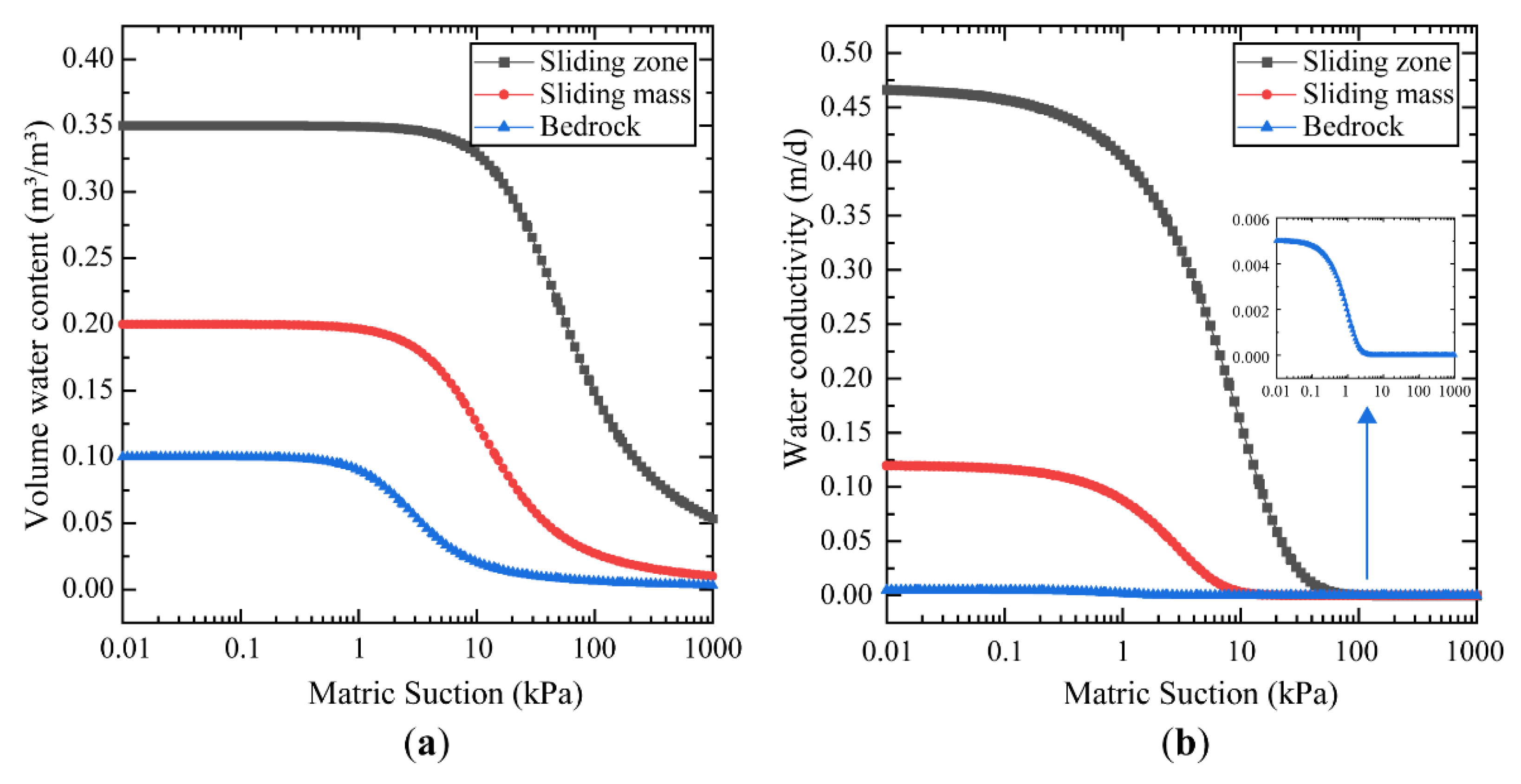
3.2. Simulation Schemes and Parameters
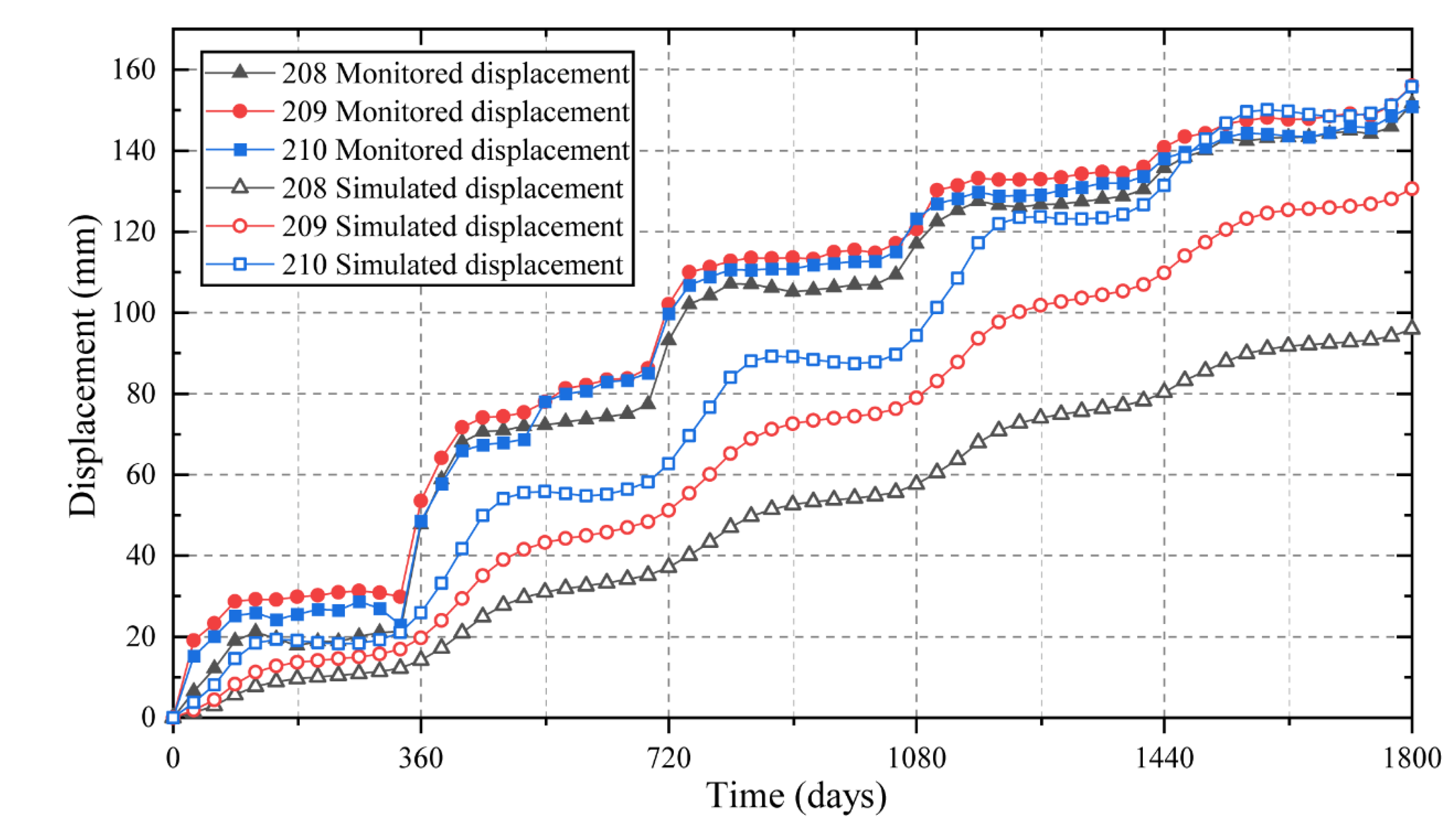
3.3. Simulation Results
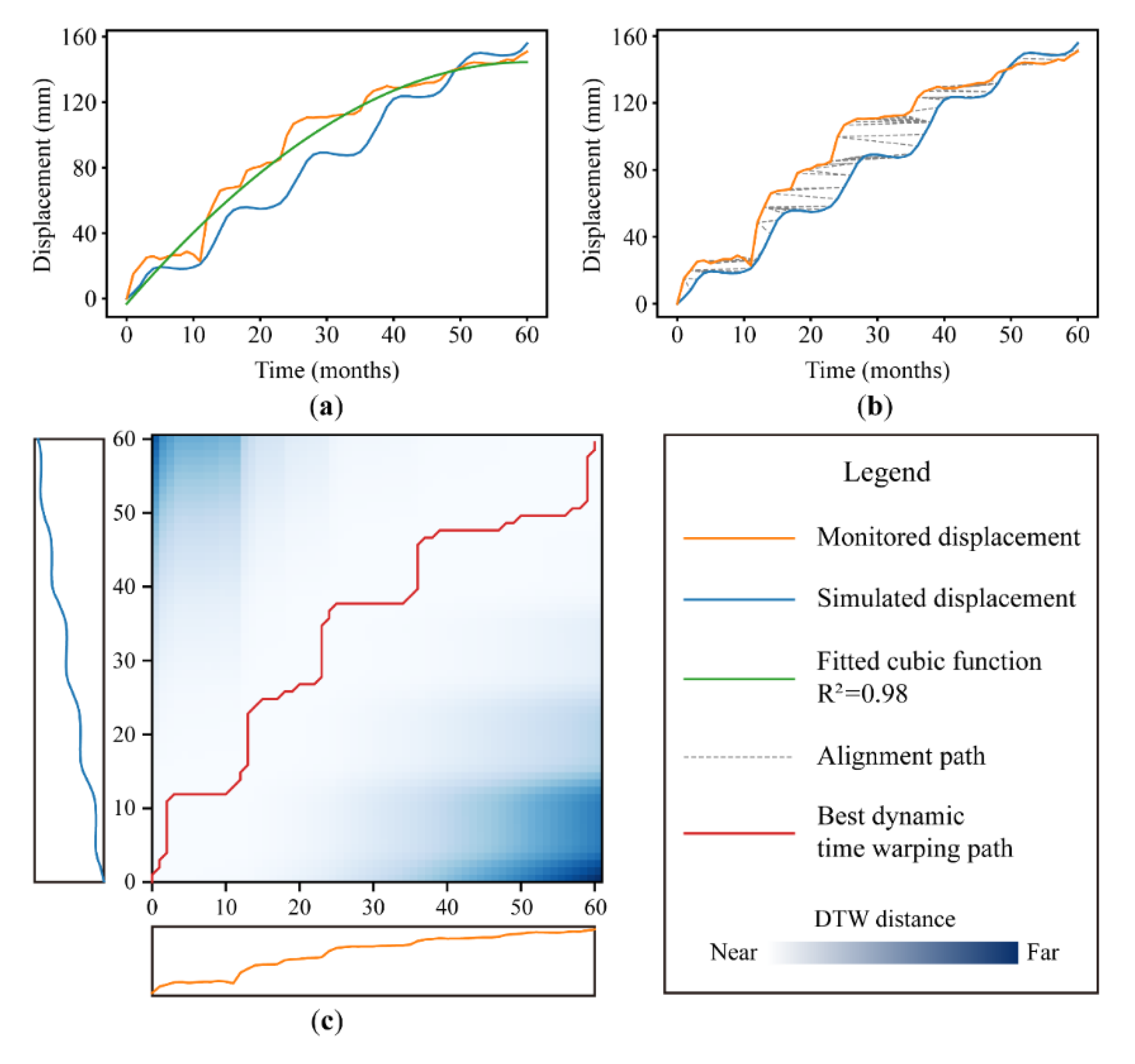
4. Displacement Time Series Similarity
4.1. Numerical Similarity
4.2. Orientation Similarity
4.3. Shape Similarity
5. Displacement Prediction Deep Learning Model
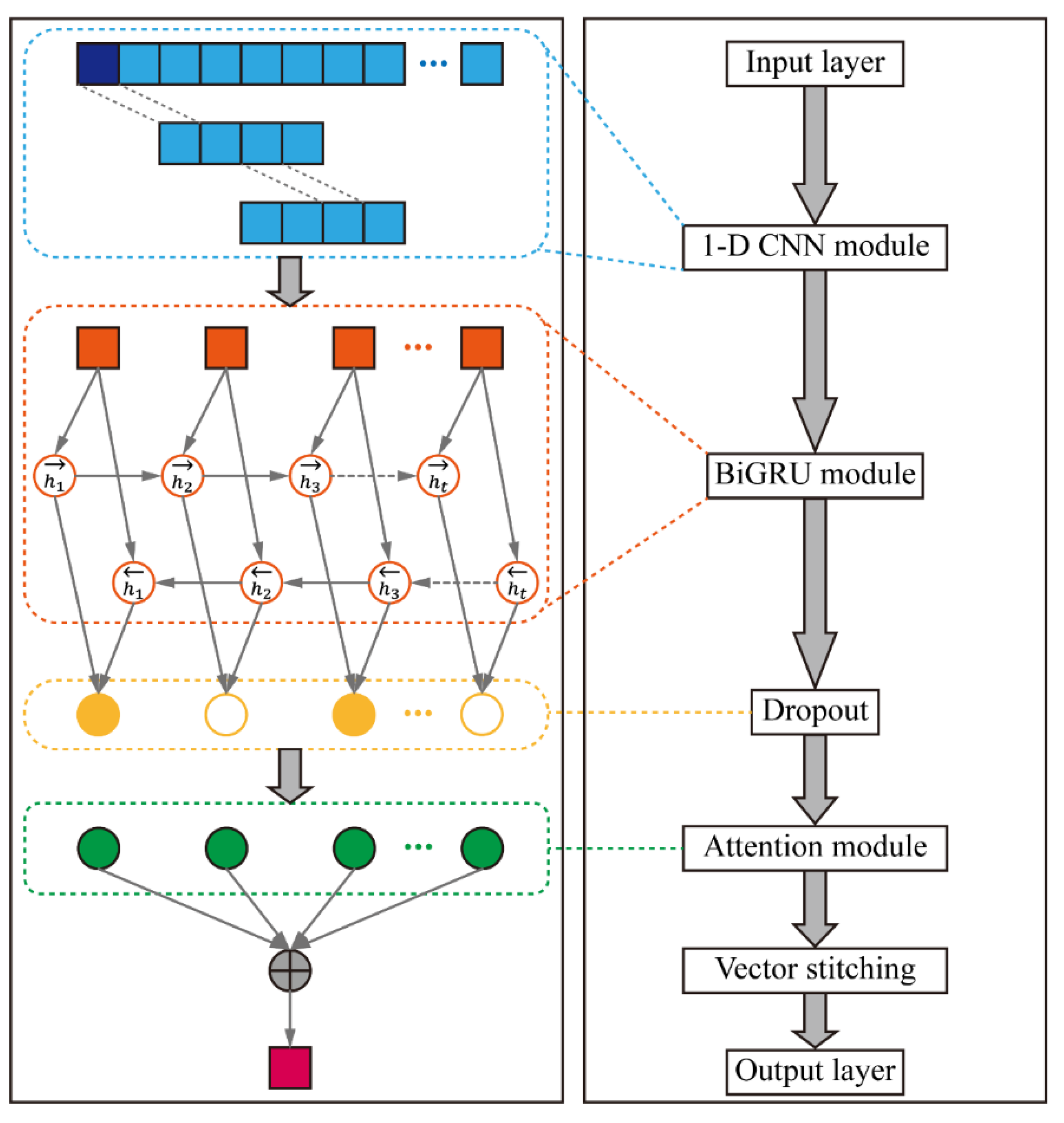
5.1. Deep Learning Model Construction
5.1.1. CNN Module
5.1.2. BiGRU Module
5.1.3. AM Module
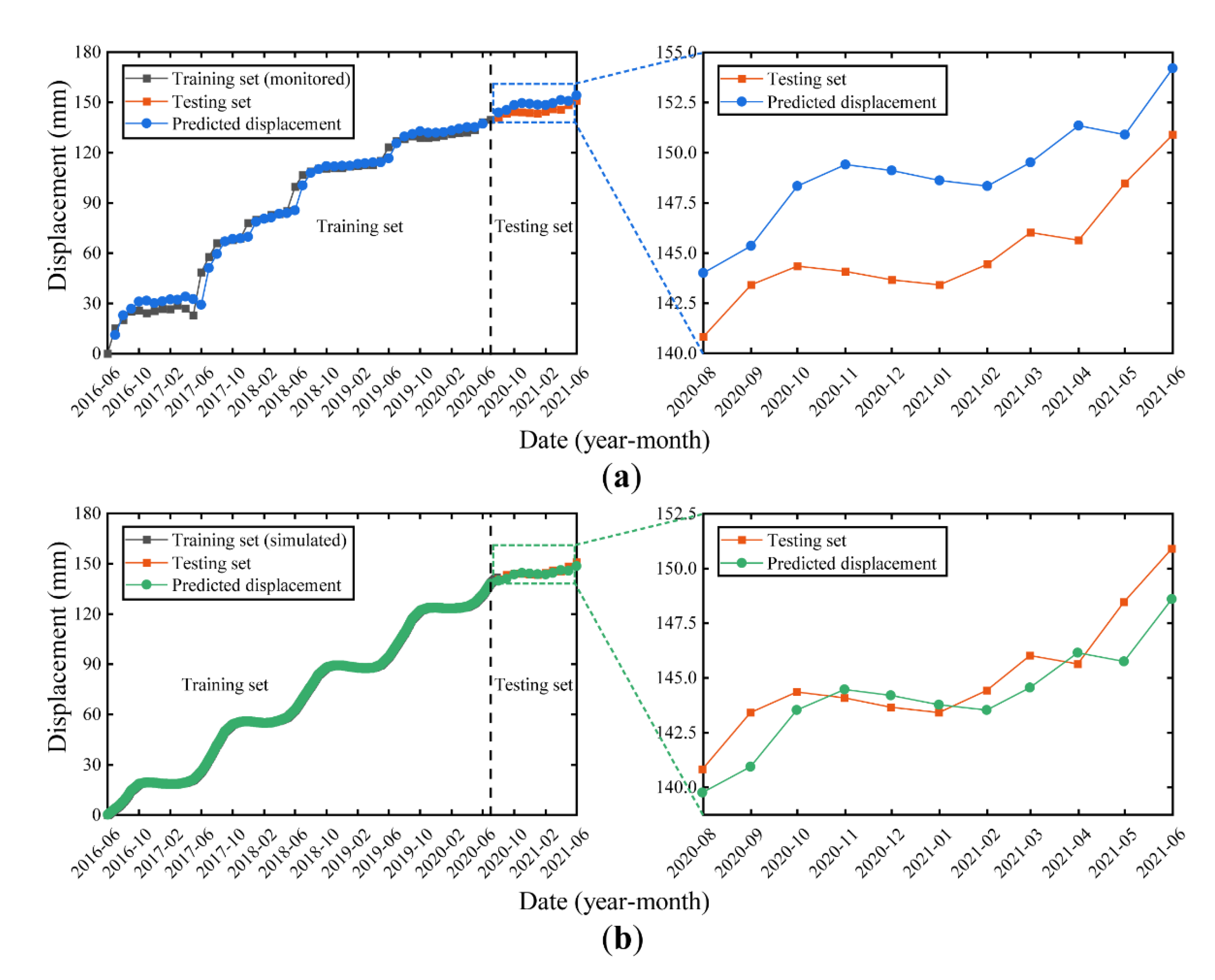
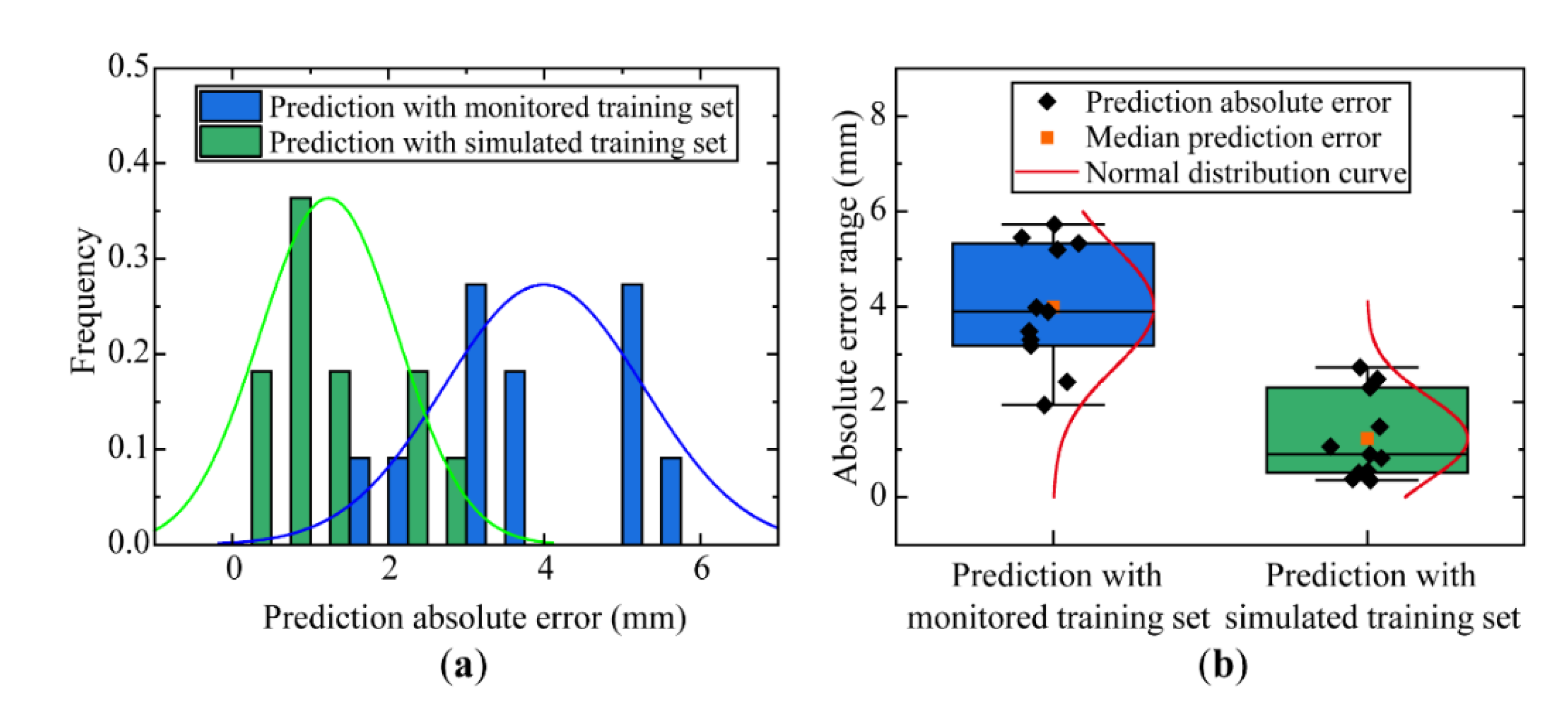
5.2. Model Training and Prediction
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vu, V.N.; Binh, T.P.; Ba, T.V.; Prakash, I.; Jha, S.; Shahabi, H.; Shirzadi, A.; Dong, N.B.; Kumar, R.; Chatterjee, J.M.; et al. Hybrid Machine Learning Approaches for Landslide Susceptibility Modeling. Forests 2019, 10, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Catane, S.G.; Veracruz, N.A.S.; Flora, J.R.R.; Go, C.M.M.; Enrera, R.E.; Santos, E.R.U. Mechanism of a low-angle translational block slide: Evidence from the September 2018 Naga landslide, Philippines. Landslides 2019, 16, 1709–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Wu, L.Z.; Huang, R.Q.; Zhang, H. Formation and characteristics of the Xiaoba landslide in Fuquan, Guizhou, China. Landslides 2018, 15, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, U.; Da Silva, P.F.; Lee, J.; Benz, S.; Auflič, M.J.; Blum, P. Increasing Fatal Landslides in Europe; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 505–512. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Xu, J.; Wen, H.; Wang, D. Assessment of landslide susceptibility mapping based on Bayesian hyperparameter optimization: A comparison between logistic regression and random forest. Eng. Geol. 2021, 281, 105972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Xu, J.; Wen, H.; Wang, Y. An Optimized Random Forest Model and Its Generalization Ability in Landslide Susceptibility Mapping: Application in Two Areas of Three Gorges Reservoir, China. J. Earth Sci. China 2020, 31, 1068–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthrie, R.H.; Evans, S.G.; Catane, S.G.; Zarco, M.A.H.; Saturay, R.M., Jr. The 17 February 2006 rock slide-debris avalanche at Guinsaugon Philippines: A synthesis. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2009, 68, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, R.M.; George, D.L.; Allstadt, K.; Reid, M.E.; Collins, B.D.; Vallance, J.W.; Schilling, S.P.; Godt, J.W.; Cannon, C.M.; Magirl, C.S.; et al. Landslide mobility and hazards: Implications of the 2014 Oso disaster. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2015, 412, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouyang, C.; Zhou, K.; Xu, Q.; Yin, J.; Peng, D.; Wang, D.; Li, W. Dynamic analysis and numerical modeling of the 2015 catastrophic landslide of the construction waste landfill at Guangming, Shenzhen, China. Landslides 2017, 14, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Yin, K.; Lacasse, S.; Liu, Z. Time series analysis and long short-term memory neural network to predict landslide displacement. Landslides 2019, 16, 677–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M. Forecasting Time of Slope Failure by Tertiary Creep; A.A. Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 1969; Volume 2, pp. 677–683. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, M. Research on Forecasting the Time of Occurrence of Slope Failure; Quarterly Reports; Railway Technical Research Institute: Tokyo, Japan, 1969; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Crosta, G.B.; Agliardi, F. Failure forecast for large rock slides by surface displacement measurements. Can. Geotech. J. 2003, 40, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvelebill, J.; Moser, M. Monitoring based time-prediction of rock falls: Three case-histories. Phys. Chem. Earth Part B Hydrol. Ocean. Atmos. 2001, 26, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, N.D.; Hungr, O. Forecasting potential rock slope failure in open pit mines using the inverse-velocity method. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 2007, 44, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mufundirwa, A.; Fujii, Y.; Kodama, J. A new practical method for prediction of geomechanical failure-time. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 2010, 47, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corominas, J.; Moya, J.; Ledesma, A.; Lloret, A.; Gili, J.A. Prediction of ground displacements and velocities from groundwater level changes at the Vallcebre landslide (Eastern Pyrenees, Spain). Landslides 2005, 2, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Tang, H.; Liu, X.; Hu, X.; Sun, M.; Song, Y. Establishment of a deformation forecasting model for a step-like landslide based on decision tree C5.0 and two-step cluster algorithms: A case study in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Landslides 2017, 14, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, C.; Zeng, Z.; Yao, W.; Tang, H.; Chen, C.L.P. Landslide Displacement Prediction with Uncertainty Based on Neural Networks with Random Hidden Weights. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2016, 27, 2683–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Z.; Kong, J.M. Application of GA-SVM method with parameter optimization for landslide development prediction. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, F.; Huang, J.; Jiang, S.; Zhou, C. Landslide displacement prediction based on multivariate chaotic model and extreme learning machine. Eng. Geol. 2017, 218, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Guo, D.; Lacasse, S.; Li, J.; Yang, B.; Choi, J. Algorithms for intelligent prediction of landslide displacements. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2020, 21, 412–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Mei, G.; Prezioso, E.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, N. A deep learning approach using graph convolutional networks for slope deformation prediction based on time-series displacement data. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 14441–14457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, L.; Gui, L.; Du, J.; Yin, K.; Do, H.M. Landslide displacement prediction based on variational mode decomposition and WA-GWO-BP model. Landslides 2020, 17, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Dai, F.; Xu, X.; Lee, Y.H. GIS-based support vector machine modeling of earthquake-triggered landslide susceptibility in the Jianjiang River watershed, China. Geomorphology 2012, 145, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, B.; Zhu, H.; Yu, X.B.; Han, H.; Fan, X. PSO-SVM-based deep displacement prediction of Majiagou landslide considering the deformation hysteresis effect. Landslides 2021, 18, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Yin, K.; Cao, Y.; Ahmed, B. Application of time series analysis and PSO-SVM model in predicting the Bazimen landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Eng. Geol. 2016, 204, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Wen, T.; Ma, J. A hybrid intelligent approach for constructing landslide displacement prediction intervals. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 81, 105506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Niu, R. Displacement prediction of Baijiabao landslide based on empirical mode decomposition and long short term memory neural network in Three Gorges area, China. Comput. Geosci. 2018, 111, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Tang, L.; Gu, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L. Displacement prediction of Jiuxianping landslide using gated recurrent unit (GRU) networks. Acta Geotech. 2022, 17, 1367–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Luo, H.; Xu, Q.; Lu, Z.; Liao, L.; Li, H.; Hao, L. A Graph Convolutional Incorporating GRU Network for Landslide Displacement Forecasting Based on Spatiotemporal Analysis of GNSS Observations. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; Xie, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, F. Data Mining and Deep Learning for Predicting the Displacement of “Step-like” Landslides. Sensors 2022, 22, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Long, G.; Liao, J.; Xu, Y.; Lv, Y. A new hybrid method for establishing point forecasting, interval forecasting, and probabilistic forecasting of landslide displacement. Nat. Hazards 2022, 111, 1479–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Yue, J.; Chen, C. Interval Estimation of Landslide Displacement Prediction Based on Time Series Decomposition and Long Short-Term Memory Network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 3187–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Wu, L.Z.; Chen, J.J.; Huang, R.Q. Multiple data-driven approach for predicting landslide deformation. Landslides 2020, 17, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Mei, G. Deep learning for geological hazards analysis: Data, models, applications, and opportunities. Earth Sci. Rev. 2021, 223, 103858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoya, N.; Yamanoi, K.; He, W.; Baier, G.; Adriano, B.; Miura, H.; Oishi, S. Breaking limits of remote sensing by deep learning from simulated data for flood and debris-flow mapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 60, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Shi, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Peng, M.; Ma, X.; Zhang, F. Unsaturated slope stability around the Three Gorges Reservoir under various combinations of rainfall and water level fluctuation. Eng. Geol. 2019, 261, 105231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Hu, B.; Yi, Q.; Yao, W.; Ma, C. The Coupling Effect of Rainfall and Reservoir Water Level Decline on the Baijiabao Landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Geofluids 2017, 2017, 3724867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.; Ehret, D.; Xiang, W.; Rohn, J.; Huang, L.; Yan, S.; Bi, R. Numerical simulation of Qiaotou Landslide deformation caused by drawdown of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Yin, K.; Lacasse, S. Displacement prediction in colluvial landslides, Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides 2013, 10, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Wasowski, J.; Juang, C.H. Geohazards in the three Gorges Reservoir Area, China Lessons learned from decades of research. Eng. Geol. 2019, 261, 105267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Li, C.; Zuo, Q.; Zhan, H.; Criss, R.E. Spatiotemporal deformation characteristics and triggering factors of Baijiabao landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir region, China. Geomorphology 2019, 343, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GEOSLOPE International Ltd. Static Stress-Strain Modeling with GeoStudio; GEOSLOPE International Ltd.: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- GEOSLOPE International Ltd. Rapid Drawdown; GEOSLOPE International Ltd.: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; He, C.; Zhou, C.; Xu, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Wu, S. Model Test and Numerical Analysis on the Deformation and Stability of a Landslide Subjected to Reservoir Filling. Geofluids 2019, 2019, 5924580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, N.; Hu, B.; Yan, E.; Xu, X.; Yi, Q. Research on the creep mechanism of Huangniba landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area of China considering the seepage-stress coupling effect. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 4107–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Tan, J.; Li, L.; Yin, X. The influence of water level fluctuation on the stability of landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, S.; Wang, R.; Xiao, M. Stability analysis of a typical landslide mass in the Three Gorges Reservoir under varying reservoir water levels. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.D.; Yang, Q.; Pan, S.H.; Ding, W.C.; Gao, Y.L. Research on the Impact of the Water-Level-Fluctuation Zone on Landslide Stability in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 188, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Tang, H.; Criss, R.E.; Hu, X.; Xiong, C.; Wu, Q.; Yuan, Y. A model for interpreting the deformation mechanism of reservoir landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 21, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhermitte, S.; Verbesselt, J.; Verstraeten, W.W.; Coppin, P. A comparison of time series similarity measures for classification and change detection of ecosystem dynamics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3129–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.; Wang, Y.; Lu, G.; Chen, P.; Ding, C.; Sun, J. A spatiotemporal correlative k-nearest neighbor model for short-term traffic multistep forecasting. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2016, 62, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwi, E.; Gyamfi, E.N.; Kyei, K.; Gill, R.; Adam, A.M. Determinants of Commodity Futures Prices: Decomposition Approach. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6032325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itakura, F. Minimum prediction residual principle applied to speech recognition. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1975, 23, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitjean, F.; Inglada, J.; Gancarski, P. Satellite Image Time Series Analysis Under Time Warping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3081–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.; van Merrienboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning Phrase Representations using RNN Encoder-Decoder for Statistical Machine Translation. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.1078. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.; Gulcehre, C.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Empirical Evaluation of Gated Recurrent Neural Networks on Sequence Modeling. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.3555. [Google Scholar]
- Treisman, A.M.; Gelade, G. A feature-integration theory of attention. Cogn. Psychol. 1980, 12, 97–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Materials | Unit Weight (kN/m3) | Elastic Modulus (MPa) | Cohesion (kPa) | Poisson Ratio | Friction Angle (°) | Permeability Coefficient (m/d) |
| Sliding mass | 23.8 | 306 | 800 | 0.25 | 33.9 | 0.12 |
| Sliding zone | 18.4 | 12.5 | 20.2 | 0.28 | 18 | 0.468 |
| Bedrock | 25.2 | 1120 | - | 0.22 | - | 0.005 |
| Metric | RMSE (mm) | MAE (mm) | DTW Distance (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monitored-Simulated | 17.58 | 14.39 | 633.47 |
| Monitored-Fitted | 6.91 | 5.06 | 642.84 |
| Data Set | Date Span | Data Length | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Training set | Monitored data | June 2016–June 2020 | 1470 |
| Simulated data | June 2016–June 2020 | 49 | |
| Testing set | Monitored data | July 2020–June 2021 | 12 |
| Hyperparameter | Dropout | Batch Size | Filter Length | GRU Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training with monitored data | 0 | 16 | 4 | 32 |
| Training with simulated data | 0.1 | 64 | 4 | 32 |
| Metric | MAE (mm) | RMSE (mm) | MAPE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prediction with monitored training set | 3.99 | 4.17 | 2.68 |
| Prediction with simulated training set | 1.23 | 1.50 | 0.85 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, W.; Xu, H.; Chen, J.; Kang, Y.; Pu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Tong, J. Combining Numerical Simulation and Deep Learning for Landslide Displacement Prediction: An Attempt to Expand the Deep Learning Dataset. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6908. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116908
Xu W, Xu H, Chen J, Kang Y, Pu Y, Ye Y, Tong J. Combining Numerical Simulation and Deep Learning for Landslide Displacement Prediction: An Attempt to Expand the Deep Learning Dataset. Sustainability. 2022; 14(11):6908. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116908
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Wenhan, Hong Xu, Jie Chen, Yanfei Kang, Yuanyuan Pu, Yabo Ye, and Jue Tong. 2022. "Combining Numerical Simulation and Deep Learning for Landslide Displacement Prediction: An Attempt to Expand the Deep Learning Dataset" Sustainability 14, no. 11: 6908. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116908
APA StyleXu, W., Xu, H., Chen, J., Kang, Y., Pu, Y., Ye, Y., & Tong, J. (2022). Combining Numerical Simulation and Deep Learning for Landslide Displacement Prediction: An Attempt to Expand the Deep Learning Dataset. Sustainability, 14(11), 6908. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116908






