Sustainable Alternatives for Tertiary Treatment of Pulp and Paper Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case-Study
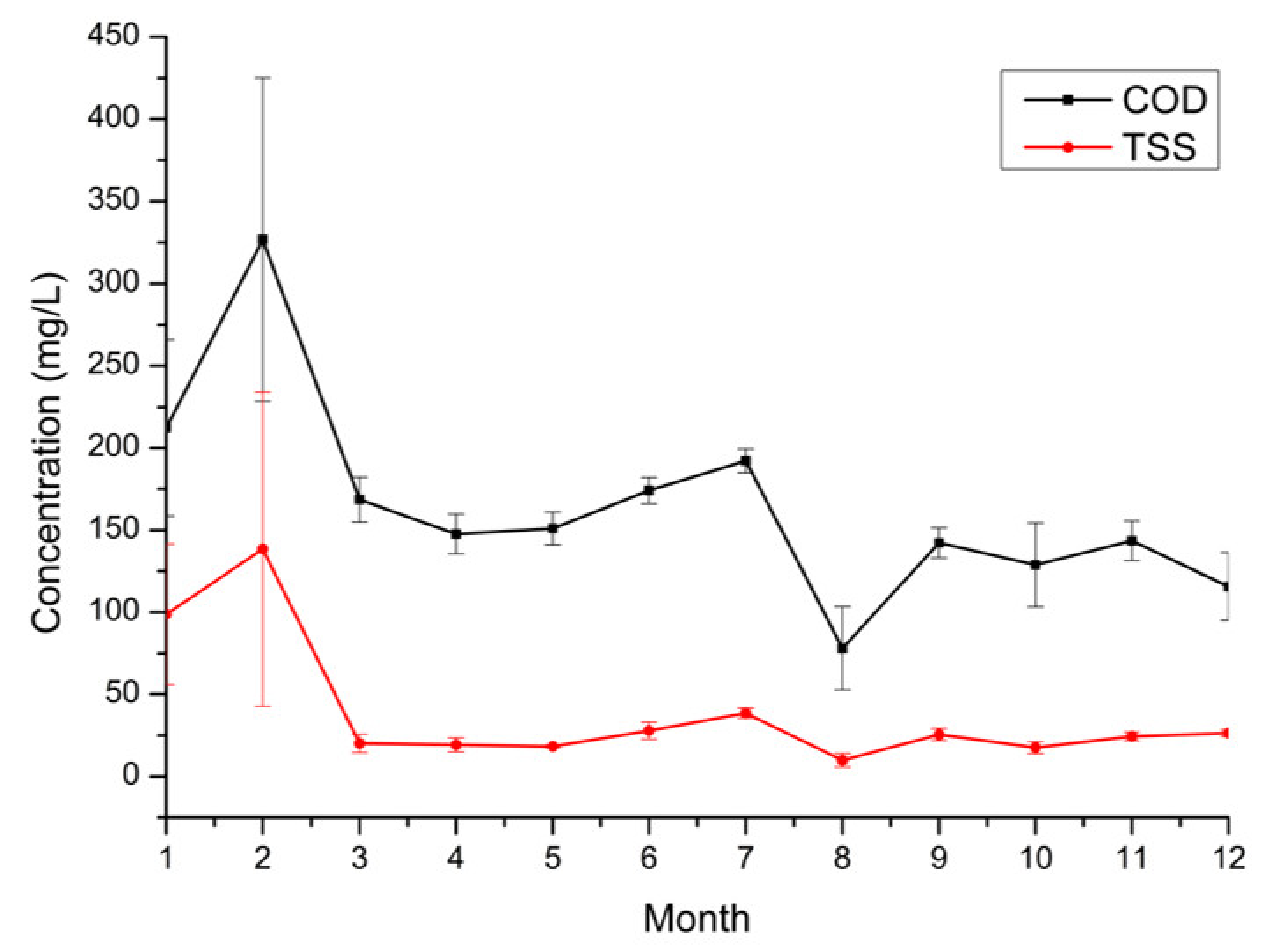
2.2. Secondary Effluent Characterization
2.3. Dimensional Analysis of Solid Matter
2.4. Pilot Cloth Filtration Tests
2.5. Adsorption Experiments
2.6. Analytical Techniques
3. Results
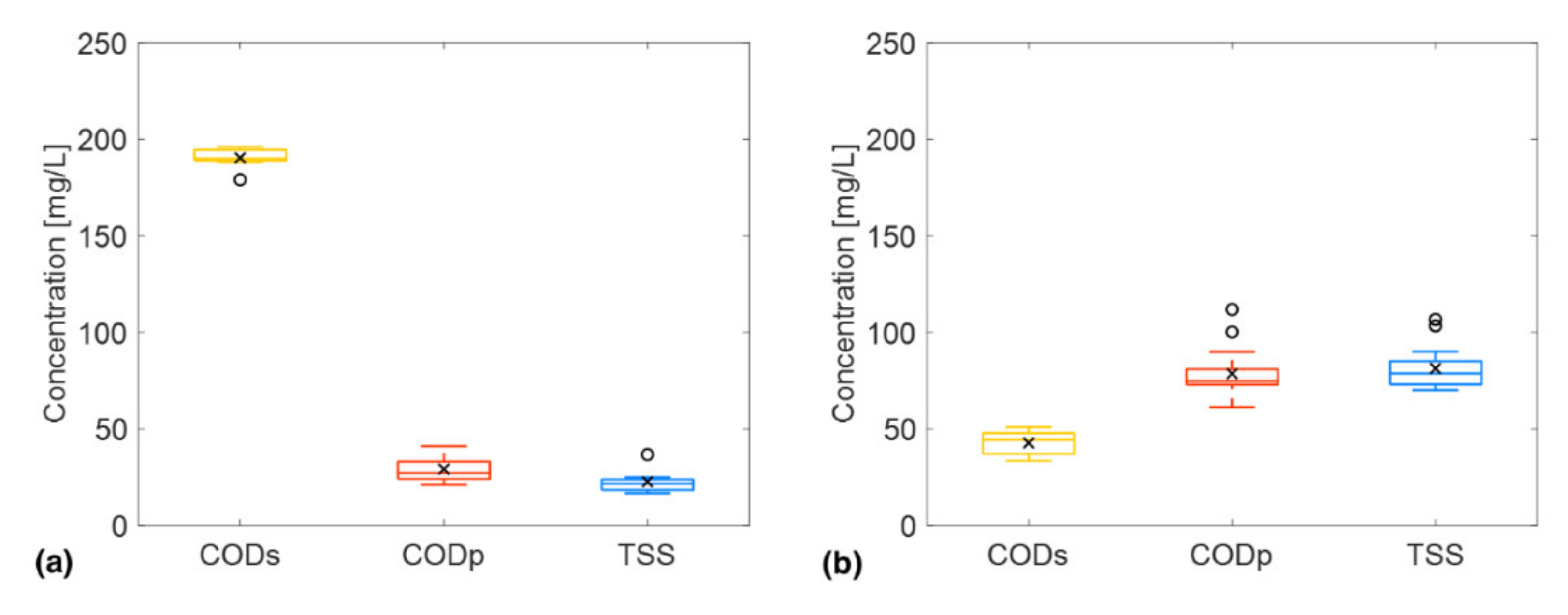
3.1. COD Fractionation
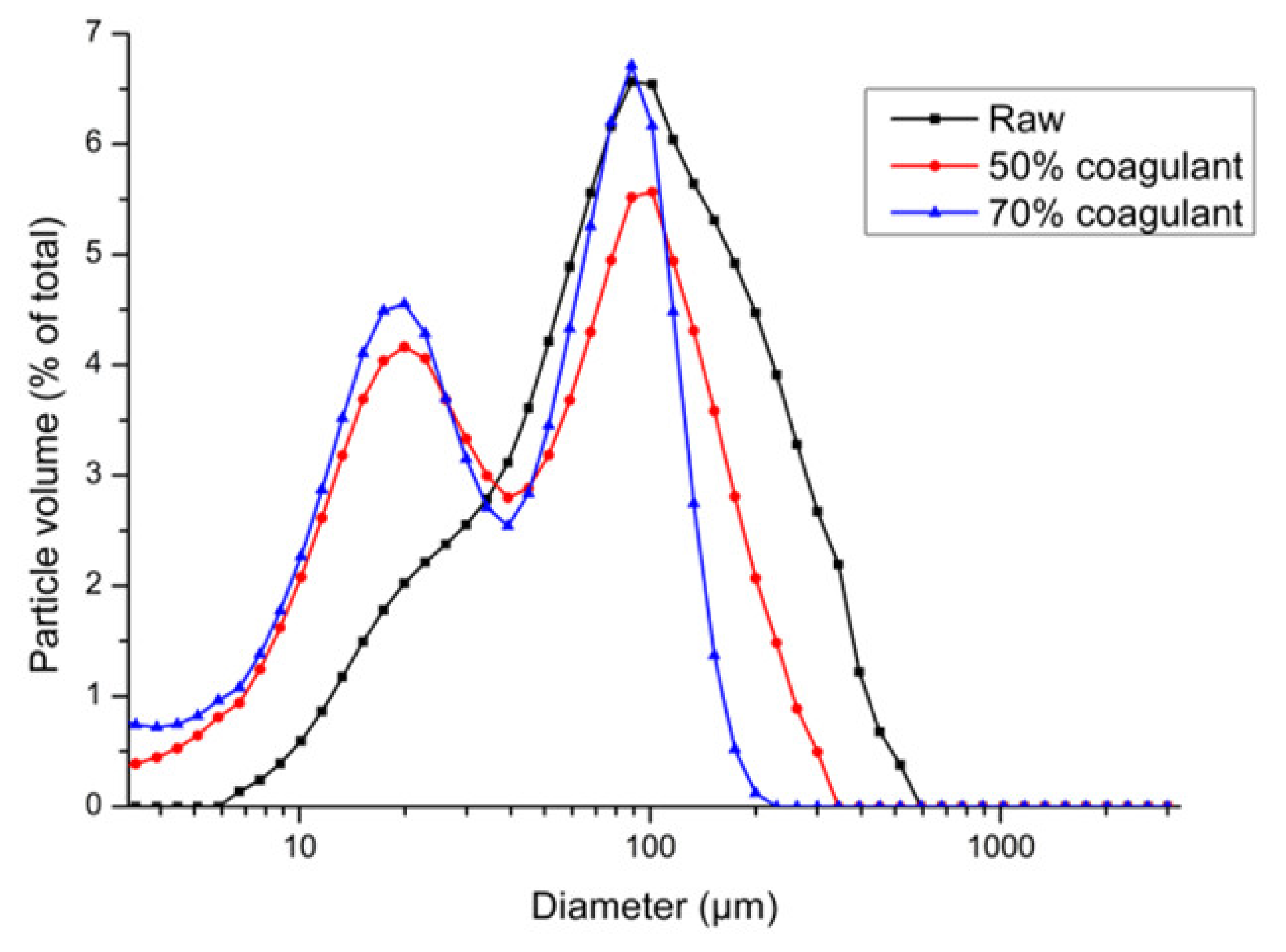
3.2. Pilot Cloth Filtration Campaign
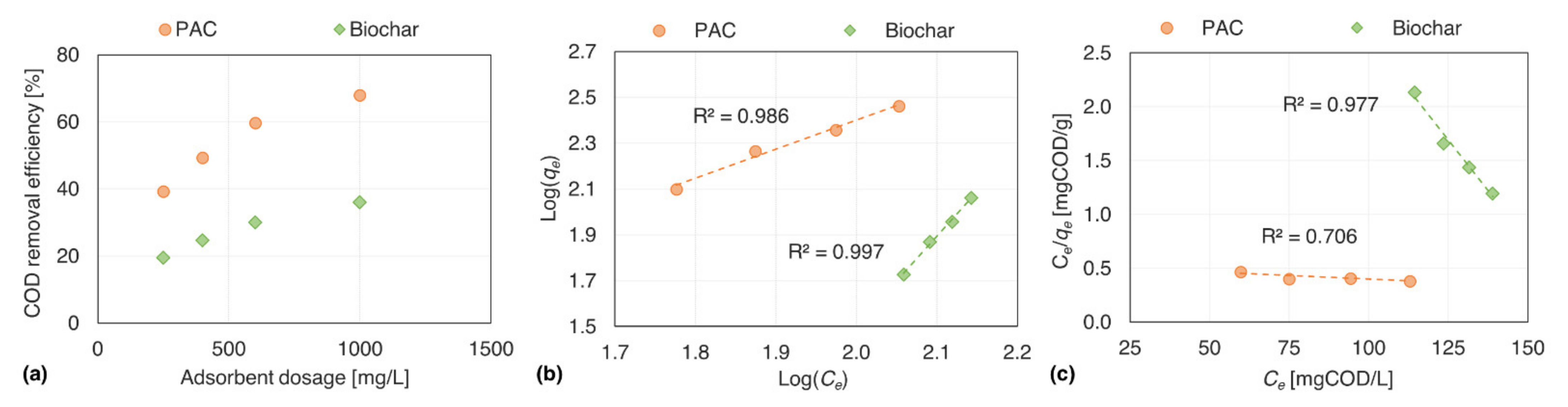
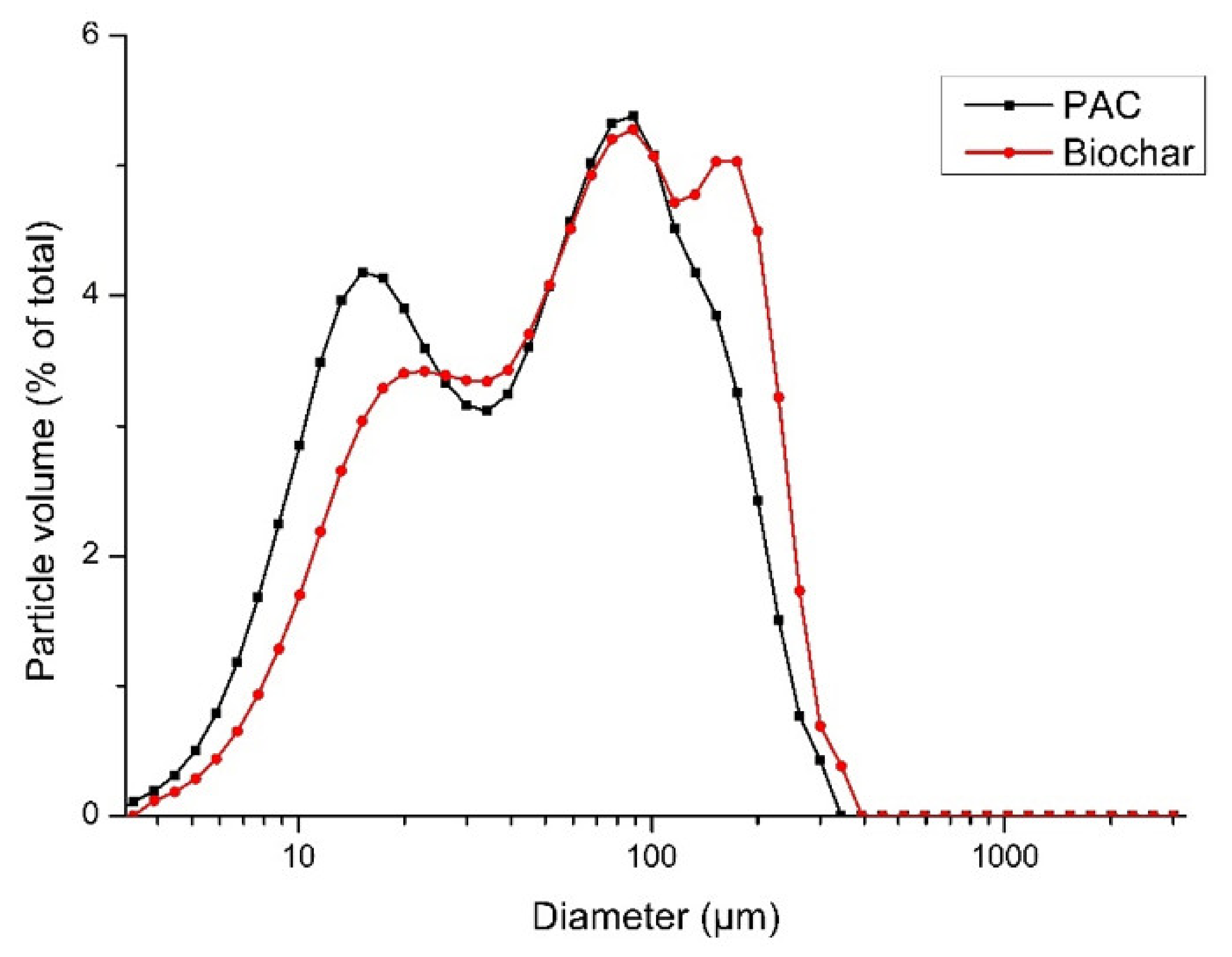
3.3. Adsorption Tests
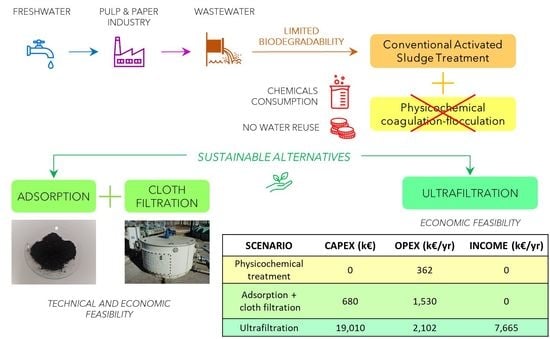
3.4. Economic Sustainability of Alternative Tertiary Treatment Technologies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toczyłowska-Mamińska, R. Limits and Perspectives of Pulp and Paper Industry Wastewater Treatment—A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 78, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Zhang, J.; Hoang, M.; Gray, S.; Xie, Z. A Review of Process and Wastewater Reuse in the Recycled Paper Industry. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Chandra, R. Pollutants Released from the Pulp Paper Industry: Aquatic Toxicity and Their Health Hazards. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 211, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, D.; Bhardwaj, N.K.; Lohchab, R.K. Effect of Incorporation of Ozone Prior to ECF Bleaching on Pulp, Paper and Effluent Quality. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 236, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainardis, M.; Goi, D. Pilot-UASB Reactor Tests for Anaerobic Valorisation of High-Loaded Liquid Substrates in Friulian Mountain Area. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, N.; Singh, S.; Garg, A. A Comparative Treatment of Bleaching Wastewater by Physicochemical Processes. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 2367–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.C.; Nesbø, C.; Edwards, E.A.; Jenson, E. Anaerobic Digestion of Kraft Pulp Mill Foul Condensate Under Thermophilic and Mesophilic Conditions. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainardis, M.; Buttazzoni, M.; Goi, D. Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) Technology for Energy Recovery: A Review on State-of-the-Art and Recent Technological Advances. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, M.; Khodaparast, Z. Review on Recent Developments on Pulp and Paper Mill Wastewater Treatment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 114, 326–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyukkamaci, N.; Koken, E. Economic Evaluation of Alternative Wastewater Treatment Plant Options for Pulp and Paper Industry. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 6070–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarshan, K.; Maruthaiya, K.; Kotteeswaran, P.; Murugan, A. Reuse the Pulp and Paper Industry Wastewater by Using Fashionable Technology. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3317–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palmieri, S.; Cipolletta, G.; Pastore, C.; Giosuè, C.; Akyol, Ç.; Eusebi, A.L.; Frison, N.; Tittarelli, F.; Fatone, F. Pilot Scale Cellulose Recovery from Sewage Sludge and Reuse in Building and Construction Material. Waste Manag. 2019, 100, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainardis, M.; Cecconet, D.; Moretti, A.; Callegari, A.; Goi, D.; Freguia, S.; Capodaglio, A.G. Wastewater Fertigation in Agriculture: Issues and Opportunities for Improved Water Management and Circular Economy. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 296, 118755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatone, F.; Di Fabio, S.; Bolzonella, D.; Cecchi, F. Fate of Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Italian Municipal Wastewater Systems: An Overview of Wastewater Treatment Using Conventional Activated-Sludge Processes (CASP) and Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs). Water Res. 2011, 45, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campana, P.E.; Mainardis, M.; Moretti, A.; Cottes, M. 100% Renewable Wastewater Treatment Plants: Techno-Economic Assessment Using a Modelling and Optimization Approach. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 239, 114214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashi, H.; Iorhemen, O.T.; Tay, J.H. Aerobic Granulation: A Recent Development on the Biological Treatment of Pulp and Paper Wastewater. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2018, 9, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Patel, N.; Vaghamshi, N.; Shah, K.; Duggirala, S.M.; Dudhagara, P. Trends and Strategies in the Effluent Treatment of Pulp and Paper Industries: A Review Highlighting Reactor Options. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2021, 2, 100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainardis, M.; Buttazzoni, M.; Gievers, F.; Vance, C.; Magnolo, F.; Murphy, F.; Goi, D. Life Cycle Assessment of Sewage Sludge Pretreatment for Biogas Production: From Laboratory Tests to Full-Scale Applicability. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 322, 129056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Tyagi, R.D.; Zhang, X. Review on Pulp and Paper Activated Sludge Pretreatment, Inhibitory Effects and Detoxification Strategies for Biovalorization. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Li, H.; Chen, H.; Yuan, R.; Wang, F.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, B. Tertiary Treatment of Biologically Treated Effluents from Pulp and Paper Industry by Microwave Modified Activated Carbon Adsorption. Desalination Water Treat. 2020, 182, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Thakur, I.S.; Shah, M.P. Bioremediation Approaches for Treatment of Pulp and Paper Industry Wastewater: Recent Advances and Challenges. In Microbial Bioremediation & Biodegradation; Shah, M.P., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 1–48. ISBN 9789811518126. [Google Scholar]
- Manna, M.; Sen, S. Advanced Oxidation Process: A Sustainable Technology for Treating Refractory Organic Compounds Present in Industrial Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainardis, M.; Buttazzoni, M.; De Bortoli, N.; Mion, M.; Goi, D. Evaluation of Ozonation Applicability to Pulp and Paper Streams for a Sustainable Wastewater Treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M.S.; Peres, J.A.; Amor, C.; Prieto-Rodríguez, L.; Maldonado, M.I.; Malato, S. Tertiary Treatment of Pulp Mill Wastewater by Solar Photo-Fenton. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 225–226, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Gu, L.; Ma, H. Electrochemical Oxidation of Pulp and Paper Making Wastewater Assisted by Transition Metal Modified Kaolin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 143, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, C. Tertiary Treatment Option for Pulp and Paper Mill Wastewater to Achieve Effluent Recycling. IPPTA Q. J. Indian Pulp Pap. Tech. Assoc. 2011, 23, 155–159. [Google Scholar]
- Obotey Ezugbe, E.; Rathilal, S. Membrane Technologies in Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Membranes 2020, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, F.R.P.; Serra, R.B.G.; de Figueirêdo, G.J.A.; da Hora, P.H.A.; de Sousa, A.C. Wastewater Treatment Using Adsorption Process in Column for Agricultural Purposes. Rev. Ambient. Água 2019, 14, e2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.S.; Cheun, J.Y.; Kumar, P.S.; Mubashir, M.; Majeed, Z.; Banat, F.; Ho, S.-H.; Show, P.L. A Review on Conventional and Novel Materials towards Heavy Metal Adsorption in Wastewater Treatment Application. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 296, 126589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, R.; Shafiq, I.; Akhter, P.; Iqbal, M.J.; Hussain, M. A State-of-the-Art Review on Wastewater Treatment Techniques: The Effectiveness of Adsorption Method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9050–9066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, K.; Rehman, S.K.U.; Wang, J.; Farooq, F.; Mahmood, Q.; Jadoon, A.M.; Javed, M.F.; Ahmad, I. Treatment of Pulp and Paper Industrial Effluent Using Physicochemical Process for Recycling. Water 2019, 11, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kakkar, S.; Malik, A.; Gupta, S. Treatment of Pulp and Paper Mill Effluent Using Low Cost Adsorbents: An Overview. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2018, 10, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mainardis, M.; Flaibani, S.; Mazzolini, F.; Peressotti, A.; Goi, D. Techno-Economic Analysis of Anaerobic Digestion Implementation in Small Italian Breweries and Evaluation of Biochar and Granular Activated Carbon Addition Effect on Methane Yield. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.; Englehardt, J.; Wu, T. Review of Cost versus Scale: Water and Wastewater Treatment and Reuse Processes. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 69, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibor, S.T.; Grande, C.A. Industrial Production of Activated Carbon Using Circular Bioeconomy Principles: Case Study from a Romanian Company. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 7, 100443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainardis, M.; Magnolo, F.; Ferrara, C.; Vance, C.; Misson, G.; De Feo, G.; Speelman, S.; Murphy, F.; Goi, D. Alternative Seagrass Wrack Management Practices in the Circular Bioeconomy Framework: A Life Cycle Assessment Approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauchauffee, S.; Denieul, M.-P.; Coste, M. Industrial Wastewater Re-Use: Closure of Water Cycle in the Main Water Consuming Industries—The Example of Paper Mills. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 2257–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, A.; Hosseini, M.; Najafpour Darzi, G.; Nabi Bidhendi, G.; Pajoum Shariati, F.; Mosaddeghi, M.R. Perspectives on Membrane Bioreactor Potential for Treatment of Pulp and Paper Industry Wastewater: A Critical Review. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 5, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzichini, M.; Russo, C.; Meo, C.D. Purification of Pulp and Paper Wastewater, with Membrane Technology, for Water Reuse in a Closed Loop. Desalination 2005, 178, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, X. The Study of PAFSSB on RO Pre-Treatment in Pulp and Paper Wastewater. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 8, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mänttäri, M.; Kuosa, M.; Kallas, J.; Nyström, M. Membrane Filtration and Ozone Treatment of Biologically Treated Effluents from the Pulp and Paper Industry. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 309, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğruel, S.; Orhon, D. Particle Size Distribution of Chemical Oxygen Demand in Industrial Effluents: Impact on Effective Filtration Size and Modelling of Membrane Bioreactors. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 1777–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.R.; Silva, C.M.; Milanez, A.F. Application of Ultrafiltration in the Pulp and Paper Industry: Metals Removal and Whitewater Reuse. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 55, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Mao, S.; Wang, J.; Bao, J.; Xu, H.; Su, W.; Dai, H. Application of Ultrafiltration in a Paper Mill: Process Water Reuse and Membrane Fouling Analysis. BioResources 2015, 10, 2376–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mainardis, M.; Buttazzoni, M.; Cottes, M.; Moretti, A.; Goi, D. Respirometry Tests in Wastewater Treatment: Why and How? A Critical Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Liu, T.; Duan, W.; Hu, H. Adsorption and Coagulation Tertiary Treatment of Pulp & Paper Mills Wastewater. In Proceedings of the 2010 4th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Chengdu, China, 18–20 June 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Bender, A.F.; de Souza, J.B.; de Sousa Vidal, C.M. Advanced Treatment Technologies for the Removal of Color and Phenol from the Effluent of Paper Industry Wastewater. Ciênc. Florest. 2019, 29, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossi, G.; Mainardis, M.; Aneggi, E.; Weavers, L.K.; Goi, D. Combined Ultrasound-Ozone Treatment for Reutilization of Primary Effluent—a Preliminary Study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqub, M.; Lee, W. Zero-Liquid Discharge (ZLD) Technology for Resource Recovery from Wastewater: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 681, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, G.; Al-Rudainy, B.; Thuvander, J.; Jönsson, A.-S. Comprehensive Analysis of Foulants in an Ultrafiltration Membrane Used for the Treatment of Bleach Plant Effluent in a Sulfite Pulp Mill. Membranes 2021, 11, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, C.R.; Santoro, D.; Gernaey, K.V.; Sin, G. Organic Carbon Recovery Modeling for a Rotating Belt Filter and Its Impact Assessment on a Plant-Wide Scale. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
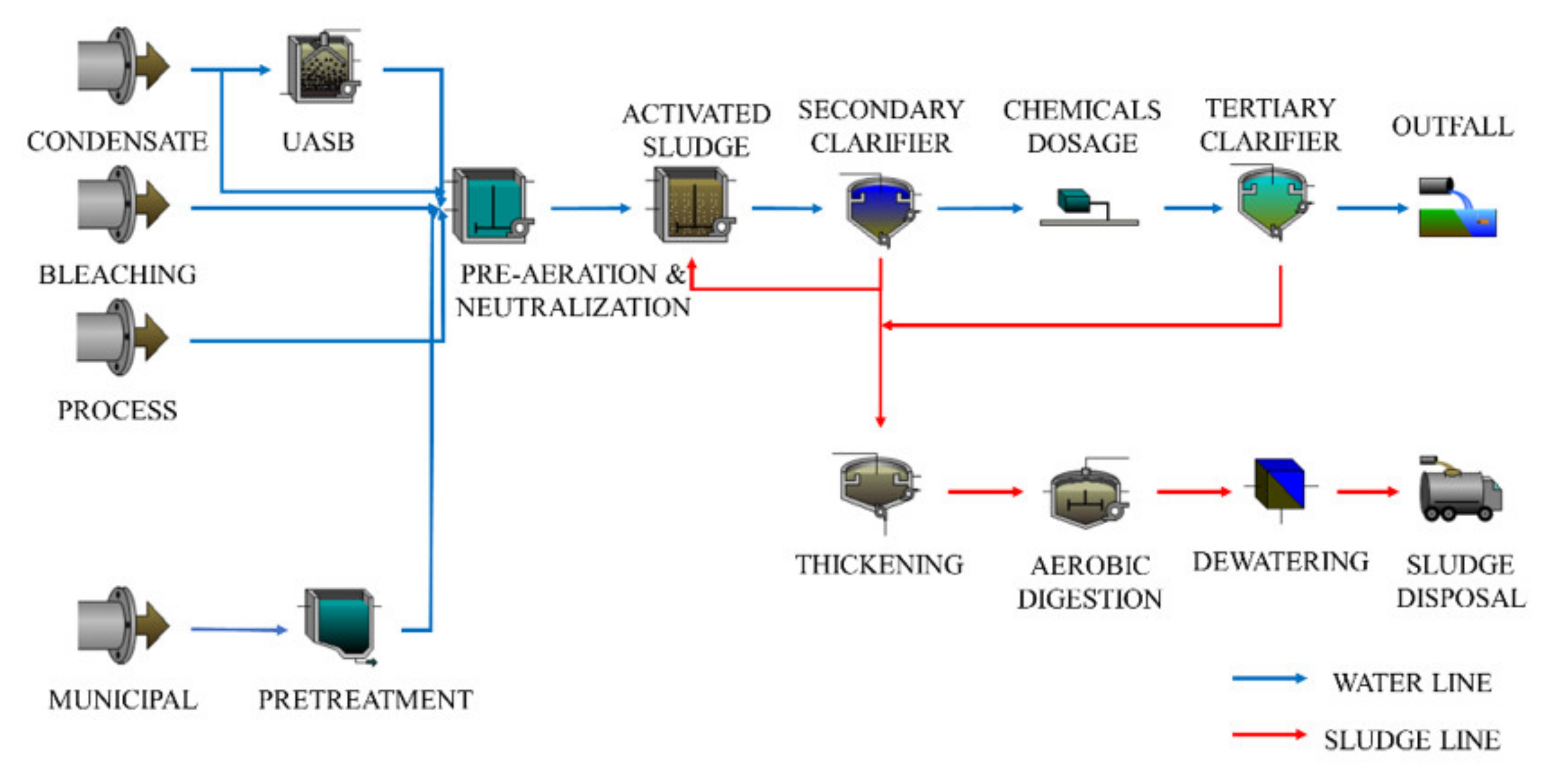



| Wastewater Stream | Flowrate (m3/h) | Flowrate (% of Total) | COD Concentration (mg/L) | COD Load (kg/Day) | COD Load (% of Total) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Condensate | 48 | 3.9 | 3566 | 4108 | 23.9 |
| Bleaching | 510 | 41.9 | 846 | 10,355 | 60.2 |
| Process | 478 | 39.2 | 156 | 1790 | 10.4 |
| Municipal | 182 | 15.0 | 214 | 935 | 5.5 |
| Total | 1218 | 100.0 | 588 1 | 17,188 | 100.0 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Filtrating surface (m2) | 10 |
| Area footprint (m2) | 6.2 |
| Installed power (kW) | 3.7 |
| Absorbed power (kW) | 1.2 |
| Treated flowrate (m3/h) | 50 |
| Frequency of washing cycles (min) | 120 |
| Duration of washing cycles (s) | 60 |
| Specific weight (cloth 1) (g/m2) | 900 |
| Fiber thickness (cloth 1) (µm) | 27 |
| Guaranteed particle filtration (µm) | >10 |
| Specific weight (cloth 2) (g/m2) | 910 |
| Fiber thickness (cloth 2) (µm) | 12 |
| Guaranteed particle filtration (µm) | >5 |
| Scenario | CAPEX (€) | OPEX (€/Year) | Income (€/Year) | ΔOPEX (€/Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1: physicochemical treatment | 0 | 361,922 | 0 | - |
| Scenario 2: adsorption + cloth filtration | 680,000 | 1,530,000 | 0 | 1,168,078 |
| Scenario 3: ultrafiltration | 19,010,032 | 2,101,502 | 7,665,000 | −5,201,576 |
| Parameter | Low Quality | Medium Quality | High Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conductivity (µS/cm) | <500 | <500 | <500 |
| Cl− (mg/L) | <300 | <200 | <200 |
| Ca2+ (mg/L) | <200 | <60 | <60 |
| Colour | Not specified | Not specified | None |
| Solids (mg/L) | Coarse filtration | 10–15 (particles < 5 µm) | 10 |
| COD (mg/L) | Not specified | <200 | <50 |
| BOD (mg/L) | Reduced | Low | <3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mainardis, M.; Mulloni, S.; Catenacci, A.; Danielis, M.; Furlani, E.; Maschio, S.; Goi, D. Sustainable Alternatives for Tertiary Treatment of Pulp and Paper Wastewater. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6047. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14106047
Mainardis M, Mulloni S, Catenacci A, Danielis M, Furlani E, Maschio S, Goi D. Sustainable Alternatives for Tertiary Treatment of Pulp and Paper Wastewater. Sustainability. 2022; 14(10):6047. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14106047
Chicago/Turabian StyleMainardis, Matia, Silvia Mulloni, Arianna Catenacci, Maila Danielis, Erika Furlani, Stefano Maschio, and Daniele Goi. 2022. "Sustainable Alternatives for Tertiary Treatment of Pulp and Paper Wastewater" Sustainability 14, no. 10: 6047. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14106047
APA StyleMainardis, M., Mulloni, S., Catenacci, A., Danielis, M., Furlani, E., Maschio, S., & Goi, D. (2022). Sustainable Alternatives for Tertiary Treatment of Pulp and Paper Wastewater. Sustainability, 14(10), 6047. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14106047