Impacts of Relative Elevation on Soil Nutrients and Apple Quality in the Hilly-Gully Region of the Loess Plateau, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Samples Collection and Processing
2.3. Measurement Items and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
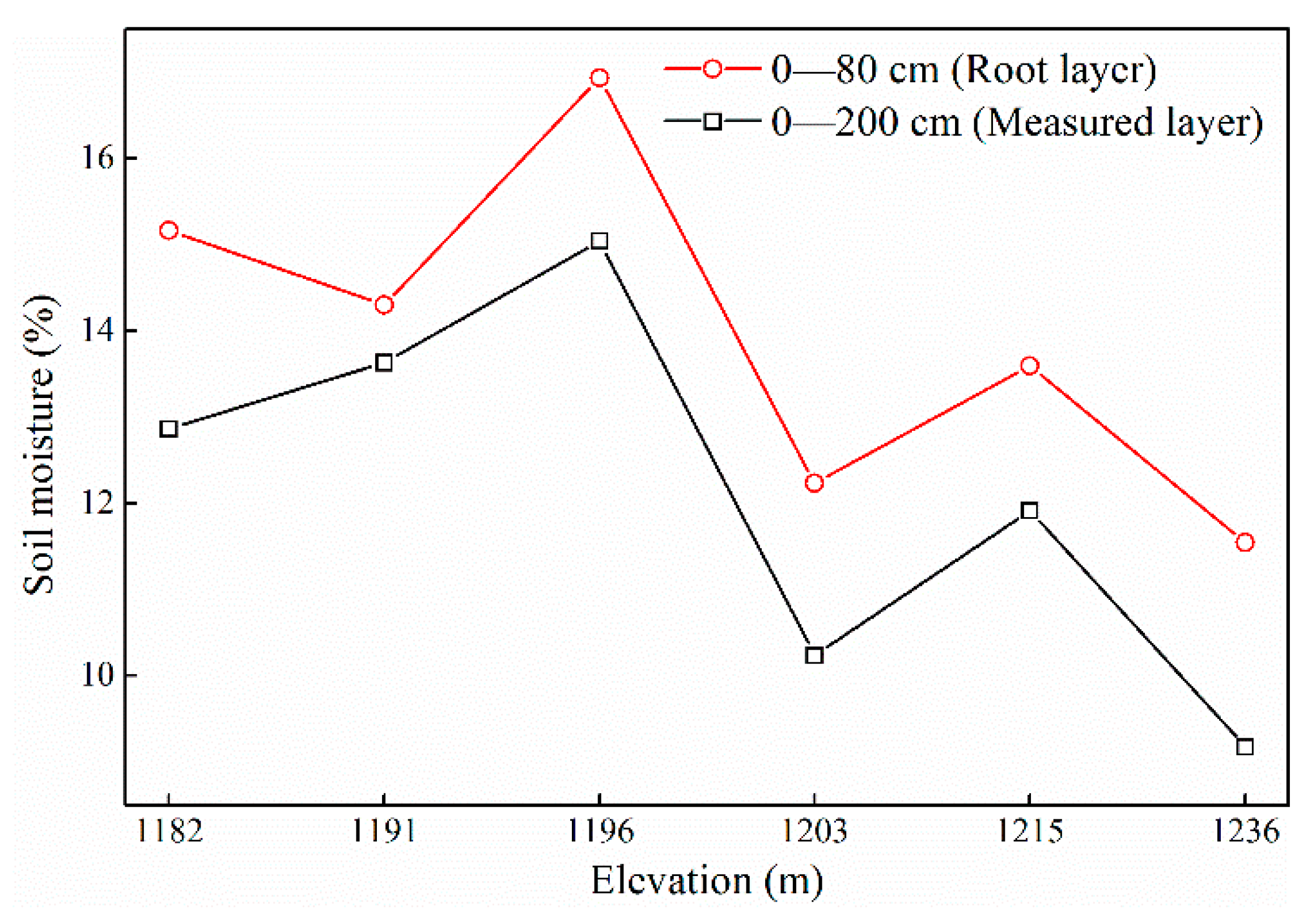
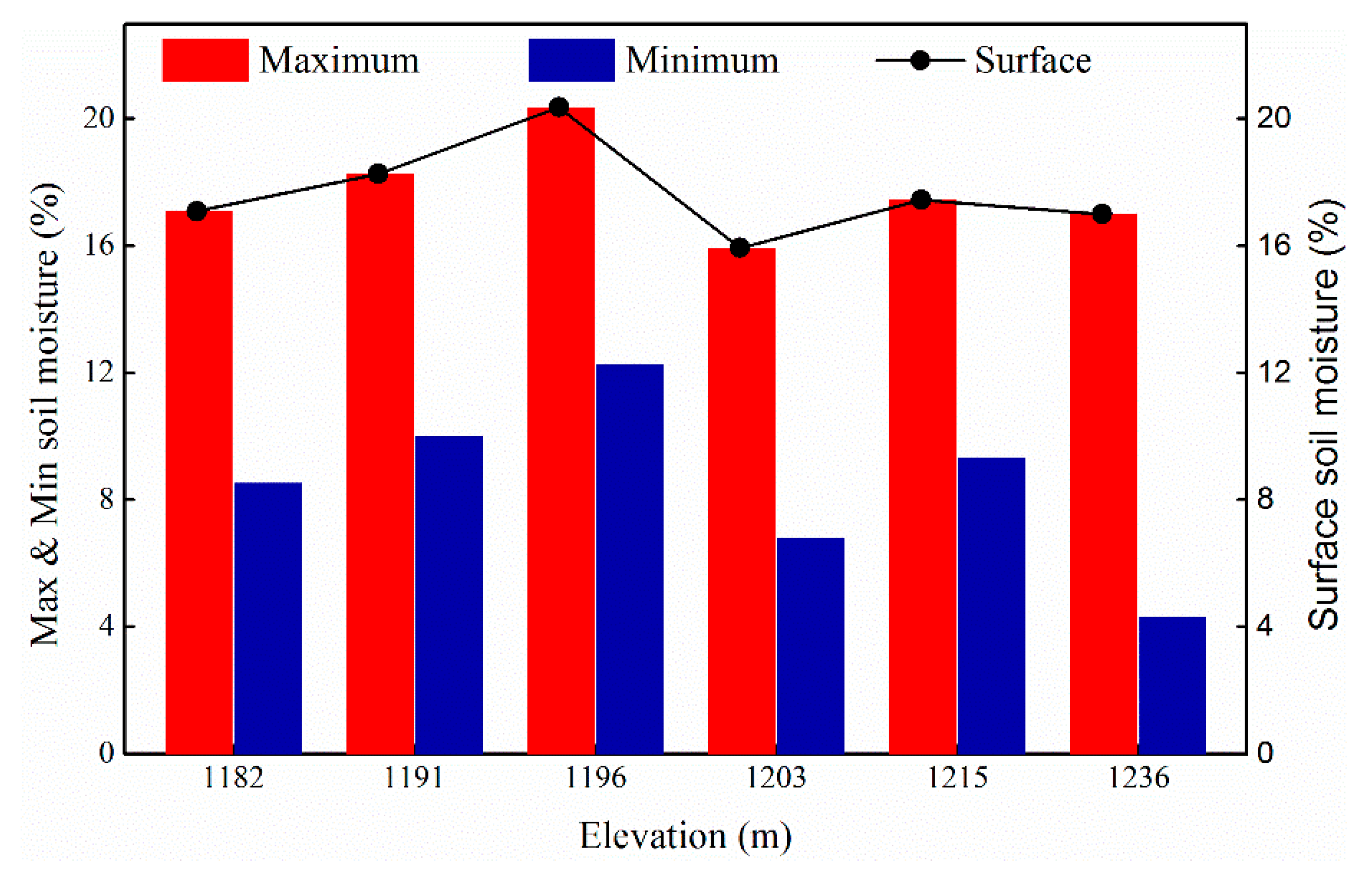
3.1. Distribution Characteristics of Soil Moisture in Orchards at Different Elevations
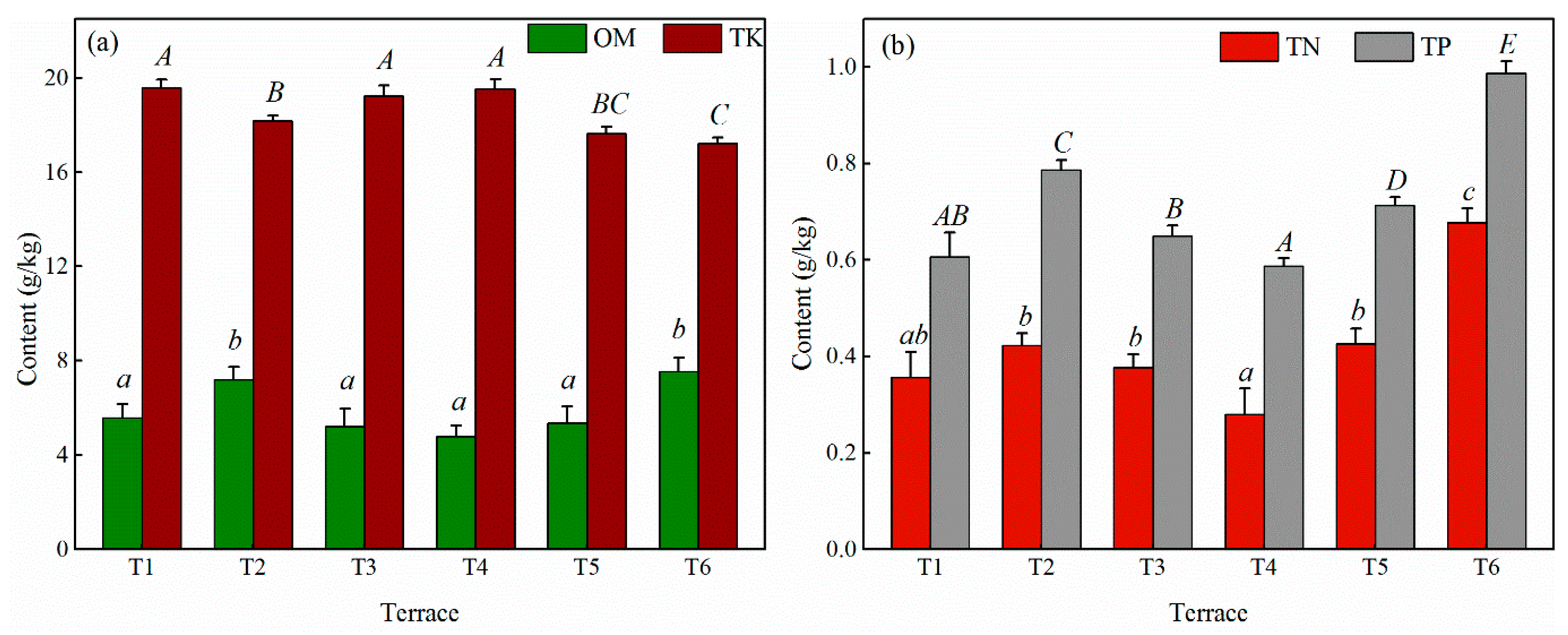
3.2. Status of Soil Nutrients in Orchards at Different Elevations
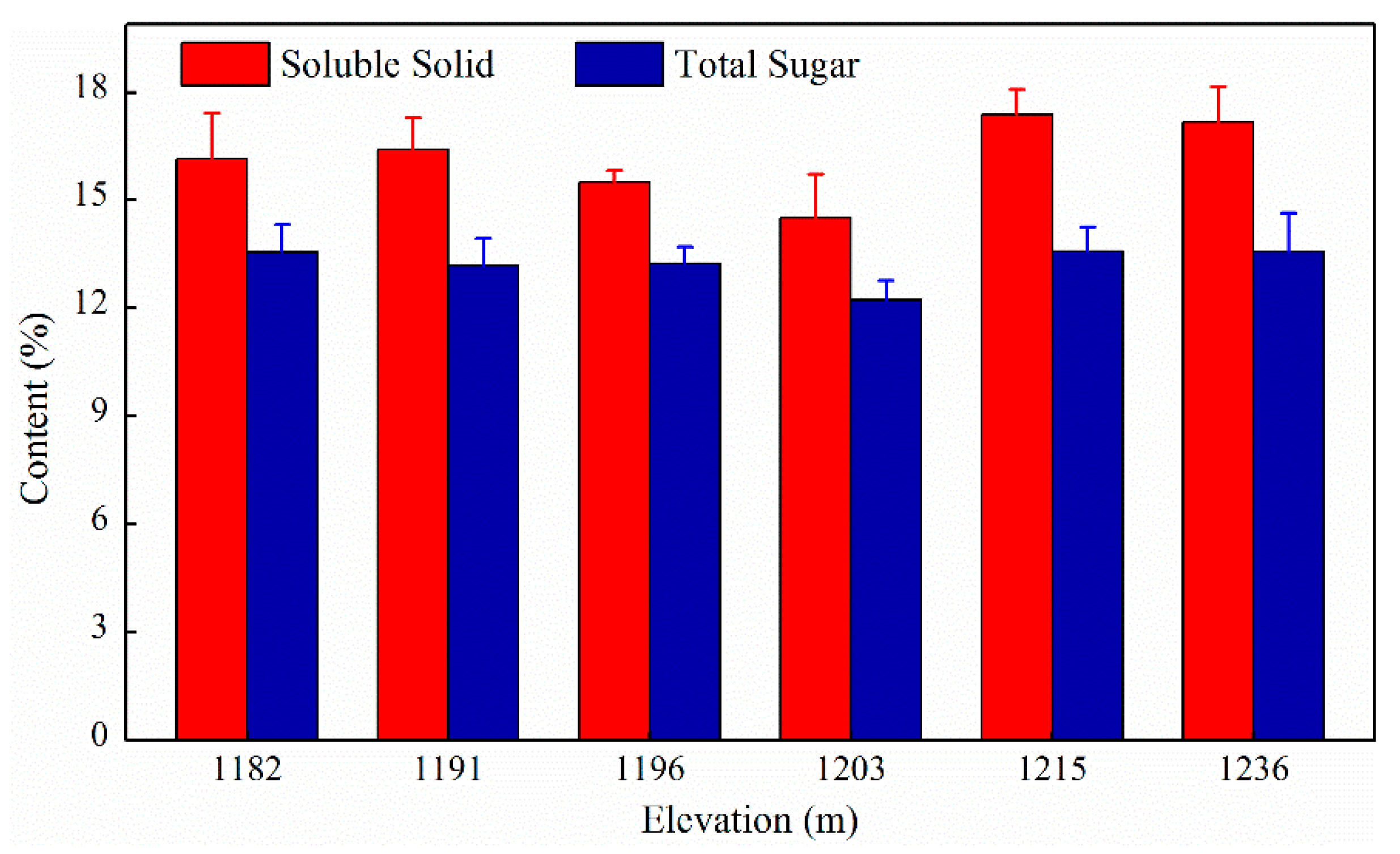
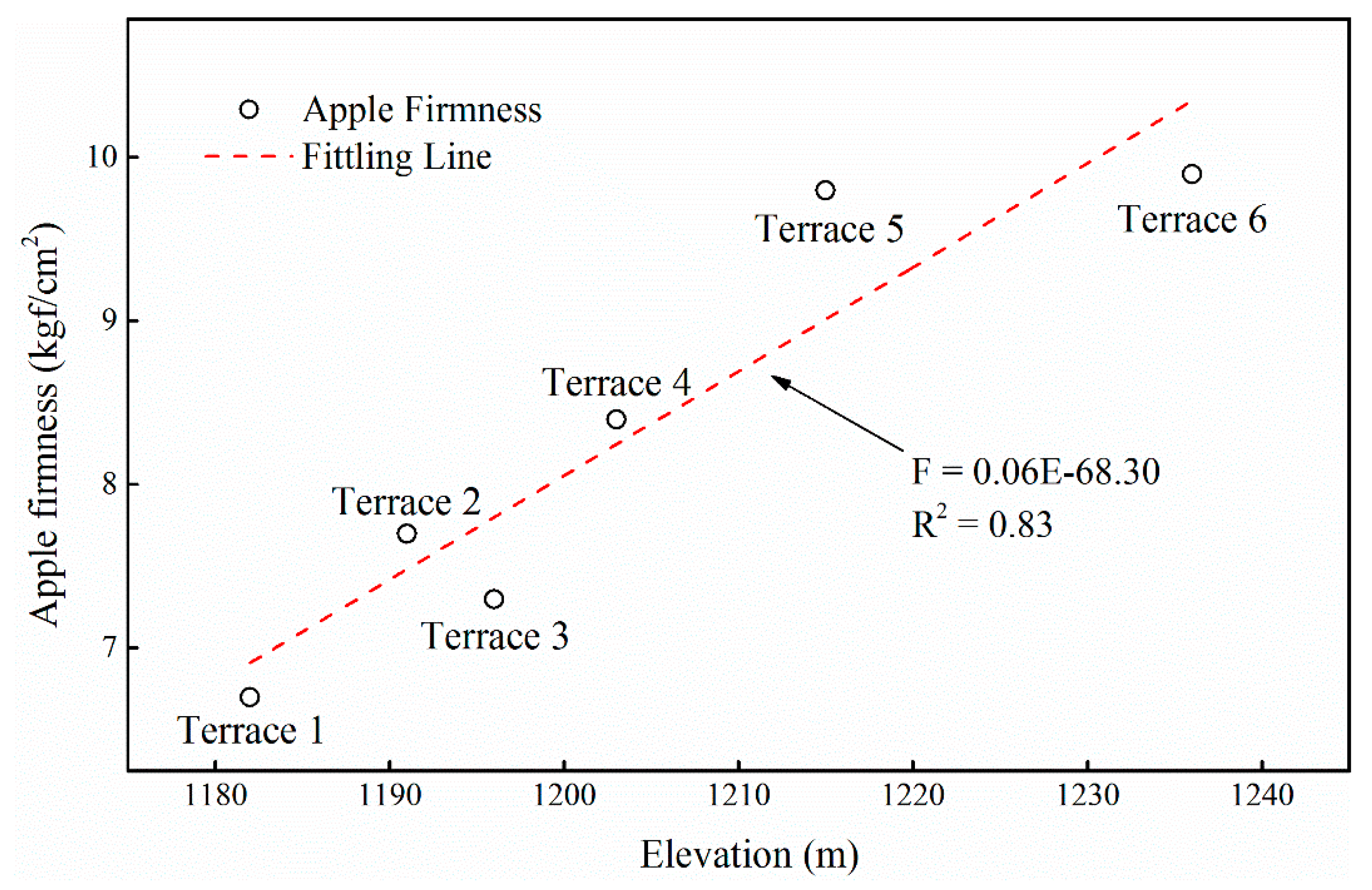
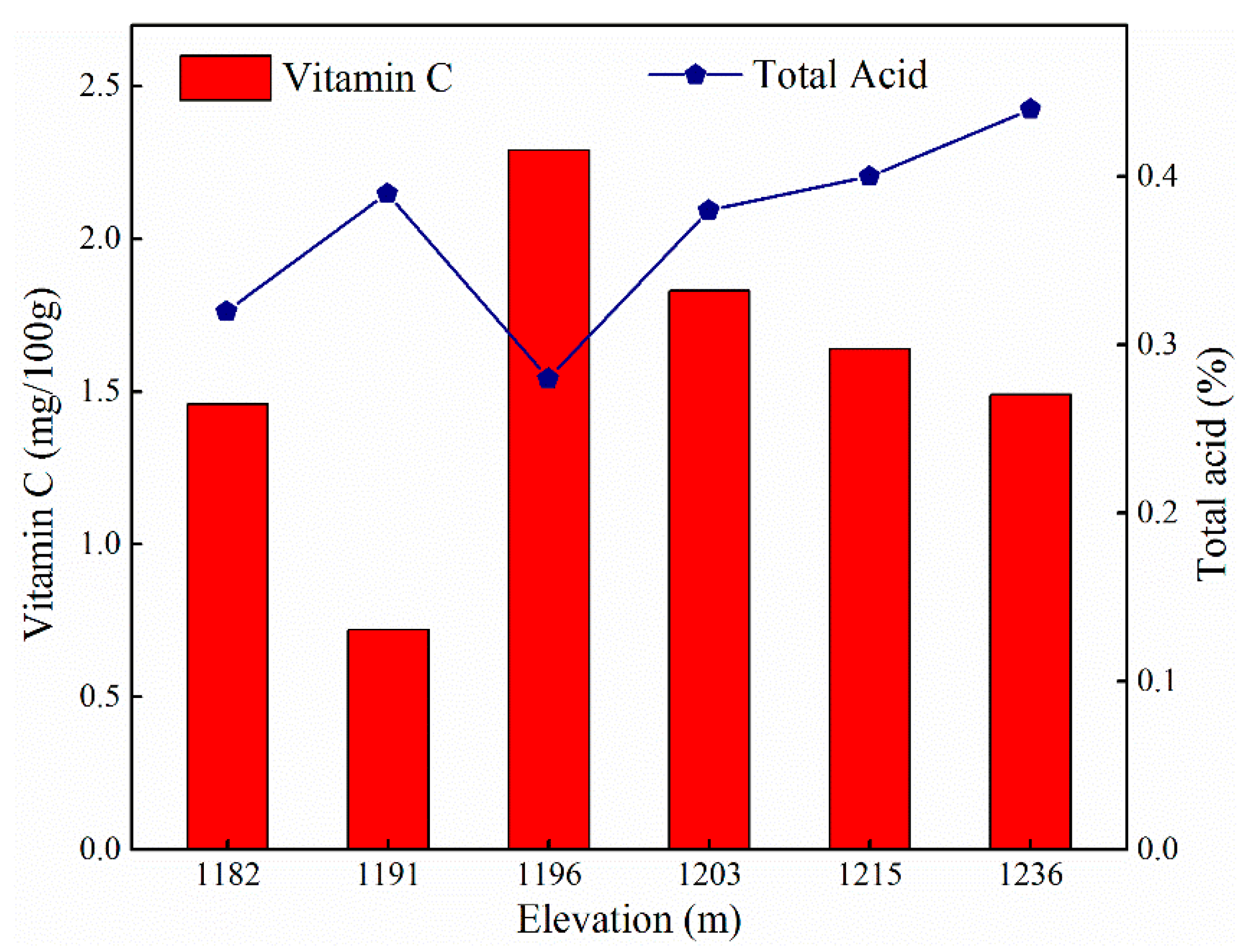
3.3. Variation of Apple Quality at Different Elevations
3.4. Relationships between Soil Nutrients and Fruit Qualities
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, W.; Bai, D.; Wang, F.; Fu, B.; Yan, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Long, D.; Feng, M. Quantifying the impacts of climate change and ecological restoration on streamflow changes based on a Budyko hydrological model in China’s Loess Plateau. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 6500–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Meng, Q.H.; Qiu, Y.; Zhao, W.W.; Zhang, Q.J.; Davidson, D.A. Effects of land use on soil erosion and nitrogen loss in the hilly area of the Loess Plateau, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2004, 15, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; An, C.; Guy, C.; Lu, C. Assessment of soil and water conservation practices in the Loess Hilly Region using a coupled rainfall-runoff-erosion model. Sustainability 2020, 12, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Lu, C. Evaluation of land-use change effects on runoff and soil erosion of a hilly basin—the Yanhe River in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Shao, M. Soil and water loss from the Loess Plateau in China. J. Arid. Environ. 2000, 45, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Mu, X.; Wen, Z.; Wang, F.; Gao, P. Soil erosion, conservation, and eco-environment changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunekawa, A.; Liu, G.; Yamanaka, N.; Du, S. Restoration and Development of the Degraded Loess Plateau, China; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2014; p. 283. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.; Gao, J.; Shao, H.; Zhang, Y. Quantitative analysis of hydrological responses to climate variability and land-use change in the hilly-gully region of the Loess Plateau, China. Water 2019, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Chen, L.; Fu, B.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Peng, H. Effect of land use on soil nutrients in the loess hilly area of the Loess Plateau, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2005, 17, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, P.; Chen, H.; Yan, R.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Y.; Liu, E.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Lv, D.; et al. Understanding land use and cover change impacts on run-off and sediment load at flood events on the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Pang, L.; Yan, Z.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Q. Formation cause and pruning defense measure of mountain apple with alternate bearing in Northern Shaanxi. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2020, 48, 55–64. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Fei, L.; Li, Y.; Zeng, J.; Dai, Z. Response of fruit yield, fruit quality, and water use efficiency to water deficits for apple trees under surge-root irrigation in the Loess Plateau of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 222, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Peng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ning, F.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Dong, Z.; Jia, G.; Wei, L.; et al. Changes in soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in apple orchards in different climate regions on the Loess Plateau. Catena 2021, 197, 104989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, G.; Yao, J.; Xing, Z. Problems and new ideas in the development of apple industry in northern Shaanxi. Shaanxi For. Sci. Technol. 2019, 47, 73–77. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Sheng, J.; Li, Z.; Weindorf, D.C.; Hu, G.; Xuan, J.; Zhao, H. Integrating rainwater harvesting and drip irrigation for water use efficiency improvements in apple orchards of northwest China. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 275, 109728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçükyumuk, C.; Kaçal, E.; Ertek, A.; Ozturk, G.; Kurttaş, Y.S.K. Pomological and vegetative changes during transition from flood irrigation to drip irrigation: Starkrimson Delicious apple variety. Sci. Hortic. 2012, 136, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Soil Agrochemical Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 30–103. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Chen, H.; Li, X. Determination of total acid and total sugar in citrus fruits. Food Res. Dev. 2012, 33, 144–146. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C. Mensuration and comparation of vitamin C content in fruit. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. 2007, 29, 90–91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mai, C.; Liang, Q. A brief analysis of Brix value determination of the soluble solids Tainnong Mango in Sanya. Hans J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 8, 486–495. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Du, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, R.; Bai, G. Study on suitable parts for apple firmness determination. North. Hortic. 2011, 24, 33–35. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Z.; Yang, P. Experimental investidation of root system distribution of apple tree. J. Agric. Univ. 1998, 3, 63–66. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kasim, J. Soil Nutrition Characters of Apple Orchard in Different Ecological Regions on the Loess Plateau; Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University: Yangling, China, 2014. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Fan, P.; Cao, Y.; Kasim, J. Distribution of NPK nutrient content in deep soil profile of typical apple orchards on the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sinaca 2013, 33, 1907–1915. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zheng, L.; Han, M.; Gao, C.; Luo, W.; Ma, J. Studies of standard range of the soil nutrients in apple orchard in the Loess Plateau. Acta Hortic. Sinaca 2016, 43, 121–131. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Krishna, M.P.; Mohan, M. Litter decomposition in forest ecosystems: A review. Energy Ecol. Environ. 2017, 2, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błońska, E.; Piaszczyk, W.; Staszel, K.; Lasota, J. Enzymatic activity of soils and soil organic matter stabilization as an effect of components released from the decomposition of litter. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 157, 103723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pisani, O.; Lin, L.H.; Lun, O.O.; Bowden, R.D.; Lajtha, K.; Simpson, A.J.; Simpson, M.J. Long-term litter manipulation alters soil organic matter turnover in a temperate deciduous forest. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 607–608, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, K.; Cong, P.; Ma, D.; Gao, R.; Li, W.; Zhang, S. Red Fuji apple. In Agricultural Standards; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2006; Volume NY/T 1075-2006, pp. 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M. Experimental Research on Rainwater Use Efficiency Enhancement of Typical Terrace Orchard in Loess Hilly Region; Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University Yangling: Xianyang, China, 2017. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Lin, G.; Liu, F. Relationship between fruit quality, storability and mineral composition of apples. J. Fruit Sci. 1995, 12, 141–145. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, D. Effect of Soil Moisture on Fruit Quality of Red Fuji Apple; Hebei Agricultural University: Hebei, China, 2009. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Zhai, B.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Yan, M.; Zhao, Z. Effect of combined application of organic and inorganic fertilizers on quality of Red Fuji apple in dry land. North. Hortic. 2013, 2013, 178–181. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Francaviglia, D.; Farina, V.; Avellone, G.; Bianco, R.L. Fruit yield and quality responses of apple cvars Gala and Fuji to partial root zone drying under Mediterranean conditions. J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 151, 556–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Tao, H.; Fan, J.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, Y. Effects of soil water stress on fruit yield, quality and their relationship with sugar metabolism in ‘Gala’ apple. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 258, 108753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Tong, Y.; Gao, Y.; Fu, Y. Effect of different fertilization on yield and quality of Fuji apple. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2009, 15, 1130–1135. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
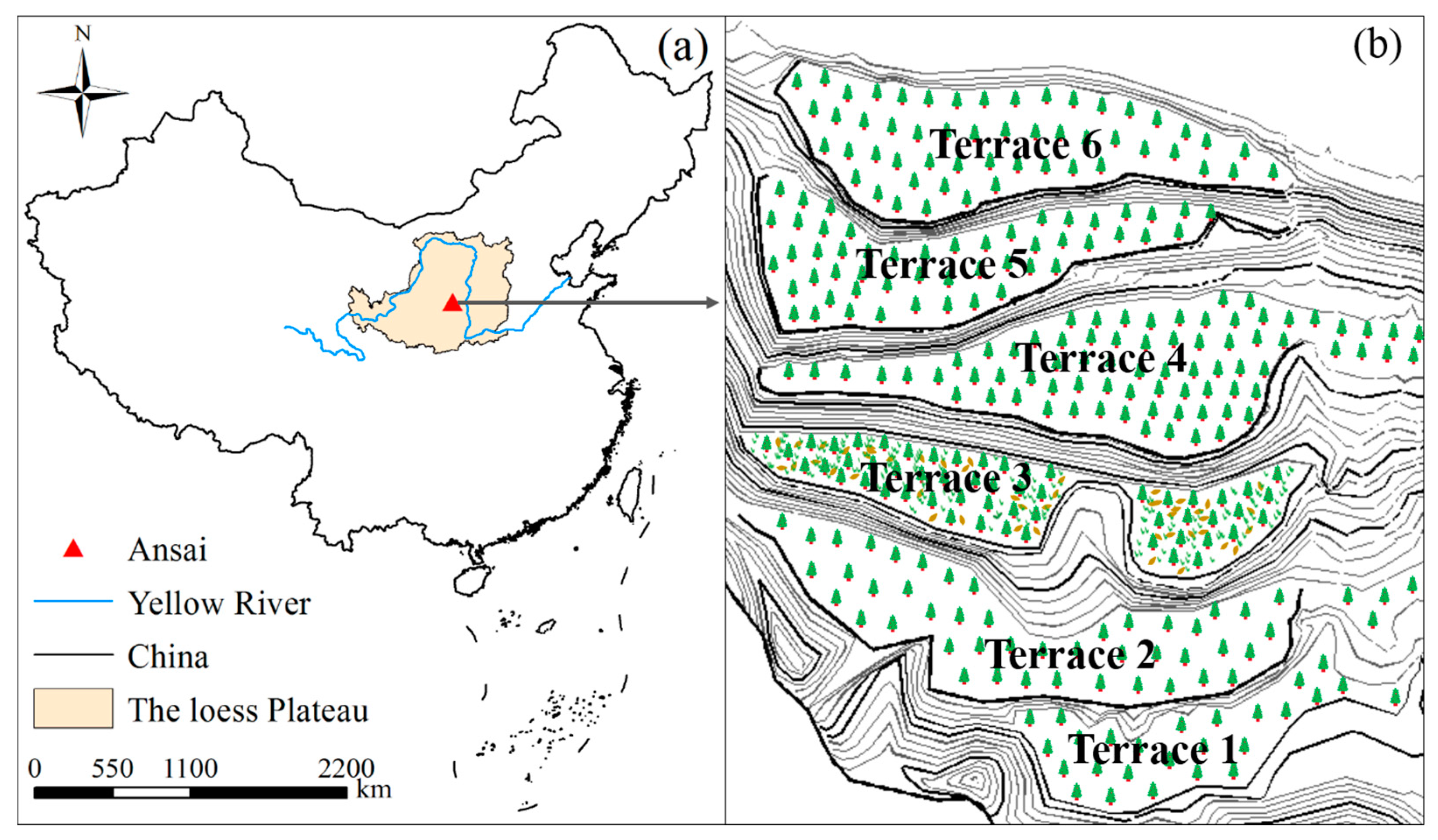
| Orchards | Elevation (m) | Tree Age (Year) | Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| Terrace 1 | 1182 | 12–20 | Normal |
| Terrace 2 | 1191 | 15–20 | Normal |
| Terrace 3 | 1196 | 16–20 | Abandoned |
| Terrace 4 | 1203 | 8–20 | Normal |
| Terrace 5 | 1215 | 13–20 | Normal |
| Terrace 6 | 1236 | 15–20 | Normal |
| Items | Methods | Instruments |
|---|---|---|
| Organic matter | Potassium dichromate outside heating | Semi-micro titrator |
| Total potassium | NaOH liquation | Flame photometer |
| Total nitrogen | NaOH alkaline hydrolysis with reducing agent—diffusion process | Automatic Kjeldahl nitrogen determination apparatus |
| Total phosphorus | NaOH liquation/Mo-Sb colorimetry | Spectrophotometer |
| Item | Methods/Instrument | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Total sugar | Fehling’s solution titration [18] | The index of apple quality was measured by the Food Detection and Identification Center of Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University |
| Total acid | Potentiometric titration [18] | |
| Vitamin C | 2-6-diohloroindophenol titration [19] | |
| Soluble solids | Refractometer [20] | |
| Firmness | Fruit firmness meter [21] |
| Soil Water | OM | TK | TN | TP | Soluble Solid | Total Sugar | Firmness | Vitamin C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OM | −0.324 | ||||||||
| TK | 0.416 | −0.634 ** | |||||||
| TN | −0.373 | 0.644 ** | −0.809 ** | ||||||
| TP | −0.450 | 0.806 ** | −0.860 ** | 0.937 ** | |||||
| Soluble solid | −0.048 | 0.433 | −0.610 ** | 0.599 ** | 0.541 * | ||||
| Total sugar | 0.193 | 0.252 | −0.385 | 0.367 | 0.272 | 0.584 * | |||
| firmness | 0.210 | 0.044 | 0.383 | −0.468 | −0.402 | −0.027 | 0.054 | ||
| Vitamin C | 0.285 | 0.604 ** | 0.354 | −0.219 | −0.383 | −0.247 | −0.067 | −0.551 * | |
| Total acid | −0.768 ** | −0.518 * | −0.679 ** | 0.543 * | 0.615 ** | 0.458 | 0.139 | −0.083 | −0.420 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hua, L.; Gao, J.; Zhou, M.; Bai, S. Impacts of Relative Elevation on Soil Nutrients and Apple Quality in the Hilly-Gully Region of the Loess Plateau, China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031293
Hua L, Gao J, Zhou M, Bai S. Impacts of Relative Elevation on Soil Nutrients and Apple Quality in the Hilly-Gully Region of the Loess Plateau, China. Sustainability. 2021; 13(3):1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031293
Chicago/Turabian StyleHua, Lei, Jianen Gao, Meifang Zhou, and Shilun Bai. 2021. "Impacts of Relative Elevation on Soil Nutrients and Apple Quality in the Hilly-Gully Region of the Loess Plateau, China" Sustainability 13, no. 3: 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031293
APA StyleHua, L., Gao, J., Zhou, M., & Bai, S. (2021). Impacts of Relative Elevation on Soil Nutrients and Apple Quality in the Hilly-Gully Region of the Loess Plateau, China. Sustainability, 13(3), 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031293





