Sustainable Use of Energy Resources, Regulatory Quality, and Foreign Direct Investment in Controlling GHGs Emissions among Selected Asian Economies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Hypotheses Development
Hypotheses Development
3. Method and Material
3.1. Data Variables
3.2. Research Framework
3.3. Econometric Strategy
3.4. Econometric Equation
4. Data Analysis and Discussion
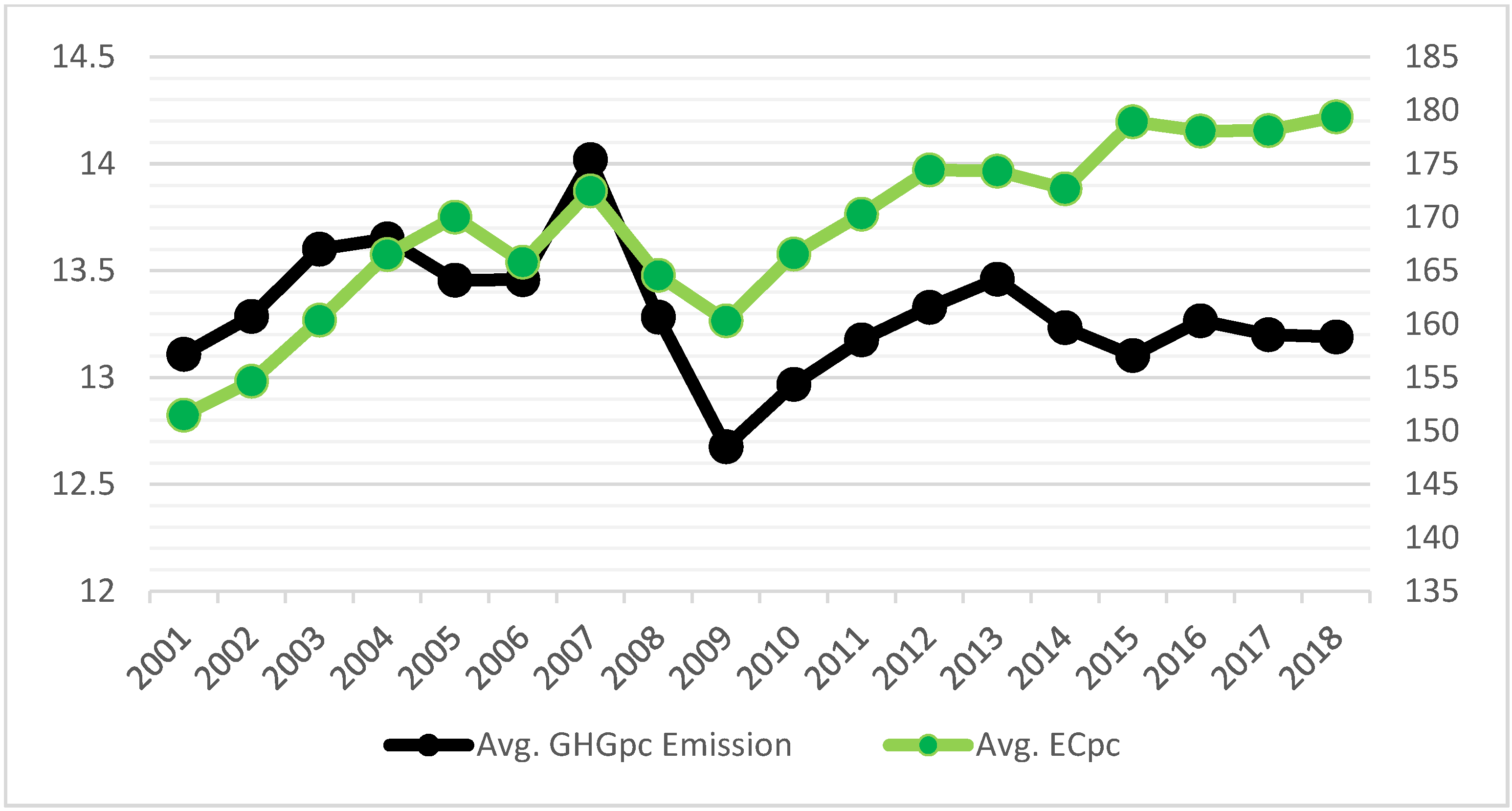
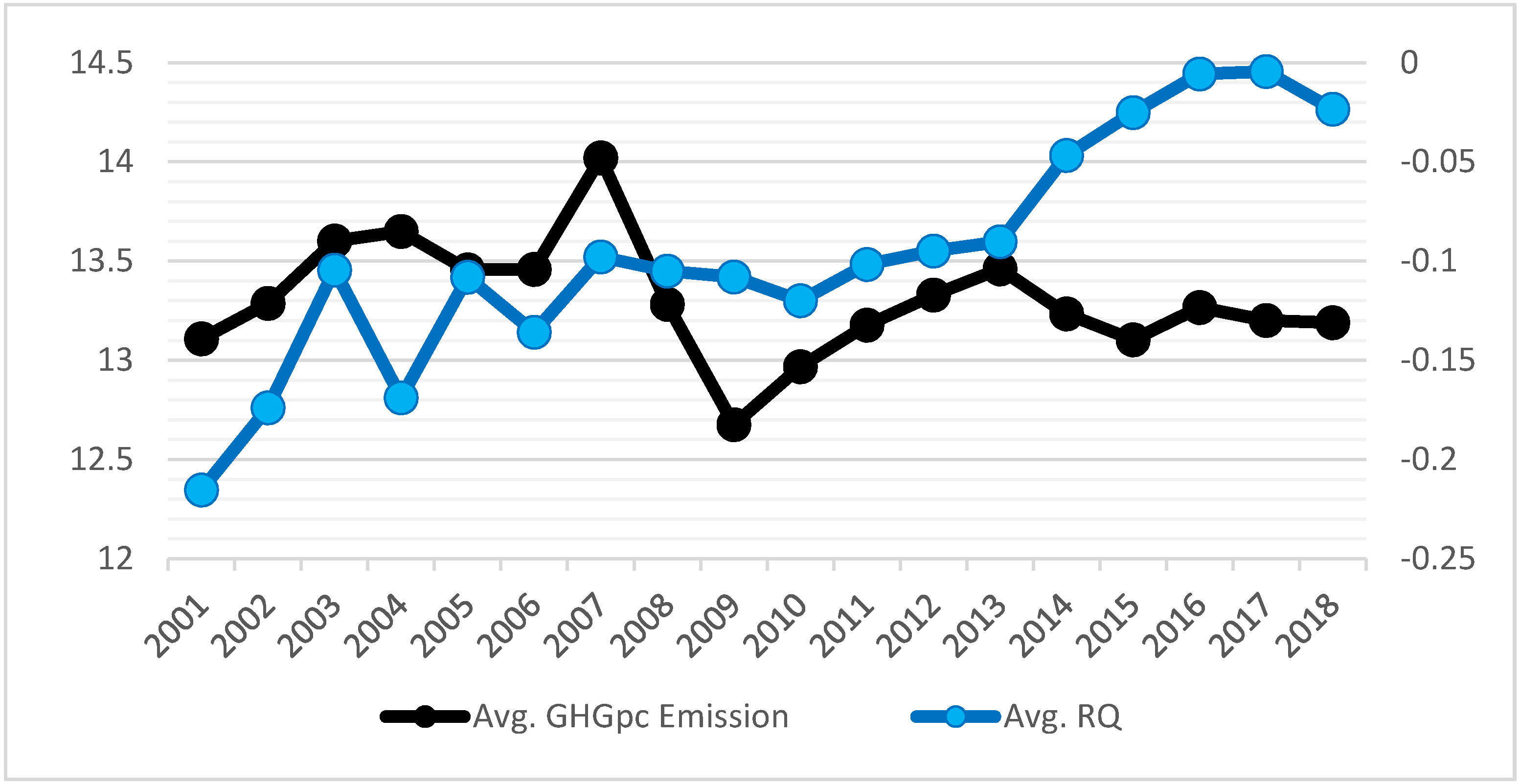
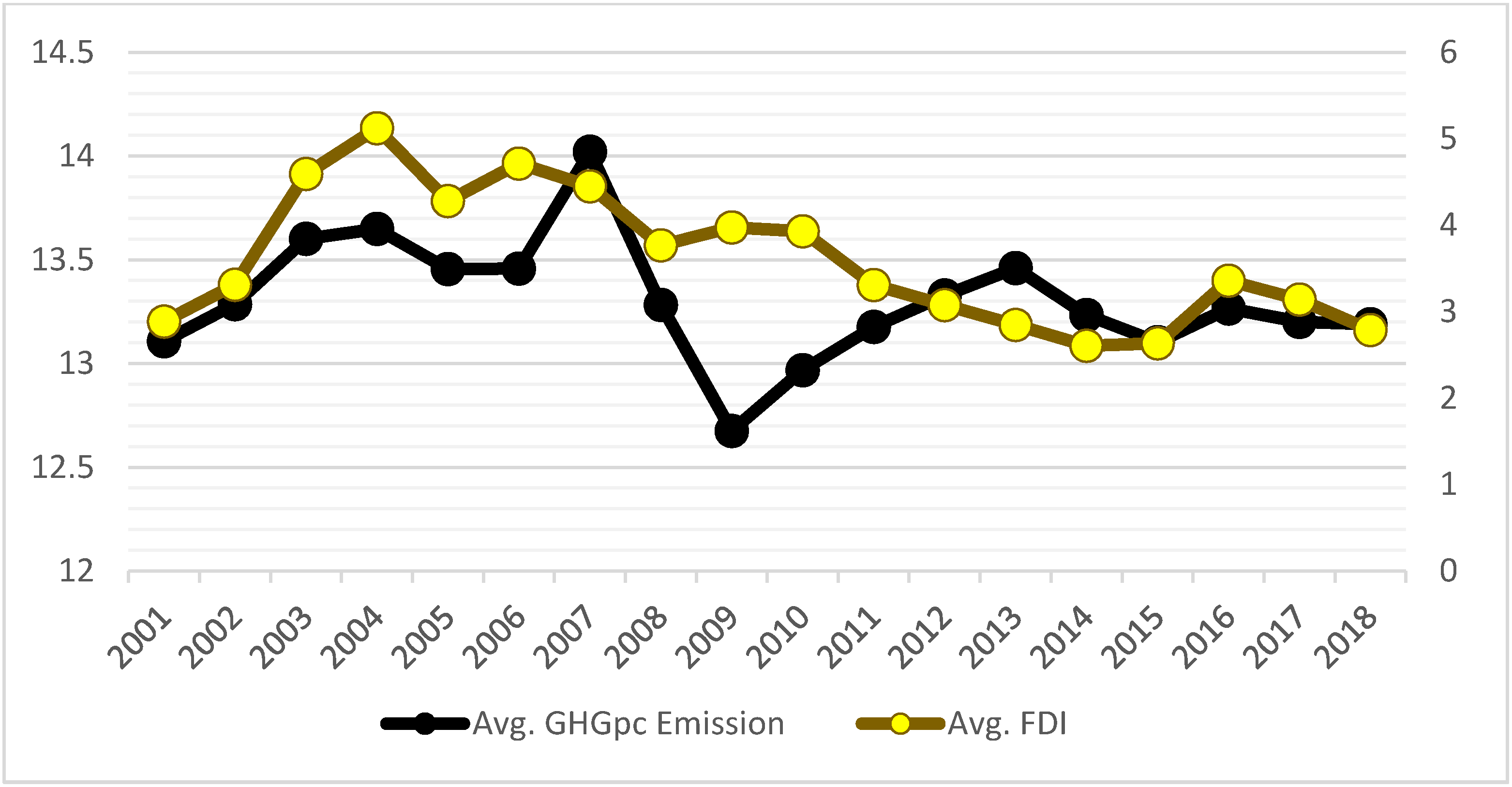
4.1. Trends and Observations
4.2. Descriptive Statistics
4.3. Correlation Analysis
4.4. Unit Root and Co-Integration
4.5. Baseline Regression Analysis of Two-Step System GMM
4.5.1. Regression with Moderating Variable—Regulatory Quality (RQ)
4.5.2. Regression with Interaction Energy Consumption per Capita (ECpc) and Regulatory Quality (RQ)
4.5.3. Regression with Interaction Energy Consumption per Capita (ECpc) and Regulatory Quality (RQ)
4.6. Robustness Check
4.7. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitation and Future Study Direction
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| List of Countries | ||
|---|---|---|
| Azerbaijan | Kazakhstan | Singapore |
| Bangladesh | Kuwait | South Korea |
| China | Malaysia | Sri Lanka |
| India | Oman | Thailand |
| Indonesia | Pakistan | Turkey |
| Iran | Philippines | Turkmenistan |
| Iraq | Qatar | United Arab Emirates |
| Israel | Russian Federation | Uzbekistan |
| Japan | Saudi Arabia | Vietnam |
Appendix B
| Variables | Pooled OLS | Fixed-Effects Regression |
|---|---|---|
| ECpc | 0.055 *** (23.380) | 0.041 *** (15.630) |
| FDI | −0.442 *** (−5.000) | −0.120 * (−2.730) |
| PGu | 0.786 * (2.560) | 0.245 * (2.020) |
| R-squared | 0.775 | 0.485 |
| Root MSE | 5.185 | - |
| F(3,17) | 7781.45 | 228.98 |
| p-value | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Number of groups | 27 | 27 |
| Number of Obs | 486 | 486 |
| Variables | Pooled OLS | Fixed-Effects Regression |
|---|---|---|
| ECpc | 0.061 *** (23.380) | 0.039 *** (15.150) |
| FDI | −0.477 *** (−5.690) | −0.105 * (−2.650) |
| PGu | 0.567 * (1.980) | 0.291 * (2.480) |
| RQ | −2.207 *** (−13.700) | 1.305 *** (5.520) |
| R-squared | 0.797 | 0.502 |
| Root MSE | 4.930 | - |
| F(4,17) | 7843.37 | 530.61 |
| p-value | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Number of groups | 27 | 27 |
| Number of Obs | 486 | 486 |
| Variables | Pooled OLS | Fixed-Effects Regression |
|---|---|---|
| ECpc | 0.075 *** (40.010) | 0.041 *** (11.540) |
| RQ | 3.407 *** (7.800) | 1.806 *** (3.810) |
| ECpc_RQ | 0.039 *** (17.360) | −0.003 * (−1.150) |
| FDI | −0.245 *** (−3.880) | −0.107 * (−2.660) |
| PGu | 0.680 *** (3.780) | 0.263 * (2.290) |
| R-squared | 0.908 | 0.506 |
| Root MSE | 3.315 | - |
| F(5,17) | 14,200.70 | 415.28 |
| p-value | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Number of groups | 27 | 27 |
| Number of Obs | 486 | 486 |
| Variables | Pooled OLS | Fixed-Effects Regression |
|---|---|---|
| ECpc | 0.063 *** (25.390) | 0.039 *** (14.980) |
| FDI | −0.492 *** (−7.030) | −0.096 * (−1.870) |
| RQ | 1.225 *** (5.030) | 1.197 *** (4.060) |
| PGu | 0.648 * (2.650) | 0.286 * (2.460) |
| FDI_RQ | −0.951 *** (16.660) | 0.042 * (0.600) |
| R-squared | 0.891 | 0.503 |
| Root MSE | 3.618 | - |
| F(5,17) | 4242.22 | 423.19 |
| p-value | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Number of groups | 27 | 27 |
| Number of Obs | 486 | 486 |
References
- World Meteorological Organization. The State of Greenhouse Gases in the atmosphere Based on Global Observations through 2019; (No. 15|23 November 2020); Atmospheric Environment Research Division, Science and Innovation Department: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- World Meteorological Organization. 2020 on track to be one of three warmest years on record. In New WMO Story Map Highlights Climate Change Indicators; United Nations, Ed.; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- UNDP Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Available online: https://www.undp.org/content/undp/en/home/sustainable-development-goals/background/ (accessed on 25 December 2020).
- UN. Public Servants Discuss Ways to Effectively Deliver on SDGs; United Nations: Baku, Azerbaijan, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- UN. E-government a powerful tool to implement global sustainability goals, UN survey finds. In Sustainable Development Goals; United Nations, Ed.; The United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, Z. Investigation of air quality over the largest city in central China using high resolution satellite derived aerosol optical depth data. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samimi, A.J.; Ahmadpour, M.; Ghaderi, S. Governance and environmental degradation in MENA region. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 62, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ilahi, S.; Wu, Y.; Raza, M.A.A.; Wei, W.; Imran, M.; Bayasgalankhuu, L. Optimization approach for improving energy efficiency and evaluation of greenhouse gas emission of wheat crop using data envelopment analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akbar, U.; Khan, M.A.; Akmal, M.; Tóth Naárné, É.Z.; Oláh, J. Trade-offs for the optimal energy efficiency of road transportation: Domestic cases in developing countries. Energies 2020, 13, 6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Fu, J.; Kong, Y.; Wu, R. How foreign direct investment influences carbon emissions, based on the empirical analysis of Chinese urban data. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Qiao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y. The “APEC blue” endeavor: Causal effects of air pollution regulation on air quality in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IMF. Fiscal Monitor, April 2020: Policies to Support People During the COVID-19 Pandemic; International Monetary Fund: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Neequaye, N.A.; Oladi, R. Environment, growth, and FDI revisited. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2015, 39, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippa, M.; Oreggioni, G.; Guizzardi, D.; Muntean, M.; Schaaf, E.; Lo Vullo, E.; Solazzo, E.; Monforti-Ferrario, F.; Olivier, J.G.; Vignati, E. Fossil CO2 and GHG Emissions of All World Countries; Publication Office of the European Union: Luxemburg, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hollweg, C.H.; Sáez, S.; Aguiar, A.; Walmsley, T.; Narayanan, G.B.; Aguiar, A.; McDougall, R.; Borchert, I.; Gootiiz, B.; et al. World Development Indicators (Database); World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Leuenberger, D. Sustainable development in public administration: A match with practice? Public Works Manag. Policy 2006, 10, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geng, N.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, C.; Zhang, R. PM2.5 in an industrial district of Zhengzhou, China: Chemical composition and source apportionment. Particuology 2013, 11, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Li, L. Impact of urbanization level on urban air quality: A case of fine particles (PM2. 5) in Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 194, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Jia, H. Particulate matter and gaseous pollutions in three megacities over China: Situation and implication. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 140, 476–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelowa, A.; Michaelowa, K. Climate or development: Is ODA diverted from its original purpose? Clim. Chang. 2007, 84, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alam, M.; Rabbani, M.G. Vulnerabilities and responses to climate change for Dhaka. Environ. Urban. 2007, 19, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sachs, J.D. From millennium development goals to sustainable development goals. Lancet 2012, 379, 2206–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griggs, D.; Stafford-Smith, M.; Gaffney, O.; Rockström, J.; Öhman, M.C.; Shyamsundar, P.; Steffen, W.; Glaser, G.; Kanie, N.; Noble, I. Sustainable development goals for people and planet. Nature 2013, 495, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, S.; Lawrence, M.; Stelzer, H.; Born, W.; Low, S.; Aaheim, A.; Adriázola, P.; Betz, G.; Boucher, O.; Carius, A. The European Transdisciplinary Assessment of Climate Engineering (EuTRACE): Removing Greenhouse Gases from the Atmosphere and Reflecting Sunlight away from Earth; EuTRACE: Potsdam, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nanaki, E.; Koroneos, C.; Roset, J.; Susca, T.; Christensen, T.H.; Hurtado, S.D.G.; Rybka, A.; Kopitovic, J.; Heidrich, O.; López-Jiménez, P.A. Environmental assessment of 9 European public bus transportation systems. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 28, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrúcaný, T.; Kendra, M.; Stopka, O.; Milojević, S.; Figlus, T.; Csiszár, C. Impact of the electric mobility implementation on the greenhouse gases production in Central European countries. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, C.; Song, Y.; He, Q.; Shen, F. Spatially explicit assessment on urban vitality: Case studies in Chicago and Wuhan. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 40, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Sengupta, T.; Alvarado, R. Interplay between technological innovation and environmental quality: Formulating the SDG policies for next 11 economies. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzagno, M.; Richiedei, A.; Tira, M. Spatial Planning Policy for Sustainability: Analysis connecting land use and GHG emission in rural areas. Sustainability 2020, 12, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franco, I.B.; Chatterji, T.; Derbyshire, E.; Tracey, J. Actioning the Global Goals for Local Impact; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ahiduzzaman, M.; Islam, A.S. Greenhouse gas emission and renewable energy sources for sustainable development in Bangladesh. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 4659–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, M.M. Promoting Sustainable Human Settlements: Its Relevance to the 2030 Agenda; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Delrue, F.; Setier, P.-A.; Sahut, C.; Cournac, L.; Roubaud, A.; Peltier, G.; Froment, A.-K. An economic, sustainability, and energetic model of biodiesel production from microalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 111, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhathlan, K.; Javid, M. Energy consumption, carbon emissions and economic growth in Saudi Arabia: An aggregate and disaggregate analysis. Energy Policy 2013, 62, 1525–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Smyth, R. Convergence in energy consumption per capita among ASEAN countries. Energy Policy 2014, 73, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, R.A.; Sohag, K.; Abdullah, S.M.S.; Jaafar, M. CO2 emissions, energy consumption, economic and population growth in Malaysia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, J.G. Greenhouse gas emission reductions through use of a sustainable alternative to SF 6. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Electrical Insulation Conference (EIC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 19–22 June 2016; pp. 535–538. [Google Scholar]
- Talbot, D.; Boiral, O. GHG reporting and impression management: An assessment of sustainability reports from the energy sector. J. Bus. Ethics 2018, 147, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, U.; Popp, J.; Khan, H.; Khan, M.A.; Oláh, J. Energy efficiency in transportation along with the belt and road countries. Energies 2020, 13, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-R.; Hwang, J.-J.; Wu, W. Environmental impact and sustainability study on biofuels for transportation applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pata, U.K. Renewable energy consumption, urbanization, financial development, income and CO2 emissions in Turkey: Testing EKC hypothesis with structural breaks. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 187, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Wang, Y.; Streimikiene, D.; Balezentis, T.; Zhang, C. Carbon dioxide emission decomposition along the gradient of economic development: The case of energy sustainability in the G7 and Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 28, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkodie, S.A.; Strezov, V.; Weldekidan, H.; Asamoah, E.F.; Owusu, P.A.; Doyi, I.N.Y. Environmental sustainability assessment using dynamic autoregressive-distributed lag simulations—nexus between greenhouse gas emissions, biomass energy, food and economic growth. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhlis, M. The causality between human capital, energy consumption, CO2 emissions, and economic growth: Empirical evidence from Indonesia. SSRN Electron. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, M.C.; Agrawal, A. Environmental governance. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2006, 31, 297–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.T.I.; Yaseen, M.R.; Ali, Q. Nexus between financial development, tourism, renewable energy, and greenhouse gas emission in high-income countries: A continent-wise analysis. Energy Econ. 2019, 83, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseeb, M.; Hassan, S.; Azam, M.; Suryanto, T. The dynamics of governance, tourism and environmental degradation: The world evidence. Int. J. Glob. Environ. Issues 2018, 17, 340–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedoyin, F.F.; Gumede, M.I.; Bekun, F.V.; Etokakpan, M.U.; Balsalobre-lorente, D. Modelling coal rent, economic growth and CO2 emissions: Does regulatory quality matter in BRICS economies? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stef, N.; Jabeur, S.B. Climate change legislations and environmental degradation. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2020, 77, 839–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldo, D. Developments in public administration. Ann. Am. Acad. Political Soc. Sci. 1972, 404, 217–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldo, D. The enterprise of public administration. Sudan J. Econ. Soc. Stud. 1982, 4. Available online: http://onlinejournals.uofk.edu/index.php/SJESS/article/view/885 (accessed on 25 December 2020).
- Bezes, P.; Demazière, D.; Le Bianic, T.; Paradeise, C.; Normand, R.; Benamouzig, D.; Pierru, F.; Evetts, J. New public management and professionals in the public sector. What new patterns beyond opposition? Sociol. Trav. 2012, 54, e1–e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simonet, D. The new public management theory in the British health care system: A critical review. Adm. Soc. 2015, 47, 802–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, P.; Stenvall, J.; Kinder, T.; Hatam, O. Do accountabilities change when public organisations transform to service systems: A new conceptual approach. Financ. Account. Manag. 2018, 34, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pao, H.-T.; Tsai, C.-M. Multivariate Granger causality between CO2 emissions, energy consumption, FDI (foreign direct investment) and GDP (gross domestic product): Evidence from a panel of BRIC (Brazil, Russian Federation, India, and China) countries. Energy 2011, 36, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, A.M.; Ali, T.; Khan, M.T.; Guo, Z. Relationship between inward FDI and environmental degradation for Pakistan: An exploration of pollution haven hypothesis through ARDL approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 15407–15425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bank, W. Urban Development. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/urbandevelopment/overview (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Liu, Y.; Gao, C.; Lu, Y. The impact of urbanization on GHG emissions in China: The role of population density. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 157, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Xia, X.-H. How does urbanization affect GHG emissions? A cross-country panel threshold data analysis. Appl. Energy 2018, 229, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liobikienė, G.; Butkus, M. Scale, composition, and technique effects through which the economic growth, foreign direct investment, urbanization, and trade affect greenhouse gas emissions. Renew. Energy 2019, 132, 1310–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Su, M.; Li, R.; Ponce, P. The effects of energy prices, urbanization and economic growth on energy consumption per capita in 186 countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 1017–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Islam, M.A.; Khan, M.A.; Hossain, M.I.; Pervaiz, K. Does financial deepening attract foreign direct investment? Fresh evidence from panel threshold analysis. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2020, 53, 101198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellano, M.; Bond, S. Some tests of specification for panel data: Monte Carlo evidence and an application to employment equations. Rev. Econ. Stud. 1991, 58, 277–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roodman, D. How to do xtabond2: An introduction to difference and system GMM in Stata. Stata J. 2009, 9, 86–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jara, M.; López-Iturriaga, F.; San Martín, P.; Saona, P.; Tenderini, G. Chilean pension fund managers and corporate governance: The impact on corporate debt. N. Am. J. Econ. Financ. 2019, 48, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekhili, M.; Gull, A.A.; Chtioui, T.; Radhouane, I. Gender-diverse boards and audit fees: What difference does gender quota legislation make? J. Bus. Financ. Account. 2020, 47, 52–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.S.M.; Gillani, S.; Ullah, S.; Raza, M.A.A.; Ullah, A. Nexus between governance and socioeconomic factors on public service fragility in Asian economies. Soc. Sci. Q. 2020, 101, 1850–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Haider Hashmi, S.; Nazir, M.R.; Bilal, A. Does financial inclusion enhance economic growth? Empirical evidence from the IDB members’ countries. Empirical evidence from the IDB members’ countries. SSRN Electron. J. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I. Unit root tests for panel data. J. Int. Money Financ. 2001, 20, 249–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroni, P. Panel co-integration: Asymptotic and finite sample properties of pooled time series tests with an application to the PPP hypothesis. Econom. Theory 2004, 20, 597–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westerlund, J. New simple tests for panel co-integration. Econom. Rev. 2005, 24, 297–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerlund, J. Panel co-integration tests of the Fisher effect. J. Appl. Econom. 2008, 23, 193–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoechle, D. Robust standard errors for panel regressions with cross-sectional dependence. Stata J. 2007, 7, 281–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maddala, G.S.; Wu, S. A comparative study of unit root tests with panel data and a new simple test. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Stat. 1999, 61, 631–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariyakhan, K.; Mohamued, E.A.; Asif Khan, M.; Popp, J.; Oláh, J. Does the level of absorptive capacity matter for carbon intensity? Evidence from the USA and China. Energies 2020, 13, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Variable | Capacity | Description | Source | Period | Expected Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GHG Emission Per Capita (GHGpc) | Dependent Variable | % of GHG consumption per capita in the country annually in Metric Ton | European Union database and World Bank database | 2001–2018 | - |
| Energy Consumption per Capita (ECpc) | Independent Variable | % of Energy consumption from all sources per capita in the country annually on Gigajoule scale | European Union database and World Bank database | 2001–2018 | - |
| Regulatory Quality (RQ) | Moderating Variable | The ability of the government in implementing sound and prudent policies and promote the development | World Governance Indicator by the World Bank | 2001–2018 | + |
| Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) | Independent Variable | It is a % of net FDI inflows to GDP per annum | World Development Indicator (WDI) by the World Bank | 2001–2018 | + |
| Urban Population Growth (PGu) | Control Variable | The annual urban population growth rate | World Development Indicator (WDI) by the World Bank | 2001–2018 | - |
| Regulatory Quality * Foreign Direct Investment (RQ * FDI) | Integrating Variable | How does the government use the FDI in drafting and implementing sound and prudent public policies | Authors Estimation | + | |
| Regulatory Quality * Energy Consumption per Capita (RQ * ECpc) | Integrating Variable | How does the government control and manage the energy consumption pattern in the country with regulations | + | ||
| Variables | Obs | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GHGpc | 486 | 11.996 | 10.911 | 1.119 | 41.887 |
| ECpc | 486 | 161.127 | 170.062 | 4.689 | 597.834 |
| RQ | 486 | −0.123 | 0.847 | −2.09 | 1.27 |
| FDI | 486 | 3.044 | 3.395 | −2.574 | 13.013 |
| PGu | 486 | 2.513 | 1.487 | −0.341 | 6.291 |
| ECpc_RQ | 486 | 48.385 | 188.246 | −446.33 | 759.249 |
| FDI_RQ | 486 | −0.193 | 4.789 | −26.547 | 16.527 |
| Variables | GHGpc | ECpc | RQ | FDI | PGu | ECpc_RQ | FDI_RQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GHGpc | 1.000 | ||||||
| ECpc | 0.862 *** | 1.000 | |||||
| RQ | 0.034 | 0.209 *** | 1.000 | ||||
| FDI | 0.394 *** | 0.323 *** | −0.07 | 1.000 | |||
| PGu | 0.270 *** | 0.474 *** | 0.063 | 0.006 | 1.000 | ||
| ECpc_RQ | 0.309 *** | 0.665 *** | 0.214 *** | 0.126 *** | 0.804 *** | 1.000 | |
| FDI_RQ | 0.026 | 0.387 *** | 0.043 | 0.056 | 0.675 *** | 0.785 *** | 1.000 |
| Unit Root Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Lag | ADF Fisher Chi-Squared | Decision |
| GHGpc | Level | 5.048 *** | (I0) |
| ECpc | Level | 9.101 *** | (I0) |
| RQ | Level | 6.255 *** | (I0) |
| FDI | Level | 6.489 *** | (I0) |
| PGu | Level | 0.721 | (l1) |
| First Difference | 13.562 *** | ||
| Wester Lund Test for Co-Integration | Statistics | p-Values | Decision |
|---|---|---|---|
| Variance ratio | 48.248 | 0.000 | Ha: Some panels are co-integrated |
| Panel means: Included Time trend: Included AR parameter: Panel specific Number of panels = 27 Number of periods = 18 | |||
| Pedroni Test for Co-Integration | Statistics | p-Values | Decision |
| Modified Phillips-Perron t | 7.146 | 0.000 | Ha: Some panels are co-integrated |
| Phillips-Perron | −14.615 | 0.000 | |
| Augmented Dickey-Fuller t | −6.849 | 0.000 | |
| Note: Panel means: Included Time trend: Included AR parameter: Panel specific Number of panels = 27 Number of periods = 18 For Pedroni: Kernel: Bartlett; Lags: 2.00 (Newey-West); Augmented lags: 1 | |||
| S.OLS | S.FE | D.OLS | D.FE | Two-Step System GMM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VARIABLES | GHGpc | GHGpc | GHGpc | GHGpc | GHGpc |
| GHGpc | 1.010 *** | 0.806 *** | 1.019 *** | ||
| (0.005) | (0.020) | (0.014) | |||
| ECpc | 0.055 *** | 0.039 ** | −0.001 *** | 0.008 *** | 0.001 ** |
| (0.002) | (0.015) | (0.000) | (0.001) | (0.000) | |
| FDI | −0.442 *** | −0.105 ** | 0.020 ** | −0.004 | 0.006 |
| (0.072) | (0.041) | (0.009) | (0.013) | (0.005) | |
| PGu | 0.786 *** | 0.291 * | −0.077 *** | −0.105 *** | −0.164 *** |
| (0.169) | (0.161) | (0.020) | (0.029) | (0.019) | |
| Observations | 486 | 486 | 459 | 459 | 459 |
| R-squared | 0.776 | 0.502 | 0.997 | 0.892 | |
| AR(1) | −2.507 | ||||
| AR(1)-p | 0.0122 | ||||
| AR(2) | −0.490 | ||||
| AR(2)-p | 0.624 | ||||
| Sargan | 97.45 | ||||
| Sargan-p | 0.000 | ||||
| Hansen | 21.78 | ||||
| Hansen-p | 0.114 | ||||
| J | 20 | ||||
| Chi(2) | 173,688 | ||||
| Chi(2)-p | 0 | ||||
| Number of Group | 27 | 27 | 27 |
| S.OLS | S.FE | D.OLS | D.FE | Two-Step System GMM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VARIABLES | GHGpc | GHGpc | GHGpc | GHGpc | GHGpc |
| GHGpc | 1.008 *** | 0.796 *** | 1.022 *** | ||
| (0.006) | (0.020) | (0.071) | |||
| ECpc | 0.061 *** | 0.039 ** | −0.001 ** | 0.007 *** | 0.006 *** |
| (0.002) | (0.015) | (0.000) | (0.001) | (0.002) | |
| FDI | −0.477 *** | −0.105 ** | 0.019 ** | −0.001 | 0.094 *** |
| (0.068) | (0.041) | (0.009) | (0.013) | (0.024) | |
| PGu | 0.567 *** | 0.291 * | −0.079 *** | −0.082 *** | −0.341 ** |
| (0.164) | (0.161) | (0.020) | (0.030) | (0.138) | |
| RQ | −2.207 *** | 1.305 * | −0.034 | 0.439 *** | −1.517 *** |
| (0.306) | (0.718) | (0.039) | (0.167) | (0.458) | |
| Observations | 486 | 486 | 459 | 459 | 459 |
| R-squared | 0.797 | 0.502 | 0.997 | 0.893 | |
| AR(1) | −2.419 | ||||
| AR(1)-p | 0.0156 | ||||
| AR(2) | −0.167 | ||||
| AR(2)-p | 0.868 | ||||
| Sargan | 54.140 | ||||
| Sargan-p | 0.000 | ||||
| Hansen | 12.38 | ||||
| Hansen-p | 0.260 | ||||
| J | 16 | ||||
| Chi(2) | 2926 | ||||
| Chi(2)-p | 0 | ||||
| Number of Group | 27 | 27 | 27 |
| S.OLS | S.FE | D.OLS | D.FE | Two-Step System GMM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VARIABLES | GHGpc | GHGpc | GHGpc | GHGpc | GHGpc |
| GHGpc | 0.999 *** | 0.799 *** | 1.080 *** | ||
| (0.008) | (0.020) | (0.104) | |||
| ECpc | 0.075 *** | 0.041 *** | −0.000 | 0.007 *** | 0.008 *** |
| (0.001) | (0.013) | (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.003) | |
| RQ | 3.407 *** | 1.806 | 0.036 | 0.257 | −1.096 ** |
| (0.310) | (1.220) | (0.063) | (0.205) | (0.505) | |
| ECpc_RQ | −0.039 *** | −0.003 | −0.001 | 0.001 | −0.004 *** |
| (0.002) | (0.005) | (0.000) | (0.001) | (0.001) | |
| FDI | −0.245 *** | −0.107 ** | 0.018 ** | 0.000 | 0.124 *** |
| (0.047) | (0.040) | (0.009) | (0.013) | (0.030) | |
| PGu | 0.680 *** | 0.263 * | −0.072 *** | −0.073 ** | −0.512 *** |
| (0.110) | (0.150) | (0.021) | (0.030) | (0.197) | |
| Observations | 486 | 486 | 459 | 459 | 459 |
| R-squared | 0.909 | 0.507 | 0.997 | 0.894 | |
| AR(1) | −2.232 | ||||
| AR(1)-p | 0.0256 | ||||
| AR(2) | −0.0637 | ||||
| AR(2)-p | 0.949 | ||||
| Sargan | 51.97 | ||||
| Sargan-p | 0.000 | ||||
| Hansen | 11.16 | ||||
| Hansen-p | 0.265 | ||||
| J | 16 | ||||
| Chi(2) | 2071 | ||||
| Chi(2)-p | 0 | ||||
| Number of Group | 27 | 27 | 27 |
| S.OLS | S.FE | D.OLS | D.FE | Two-Step System GMM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VARIABLES | GHGpc | GHGpc | GHGpc | GHGpc | GHGpc |
| GHGpc | 1.006 *** | 0.795 *** | 1.117 *** | ||
| (0.008) | (0.020) | (0.083) | |||
| ECpc | 0.063 *** | 0.039 ** | −0.001 | 0.007 *** | 0.003 |
| (0.001) | (0.015) | (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.003) | |
| FDI | −0.492 *** | −0.096 ** | 0.018 * | 0.007 | 0.116 *** |
| (0.050) | (0.038) | (0.009) | (0.014) | (0.031) | |
| RQ | 1.225 *** | 1.197 | −0.025 | 0.351 ** | −1.768 *** |
| (0.281) | (0.758) | (0.048) | (0.169) | (0.585) | |
| FDI_RQ | −0.951 *** | 0.042 | −0.004 | 0.038 ** | 0.083 *** |
| (0.047) | (0.048) | (0.011) | (0.015) | (0.015) | |
| PGu | 0.648 *** | 0.286 * | −0.078 *** | −0.084 *** | −0.497 *** |
| (0.120) | (0.164) | (0.021) | (0.030) | (0.131) | |
| Observations | 486 | 486 | 459 | 459 | 459 |
| R-squared | 0.891 | 0.504 | 0.997 | 0.895 | |
| AR(1) | −2.677 | ||||
| AR(1)-p | 0.007 | ||||
| AR(2) | −0.278 | ||||
| AR(2)-p | 0.781 | ||||
| Sargan | 49.79 | ||||
| Sargan-p | 0.0000 | ||||
| Hansen | 12.21 | ||||
| Hansen-p | 0.202 | ||||
| J | 16 | ||||
| Chi(2) | 2061 | ||||
| Chi(2)-p | 0 | ||||
| Number of Group | 27 | 27 | 27 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbas, H.S.M.; Xu, X.; Sun, C.; Ullah, A.; Nabi, G.; Gillani, S.; Raza, M.A.A. Sustainable Use of Energy Resources, Regulatory Quality, and Foreign Direct Investment in Controlling GHGs Emissions among Selected Asian Economies. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031123
Abbas HSM, Xu X, Sun C, Ullah A, Nabi G, Gillani S, Raza MAA. Sustainable Use of Energy Resources, Regulatory Quality, and Foreign Direct Investment in Controlling GHGs Emissions among Selected Asian Economies. Sustainability. 2021; 13(3):1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031123
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbas, Hafiz Syed Mohsin, Xiaodong Xu, Chunxia Sun, Atta Ullah, Ghulam Nabi, Samreen Gillani, and Muhammad Ahsan Ali Raza. 2021. "Sustainable Use of Energy Resources, Regulatory Quality, and Foreign Direct Investment in Controlling GHGs Emissions among Selected Asian Economies" Sustainability 13, no. 3: 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031123
APA StyleAbbas, H. S. M., Xu, X., Sun, C., Ullah, A., Nabi, G., Gillani, S., & Raza, M. A. A. (2021). Sustainable Use of Energy Resources, Regulatory Quality, and Foreign Direct Investment in Controlling GHGs Emissions among Selected Asian Economies. Sustainability, 13(3), 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031123








