Comparative Evaluation of Simplified Surface Energy Balance Index-Based Actual ET against Lysimeter Data in a Tropical River Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
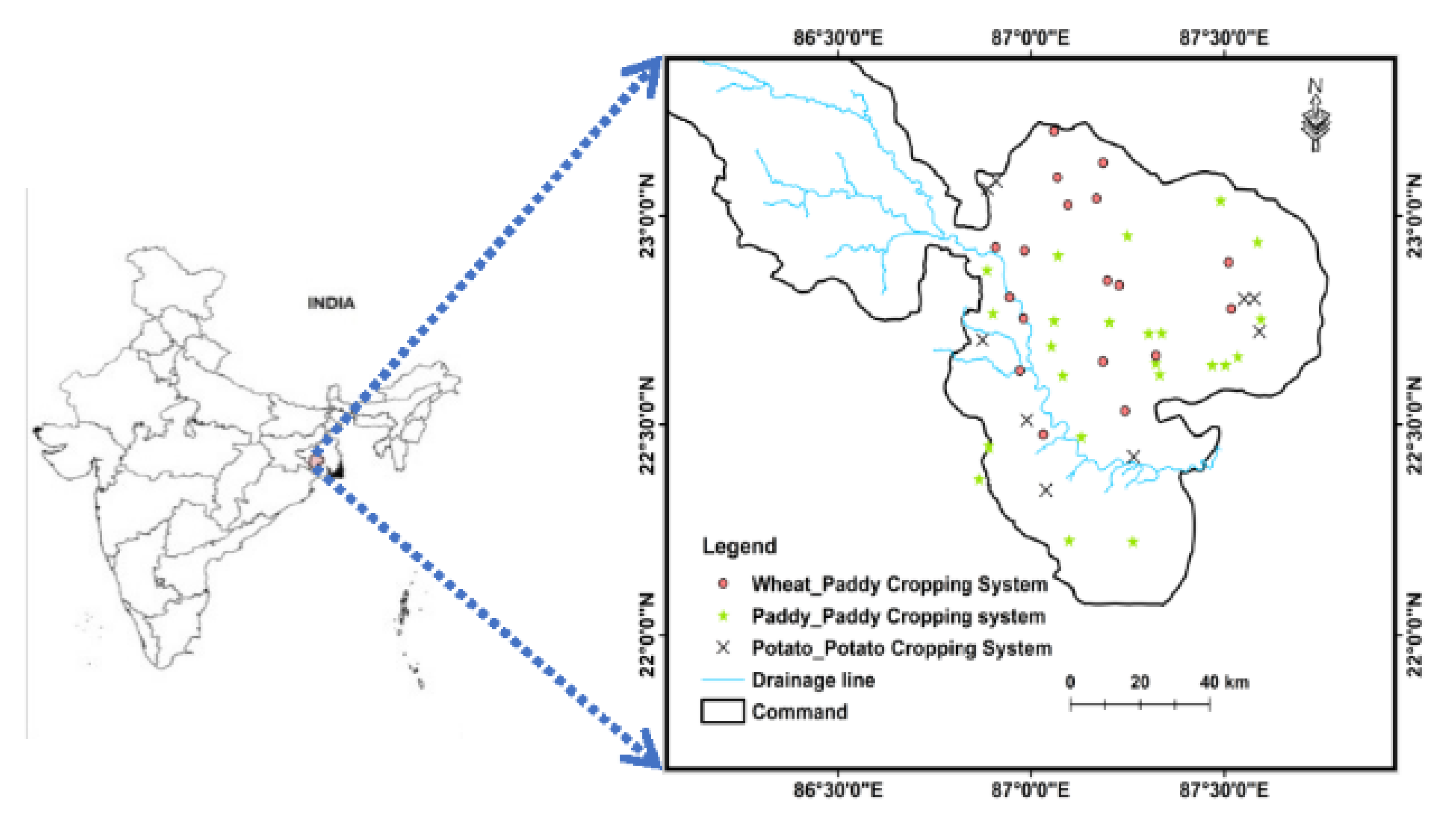
2. Project Site Description and Data Used
3. Remotely Sensed Data
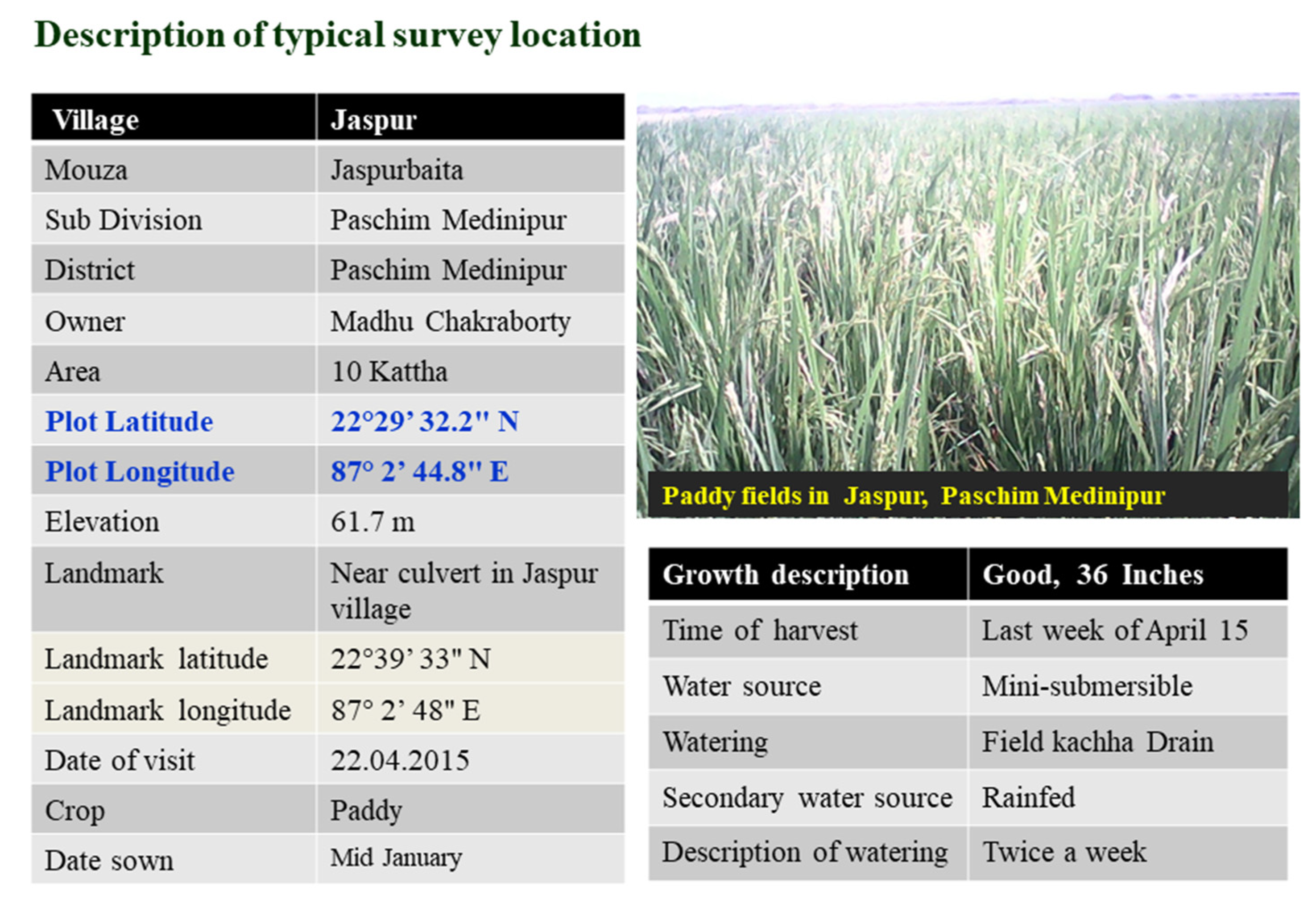
4. Survey Data for Crop Coefficient Vegetation Modeling
5. Meteorological Data
6. Methodology
6.1. Computation of Surface Energy Fluxes from Landsat 8 Imagery
6.2. Estimation of Surface Energy Flux Using Landsat 8
6.2.1. Net Radiation
6.2.2. Soil Heat Flux (G)
6.3. Evaporative Fraction (Λ)
6.4. Estimation of Actual ET Using S-SEBI
6.5. Calculation of Reference ET
6.6. Performance Indicator
7. Results and Discussion
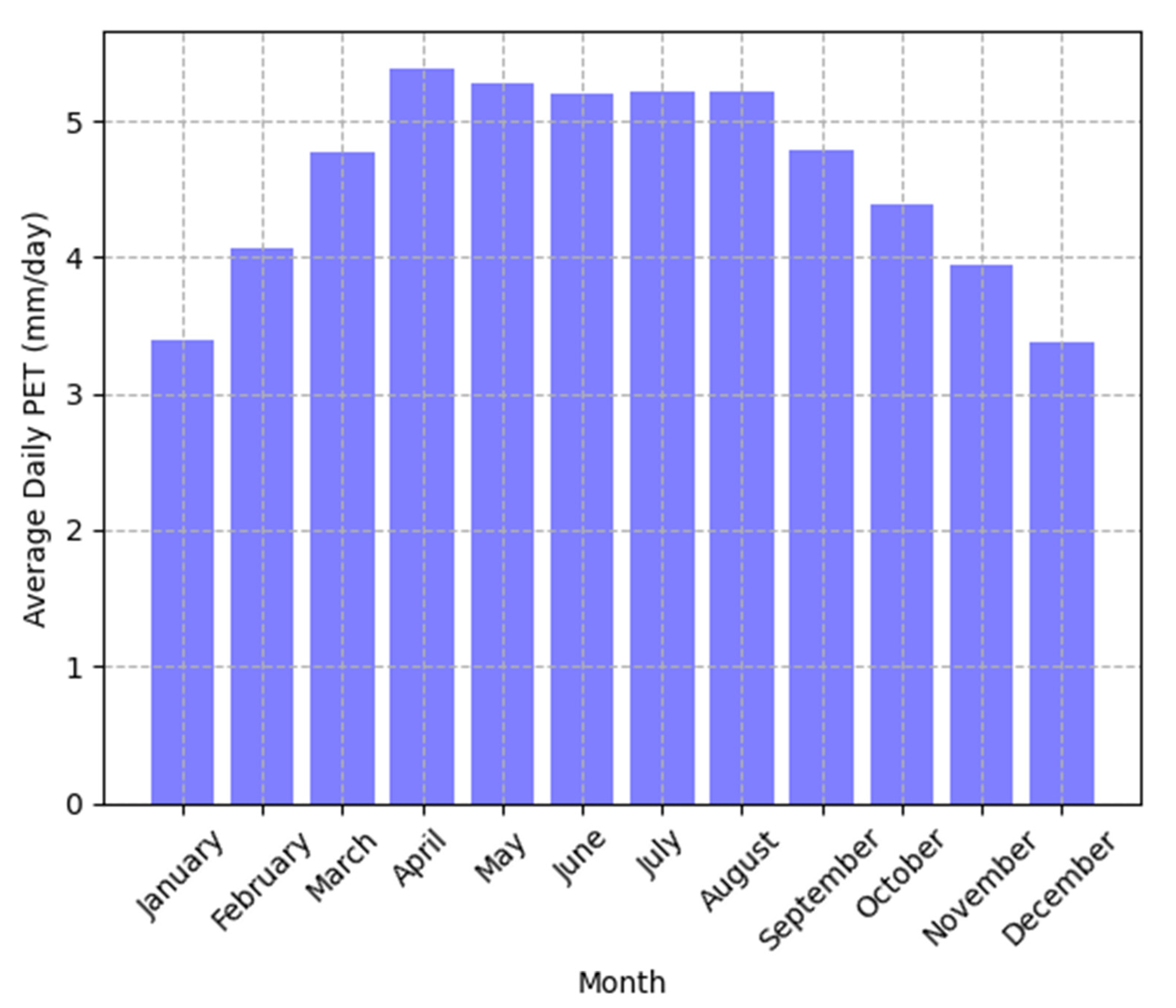
7.1. Seasonal Variation of ETo
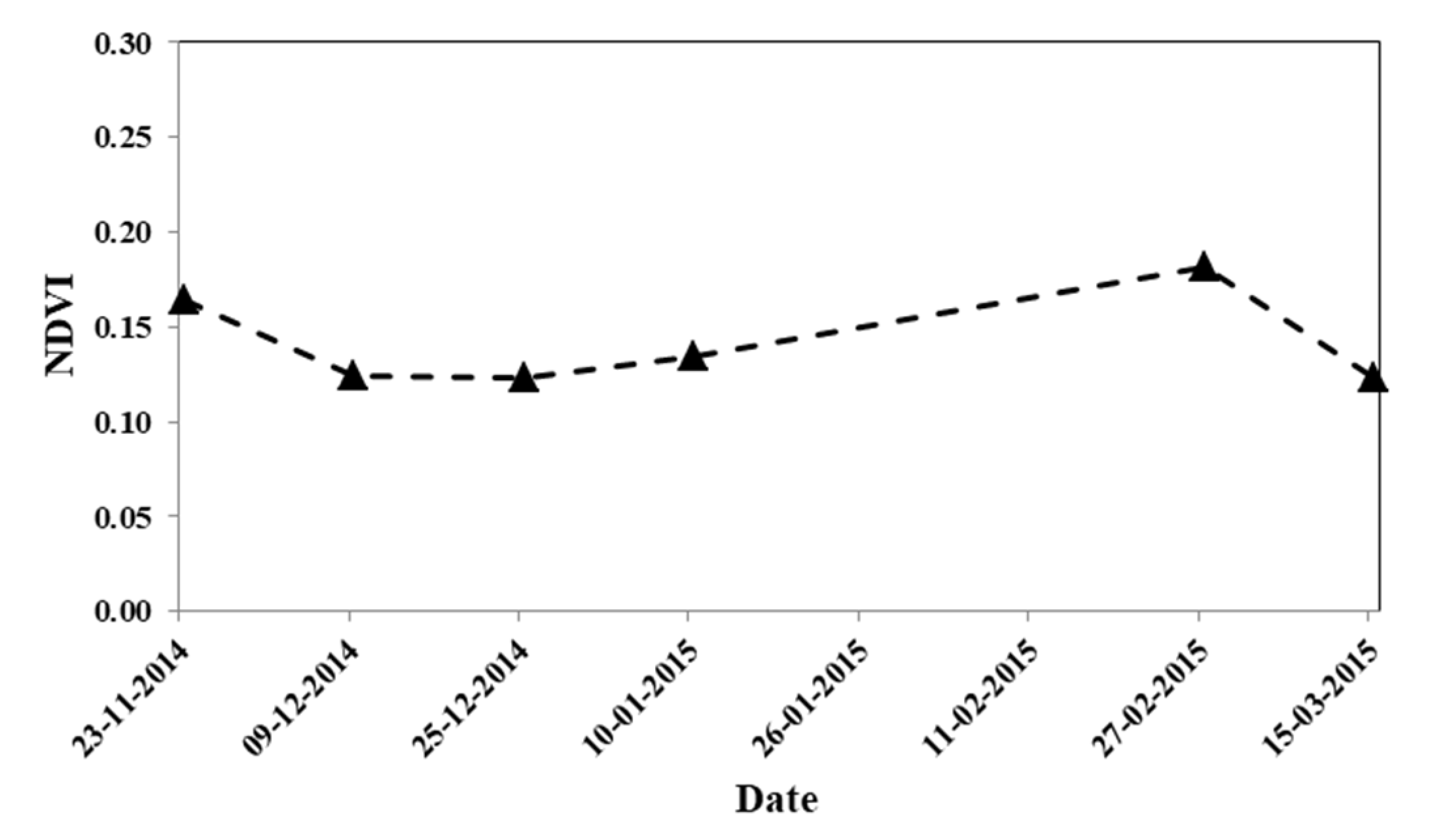
7.2. Temporal Variation of NDVI
7.3. Spatial–Temporal Variation of NDVI over Study Region
7.4. Calculation of Tabulated Crop Coefficient Value to Local Condition
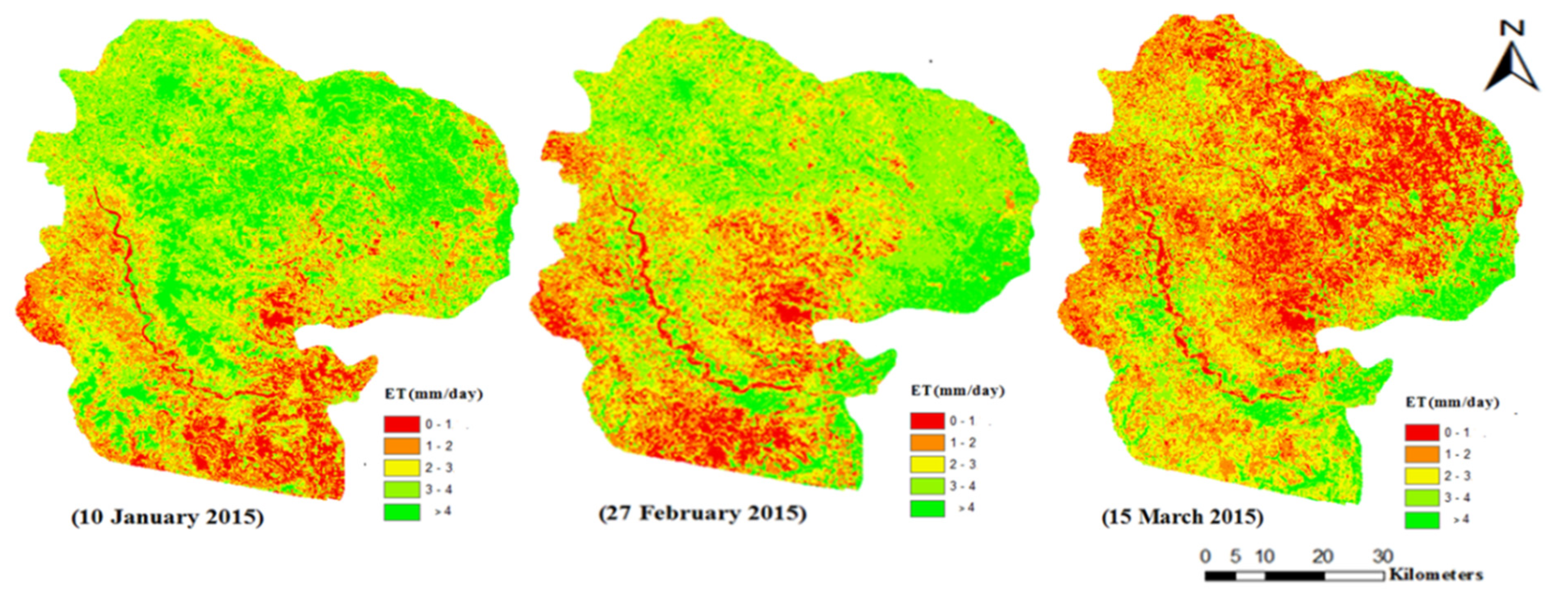
7.5. Spatial–Temporal Variation of ET over Study Area
7.6. Lysimeter ETc
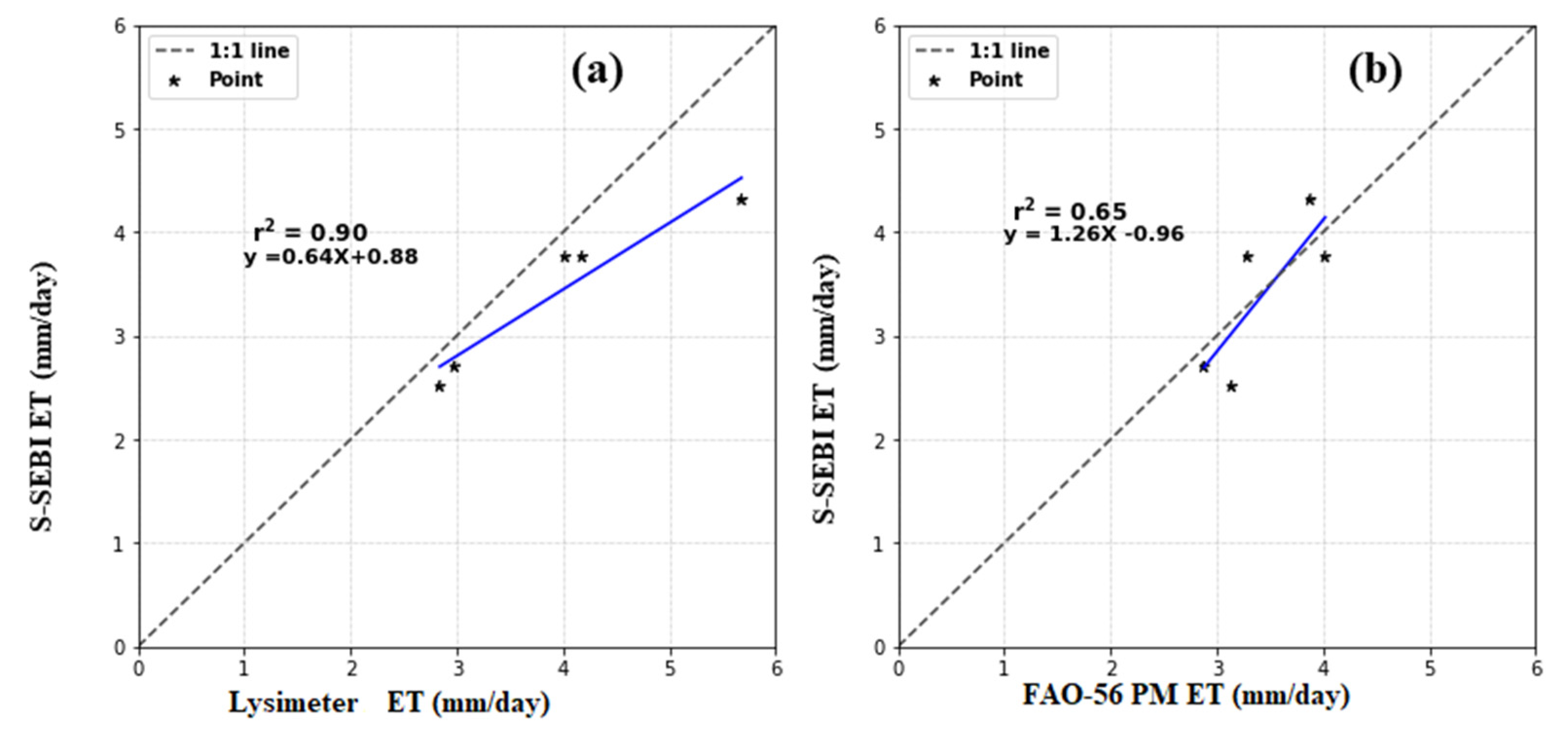
7.7. Validation of S-SEBI ETc
8. Conclusions
- 1.
- Seasonal variations in the NDVI were shown to indicate the vegetation response toward the rainfall for the available data period. The study developed a vegetation index-based crop coefficient model, which is based on a simple linear regression approach.
- 2.
- The study calculated the crop coefficient from the field information collected from survey data. The location-wise ET was calculated from the product of the reference ET calculated from FAO-56 PM and the crop coefficient calculated from survey data. The crop actual evapotranspiration was generated spatially and temporally using remote sensing data.
- 3.
- A spatial and temporal map of ET was obtained on the basis of the evaluation of satellite-based ET with the lysimetric data, which showed good performance in capturing the seasonality.
- 4.
- This research found that the ETc estimated using the remote sensing-based S-SEBI approach showed good performance (r2 = 0.90). Furthermore, it is noticeable that the spatial resolution in the TIR sensor of Landsat 8 imagery is not properly suitable to represent the test site for the validation of ET. The S-SEBI is a simplified model of the surface energy balance approach that depends less on a complicated input model that can adequately capture the spatial evaporative demand and reproduce the daily ET map for the study area. Therefore, the S-SEBI can be applied to compute ETc agriculture land use with better accuracy, and thus the S-SEBI can be operationally implemented for computing ETc using remotely sensed data with a thermal band for efficient water management and irrigation scheduling. This study concludes that the estimation of ETc using the remote sensing-based S-SEBI model using exhaustive survey data offers a powerful tool for near-real-time ETc calculation for irrigation water management in data-scarce regions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abrahams, A.D.; Parsons, A.J. Geomorphology of Desert Environments; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Gowda, P.H.; Chavez, J.L.; Colaizzi, P.D.; Evett, S.R.; Howell, T.A.; Tolk, J.A. ET mapping for agricultural water management: Present status and challenges. Irrigat. Sci. 2008, 26, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R.A.; Holtslag, A.A.M. A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL): 1. Formulation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goward, S.N.; Markham, B.; Dye, D.G.; Dulaney, W.; Yang, J. Normalized difference vegetation index measurements from the advanced very high resolution radiometer. Remote. Sens. Environ. 1991, 35, 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, E.P.; Neale, C.M.U.; Hunsaker, D.J.; Nagler, P.L. Vegetation index-based crop coefficients to estimate evapotranspiration by remote sensing in agricultural and natural ecosystems. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 4050–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Sahoo, B.; Raghuwanshi, N.S.; Singh, R. Evaluation of Variable Infiltration Capacity model and MODIS-Terra satellite-derived grid-scale evapotranspiration estimates in a river basin with tropical monsoon-type climatology. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2017, 143, 04017028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration–Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements-FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; 300p. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, U.; Sahoo, B.; Chatterjee, C.; Raghuwanshi, N. Evaluation of simplified surface energy balance index (S−SEBI) method for estimating actual evapotranspiration in Kangsabati reservoir command using landsat 8 imagery. J. Indian Soc. Remote. Sens. 2020, 48, 1421–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senay, G.B.; Friedrichs, M.; Singh, R.K.; Velpuri, N.M. Evaluating Landsat 8 evapotranspiration for water use mapping in the Colorado River Basin. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, U.; Singh, S.; Bisht, J.K.; Kant, L. Use of meteorological data for identification of agricultural drought in Kumaon region of Uttarakhand. J Earth Syst Sci. 2021, 130, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samani, Z.; Bawazir, A.S.; Bleiweiss, M.; Skaggs, R.; Longworth, J.; Tran, V.D.; Pinon, A. Using remote sensing to evaluate the spatial variability of evapotranspiration and crop coefficient in the lower Rio Grande Valley, New Mexico. Irrig. Sci. 2009, 28, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, R.S.; Nagler, P.L.; Morino, K.; Glenn, E.P. An Empirical Algorithm for Estimating Agricultural and Riparian Evapotranspiration Using MODIS Enhanced Vegetation Index and Ground Measurements of ET. II. Application to the Lower Colorado River, U.S. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 1125–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, U.; Panday, S.C.; Kumar, J.; Meena, V.S.; Parihar, M.; Singh, S.; Bisht, J.K.; Kant, L. Comparison of recent rainfall trend in complex hilly terrain of sub−temperate region of Uttarakhand. MAUSAM 2021, 72, 349−358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharples, J.A. The Corn Blight Watch Experiment: Economic Implications for Use of Remote Sensing for Collecting Data on Major Crops; LARS Technical Reports; Purdue University Publication: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 1973; p. 121. [Google Scholar]
- Hunsaker, D.J.; Pinter, P.J.; Barnes, E.M.; Kimball, B.A. Estimating cotton evapotranspiration crop coefficients with a multispectral vegetation index. Irrig. Sci. 2003, 22, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunsaker, D.J.; Hendrey, G.R.; Kimball, B.A.; Lewin, K.F.; Mauney, J.R.; Nagy, J. Cotton evapotranspiration under field conditions with CO2 enrichment and variable soil moisture regimes. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1994, 70, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.; Srivastava, A.; Kumari, N.; Rashmi; Sahoo, B.; Chatterjee, C.; Raghuwanshi, N.S. Evaluation of spatio−temporal evapotranspiration using satellite−based approach and lysimeter in the agriculture dominated catchment. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2021, 49, 1939–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustas, W.P.; Norman, J.M.; Schmugge, T.J.; Anderson, M.C. Mapping surface energy fluxes with radiometric temperature. In Thermal Remote Sensing in Land Surface Processes; Quattrochi, D., Luvall, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 205–253. [Google Scholar]
- Bausch, W.C. Soil background effects on reflectance-based crop coefficients for corn. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 46, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bausch, W.C.; Neale, C.M.U. Crop coefficients derived from reflected canopy radiation: A concept. Trans. ASAE 1987, 30, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontia, N.K.; Tiwari, K.N. Estimation of crop coefficient and evapotranspiration of wheat (Triticum aestivum) in an irrigation command using remote sensing and GIS. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 1399–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.F.; Trout, T.J. Satellite NDVI assisted monitoring of vegetable crop evapotranspiration in California’s San Joaquin Valley. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roerink, G.J.; Su, Z.; Menenti, M. S-SEBI: A simple remote sensing algorithm to estimate the surface energy balance. Phys. Chem. Earth Part B Hydrol. Ocean. Atmos. 2000, 25, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorenbos, J.; Pruitt, W.O. Guidelines for Prediction of Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 24 (revised); Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Tasumi, M.; Trezza, R. Satellite-based energy balance for mapping evapotranspiration with internalized calibration (METRIC)-Model. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. ASCE 2007, 133, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Xi, G.; Liu, S.; Huang, C.; Yan, Y.; Liu, G. Regional estimation of daily to annual regional evapotranspiration with MODIS data in the Yellow River Delta wetland. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 1775–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kustas, W.P.; Daughtry, C.S.T. Estimation of soil heat flux/net radiation ratio from spectral data. Agric. Forest Meteorol. 1990, 49, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S. Narrowband to broadband conversions of land surface albedo I: Algorithms. Rem. Sens. Environ. 2001, 76, 213–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menenti, M.; Choudhury, B.J. Parametrization of land surface evapotranspiration using a location dependent potential evapotranspiration and surface temperature range. In Exchange Processes at the Land Surface for a Range of Space and Time Scales; Bolle, H.J., Ed.; IAHS Press IAHS: Wallingford, UK, 1993; pp. 561–588. [Google Scholar]
- Sobrino, J.A.; El Kharraz, J.; Li, Z.-L. Surface temperature and water vapour retrieval from MODIS data. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2003, 24, 5161–5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.W.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring vegetation system in great plains with ERTS. In Proceedings of the 3rd ERTS-1 Symposium, Washington, DC, USA, 10–14 December 1973. GSFC, NASA; SP-351: 48–62. [Google Scholar]
- Sellers, P.J. Canopy reflectance, photosynthesis, and transpiration. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 1985, 6, 1335–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Raissouni, N. Toward remote sensing methods for land cover dynamic monitoring. Application to Morocco. Int. J. Rem. Sens. 2000, 21, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Gómez, M.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Olioso, A.; Chehbouni, G. A simple algorithm to estimate evapotranspiration from DAIS data: Application to the DAISEX campaigns. J. Hydrol. 2005, 315, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Jiménez-Munoz, J.C.; Sòria, G.; Romaguera, M.; Guanter, L.; Moreno, J.; Plaza, A.; Martínez, P. Land surface emissivity retrieval from different VNIR and TIR sensors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2008, 46, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.Y.; Singh, V.P. Evaluation of three complementary relationship evapotranspiration models by water balance approach to estimate actual regional evapotranspiration in different climatic regions. J. Hydrol. 2005, 308, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.; Meena, V.S.; Singh, S.; Bisht, J.K.; Pattanayak, A. Evaluation of digital elevation model in hilly region of Uttarakhand: A case study of experimental farm Hawalbagh. Indian J. Soil Conserv. 2021, 49, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Vyas, S.P.; Oza, M.P.; Dadhwal, V.K. Multi-crop separability study of Rabi crops using multi-temporal satellite data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2005, 33, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.G.; Vaughan, R.A. Integrated Applications: Precision Agriculture and Crop Management. In Remote Sensing of Vegetation: Principles, Techniques, and Applications; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; ISBN 978-0199207794. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, K.; Zhou, J. Assessing the impacts of an ecological water diversion project on water consumption through high-resolution estimations of actual evapotranspiration in the downstream regions of the Heihe River Basin, China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 249, 210–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Ahmad, M.-U.-D.; Chemin, Y. Satellite surveillance of evaporative depletion across the Indus Basin. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wei, B.; Su, W.; Shen, W.; Wang, C.; You, D.; Liu, Z. Evapotranspiration estimation based on the SEBAL model in the Nansi Lake Wetland of China. Math. Comput. Model. 2011, 54, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwart, S.J.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. SEBAL for detecting spatial variation of water productivity and scope for improvement in eight irrigated wheat systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 89, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. SEBAL-based sensible and latent heat fluxes in the irrigated Gediz Basin, Turkey. J. Hydrol. 2000, 229, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.; Irmak, A.; Trezza, R.; Hendrickx, J.M.H.; Bastiaanssen, W.; Kjaersgaard, J. Satellite-based ET estimation in agriculture using SEBAL and METRIC. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 4011–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wang, Q.; Matsushita, B.; Fukushima, T.; Ouyang, Z.; Watanabe, M.; Gebremichael, M. Further evaluation of the Sim-ReSET model for ET estimation driven by only satellite inputs. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 994–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, P.; Tiwari, K.N.; Chowdary, V.M.; Gontia, N.K. Irrigation water demand and supply analysis in the command area using remote sensing and GIS. Hydrol J IAH 2005, 28, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, S.S.; Dadhwal, V.K. Estimation of evapotranspiration of irrigation command area using remote sensing and GIS. Agric. Water Manag. 2000, 49, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwetha, H.R.; Kumar, D.N. Estimation of Daily Actual Evapotranspiration Using Vegetation Coefficient Method for Clear and Cloudy Sky Conditions. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2020, 13, 2385–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.Z.; Xu, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.S.; Cai, J.B.; Du, L.J. Multi-scale evapotranspiration of summer maize and the controlling meteorological factors in north China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 216, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danodia, A.; Patel, N.R.; Chol, C.W.; Nikam, B.R.; Sehgal, V.K. Application of S-SEBI model for crop evapotranspiration using Landsat-8 data over parts of North India. Geocarto Int. 2019, 34, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Path | Row | Sensor | Spatial Resolution | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 139 | 44 | Operational Land Imager (OLI), Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) | 30 m, 100 m (resample to 30 m) | 10 January 2015, 27 February 2015, 15 March 2015 |
| Growth Stage | Paddy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FAO Kc | 10 January 2015 | 27 February 2015 | 15 March 2015 | |
| Mod_Kc | ||||
| Initial | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Development | 1.15 | 1.18 | 1.13 | 1.12 |
| Maturity | 0.70 | 0.80 | 0.72 | 0.71 |
| Crops | Date | Pearson’s r | p-Value | MSE | RMSE | d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paddy | 10 January 2015 | 0.06 | 0.89 | 1.29 | 1.13 | 0.37 |
| 27 February 2015 | 0.85 | 0.009 | 0.25 | 0.48 | 0.73 | |
| 15 March 2015 | 0.77 | 0.007 | 0.28 | 0.52 | 0.68 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, U.; Rashmi; Chatterjee, C.; Raghuwanshi, N.S. Comparative Evaluation of Simplified Surface Energy Balance Index-Based Actual ET against Lysimeter Data in a Tropical River Basin. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13786. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413786
Kumar U, Rashmi, Chatterjee C, Raghuwanshi NS. Comparative Evaluation of Simplified Surface Energy Balance Index-Based Actual ET against Lysimeter Data in a Tropical River Basin. Sustainability. 2021; 13(24):13786. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413786
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Utkarsh, Rashmi, Chandranath Chatterjee, and Narendra Singh Raghuwanshi. 2021. "Comparative Evaluation of Simplified Surface Energy Balance Index-Based Actual ET against Lysimeter Data in a Tropical River Basin" Sustainability 13, no. 24: 13786. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413786
APA StyleKumar, U., Rashmi, Chatterjee, C., & Raghuwanshi, N. S. (2021). Comparative Evaluation of Simplified Surface Energy Balance Index-Based Actual ET against Lysimeter Data in a Tropical River Basin. Sustainability, 13(24), 13786. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413786






