Temperature Variations and Possible Forcing Mechanisms over the Past 300 Years Recorded at Lake Chaonaqiu in the Western Loess Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
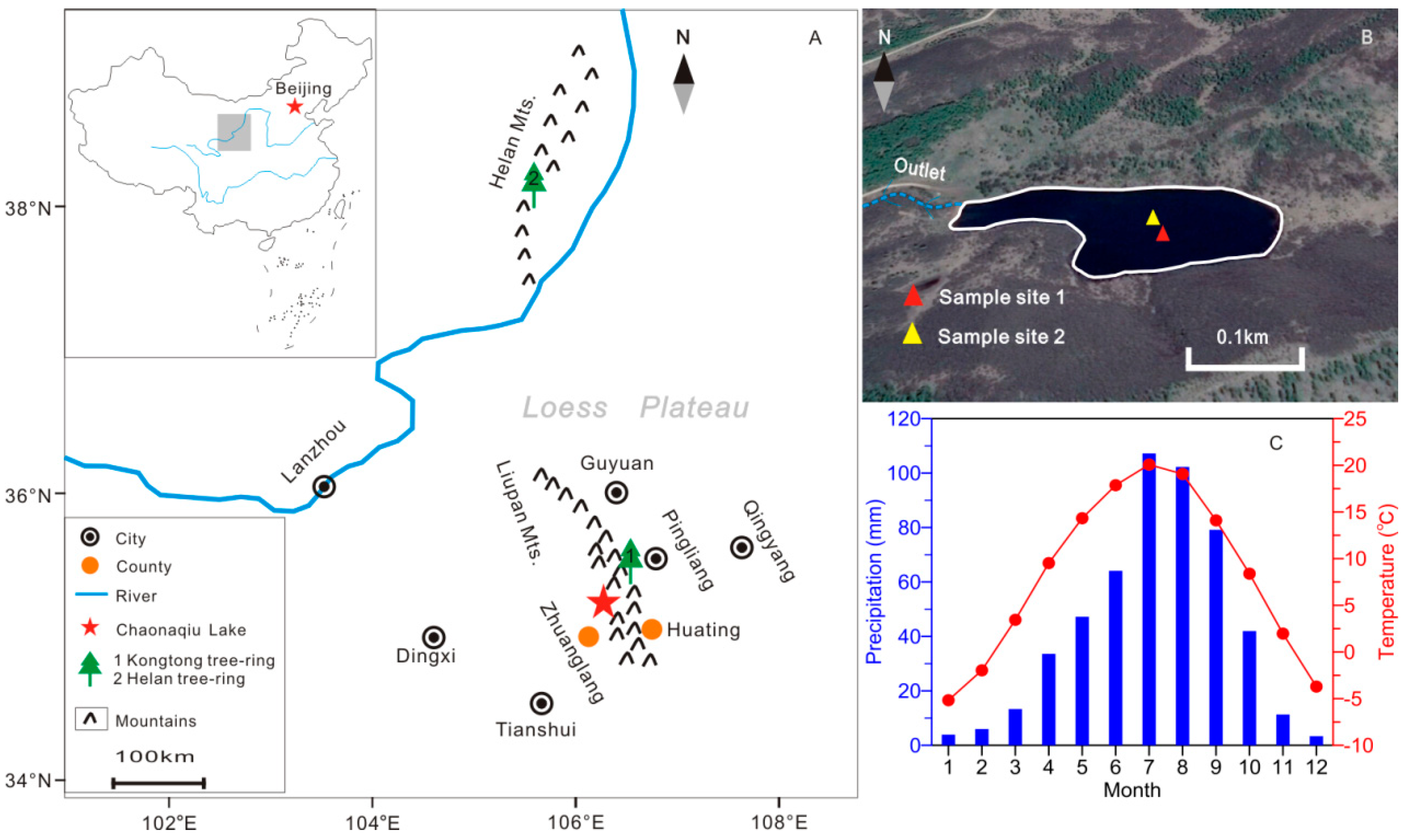
2.1. Background and Sampling
2.2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Chronology
3.2. Proxy Indices
4. Discussion
4.1. Climatic Significance of the Authigenic Carbonate
4.2. Temperature Variations at Lake Chaonaqiu over the Past 300 Years
4.3. Temperature Variations on the Western Loess Plateau over the Past 300 Years

| No. | Solar Calendar Dates | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 31 July 1744 | The 9th year of the reign of Emperor Qianlong, Qing Dynasty: On 25 July, uncovered oats in Haiyuan, Guyuan, and Huating Counties were damaged by frost. |
| 2 | 24 April1748 | The 13th year of the reign of Emperor Qianlong, Qing Dynasty: On the evening of 1 March, seedlings were killed by frost in Gangu, while on the same night, heavy snow fell on the suburbs in Guyuan. |
| 3 | 1749 | The 14th year of the reign of Emperor Qianlong, Qing Dynasty: Longde, Guyuan, and other counties were affected by summertime and autumn frosts. |
| 4 | December 1773 | The 38th year of the reign of Emperor Qianlong, Qing Dynasty: In November, relief aid was provided to refugees of frost and famine in Jingchuan. |
| 5 | 1776 | The 41st year of the reign of Emperor Qianlong, Qing Dynasty: Chongxin, Jingchuan, and Lingtai Counties were affected by frost. |
| 6 | 4 June 1777 | The 42nd year of the reign of Emperor Qianlong, Qing Dynasty: On 2 May, Dingxi experienced frost. |
| 7 | December 1783 | The 48th year of the reign of Emperor Qianlong, Qing Dynasty: In November, wildflowers were in full bloom in Zhenyuan. ★ |
| 8 | November 1817 | The 22nd year of the reign of Emperor Jiaqing, Qing Dynasty: In November, peach trees were blooming in Zhenyuan. ★ |
| 9 | December 1818 | The 23rd year of the reign of Emperor Jiaqing, Qing Dynasty: In November, peaches and winter jasmine were blooming in Zhenyuan. ★ |
| 10 | 1837 | The 18th year of the reign of Emperor Daoguang, Qing Dynasty: On 12 January (equivalent to 5 March 1838), grain rations and seeds were provided to frost refugees in Guyuan and Longde. |
| 11 | 19 December 1840 | The 20th year of the reign of Emperor Daoguang, Qing Dynasty: On 26 November, the old and new taxes were postponed for frost refugees in Longde. |
| 12 | December 1841 | The 21st year of the reign of Emperor Daoguang, Qing Dynasty: In November, the old taxes were postponed due to frost in Guyuan and Lingtai. |
| 13 | 14 November 1868 | The 7th year of the reign of Emperor Tongzhi, Qing Dynasty: On 1 October, Zhuanglang County was seriously impacted by a snowstorm, which buried roads and crushed vegetation. |
| 14 | April 1871 | The 10th year of the reign of Emperor Tongzhi, Qing Dynasty: In April, Lingtai County suffered heavy frost, resulting in serious damage to seedlings. |
| 15 | 1873 | The 12th year of the reign of Emperor Tongzhi, Qing Dynasty: During summer, Lingtai County suffered heavy frost, resulting in the loss of seedlings and crops. |
| 16 | 30 May 1884 | The 10th year of the reign of Emperor Guangxu, Qing Dynasty: On 8 April heavy sleet fell in Jingchuan. |
| 17 | May,1890 | The 16th year of the reign of Emperor Guangxu, Qing Dynasty: In April, crops in Jingyuan were killed by frost. |
| 18 | September 1902 | The 28th year of the reign of Emperor Guangxu, Qing Dynasty: In August, seedlings in Guangleli (an ancient placename), Zhuanglang County, were damaged by heavy frost. |
| 19 | 1911 | The 3rd year of the reign of Emperor Xuantong, Qing Dynasty: In Autumn, vegetation bloomed again in Huating. ★ |
| 20 | 1915 | The 4th year of the Republic of China: In Autumn, vegetation bloomed again in Huating. ★ |
| 21 | 1930 | The 19th year of the Republic of China: Longde was affected by black frost, resulting in famine refugees. |
| 22 | 1932 | The 21st year of the Republic of China: Piangliang County was affected by frost during the first half of the year. Black frost during the autumn damaged seedlings in Lingtai, impacting an area spanning >100 miles from north to south. |
| 23 | 2 May 1933 | The 22nd year of the Republic of China: On 8 April, Jingyuan County was impacted by a blizzard and intense cold, with >5 feet (equivalent to 155 cm) of snow falling in the Longshan Mountains. |
| 24 | 1938 | The 27th year of the Republic of China: It took quite a long time for the heavy snow in Huating to melt. |
| 25 | 1940 | The 29th year of the Republic of China: Black frost killed seedlings in Lingtai, Huanting, Chongxin, Pingliang, Zhenyuan, Zhuanglang, and Jingning Counties. |
| 26 | 1941 | The 30th year of the Republic of China: Black frost killed seedlings in Pingliang, Huanting, Chongxin, Jingning, and Longde Counties. |
| 27 | 1942 | The 31st year of the Republic of China: Black frost killed crops in Huanting, Zhuanglang, Pingliang, and Jingning Counties. |
| 28 | 1943 | The 32nd year of the Republic of China: Frost caused extensive damage in Baishui (and thirteen other towns in Pingliang County), Jingfchuan and Shuiluo (and eleven other towns in Zhuanglang County), and Jingning. |
| 29 | 1945 | The 34th year of the Republic of China: Pingliang suffered frost. On 4 October, early frost in Zhenyuan resulted in extensive ice cover (frost of 0.3 cm depth) and killed >80% of the buckwheat crop. In May, black frost occurred in Chengguan and five other towns in Huating County, damaging the majority of the sprouting wheat crop. |
| 30 | 1947 | The 36th year of the Republic of China: On 9 and 10 October heavy frost occurred in Longpan town in Pingliang County, killing the foxtail millet and buckwheat crops. Black frost occurred in Ankou and Longyan towns, Huating County, resulting in the destruction of sprouting wheat and other crops. On 15 May frost damaged crops in Shenshangu town, Chongxin County. |
| 31 | 1971 | On 25 September early frost occurred in Pingliang and other regions, with minimum ground temperatures of −4 °C to −1 °C. |
| 32 | 1972 | Between 13 and 15 May late frosts occurred in Dingxi, Pingliang, and Qingyang, with minimum ground temperatures of −5°C and widespread cotton, corn, and crop failures. |
| 33 | 1974 | Late frost ends on 9–10 May in Gansu Province, and is delayed for 15–22 days in Tianshui and Longdong. Such an occurrence is rare in recent decades. |
| 34 | 1976 | The average temperature for July in Pingliang dropped by 0.1–1.0 °C. |
| 35 | 1979 | Extreme cold events occurred in 1979, 1987, 1993, and 1995 in Ningxia Province (1949~2000). |
| 36 | 1987 | |
| 37 | 1993 | |
| 38 | 1995 |
4.4. Possible Forcing Mechanisms of WLP Temperature Variations over the Past 300 Years

5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Della-Marta, P.M.; Haylock, M.R.; Luterbacher, J.; Wanner, H. Doubled length of western European summer heat waves since 1880. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D15103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perkins, S.E.; Alexander, L.V.; Nairn, J.R. Increasing frequency, intensity and duration of observed global heatwaves and warm spells. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L20714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. In Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Boeck, H.; Dreesen, F.E.; Janssens, I.A.; Nijs, I. Climatic characteristics of heat waves and their simulation in plant experiments. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 1992–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, A.; Gouveia, C.M.; Trigo, R.M.; Running, S.W. Analysing the spatio-temporal impacts of the 2003 and 2010 extreme heatwaves on plant productivity in Europe. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 3421–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.W.; Wen, X.Y.; Luo, Y.; Dong, W.J.; Yang, Z.B. Reconstruction of temperature series of China for the last 1000 years. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2007, 8, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, M.E.; Zhang, Z.; Rutherford, S.; Bradley, R.S.; Hughes, M.K.; Shindell, D.; Ammann, C.; Faluvegi, G.; Ni, F. Global signatures and dynamical origins of the Little Ice Age and Medieval Climate Anomaly. Science 2009, 326, 1256–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Song, M.; Liu, W.; Liu, Z. Late Holocene coupled moisture and temperature changes on the northern Tibetan Plateau. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2013, 80, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.X.; Liu, W.G.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, Y.; Qin, X.Y.; Hu, Q.H.; An, Z.S.; Liu, Z.H. Solar influenced late Holocene temperature changes on the northern Tibetan Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.K.; Liu, G.N.; Chen, Y.X.; Li, Y.N.; Harbor, J. Timing and extent of Quaternary glaciations in the Tianger Range, eastern Tian Shan, China, investigated using 10Be surface exposure dating. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2014, 98, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Sheng, E.; Lan, J.; Liu, B.; Yu, K.; Che, S. Decadal/multi-decadal temperature discrepancies along the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2014, 89, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aichner, B.; Feakins, S.J.; Lee, J.E.; Herzschuh, U.; Liu, X. High resolution leaf wax carbon and hydrogen isotopic record of late Holocene paleoclimate in arid Central Asia. Clim. Past 2015, 11, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Herzschuh, U.; Wang, Y.; Kuhn, G.; Yu, Z. Glacier fluctuations of Muztagh Ata and temperature changes during the late Holocene in westernmost Tibetan Plateau, based on glaciolacustrine sediment records. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 41, 6265–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffel, M.; Khodri, M.; Corona, C.; Guillet, S.; Poulain, V.; Bekki, S.; Guiot, J.; Luckman, B.H.; Oppenheimer, C.; Lebas, N. Estimates of volcanic-induced cooling in the Northern Hemisphere over the past 1500 years. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, C.W. Evolution of global temperature over the past two million years. Nature 2016, 538, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Xu, H.; Sheng, E.; Yu, K.; Wu, H.; Zhou, K.; Yan, D.; Ye, Y.; Wang, T. Climate changes reconstructed from a glacial lake in High Central Asia over the past two millennia. Quat. Int. 2018, 487, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.D.; Mann, M.E. Climate over past millennia. Rev. Geophys. 2004, 42, RG2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Leavitt, S.W.; Hughes, M.K. Stable carbon isotope in tree rings from Huangling, China and climatic variation. Sci. China (Ser. D) 1996, 39, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Liu, Y. Temperature variability since 1776 inferred from tree-rings of Pinus tabulaeformis in Mt. Helan. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2006, 61, 929–936, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Q.F.; Liu, Y.; Song, H.M.; Sun, J.Y. Tree-ring-based reconstruction of the April to September mean temperature since 1826 AD for north-central Shaanxi Province,China. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2008, 51, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.M.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Hans, L. Tree-ring derived temperature records in the central Loess Plateau, China. Quat. Int. 2013, 283, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yu, K.K.; Lan, J.H.; Sheng, E.G.; Liu, B.; Ye, Y.D.; Hong, B.; Wu, H.X.; Zhou, K.E.; Yeager, K.M. Different responses of sedimentary δ15N to climatic changes and anthropogenic impacts in lakes across the Eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2016, 123, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Xie, C.; Chen, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, A.; Rühland, K.; Smol, J.P.; Chen, F. Biogeochemical responses to climate change and anthropogenic nitrogen deposition from a 200-year record from Tianchi Lake, Chinese Loess Plateau. Quat. Int. 2018, 493, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.F.; Sun, H.L.; Chen, F.H.; Zhao, Y.; An, C.B. High-resolution climate change in mid-late Holocene on Tianchi Lake,Liupan Mountain in the Loess Plateau in central China and its significance. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 2118–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Wang, T.; Chawchai, S.; Cheng, P.; Xu, H. Time marker of 137Cs fallout maximum in lake sediments of Northwest China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 241, 106413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.H.; Xu, H.; Yu, K.K.; Sheng, E.G.; Zhou, K.E.; Wang, T.L.; Ye, Y.D.; Yan, D.N.; Wu, H.X.; Cheng, P.; et al. Late Holocene hydroclimatic variations and possible forcing mechanisms over the eastern Central Asia. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Xu, H.; Lang, Y.C.; Yu, K.K.; Zhou, P.; Kang, S.G.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, T.L.; Cheng, P.; Yan, D.N.; et al. Dramatic weakening of the East Asian summer monsoon in northern China during the transition from the Medieval Warm Period to the Little Ice Age. Geology 2020, 48, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Song, Y.G.; Zeng, M.X.; Lin, W.W.; Orozbaev, R. Evaluating the paleoclimatic significance of clay mineral records from a late Pleistocene loess-paleosol section of the Ili Basin, Central Asia. Quat. Res. 2018, 89, 660–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhou, X.; Lan, J.; Liu, B.; Sheng, E.; Yu, K.; Cheng, P.; Wu, F.; Hong, B.; Yeager, K.M. Late Holocene Indian summer monsoon variations recorded at Lake Erhai, Southwestern China. Quat. Res. 2015, 83, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.K.; Xu, H.; Lan, J.H.; Sheng, E.G.; Liu, B.; Wu, H.X.; Tan, L.C.; Yeager, K.M. Climate change and soil erosion in a small alpine lake basin on the Loess Plateau, China. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 2017, 42, 1238–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, X.Y.; An, Z.S.; Hou, Z.H.; Liu, D.B. Spatial pattern of modern sedimentation rate of Qinghai Lake and a preliminary estimate of the sediment flux. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.J.; Chen, J.A.; Wu, F.C.; Xu, S.Q.; Bai, Z.G.; Wan, E.Y.; Wang, C.S.; Huang, R.G.; Yeager, K.M.; Santschi, P.H. Coupling between 210Pbex and organic matter in sediments of a nutrient-enriched lake: An example from Lake Chenhai, China. Chem. Geol. 2005, 224, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhou, A.; Yu, Z.; Ke, Z. Vegetation history, climate change and human activities over the last 6200 years on the Liupan Mountains in the southwestern Loess Plateau in central China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2010, 293, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; James, B.; Osamu, S.; Zhou, A. Mid- to- late Holocene hydroclimatic changes on the Chinese Loess Plateau: Evidence from n-alkanes from the sediments of Tianchi Lake. J. Paleolimnol. 2018, 60, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, A.F.; Zhang, H.X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.N.; Sun, H.L.; Zhao, C. Soil erosion in relation to climate change and vegetation cover over the past 2000 years as inferred from the Tianchi lake in the Chinese Loess Plateau. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 180, 103850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ai, L.; Tan, L.; An, Z. Stable isotopes in bulk carbonates and organic matter in recent sediments of Lake Qinghai and their climatic implications. Chem. Geol. 2006, 235, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzhou Branch of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Evolution of Recent Environment in Qinghai Lake and Its Prediction; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, E.G.; Yu, K.K.; Xu, H.; Lan, J.H.; Liu, B.; Che, S. Late Holocene Indian summer monsoon precipitation history at Lake Lugu, northwestern Yunnan Province, southwestern China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2015, 438, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.H.; Huang, X.Z.; Zhang, J.W.; Holmes, J.A.; Chen, J.H. Humid little ice age in arid central Asia documented by Bosten Lake, Xinjiang. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2006, 49, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.L.; Wu, J.; Si, B.; Liang, W.; Nakamura, T.; Liu, B.; Inouchi, Y. Holocene climate changes in the monsoon/arid transition reflected by carbon concentration in Daihai Lake of Inner Mongolia. Holocene 2006, 16, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Si, B.; Zhai, D.; Itoh, S.; Lomtatidze, Z. Hydrology of Dali Lake in central-eastern Inner Mongolia and Holocene East Asian monsoon variability. J. Paleolimnol. 2008, 40, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, X.; Hou, Z. Temperature variations at Lake Qinghai on decadal scales and the possible relation to solar activities. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2008, 70, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Feng, Z.; Yang, Q.; Gou, X.; Sun, F. Holocene environmental variations recorded by organic-related and carbonate-related proxies of the lacustrine sediments from Bosten Lake, northwestern China. Holocene 2010, 20, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Tian, L.D.; Bird, B.W.; Hou, J.Z.; Ding, L.; Oimahmadov, I.; Gadoev, M. A 2540-year record of moisture variations derived from lacustrine sediment (Sasikul Lake) on the Pamir Plateau. Holocene 2014, 24, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.M.; Yu, Z.J.; Zhu, R.B.; Jin, J.W.; Jing, Z.B. Comprehensive Scientific Investi-Gation Report of Liupan Mountains National Nature Reserve; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2013; pp. 8–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.W.; Gong, D.Y. Climate in China during the four special periods in Holocene. Progr. Nat. Sci. 2000, 10, 325–332. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Braeuning, A.; Johnson, K.R.; Shi, Y.F. General characteristics of temperature variation in China during the last two millennia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, K.G. Chinese meteorological disasters ceremony. In Gansu Volume; Dong, A.X., Ed.; Meteorology: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 288–308. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Q.S.; Zhang, X.Z.; Hao, Z.X.; Zheng, J.Y. Rates of temperature change in China during the past 2000 years. Sci. China 2011, 54, 1627–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; An, Z.S.; Linderholm, H.W.; Chen, D.L.; Tian, H. Annual temperatures during the last 2485 years in the Mid-Eastern Tibetan Plateau inferred from tree rings. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2009, 52, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, K.G. Chinese meteorological disasters ceremony. In Ningxia Volume; Xia, P.M., Ed.; Meteorology: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 207–226. [Google Scholar]
- Beer, J.; Mende, W.; Stellmacher, R. The role of the sun in climate forcing. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2000, 19, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindell, D.T. Solar forcing of regional climate change during the maunder minimum. Science 2001, 294, 2149–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steinhilber, F.; Beer, J.; Frhlich, C. Total solar irradiance during the Holocene. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L19704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gray, L.J. Solar influence on climate. Rev. Geophys. 2010, 48, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, K.L.; Solanki, S.K.; Krivova, N.A.; Rempel, M.; Witzke, V. The Dimmest State of the Sun. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 47, e2020GL090243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, N.E. Simulation of recent global temperature trends. Science 1995, 267, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Hong, Y.; Bing, H.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, W. Influence of ENSO on multi-annual temperature variations at Hongyuan, NE Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.M.; Yang, X.Q. Relationships between Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) and climate variabilities in China. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2003, 61, 641–653, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tollefson, J. Climate change: The case of the missing heat. Nature 2014, 505, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, Z.G. The interdecadal trend and shift of dry/wet over the central part of North China and their relationship to the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO). Chin. Sci. Bull. 2007, 52, 2130–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantua, N.J.; Hare, S.R. The Pacific Decadal Oscillation. J. Oceanogr. 2002, 58, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.W.; Gong, D.Y.; Zhu, J.H. Twentieth-century climatic warming in China in the context of the Holocene. Holocene 2001, 11, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.W.; Ye, J.L.; Gong, D.Y.; Zhu, J.H.; Yao, T.D. Construction of mean annual temperature series for the last one hundred years in China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 1998, 9, 392–401, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.; Wang, W.C.; Gong, W.; Hao, Z. A Pacific Decadal Oscillation record since 1470 AD reconstructed from proxy data of summer rainfall over eastern China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L03702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, K.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Sheng, E.; Liu, X.; Lan, J. Temperature Variations and Possible Forcing Mechanisms over the Past 300 Years Recorded at Lake Chaonaqiu in the Western Loess Plateau. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11376. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132011376
Yu K, Wang L, Liu L, Sheng E, Liu X, Lan J. Temperature Variations and Possible Forcing Mechanisms over the Past 300 Years Recorded at Lake Chaonaqiu in the Western Loess Plateau. Sustainability. 2021; 13(20):11376. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132011376
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Keke, Le Wang, Lipeng Liu, Enguo Sheng, Xingxing Liu, and Jianghu Lan. 2021. "Temperature Variations and Possible Forcing Mechanisms over the Past 300 Years Recorded at Lake Chaonaqiu in the Western Loess Plateau" Sustainability 13, no. 20: 11376. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132011376
APA StyleYu, K., Wang, L., Liu, L., Sheng, E., Liu, X., & Lan, J. (2021). Temperature Variations and Possible Forcing Mechanisms over the Past 300 Years Recorded at Lake Chaonaqiu in the Western Loess Plateau. Sustainability, 13(20), 11376. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132011376







