Measuring Soil Colour to Estimate Soil Organic Carbon Using a Large-Scale Citizen Science-Based Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Research Design
2.2. Visual Determination of Soil Colour
2.2.1. Citizen Scientists
2.2.2. Scientists
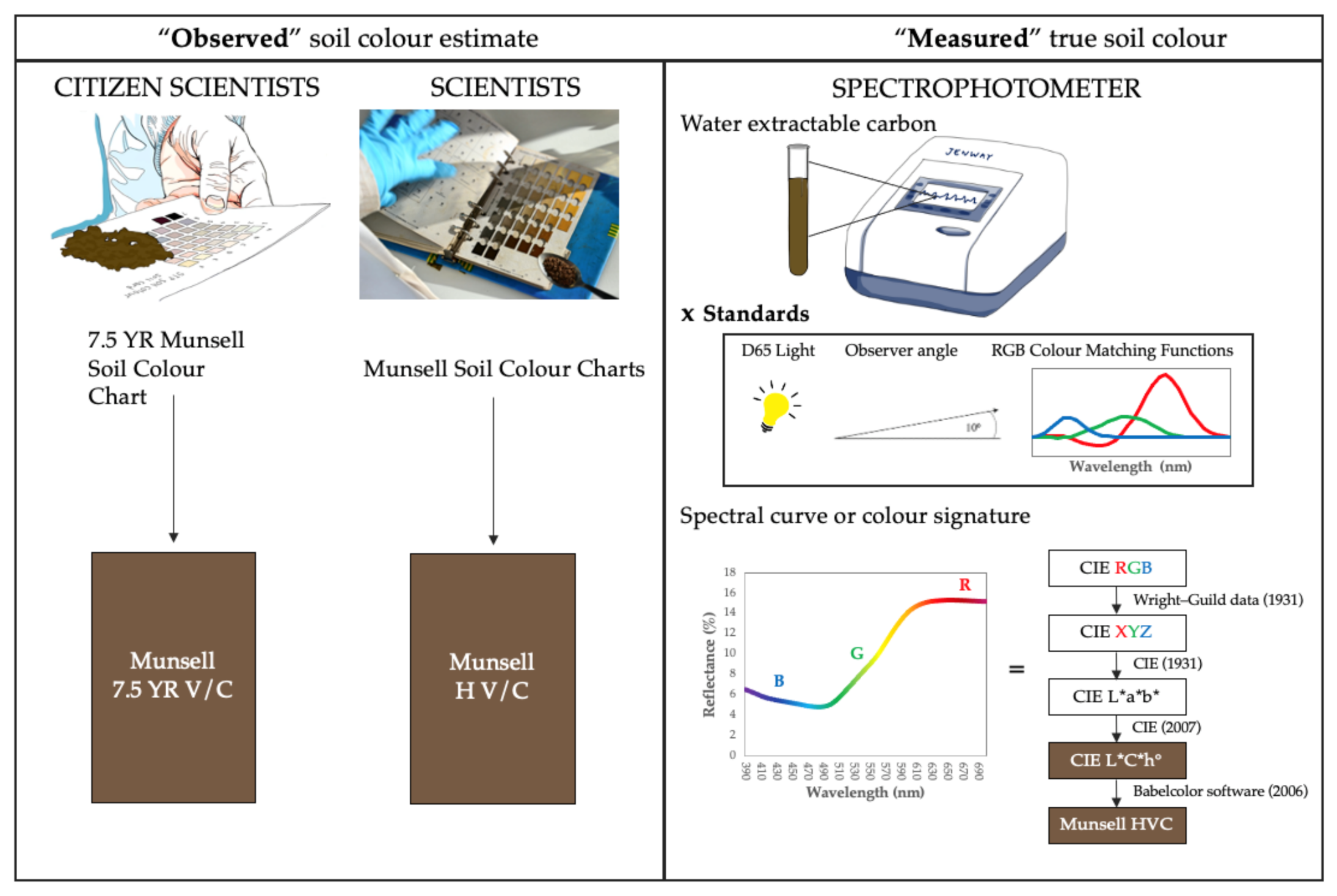
2.3. Determination of Colour from Spectroscopic Analysis
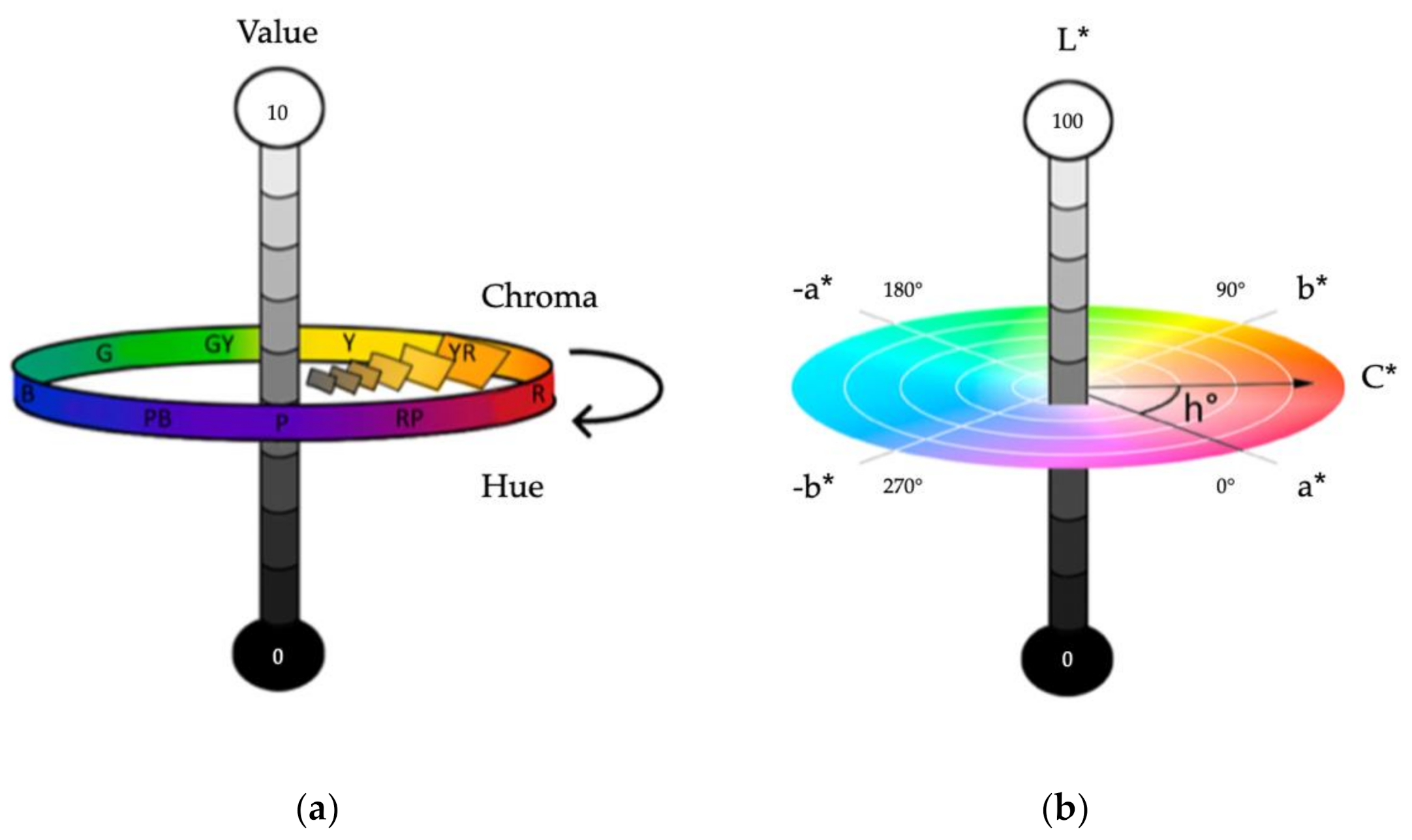
2.4. Colour Transformations for Data Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
2.5.1. Descriptive Statistics
2.5.2. Correlation and Regression Analysis
2.5.3. Colour Difference Calculations
3. Results
3.1. Reproducibility of Spectral Measurements
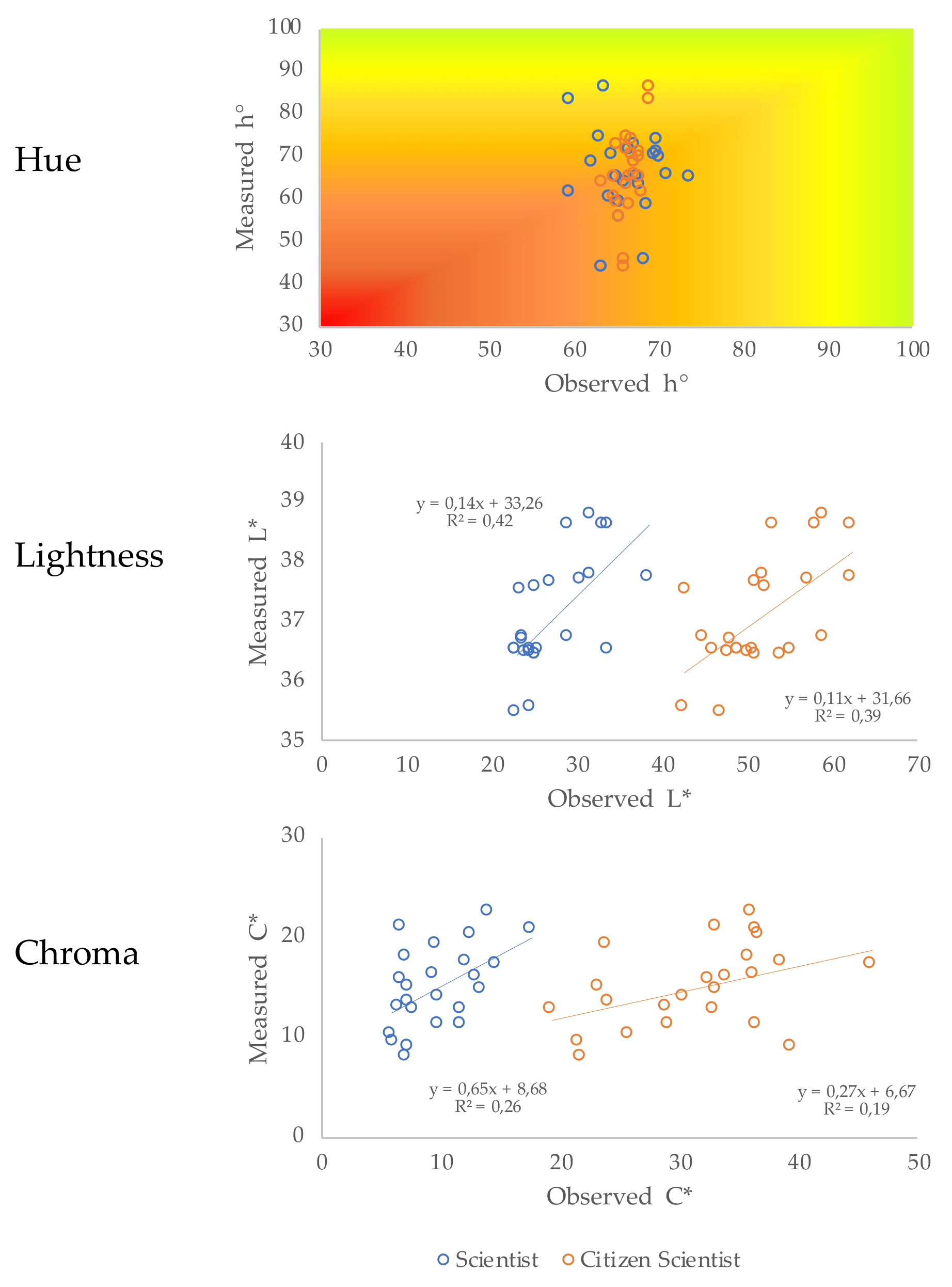
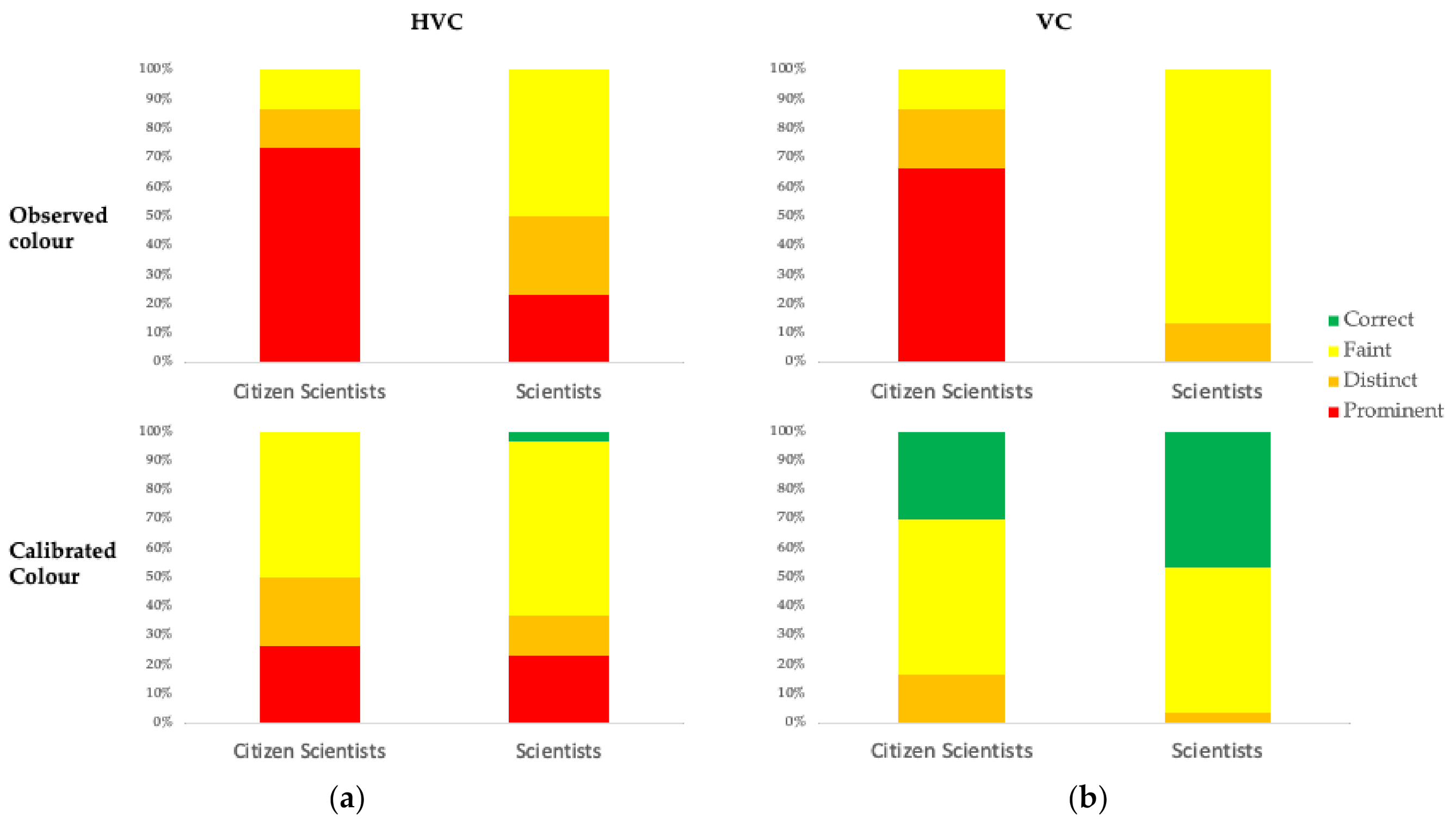
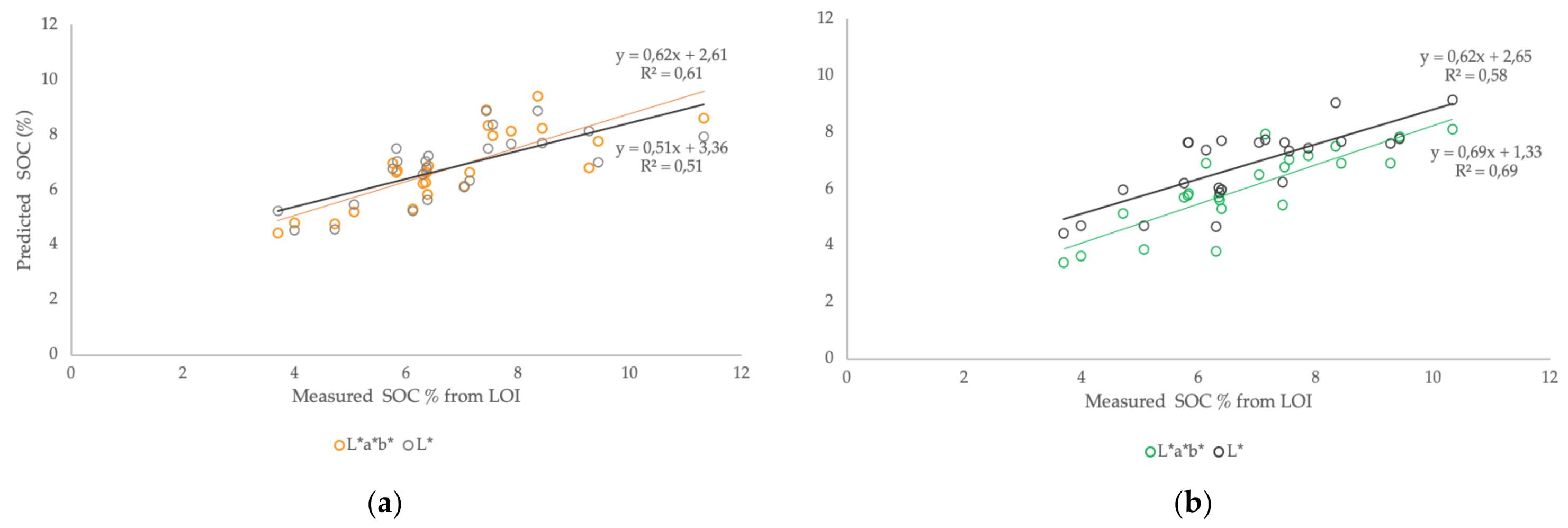
3.2. Comparison of Visual and Spectroscopic Soil Colour Measurements
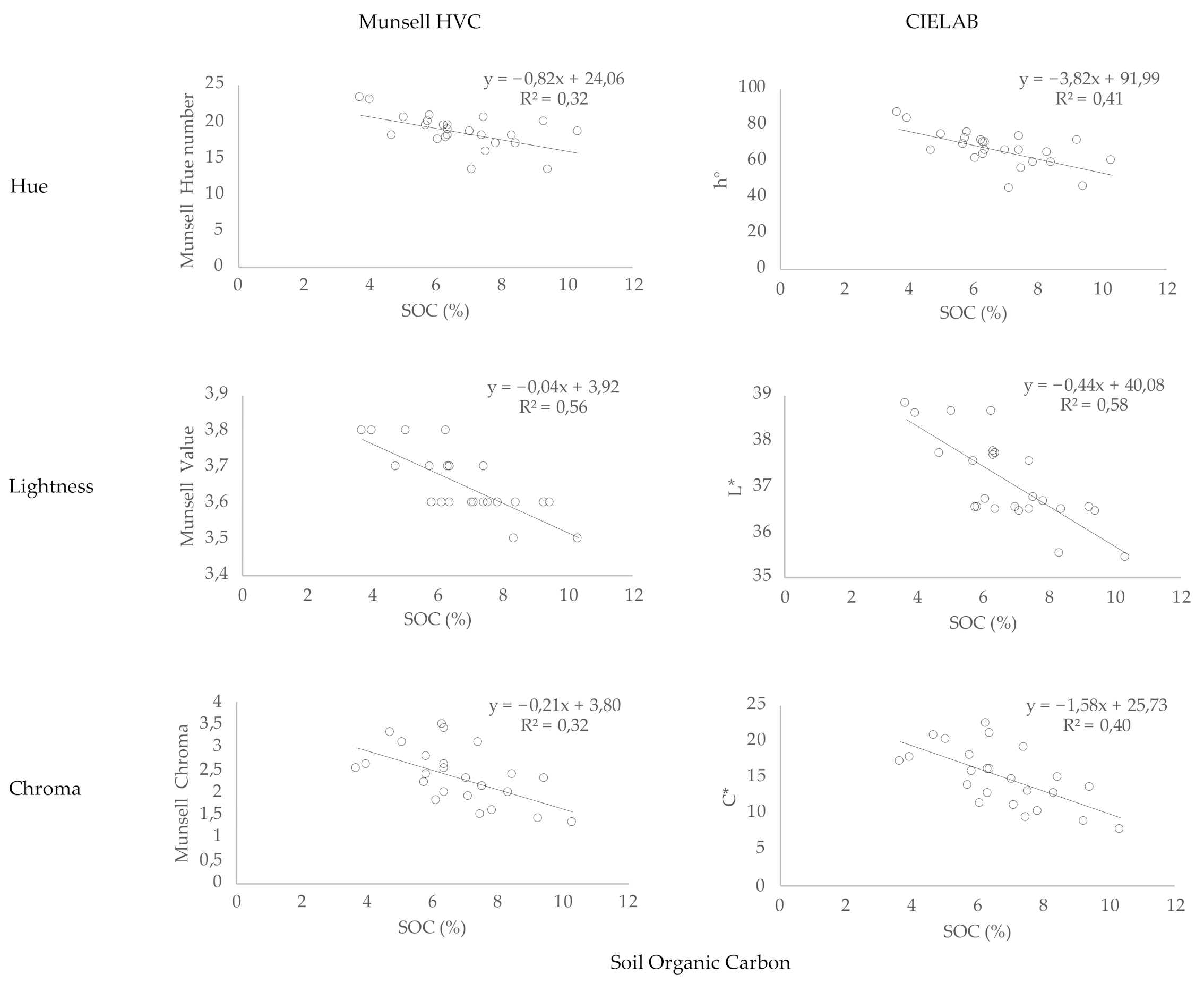
3.3. Soil Colour and Carbon
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lefèvre, C.; Rekik, F.; Viridiana, A.; Liesl, W. Soil Organic Carbon. The Hidden Potential; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2017; pp. 1–76. Available online: www.fao.org/3/i6937e/i6937e.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Scharlemann, J.; Tanner, E.; Hiederer, R.; Kapos, V. Global Soil Carbon: Understanding and Managing the Largest Terrestrial Carbon Pool. Carbon Manag. 2014, 5, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrington, G.; Fishwick, S.; Barraclough, D.; Morris, J.; Preedy, N.; Bourcard, T.; Reeve, M.; Smith, P.; Fang, C. The Development and Use of Soil Quality Indicators for Assessing the Role of Soil in Environmental Interactions; Environmental Agency: Bristol, UK, 2006. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/290729/scho0306bkiq-e-e.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Setälä, H.; Bardgett, R.; Birkhofer, K.; Brady, M.; Byrne, L.; de Ruiter, P.; de Vries, F.; Gardi, C.; Hedlund, K.; Hemerik, L.; et al. Urban and Agricultural Soils: Conflicts and Trade-Offs in the Optimization of Ecosystem Services. Urban Ecosyst. 2013, 17, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Hundal, L. Soil in the City: Sustainably Improving Urban Soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zomer, R.; Bossio, D.; Sommer, R.; Verchot, L. Global Sequestration Potential of Increased Organic Carbon in Cropland Soils. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lal, R. Soil carbon sequestration impacts on global climate change and food security. Science 2004, 304, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wills, S.; Sandor, J.; Burras, L. Prediction of soil organic carbon content using field and laboratory measurements of soil color. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 71, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liles, G.; Beaudette, D.; O-Geen, A.; Horwath, W. Developing predictive soil C models for soils using quantitative color measurements. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 2173–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Soussana, J.; Angers, D.; Schipper, L.; Chenu, C.; Rasse, D.; Batjes, N.; Egmond, F.; McNeill, S.; Kuhnert, M.; et al. How to Measure, Report and Verify Soil Carbon Change to Realize the Potential of Soil Carbon Sequestration for Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Removal. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 26, 219–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Angelopoulou, T.; Balafoutis, A.; Zalidis, G.; Bochtis, D. From Laboratory to Proximal Sensing Spectroscopy for Soil Organic Carbon Estimation—A Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanguelova, E.; Bonifacio, E.; De Vos, B.; Hoosbeek, M.; Berger, T.; Vesterdal, L.; Armolaitis, K.; Celi, L.; Dinca, L.; Kjønaas, O.; et al. Sources of Errors and Uncertainties in the Assessment of Forest Soil Carbon Stocks at Different Scales—Review and Recommendations. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, A.; Saberioon, M.; Viscarra Rossel, R.; Boruvka, L.; Klement, A. Spectroscopic Measurements and Imaging of Soil Colour for Field Scale Estimation of Soil Organic Carbon. Geoderma 2020, 357, 113972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil Survey Staff. Soil Taxonomy: A Basic System of Soil Classification for Making and Interpreting Soil Surveys, 2nd ed.; U.S. Dept. of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1999.
- Leone, A.; Escadafal, R. Statistical analysis of soil colour and spectroradiometric data for hyperspectral remote sensing of soil properties (example in a southern Italy Mediterranean ecosystem). Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 2311–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscarra-Rossel, R.; Minasny, B.; Roudier, P.; McBratney, A. Colour space models for soil science. Geoderma 2006, 133, 320–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, N.; Weil, R. Elements of the Nature and Properties of Soils; Pearson Prentice Hall: Boston, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Soil Color. USDA. 2020. Available online: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/wi/soils/?cid=NRCSEPRD1370419 (accessed on 10 April 2021).
- Aitkenhead, M.; Coull, M.; Towers, W.; Hudson, G.; Black, H. Prediction of Soil Characteristics and Colour Using Data from The National Soils Inventory of Scotland. Geoderma 2013, 200–201, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrent, J.; Barrón, V. Laboratory measurements of soil color: Theory and practice. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. 1993, 31, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Konen, M.; Burras, C.; Sandor, J. Organic carbon, texture, and quantitative color measurement relationships for cultivated soils in north central Iowa. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodyanitskii, Y.; Savichev, A. The influence of organic matter on soil color using the regression equations of optical parameters in the system CIE- L*a*b*. Ann. Agrar. Sci. 2017, 15, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabenhorst, M.; Schmehling, A.; Thompson, J.; Hirmas, D.; Graham, R.; Rossi, A. Reliability of soil color standards. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, J.; Zuckerberg, B.; Bonter, D. Citizen science as an ecological research tool: Challenges and benefits. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2010, 41, 149–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Qiu, M.; Liu, C.; Guo, Z. Big data challenges in ocean observation: A survey. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2017, 21, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, L. Spectrophotometric colour measurement in situ in well drained sandy soils. Geoderma 2002, 108, 49–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Marañón, M.; Delgado, G.; Delgado, R.; Pérez, M.; Melgosa, M. Spectroradiometric and visual color measurements of disturbed and undisturbed soil samples. Soil Sci. 1995, 160, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Marañón, M.; Huertas, R.; Melgosa, M. Colour variation in standard soil-colour charts. Aust. J. Soil Resour. 2005, 43, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Marañón, M.; García, P.; Huertas, R.; Hernández-Andrés, J.; Melgosa, M. Influence of Natural Daylight on Soil Color Description: Assessment Using a Color-Appearance Model. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marqués-Mateu, Á.; Moreno-Ramón, H.; Balasch, S.; Ibáñez-Asensio, S. Quantifying the uncertainty of soil colour measure-ments with Munsell charts using a modified attribute agreement analysis. Catena 2018, 171, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouazen, A.; Karoui, R.; Deckers, J.; De Baerdemaeker, J.; Ramon, H. Potential of visible and near-infrared spectroscopy to derive colour groups utilising the Munsell soil colour charts. Biosyst. Eng. 2007, 97, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillova, N.; Vodyanitskii, Y.; Sileva, T. Conversion of soil color parameters from the Munsell System to the CIE-Lab System. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2014, 48, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiglitz, R. Evaluation of an Inexpensive Sensor to Measure Soil Color. All Theses 2016, 2367. Available online: https://tigerprints.clemson.edu/all_theses/2367 (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Gómez-Robledo, L.; López-Ruiz, N.; Melgosa, M.; Palma, A.; Capitan-Vallvey, L.; Sánchez-Marañon, M. Using the mobile phone as Munsell soil-colour sensor: An experiment under controlled illumination conditions. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2013, 99, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, D.; Levine, S.; Bryant, R.; Mays, M.; Batchily, K.; Escadafal, R.; Huete, A. Correlations between field and laboratory measurements of soil color. In Soil Color; Bigham, J., Ciolkosz, E., Eds.; SSSA. Special Publication 31; SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1993; pp. 35–50. [Google Scholar]
- IUSS Working Group (WRB). World Reference Base for Soil Resources; World Soil Resources Reports No. 103; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bloch, L.; Hosen, J.; Kracht, E.; LeFebvre, M.; Jazmine-Lopez, C.; Woodcock, R.; Keegan, W. Is it better to be objectively wrong or subjectively right?: Testing the accuracy and consistency of the Munsell capsure spectrocolorimeter for archaeological applications. Adv. Archaeol. Pract. 2021, 9, 132–144. [Google Scholar]
- Doi, R.; Wachrinrat, C.; Teejuntuk, S.; Sakurai, K.; Sahunalu, P. Semiquantitative color profiling of soils over a land degradation gradient in Sakaerat, Thailand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 170, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warr, B. Soil Colour; INSEAD: Fontainebleau, Singapore, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Turk, J.; Rebecca, Y. Field Conditions and the Accuracy of Visually Determined Munsell Soil Color. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate-Data. Climate: Europe. 2020. Available online: https://en.climate-data.org/europe/ (accessed on 20 June 2021).
- Dean, W. Determination of carbonate and organic matter in calcareous sediments and sedimentary rocks by loss on ignition: Comparison with other methods. J. Sediment. Petrol. 1974, 44, 242–248. [Google Scholar]
- United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Soil Survey Manual. Agriculture Handbook No. 18. 2017. Available online: https://www.iec.cat/mapasols/DocuInteres/PDF/Llibre50.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Nelson, D.; Sommers, L. Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 3. Chemical Methods; Sparks, D., Ed.; SSSA Book Series No. 5; SSSA-ASA: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 961–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Munsell, A. Munsell Soil Color Charts; Munsell Color Company: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Wyszecki, G.; Stiles, W. Concepts and Methods. Quantitative Data and Formulae, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Interscience Publication: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Stiles, W.; Burch, J.N.P.L. Colour matching investigation: Final report (1958). Opt. Acta 1959, 6, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, J.; Arnaud, R.; Paul, E.; Clayton, J. Measurement of soil color. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1966, 46, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández, R.; Schulze, D. Calculation of soil color from reflectance spectra. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1987, 51, 1277–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guild, J. The colorimetric properties of the spectrum. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 1931, 230, 149–187. [Google Scholar]
- CIE. Colorimetry—Part 4: CIE 1976 L*a*b* Colour Space (Report). Draft Standard. 2007. Available online: http://cie.co.at/publications/colorimetry-part-4-cie-1976-lab-colour-space-1 (accessed on 10 April 2021).
- Hurst, V. Visual estimation of iron in saprolite. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1977, 88, 174–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodyanitskii, Y.; Kirillova, N. Conversion of Munsell color coordinates to Cie-L*a*b* system: Tables and calculation examples. Mosc. Univ. Soil Sci. Bull. 2016, 71, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudifoot, B.; Cárdenas, M.; Buytaer, W.; Paul, J.; Narraway, C.; Loiselle, S. When it rains, it pours: Integrating citizen science methods to understand resilience of urban green spaces. Front. Water 2021, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmala, M.; Wiggins, A.; Swanson, A.; Simmons, B. Assessing data quality in citizen science. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 10, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moritsuka, N.; Matsuoka, K.; Katsura, K.; Sano, S.; Yanai, J. Soil color analysis for statistically estimating total carbon, total nitrogen and active iron contents in Japanese agricultural soils. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2014, 60, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spielvogel, S.; Knicker, H.; Köel-Knabner, I. Soil organic matter composition and soil lightness. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2004, 167, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaee, S.; Ghobani-Dashtaki, S.; Mohammadi, J.; Asadi, H.; Asadzadeh, F. Spatial variability of soil organic matter using remote sensing data. Catena 2016, 145, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Ramón, H.; Marqués-Mateu, Á.; Ibañez Asensio, S. Significance of Soil Lightness Versus Physicochemical Soil Properties in Semiarid Areas. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2014, 28, 371–382. [Google Scholar]
| Sampling Location | Number of Colour Measurements | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Park Site | Land Management | Tree Number | Orientation | Canopy Position | Citizen Scientists | Scientists | Spectral | SOC by LOI (%) | |
| 1 | Cannon Hill | Managed | 1 | North | Inner | 8 | 8 | 3 | 7.1 |
| 2 | Cannon Hill | Managed | 1 | South | Outer | 8 | 8 | 3 | 5.8 |
| 3 | Cannon Hill | Managed | 2 | North | Inner | 8 | 8 | 3 | 7.5 |
| 4 | Cannon Hill | Managed | 2 | South | Outer | 8 | 8 | 3 | 6.4 |
| 5 | Cannon Hill | Managed | 3 | North | Inner | 8 | 8 | 3 | 5.8 |
| 6 | Cannon Hill | Managed | 3 | South | Outer | 8 | 8 | 3 | 5.8 |
| 7 | Cannon Hill | Unmanaged | 4 | North | Inner | 8 | 8 | 3 | 4.0 |
| 8 | Cannon Hill | Unmanaged | 4 | South | Outer | 8 | 8 | 3 | 3.7 |
| 9 | Cannon Hill | Unmanaged | 5 | North | Inner | 8 | 8 | 3 | 11.3 |
| 10 | Cannon Hill | Unmanaged | 5 | South | Outer | 8 | 8 | 3 | 6.1 |
| 11 | Cannon Hill | Unmanaged | 6 | North | Inner | 8 | 8 | 3 | 9.4 |
| 12 | Cannon Hill | Unmanaged | 6 | South | Outer | 8 | 8 | 3 | 9.3 |
| 13 | Kew Garden | Managed | 7 | North | Inner | 9 | 9 | 3 | 6.3 |
| 14 | Kew Garden | Managed | 7 | South | Outer | 9 | 9 | 3 | 5.1 |
| 15 | Kew Garden | Managed | 8 | North | Inner | 9 | 9 | 3 | 6.4 |
| 16 | Kew Garden | Managed | 8 | South | Outer | 9 | 9 | 3 | 7.0 |
| 17 | Kew Garden | Managed | 9 | North | Inner | 9 | 9 | 3 | 6.4 |
| 18 | Kew Garden | Managed | 9 | South | Outer | 9 | 9 | 3 | 4.7 |
| 19 | Kew Garden | Unmanaged | 10 | North | Inner | 9 | 9 | 3 | 7.4 |
| 20 | Kew Garden | Unmanaged | 10 | South | Outer | 9 | 9 | 3 | 8.4 |
| 21 | Kew Garden | Unmanaged | 11 | North | Inner | 9 | 9 | 3 | 7.9 |
| 22 | Kew Garden | Unmanaged | 11 | South | Outer | 9 | 9 | 3 | 6.4 |
| 23 | Kew Garden | Unmanaged | 12 | North | Inner | 9 | 9 | 3 | 8.3 |
| 24 | Kew Garden | Unmanaged | 12 | South | Outer | 9 | 9 | 3 | 7.5 |
| 25 | Les Fontaines | Street tree | 13 | North | Inner | 11 | 11 | 3 | - |
| 26 | Les Fontaines | Street tree | 14 | North | Inner | 11 | 11 | 3 | - |
| 27 | Les Fontaines | Street tree | 15 | North | Inner | 11 | 11 | 3 | - |
| 28 | Les Fontaines | Managed | 16 | North | Inner | 11 | 11 | 3 | - |
| 29 | Les Fontaines | Managed | 17 | North | Inner | 11 | 11 | 3 | - |
| 30 | Les Fontaines | Managed | 18 | North | Inner | 11 | 11 | 3 | - |
| Hue Number | Munsell Value | Munsell Chroma | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Range | 11.7 to 20.5 | 3.5 to 3.6 | 0.9 to 1.3 |
| Mean | 16.7 | 3.6 | 1.1 |
| SD | 3.1 | 0.04 | 0.1 |
| CV (%) | 18.3 | 1.1 | 12.8 |
| Munsell Hue Number | Munsell Value | Munsell Chroma | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Max.–Min. | Mean | Mode | Range | Max.–Min. | Mean | Mode | Range | Max.–Min. | Mean | Mode | |
| Scientists | 15.0–20 | 5.0 | 19.2 | 20 | 1.0–4.0 | 3.0 | 2.7 | 3.0 | 1.0–4.0 | 3.0 | 1.6 | 2 |
| Citizen Scientists | 17.5 | 0 | 17.5 | 17.5 | 3.0–8.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 2.0–8.0 | 6.0 | 5.1 | 6.0 |
| Spectroscopic | 13.3–23.2 | 9.9 | 18.5 | 18 | 3.5–3.8 | 0.3 | 3.7 | 3.6 | 1.3–3.5 | 2.2 | 2.4 | 2.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferrando Jorge, N.; Clark, J.; Cárdenas, M.L.; Geoghegan, H.; Shannon, V. Measuring Soil Colour to Estimate Soil Organic Carbon Using a Large-Scale Citizen Science-Based Approach. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11029. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131911029
Ferrando Jorge N, Clark J, Cárdenas ML, Geoghegan H, Shannon V. Measuring Soil Colour to Estimate Soil Organic Carbon Using a Large-Scale Citizen Science-Based Approach. Sustainability. 2021; 13(19):11029. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131911029
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerrando Jorge, Nerea, Joanna Clark, Macarena L. Cárdenas, Hilary Geoghegan, and Vicky Shannon. 2021. "Measuring Soil Colour to Estimate Soil Organic Carbon Using a Large-Scale Citizen Science-Based Approach" Sustainability 13, no. 19: 11029. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131911029
APA StyleFerrando Jorge, N., Clark, J., Cárdenas, M. L., Geoghegan, H., & Shannon, V. (2021). Measuring Soil Colour to Estimate Soil Organic Carbon Using a Large-Scale Citizen Science-Based Approach. Sustainability, 13(19), 11029. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131911029






