Influence of Iron Plaque on Accumulation and Translocation of Cadmium by Rice Seedlings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
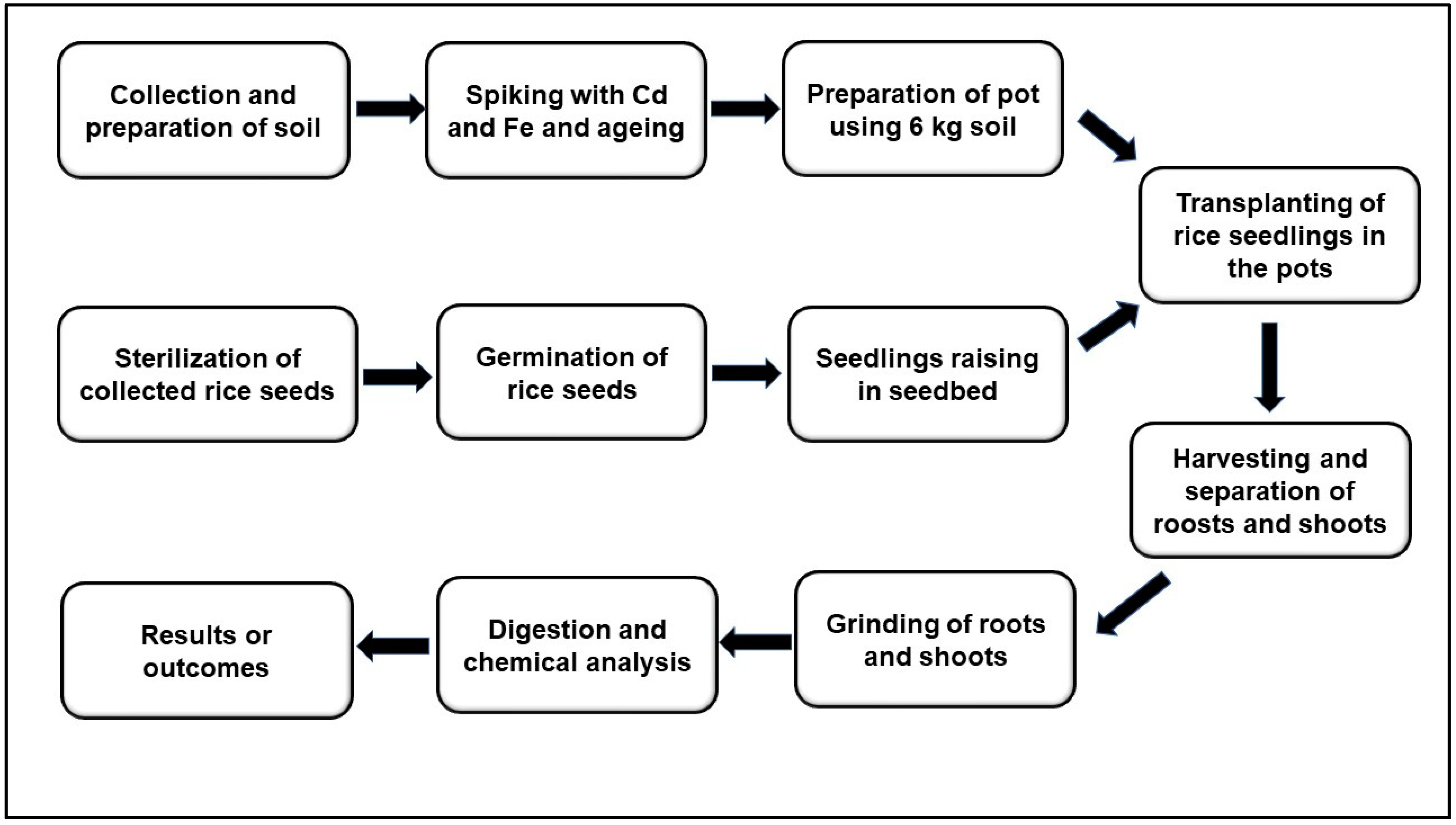
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Collection, Processing and Preparation
2.2. Pot Experiment Design and Rice Cultivars Used
2.3. Seedlings Establishment and Fertilizer Application
2.4. Experimental Treatments
2.5. Harvesting and CBD Extraction of Iron Plaque from Roots
2.6. Digestion and Analysis of Rice Plant Parts
2.7. Analytical Performances
2.8. Statistics Used
3. Results
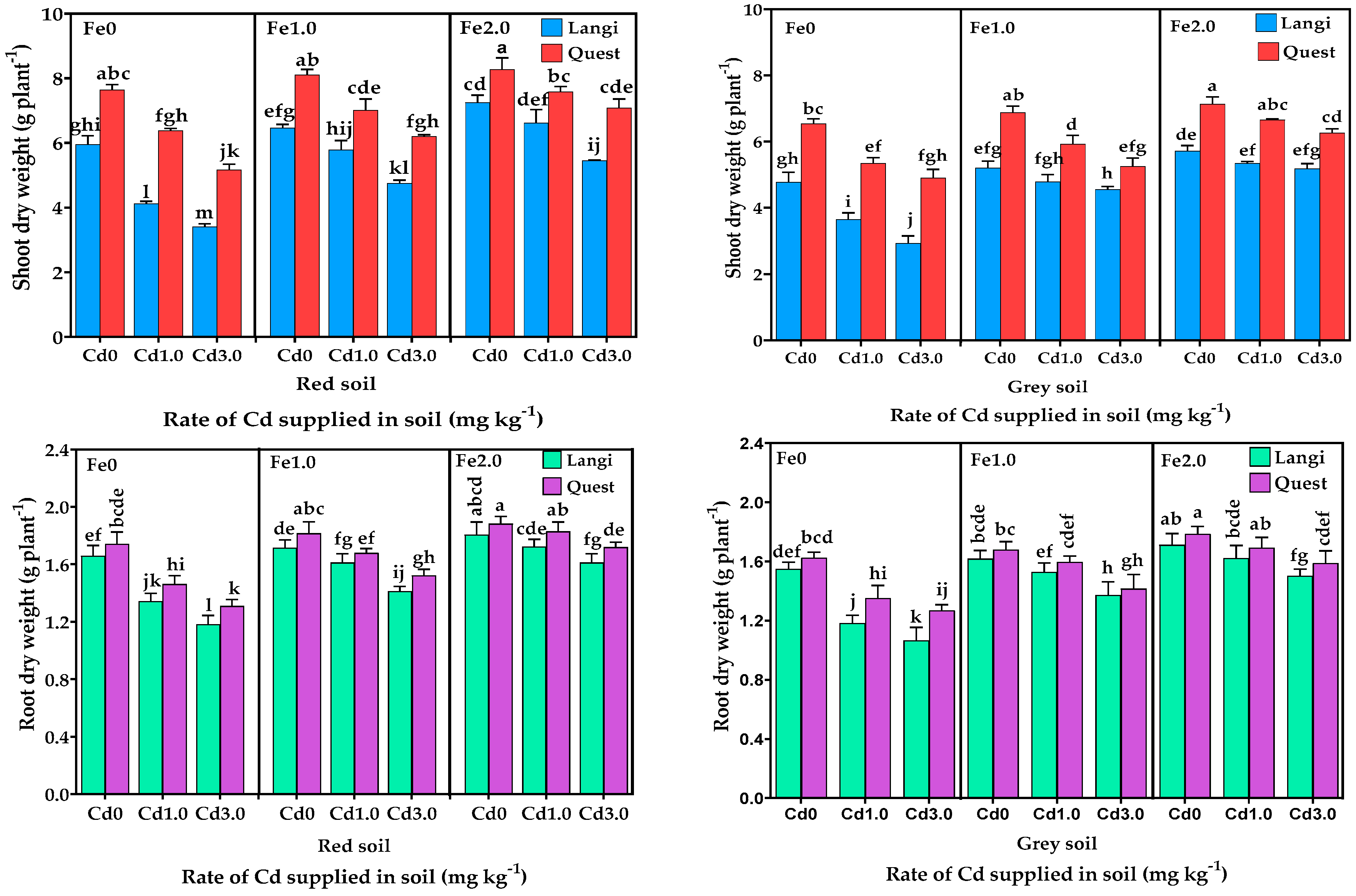
3.1. Biomass of Rice Seedlings
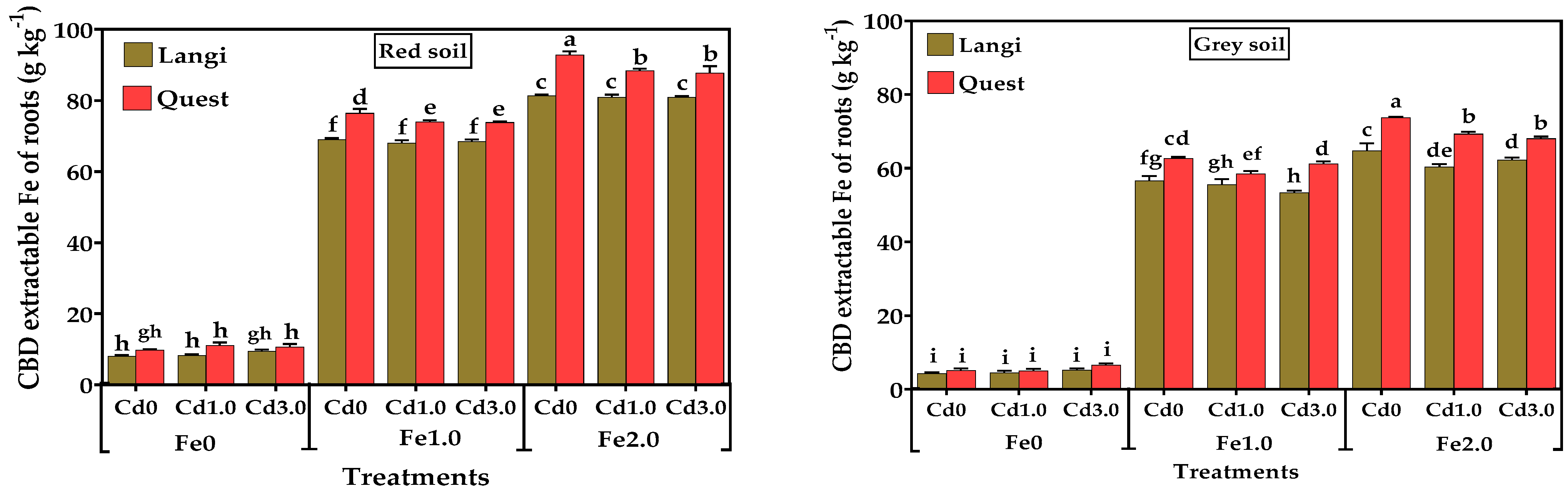
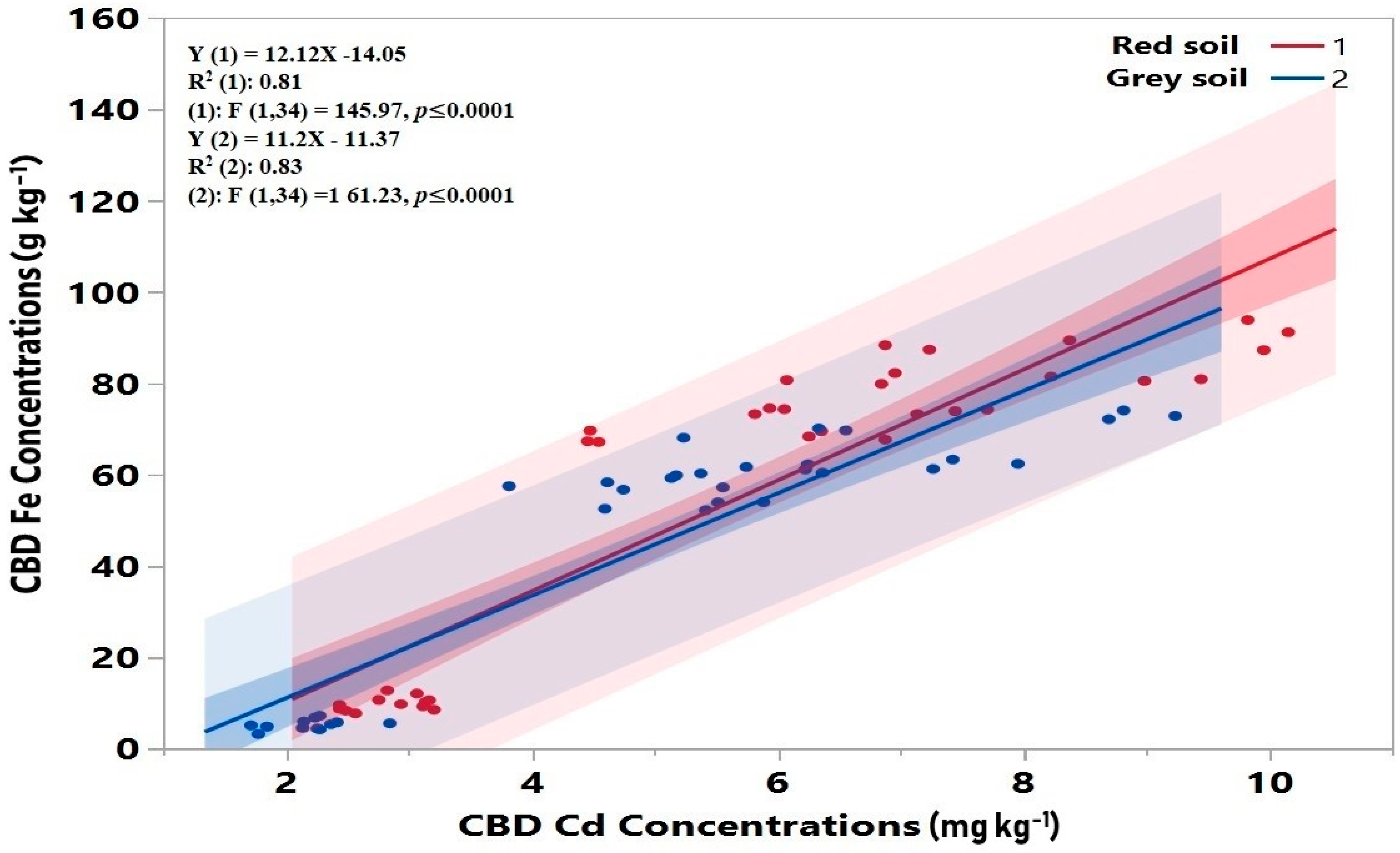
3.2. Concentration of Fe and Cd in Iron Plaque on the Root Surface of Rice Cultivars
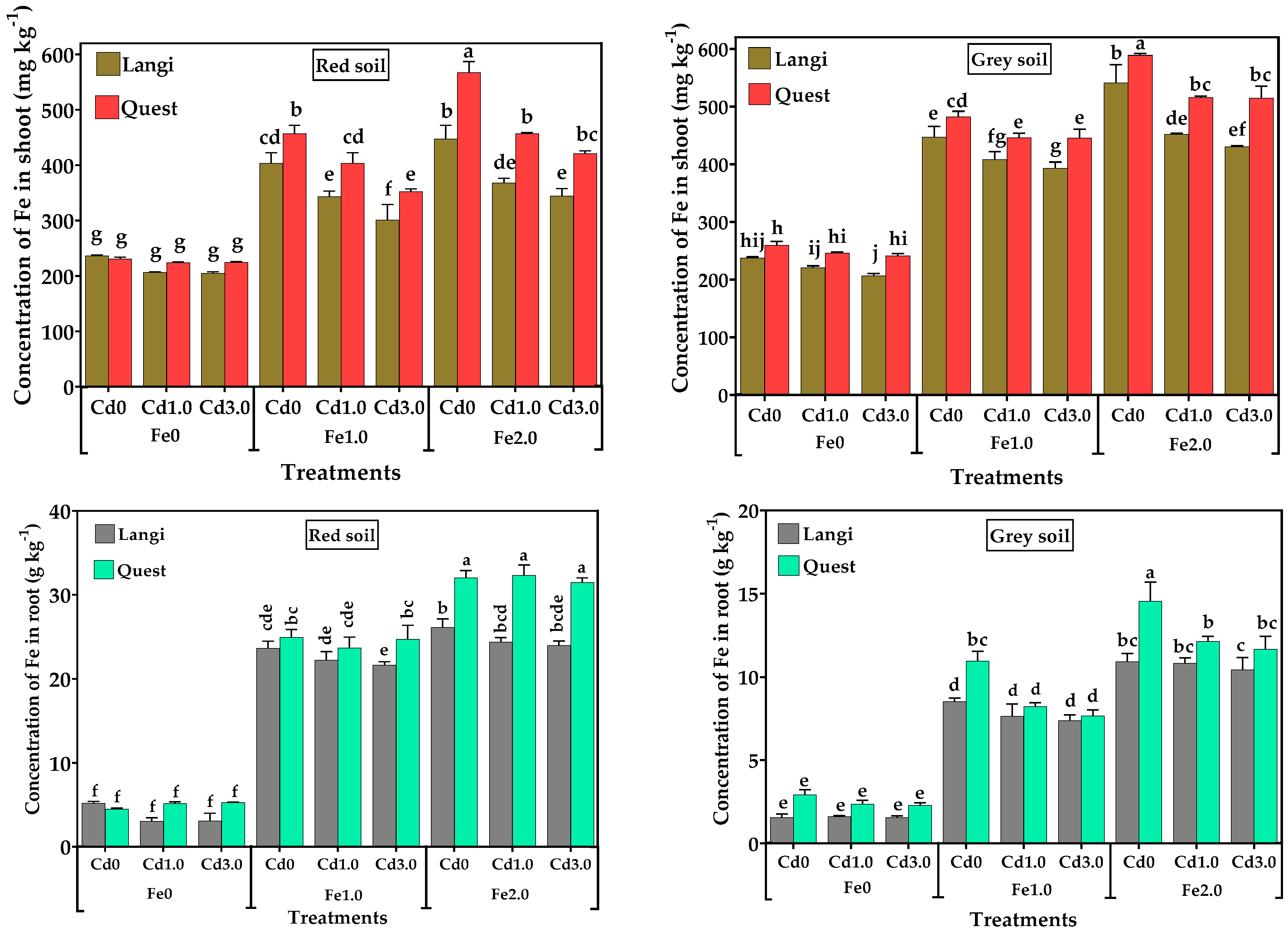
3.3. Concentration of Fe in Rice Seedlings
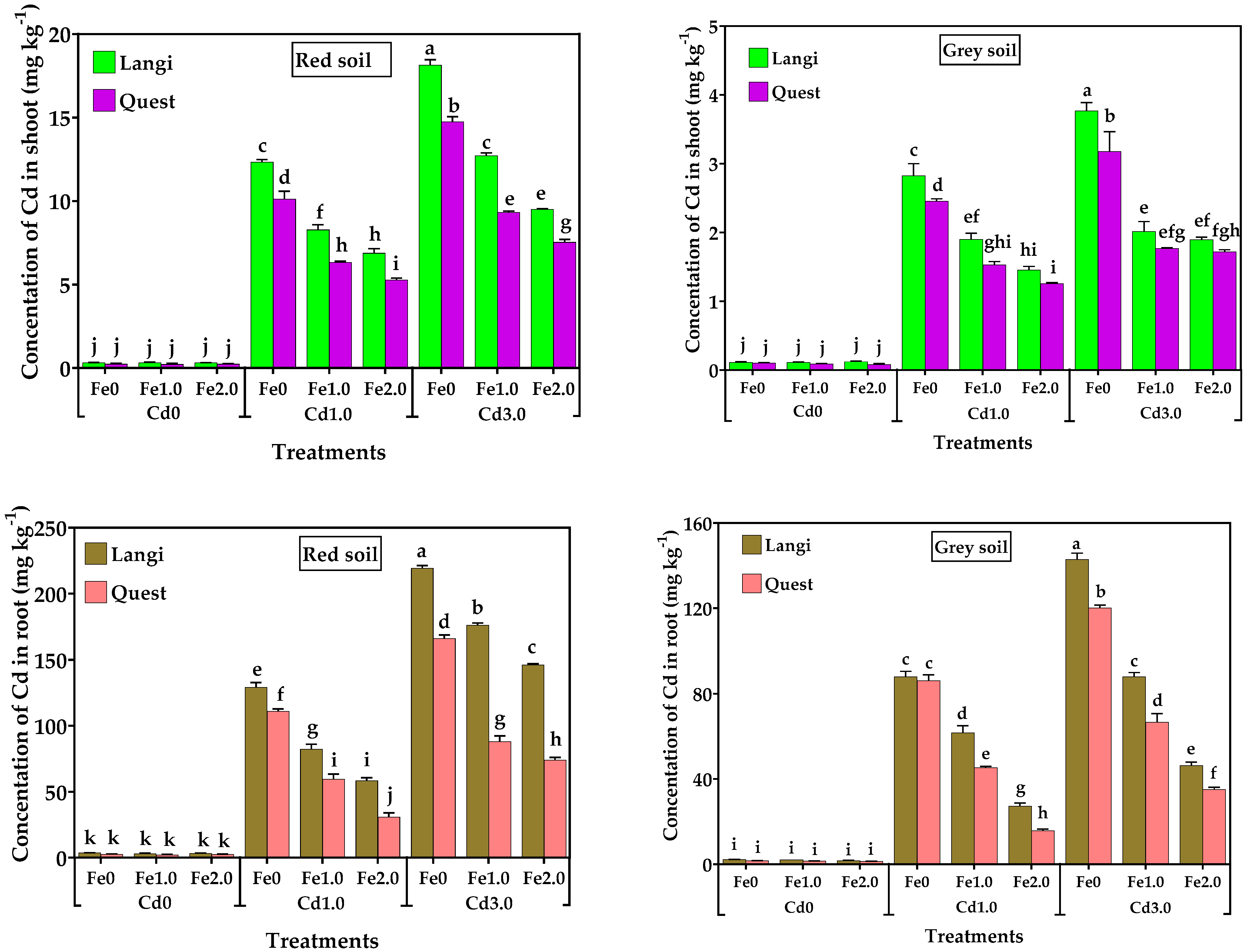
3.4. Concentration of Cd in Rice Seedlings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, X.B.; Huang, W.; Bian, Y.B.; Feng, X.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Shi, D.F.; Qiao, X.; Liu, Y. Remediation and Mechanisms of Cadmium Biosorption by a Cadmium-Binding Protein from Lentinula edodes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 11373–11379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, B.; Umer, M.J.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Abbas, Y.; Ashraf, M.N.; Tahir, N.; Ullah, A.; Gogoi, N.; Farooq, M. Strategies for reducing cadmium accumulation in rice grains. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 125557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, Z.; Guo, T.; Wang, J. Cadmium pollution of soil-rice ecosystems in rice cultivation dominated regions in China: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Nahar, K.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Fujita, M. Manganese-induced cadmium stress tolerance in rice seedlings: Coordinated action of antioxidant defense, glyoxalase system and nutrient homeostasis. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2016, 339, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Cadmium Immobilization in the Rhizosphere and Plant Cellular Detoxification: Role of Plant-Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria as a Sustainable Solution. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 13497–13529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriar, S.; Rahman, M.M.; Naidu, R. Geographical variation of cadmium in commercial rice brands in Bangladesh: Human health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Singh, I.; Shah, K. Alterations in antioxidative machinery and growth parameters upon application of nitric oxide donor that reduces detrimental effects of cadmium in rice seedlings with increasing days of growth. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 131, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Adrees, M.; Rizvi, H.; Zia-Ur-Rehman, M.; Hannan, F.; Qayyum, M.F.; Hafeez, F.; Ok, Y.S. Cadmium stress in rice: Toxic effects, tolerance mechanisms, and management: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 17859–17879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Subrahmanyam, G.; Mondal, R.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.S.; Shabnam, A.A.; Jigyasu, D.K.; Malyan, S.K.; Fagodiya, R.K.; Khan, S.A.; Kumar, A.; et al. Bio-remediation approaches for alleviation of cadmium contamination in natural resources. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 128855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.-E.; Chen, S.-B.; Liu, J.-F.; Chen, L.; Song, N.-N.; Li, N.; Liu, B. Variation of Cd concentration in various rice cultivars and derivation of cadmium toxicity thresholds for paddy soil by species-sensitivity distribution. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 1845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, I.; Chtourou, Y.; Djebali, W. Selenium alleviates cadmium toxicity by preventing oxidative stress in sunflower (Helianthus annuus) seedlings. J. Plant Physiol. 2014, 171, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, N.; Malhi, S.S.; Zia, M.H.; Naeem, A.; Bibi, S.; Farid, G. Role of mineral nutrition in minimizing cadmium accumulation by plants. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinadasa, N.; Milham, P.; Hawkins, C.; Cornish, P.; Williams, P.; Kaldor, C.; Conroy, J. Cadmium Levels in Soils and Vegetables of the Greater Sydney Region. Austrália. Available online: https://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=US201300041214 (accessed on 15 September 2013).
- Jinadasa, K.; Milham, P.; Hawkins, C.; Cornish, P.; Williams, P.; Kaldor, C.; Conroy, J. Survey of cadmium levels in vegetables and soils of greater Sydney, Australia. J. Environ. Qual. 1997, 26, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricepedia, An Online Counterpart of Rice Almanac, An Encyclopedia on Rice. 2021. Available online: http://ricepedia.org/rice-as-food/the-global-staple-rice-consumers (accessed on 26 March 2021).
- Jiang, M.; Jiang, J.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Tan, Y.; Song, S.; Shu, Q.; Huang, J. Glutamate alleviates cadmium toxicity in rice via suppressing cadmium uptake and translocation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Zhang, C.X.; Wang, J.M.; Zhou, C.J.; Feng, H.; Mahajan, M.D.; Han, X.R. Influence and interaction of iron and cadmium on photosynthesis and antioxidative enzymes in two rice cultivars. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, A.B.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.R.; Naidu, R. Varietal variation and formation of iron plaques on cadmium accumulation in rice seedling. Environ. Adv. 2021, 5, 100075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoshima, K. Itai-itai disease: Renal tubular osteomalacia induced by environmental exposure to cadmium—Historical review and perspectives. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2016, 62, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- International Agency for Reseach on Cancer (IARC). IARC Cadmium and Cadmium Compounds. Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 1993, 58, 119–237. [Google Scholar]
- MHPRC. China National and Food Safety Standard-Maximum Residue Limits of Contaminants in Food (GB 2762–2017); China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yao, H.; Wong, M.H.; Ye, Z. Dynamic changes in radial oxygen loss and iron plaque formation and their effects on Cd and As accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ. Geochem. Health 2013, 35, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Wang, M.; Wong, M.H.; Ye, Z. Does radial oxygen loss and iron plaque formation on roots alter Cd and Pb uptake and distribution in rice plant tissues? Plant Soil 2014, 375, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, S.; Wang, M.; Lei, X.; Zheng, H.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.; Han, Y. Iron fractions responsible for the variation of Cd bioavailability in paddy soil under variable pe+pH conditions. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, H.; Xu, C.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, Q. Heavy metal uptake in rice is regulated by pH-dependent iron plaque formation and the expression of the metal transporter genes. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 162, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Leng, X.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Z.; Dai, Q. Iron plaque formation on roots of different rice cultivars and the relation with lead uptake. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Christie, P.; Zhang, F. Influence of iron plaque on uptake and accumulation of Cd by rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings grown in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 394, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sebastian, A.; Prasad, M.N.V. Iron plaque decreases cadmium accumulation in Oryza sativa L. and serves as a source of iron. Plant Biol. 2016, 18, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, J.; Wan, X.; Peng, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, M. How Red Mud-Induced Enhancement of Iron Plaque Formation Reduces Cadmium Accumulation in Rice with Different Radial Oxygen Loss. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 1603–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Abdula, S.E.; Jang, D.W.; Park, S.-H.; Yoon, U.-H.; Jung, Y.J.; Kang, K.K.; Nou, I.S.; Cho, Y.-G. Overexpression of the glutamine synthetase gene modulates oxidative stress response in rice after exposure to cadmium stress. Plant Cell Rep. 2013, 32, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, T.; Nakamura, K.; Katou, H.; Ishikawa, S.; Ito, M.; Honma, T.; Miyazaki, N.; Takehisa, K.; Sano, S.; Matsumoto, S. Simultaneous decrease of arsenic and cadmium in rice (Oryza sativa L.) plants cultivated under submerged field conditions by the application of iron-bearing materials. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2016, 62, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.; Yang, X.; Shen, H. Root iron plaque alleviates cadmium toxicity to rice (Oryza sativa) seedlings. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Camara, A.Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Guo, T.; Zhu, L.; Li, H. Cadmium dynamics in soil pore water and uptake by rice: Influences of soil-applied selenite with different water managements. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Owens, G.; Naidu, R. Arsenic levels in rice grain and assessment of daily dietary intake of arsenic from rice in arsenic-contaminated regions of Bangladesh—Implications to groundwater irrigation. Environ. Geochem. Health 2009, 31, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahsan, N.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, D.-G.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.W.; Bahk, J.D.; Lee, B.-H. Physiological and protein profiles alternation of germinating rice seedlings exposed to acute cadmium toxicity. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2007, 330, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Li, K.; Wu, M.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, L.; Chen, G. Photosynthetic responses of Oryza sativa L. seedlings to cadmium stress: Physiological, biochemical and ultrastructural analyses. Biometals 2014, 27, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Wang, X.; Qi, X.; Huang, L.; Ye, Z. Identification of rice cultivars with low brown rice mixed cadmium and lead contents and their interactions with the micronutrients iron, zinc, nickel and manganese. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 1790–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Liu, W.X.; Sehar, S.; Zheng, W.T.; Zhang, G.P.; Wu, F.B. Application of sulfur fertilizer reduces cadmium accumulation and toxicity in tobacco seedlings (Nicotiana tabacum). Plant Growth Regul. 2018, 85, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Abbas, T.; Adrees, M.; Zia-Ur-Rehman, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Abbas, F.; Qayyum, M.F.; Nawaz, R. Residual effects of biochar on growth, photosynthesis and cadmium uptake in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Cd stress with different water conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 206, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, T.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Adrees, M.; Mahmood, A.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Arshad, M.; Qayyum, M.F. Biochar application increased the growth and yield and reduced cadmium in drought stressed wheat grown in an aged contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, A.B.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.R.; Mondal, D.; Naidu, R. Response of Iron and Cadmium on Yield and Yield Components of Rice and Translocation in Grain: Health Risk Estimation. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 716770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.-F.; Li, B.; Gao, Y.; Chai, Z. The influence of iron plaque on the absorption, translocation and transformation of mercury in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings exposed to different mercury species. Plant Soil 2016, 398, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Z.; Jiang, R.; Li, H. Uptake kinetics and translocation of selenite and selenate as affected by iron plaque on root surfaces of rice seedlings. Planta 2015, 241, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, W. Influence of iron plaque and cultivars on antimony uptake by and translocation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings exposed to Sb(III) or Sb(V). Plant Soil 2012, 352, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Zhu, Y.G.; Smith, F.A.; Smith, S.E. Do iron plaque and genotypes affect arsenate uptake and translocation by rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.) grown in solution culture? J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 1707–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, N.; Seshadri, B.; Bolan, N.; Saint, C.P.; Kirkham, M.B.; Chowdhury, S.; Yamaguchi, N.; Lee, D.Y.; Li, G.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; et al. Chapter One—Root Iron Plaque on Wetland Plants as a Dynamic Pool of Nutrients and Contaminants. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 138, pp. 1–96. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-C.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, H.-W.; Baek, K. Oxalate-based remediation of arsenic bound to amorphous Fe and Al hydrous oxides in soil. Geoderma 2016, 270, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Tan, N.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Liang, X.; Qu, M.; Feng, X.; Qiu, G.; Tan, W.; Liu, F. The associations of heavy metals with crystalline iron oxides in the polluted soils around the mining areas in Guangdong Province, China. Chemosphere 2016, 161, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Mao, D. Effect of iron plaque outside roots on nutrient uptake by rice (Oryza sativa L.). Zinc uptake by Fe-deficient rice. Plant Soil 1998, 202, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Lan, Q.; Liu, C.; Guo, X.; Cai, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, G.; Ding, J. Influence of iron plaque on the uptake and accumulation of chromium by rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings: Insights from hydroponic and soil cultivation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 162, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.H.; Baker, A.J.; WONG, M.H.; Willis, A.J. Copper and nickel uptake, accumulation and tolerance in Typha latifolia with and without iron plaque on the root surface. New Phytol. 1997, 136, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Zhang, J.L.; Zhang, F.S. Role of iron plaque in Cd uptake by and translocation within rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings grown in solution culture. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2007, 59, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, M.K.; Moulick, D.; Choudhury, S. Iron (Fe3+)-mediated redox responses and amelioration of oxidative stress in cadmium (Cd2+) stressed mung bean seedlings: A biochemical and computational analysis. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowardhara, B.; Borgohain, P.; Saha, B.; Awasthi, J.P.; Moulick, D.; Panda, S.K. Phytotoxicity of Cd and Zn on three popular Indian mustard varieties during germination and early seedling growth. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 21, 101349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, K.; Xu, J.; Liang, J.; Lu, X.; Yang, J.; Zhu, Q. Interaction of Cd and five mineral nutrients for uptake and accumulation in different rice cultivars and genotypes. Field Crop. Res. 2003, 83, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, A.; Prasad, M.N.V. Cadmium minimization in rice. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 34, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, Q.; An, J.; Sun, Y.; Liu, R. Variations in cadmium accumulation among Chinese cabbage cultivars and screening for Cd-safe cultivars. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, D.; Koyama, E.; Yamaji, N.; Ma, J.F. Physiological, genetic, and molecular characterization of a high-Cd-accumulating rice cultivar, Jarjan. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 2265–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, S.; Abe, T.; Kuramata, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Ando, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Yano, M. A major quantitative trait locus for increasing cadmium-specific concentration in rice grain is located on the short arm of chromosome 7. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arao, T.; Ae, N. Genotypic variations in cadmium levels of rice grain. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2003, 49, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, D.; Koyama, E.; Kono, I.; Ando, T.; Yano, M.; Ma, J.F. Identification of a novel major quantitative trait locus controlling distribution of Cd between roots and shoots in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009, 50, 2223–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Cai, G.; Qian, M.; Wang, D.; Xu, J.; Yang, J.; Zhu, Q. Effect of Cd on the growth, dry matter accumulation and grain yield of different rice cultivars. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2007, 87, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junyu, H.; Cheng, Z.; Yanfang, R.; Yuping, Y.; Dean, J. Genotypic variation in grain cadmium concentration of lowland rice. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2006, 169, 711–716. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.; Ma, Y.; Sun, B. Influence of soil type and genotype on Cd bioavailability and uptake by rice and implications for food safety. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Römkens, P.F.A.M.; Brus, D.J.; Guo, H.Y.; Chu, C.L.; Chiang, C.M.; Koopmans, G.F. Impact of model uncertainty on soil quality standards for cadmium in rice paddy fields. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3098–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, S.; Liu, Z. Effects of growing seasons and genotypes on the accumulation of cadmium and mineral nutrients in rice grown in cadmium contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hongjiang, Z.; Xizhou, Z.; Tingxuan, L.; Fu, H. Variation of cadmium uptake, translocation among rice lines and detecting for potential cadmium-safe cultivars. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 71, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siddique, A.B.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.R.; Shehzad, M.T.; Nath, B.; Naidu, R. Influence of Iron Plaque on Accumulation and Translocation of Cadmium by Rice Seedlings. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10307. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810307
Siddique AB, Rahman MM, Islam MR, Shehzad MT, Nath B, Naidu R. Influence of Iron Plaque on Accumulation and Translocation of Cadmium by Rice Seedlings. Sustainability. 2021; 13(18):10307. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810307
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiddique, Abu Bakkar, Mohammad Mahmudur Rahman, Mohammad Rafiqul Islam, Muhammad Tahir Shehzad, Bibhash Nath, and Ravi Naidu. 2021. "Influence of Iron Plaque on Accumulation and Translocation of Cadmium by Rice Seedlings" Sustainability 13, no. 18: 10307. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810307
APA StyleSiddique, A. B., Rahman, M. M., Islam, M. R., Shehzad, M. T., Nath, B., & Naidu, R. (2021). Influence of Iron Plaque on Accumulation and Translocation of Cadmium by Rice Seedlings. Sustainability, 13(18), 10307. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810307








