Psychoacoustic Evaluation of Hydraulic Pumps
Abstract
1. Motivation and Introduction
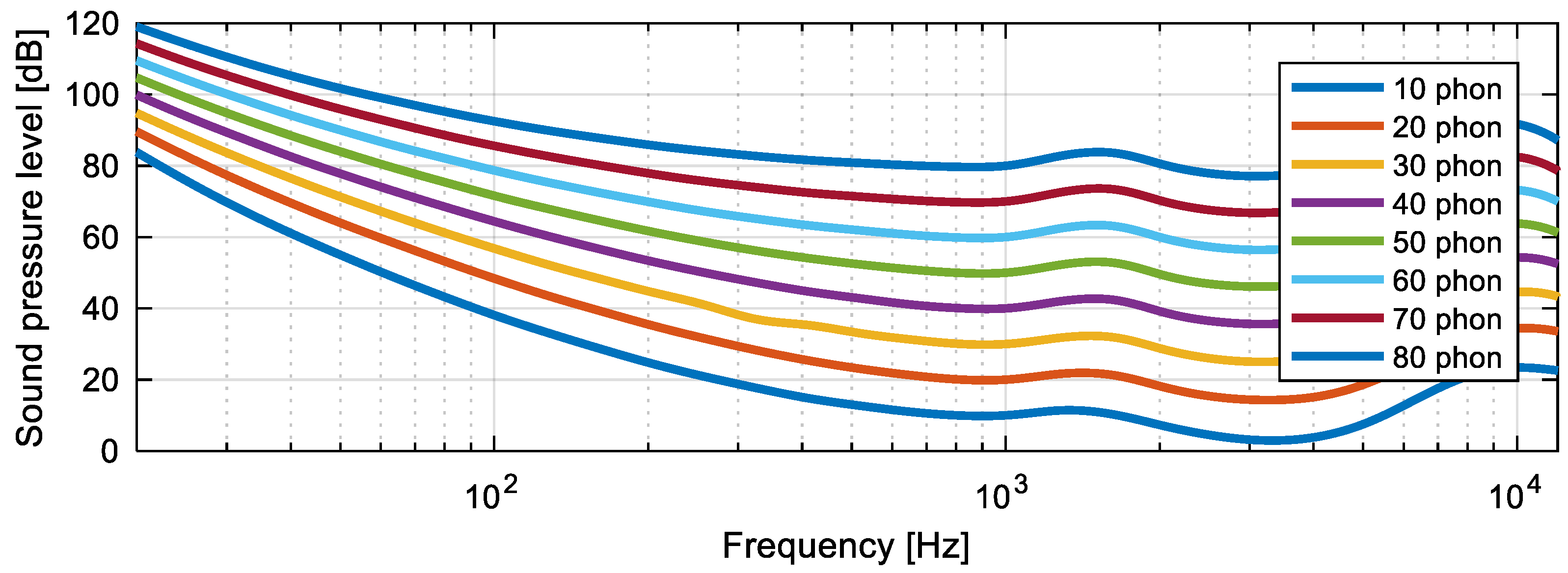
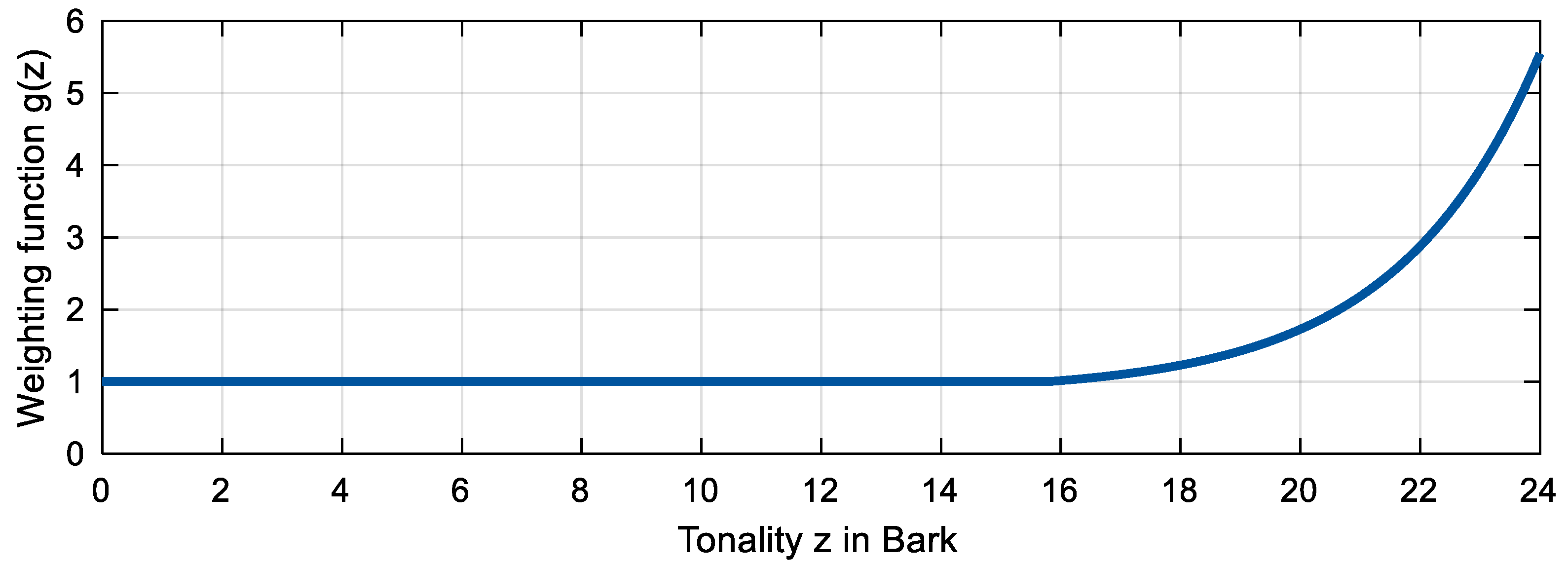
1.1. Basics of Acoustics and Psychoacoustics
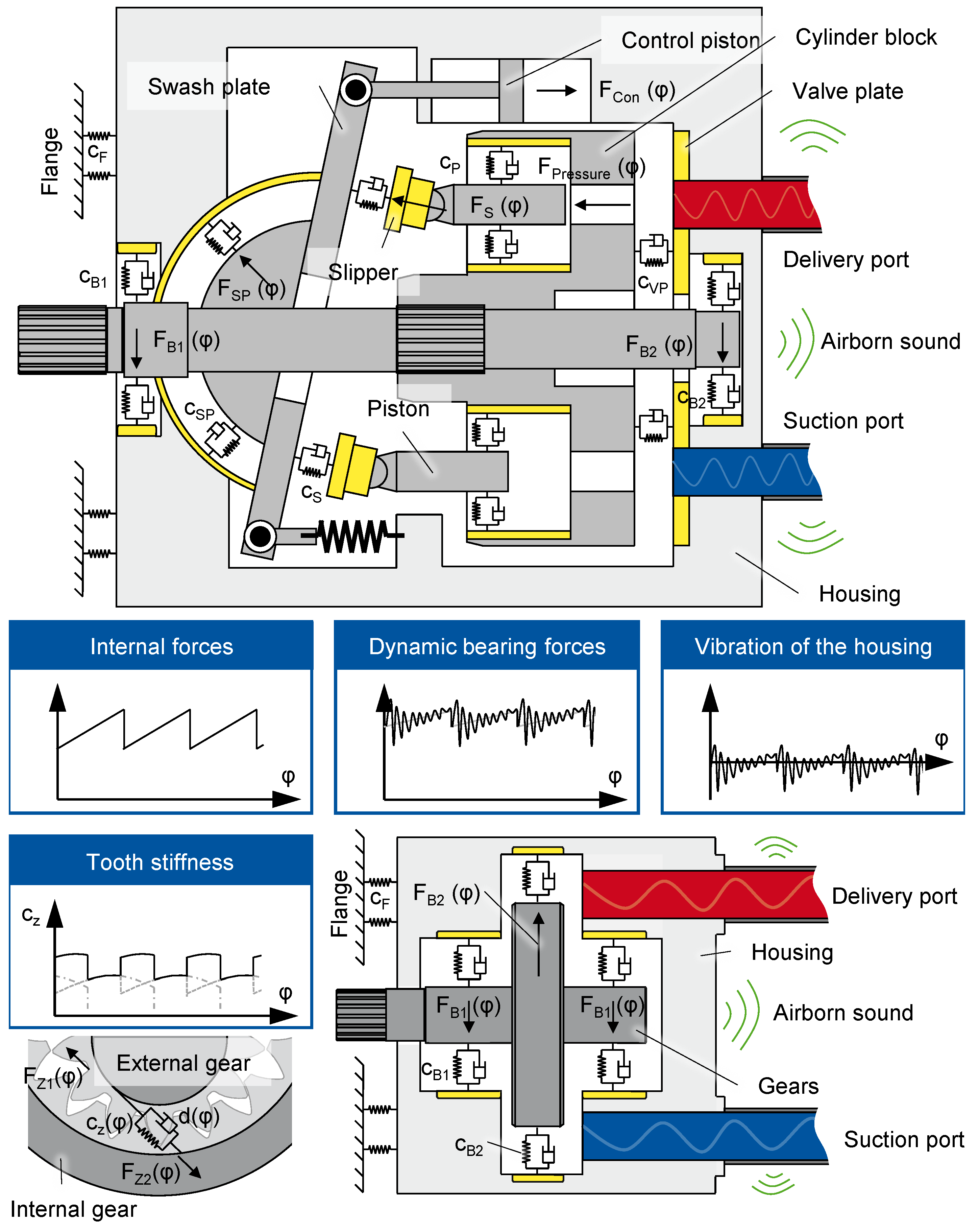
1.2. Noise Generation in Hydraulic Systems
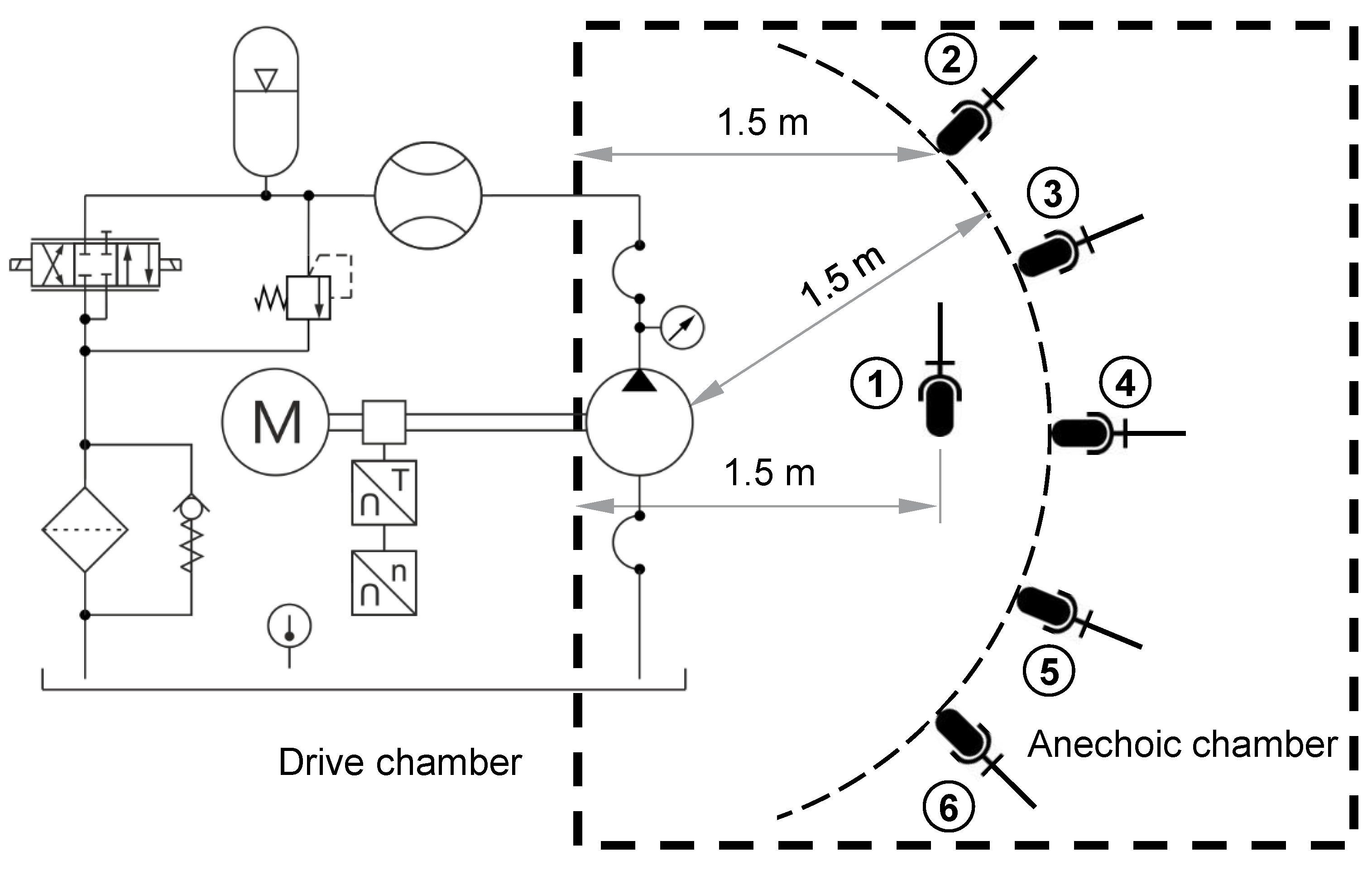
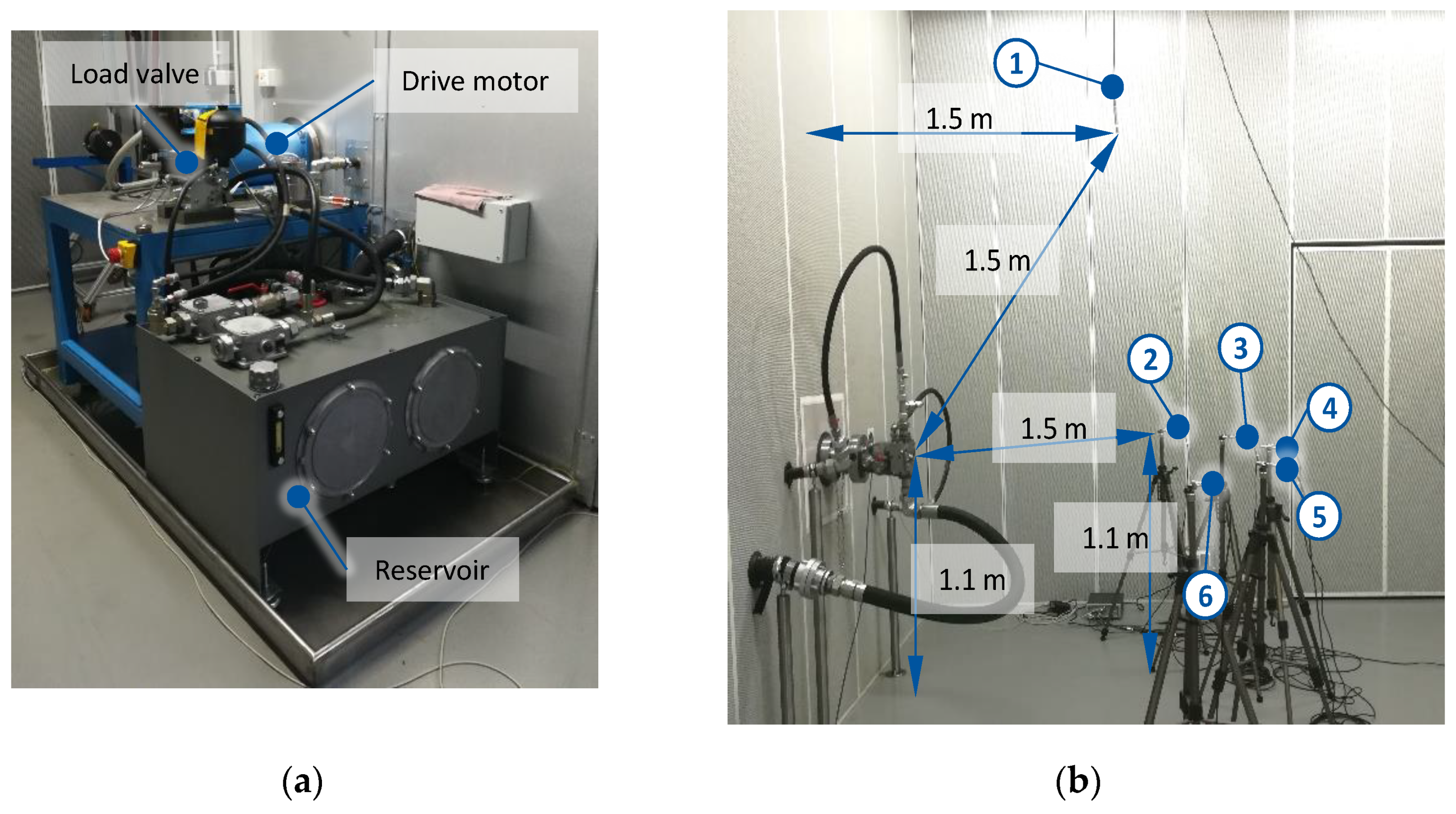
2. Materials and Methods
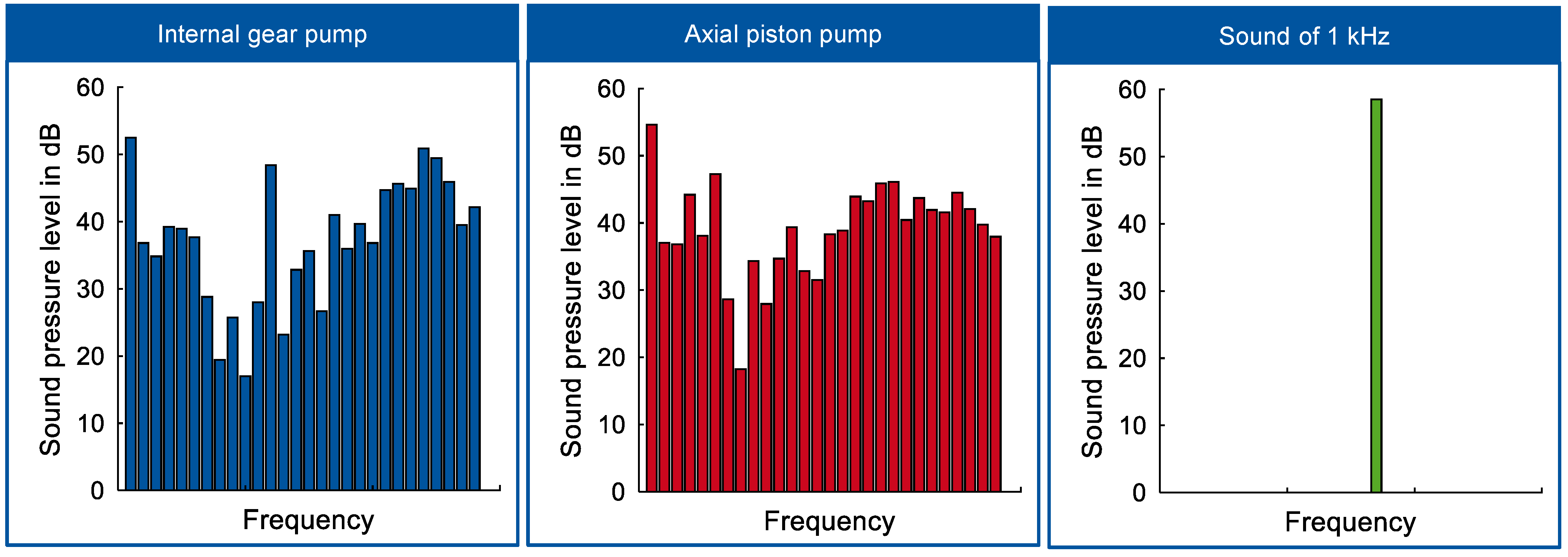
Instrumental Measurement of an Axial Piston Pump and an Internal Gear Pump
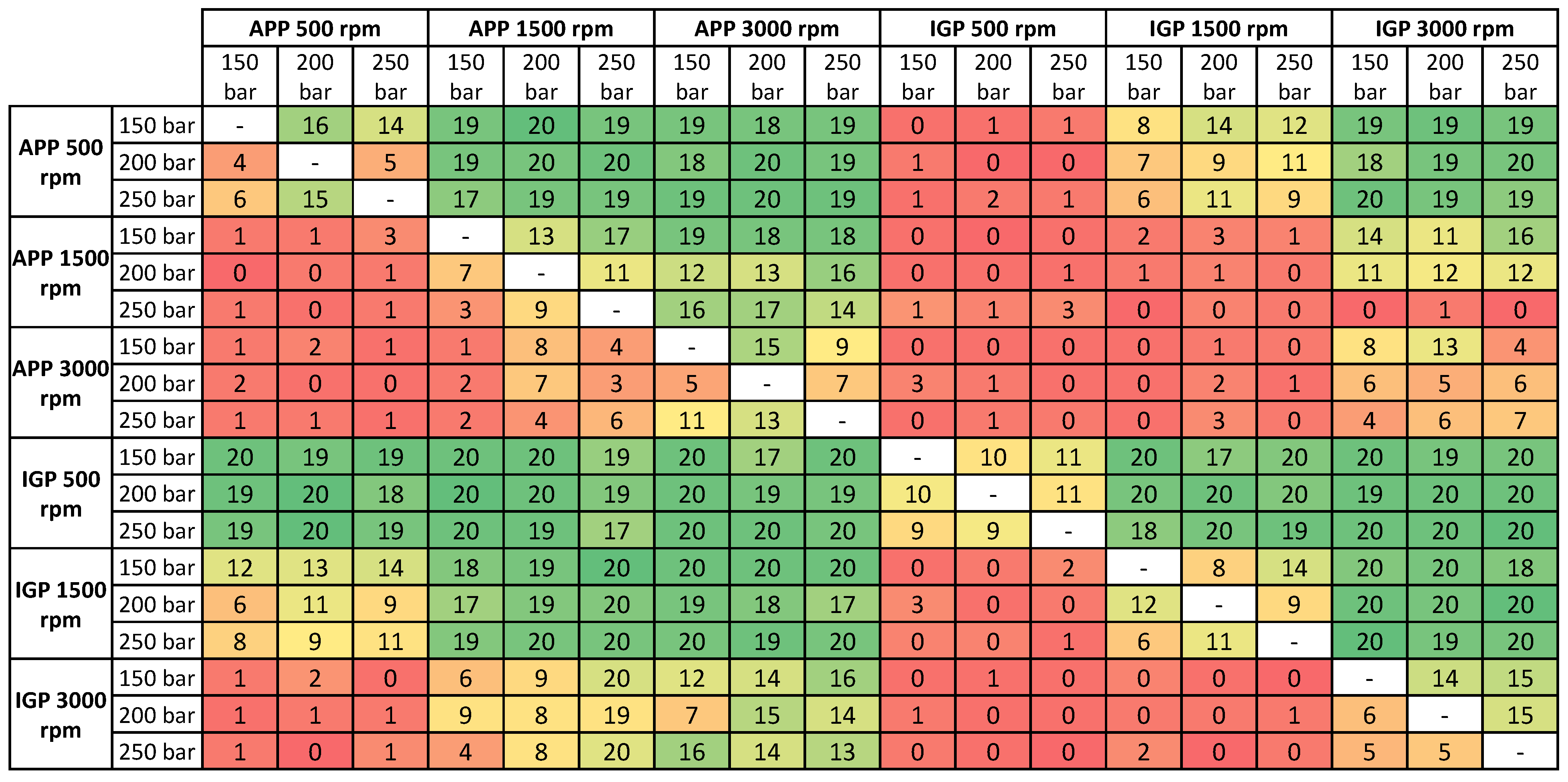
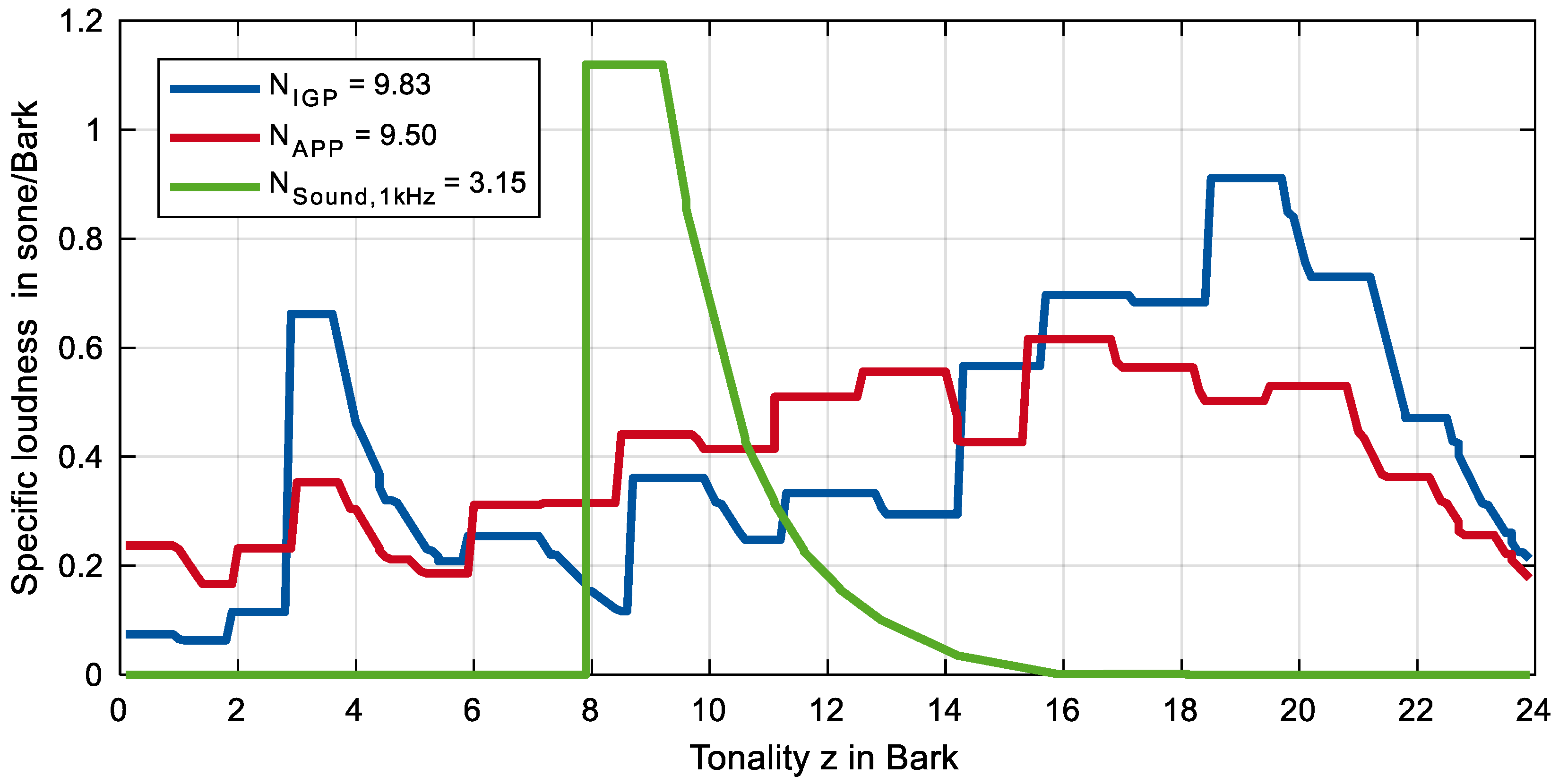
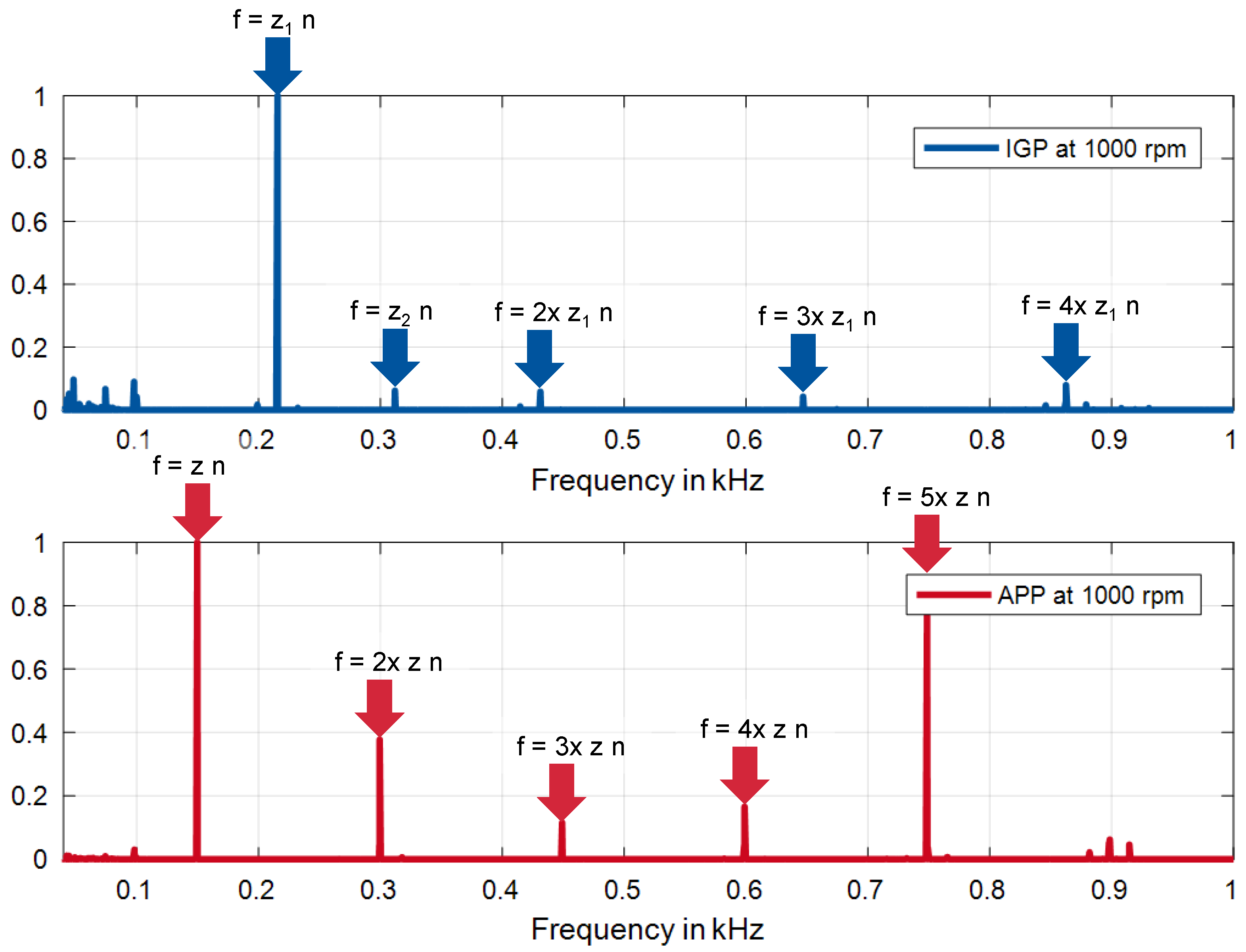
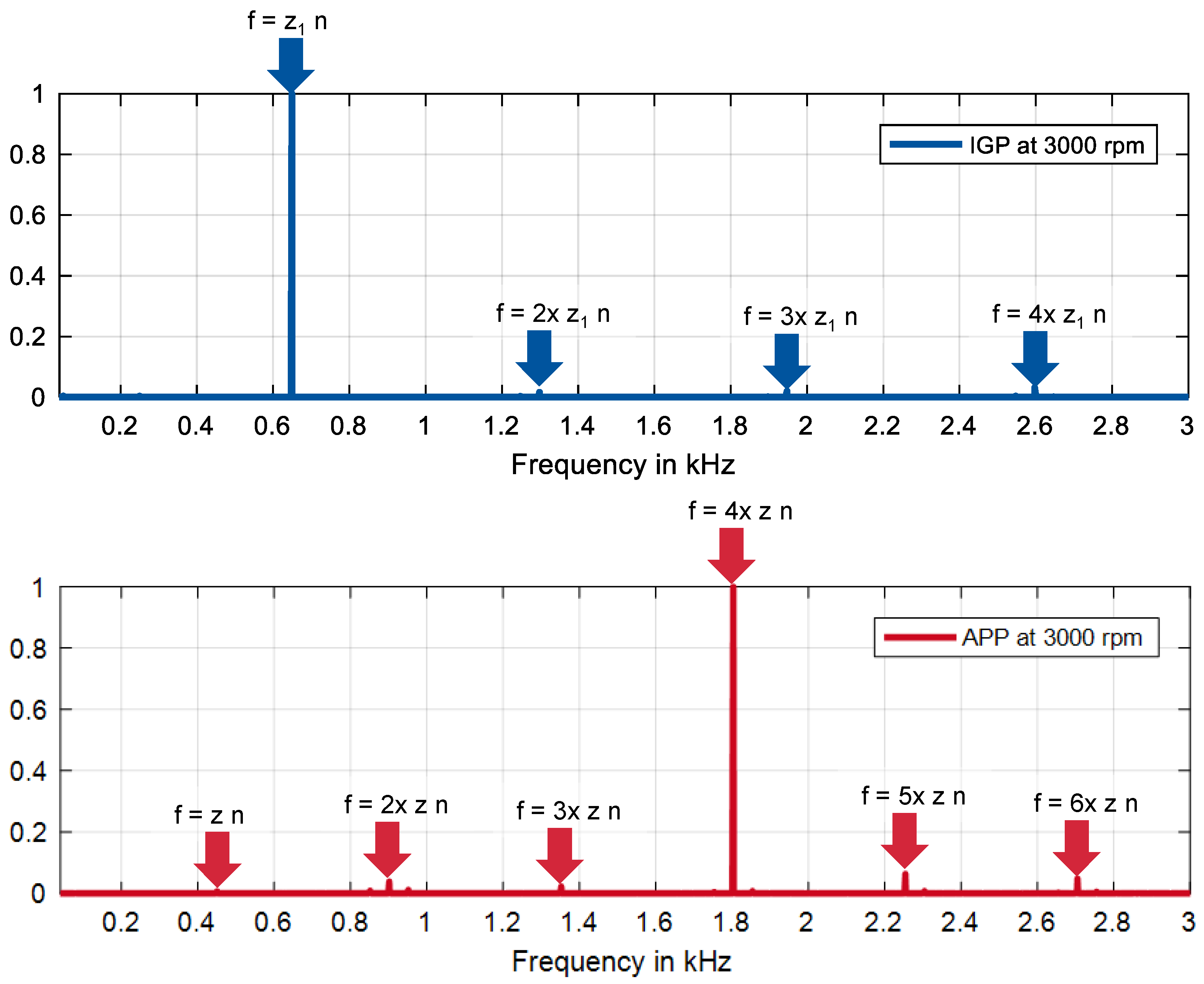
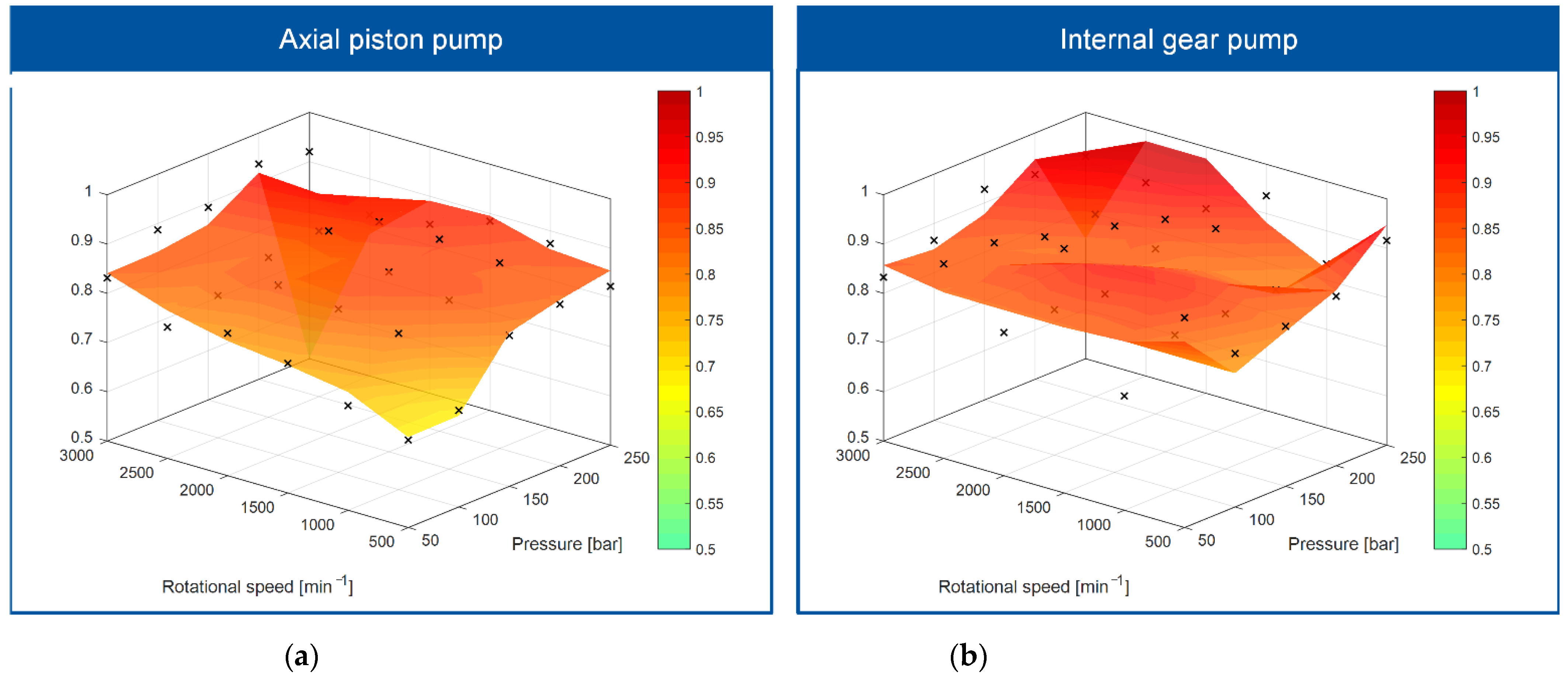
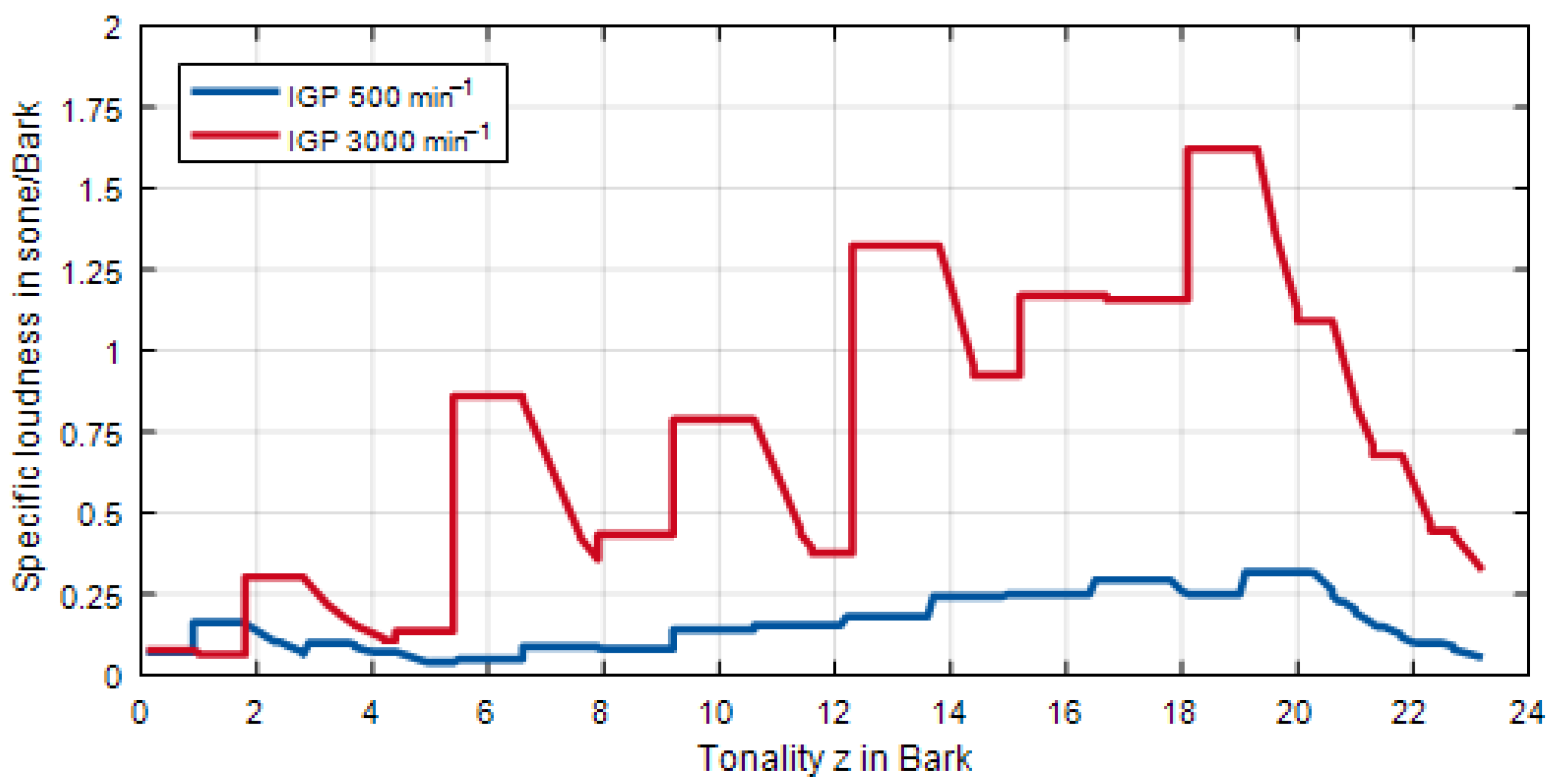
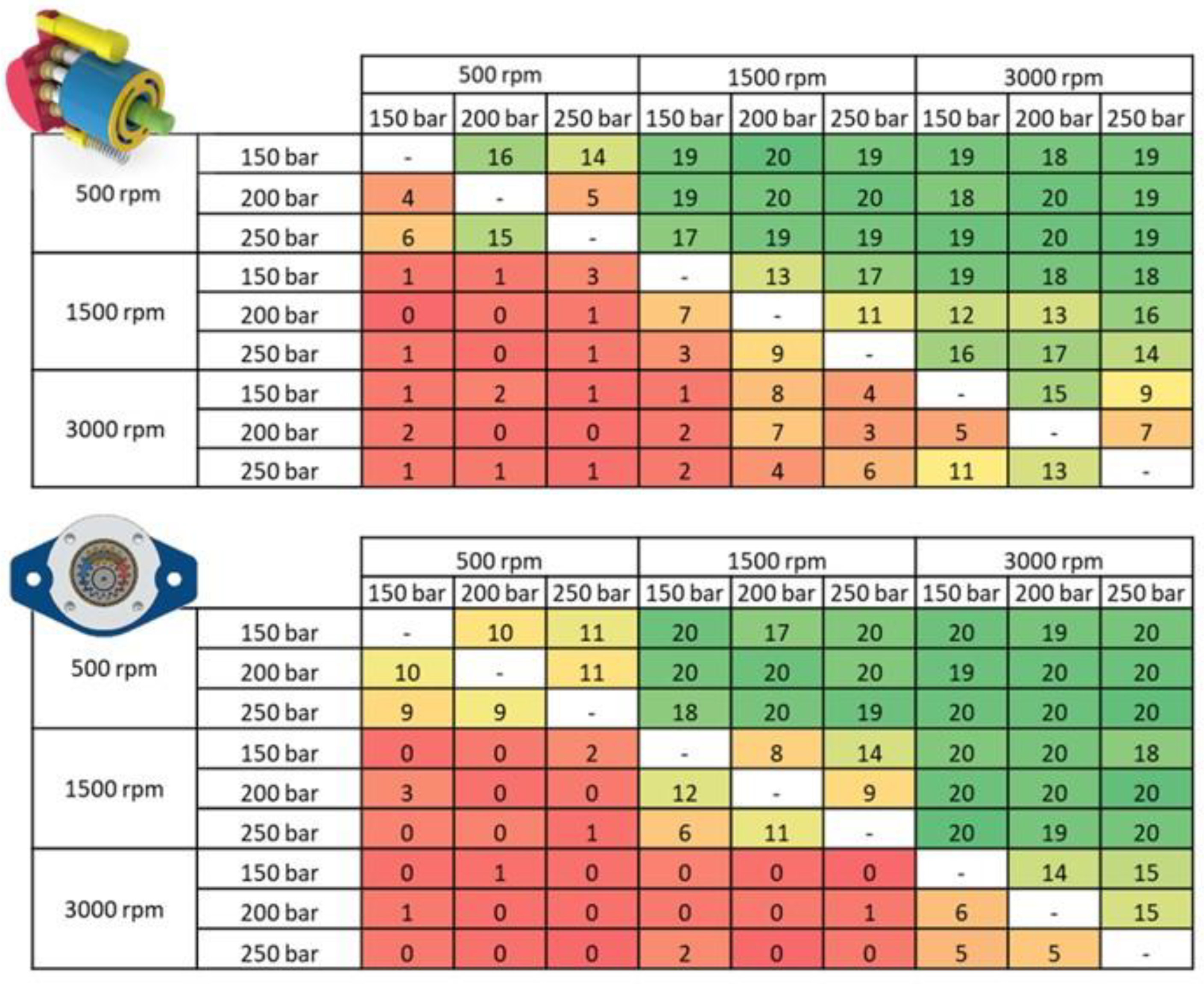
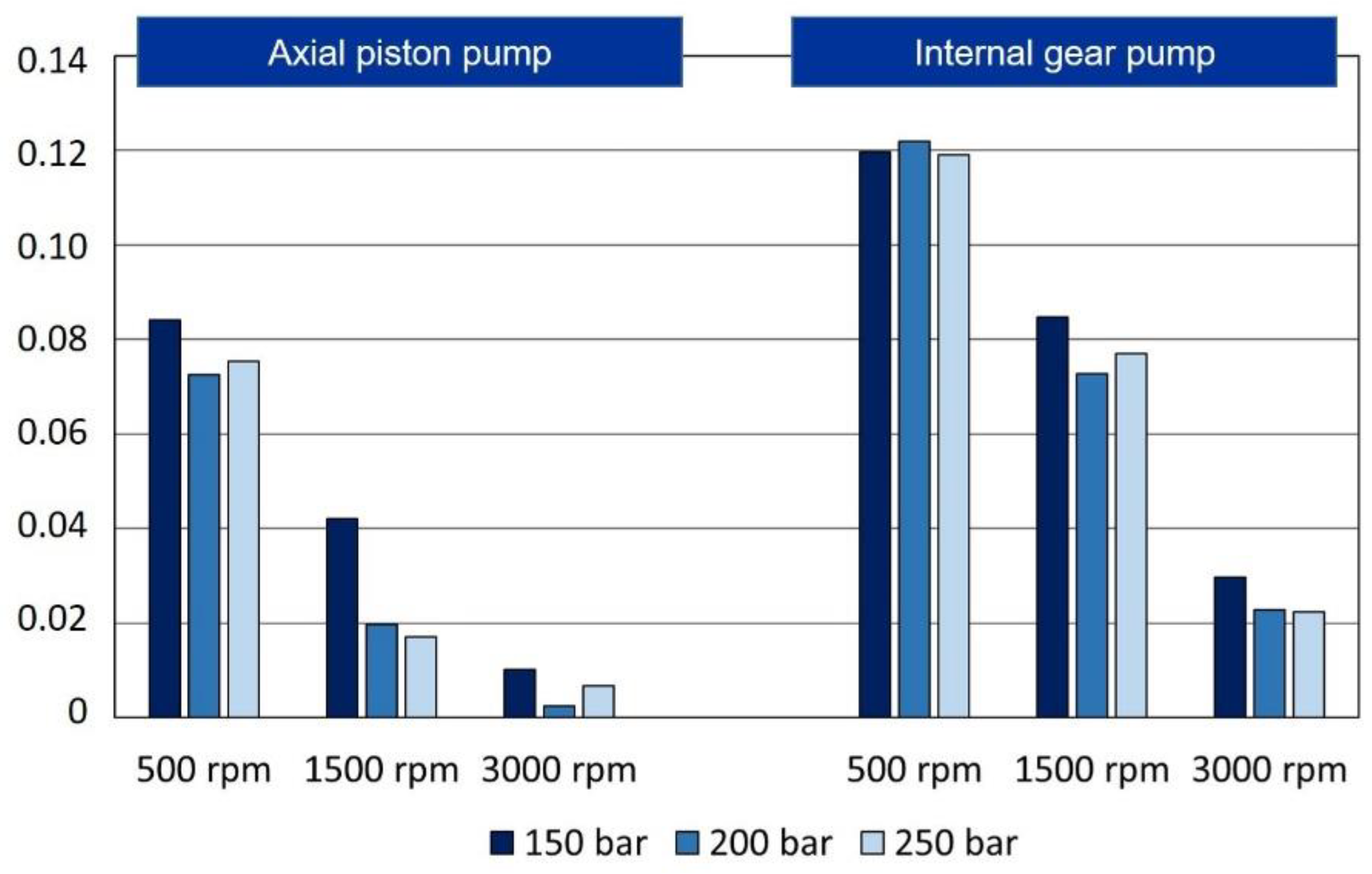
3. Analysis of Results
3.1. Listening Tests to Determine the Subjectively Perceived Pleasantness or Annoyance
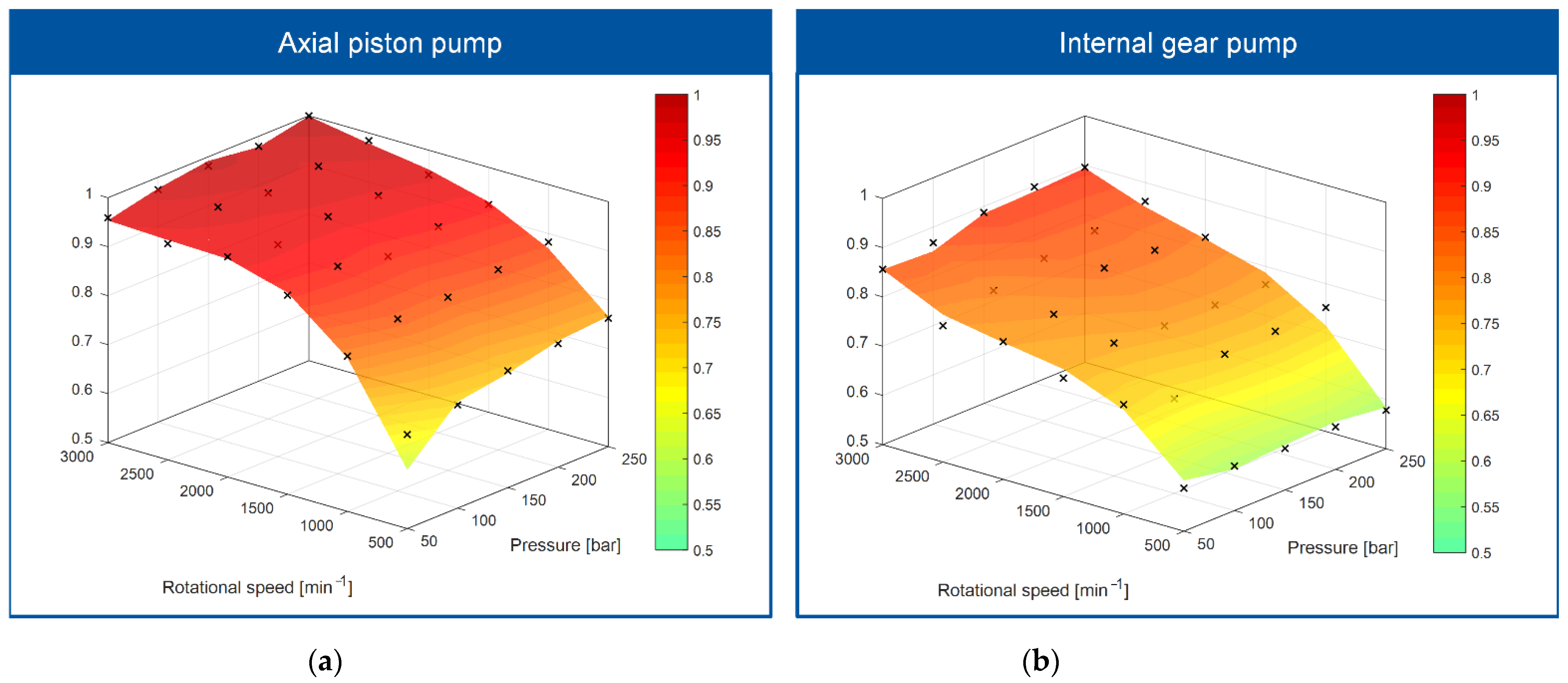
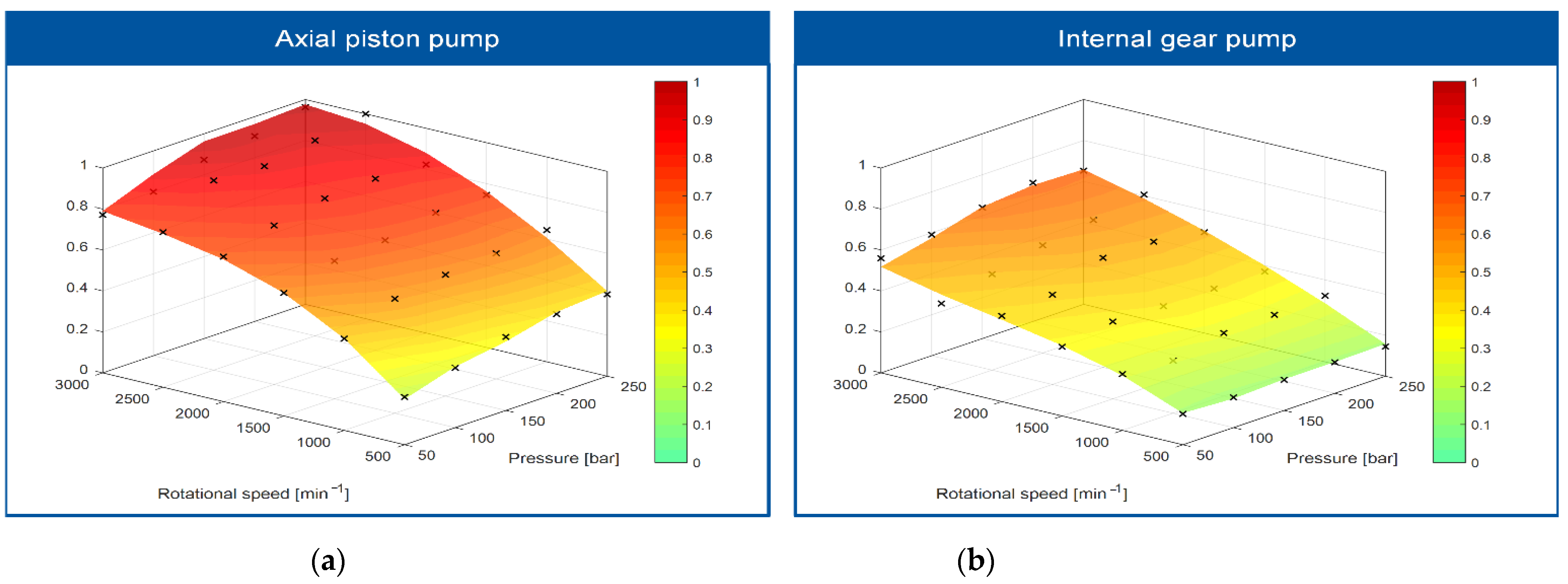
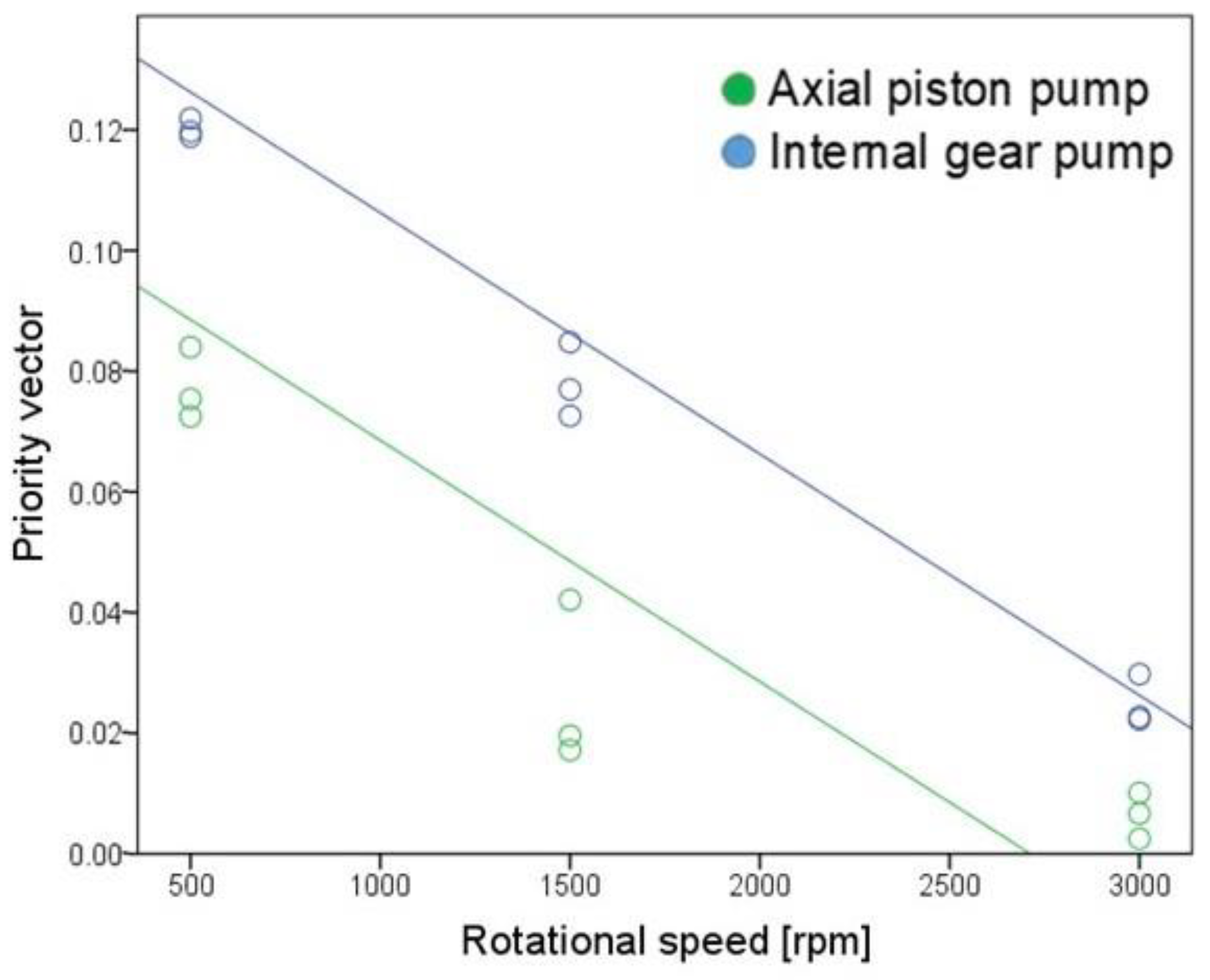
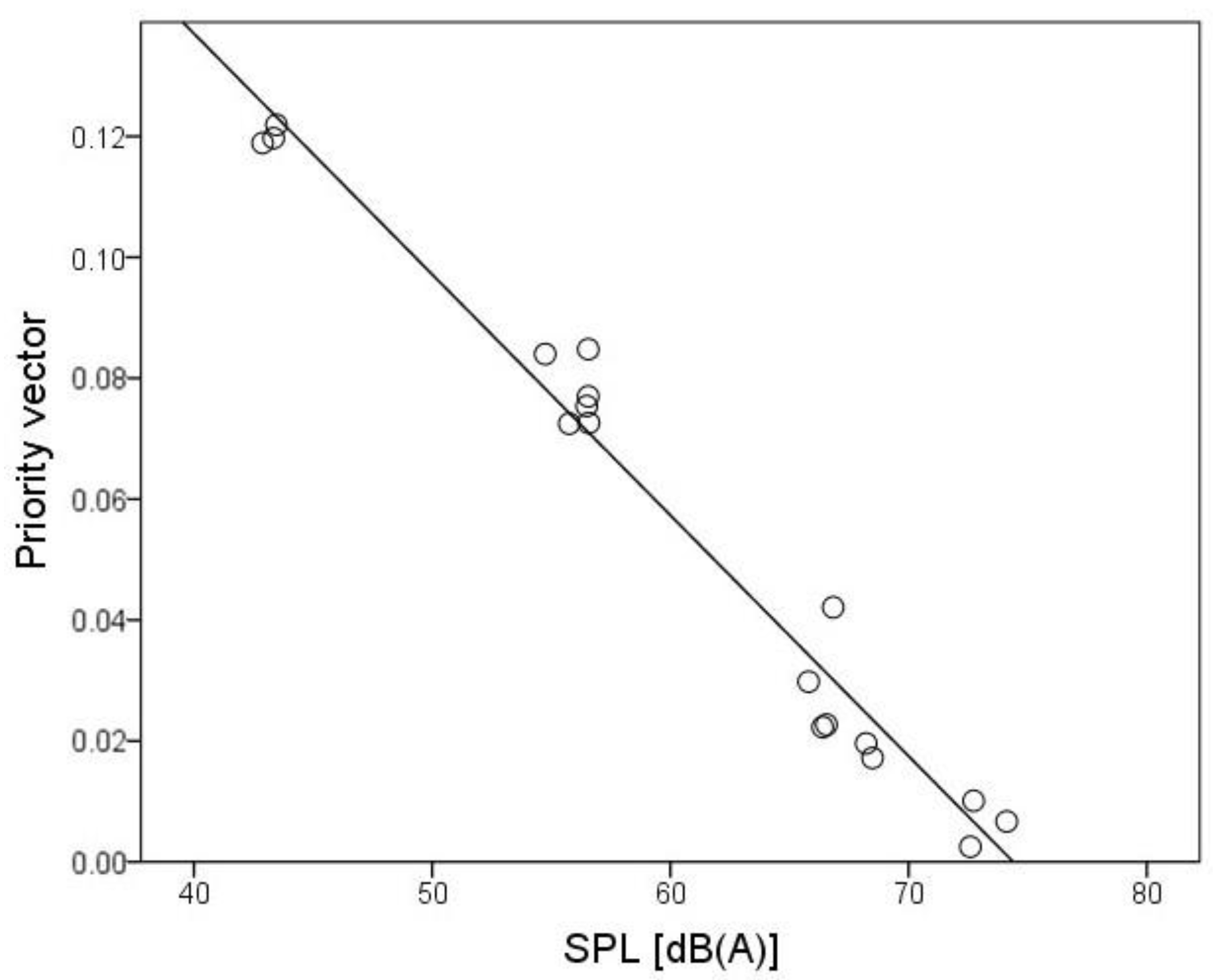
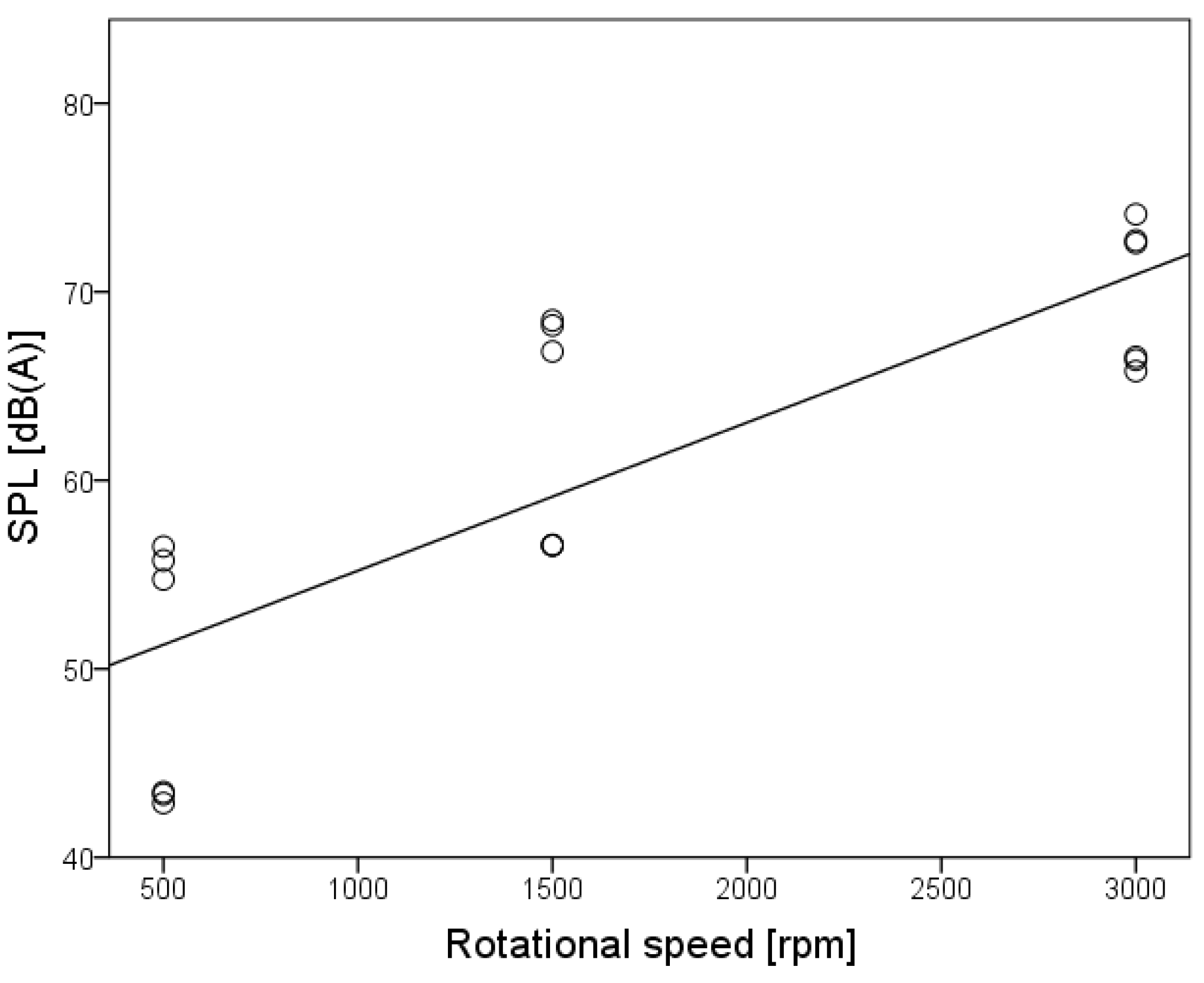
3.2. Regression Analyses to Predict the Subjectively Perceived Pleasantness or Annoyance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Holzer, A.; Leifeld, R.; Opgenoorth, A.; Pietrzyk, T.; Schoemacker, F.; Vonderbank, T.; Schmitz, K. Trends und Highlights der BAUMA 2019, O+P Fluidtechnik, 7-8/2019. Available online: https://digital.oup-fluidtechnik.de/o-p-fluidtechnik-7-8-2019/62756917/34 (accessed on 29 June 2021).
- WHO. Burden of Disease from Environmental Noise-Quantification of Healthy Life Years Lost in Europe; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Genuit, K. Erweiterung von Lärmprognosen durch die Psychoakustik; DAGA: Oldenburg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Schleihs, C.W. Acoustic Design of Hydraulic Axial Piston Swashplate Machines. Ph.D. Thesis, RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Xia, S.; Ye, S.; Xu, B.; Zhu, S.; Xiang, J.; Tang, H. Sound quality evaluation and prediction for the emitted noise of axial piston pumps. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 145, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN 45630. Grundlagen der Schallmessung–Physikalische und subjektive Größen von Schall. December 1971. Available online: https://webstore.ansi.org/standards/din/din456301971de (accessed on 29 June 2021).
- DIN ISO 226. Akustik–Normalkurven Gleicher Lautstärkepegel (ISO 226:2003). April 2006. Available online: https://www.beuth.de/de/norm/din-iso-226/86282153 (accessed on 29 June 2021).
- Klocke, F.; Brecher, C. Zahnrad-und Getriebetechnik; Carl Hanser Verlag München: Munich, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- DIN 45631. Berechnung des Lautstärkepegels und der Lautheit aus dem Geräuschspektrum–Verfahren nach E. Zwicker. March 1991. Available online: https://www.en-standard.eu/din-45631-berechnung-des-lautstarkepegels-und-der-lautheit-aus-dem-gerauschspektrum-verfahren-nach-e-zwicker/ (accessed on 29 June 2021).
- Neubauer, P. Konzeption und Auslegung von Geräuschoptimierten Inäquidistanten Verzahnungen. Ph.D. Thesis, TU Darmstadt, Darmstadt, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zwicker, E. Unterteilung des hörbaren Frequenzbereichs in Frequenzgruppen. Acustica 1960, 10, 185. [Google Scholar]
- Zwicker, E. Psychoakustik; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Fastl, H.; Zwicker, E. Psychoacoustics: Facts and Models, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Head Acoustics: Lautheits-und Schärfeberechnung in der ArtemiS Suite–Application Note 02/18. 2018. Available online: https://global.head-acoustics.com/downloads/de/application_notes/Psychoakustische-Analysen_I_d.pdf (accessed on 29 June 2021).
- Möser, M. Psychoakustische Messtechnik; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Carl, C. Gehörbezogene Analyse und Synthese der Vibroakustischen Geräuschanregung von Verzahnungen. Ph.D. Thesis, RWTH Aachen, Aachen, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- DIN 45692. Messtechnische Simulation der Hörempfindung Schärfe. August 2009. Available online: https://webstore.ansi.org/standards/din/din456922009de (accessed on 29 June 2021).
- Nafz, T.M. Aktive Ventilumsteuerung von Axialkolbenpumpen zur Geräuschreduktion Hydraulischer Anlagen. Ph.D. Thesis, RWTH Aachen, Aachen, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, B. Einsatz der Simulation zur Pulsations-und Geräuschminderung Hydraulischer Anlagen. Ph.D. Thesis, RWTH Aachen, Aachen, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Schoemacker, F.; Murrenhoff, H. Interaction between Swash Plate Movement and Commutation in Axial Piston Machines. In Proceedings of the 10th JFPS International Symposium on Fluid Power, Fukuoka, Japan, 24–27 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jarchow, M. Maßnahmen zur Minderung Hochdruckseitiger Pulsation Hydrostatischer Schrägscheibeneinheiten. Ph.D. Thesis, RWTH Aachen, Aachen, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Edge, K. Designing quieter hydraulic systems-some recent developments and contributions. In Proceedings of the 4 JHPS International Symposium on Fluid Power, Tokyo, Japan, 15–17 November 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ericson, L. On Fluid Power Pump and Motor Design-Tools for Noise Reduction. Ph.D. Thesis, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, A. Design Principles for Noise Reduction in Hydraulic Piston Pumps-Simulation, Optimisation and Experimental Verification. Ph.D. Thesis, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, A.; Ölvander, J.; Palmberg, J.-O. Experimental verification of cross-angle for noise reduction in hydraulic piston pumps. J. Syst. Control Eng. 2007, 221, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klop, R.J. Investigation of Hydraulic Transmission Noise Sources; Purdue University: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Klop, R.; Ivantysynova, M. Sound intensity measurement to investigate noise generation of hydrostatic transmissions. In Proceedings of the 7th International Fluid Power Conference (IFK), Aachen, Germany, 22–24 March 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Klop, R.; Ivantysynova, M. Investigation of Noise Sources on a Series Hybrid Transmission. Int. J. Fluid Power 2011, 12, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunze, T.; Berneke, S. Noise reduction at hydrostatic pumps by structure optimization and acoustic simulation. In Proceedings of the 5th International Fluid Power Conference (IFK), Aachen, Germany, 20–22 March 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ohuchi, H.; Masuda, K. Active noise control of a variable displacement axial piston pump with even number of cylinders. In Proceedings of the 4 JHPS International Symposium on Fluid Power, Tokyo, Japan, 15–17 November 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Opperwall, T.; Vacca, A. Performing and Interpreting Experiments towards Understanding Noise Generation in Displacement Machines; SICFP2013: Linköping, Sweden, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Opperwall, T.; Vacca, A. Modeling noise sources and propagation in displacement machines and hydraulic lines. In Proceedings of the 9th JFPS International Symposium on Fluid Power, Matsue, Japan, 28–31 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Seeniraj, G.K. Model Based Optimization of Axial Piston Machines Focusing on Noise and Efficiency. Ph.D. Thesis, Perdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Schleihs, C.; Murrenhoff, H. Modal Analysis Simulation and Validation of a Hydraulic Motor. In Proceedings of the 9th JFPS International Symposium on Fluid Power, Matsue, Japan, 28–31 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Schleihs, C.; Murrenhoff, H. Acoustical simulation of a hydraulic swash plate motor. In Proceedings of the ASME/Bath Symposium on Fluid Power and Motion Control (FPMC), Chicago, IL, USA, 12–14 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, T.; Kojima, E. Prediction of sound power radiated from oil hydraulic pump using FEM and BEM. Acoust. Sci. Technol. 2003, 24, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thurstone, L.L. A law of comparative judgement. Psychol. Rev. 1927, 34, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. How to make a decision: The Analytic Hierarchy Process. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1990, 48, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | B | SE B | β | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| constant | 0.11 | 0.15 | |||
| Pump type | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.47 | 6.78 | <0.001 |
| Speed (rpm) | −0.001 | 0.001 | −0.84 | −12.00 | <0.001 |
| Pressure (bar) | −0.001 | 0.001 | −0.09 | −1.29 | 0.22 |
| Variable | B | SE B | β | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| constant | 0.30 | 0.03 | |||
| SPL (dB(A)) | −0.004 | 0.001 | −0.99 | −21.11 | <0.001 |
| Sharpness (acum) | 0.001 | 0.02 | 0.001 | 0.03 | 0.98 |
| Variable | B | SE B | β | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| constant | 50.82 | 3.60 | |||
| Pump type | −10.21 | 1.35 | −0.52 | −7.58 | < 0.001 |
| Speed (rpm) | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.82 | 11.99 | < 0.001 |
| Pressure (bar) | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.50 | 0.63 |
| Variable | B | SE B | β | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| constant | 45.72 | 7.72 | |||
| Speed (rpm) | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.82 | 5.49 | <0.001 |
| Pressure (bar) | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.23 | 0.82 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pietrzyk, T.; Georgi, M.; Schlittmeier, S.; Schmitz, K. Psychoacoustic Evaluation of Hydraulic Pumps. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7320. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137320
Pietrzyk T, Georgi M, Schlittmeier S, Schmitz K. Psychoacoustic Evaluation of Hydraulic Pumps. Sustainability. 2021; 13(13):7320. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137320
Chicago/Turabian StylePietrzyk, Tobias, Markus Georgi, Sabine Schlittmeier, and Katharina Schmitz. 2021. "Psychoacoustic Evaluation of Hydraulic Pumps" Sustainability 13, no. 13: 7320. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137320
APA StylePietrzyk, T., Georgi, M., Schlittmeier, S., & Schmitz, K. (2021). Psychoacoustic Evaluation of Hydraulic Pumps. Sustainability, 13(13), 7320. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137320






