Abstract
The purpose of our study is to identify the nature of the link between government spending and economic growth, in order to test the two theories of Wagner and Keynes, in the case of Romania. On the one hand, Keynes argues that public spending is an important tool to stimulate growth. On the other hand, Wagner says that increased public spending is a result of economic growth. We analyzed the long-term dynamics of the two time series through Johansen’s cointegration approach and, in the short term, with the help of Granger’s causality test. The obtained results do not indicate the existence of long-term cointegration vectors, but they support the double causality relation in the short term. Therefore, not only does GDP represent a Granger cause for government spending but also vice versa. Our results validate the liberal criticism of the state’s involvement in supporting economies. As the critics of the monetarist school said, the effect of multiplying government spending on national income is short-term. The long-term effect appears under the action of inflationary macroeconomic bottlenecks.
1. Introduction
Modern economies involve a substantial presence of the state which, very often, is no longer limited to being an arbitrator. The attributes of the state have become much broader with the economic advantage of the modern world. Thus, in order to cope with the multiple responsibilities that are assumed, more and more resources are required.
Our study presents two different approaches. On the one hand, the opinion issued by Wagner at the end of the 19th century [1] is that the economic growth entails an increase in government spending.
Adolph Wagner’s law, though considered by some analysts to be simplistic, had the power to synthesize the transformations of the era in which it was enunciated. In the second half of the 19th century, Germany, as with the rest of the Western European countries, was undergoing an intense industrialization process. This was putting pressure on the increasing role of the state and its attributes in the social area. In the period when Marxism began to be known, Wagner, following the German Historical School more, noted that governments should increase their protective and administrative actions in order to meet the demands of an increasingly active economy. Then, as Wagner said, “cultural and welfare” spending, and especially those related to health and education, should increase as the economy develops. Moreover, as Smith also mentioned in the Wealth of Nations [2], Wagner argues that governments should sometimes interfere when the private initiative is not interested in doing so.
Wagner’s law was reinforced again in the second half of the 20th century. Benefiting from the new econometric techniques and the existence of long-term observations, authors such as Peacock and Wiseman [3], Musgrave [4], Michas [5], Mann [6] and Khan [7] have succeeded in certifying the validity of the law. Moreover, the law was improved. Pryor [8] tested the relationship between GDP and government consumption expenditure, Goffman [9] analyzed the link between the total government expenditure and GDP per capita, Peacock and Wiseman [3] studied the functional relationship between the percentage of total government expenditure in GDP and the evolution of GDP and Gupta [10] investigated the influence of the evolution of GDP per capita on total government expenditure per capita. Meanwhile, Musgrave [4] analyzed the influence of the evolution of GDP per capita on the percentage of government spending in the total output [11].
On the other hand, Keynes [12] argued that government spending can be actively used as a tool for inducing economic growth. Although not completely original, Keynes managed to impose his ideas for a long time. Using an exceptional econometric argumentation and gaining a large popularity, both because of his personal abilities and of the elitist environment in which he acted, Keynes has overwhelmingly influenced economic policies since the 1950s. Starting from the simple idea that the failures of the free market can be corrected with public policy instruments, he emphasized the role of public spending in increasing the effective demand and in boosting economic growth.
Strongly criticized by liberal authors, starting with the Austrians Hayek and Mises and continuing with the liberal American schools (Friedman’s monetarists, Public Choice supporters—Tullock and Buchanan) and the ultra-liberals (Rothbard, de Soto and many others), Keynes’ theory is, even nowadays, the subject of some analyses meant to confirm or refute its validity.
In the present study, we intend to analyze if there is a connection between economic growth and the increase in public spending in Romania and to identify its direction. The paper is structured as follows: in the next section, we present a brief literature overview of the theoretical and empirical approaches conducted on the topic. Section 3 underlines the data and the methods used, Section 4 discusses the results of our analysis and underlines some policy implications, and Section 5 concludes the paper.
2. Literature Review
The nature and the direction of the link between economic growth and public spending have been analyzed in various studies. However, the findings were not able to provide a clear picture, because, very often, they were contradictory.
Some studies, which assumed that there is a link between the two variables, tried to identify the direction of this connection. Ram [13], Ahsan et al. [14], Holmes and Hutton [15] and Singh and Sahni [16] noticed a positive influence. Other authors, such as Barth et al., 1990 [17] and Landau [18,19], have shown that the increase in public spending had a negative effect on economic growth.
Meanwhile, there are other studies that validated Wagner’s law. Thus, the unidirectional causality, from GDP to public expenditures, has been found in the long term in the analysis of Bayrakdar et al. [20], conducted in the case of Turkey. Gül and Yavuz [21], in a study on several developing countries, including Romania, identified the same type of causality. In a research study focused on the case of India, Srinivasan [22] found that the one-way causality runs from economic growth to public expenditure in both the short and long run. In a G7 case study, Bohl [23] identified the positive link only in the case of UK and Canada. Similar results were found by Chletsos and Kollias [24] for Greece, by Ghali [25] for 10 OECD states and by Rehman et al. [26] for Pakistan. Al-Faris [27], analyzing the Gulf Cooperation Council countries and using multivariate cointegration and Granger causality tests, validated Wagner’s law in most cases. The majority of the studies that validated Wagner’s law have been conducted in developing countries. However, it seems that the best usage of the law can be noticed in developed states [28].
There are several studies that have identified the interactions between the two variables in both directions. Devlin and Hansen [29] and Biswal et al. [30] have succeeded in showing that both Wagner’s law and Keynes’ hypothesis are validated.
From the methodological point of view, there is also great diversity in the analysis of the link between government spending and economic growth. Some studies used cointegration analysis to show the long-term relationship between the two variables [31,32,33]. Meanwhile, other research has followed the two-step method from Engle and Granger’s cointegration approach. For example, Ghali uses this methodology for states that implemented the IMF debt-stabilization programs and he concludes that public investment has a negative short-term impact on private investment and a negative long-term effect on both private investment and economic growth [25]. Meanwhile, Ashan et al. [14], also using the two-step method from Engle and Granger’s cointegration approach, find that the long-term validity of Wagner’s hypothesis is maintained. Another group of studies used mixed techniques. Jalles [34], willing to assess the responses of different categories of government spending to changes in economic activity, used panel data instrumental variables and time-series SUR approaches. He found out that Wagner’s law is more prevalent in advanced economies than in emerging ones. Meanwhile, Babatunde [35] used the bounds test approach, based on an unrestricted error correction model, and Granger noncausality tests. The results of both tests showed that there is no long-term relationship between government expenditure and output in Nigeria. The analyzed sample also varies. While some studies used cross-country analysis, such as Ghali [25] who focused on 10 OECD countries, Ram [36] who took into account 115 economies or Quah [33] who investigated different types of states according to income level, others focused only on one country: Chletsos and Kollias [24] on Greece, Bayrakdar et al. [20] on Turkey and Babatunde [35] on Nigeria. As it is a long-term analysis, they are usually applied for long periods of time.
Another group of studies is represented by those research works in which a clear causality between economic growth and public spending has not been identified. Conducting cross-country studies, authors such as Afxentiou and Serletis [37], Ansari et al. [38] and Abizadeh and Yousefi [39] did not find clear evidence in favor of Wagner’s law. In the case of Turkey, there are many approaches. For example, Bagdigen and Cetintas [40], and Başar et al. [41], using Granger’s causality test, concluded that there is no clear long-term causality between economic growth and public spending. Similar results were obtained in the case of Pakistan [11,42] and in India, for the period 1950–1981 [11].
There are also studies that have shown a bi-directional causality [32], especially in certain types of expenditures and fiscal instruments.
There are many research works that validate Keynes’ theory: Jiranyakul and Brahmasrene [43] for Thailand, Holmes and Hutton [15] and Pradhan [44] for India, Babatunde [35] and Ighodaro and Oriakhi [31] for Nigeria, Magazzino [45] for Italy. Tang and Chrsquo [46], conducting a cross-country study in five Asian countries and using Granger’s causality test, found a Keynesian connection only in the case of Philippines.
From the methodological point of view, many researchers used Granger’s causality test and cointegration test. Thus, Chletsos and Kollias [24] suggest that in the case of Greece, only the growth of defense expenditure may be explained in terms of Wagner’s law. Yet, Abu-Bader and Abu-Qarn [32] suggest that military burden negatively affects economic growth for all the countries, and that civilian government expenditures cause positive economic growth in Israel and Egypt. Meanwhile, Ansari et al. [38] noticed that Keynes’ law does not apply to Ghana, Kenya and South Africa. In the case of Turkey, neither Wagner’s Law nor Keynes hypothesis is valid [40]. Interesting results were obtained by Nurudeen and Usman [47] in the case of Nigeria. They found out that, in this country, government total capital expenditure, total recurrent expenditures and government expenditure on education have negative effects on economic growth. On the contrary, an increased level of government expenditure on transport and communication and health leads to an increase in economic growth. An explanation of these different results in the empirical studies may be offered by Hsieh and Lai [48], who argued that the relationship between government spending and growth can vary significantly across time as well as across the major industrialized countries.
Despite the large amount of studies available in the literature, only a very small number of research studies analyzed the relationship between public spending and economic growth in countries of Central and Eastern Europe, including Romania. For example, Alexiou [49] used, for the first time, two different panel data methodologies with seven transition economies in South Eastern Europe (SEE) and found that government spending on capital formation has a positive and significant effect on economic growth. Analyzing the twelve new members of the EU—Bulgaria, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Lithuania, Latvia, Malta, Poland, Romania, Slovenia and Slovakia—Dritsaki and Dritsaki [50] suggest that Keynes’ law is supported in the case of Romania and Bulgaria, while Wagner’s law was demonstrated in Cyprus, Poland, and Romania. Yet, Brașoveanu [51] indicates that there is a negative effect of defense expenditures on economic growth in Romania. Similar results were found by Chang [52], not only for Romania, but also for the rest of the European and Middle East/South Asian states.
Most of the studies on Eastern Europe were conducted for the case of Turkey. Using Johansen’s cointegration test and Granger’s causality test for the period 1975–2014, Uzuner et al. [53] confirm Wagner’s law through the existence of a long-term relationship between public expenditures and economic growth in Turkey. Moreover, Sagdic et al. [54] provide strong support not only for Wagner’s law but also for Keynes’ hypothesis in the case of the 81 provinces of Turkey. Focusing on health expenditure, Atilgan et al. [55] concluded that there is a dynamic causal relationship between them and economic growth in Turkey. Meanwhile, military spending does not promote growth in the long run [56].
Since studies on Romania’s case show that there is a positive impact of public spending on growth [57], this somehow contradicts the reality. The fact that there are researchers that, starting from the dissonance of the ideas of Wagner and Keynes, come to the conclusion that Keynes is right in the case of Romania [58], is somewhat contradictory for us. Romania, although it has made major progress over the last 30 years [59], has lost important steps precisely due to inadequate fiscal policies, massive misappropriation of public money and erroneous budget allocation decisions [60]. Most of Romania’s economic growth was not due to adequate public policies [61] but, rather, the public sector has benefited from increasing resources due to the continuous expansion of the private sector. Our study comes to test this hypothesis.
3. Data and Method
The purpose of our study is to identify the nature of the link between government expenditure (exgov) and economic growth (gdp) in order to test the two theories belonging to Wagner and Keynes, for the case of Romania (see Figure 1). To achieve this objective, we used half-yearly data, for the period 1995–2018. For government expenditures (exgov), we used the collective final consumption expenditure of the general government (adjusted series) and price indices in % against 2000. The seasonally adjusted series was obtained by removing this effect from the unadjusted series, by means of correction coefficients, selected according to the regression model that was used—additive or multiplicative [62]. For the Gross Domestic Product series (gdp), we used quarterly gross domestic product—seasonally adjusted series, price indices in % against 2000. The seasonally adjusted GDP is obtained through the direct method, thus leading to a statistical discrepancy between the GDP and the sum of its components, which are independently and seasonally adjusted [63].
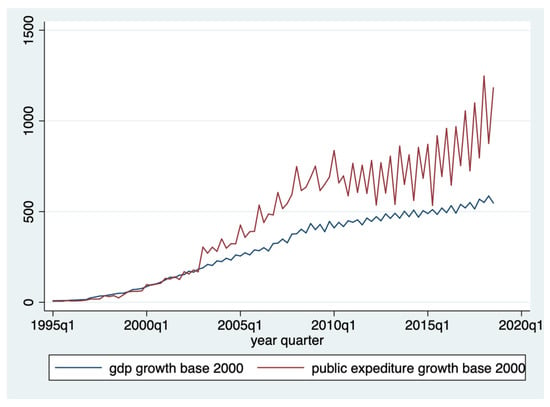
Figure 1.
The quarterly evolution of GDP and public expenditure.
On the one hand, the analysis aims to identify a long-term cointegration link between the two variables using Johansen’s cointegration model. On the other hand, we intend to identify a short-term causality between the variables through Granger’s causality model.
3.1. Augmented Dickey–Fuller (ADF) Test
In order to talk about cointegration, the series must be non-stationary at level 0 and stationary at level 1 or higher. For this, the Dickey–Fuller test can be applied. The autocorrelation problem may appear in the original test. To solve this situation, the Augmented Dickey–Fuller test can be used, adding various lagged dependent variables.
The general form of the regression function used in the ADF test is defined by the following formula:
If we want to emphasize the inverse dependence, then the equation is:
In our case, Y represents the growth rate of GDP, in the adjusted series, against 2000, and G represents the growth rate of the government expenditure in the adjusted series, against 2000.
Meanwhile, is the drift term, t denotes the time trend and p is the largest lag-length used. Equations have both intercept and trend. The value of p (number of lags) can be determined by making reference to a commonly produced information criteria, such as the Akaike criteria (AIC), Schwarz–Bayesian (SBIC) criteria or Hannan and Quinn information criteria (HQIC). The most stable method is AIC.
Since we use growth indexes against a reference period, we cannot talk about a drift effect, especially because the series were adjusted by eliminating the seasonal effect from the gross series, so that = 0. The trend effect, which can be easily noticed in the graphical analysis of the two series of data, is present.
3.2. DF-GLS Test
This test is additional to the ADF test, as a test for a unit root for time series. It is a powerful test, based on removing the means and linear trends for those series that may be non-stationary. This test uses the null hypothesis that a series contains a unit root.
3.3. Phillipps–Perron Test
This test involves fitting Δyt = ρyt−1 + (constant, time trend) + μt. Its results are used for calculating t statistics. They estimate yt = πyt−1 + (constant, time trend) + μt.
The PP test, unlike the ADF test, ignores any serial correlation in the regression test.
3.4. Ng Perron Test
This test modifies the basic equation of Z statistics, leading to a modification of the unit root test. For this reason, the Stata software does not include it in its list of specific tests. Therefore, Eviews was used for this test.
3.5. Johansen Cointegration Analysis
We can say that the two series are cointegrated when there is a linear combination of two processes—more precisely, when I (t) process becomes an I (t − 1) process. As Johansen [64,65] mentioned, cointegration implies common stochastic trend and long-term equilibrium. Granger [66] defines cointegration as a phenomenon in which non-stationary processes can have linear combinations that are stationary.
Cointegration will be tested using the Vector Autoregressive (VAR) approach.
Being two stationary time series, a vector of variables is modeled as depending on its own lags and on the lags of each variable. A VAR system will contain m variables (two in our case). Each of these is expressed as a linear function of p lags of itself and of all other m − 1 variables and an error term. If we consider two variables y and z, then:
where and are white noise disturbances.
Equations (3) and (4) represent first-order VAR, meaning that the introduced p lag is equal to 1.
If we have p lags and the variables are y—the rate of GDP growth (gdp) and z—the growth rate of public expenditure (exgov), then the VAR system will be:
where is a vector of intercept terms and Ai represents the matrix of the coefficients.
3.6. Granger Causality Analysis
The Granger causality test can be used to analyze the direction of the short-term link between the variables. A variable x Granger causes y if y can be better predicted using the histories of both x and y than only using the history of y.
The most common method for testing Granger causality is to use y in the regression on its own lagged values and on the lagged values of x and to test the null hypothesis that the estimated coefficients on the lagged values of x are jointly zero. The acceptance of the null hypothesis means that x has no Granger-cause on y (Granger-cause y) [66].
Therefore, with the two variables x and y, we first use y in the regression on y lags without x lags, meaning that a restricted model is constructed:
After that, we add the x lags and we regress again, which leads to an unrestricted model:
Finally, the null hypothesis is tested ( ), by using an F-test.
If the analyzed series are not cointegrated, then the best method to use for the causality analysis is that developed by Toda and Yamamoto [67]. It is an improved version of Granger’s method, which offers the possibility to test the causality between integrated variables based on the asymptotic theory.
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Cointegration Analysis
According to Levin and Lin [68], the first step for testing cointegration in the case of non-stationary series is to determine the order of VAR (p). For this, the VAR function is created:
where B0 is the vector of constants and B1 represents the matrix of lag coefficients, y is gdp and x is exgov.
As can be noted in Table 1, the tests indicate a different number of lags. Since the AIC test is considered to be the strongest, we will consider eight lags.

Table 1.
Selection order determination.
Subsequently, the augmented Dickey–Fuller test for unit root is applied. The non-stationarity in the level and the stationarity in the first difference are tested. Applying the test in the level shows that the series is non-stationary if p of z is higher than 0.01, 0.05 or 0.1. Alternatively, when comparing the computed test statistics and critical value, the null hypothesis has to be rejected if computed value is smaller than the critical value. Afterwards, the stationarity for the first difference is tested (that is, the ADF test is applied to the stationary series by the difference method). If p is less than 0.01, 0.05 or 0.1, then the series is stationary in the first difference with a lag = 2, so the series is integrated by the first order and the analysis can move to the second step. If not, the ADF test is used again on the series processed according to the difference method.
In order to verify the results of the ADF test, we will also apply the DF-GLS stationarity test, with the null hypothesis “Series has a unit root”. If the critical value is higher than the statistical test, then the null hypothesis is rejected.
Since the two tests are irrelevant for a 10% level, we also apply the Phillips–Perron (PP) and Ng Perron (NGP) tests. The only test that shows non-stationarity for 10% for the exgov variable is the Phillips–Perron test.
We apply the stationarity tests in the level (see Table 2).

Table 2.
Stationarity in the level.
It can be noticed that both series are non-stationary in the level for intervals of 1% and 5%. We will now test the stationarity in the first and second differences. The sgdp and sexgov series were calculated by using the first difference level method and the ssgdp and ssexgov series were determined with the help of the second difference level method, if testing will be needed for the second difference. Then, the above-mentioned tests are applied again (see Table 3).

Table 3.
Stationarity for the first difference.
As can be observed, in all the tests, the series are stationary in level 1, which means that we can apply the cointegration test (Table 4).

Table 4.
Johansen test for cointegration.
Since trace statistics are smaller than the critical value at r = 0 for both the trend model and the restricted trend model, the null hypothesis is accepted, meaning that there is no cointegration vector. Therefore, the gdp and exgov series are not cointegrated. There is no reason to believe that there was a significant influence of the evolution of government spending on GDP, during the analyzed period.
Many multiple testing problems in the time-series literature have been solved by defining an estimator that minimizes an information criterion with known asymptotic properties. Selecting the lag-length in an autoregressive model is probably the best-known example. Gonzalo and Pitarakis [69] and Aznar and Salvador [70] have shown that this approach can be applied to determine the number of cointegrating equations in a VECM. As in the lag-length selection problem, choosing the number of cointegrating equations that minimizes either the Schwarz–Bayesian information criterion (SBIC) or the Hannan and Quinn information criterion (HQIC) provides a consistent estimator of the number of cointegrating equations.
As noted in Table 5, the HQIC and SBIC criteria do not show that there could be a cointegration vector.

Table 5.
Johansen test while minimizing the information criterion.
Therefore, we can support the null hypothesis that the two analyzed series are not cointegrated.
4.2. Granger Testing According to Toda and Yamamoto Approach
We will test Granger causality, which can show if there is a short-term relationship in the variables’ changes. Theoretically, failure to reject the null hypothesis is equivalent to failing to reject the hypothesis that x does not Granger-cause y (Granger, 1969).
Since the series are not cointegrated and they are stationary at the second level, then we will use Toda and Yamamoto’s (1995) improved method.
The VAR model can be described with the help of the following equations:
The order of integration is tested for each time series. We apply the ADF test for gdp and exgov variables (Table 6). It can be observed that both series are stationary at level two I (2). We retain the value m = 2.

Table 6.
ADF test for gdp and exgov variables.
Next, we will determine the appropriate max length for the VAR model.
Three out of five tests show that p = 9. Even if we have two tests with lower values, it is advisable to take the highest value.
We test the VAR model for the serial correlation in residuals, applying the Lagrange-multiplier test (Table 7).

Table 7.
Lagrange-multiplier test.
This test gives no hint of model misspecification.
Therefore, since we have stationary series at the second level and the max length is 9, then p’ + m’ = 11.
We rewrite the VAR model:
We have the value of p’ + m’ = 11 for unrestricted VAR and p’ = 9 for restricted VAR.
The non-causality Granger for unrestricted VAR is further tested (see Table 8).

Table 8.
Granger causality test’s results.
The test shows that exgov is Granger causality for gdp (significant at 0.05 level), while gdp is Granger causality for exgov (significant at 0.1 level). Therefore, in the short term, there is causality in both directions for a 0.1 level of significance.
Additional to our analysis, we will test the impulse–response function (see Figure 2). In order to identify the effects of shocks on domestic product growth and on government spending, we will try to identify, as a matter of priority, as the Granger analysis suggested, whether GDP growth influences government spending growth. We will test the reverse path.
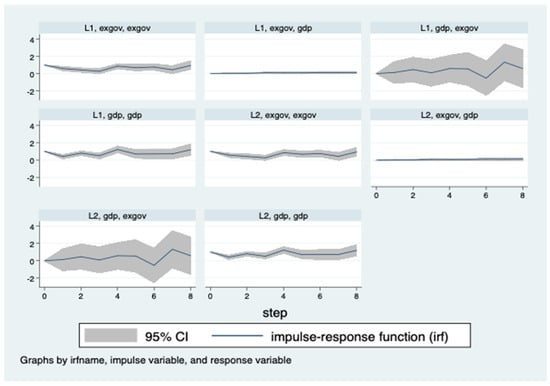
Figure 2.
Results of testing the impulse–response function.
4.3. Policy Implications
Over the last half of the 20th century, economic growth represented a target for all governments’ working agenda. Under the influence of the Keynesian theories that proliferated and had relative success during the 1950s and the 1970s, states developed complicated public systems to implement Keynes’ ideas. The fragile liberal critic from that period failed to temper this enthusiasm. A vicious circle occurred. The need for more serious involvement of the state in issues considered to be vital, such as infrastructure, education, health, defense, research-innovation, etc., was argued. Abandoning the idea that stimulating effective demand is the engine of growth, endogenous growth theories have largely supported the view that the state should allocate resources for those sectors with the highest impact on sustainable growth. Thus, starting from Solow’s conclusions, according to which most economic growth is based on innovation and technical progress, researchers have provided models in which the role of public spending is extremely important. Thus, whether we speak about the Keynesian or the neoclassical view, public policies and the state budget have been considered essential elements in sustaining wellbeing.
Despite all of these approaches, other studies, and also our research, confirmed that there is no clear evidence that, in the long term, there is a link between increased public spending and economic growth, for developing countries. As analysis of the shock response shows, the response effect from GDP tends asymptotically to zero, so it is quite weak. On the contrary, GDP growth may influence, albeit with a delayed response, the increase in government spending.
As the above-mentioned theories cannot be supported by empirical evidence, then the governments and, in our case, the Romanian government, should be much more careful in how they approach the problem of public finances. Since no cointegration vector can be found between the two variables, the whole scenario must be rethought. The smartest decision would be to continuously reduce the public sector, in order to avoid the eviction phenomenon through which the resources from the private sector could be redirected to the public sector. The efficiency of the private sector is clearly superior and this reality should dominate the criteria of taxation and the shaping of public budgets.
Considering that the restructuring of the public sector is an objective only possible to achieve in the long run, the Romanian government should pay more attention to the destination of public spending. The focus should be on the major implications in terms of employment, the leverage of decisional and functional interdependence and the dependence behavior on public money, developed over time. We already know, from the long-term experience of developed countries, that stimulating investments has the strongest multiplying impact on growth and that social spending produces increases in consumers’ demand without an impact on the growth of domestic supply. In open economies, any stimulation of consumers’ demand tends to be balanced with supply, by increasing the trade deficit and, implicitly, the balance of payments. This makes a Keynesian-type growth impossible to achieve. Considering that Romania, as with many other states, has a huge trade deficit and its external debt has increased considerably, especially in recent years, the government should be concerned by the structure of the current account and should insist more on policies that stimulate supply.
In Romania, there is a shortage in domestic supply. The destruction of the capital in the 1990s, the lack of financial capital necessary to start new businesses, the hesitant legislative framework and the incoherence of the political decisions of that period led to an insufficient maturation of domestic production capacities. The attitude of rejecting foreign capital up to 2004 made Romania lag behind most of its former socialist neighbors. This situation was reflected in a household welfare gap, high unemployment rates and a huge need for social assistance, which put pressure on the country’s budget and, perhaps most importantly, led to a change in the behavior of individuals, negatively influencing their attitude towards work and entrepreneurial initiative.
Therefore, beyond the popularity governments can gain by implementing generous social assistance programs, with short-term effects on stimulating demand and, implicitly, growth, one should be aware that the nation’s interest is to achieve a stable growth in the long term. Or, as it results from our study, there is no clear evidence that the involvement of the state through budgetary resources could lead to such an effect.
Even if there is evidence of short-term causality between government spending and GDP increase, they are still quite weak. Therefore, politicians should take into account the long-term interests of the country and its citizens. Unfortunately, as long as policymakers are politicians, they will subordinate their decisions to the purpose of being re-elected, as Buchanan and Tullock [71] stated.
Meanwhile, it can be mentioned that, due to the existence of short-term causality, public spending can be used as a cyclical adjustment tool [60]. If the increase in expenses stimulates economic growth in the short term, then this mechanism can be used in the opposite direction, in order to temper the expansion periods, specific to the Romanian economy. As it happened during the period 2004–2008, in these phases, too much tension accumulates, which, eventually, can severely destabilize the economy (as noticed during the period 2009–2011). Thus, the fact that government spending is Granger-causes for gross domestic product shows that countercyclical policies can be successful, although quite temperate, as the shock response shows. Moreover, this idea is supported by the fact that the causality can also be noticed in the opposite direction. The economic growth from the expansion period would allow the accumulation of important budgetary reserves that could be used during recession times, thus alleviating the economic and social shocks.
Moreover, as mentioned before, in the absence of long-term evidence regarding the meaning and magnitude of the budget spending’s influence on the economy’s positive response, the government should better analyze the level of involvement in sizing the effective demand. Policies to encourage investment, to attract foreign capital, and to educate the population in an entrepreneurial spirit could be considered more appropriate, especially since there are so many opportunities generated by the possibility of accessing European funds.
5. Conclusions
In our attempt to test the dynamics of the link between the increase in government spending and the growth of gross domestic product in Romania, from the perspective of Wagner’s law and Keynes’ hypothesis, we have shown that there is no vector of cointegration between the variables in the long-term equilibrium.
Instead, in the short term, both theories are validated. We found that not only does GDP represent a Granger cause for government spending, but also vice versa. Therefore, our results validate the liberal criticism of the state’s involvement in supporting economies. As the critics of the monetarist school said, the effect of multiplying government spending on national income is short-term. The long-term effect appears under the action of inflationary macroeconomic bottlenecks.
Moreover, the fact that Wagner’s law was not validated in the long run supports the theory of the inefficient state, largely debated by the Public Choice School. Although economic growth may attract additional budgetary resources, allocating them to the public sector often leads to inefficiency than to increased welfare.
Our study considered the link between collective government spending and GDP. In future research, a possible development of this model could take into account the destination of this spending, in order to test if there are certain types of expenditures that could provide a clearer proof of the dynamics of the link (particular attention must be paid to education and health spending). These analyses may underline the presence of some cointegration vectors, which would confirm the hypotheses of the Human Capital Theory’s models.
Author Contributions
The authors contributed equally to this paper. L.D. and C.C.P. described the context of the analysis and conducted the literature review. C.C.P. developed the research approach and performed the data analysis. C.C.P., with the help of L.D., described the main results. L.D. and C.C.P. formulated the main conclusions. L.D. edited the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wagner, A. Finanzwissenschaft; C.F. Winter: Leipzig, Germany, 1890. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A. An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1776; Volume one. [Google Scholar]
- Peacock, A.T.; Wiseman, J. The Growth of Public Expenditure in the United Kingdom; Allen & Unwin: Crows Nest, Australia, 1967; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Musgrave, R.A. Cost-benefit analysis and the theory of public finance. J. Econ. Lit. 1969, 7, 797–806. [Google Scholar]
- Michas, N.A. Wagner’s Law of public expenditures: What is the appropriate measurement for a valid test? Public Financ Financ. Publiques 1975, 30, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, A.J. Wagner’s law: An econometric test for Mexico, 1925–1976. Natl. Tax J. 1980, 33, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.R. Poverty in Bangladesh: A Consequence of and a Constraint on Growth. Bangladesh Dev. Stud. 1990, 18, 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Pryor, F.L. Public Expenditures in Communist and Capitalist Nations; RD Irwin: Homewood, IL, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Goffman, I.J. Empirical testing of Wagner’s law-technical note. Public Finance Financ. Publiques 1968, 23, 359–366. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.P. Public Expenditure and Economic Growth a Time-Series Analysis. Public Finance Financ. Publiques 1967, 22, 423–454. [Google Scholar]
- Afzal, M.; Abbas, Q. Wagner’s law in Pakistan: Another look. J. Econ. Int. Finance 2009, 2, 012–019. [Google Scholar]
- Keynes, J.M. The General Theory of Money, Interest and Employment; Macmillan: London, UK, 1936. [Google Scholar]
- Ram, R. Government size and economic growth: A new framework and some evidence from cross-section and time-series data. Am. Econ. Rev. 1986, 76, 191–203. [Google Scholar]
- Ahsan, S.M.; Kwan, A.C.; Sahni, B.S. Cointegration and Wagner’s hypothesis: Time series evidence for Canada. Appl. Econ. 1996, 28, 1055–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, J.M.; Hutton, P.A. On the casual relationship between government expenditures and national income. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1990, 72, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Sahni, B.S. Causality between public expenditure and national income. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1984, 66, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, J.R.; Keleher, R.E.; Russek, F.S. The scale of government and economic activity. South. Econ. J. 1990, 13, 142–183. [Google Scholar]
- Landau, D. Government expenditure and economic growth: A cross-country study. South. Econ. J. 1983, 49, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, D. Government and economic growth in the less developed countries: An empirical study for 1960–1980. Econ. Dev. Cult. Change 1986, 35, 35–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrakdar, S.; Demez, S.; Yapar, M. Testing the Validity of Wagner’s Law: 1998–2004, The Case of Turkey. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 195, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gül, E.; Yavuz, H. New Public Expenditure and Growth: The period 1996–2008 in Turkey. J. Finance 2010, 158, 164–178. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, P. Causality between Public Expenditure and Economic Growth: The Indian Case. Int. J. Econs. Mgmt. 2013, 7, 335–347. [Google Scholar]
- Bohl, M.T. Some international evidence on Wagner’s Law. Public Finance Financ. Publiques 1996, 51, 185–200. [Google Scholar]
- Chletsos, M.; Kollias, C. Testing Wagner’s law using disaggregated public expenditure data in the case of Greece: 1958–93. Appl. Econ. 1997, 29, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghali, K.H. Public investment and private capital formation in a vector error-correction model of growth. Appl. Econ. 1998, 30, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, J.; Iqbal, A.; Siddiqi, M.W. Cointegration-causality analysis between public expenditures and economic growth in Pakistan. Eur. J. Soc. Sci. 2010, 13, 556–565. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Faris, A.F. Public expenditure and economic growth in the Gulf Cooperation Council countries. Appl. Econ. 2002, 34, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.Y.; Tang, J.H.; Lin, E.S. The impact of government expenditure on economic growth: How sensitive to the level of development? J. Policy Model. 2010, 32, 804–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, N.; Hansen, P. Health care spending and economic output: Granger causality. Appl. Econ. Lett. 2001, 8, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.; Dhawan, U.; Lee, H.Y. Testing Wagner versus Keynes using disaggregated public expenditure data for Canada. Appl. Econ. 1999, 31, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighodaro, C.A.; Oriakhi, D.E. Does the Relationship between Government Expenditure and Economic Growth Follow Wagner’s Law in Nigeria. Ann. Univ. Petrosani. Econ. 2010, 10, 185–198. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Bader, S.; Abu-Qarn, A.S. Government expenditures, military spending and economic growth: Causality evidence from Egypt, Israel, and Syria. J. Policy Model. 2003, 25, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quah, D. Empirical cross-section dynamics in economic growth. Eur. Econ. Rev. 1993, 37, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalles, J. Wagner’s law and governments’ functions: Granularity matters. J. Econ. Stud. 2019, 46, 446–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babatunde, M.A. A bound testing analysis of Wagner’s law in Nigeria: 1970–2006. Appl. Econ. 2011, 43, 2843–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, R. Wagner’s hypothesis in time-series and cross-section perspectives: Evidence from “real” data for 115 countries. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1987, 69, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afxentiou, P.C.; Serletis, A. Government expenditures in the European Union: Do they converge or follow Wagner’s Law? Int. Econ. J. 1996, 10, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.I.; Gordon, D.V.; Akuamoah, C. Keynes versus Wagner: Public expenditure and national income for three African countries. Appl. Econ. 1997, 29, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abizadeh, S.; Yousefi, M. An empirical analysis of South Korea’s economic development and public expenditures growth. J. Socio Econ. 1998, 27, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagdigen, M.; Cetintas, H. Causality between public expenditure and economic growth: The Turkish case. J. Econ. Soc. Res. 2004, 1, 53–72. [Google Scholar]
- Başar, S.; Aksu, H.; Temurlenk, M.S.; Polat, Ö. Government Spending and Economic Growth Relationship in Turkey: A Bound Testing Approach. Atatürk Üniv. Sos. Bilimler Enstitüsü Derg. 2009, 13, 301–314. [Google Scholar]
- Rauf, A.; Qayum, A.; Zaman, K.U. Relationship between public expenditure and national income: An empirical investigation of Wagner’s law in case of Pakistan. Acad. Res. Int. 2012, 2, 533. [Google Scholar]
- Jiranyakul, K.; Brahmasrene, T. The relationship between government expenditures and economic growth in Thailand. J. Econ. Econ. Educ. Res. 2007, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Pradhan, R.P. Wagner’s Law: Is it Valid in India? IUP J. Public Finance 2007, 2, 7–20. [Google Scholar]
- Magazzino, C. Wagner’s Law in Italy: Empirical Evidence from 1960 to 2008; University Library of Munich: Munich, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.F.; Chrsquo, K.S. The Granger causality between health expenditure and income in Southeast Asia economies. Afr. J. Bus. Manag. 2011, 5, 6814–6824. [Google Scholar]
- Nurudeen, A.; Usman, A. Government expenditure and economic growth in Nigeria, 1970–2008: A disaggregated analysis. J. Bus. Econ. 2010, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, E.; Lai, K.S. Government spending and economic growth: The G-7 experience. Appl. Econ. 1994, 26, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexiou, C. Government spending and economic growth: Econometric evidence from the South Eastern Europe (SEE). J. Econ. Soc. Res. 2009, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Dritsaki, C.; Dritsaki, M. Government expenditure and national income: Causality tests for twelve new members of EE. Rom. Econ. J. 2010, 13, 67–89. [Google Scholar]
- Braşoveanu, L.O. The impact of defense expenditure on economic growth. Rom. J. Econ. Forecast. 2010, 148, 148–167. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.C.; Huang, B.N.; Yang, C.W. Military expenditure and economic growth across different groups: A dynamic panel Granger-causality approach. Econ. Model. 2011, 28, 2416–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzuner, G.; Bekun, F.V.; Akadiri, S.S. Public Expenditures and Economic Growth: Was Wagner Right? Evidence from Turkey. Acad. J. Econ. Stud. 2017, 3, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Sagdic, E.N.; Sasmaz, M.U.; Tuncer, G. Wagner versus Keynes: Empirical Evidence from Turkey’s Provinces. Panoeconomicus 2020, 67, 657–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atilgan, E.; Kilic, D.; Ertugrul, H.M. The dynamic relationship between health expenditure and economic growth: Is the health-led growth hypothesis valid for Turkey? Eur J. Health Econ. 2017, 18, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, U.; Habimana, O. Military Spending and Economic Growth in Turkey: A Wavelet Approach. Defence Peace Econ. 2021, 32, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunc, O.F.; Aydın, C. The relationship between optimal size of government and economic growth: Empirical evidence from Turkey, Romania and Bulgaria. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 92, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingxiao, W.A.N.G.; Peculea, A.D.; Xu, H. The relationship between public expenditure and economic growth in Romania: Does it obey Wagner’s or Keynes’s Law? Theor. Appl. Econ. 2016, 23, 41–52. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. From Uneven Growth to Inclusive Development: Romania’s Path to Shared Prosperity. Systematic Country Diagnostic; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/29864 (accessed on 10 April 2021).
- Bostan, I.; Onofrei, M.; Popescu, C.; Lupu, D.; Firtescu, B. Efficiency and Corruption in Local Counties: Evidence from Romania. Lex Localis 2018, 16, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simionescu, M.; Lazányi, K.; Sopková, G.; Dobeš, K.; Balcerzak, A.P. Determinants of economic growth in V4 countries and Romania. J. Compet. 2017, 9, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INS. Quarterly Gross Domestic Product—Seasonally Adjusted Series. National Institute of Statistics Portal. 2018. Available online: https://insse.ro/cms/en/content/gross-domestic-product (accessed on 11 December 2019).
- INS. Collective Final Consumption Expenditure. National Institute of Statistics Portal. 2018. Available online: https://insse.ro/cms/en/content/gross-domestic-product (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- Johansen, S. Statistical analysis of cointegration vectors. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 1988, 12, 231–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, S. Identifying restrictions of linear equations with applications to simultaneous equations and cointegration. J. Econ. 1995, 69, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, C.W.J. Co-Investigated Variables and Error-Correction Models; Working Paper; University of California: San Diego, CA, USA, 1983; pp. 83–113. [Google Scholar]
- Toda, H.Y.; Yamamoto, T. Statistical inference in Vector Autoregressions with possibly integrated processes. J. Econ. 1995, 66, 225–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Lin, C.F. Unit root tests in panel data: Asymptotic and finite-sample properties. J. Econ. 2002, 108, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalo, J.; Pitarakis, J.Y. Specification via model selection in vector error correction models. Econ. Lett. 1998, 60, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar, A.; Salvador, M. Selecting the Rank of the Cointegration Space and the Form of the Intercept Using an Information Criterion. Econ. Theory 2002, 18, 926–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, J.M.; Tullock, G. The Calculus of Consent; University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1962; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).