Rating Regulatory Mechanism Effect Promotion under the Environmental Issuance Effects: Based on the Incentive Difference Hotelling Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Review of the Literature
3. The Incentive Difference Hotelling Model
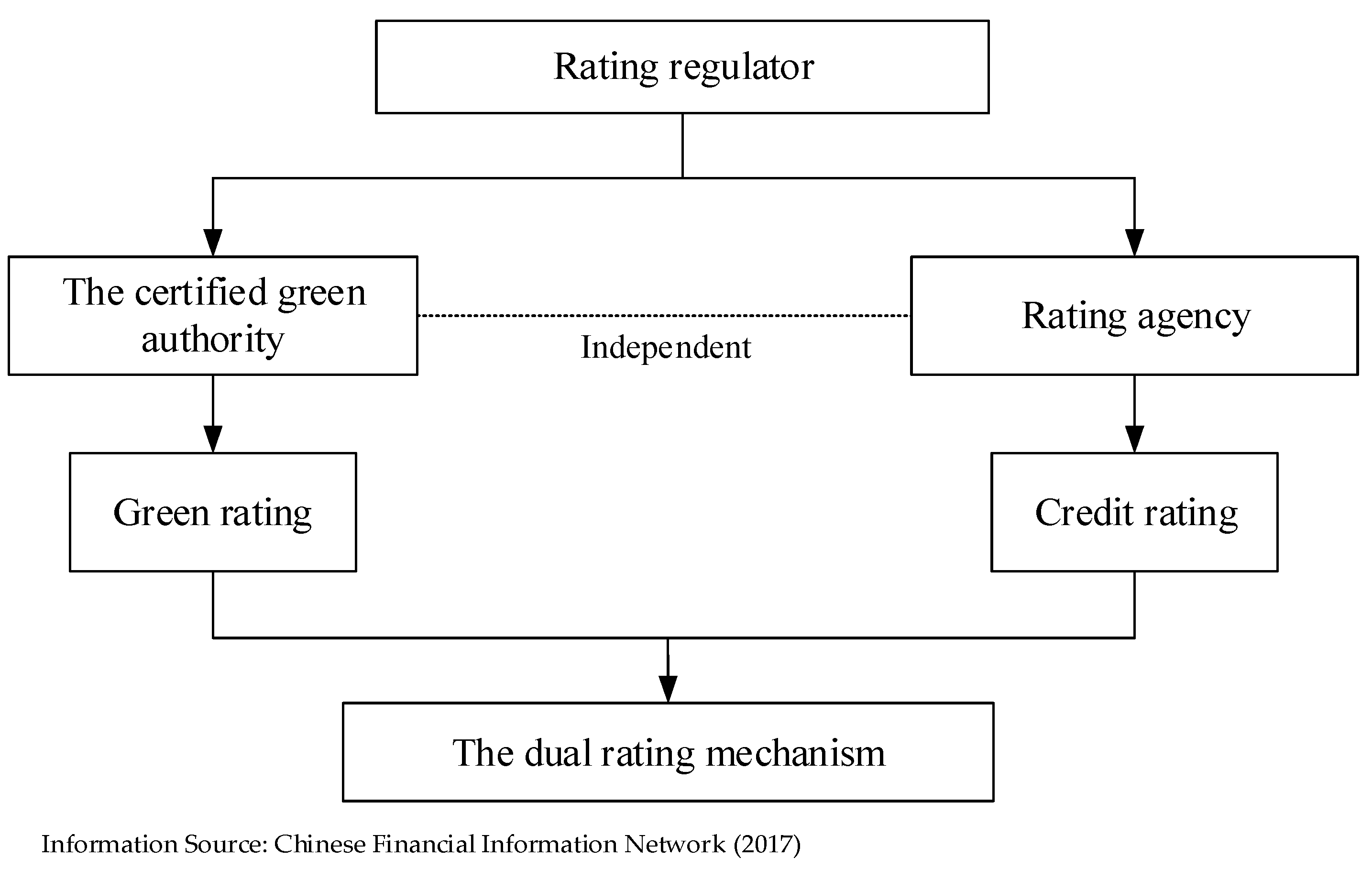
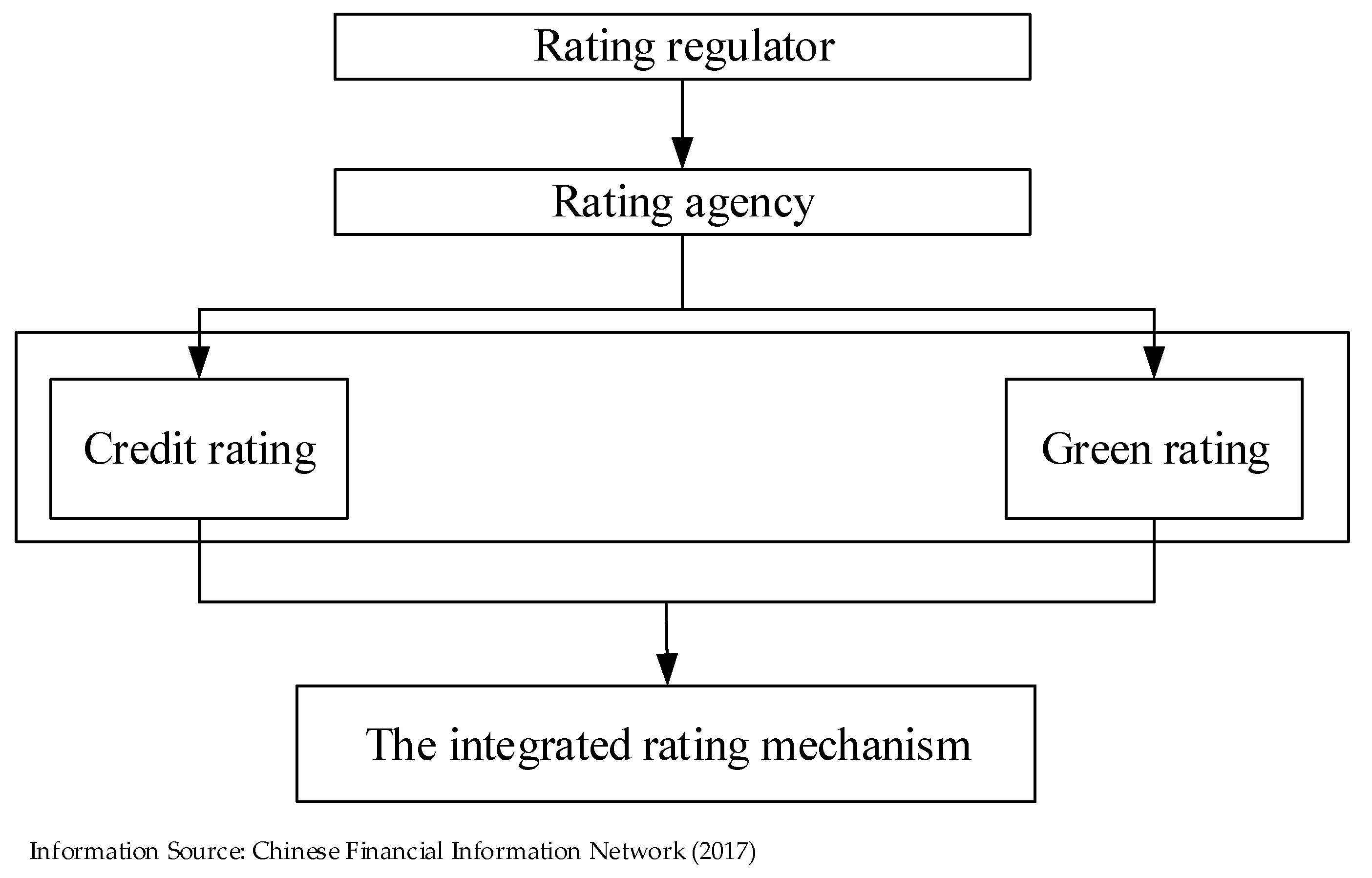
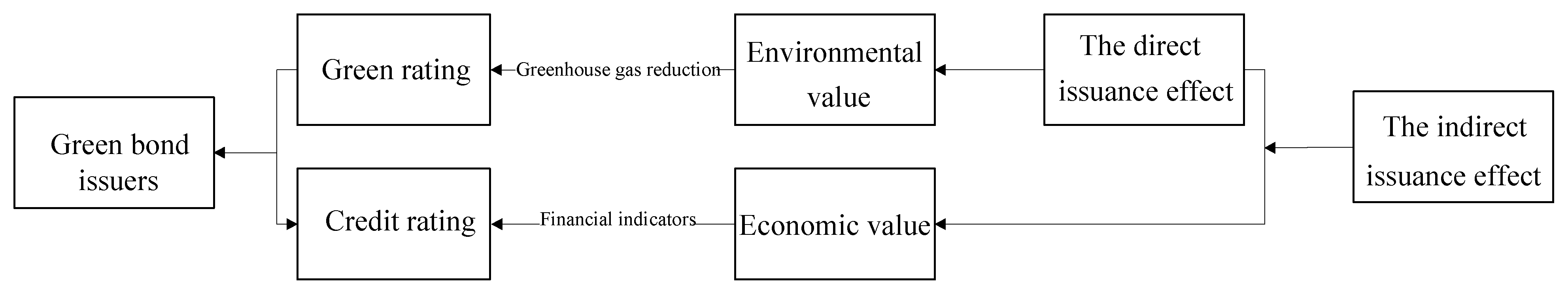
3.1. Model Assumptions
3.2. Construction of the Incentive Difference Hotelling Model
4. Analysis of the Factors in the Incentive Difference Hotelling Model
4.1. The First Stage of Game Model
4.2. The Second Stage of Game Model
5. Numerical Analysis and Simulations
5.1. Data Assignment
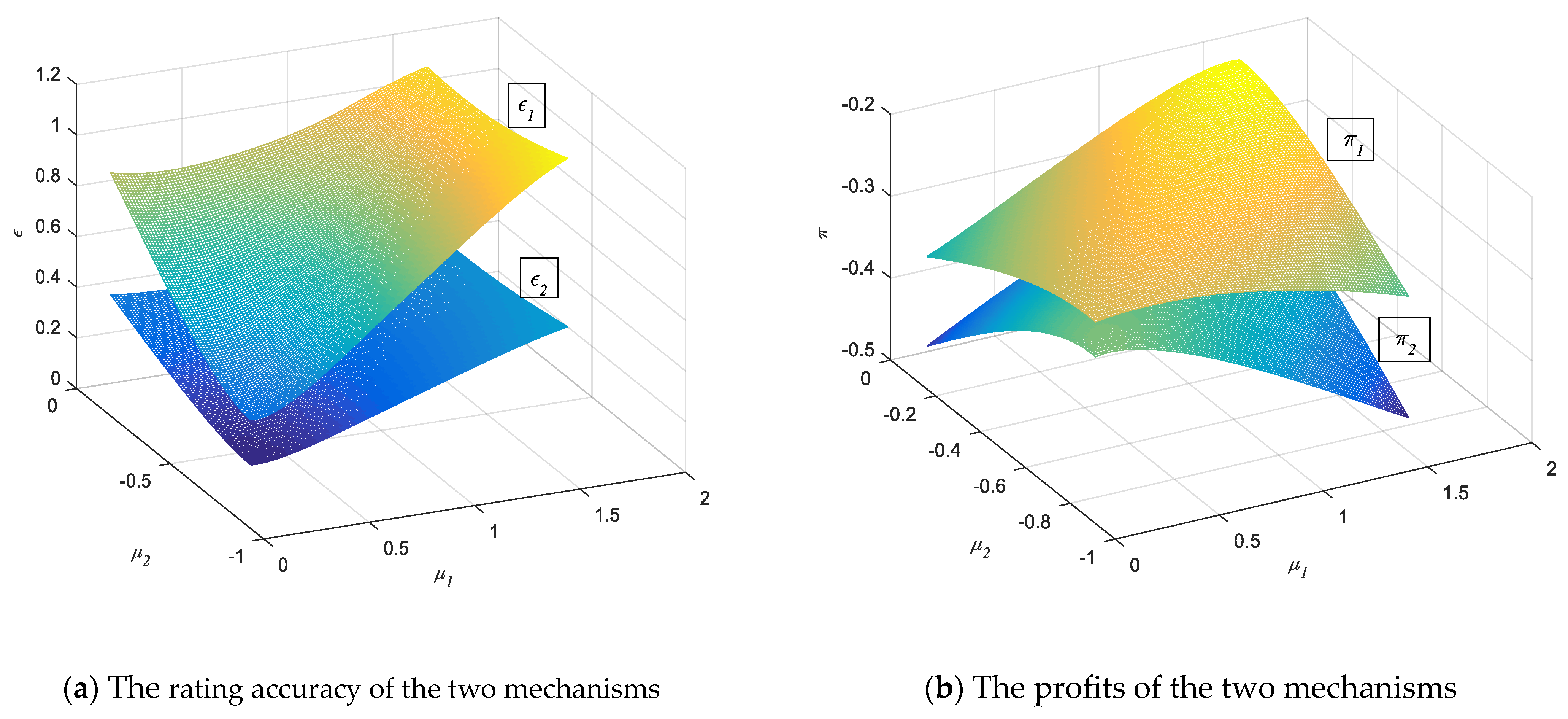
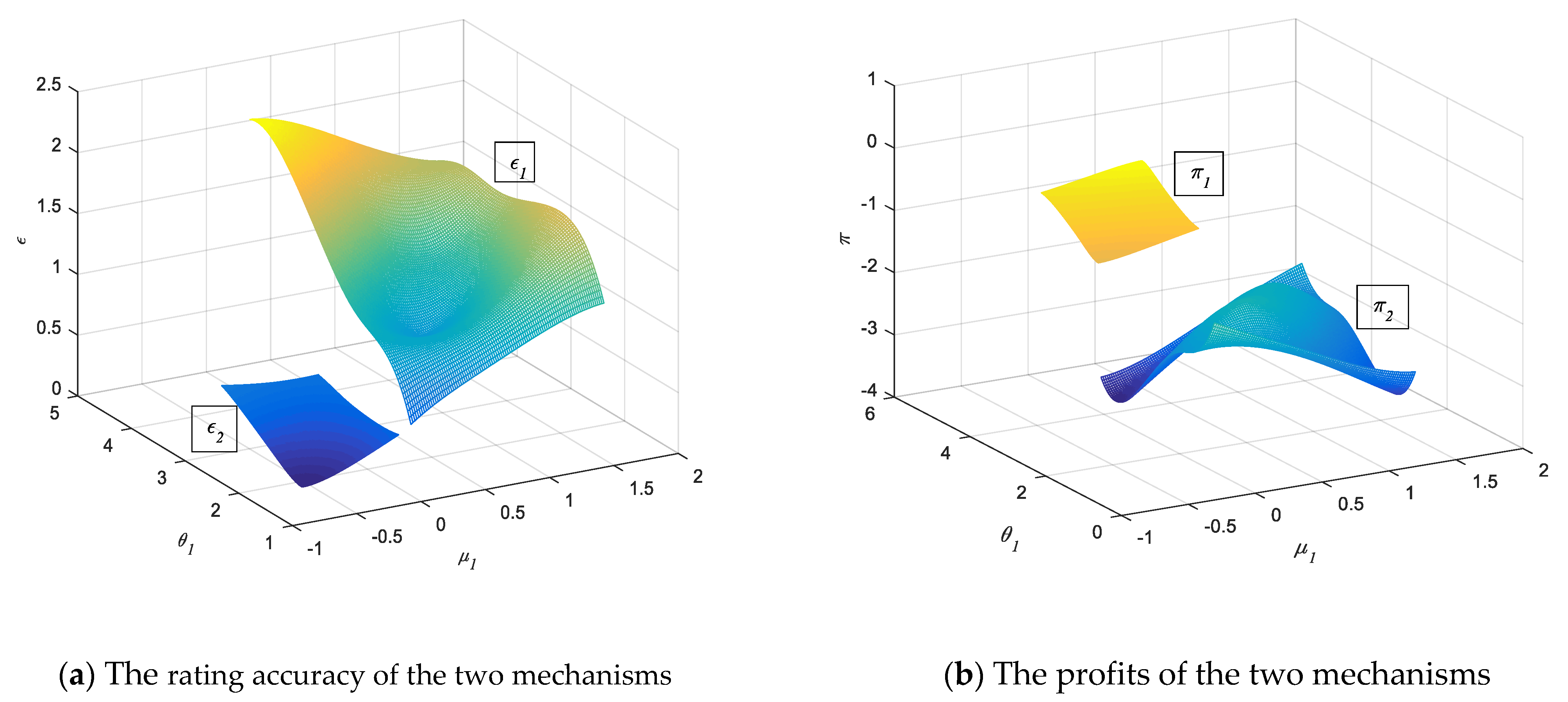
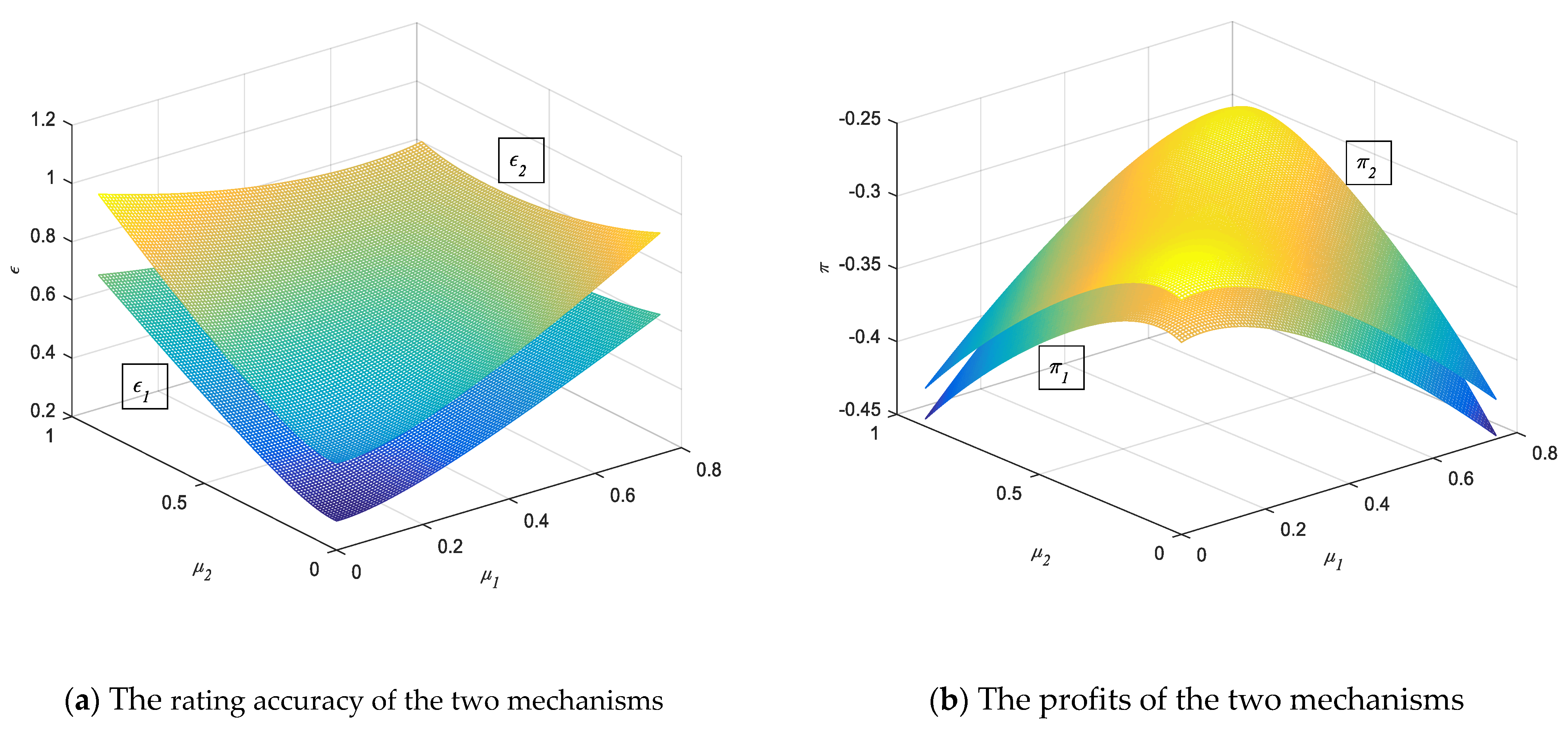
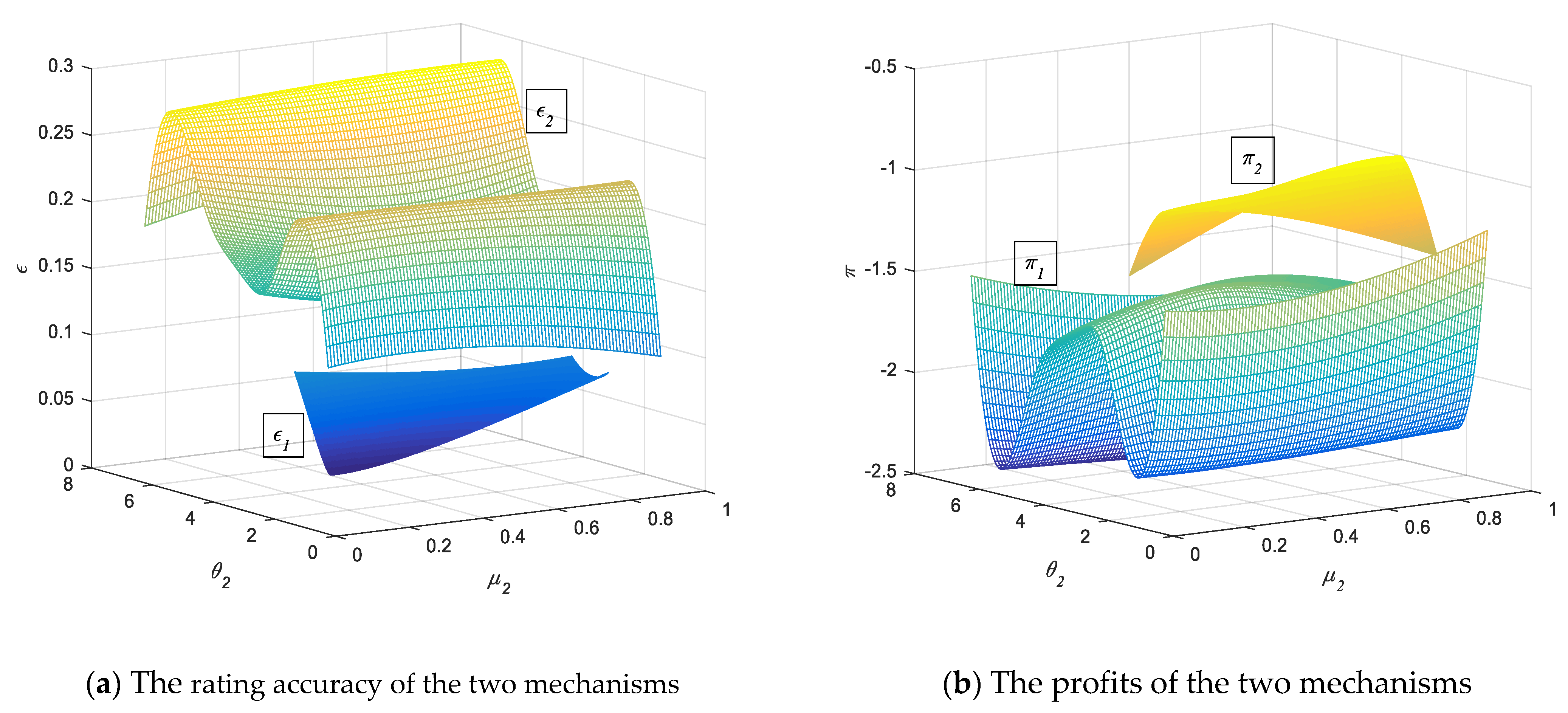
5.2. Simulation of Rating Regulatory Mechanism Effect under Proposition 1
5.3. Simulation of Rating Regulatory Mechanism Effect under Proposition 2
5.4. Numerical Analysis of Rating Regulatory Mechanism Effect under Proposition 3
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banga, J. The green bond market: A potential source of climate finance for developing countries. J. Sustain. Financ. Investig. 2018, 9, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trompeter, L. Green is good: How green bonds cultivated into Wall Street’s environmental paradox. Sustain. Dev. Law Policy 2017, 17, 30–43. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. Green Bond Series Study—Evaluation and Certification of Green Bond; China Bond Rating Co., Ltd.: Shanghai, China, 2020; pp. 6–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Problems and Optimization of the Indicator System of the Third-Party Evaluation Method for Green Bonds; Northwest Normal University: Chongqing, China, 2018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gu, M. Research on the Third-Party Certification Method and Function in Green Bond Issuance; Nankai University: Nanjing, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Climate Bonds Initiative. Green Bond Market SummaryQ3 2020. Clim. Bonds 2020, 11, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C. Analysis of the impact of third-party certification on the issuance cost of green bonds. Bond 2019, 4, 67–71. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers, T.; Packer, F. Green bond finance and certification. BIS Q. Rev. 2017, 1, 89–104. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, C. Games between e-finance and traditional banking: Based on a three-stage difference Hotelling model under double oligarch monopolization. Syst. Eng. 2016, 34, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.Q.; Wang, H. The effect of environmental regulation on green technology progress of “local-neighborhood”. China Ind. Econ. 2019, 1, 100–118. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, S.R.; Jin, G.; Fang, X. Does environmental regulation cause pollution to be transferred nearby? China Ind. Econ. 2017, 5, 46–61. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.; Zhang, W.G.; Feng, Z.B. How to “remove” resource mismatch in environmental regulation. China Ind. Econ. 2017, 4, 115–134. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, S.; Zhang, K.; Dou, J.M. Energy saving and emission reduction effects of economic agglomeration: Theory and experience of China. Manag. World 2019, 1, 36–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, B.Q.; Tan, R.P. China’s economic agglomeration and green economic efficiency. Econ. Res. J. 2019, 2, 119–132. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, M.; Li, G.; Peng, J.C. Study on the spatial-temporal differentiation of green TFP in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Manag. World 2018, 34, 178–179. [Google Scholar]
- Bolton, P.; Freixas, X.; Shapiro, J. The credit ratings game. J. Financ. 2012, 67, 85–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manso, G. Feedback effects of credit ratings. J. Financ. Econ. 2013, 109, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L. Game Analysis on the evolution of public private partnership project supervision considering reputation. J. Syst. Eng. 2013, 32, 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, B.; Milbourn, T. How did increased competition affect credit ratings? J. Financ. Econ. 2011, 101, 93–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathis, J.; Mc Andrews, J.; Rochet, J.C. Rating the raters: Are reputation concerns powerful enough to discipline rating agencies? J. Monet. Econ. 2009, 56, 657–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolper, A. Regulation of credit rating agencies. J. Bank. Financ. 2009, 33, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.L.; Zhu, S.; Chen, G. The impact of bond default on credit ratings agencies: Analysis based on bond default in Chinese bond market. Financ. Res. 2017, 441, 130–144. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Q.F. Dynamic analysis on the evolution of enterprise environment compliance behavior under dynamic punishment mechanism. J. Syst. Manag. 2017, 26, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Tian, Y. Incentive and constraint regulations of rating inflation in collusion over the separation of economic cycles—Markov rating shopping dual reputation model. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotelling, H. Stability in competition. Econ. J. 1929, 39, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Huo, Y.; Zhang, X. Endogenous third-degree price discrimination in Hotelling model with elastic demand. J. Econ. 2018, 2, 125–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Chen, Z.; Yang, C. Green innovative strategy of logistics enterprises based on Hotelling expansion model. J. Interdiscip. Math. 2018, 21, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, D.R. Economic accounting in the simple Hotelling model. Resour. Energy Econ. 2018, 51, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, S.W.; Huang, B. Embeddedness effect in environmental policy benefit evaluation: Based on a case of haze and dust control policies in Beijing. China Ind. Econ. 2016, 8, 25–41. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, E. Research on Substitution Sequential Auction and Information Disclosure with Hotelling Difference; Huazhong University of Science and Technology: Wuhan, China, 2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.; Zhu, J.; Sheng, Z. Dynamic Incentive Mechanism of Factory Prefabrication Based on Double Reputation. J. Syst. Manag. 2017, 26, 338–345. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Tian, Y.X. Research on incentive and constraint mechanism of rating agencies collusion under economic cycle separation. J. Syst. Eng. 2020, 2, 210–221. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
| Indicators | Values |
|---|---|
| Market share of rating agencies | 0.5 |
| Market share of certified green authorities | 0.3 |
| Rating accuracy in the dual rating mechanism | 0.3 |
| Rating accuracy in the integrated rating mechanism | 0.5 |
| Green rating accuracy in the dual rating mechanism | 0.5 |
| Green rating accuracy in the integrated rating mechanism | 0.4 |
| Rating costs of rating agencies | 0.3 |
| Rating costs of certified green authorities | 0.6 |
| The total reputation of rating agencies and certified green authorities in the dual rating mechanism | 0.5 |
| The total reputation of rating agencies and certified green authorities in the integrated rating mechanism | 0.2 |
| Regulatory punishments | 0.5 |
| Indicators | The First Stage | The Second Stage |
|---|---|---|
| The direct effect in the dual rating mechanism | [0.1, 1.6] | [0.1, 1.6] |
| The direct effect in the integrated rating mechanism | [−1.025, −0.125] | [−0.82, −0.07] |
| The indirect effect in the dual rating mechanism | 1 | [1.4286, 4.4286] |
| The indirect effect in the integrated rating mechanism | 1 | [1.25, 2.75] |
| Indicators | The First Stage | The Second Stage |
|---|---|---|
| The direct effect in the dual rating mechanism | [0, 0.75] | [0, 0.75] |
| The direct effect in the integrated rating mechanism | [0, 1] | [0, 1] |
| The indirect effect in the dual rating mechanism | 1 | (1, 1.35] |
| The indirect effect in the integrated rating mechanism | 1 | (1, 6.25] |
| Indicators | The First Stage | The Second Stage |
|---|---|---|
| The direct effect in the dual rating mechanism | 7.82 | 7.82 |
| The direct effect in the integrated rating mechanism | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| The indirect effect in the dual rating mechanism | 1 | 1.1188 |
| The indirect effect in the integrated rating mechanism | 1 | 3.1319 |
| Rating accuracy in the dual rating mechanism | 4.21 | 4.7100 |
| Rating accuracy in the integrated rating mechanism | 1.10 | 1.3596 |
| Profit in the dual mechanism | 0.9392 | 1.0503 |
| Profit in the integrated mechanism | 0.0670 | 0.1846 |
| Indicators | The First Stage | The Second Stage |
|---|---|---|
| The direct effect in the dual rating mechanism | 3.5870 | 3.5870 |
| The direct effect in the integrated rating mechanism | 8.7250 | 8.7250 |
| The indirect effect in the dual rating mechanism | 1 | 1.1200 |
| The indirect effect in the integrated rating mechanism | 1 | 1.1319 |
| Rating accuracy in the dual rating mechanism | 2.0935 | 2.3447 |
| Rating accuracy in the integrated rating mechanism | 3.9900 | 4.5164 |
| Profit in the dual rating mechanism | 0.2499 | 0.2713 |
| Profit in the integrated rating mechanism | 0.3667 | 0.2786 |
| Situation | The Direct Issuance Effect | The Indirect Issuance Effect | The Choice of Mechanisms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-equilibrium state | The dual rating mechanism | ||
| The integrated rating mechanism | |||
| Equilibrium state | The dual rating mechanism | ||
| The integrated rating mechanism |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, H.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, L.; Meng, W. Rating Regulatory Mechanism Effect Promotion under the Environmental Issuance Effects: Based on the Incentive Difference Hotelling Model. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5368. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105368
Zhao H, Tian Y, Zhou X, Zhang L, Meng W. Rating Regulatory Mechanism Effect Promotion under the Environmental Issuance Effects: Based on the Incentive Difference Hotelling Model. Sustainability. 2021; 13(10):5368. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105368
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Hanyi, Yixiang Tian, Xiangyun Zhou, Luping Zhang, and Wei Meng. 2021. "Rating Regulatory Mechanism Effect Promotion under the Environmental Issuance Effects: Based on the Incentive Difference Hotelling Model" Sustainability 13, no. 10: 5368. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105368
APA StyleZhao, H., Tian, Y., Zhou, X., Zhang, L., & Meng, W. (2021). Rating Regulatory Mechanism Effect Promotion under the Environmental Issuance Effects: Based on the Incentive Difference Hotelling Model. Sustainability, 13(10), 5368. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105368








