Probiotics in Animal Husbandry: Applicability and Associated Risk Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Significance of Probiotics in Animal Health
2.2. Probiotics as a Viable Alternative to In-Feed Antibiotics
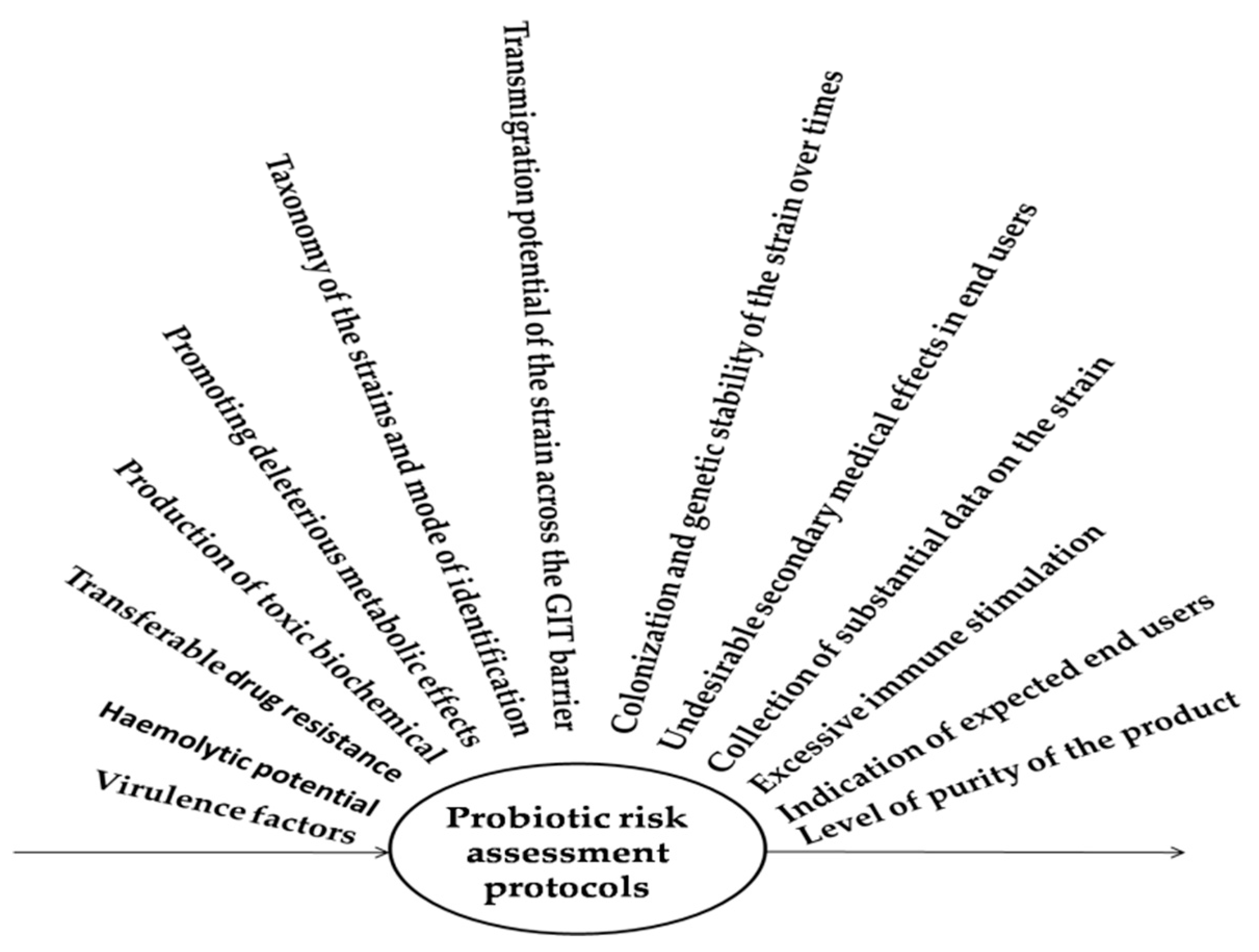
2.3. Established Risk Assessment Protocol for the Probiotics
2.4. Adverse Effects Due to Application of Probiotics
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Celiberto, L.S.; Bedani, R.; Rossi, E.A.; Cavallini, D.C. Probiotics: The scientific evidence in the context of inflammatory bowel disease. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C.M.; Gong, J. Issues deserve attention in encapsulating probiotics: Critical review of existing literature. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Llano, D.G.; Gil-sánchez, I.; Esteban-fernández, A.; Ramos, A.M.; Fernández-díaz, M.; Cueva, C.; Moreno-arribas, M.V.; Bartolomé, B. Reciprocal beneficial effects between wine polyphenols and probiotics: An exploratory study. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2016, 243, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushelaibi, A.; Al-mahadin, S.; El-tarabily, K.; Shah, N.P.; Ayyash, M. Characterization of potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria isolated from camel milk. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 79, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, B.; Rani, G.S.; Kumar, B.K.; Chandrasekhar, B.; Krishna, K.V.; Devi, T.A.; Bhima, B. Evaluating the probiotic and therapeutic potentials of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain (OBS2) isolated from fermented nectar of toddy palm. AMB Express 2017, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalheiro, C.P.; Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Herrero, A.M.; Jiménez-Colmenero, F.; Ragagnin, M.C.; Martins, F.L.L. Application of probiotic delivery systems in meat products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 46, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Kim, I. Effect of direct-fed microbial on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, fecal noxious gas emission, fecal microbial flora and diarrhea score in weanling pigs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2015, 200, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, R.; Tran, H.; Kim, I. Effects of probiotic supplementation in different nutrient density diets on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, blood profiles, fecal microflora and noxious gas emission in weaning pig. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.I.; Sadekuzzaman, M.; Ha, S.D. Probiotics as potential alternative biocontrol agents in the agriculture and food industries: A review. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Estellé, J.; Kiilerich, P.; Ramayo-Caldas, Y.; Xia, Z.; Feng, Q.S.; Pedersen, A.Ø.; Kjeldsen, N.J.; Liu, C. A reference gene catalogue of the pig gut microbiome. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Tawab, M.M.; Youssef, I.M.; Bakr, H.A.; Fthenakis, G.C.; Giadinis, N.D. Role of probiotics in nutrition and health of small ruminants. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2016, 19, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Isolauri, E.; Salminen, S.; Ouwehand, A.C. Probiotics. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2004, 18, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, C.E.; Seo, W.T.; Cho, K.M. Enhanced antioxidant effect of black soybean by cheonggukjang with potential probiotic Bacillus subtilis CSY191. Korean J. Microbiol. 2013, 49, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.; Vidal, L.; Ares, G.; Walter, E.H.M.; Rosenthal, A.; Deliza, R.S. Microbiological and physicochemical screening of probiotic cultures for the development of non-fermented probiotic milk. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 79, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardeau, M.; Vernoux, J. Overview of the use of probiotics in the feed/food chain. Probiotics: Production, evaluation and uses in animal feed. Kerala India Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2009, 2009, 15–45. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardeau, M.; Vernoux, J.P. Overview of differences between microbial feed additives and probiotics for food regarding regulation, growth promotion effects and health properties and consequences for extrapolation of farm animal results to humans. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-vergara, L.; Pereyra, C.M.; Montenegro, M.; Pena, G.A.; Aminahuel, C.A.; Cavaglieri, L.R. Encapsulated whey-native yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus as a feed additive for animal production. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2017, 34, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smialek, M.; Burchardt, S.; Koncicki, A. The influence of probiotic supplementation in broiler chickens on population and carcass contamination with Campylobacter spp-Field study. Res. Vet. Sci. 2018, 118, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselli, M.; Pieper, R.; Rogel-Gaillard, C.; De Vries, H.; Bailey, M.; Smidt, H.; Lauridsen, C. Immunomodulating effects of probiotics for microbiota modulation, gut health and disease resistance in pigs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2017, 233, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanczakowska, E.; Świątkiewicz, M.; Natonek-Wiśniewska, M.; Okoń, K. Medium chain fatty acids (MCFA) and/or probiotic Enterococcus faecium as a feed supplement for piglets. Livest. Sci. 2016, 192, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggia, F.; Mattarelli, P.; Biavati, B. Probiotics and prebiotics in animal feeding for safe food production. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 141, S15–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servin, A.L. Antagonistic activities of lactobacilli and bifidobacteria against microbial pathogens. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 28, 405–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apás, A.L.; Dupraz, J.; Ross, R.; González, S.N.; Arena, M.E. Probiotic administration effect on fecal mutagenicity and microflora in the goat’s gut. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2010, 110, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, M.L.; Chen, H.C.; Chen, K.N.; Lin, Y.C.; Lin, Y.T.; Chen, M.-J. Optimizing production of two potential probiotic lactobacilli strains isolated from piglet feces as feed additives for weaned piglets. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 28, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giang, H.H.; Viet, T.Q.; Ogle, B.; Lindberg, J.E. Growth performance, digestibility, gut environment and health status in weaned piglets fed a diet supplemented with potentially probiotic complexes of lactic acid bacteria. Livest. Sci. 2010, 129, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowarah, R.; Verma, A.K.; Agarwal, N.; Patel, B.H.M.; Singh, P. Effect of swine based probiotic on performance, diarrhoea scores, intestinal microbiota and gut health of grower-finisher crossbred pigs. Livest Sci. 2017, 195, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadde, U.; Kim, W.H.; Oh, S.T.; Lillehoj, H.S. Alternatives to antibiotics for maximizing growth performance and feed efficiency in poultry: A review. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2017, 18, 26–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Ragione, R.; Narbad, A.; Gasson, M.; Woodward, M.J. In vivo characterization of Lactobacillus johnsonii FI9785 for use as a defined competitive exclusion agent against bacterial pathogens in poultry. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 38, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Cyr, M.J.; Haddad, N.; Taminiau, B.; Poezevara, T.; Quesne, S.; Amelot, M.; Daube, G.; Chemaly, M.; Dousset, X.; Guyard-Nicodeme, M. Use of the potential probiotic strain Lactobacillus salivarius SMXD51 to control Campylobacter jejuni in broilers. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 247, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maragkoudakis, P.A.; Mountzouris, K.C.; Psyrras, D.; Cremonese, S.; Fischer, J.; Dalaka, E.; Hadjipetrou, A.; Theofanous, G.; Strozzi, G.P.; Carlini, N. Functional properties of novel protective lactic acid bacteria and application in raw chicken meat against Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella enteritidis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 130, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, F.; Thacker, P.A.; Zhang, G.; Qiao, S.; Ma, X. Oral administration of Lactobacillus fermentum I5007 favors intestinal development and alters the intestinal microbiota in formula-fed piglets. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, C.; Baffoni, L.; Gaggia, F.; Granata, M.; Gasbarri, R.; Di Gioia, D.; Biavati, B. Characterization of probiotic strains: An application as feed additives in poultry against Campylobacter jejuni. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 141, S98–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada, A.; Wilkins, D.C.; Drew, M. Administration of Bifidobacterium bifidum to chicken broilers reduces the number of carcass condemnations for cellulitis at the abattoir. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2001, 10, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Ma, F.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Bifidobacteria attenuate the development of metabolic disorders, with inter-and intra-species differences. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 3509–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.E.; Jeong, J.J.; Kim, J.K.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.H. Simultaneous Amelioratation of Colitis and Liver Injury in Mice by Bifidobacterium longum LC67 and Lactobacillus plantarum LC27. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaillou, S.; Christieans, S.; Rivollier, M.; Lucquin, I.; Champomier-Verges, M.-C.; Zagorec, M. Quantification and efficiency of Lactobacillus sakei strain mixtures used as protective cultures in ground beef. Meat Sci. 2014, 97, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, S.H. Released exopolysaccharide (r-EPS) produced from probiotic bacteria reduce biofilm formation of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157: H7. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 379, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maragkoudakis, P.A.; Mountzouris, K.C.; Rosu, C.; Zoumpopoulou, G.; Papadimitriou, K.; Dalaka, E.; Hadjipetrou, A.; Theofanous, G.; Strozzi, G.P.; Carlini, N. Feed supplementation of Lactobacillus plantarum PCA 236 modulates gut microbiota and milk fatty acid composition in dairy goats—A preliminary study. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 141, S109–S116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajecka, M.; Jakimiuk, E.; Skorska-Wyszynska, E.; Zielonka, Ł.; Polak, M.; Paluszewski, A.; Rybarczyk, L.; Gajecki, M. Influence of zearalenone micotoxicosis on selected immunological, haematological and biochemical index of blood plasma in bitches. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2004, 7, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Anfossi, L.; Giovannoli, C.; Baggiani, C. Mycotoxin detection. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 37, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowiak, P.; Ślizewska, K.; Nowak, A.; Chlebicz, A.; Zbikowski, A.; Pawłowski, K.; Szeleszczuk, P. Probiotic microorganisms detoxify ochratoxin A in both a chicken liver cell line and chickens. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 4309–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlebicz, A.; Śliżewska, K. In Vitro Detoxification of Aflatoxin B1, Deoxynivalenol, Fumonisins, T-2 Toxin and Zearalenone by Probiotic Bacteria from Genus Lactobacillus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae Yeast. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Hassan, Y.I.; Lepp, D.; Shao, S.; Zhou, T. Strategies and methodologies for developing microbial detoxification systems to mitigate mycotoxins. Toxins 2017, 9, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, J.; Heidari, S. Stability of ochratoxin A during bread making process. J. Food Saf. 2017, 37, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wu, W.; Pan, J.; Long, M. Detoxification Strategies for Zearalenone Using Microorganisms: A Review. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrazin, S.; Joosten, P.; Gompel, L.V.; Luiken, R.E.C.; Mevius, D.J.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Heederik, D.J.J. Quantitative and qualitative analysis of antimicrobial usage patterns in 180 selected farrow-to-finish pig farms from nine European countries based on single batch and purchase data. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, E.T.; Curry, S.; Trachsel, J.M.; Schroyen, M.; Gabler, N.K. Evaluating nursery pig responses to in-feed sub-therapeutic antibiotics. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.A.; Sylte, M.J.; Looft, T. In-feed bacitracin methylene disalicylate modulates the turkey microbiota and metabolome in a dose-dependent manner. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieco-Saiz, N.; Belguesmia, Y.; Raspoet, R.; Auclair, E.; Gancel, F.; Kempf, I.; Drider, D. Benefits and Inputs from Lactic Acid Bacteria and Their Bacteriocins as Alternatives to Antibiotic Growth Promoters During Food-Animal Production. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, A.A.; Wilson, R.; Doohan, D.; Lejeune, J.T. Bovine veterinarians’ knowledge, beliefs, and practices regarding antibiotic resistance on Ohio dairy farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 3494–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Ying, G.-G.; Singer, A.C.; Zhu, Y.-G. Review of antibiotic resistance in China and its environment. Environ. Int. 2018, 110, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyne, L.A.; Latham, S.M.; Dawson, S.; Donald, I.J.; Pearson, R.B.; Smith, R.F.; Williams, N.J.; Pinchbeck, G.L. Antimicrobial use practices, attitudes and responsibilities in UK farm animal veterinary surgeons. Prev. Vet. Med. 2018, 161, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temkin, E.; Adler, A.; Lerner, A.; Carmel, Y. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae: Biology, epidemiology, and management. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1323, 22–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, S.Q.; Li, C.Q.; Xu, Q.; Zeng, Q.P. Akkermansiamuciniphila May Determine Chondroitin Sulfate Ameliorating or Aggravating Osteoarthritis. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.-H.; Feng, Y. Towards Understanding MCR-like Colistin Resistance. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 794–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Yin, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Shen, J.; Shen, Z.; Wang, Y. Emergence of a novel mobile colistin resistance gene, mcr-8, in NDM-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Wang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Du, X.-D.; Gao, B.; Zhou, Y.; He, J.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J.; Jiang, H.; et al. Association of colistin residues and manure treatment with the abundance of mcr-1 gene in swine feedlots. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xie, J.; He, L. Rapid multiresidue analysis of authorized/banned cyclopolypeptide antibiotics in feed by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry based on dispersive solid-phase extraction. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2019, 170, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourély, C.; Fortanéd, N.; Calavas, D.; Leblond, A.; Gay, É. Why do veterinarians ask for antimicrobial susceptibility testing? A qualitative study exploring determinants and evaluating the impact of antibiotic reduction policy. Prev. Vet. Med. 2018, 159, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burow, E.; Rostalski, A.; Harlizius, J.; Gangl, A.; Simoneit, C.; Grobbel, M.; Kollas, C.; Tenhagen, B.-A.; Käsbohrer, A. Antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli from pigs from birth to slaughter and its association with antibiotic treatment. Prev. Vet. Med. 2019, 165, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, B.S.; Drider, D.; Oakley, B.B.; Brüssow, H.; Bikard, D.; Rich, J.O.; Miller, S.; Devillard, E.; Kwan, J.; Bertin, G.; et al. Microbial-derived products as potential new antimicrobials. Vet. Res. 2018, 49, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowieson, A.J.; Kluenter, A.M. Contribution of exogenous enzymes to potentiate the removal of antibiotic growth promoters in poultry production. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2019, 250, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, C.H.; Dilorenzo, N.; Quinn, M.J.; Smith, D.R.; May, M.L.; Galyean, M.L. Case study: Effects of a directfed microbial on finishing beef cattle performance, carcass characteristics, and in vitro fermentation. Prof. Anim. Sci. 2011, 27, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocyigit, R.; Aydin, R.; Yanar, M.; Diler, A.; Avci, M.; Ozyurek, S. The Effect of Direct-Fed Microbials Plus Exogenous Feed Enzyme Supplements on the Growth, Feed Efficiency Ratio and Some Behavioural Traits of Brown Swiss x Eastern Anatolian Red F1 Calves. Pak. J. Zool. 2016, 48, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, T.; Gomaa, W.M.S.; Shen, Y.Z.; Saleem, A.M.; Yang, W.Z.; McAllister, T.A. Use of naturally sourced feed additives (lactobacillus fermentation products and enzymes) in growing and finishing steers: Effects on performance, carcass characteristics and blood metabolites. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2019, 254, 114190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moraes, A.V.; Pereira, M.D.O.; Moraes, K.N.; Rodrigues-Soares, J.P.; Jesus, G.F. Autochthonous probiotic as growth promoter and immunomodulator for Astyanax bimaculatus cultured in water recirculation system. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 2808–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vase-Khavari, K.; Mortezavi, S.-H.; Rasouli, B.; Khusro, A.; Salem, A.Z.M. The effect of three tropical medicinal plants and superzist probiotic on growth performance, carcass characteristics, blood constitutes, immune response, and gut microflora of broiler. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2019, 51, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujnisa, A.; Gustina, L.; Natsir, A.; Hasan, S. Dosage Effects of Lactococcuslactis ssp. lactis 2 as a Probiotic on the Percentage of Carcass, Abdominal Fat Content and Cholesterol Level in Broilers. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2018, 17, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Askelson, T.E.; Campasino, A.; Lee, J.T.; Duong, T. Evaluation of Phytate-Degrading Lactobacillus Culture Administration to Broiler Chickens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 80, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, B.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, R.; Tang, L.; Gong, L.; LI, W. Effects of probiotics Lactobacillus plantarum 16 and Paenibacilluspolymyxa 10 on intestinal barrier function, antioxidative capacity, apoptosis, immune response, and biochemical parameters in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5028–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlamini, Z.C.; Langa, R.L.S.; Aiyegoro, O.A.; Okoh, A.I. Effects of probiotics on growth performance, blood parameters, and antibody stimulation in piglets. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.; Lee, S.; Park, H.; Shin, H.; Holzapfel, W. Development of putative probiotics as feed additives: Validation in a porcine-specific gastrointestinal tract model. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 10043–10054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hou, S.; Peng, W.; Lin, Q.; Chen, F.; Yang, L.; Li, F.; Huang, X. Oral Administration of Lactobacillus delbrueckii during the Suckling Phase Improves Antioxidant Activities and Immune Responses after the Weaning Event in a Piglet Model. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 6919803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, A.; Hailu, Y. The Effects of Probiotics Supplementation on Milk Yield and Composition of Lactating Dairy Cows. J. Phytopharmacol. 2019, 8, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.C.; Leu, S.F.; Huang, Q.R.; Chou, L.C.; Huang, C.C. Safety evaluation of multiple strains of Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcuspentosaceus in Wistar rats based on the Ames test and a 28-day feeding study. Sci. World J. 2014, 928652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plessas, S.; Nouska, C.; Karapetsas, A.; Kazakos, S.; Alexopoulos, A.; Mantzourani, I.; Chondrou, P.; Fournomiti, M.; Galanis, A.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Isolation, characterization and evaluation of the probiotic potential of a novel Lactobacillus strain isolated from Feta-type cheese. Food Chem. 2017, 226, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, D.C. Safety of probiotics. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 15, 563–569. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Jin, Y.-I.; Jeong, J.-C.; Chang, Y.H.; Lee, Y.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, M. Probiotic characteristics of Bacillus strains isolated from Korean traditional soy sauce. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 79, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vankerckhoven, V.; Huys, G.; Vancanneyt, M.; Vael, C.; Klare, I.; Romond, M.; Entenza, J.M.; Moreillon, P.; Wind, R.D.; Knol, J.; et al. Biosafety assessment of probiotics used for human consumption: Recommendations from the EU-PROSAFE project. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation on Evaluation of Health and Nutritional Properties of Probiotics in Food including Powder Milk with Live. In Health and Nutrition Properties of Probiotics in Food including Powder Milk with Live Lactic Acid Bacteria; FAO Food and Nutrition Paper 85; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2006.
- Sanders, M.E.; Akkermans, L.M.; Haller, D.; Hammerman, C.; Heimbach, J.; Hormannsperger, G.; Huys, G.; Levy, D.D.; Lutgendorff, F.; Mack, D.; et al. Safety assessment of probiotics for human use. Gut Microbes 2010, 1, 164–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huys, G.; Botteldoorn, N.; Delvigne, F.; De Vuyst, L.; Heyndrickx, M.; Pot, B.; Dubois, J.J.; Daube, G. Microbial Characterization of Probiotics-Advisory Report of theWorking Group “8651 Probiotics” of the Belgian Superior Health Council (SHC). Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1479–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, K.; Srinath, K.; Pravesh, B. Safety concerns of Probiotic use: A review. IOSR J. Dent. Med. Sci. 2013, 12, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Sornplang, P.; Piyadeatsoontorn, S. Probiotic isolates from unconventional sources: A review. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2016, 58, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joint FAO/WHO Working Group Report on Drafting Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics in Food; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 30 April and 1 May 2002; Available online: https://www.who.int/foodsafety/fs_management/en/probiotic_guidelines.pdf (accessed on 6 April 2019).
- Kim, M.J.; Ku, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, H.H.; Jin, H.; Kang, S.; Li, R.; Johnston, T.V.; Park, M.S.; Ji, G.E. Safety Evaluations of Bifidobacterium bifidum BGN4 and Bifidobacterium longum BORI. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajagai, Y.S.; Klieve, A.V.; Dart, P.J.; Bryden, W.L. Probiotics in Animal Nutrition–Production, Impact and Regulationby FAO Animal Production and Health Paper No. 179; Harinder, P.S., Ed.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2016; ISBN 978-92-5-109333-7. [Google Scholar]
- Hempel, S.; Newberry, S.; Ruelaz, A.; Wang, Z.; Miles, J. Safety of Probiotics to Reduce Risk and Prevent or Treat Disease. Evidence Report/Technology Assessment No. 200; (Prepared by the Southern California Evidence-Based Practice Center under Contract No. 290-2007-10062-I.) AHRQ Publication No. 11-E007; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alayande, K.A.; Aiyegoro, O.A.; Ateba, C.N. Probiotics in Animal Husbandry: Applicability and Associated Risk Factors. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12031087
Alayande KA, Aiyegoro OA, Ateba CN. Probiotics in Animal Husbandry: Applicability and Associated Risk Factors. Sustainability. 2020; 12(3):1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12031087
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlayande, Kazeem Adekunle, Olayinka Ayobami Aiyegoro, and Collins Njie Ateba. 2020. "Probiotics in Animal Husbandry: Applicability and Associated Risk Factors" Sustainability 12, no. 3: 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12031087
APA StyleAlayande, K. A., Aiyegoro, O. A., & Ateba, C. N. (2020). Probiotics in Animal Husbandry: Applicability and Associated Risk Factors. Sustainability, 12(3), 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12031087




