Dynamics of Regional Development in Regional and Municipal Economy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Optimization Prerequisites/Investments and Budgets
- Investment limit;
- Limit period for return on invested capital.
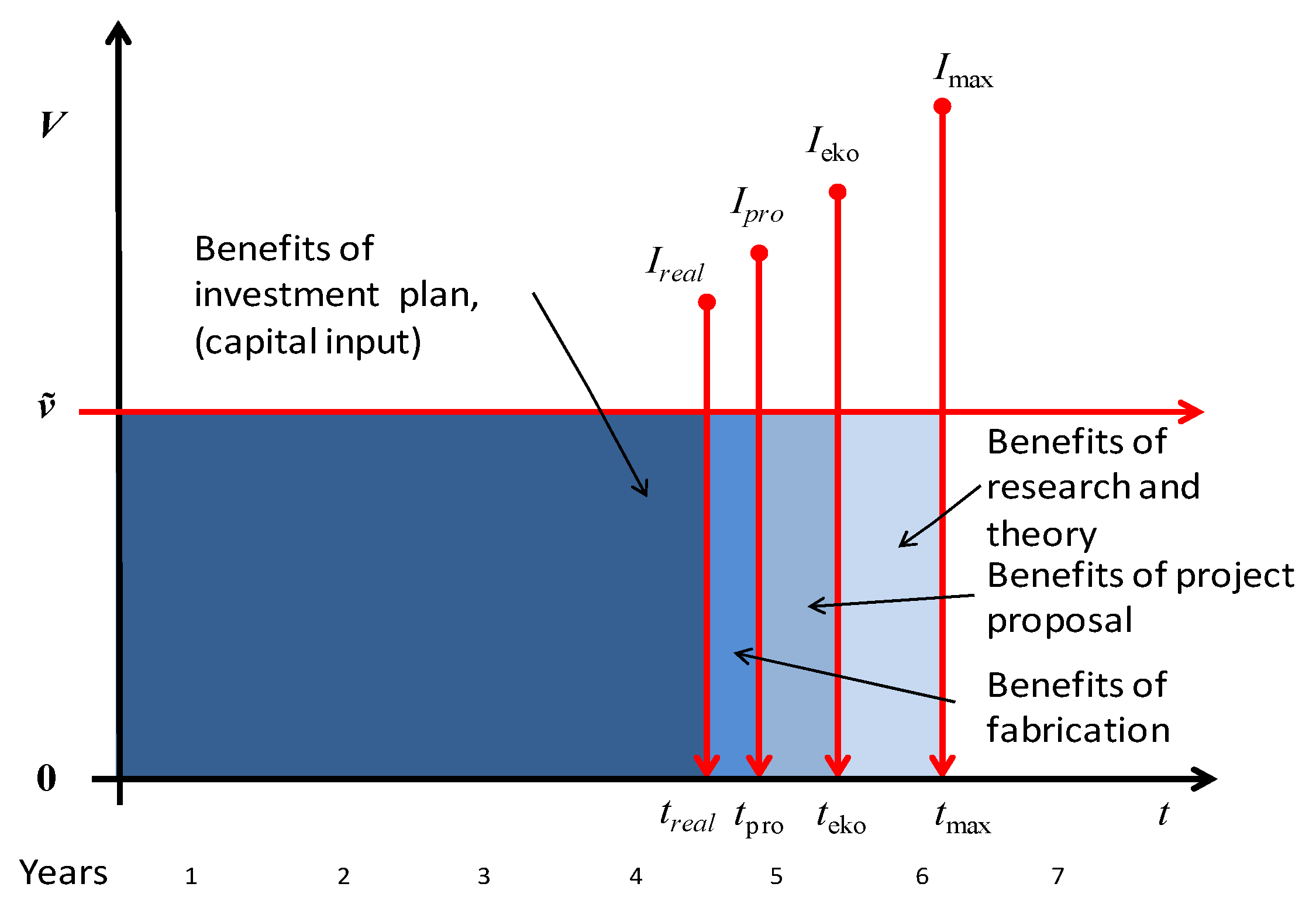
2.1.1. Maximal Limit Range of Investment in Design and Implementation
- Market conditions, from which it follows a maximum allowable scope of the investment as Imax, see Figure 1;
- Practices of the capital providers Ieko, (weighing market conditions and their risks);
- The standard of economical-technical solution of the project Ipro, that is, the ability to project the capital provider’s requirements into the project design;
- The ability to reflect the project briefly into the functional unit, limit Ireal during its implementation.
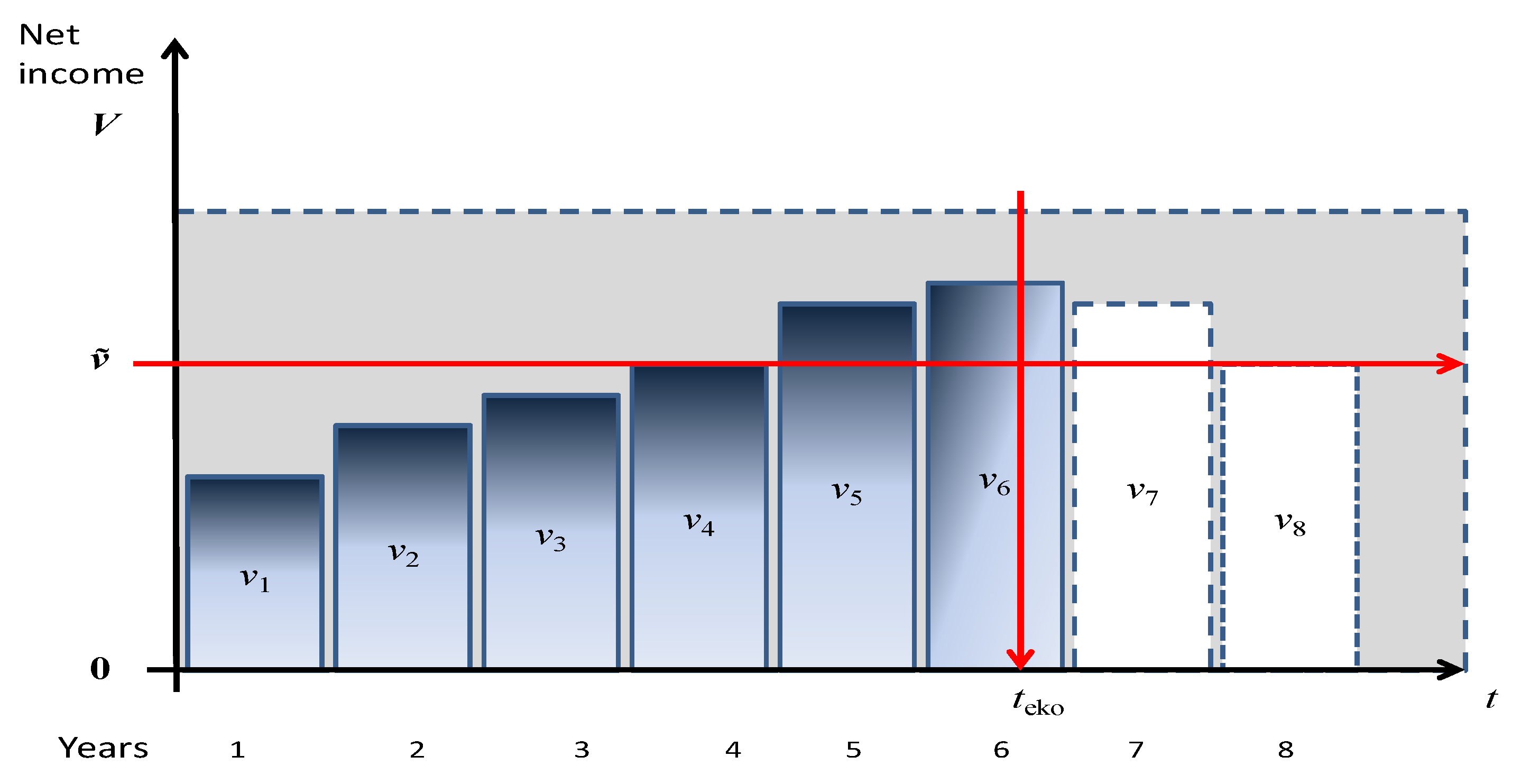
2.1.2. Maximal Limit Payback Time of Invested Resources
- placement of investments in the location;
- interaction with the region;
- nature of commercial activity;
- chosen technical execution of plan.
- teko is the proposed economic return time for the project;
- tpro is the payback time of the project is reduced by the limits created by the project solution;
- treal is the payback time of the project is reduced by the limits created by the realization requirements;
- Ieko is the investment cost at the assumed economic return and the risk weight of the investment project;
- Iprop is the maximum investment cost created by the project solution;
- Ireal is the maximum investment cost in the course of implementing the project solution;
- r is the level of costs and risks of accepted commercial commitments;
- rpro is the level of costs and risks created in the technical design of the method of realization of the investment unit;
- rreal is the extent of costs and risks incurred in the execution of the investment scheme.
2.2. Methods of Economic-Technical Breakdown of Investment Development Projects of the Region
3. Results and Discussion
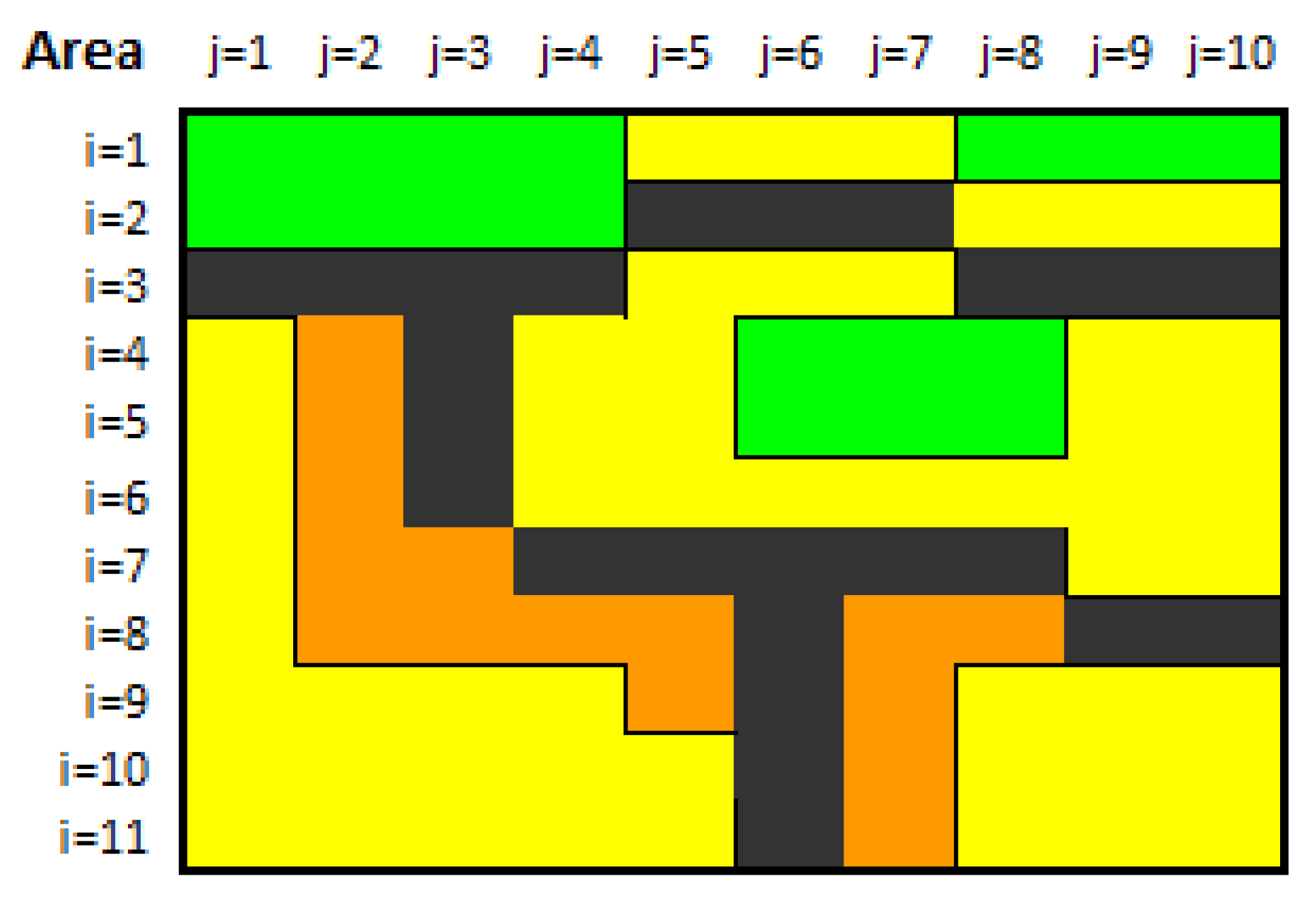
3.1. Illustrative Data–Examples
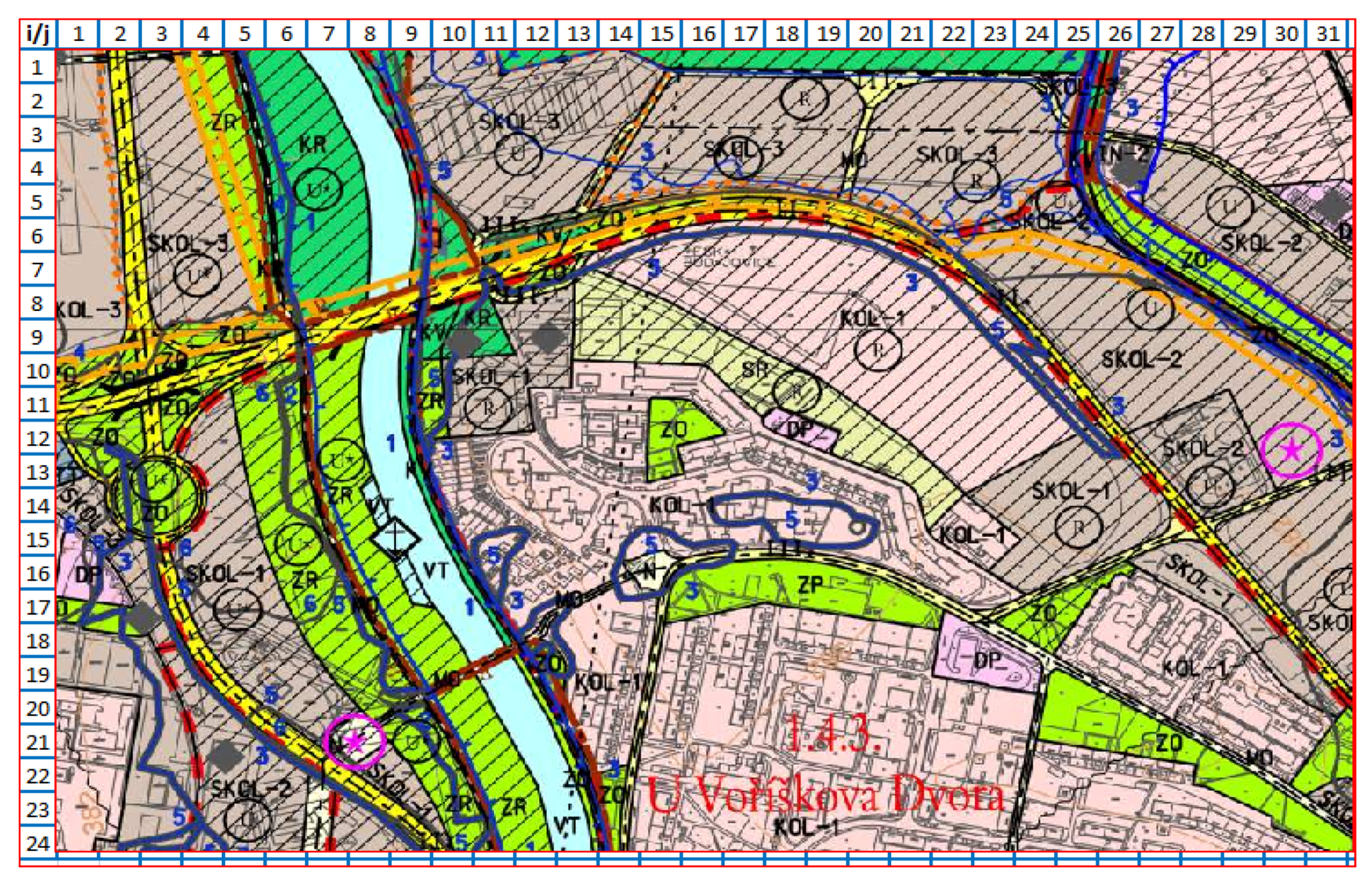
3.2. Investment and Optimalization of Land-Use Plan Infrastructure
3.2.1. Optimizing Procedures and Their Limits
3.2.2. Analysis–Calculation of Achievable Limits
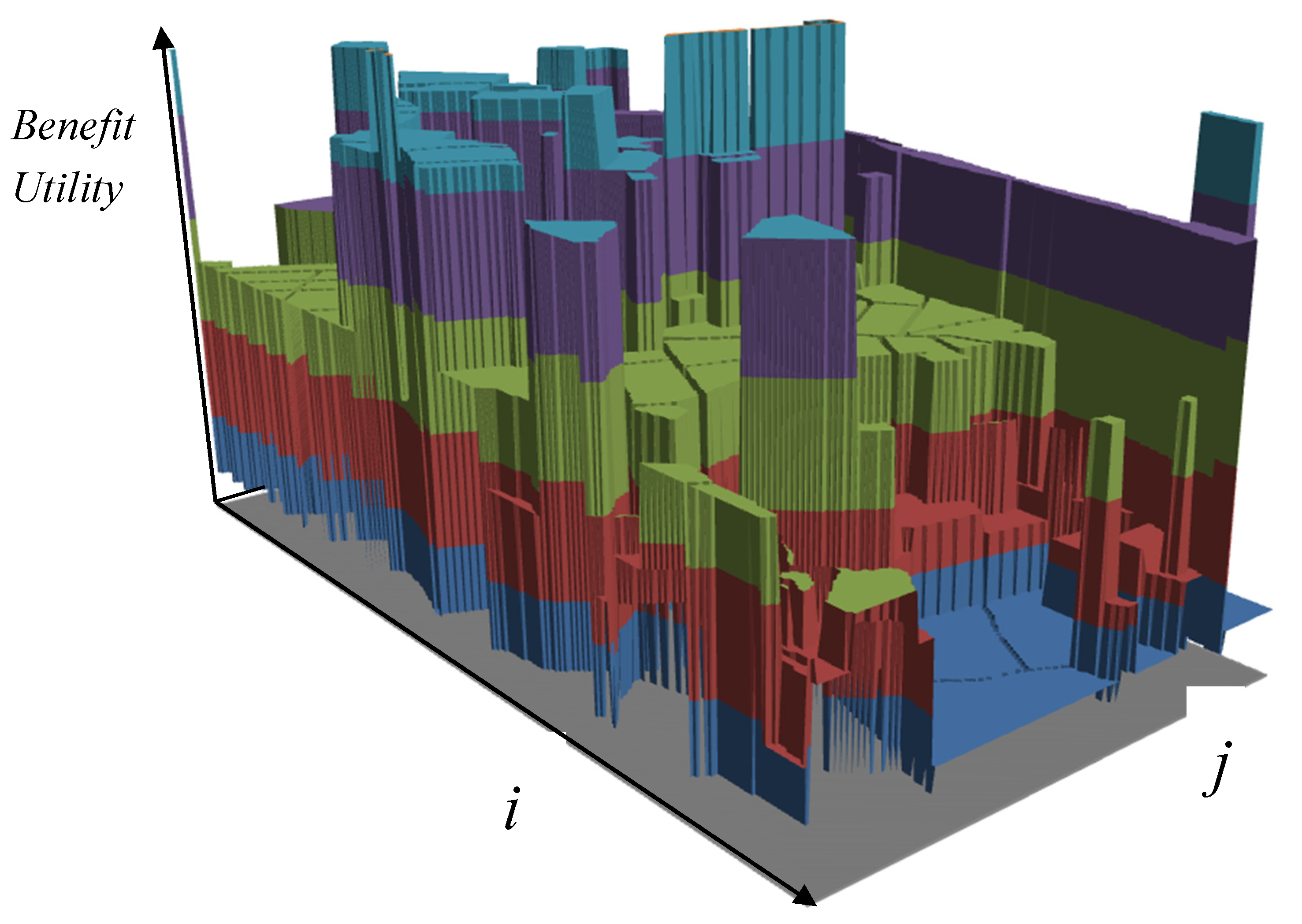
- uTx is a linear relation, the product of the utility matrix u and the range proposal vector (volume) x; interpretation for determining the sought optimal range of functional activities xo in the area is based on yields, benefits (maximizing uT), alternatively minimizing (resources, capital, etc.);
- M set of managerial solutions, optimal for proposals A, B, C … (xo│proposal), optimal for critical(é) resources (e) bx, by … (xo│resources), or optimal for use standards ux, uy, …, (xo│benefit);
- N set of proposals (downstream processes) of the land-use concept;
- Np examined downstream process p;
- A matrix characterizes structure of use (territory, areas, legislation, requests, etc.) is of the order of m × n;
- b vector of available resources, order of m;
- u vector of valuation of returns, an order of m;
- x vector of proposed solution, an order of n.
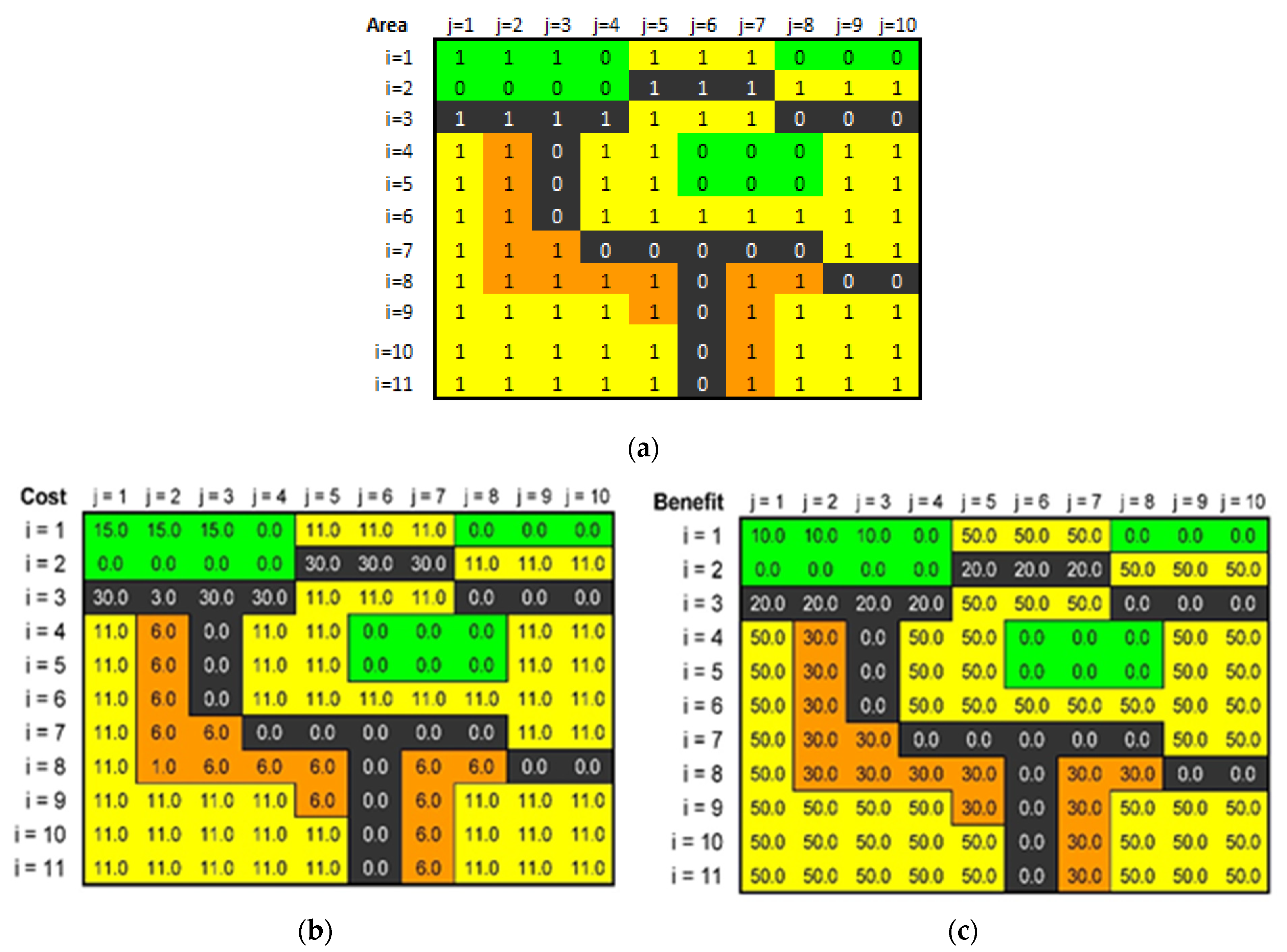
3.2.3. Illustrative Example–Investment in the Territory
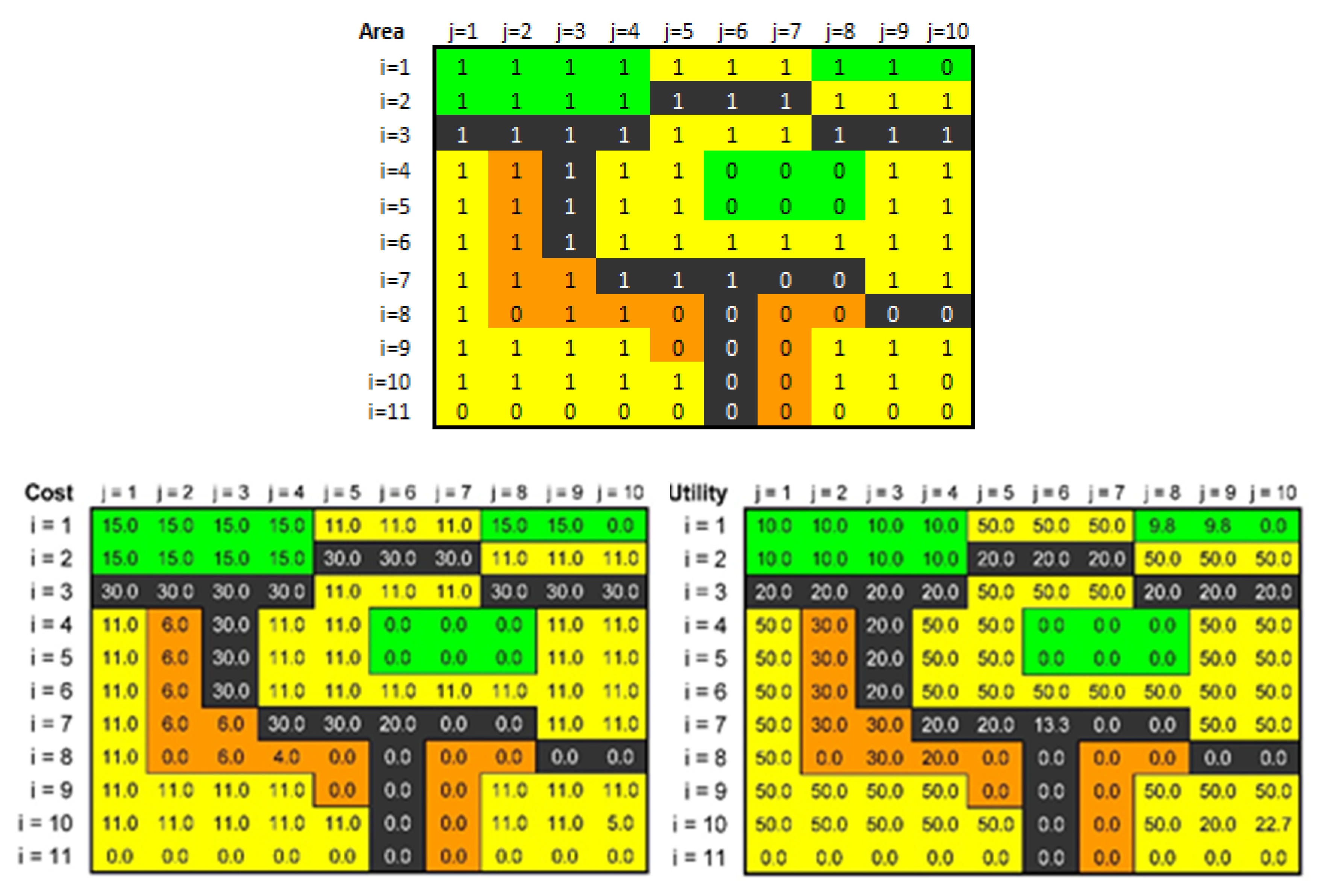
3.2.4. Usability–Design Solution Limits
3.2.5. Optimization–Effectiveness and Efficiency of the Proposal
3.2.6. Productiveness of Investment Resources Used—Effectiveness and Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hirschmann, A.O. The Strategy of Economic Development; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1958; ISBN 0-8133-7419-7. [Google Scholar]
- The World Bank. World Development Indicators 2014; International Bank for Deconstruction and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-1-4648-0164-8. [Google Scholar]
- Samuelson, P. Foundations of Economic Analysis; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1947; ISBN 9780674313033. [Google Scholar]
- Dlask, P.; Beran, V.; Matejka, P. Optimization and Decision Making in Development Area; CVUT: Prague, Czech Republic, 2012; ISBN 978-80-01-04978-5. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Brock, W.A.; Xepapadeas, A.; Yannacopoulos, A.N. Optimal Control in Space and Time and the Management of Environmental Resources. Annu. Rev. Resour. Econ. 2014, 6, 33–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normand, G. EU Economies Hit by Collapse in Investment, New Data Shows. Euro and Finance. LA Tribune, 16 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Holman, R. History of Economic Thought; C.H. Beck: Prague, Czech Republic, 2005; ISBN 80-7179-380-9. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Weigrich, K.; Kostka, G.; Hammerschmid, G. The Governance of Infrastructure; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017; ISBN 9780198787310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zheng, X.Q.; Huang, Q. Predictive Measurement of the Structure of Land Use in an Urban Agglomeration Space. Sustainability 2018, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.B.; Ren, Z.B.; Tan, J.T. The Spatial Patterns of Land Surface Temperature and Its Impact Factors: Spatial Non-Stationarity and Scale Effects Based on a Geographically-Weighted Regression Model. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.F.; Li, Y.W.; Yin, H.; Zhang, J.X. A Stochastic Interpolation-Based Fractal Model for Vulnerability Diagnosis of Water Supply Networks against Seismic Hazards. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobotaru, A.-M.; Andronache, I.; Ahammer, H.; Radulovic, M.; Peptenatu, D.; Pintilii, R.-D.; Drăghici, C.-C.; Marin, M.; Carboni, D.; Mariotti, G.; et al. Application of Fractal and Gray-Level Co-Occurrence Matrix Indices to Assess the Forest Dynamics in the Curvature Carpathians-Romania. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Xu, Y.Y. Efficiency and Multifractality Analysis of the Chinese Stock Market: Evidence from Stock Indices before and after the 2015 Stock Market Crash. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.W.; Li, H.; Sun, D.F. Fractal Feature Analysis and Information Extraction of Woodlands Based on MODIS NDVI Time Series. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havel, M.B. How the distribution of rights and liabilities in relation to betterment and compensation links with planning and the nature of property rights: Reflections on the Polish experience. Land Use Policy 2017, 67, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Eye. Abandoned Construction Projects. Youtube.com. American Eye. [cit: 17. 09. 2018]. Available online: www.youtube.com/watch?v=pLS0xiCC9ZU (accessed on 23 April 2018).
- Kuda, F.; Beran, V.; Dlask, P.; Wernerova, E. Management of Property Management Economy; Professional Publishing: Prgue, Czech Republic, 2018; ISBN 978-80-88260-03-5. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Land Use Planning Act and Building Code (Building Act). Laws for People. AION CS, s.r.o., 2010–2018. [cit: 11. 7. 2018]. Available online: https://zakonyprolidi.cz/ (accessed on 11 May 2006). (In Czech).
- Piketty, T. Capital in the Twenty-First Century; The Belknap Press of Harward University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-0-674-43000-6. [Google Scholar]
- Boushey, H.; Bradford DeLong, J.; Steinbaum, M. After Piketty; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; ISBN 9780674504776. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Lee, L.H. Stochastic Simulation Optimization: An Optimal Computing Budget Allocation; World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd.: Singapore, 2011; ISBN 978-981-4282-64-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Finance of the Czech Republic. Why Educate Financially; Ministry of Finance of the Czech Republic: Prague, Czechia, 2015; Volume 2, p. 2014, [cit: 17. 10 2017]. Available online: http://www.psfv.cz/cs/investice/investice-obecne (accessed on 13 February 2015). (In Czech)
- Lage der Berliner Flughäfens.svg. Wikipedia. [cit: 01. 06 2018]. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Berlin.svg (accessed on 17 July 2011).
- Delius, M. Bericht des 1. Untersuchungsausschusses des Abgeordnetenhauses von Berlin; Drucksache 17/3000; Abgeordnetenhaus: Berlin, Germany, 2016; p. 443. (In German)
- Berliner Zeitung. BER-Baustelle. B.Z.-Berlin. B. Z. [cit: 17. 10 2017]. Available online: https://www.bz-berlin.de/artikel-archiv/ber-baustelle-66-500-mal-pfusch (accessed on 3 September 2013). (In Deutch).
- Lutte, R. BER Flughafen Kabel. Bz-Berlin. [cit: 11. 04. 2018]. Available online: https://www.bz-berlin.de/media/ralf-lutter-300 (accessed on 28 September 2015). (In Deutch).
- Santamaria, O.G.R. Analysis of Delays in Construction Tasks; CTU: Prague, Czech Republic, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Song, K.; Pu, F.A. Laws and Trends of the Evolution of Traditional Villages in Plane Pattern. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, S.S.; Liang, Q.H.; Zhong, S.M. Design of Urban Rail Transit Network Constrained by Urban Road Network, Trips and Land-Use Characteristics. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarini, M.R.; Chiovitti, A.; Battisti, F.; Morano, P. An integrated approach for the assessment of urban transformation proposals in historic and consolidated tissues. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2017, 10406, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarini, M.R.; Battisti, F.; Buccarini, C. Rome: Re-qualification program for the street markets in public-private partnership. A further proposal for the flaminio II street market. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 838–841, 2928–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beran, V.; Dlask, P. Dynamic Schedule; Academia: Prague, Czech Republic, 2002; ISBN 80-200-1007-6. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Beran, V.; Dlask, P. Management of Sustainable Development of Regions, Settlements and Municipalities; Academia: Prague, Czech Republic, 2005. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- OECD. OECD Regions and Cities at a Glance 2018; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2018; ISBN 9789264305090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Gao, X.B.; Li, C.P. Relationship between Urban Transport and Residential Location Choice. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2018, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Project | Start (Year) | Duration (Years) | Delay (Years) | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sydney Opera House | 1958 | 15 | 10 | |
| Elbe Philharmonic Hall, Hamburg | 2007 | 3 | 16 | 3.26 × cost increase |
| Berlin Brandenburg Airport (BBA) | 2006 | 5 | 9 | 6.00 × cost increase |
| Leaning Tower of Pisa | 1173 | 177 | 94 + 35 | |
| Suez Canal | 1859 | 10 | 2 | |
| Panama Canal | 1880 | 13 + 4 | 34 | |
| Temelin Nuclear Power Station | 1979 | 24 |
| Symbol | Function in Region | Limits of Space Units * | Resource Cost t.€ | Utility | Budget/B. Structure t.€ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green, park | 17.0 | EUR 10 | 15.0 | EUR 50 | |
| Communication, transport | 24.0 | EUR 20 | 30.0 | EUR 220 | |
| Housing construction | 54.0 | EUR 50 | 11.0 | EUR 700 | |
| Civil construction | 15.0 | EUR 30 | 6.0 | EUR 190 | |
| Total | 110.0 | EUR 110 | 1659.0 | EUR 1160 |
| Symbol | Function in Region | Applied Space Units * | Limits of Space Units ** | Budget Limit of Units *** | Resource Cost t.€ | Utility | Budget t.€ (EUR) | Budget Spending |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green, park | 3.0 | 17.0 | 3.3 | 15.0 | 10.0 | 50 | 17.60% | |
| Communication, transport | 7.0 | 24.0 | 7.3 | 30.0 | 20.0 | 220 | 29.20% | |
| Housing construction | 54.0 | 54.0 | 63.6 | 11.0 | 50.0 | 700 | 100.00% | |
| Civil construction | 15.0 | 15.0 | 31.7 | 6.0 | 30.0 | 190 | 100.00% | |
| Units: Applied/Proposal limit/Budget limit | 79.0 | 110.0 | 106.0 | 1160 | ||||
| Cost optimal/Proposal limit/Budget limit (EUR) | 939 | 1659 | 1160 | 56.60% | ||||
| Benefit Applied/Proposal limit/Budget limit | 3320 | 3800 | 4312 | 87.40% | ||||
| Symbol | Function in Region | Applied Space units * | Limits of Space units ** | Budget limit of Units *** | Resource Cost t.€ | Utility | Budget t.€ (EUR) | Budget Spending |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green, park | 10.0 | 17.0 | 10.0 | 15.0 | 10.0 | 150 | 58.80% | |
| Communication, transport | 15.7 | 24.0 | 15.7 | 30.0 | 20.0 | 470 | 65.30% | |
| Housing construction | 45.5 | 54.0 | 45.5 | 11.0 | 50.0 | 500 | 84.20% | |
| Civil construction | 6.7 | 15.0 | 6.7 | 6.0 | 30.0 | 40 | 44.40% | |
| Units: Applied/Proposal limit/Budget limit | 77.8 | 110.0 | 77.8 | 1160 | ||||
| Cost optimal/Proposal limit/Budget limit (EUR) | 1160 | 1659 | 1160 | 69.90% | ||||
| Benefit Applied/Proposal limit/Budget limit | 2886 | 3798 | 2886 | 76.00% | ||||
| Budget Structure | Proposal and Solution Data | Effectivity | Efficiency | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units Engaged | Cost [t.€] Incurred | Potential Utility | Optimal Utility obtained | Units Involved | Cost *** Incurred | Utility (Benefit) obtained | Cost per Unit [t.€] | Utility per Unit | Cost of 1 t.€ Utility | Utility of 1t.€ Cost | |
| Nurban plan * | 110 | 1659 | 3800 | 100% | 100% | 100% | 15.08 | 34.55 | 2.29 | 0.44 | |
| N50/220/700/190 ** | 79 | 939 | 3320 | 71.8% | 56.6% | 87.4% | 11.89 | 42.03 | 3.54 | 0.28 | |
| N150/470/500/40 ** | 78 | 1160 | 2886 | 70.7% | 69.9% | 75.9% | 14.91 | 37.10 | 2.49 | 0.40 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beran, V.; Teichmann, M.; Kuda, F.; Zdarilova, R. Dynamics of Regional Development in Regional and Municipal Economy. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9234. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219234
Beran V, Teichmann M, Kuda F, Zdarilova R. Dynamics of Regional Development in Regional and Municipal Economy. Sustainability. 2020; 12(21):9234. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219234
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeran, Vaclav, Marek Teichmann, Frantisek Kuda, and Renata Zdarilova. 2020. "Dynamics of Regional Development in Regional and Municipal Economy" Sustainability 12, no. 21: 9234. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219234
APA StyleBeran, V., Teichmann, M., Kuda, F., & Zdarilova, R. (2020). Dynamics of Regional Development in Regional and Municipal Economy. Sustainability, 12(21), 9234. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219234





