Impacts of Erratic Snowfall on Apple Orchards in Kashmir Valley, India
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
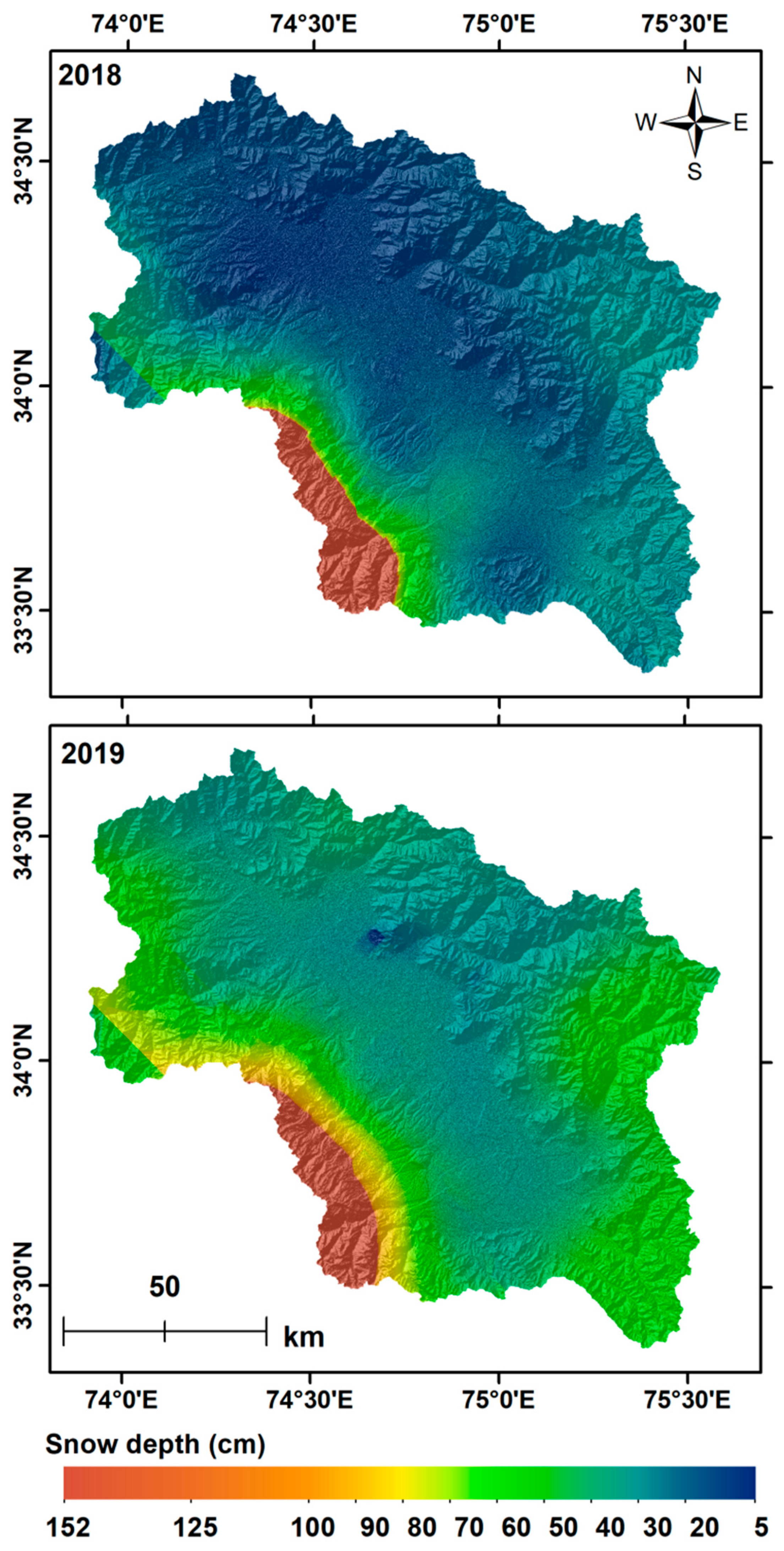
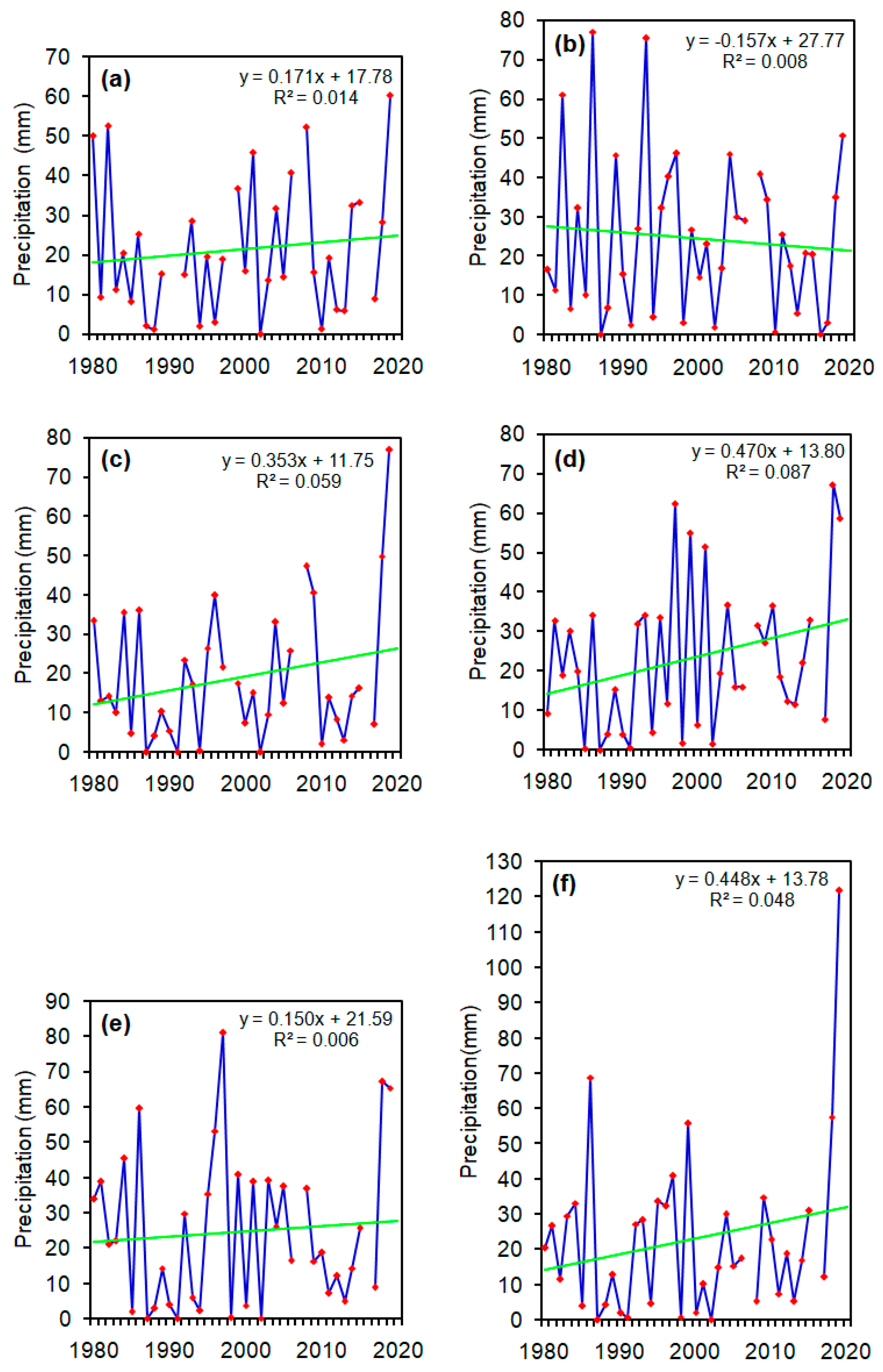
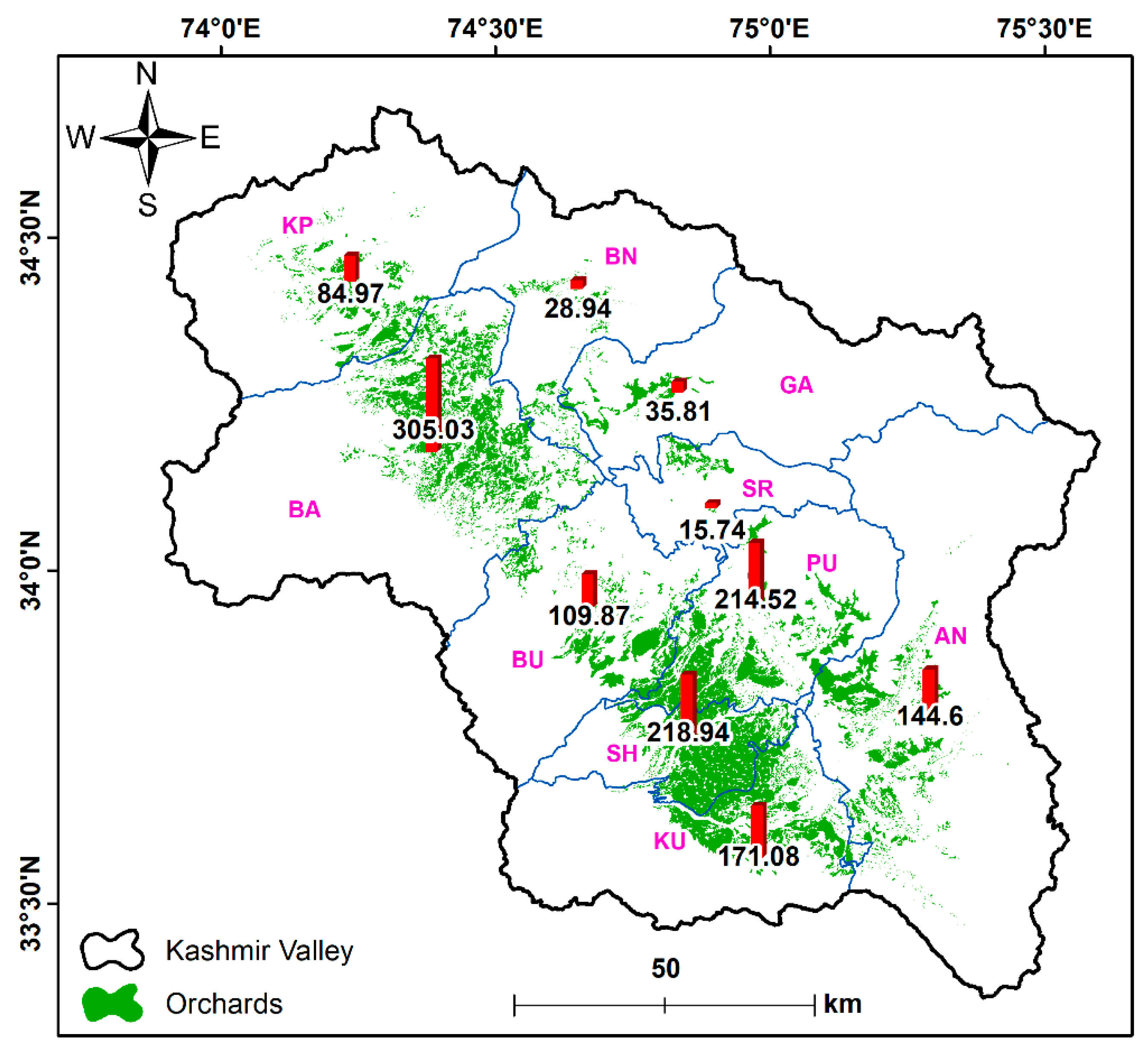
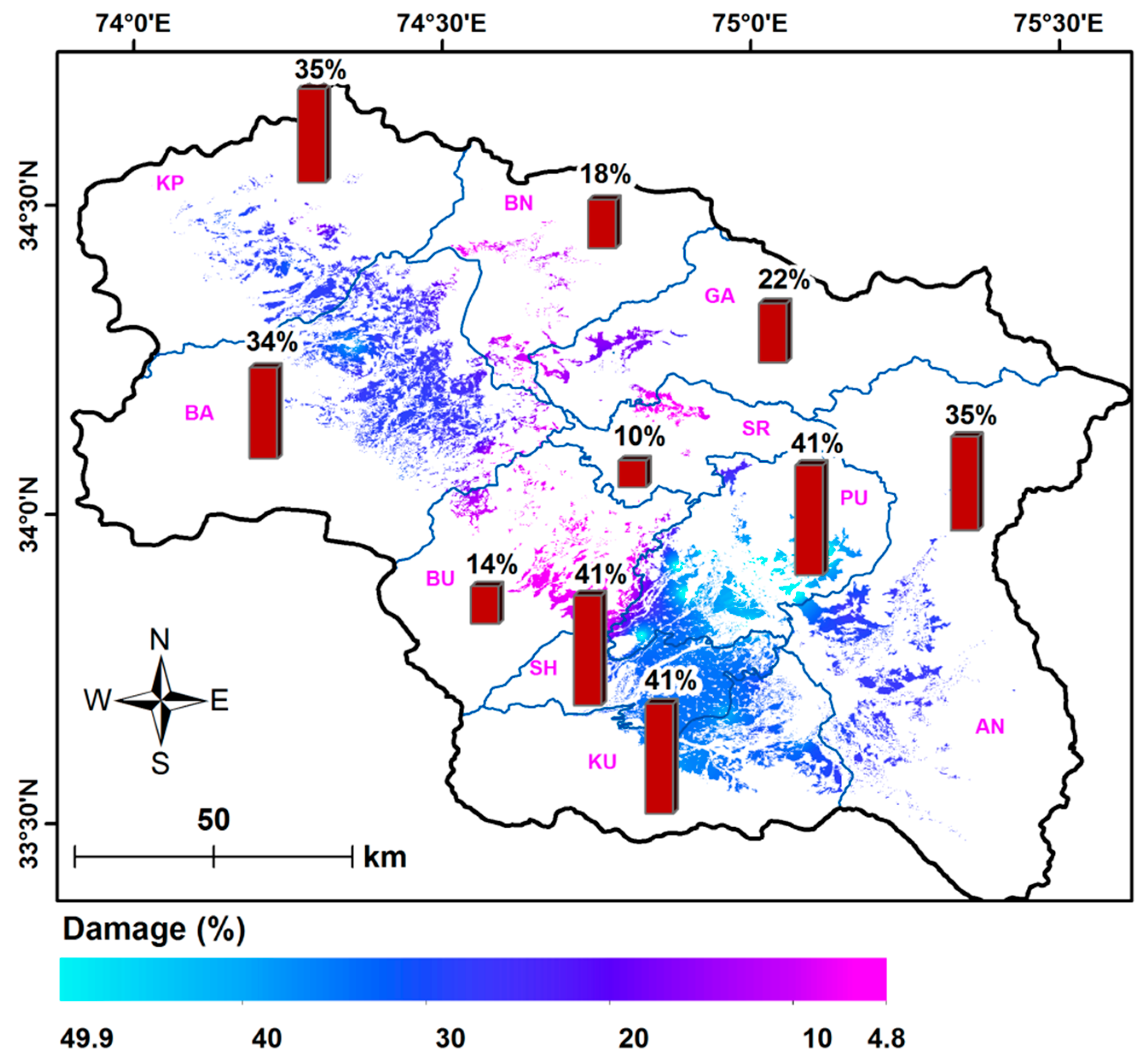
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nandargi, S.; Dhar, O.N. Extreme rainfall events over the Himalayas between 1871 and 2007. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2011, 56, 930–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Droogers, P.; de Jong, S.M.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Large-Scale monitoring of snow cover and runoff simulation in Himalayan river basins using remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, R.A.; Rashid, I.; Romshoo, S.A.; Marazi, A. Sustainability of winter tourism in a changing climate over Kashmir Himalaya. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 2549–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurung, D.R.; Maharjan, S.B.; Shrestha, A.B.; Shrestha, M.S.; Bajracharya, S.R.; Murthy, M.S.R. Climate and topographic controls on snow cover dynamics in the Hindu Kush Himalaya. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 3873–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolch, T.; Kulkarni, A.; Kääb, A.; Huggel, C.; Paul, F.; Cogley, J.G.; Frey, H.; Kargel, J.S.; Fujita, K.; Scheel, M.; et al. The state and fate of Himalayan glaciers. Science 2012, 336, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, I.; Majeed, U. Recent recession and potential future lake formation on Drang Drung glacier, Zanskar Himalaya, as assessed with earth observation data and glacier modelling. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros-Cánovas, J.A.; Trappmann, D.; Madrigal-González, J.; Eckert, N.; Stoffel, M. Climate warming enhances snow avalanche risk in the Western Himalayas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3410–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veh, G.; Korup, O.; Walz, A. Hazard from Himalayan glacier lake outburst floods. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, R.K.; Gopalakrishnan, R.; Jayaraman, M.; Bala, G.; Joshi, N.V.; Sukumar, R.; Ravindranath, N.H. Impact of climate change on Indian forests: A dynamic vegetation modeling approach. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2011, 16, 119–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottfried, M.; Pauli, H.; Futschik, A.; Akhalkatsi, M.; Barančok, P.; Benito Alonso, J.L.; Coldea, G.; Dick, J.; Erschbamer, B.; Fernández Calzado, M.R.; et al. Continent-Wide response of mountain vegetation to climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamududu, B.; Killingtveit, A. Assessing climate change impacts on global hydropower. Energies 2012, 5, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Katoch, S.S. Environmental sustainability of run of the river hydropower projects: A study from western Himalayan region of India. Renew. Energy 2016, 93, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyaupane, G.P.; Chhetri, N. Vulnerability to climate change of nature-based tourism in the Nepalese Himalayas. Tour. Geogr. 2009, 11, 95–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, S.K. Mountain tourism and climate change: Implications for the Nepal Himalaya. Nepal Tour. Dev. Rev. 2013, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Grumbine, R.E.; Shrestha, A.; Eriksson, M.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.U.N.; Wilkes, A. The melting Himalayas: Cascading effects of climate change on water, biodiversity, and livelihoods. Conserv. Biol. 2009, 23, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujakhu, N.M.; Ranjitkar, S.; He, J.; Schmidt-Vogt, D.; Su, Y.; Xu, J. Assessing the livelihood vulnerability of rural indigenous households to climate changes in Central Nepal, Himalaya. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nüsser, M.; Dame, J.; Parveen, S.; Kraus, B.; Baghel, R.; Schmidt, S. Cryosphere-Fed irrigation networks in the northwestern himalaya: Precarious livelihoods and adaptation strategies under the impact of climate change. Mt. Res. Dev. 2019, 39, R1–R11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamil, S.; Almazroui, M.; Kang, I.S.; Hanif, M.; Kucharski, F.; Abid, M.A.; Saeed, F. Long-Term ENSO relationship to precipitation and storm frequency over western Himalaya–Karakoram–Hindukush region during the winter season. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 5265–5278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, L.; Meher, J.K. Drivers of climate over the Western Himalayan region of India: A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2019, 198, 102935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, M.; Mishra, A.K. A study of heavy snowfall in Kashmir, India in January 2017. Weather 2018, 73, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romshoo, S.A.; Altaf, S.; Rashid, I.; Ahmad Dar, R. Climatic, geomorphic and anthropogenic drivers of the 2014 extreme flooding in the Jhelum basin of Kashmir, India. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2018, 9, 224–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Para, J.A.; Kesarkar, A.; Bhate, J.; Singh, V.; Panchal, A.; Munsi, A.; Shivamurthy, Y.; Lotus, S.; Ahmad, N.; Sheikh, J.A. Large-Scale dynamics of western disturbances caused extreme precipitation on 24–27 January 2017 over Jammu and Kashmir, India. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 6, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujree, I.; Wani, I.; Muslim, M.; Farooq, M.; Meraj, G. Evaluating the variability and trends in extreme climate events in the Kashmir Valley using PRECIS RCM simulations. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2017, 3, 1647–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Jhelum and Tawi Flood Recovery Project: Environment and Social Management Framework; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; p. 110. [Google Scholar]
- Ballesteros-Cánovas, J.A.; Koul, T.; Bashir, A.; del Pozo, J.M.B.; Allen, S.; Guillet, S.; Rashid, I.; Alamgir, S.H.; Shah, M.; Bhat, M.S.; et al. Recent flood hazards in Kashmir put into context with millennium-long historical and tree-ring records. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, S.; Giri, R.; Kumar, R. An analysis of western disturbance during 17th to 21st february 2005 over western Himalayan region. Invertis J. Sci. Technol. 2012, 5, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Mushtaq, H.; Rehman, S.; Margoob, M.A. Understanding long term community psychosocial needs of children and adolescent survivors of a natural disaster: One decade after 2005, ’Snow-Tsunami’ in Kashmir. JK Pract. 2017, 22, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnouls, F. Bioclimatic Types of South-East Asia; Institute Francais de Pondichery: Pondicherry, India, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, I.; Parray, A.A.; Romshoo, S.A. Evaluating the performance of remotely sensed precipitation estimates against in-situ observations during the september 2014 mega-flood in the Kashmir Valley. Asia Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 55, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, K.; Bhan, S.C.; Bandopadhyay, B.K. The catastrophe over Jammu and Kashmir in september 2014: A meteorological observational analysis. Curr. Sci. 2015, 109, 580–591. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, I.; Romshoo, S.A.; Chaturvedi, R.K.; Ravindranath, N.H.; Sukumar, R.; Jayaraman, M.; Lakshmi, T.V.; Sharma, J. Projected climate change impacts on vegetation distribution over Kashmir Himalayas. Clim. Chang. 2015, 132, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, I.; Romshoo, S.A.; Abdullah, T. The recent deglaciation of Kolahoi valley in Kashmir Himalaya, India in response to the changing climate. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 138, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimri, A.P.; Niyogi, D.; Barros, A.P.; Ridley, J.; Mohanty, U.C.; Yasunari, T.; Sikka, D.R. Western disturbances: A review. Rev. Geophys. 2015, 53, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, K.M.R.; Turner, A.G.; Shaffrey, L.C. The evolution, seasonality and impacts of western disturbances. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 144, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, T.J.; Barros, A.P. Winter storms in the central Himalayas. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2004, 82, 829–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiemann, R.; Lüthi, D.; Schär, C. Seasonality and interannual variability of the westerley jet in the Tibetan Plateau region. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 2940–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lone, A.; Achyuthan, H.; Chakraborty, S.; Metya, A.; Datye, A.; Kriplani, R.H.; Fousiya, A.A. Controls on the isotopic composition of daily precipitation characterized by dual moisture transport pathways at the monsoonal margin region of North-Western India. J. Hydrol. 2020, 588, 125106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandargi, S.; Dhar, O.N. Extreme rainstorm events over the northwest Himalayas during 1875–2010. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Yadav, B.P.; Gahlot, S.; Singh, M. Winter frequency of western disturbances and precipitation indices over Himachal Pradesh, India: 1977–2007. Atmosfera 2015, 28, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimri, A.P.; Mohanty, U.C. Snowfall statistics of some SASE field stations in J&K. Def. Sci. J. 1999, 49, 437–445. [Google Scholar]
- Dimri, A.P.; Chevuturi, A. Model sensitivity analysis study for western disturbances over the Himalayas. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2014, 123, 155–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, J.; Wiltshire, A.; Mathison, C. More frequent occurrence of westerly disturbances in Karakoram up to 2100. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 468–469, S31–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, M.A.; Webster, R. Kriging: A method of interpolation for geographical information systems. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1990, 4, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, D.; Zhang, C.; Carton, O.T. Geostatistical analyses and hazard assessment on soil lead in Silvermines area, Ireland. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 127, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, U.S.; Dube, R.K.; Rao, G.S.P. Extreme weather events over India in the last 100 years. J. Ind. Geophys. Union 2005, 9, 173–187. [Google Scholar]
- Shekhar, M.S.; Devi, U.; Paul, S.; Singh, G.P.; Singh, A. Analysis of trends in extreme precipitation events over Western Himalaya Region: Intensity and duration wise study. J. Indian Geophys. Union 2017, 21, 223–229. [Google Scholar]
- Rasool, R.; Shafiq, M.; Ahmed, P.; Ahmad, P. An analysis of climatic and human induced determinants of agricultural land use changes in Shupiyan area of Jammu and Kashmir state, India. GeoJournal 2018, 83, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, I.; Romshoo, S.A. Impact of anthropogenic activities on water quality of Lidder River in Kashmir Himalayas. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 4705–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, M.I.; Rashid, I.; Shahi, N.; Murtaza, K.O.; Hassan, K.; Yousuf, A.R.; Romshoo, S.A. Massive land system changes impact water quality of the Jhelum River in Kashmir Himalaya. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, I.; Bhat, M.A.; Romshoo, S.A. Assessing changes in the above ground biomass and carbon stocks of Lidder valley, Kashmir Himalaya, India. Geocarto Int. 2017, 32, 717–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, I.; Majeed, U.; Aneaus, S.; Pelto, M. Linking the recent glacier retreat and depleting streamflow patterns with land system changes in Kashmir himalaya, India. Water 2020, 12, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romshoo, S.A.; Bashir, J.; Rashid, I. Twenty-First century-end climate scenario of Jammu and Kashmir Himalaya, India, using ensemble climate models. Clim. Chang. 2020, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.R.; Wani, M.A.; Kirmani, A.R.; Raina, T.H. Pesticides and brain cancer linked in orchard farmers of Kashmir. Indian J. Med. Paediatr. Oncol. 2010, 31, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.R.; Wani, M.A.; Kirmani, A.R. Brain cancer and pesticide relationship inorchard farmers of kashmir. Indian J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2010, 14, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, R.S.; Bhagat, R.M.; Kalia, V. Impact of climate change on apple crop in Himachal Pradesh. J. Agrometeorol. 2011, 13, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Kuniyal, C.P. Climate change is affecting apple cultivation in Himachal Pradesh. Curr. Sci. 2014, 106, 498–499. [Google Scholar]
- Basannagari, B.; Kala, C.P. Climate change and apple farming in Indian Himalayas: A study of local perceptions and responses. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, F.; Carvalho, L.M.V.; Jones, C.; Bookhagen, B. Multi-Annual variations in winter westerly disturbance activity affecting the Himalaya. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 44, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimri, A.P.; Chevuturi, A.; Dimri, A.P.; Chevuturi, A. Western disturbances—Structure. In Western Disturbances—An Indian Meteorological Perspective; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Jain, S.K. Trends in seasonal and annual rainfall and rainy days in Kashmir Valley in the last century. Quat. Int. 2010, 212, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhura, R.K.; Krishnan, R.; Revadekar, J.V.; Mujumdar, M.; Goswami, B.N. Changes in western disturbances over the Western Himalayas in a warming environment. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 44, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Singh, S.; Rajagopal, E.N.; Gall, R. Mesoscale modeling for mountain weather forecasting over the Himalayas. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shekhar, M.S.; Chand, H.; Kumar, S.; Srinivasan, K.; Ganju, A. Climate-Change studies in the western Himalaya. Ann. Glaciol. 2010, 51, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

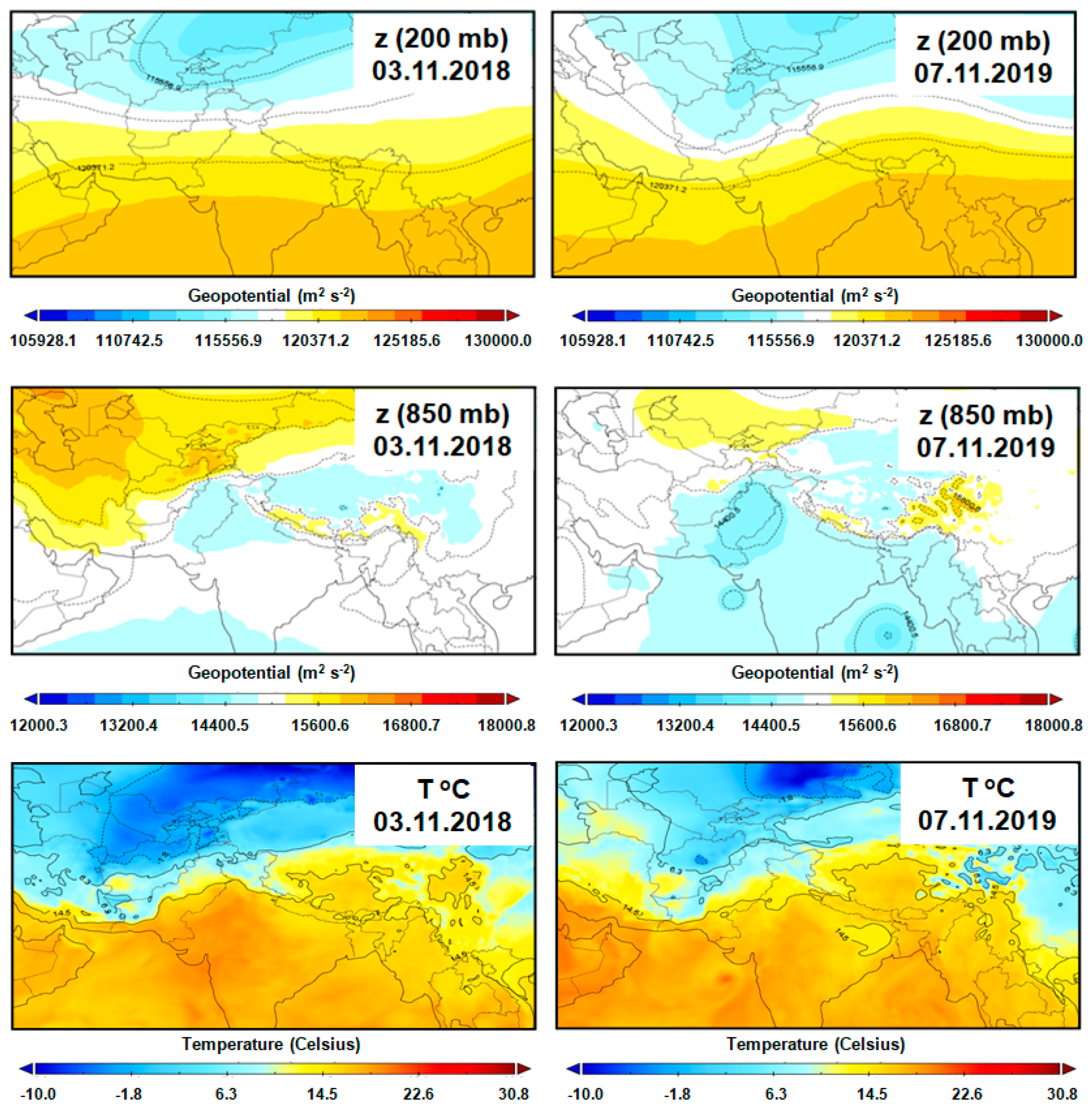
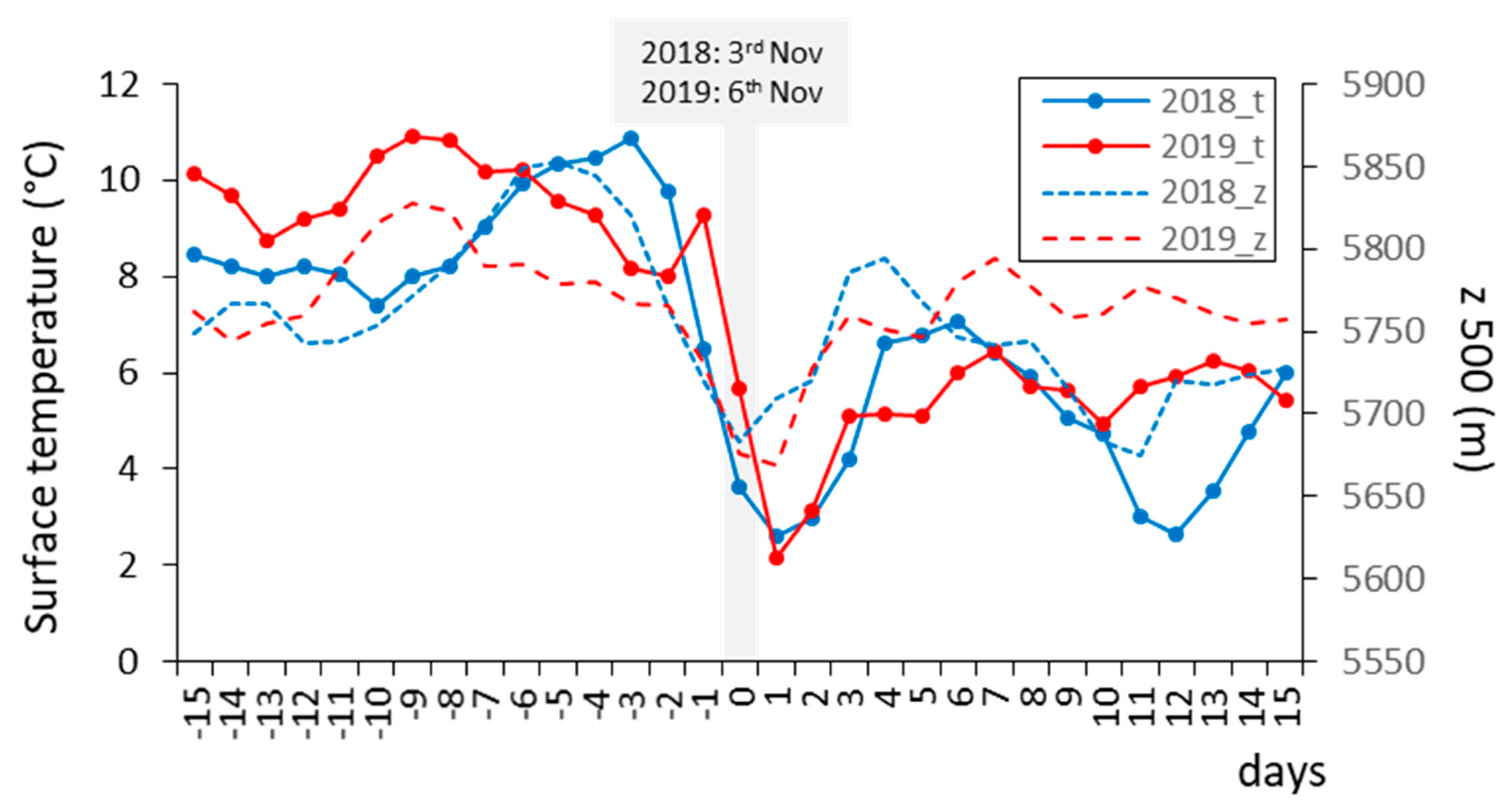
| Dataset | Scene ID/Acquisition Date | Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| A. Remote Sensing Imagery | ||
| Basemap in ESRI ArcMap 10.1 | 2016–2018 | 1:5000 scale |
| ECMWF Re-Analysis (ERA-5) | 1–7 November 2018 1–7 November 2019 | 0.25° |
| B. Precipitation Data | November (1980–2019) | Point data |
| C. Field Data | ||
| GPS measurements | 5 November 2018 | Point data |
| 7 November 2019 | Point data | |
| Photographs | 5 November 2018 | Point data |
| 7 November 2019 | Point data | |
| Damage assessment data | November 2018 | Point data |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rashid, I.; Majeed, U.; Aneaus, S.; Cánovas, J.A.B.; Stoffel, M.; Najar, N.A.; Bhat, I.A.; Lotus, S. Impacts of Erratic Snowfall on Apple Orchards in Kashmir Valley, India. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9206. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219206
Rashid I, Majeed U, Aneaus S, Cánovas JAB, Stoffel M, Najar NA, Bhat IA, Lotus S. Impacts of Erratic Snowfall on Apple Orchards in Kashmir Valley, India. Sustainability. 2020; 12(21):9206. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219206
Chicago/Turabian StyleRashid, Irfan, Ulfat Majeed, Sheikh Aneaus, Juan Antonio Ballesteros Cánovas, Markus Stoffel, Nadeem Ahmad Najar, Imtiyaz Ahmad Bhat, and Sonam Lotus. 2020. "Impacts of Erratic Snowfall on Apple Orchards in Kashmir Valley, India" Sustainability 12, no. 21: 9206. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219206
APA StyleRashid, I., Majeed, U., Aneaus, S., Cánovas, J. A. B., Stoffel, M., Najar, N. A., Bhat, I. A., & Lotus, S. (2020). Impacts of Erratic Snowfall on Apple Orchards in Kashmir Valley, India. Sustainability, 12(21), 9206. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219206





