Abstract
Due to climate change, two-thirds of mankind will face water scarcity by 2025, while by 2050, global food production must increase by at least 50% to feed 9 billion people. To overcome water scarcity, 15 million m3/day of untreated wastewater is used globally for crop irrigation, polluting the soil with pathogens, heavy metals and excess salts. Since 10% of the global population consumes food from crops irrigated with wastewater, pathogens transmitted through the food chain cause diseases especially in young children and women. In this paper, we discuss the status of water scarcity and the challenges to food security, the reuse of wastewater in agriculture and the possible risks to human and environmental health. The efficiency of different irrigation systems in limiting the risks of wastewater reuse and the latest regulations of the European Commission on effluent recovery are also presented. Hence, we emphasize that irrigation offers real perspectives for large-scale recovery of wastewater, helping to reduce the deficit and conserve water resources, and increasing food safety, with the express mention that investments must be made in wastewater treatment plants and wastewater must be properly treated before recovery, to limit the risks on human health and the environment.
1. Water Scarcity
As a result of the development of different industries and activities that contribute to the increase in greenhouse gas emissions, climate change has become a reality that humanity faces every day. Climate change has significant negative effects on the quality and availability of water resources, food security and human health throughout the world. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, in 2017, global warming due to human activities reached an average of 1 °C above the pre-industrial levels [1]. By 2100, global mean temperature could increase by 3.5 °C compared to the same period mentioned above [2], with regional average variations of global temperatures between 1.4–5.8 °C [3]. It is predicted that climate change will account for about 20% of the global expansion in water scarcity [4], and this would affect the development and functioning of communities worldwide, both in social and economic terms.
Earth contains approximately 1351 million km3 of water [5], of which only 3% is available freshwater resources suitable for drinking and irrigation [6]. In the ideal situation when all available water on Earth would have been evenly distributed to a uniformly distributed population, a report by FAO [4] mentions that each person would have had access to 5000–6000 m3 of freshwater/year. Since experts claim that people experience water scarcity below a threshold of 1700 m3/person, the ideal situation would have meant access to abundant freshwater resources for each person. In reality, however, neither freshwater resources nor the population is evenly distributed globally. Variable densities of human communities and uneven distribution of water resources, are factors that determine the manifestation of water scarcity at several levels of risk.
The scarcity of freshwater resources is influenced, among others, by the growth of population, urbanization, consumption per person, water pollution and climate change. Water scarcity is an important indicator of health, and an issue of poverty, which mostly affects the people in rural areas, where high population densities are prevailing [7]. A presumed 1.2 billion people live in river basins facing physical water scarcity, and another 1.6 billion live in water-deficient areas, where affordable water supply works are not available [7].
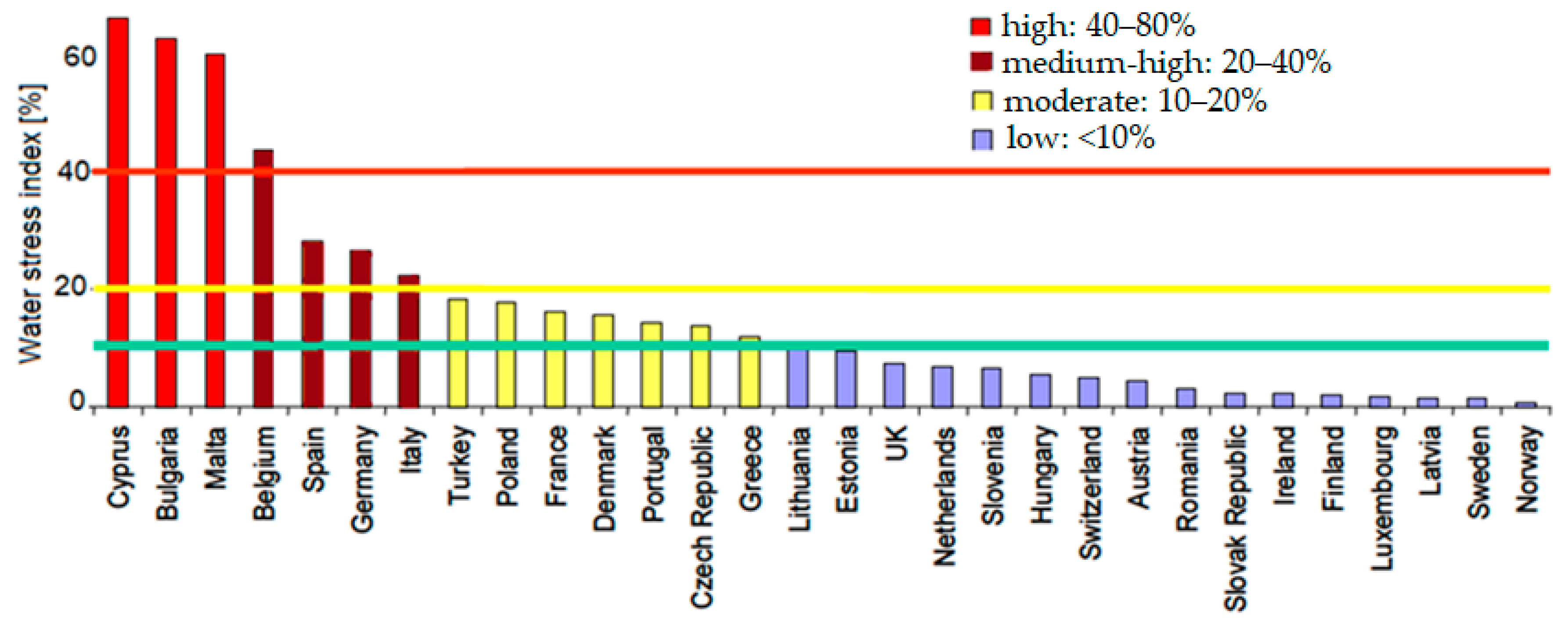
The intensity of water scarcity, either in a region or at the country level, is assessed as the water stress index, which is estimated as the ratio between the annual water withdrawal from ground and surface water to the total renewable freshwater resources [8]. Worldwide, 40% of the total land area is arid, semi-arid and dry-subhumid [9]. Half of the European countries are facing water stress, as stated by Bixio et al. [10] (Figure 1), and a survey by Aquarec [11] classified the Member States into four categories of risk according to the water stress index, highlighting that 10% of the European territory and 14% of the population were subjected to water scarcity.
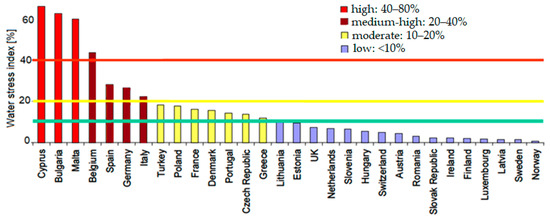
Figure 1.
European Union member states ranked according to their water stress index (green, yellow and red horizontal lines represent the thresholds for low, moderate and high water stress, respectively) (adapted from [10]).
A report by FAO [12] explains that a country experiences water stress when it withdraws over 25% of its renewable freshwater resources; physical water scarcity occurs at over 60% withdrawals and severe physical water scarcity occurs at over 75% withdrawals. Thus, countries subjected to extremely high water stress (>80%) are Libya, Israel, Egypt, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan, while high water stress (40–80%) affects China, India, Afghanistan and South Africa. The United States and Kazakhstan have low–moderate water stress (10–20%), and South America, Canada and Russia respectively, experience low water stress (<10%).
An analysis of data collected in 2019 by Aqueduct, a tool developed by World Resources Institute, was conducted by Hofste et al. [13] and found that water stress is extremely high in 17 countries, high in 27 countries, medium-high in 24 countries, low-medium in 32 countries and low in 63 countries. Nowadays, one-third of major cities are subjected to high or extremely high water stress [14] and at least 11% of the European population experiences water deficit [15]. Taking 2025 as a reference year, it was estimated that approximately 3.5 million people worldwide could experience water scarcity [16], while in developing countries 1.2 million people (with a risk of increase to 1.8 million) will live in water-scarce areas due to the absence of unreliable policies or convenient management strategies for reusing treated wastewater in crop production [7].
Water consumption registers a significant increase from year to year. A report released in 2017 by the European Environment Agency shows that in Europe, agriculture consumes 36% of total water use/year (and up to 60% during summer and to 80% in some southern European regions), public water demand consumes 32%, service sector 11% and other needs 21% [17].
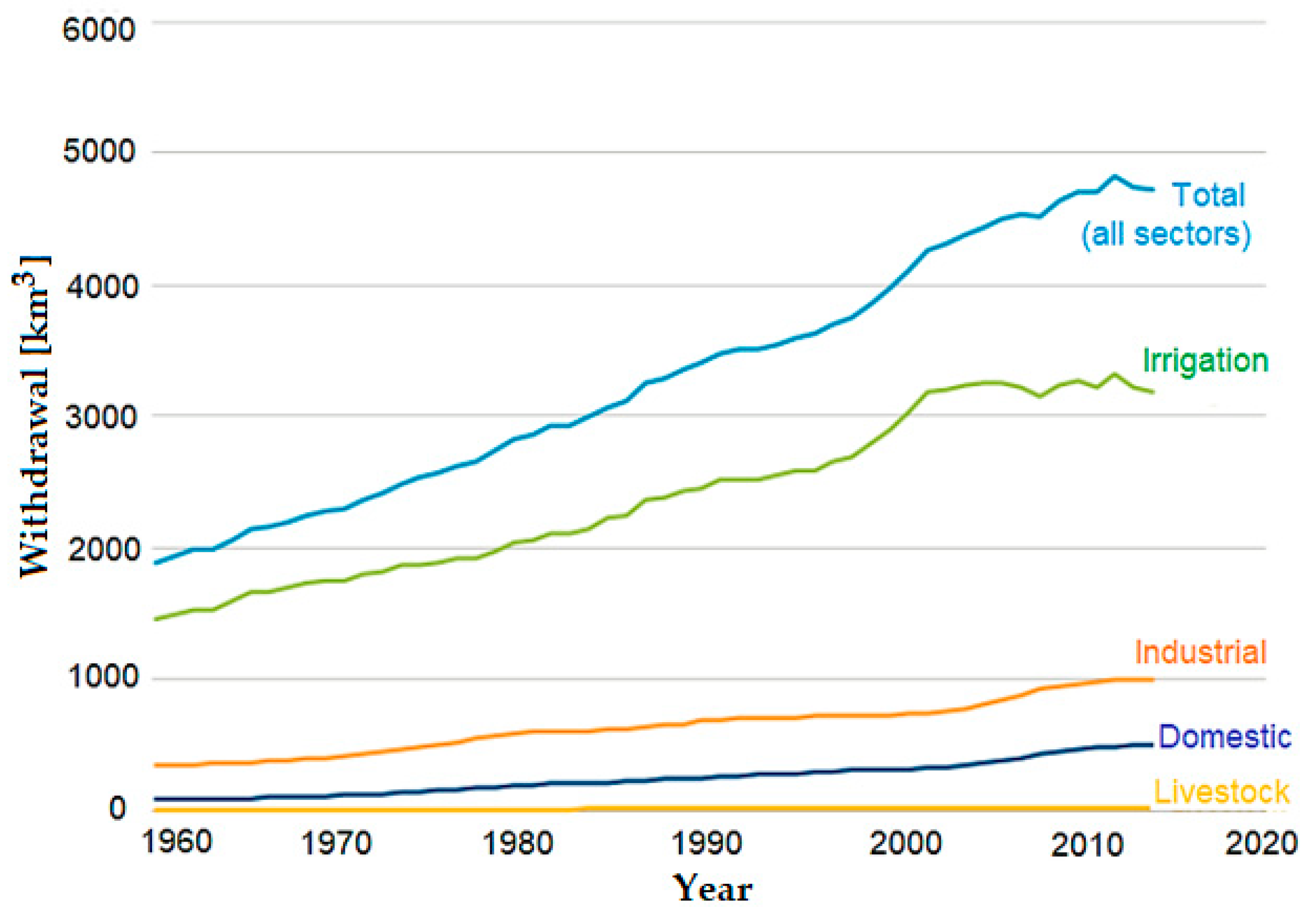
Based on the evolution of freshwater withdrawals between 1960 and 2014 [14], it is concluded that agriculture is the largest global user of freshwater (70%) for crop cultivation and animal husbandry, registering an increase of 100% in the last century; the industry consumes 19%, meaning that industrial water demand increased three-fold in the last century; since the 1960s, the population grew by more than 4 billion and the withdrawals for domestic consumption increased by 600% (Figure 2).
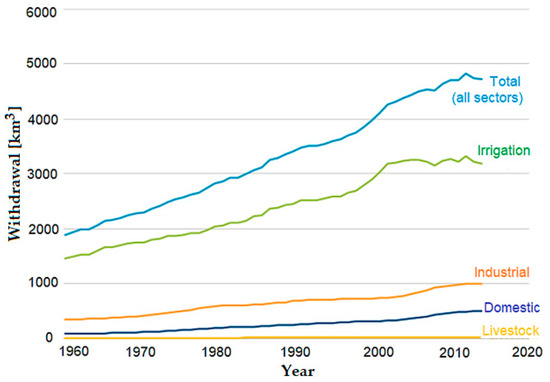
Figure 2.
Global water withdrawals by sector, between the years 1960–2014 (data from [14]).
The economic and social well-being of any nation is in close correlation with the level of development in agriculture. Irrigation is the major consumer of fresh water in agriculture (70% of the overall withdrawal). An estimated 20% of the overall agricultural land is presently irrigated, contributing 40% of the total food production [18]. Worldwide, in 2011, the average cultivated cropland was 0.23 ha/person, with 0.17 ha/person in low-income countries, 0.23 ha/person in middle-income countries and 0.37 ha/person in high-income countries [19].
In 2010, about 16% of the world’s cultivated cropland was equipped with irrigation systems [20], with shares of 70% in 15 Asian countries, 16% in America, 8% in Europe, 5% in Africa and 1% in Oceania [21], located thus: 70% in 15 Asian countries, 16% in America, 8% in Europe, 5% in Africa and 1% in Oceania. To the best of our knowledge, FAO has so far not published maps based on more recent or significantly different data than those in 2011. FAO reported that of the 219 million ha irrigated then in developing countries, 40 million ha were on arid and hyper-arid land, which could increase to 43 million ha by 2050 [19].
Worldwide, by 2050, the volume of water withdrawn for irrigation will increase to 2.9 thousand km3, with most of the net increase arising in low-income countries [22] and the net global irrigated area will continue to increase by at least 20 million ha [23], almost entirely in land-scarce developing countries.
The increasing competition between the agricultural and domestic use of high-quality freshwater supply, mostly in arid, semi-arid and densely populated regions, will put even more pressure on the already scarce water resources. It was reported by FAO [4] that 2000–3000 L of water/person are consumed daily to ensure food needs, to which are added another 2–3 L necessary for drinking purposes and between 20–300 L for domestic purposes. For the latter category, it was estimated that in urban areas of developed countries, daily water consumption can vary from 15–55 L/person and up to 90–120 L/person [24]. By 2030, more than 160% of the total available water volume in the world will be needed to satisfy the global water requirements [25]. Demands for food production, water and energy are expected to expand by 35%, 40% and 50% respectively by 2030 [26], as consequences of demographic growth, economic development, improvement of living standards, pollution and climate change.
The growing scarcity of freshwater resources is currently one of the most important limiting factors for crop production and food security. The World Research Institute’s Aqueduct tool [27] can predict the impact of irrigated or rain-fed agriculture (either at the global level or customized for a certain country), on each type of crop, under the influence of either water stress or seasonal variability, in terms of food demand for crops, total crop production, crop net trade, population at risk of hunger and kilocalories/person.
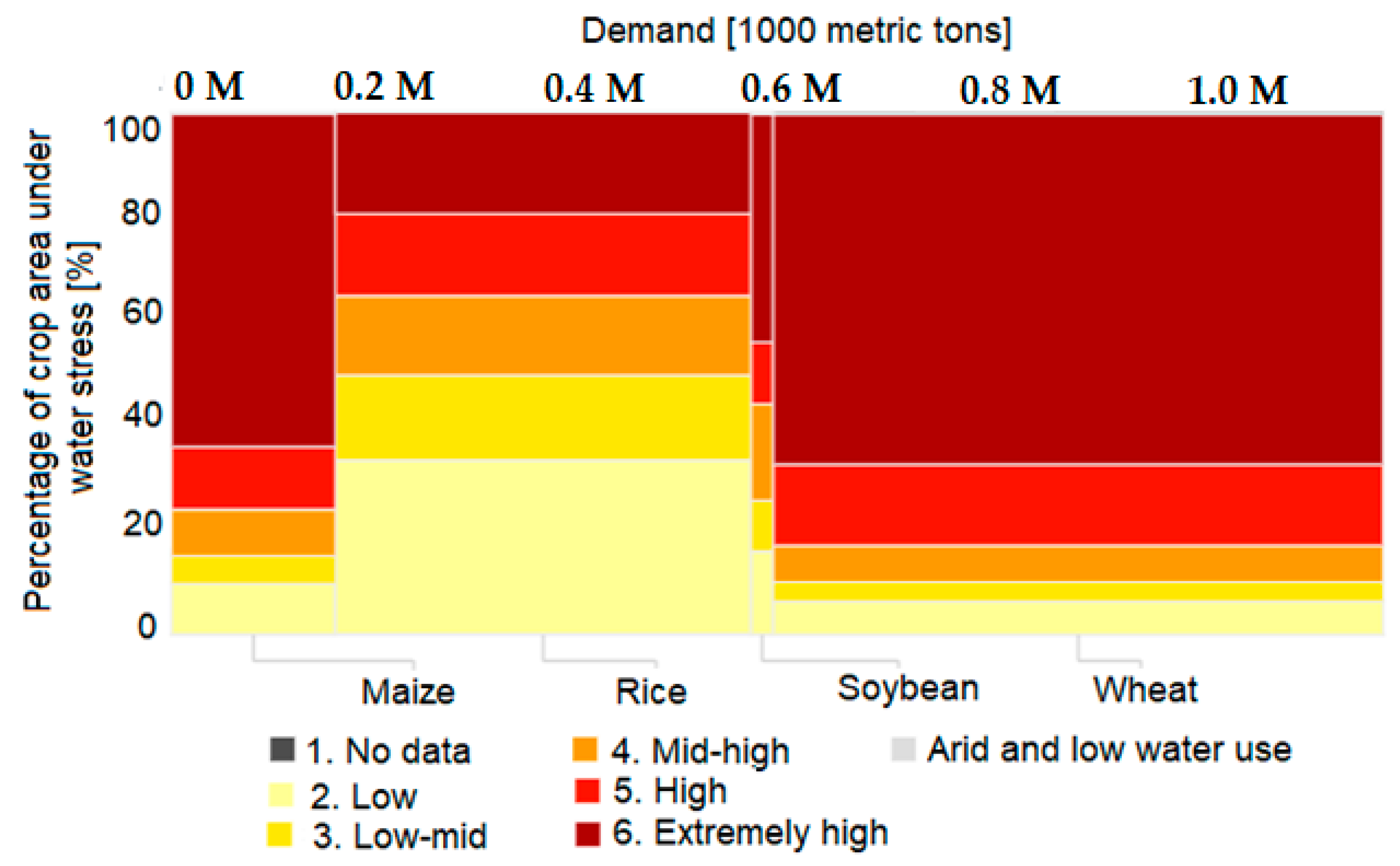
The diagram in Figure 3, generated using [27], shows the estimated situation at the global level, in areas with water stress, and in terms of total crop production, at a global level, when choosing the year 2040 as the baseline in the Aqueduct tool. The tool directly displays the percentage of all irrigated crop areas facing each level of water stress (vertical axis) and the volume of the demand (width of bars, delimited by the value intervals on the upper horizontal axis in Figure 3) for maize, rice, soybean and wheat. The interactive analysis of the diagram showed that the highest demand for food needs is estimated to be recorded for wheat crops. Thus, there is a projected 66.91% physical water risk (exposure to changes in water availability) for wheat to grow in areas with extremely high water stress. For maize crops, there is a 63.71% physical water risk to grow in areas with extremely high water stress, 19.43% for rice and 43.65% for soybean respectively, for the latter registering the lowest requirement for household use. Therefore, it is estimated that in 2040, there will be a reduced demand for soy to provide food at the household level, and the main crops will be wheat, rice and maize.
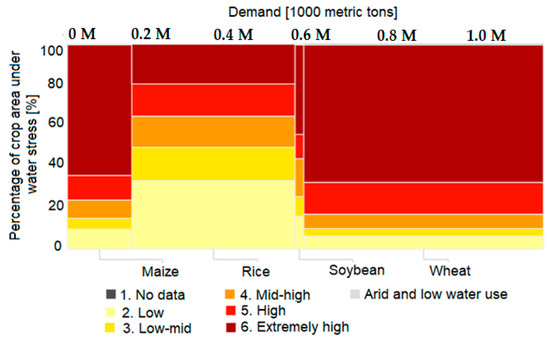
Figure 3.
Projected percentage of irrigated crop area by water stress level and volume of demand in 2040, worldwide (diagram generated using [27]).
Studies in the literature mention different data for increasing the global food production needed to provide food for the 9 billion people [6] by 2015: 56% [28], 60% [7], respectively 70% [29]. Although some researchers [30,31] believe that this can be achieved through judicious distribution and use of freshwater resources, the farmers, who are typically very adaptable to changes, have already turned their attention to unconventional, alternative sources of water for crop irrigation, such as domestic and municipal wastewater (both treated and untreated). In order to control the current water deficit in Europe, the amount of municipal treated wastewater reused for crop irrigation should increase more than twice in 2025 compared to 2000 [15].
2. Wastewater Reuse in Irrigation, a Sustainable Practice
Huge volumes of wastewater are generated daily in households, industries and agriculture. The volume of wastewater accounts for 50–80% of the domestic household water uses [32] and the global wastewater discharge was estimated at 400 billion m3/year, polluting approximately 5500 billion m3 of water/year, as reported previously [33]. Wastewater usually consists of 99% water and 1% suspended, colloidal and dissolved solids [34].
It is well known that wastewater, depending on its source, is loaded with pollutants such as organic matter, suspended solids, nutrients (mainly nitrogen and phosphorus), heavy metals, emerging contaminants (antibiotics, hormones, personal care products, pesticides, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, phenolic compounds, volatile organic compounds, antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes) and pathogenic microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, protozoans and parasitic worms).
Wastewater has an important content of nutrients and hence, high potential to be used in agricultural irrigation because it supplies organic carbon, nutrients (NPK) and inorganic micronutrients to the crops [35]. Many studies emphasize the usefulness of wastewater and especially of treated water for crop irrigation, in terms of benefits expressed by increased crop productivity [34,36] due to the high content of nutrients in these waters. Jang et al. [37] reported a 15% increase in rice productivity and Emongor et al. [38] obtained a 114.9% increase in tomato irrigated with wastewater. A recent study [39] showed that due to the nutrient content, the reuse of treated municipal wastewater in countries like Brazil, Poland and Saudi Arabia would cover 100% of both phosphorus and potassium requirements for maize crops.
Wastewater reuse for irrigation of agricultural crops is a market-driven action based on the requirements of the agricultural sector and can contribute to the promotion of the circular economy by recovering nutrients from the reclaimed water and applying them to crops by different fertigation methods. Wastewater reuse in irrigation is often practiced in low-income, arid and semi-arid countries [40] where evapotranspiration outpaces precipitations for most of the year [41]. The availability of wastewater in nearby communities increases the selection of crops that farmers can grow. In the literature, there are numerous experimental studies in which wastewater has been used successfully for the irrigation of various agricultural crops, including: lettuce [5,38,42,43,44,45], tomatoes [44,46,47,48,49], potatoes [5], carrots [50], radishes [42,51], cucumbers [39], spinach [50], onions [5,43], fennel [44], asparagus [5], eggplants [47,49], broccoli [52,53], cabbage [5], beet (Beta vulgaris L.) [54], avocado [5], aromatic (culinary) herbs [55], grape [56,57], apple trees [58], nectarine trees [58], banana trees [59], lemon trees [60], orange trees [61], olive trees [62,63,64,65], maize [42,43,66], wheat [67,68,69], rice [37], peanuts [5], sunflower [66], alfalfa [66,70], sorghum [71,72], red amaranth [73], napier grass [66], switchgrass [74], Jatropha curcas L. [75], Typha latifolia, Arundo donax and Phragmites australis [76], flowers [5], conifers, eucalyptus, poplar [5].
Due to its multiple benefits, this practice is gaining wider acceptance in many parts of the world. Although the younger population, which has access to education and sources of information on the benefits of reusing wastewater as irrigation water, has a positive attitude towards this practice, the older population is still reluctant in accepting to consume food from crops irrigated with wastewater [77]. Some of the advantages offered by the capitalization of wastewater (treated, partially treated or diluted) in agriculture are the following: availability of large quantities of water throughout the year without being affected by climatic conditions, high nutrient content that can reduce the use of chemical fertilizers, increasing the productivity on less fertile soils, reducing the damage to freshwater ecosystems associated with eutrophication and algal blooms, etc. [78]. Although the benefits of wastewater use in agriculture are multiple, there are also various disadvantages of this practice, including various diseases in farmers and consumers of food from wastewater irrigated crops; accumulation of heavy metals, salts, antibiotics, growth hormones and other hazardous substances into the soil; low hydraulic conductivity due to clogging of soil pores with suspended solids from wastewater; decreased quality of agricultural crops, because they will accumulate the pollutants transferred from wastewater to the soil, etc. These issues are discussed in Section 3.
A Global Water Intelligence [79] report mentions that 7.1 billion m3/year (5% of treated wastewater and 0.18% of water consumption) was reused for irrigation (about 50%) and industrial applications (about 20%). At least 20 million hectares in 50 countries (10% of the total irrigated land, which is 17% of the total arable land) are irrigated with untreated, partially treated or partially diluted wastewater worldwide. Of the global water consumption for agriculture (70% of withdrawals), irrigation with recovered wastewater represents only 1% [80] and this agricultural practice is applied on 525,000 ha of agricultural land [5].
Study [81] presents a top of countries that reuse untreated wastewater as source of irrigation water for agricultural crops, placing China in first place (with 200 thousand ha irrigated with wastewater), followed closely by Mexico (with about 190 thousand ha) and India (with about 70 thousand ha). Among the countries that irrigate less than 50 thousand ha with untreated wastewater are mentioned Pakistan, Colombia, Chile, Syria, South Africa, Ghana, Turkey, etc. According to the same study, Chile and Mexico occupy the first two places in the top of the countries that reuse treated wastewater as irrigation water in agriculture, followed by Israel, Egypt, Cyprus, Italy, Argentina and others. Although according to Figure 1, Cyprus is the country with the highest water stress index, it does not practice irrigation with untreated wastewater.
Although issues of public opinion and merchandisability of crops might appear sometimes, World Health Organization (WHO) [82] reported that 10% of the world population consumes food from agricultural crops irrigated with wastewater. Another study [83] mentions that 15 million m3 of treated wastewater/day are reused by 200 million farmers in 44 countries for irrigation of food and energy crops.
Only 2.4% of treated wastewater (700 Mm3/year) is reused in Europe [84,85], or the equivalent of 0.5% of annual freshwater withdrawal [86]. According to data from the LIFE+ REQpro project [87], in Europe, 52% of the total volume of recycled water is used for irrigation, with 32% for agricultural irrigation and 20% for landscape irrigation. In South Europe, where water scarcity will expand in the future, out of 15 countries, only Greece, Italy, Portugal and Spain have already adopted national regulations on the reuse of wastewater [78]. This could be partly due to the high costs of wastewater reuse systems, and the lack of common environmental and health standards for water reuse and, as regards, in particular, agricultural products, due to the potential health and environmental risks and potential obstacles to the free movement of such products irrigated with reclaimed water. If the entire volume of treated wastewater in Europe would be reused, it would ensure 44% of agricultural irrigation needs and reduce 13% of withdrawals from natural sources [88].
In order to capitalize on the wastewater in agriculture in safe conditions for health and the environment, it is imperative that farmers be informed about the risks and measures of good practice in this activity. The best example of good practice is to use only treated wastewater whenever possible because this reduces both freshwater consumption and health and environmental risks. Another measure is the permanent monitoring of effluent quality or of wastewater that will be reused, in order to verify the conformity with the standards imposed by each country (if any) or with the minimum regulations of WHO. In the absence of complete treatment technologies, it is necessary to treat the wastewater by settling and/or filtration, to avoid clogging of soil pores and emitters of irrigation systems. Sanitation systems are completely lacking in some areas, with farmers and agricultural workers in these areas being the most exposed to the risk of contamination and health problems. Therefore, it is very important that they wear protective suits when working with wastewater, to avoid direct handling of wastewater irrigation products and to disinfect their hands when they come in direct contact with wastewater or wastewater irrigated products. If there are no possibilities for wastewater treatment, it is advisable to avoid the irrigation of vegetable crops and to limit its use only for fodder crops and fruit trees. If, however, untreated wastewater is used to irrigate vegetables, it is recommended to apply drip irrigation to avoid direct contact between wastewater and plant leaves, but also to reduce water consumption and avoid direct contact of agricultural workers with wastewater. Farmers must monitor the properties of soils irrigated with wastewater and the irrigation scheduling because if the crop is irrigated before the development of the edible part, it can reduce the risk of contamination with pathogens. Irrigation of crops with wastewater should stop before harvest.
3. Risks of Irrigation with Untreated Wastewater
3.1. Health and Environmental Risks
The safety of reusing wastewater for crop irrigation is an important subject worldwide. If wastewater is not treated properly prior to being capitalized in irrigation, it can cause serious problems to the soil (salinization, toxicity due to sodium, chloride and boron ions, structural degradation, reduced aeration and pore-clogging due to suspended solids in wastewater, reduced soil hydraulic conductivity), to agricultural crops (heavy metal accumulation, microbial load; delayed or irregular plant maturity due to excessive nutrients), to groundwater (by leaching of excessive nitrates), but also to the health of farmers and consumers of irrigated crops.
Treated wastewater must be reused whenever appropriate and disposal routes must minimize all possible adverse effects on the environment and human health. The most suitable treatment method that can be applied to wastewater before being used as irrigation water is the one that can produce an effluent that meets the quality standards, from the microbiological and chemical point of view, with minimum operation and maintenance requirements. As reported by Norton-Brandão et al. [89], depending on wastewater quality and crop requirements, the most suitable technologies for wastewater treatment prior to being used for irrigation include sedimentation, filtration and disinfection by ClO2, O3, UV or TiO2 as tertiary treatments; the authors also reported that in terms of microorganisms, membrane bioreactors have high efficiency, while technologies like ponds, constructed wetlands and disinfection oxidants can achieve good removal rates.
The quality of effluents (treated wastewater) used in agriculture has a great influence on the operation and performance of the wastewater-soil-plant system. In irrigation, the required quality of effluents is determined by the restrictions imposed by soil conditions, type of crop and irrigation systems, constantly pursuing the minimization of risks. Operators of wastewater treatment plants should cooperate with the farmers (end-users of reclaimed wastewater) to ensure that the quality parameters of the effluents correspond to the requirements of each category of agricultural crops in terms of irrigation water. Also, end-users should be trained in good practices for the reuse of wastewater and effluents.
Human health is threatened by the wide range of pathogens in wastewater. A review [90] compiled the limits of numbers between which the pathogens excreted by humans can be found in raw wastewater (Table 1).

Table 1.
Common numbers of excreted organisms in raw wastewater (data from [90]).
Pathogen microorganisms in untreated or improperly treated wastewater can survive in the environment long enough to be transmitted to humans by aerosols, causing bacterial, parasitic and viral infections. However, in arid and semi-arid areas, UV radiation from natural sunlight could be an important factor in the process of inactivation of microorganisms [91]. When reusing wastewater in irrigation, people are exposed to pathogens by direct contact with the contaminated water (accidental ingestion, inhalation or dermal contact) prior, during or after irrigation; ingestion of irrigated vegetables; consumption of animal products that have been exposed to wastewater and became contaminated [82]. Other possibilities of infection are, as previously reviewed [92]: recreational swimming and bathing in lakes or rivers fed by wastewater, floodings following heavy rains, respectively emptying of on-site sanitation facilities and managing wastewater treatment processes.
Through the food chain, pathogens in wastewater can trigger serious diseases and can even lead to death. In developing countries, often affected by lack of sanitation systems and poor quality of drinking water, diarrhea is the second leading cause of death for 800,000 young children [93]. Cholera, typhoid fever and shigellosis epidemics, as well as sero-positive responses for Helicobacter pylori [90], the latter leading to chronic infection and even cancer [94] are consequences of using untreated wastewater [90] and of consumption of unprocessed vegetables from crops irrigated with wastewater. Among the species of intestinal nematodes, Ascaris lumbricoides, Anclyostoma duodenale, Necator americanus and Trichuris pose the highest health risk [34]. In developed countries, 2% of adults and 6–8% of children are infected with protozoan cysts of Giardia, causing virulent outbreaks [95]. Cryptosporidium parvum, the second most common waterborne pathogen worldwide, is responsible for 2% of all diarrhea cases in developed countries, including 7% in children and 14% in AIDS patients [96].
Leafy greens, often as packed salads, are usually consumed raw, increasing the risk of human exposure to persistent Escherichia coli originating from irrigation with wastewater [97] and cause enteric viral infections like acute gastroenteritis [98]. In study [99], the authors reported that the enteric viruses present in domestic wastewater can spread by irrigation systems and cause respiratory infections, hepatitis, conjunctivitis, various chronic diseases and central nervous system infections. Women are much more vulnerable to pathogens because they spend more time in contact with wastewater during field labor, after which they prepare meals for the family which, unless they have rigorous hygiene, will transmit the pathogens [100]. Emerging contaminants including antibiotics, estrogen hormones, pesticides and surfactants are very recalcitrant to removal by conventional wastewater treatment plants and they will pose additional risks to public health [101].
Heavy metals are of little concern if treated or partially treated domestic wastewater is reused in irrigation because they are usually within the admissible limits for the quality of irrigation water [102] and can be efficiently removed during common treatment processes. In small concentrations, heavy metals like Cd, Cr and Ni are useful nutrients for crops, but in higher concentrations, they can be toxic to vegetables and fodder crops due to their high uptake rates. Higher risks occur when industrial wastewater is used for irrigation, as such or blended with domestic wastewater [103] because heavy metals from untreated wastewater are non-biodegradable and have a long biological half-life [104]; they accumulate in the topsoil (at a depth of 20 cm), and also in leafy vegetables, in higher concentrations in roots than in leaves [100]; they enter the human and animal body by consumption of contaminated food crops, water or inhalation of dust particles from contaminated soils [105]. Heavy metals are especially toxic for the health of children [106] because they decrease children’s intrauterine growth, immunological defenses and increase the risk of cancer [107].
Nutrients in wastewater concentrate in the root zone and leach downward, contaminating the soil and groundwater [108]. Conventional wastewater treatment processes are not efficient enough in eliminating excess salts and sodium [109]. High concentrations of soluble salts in wastewater are responsible for soil salinization or sodification. Salinity (determined as electrical conductivity) is the second major cause of degradation of agricultural soil because it leads to swelling and dispersal of soil aggregates. In the semi-arid areas, in soils irrigated with high salinity wastewater decreased plant growth [110], a decline of crop yield [8] which occurs gradually allowing crop selection [111] and limited oxygenation were observed [112]. In soils with high sodicity, deterioration of soil structure, waterlogging, nutrient imbalances in crops [110], reduced germination [113], increased artificial compaction, increased erosion and difficult drainage were observed. To reduce the negative effects of highly sodic wastewaters on soil and crops, calcium-based amendments [114], biochar or humic substances [115] must be applied. The content of organic matter is higher in irrigated soils and leads to the formation of soil aggregates and increased water retention capacity [116].
3.2. Issues of Irrigation Systems Used in Wastewater Recovery
Water reuse systems are made up of the following components: raw wastewater entering the wastewater treatment plant (the influent); the multitude of treatments to which the wastewater is subjected inside the treatment plant; supplementary treatments to obtain treated (reclaimed) water with suitable quality parameters for reuse; effluent storage and distribution systems; irrigation system [35]. When designing an irrigation system dependent solely on wastewater, in addition to the high costs of equipment and land [114], one should have in mind that wastewater is generated continuously and equally throughout the year, but the demand for irrigation is cyclic.
There are three categories of irrigation methods: flood and furrow—wastewater is applied at the soil surface, usually implemented in peri-urban and rural agriculture; spray and sprinkler—wastewater is applied on top of the crop; localized (drip irrigation)—wastewater is directly applied to the soil in a localized manner [117].
Flood irrigation can severely contaminate an entire field [118] but is effective in limiting the accumulation of salts in the root zone [74]. Suspended solids, organic matter, microorganisms [119], mineral precipitation due to the high pH of wastewater or algal growth in wastewater can clog the nozzles of drip and sprinkler irrigation systems [120], with the highest occurrence rate in case of the latter. Clogging of nozzles and pipes means higher maintenance costs and reduced profits for farmers. So, for wastewater reuse, when choosing the emitter type for the drip irrigation system, one must know that vortex emitters are more sensitive to clogging than labyrinth emitters [121,122] and that the risk of clogging is smaller in emitters with higher discharge rate than in similar emitters with lower discharge rates [123]. As reported by the authors of study [124], clogging of drip irrigation systems by algal growth can be avoided or treated by chlorination of reclaimed water.
Underground drip irrigation gives higher crop yield compared to surface drip irrigation [125], it can reduce the environmental risks and decrease nitrate leaching rates [126], but it has the disadvantage that it is very difficult to observe when a transmitter gets clogged [75]. Underground drip irrigation with untreated or inefficiently treated wastewater, which contains different concentrations of fecal microorganisms and human pathogens, poses a risk of groundwater contamination [44]. Sprinkler irrigation systems can improve salt leaching under plant roots but they can also increase the effect of ion toxicity on sensitive crops because salt accumulates in their leaves. For saline wastewater, drip irrigation systems are more efficient, although salt will accumulate between drip points [109]. One parameter that must be monitored when using sprinkler irrigation is the residual chlorine concentration; in the ideal situation, residual chlorine must be less than 1 mg/L to not affect the foliage, and at values exceeding 5 mg/L severe damage to the foliage has been observed [122].
The level of contamination of soil and agricultural crops with wastewater is influenced by the type of irrigation system. Various studies have shown that drip irrigation is a water-saving technology with positive effects on crop productivity [60], and is more effective in avoiding contamination with pathogens [112], thus minimizing the health and environmental risks [126], as the application of wastewater directly on the ground ensures greater protection of workers’ health. On the other hand, the need to disinfect wastewater during sprinkler irrigation is emphasized, as this method of irrigation increases the risk of contamination of crops with pathogens, but also of the area near crops, with bacteria and viruses that are easily transmitted by aerosols [90]. Unlike drip irrigation, furrow irrigation increases the likelihood of direct contact between wastewater contaminated with human pathogens and the edible part of plants [127] and therefore poses greater risks to the health of consumers of wastewater irrigated food. A study of a radish culture irrigated with wastewater showed that, compared to the surface drip system, the subsurface drip irrigation system was more effective in reducing contamination with fecal coliform bacteria and fecal streptococci [51].
Given the experience gained so far by users of different wastewater irrigation systems, and the problems arising from them, the minimum regulations [88] that will enter into force in 2023 require that all Member States will have to use specific irrigation systems depending on the class of water quality and crop to be irrigated, as described in Table 2.

Table 2.
Classes of treated water quality, by agricultural use and irrigation method (data from [88]).
Affordable technological solutions of irrigation systems and good management practices with minimal environmental impacts shall be adopted by farmers to ensure the sustainable use of wastewater effluents in agriculture.
4. Recent Guidelines for the Safe Reuse of Wastewater Irrigation
Although the reuse of treated wastewater for agricultural crop irrigation is encouraged by governments and official entities around the world, only a few countries with higher income level have implemented different standards or directives on the physico-chemical and biological parameters of treated wastewater to protect human health and the environment when used in agriculture [78]. Low-income countries have no resources for wastewater treatment plants and no capacity to treat their wastewater properly, and hence they often use it as such, having no choice but to take the risks arising from these practices. Currently, in three out of four cities in developing countries, farmers are forced to use untreated or partially treated wastewater to irrigate their crops and provide their food needs [128]. It is estimated that in 2035, more than 5.5 billion people will live in areas without sewerage systems [129], and if we correlate with the water deficit, it is expected that in those areas, there will be an increase in the incidence of diseases caused by consumption of vegetables and fruits from crops irrigated with wastewater.
Usually, physico-chemical parameters including biological oxygen demand, chemical oxygen demand, nutrients, turbidity, pH, salinity (electrical conductivity and sodium absorption rate), suspended solids, heavy metals and microbiological parameters (Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Shigella, fecal coliforms, fecal enterococci, nematode eggs) are specified in guidelines regarding the capitalization of wastewater in agriculture. Regulations in various countries impose different limits for total coliforms (colony forming units/100 mL), fecal coliforms (colony forming units/100 mL), Escherichia coli (colony forming units/100 mL) and nematode eggs (number/L), and set the categories of crops and/or soils which can be irrigated with wastewater, depending on its quality.
In 2006, WHO provided a series of guidelines for the safe reuse of wastewater in agriculture, including treatment and non-treatment recommendations, covering the entire food chain. Worldwide, bacterial pathogens (Salmonella sp., Shigella sp., Legionella sp., Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae), helminths (Ascaris and Tenia sp.) and intestinal protozoans (Giardia and Crysptospridium) are of public health concern. Waterborne viruses like HAV, HEV, adenovirus and rotavirus pose the greatest risk of transmission through wastewater reuse [82]. Thus, the use of microbial indicators of fecal contamination has been considered by health and environmental authorities to be the most reliable method of monitoring water quality and the performance of water treatment systems [130].
The low uptake of water reuse practices is justified by the fact that until recently there were no unitary regulations at the European level regarding the recovery of wastewater [57]. However, to achieve unitary environmental and health standards in relation to food hygiene for agricultural products irrigated with treated wastewater, the quality of reclaimed water should not differ between the Member States.
On 25 May 2020, the European Commission published the new regulation on minimum requirements for water reuse for agricultural irrigation, which has entered into force but the new guidelines will be applied starting on 26 June 2023 and are expected to stimulate and facilitate water reuse in the European Union [88]. Table 3 presents the parameters that will be required for the quality of effluents used in crop irrigation.

Table 3.
Quality requirements for reclaimed water intended for agricultural irrigation (data from [88]).
In addition to the parameters specified in Table 3, regulation [88] also provides, for the four classes of effluent quality, the following: Legionella sp.: <1000 colony forming units/L, where there is a risk of aerosolization and intestinal nematodes (helminth eggs): ≤1 egg/L for irrigation of pastures of forage.
The implementation by the Member States of these minimum requirements will contribute to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals of the United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, where Goal 6 aims at ensuring the availability and management of water and sanitation for the global population, as well as a considerable boost in water recycling and safe water reuse globally [88]. Stronger guidelines and financial stimulus could help the European farmers to reuse more than 6000 million m³ of water/year by 2025 [88].
To conclude, in the context of accentuating climate change and diminishing freshwater resources, wastewater can partially cover the need for water for irrigating agricultural crops. Although the reuse of wastewater brings many benefits in terms of reducing volumes discharged into receiving watercourses, as well as increasing crop yields and reducing the need for chemical fertilizers due to nutrients in wastewater, it should not be overlooked that untreated wastewater can have devastating effects on human health. Given the multitude of studies that address the growing practice of wastewater recovery, as well as the need to reduce risks to health and the environment, it is clear that the ideal option is to use only effluents of appropriate quality for crop irrigation. The newest and mandatory guidelines for the safe reuse of wastewater will significantly mitigate the risks to human health and the environment. Until their entry in force, the operators of wastewater treatment plants should improve their treatment methods and equipment so as to obtain polished effluents whose physico-chemical and bacteriological parameters fall within the regulated limits for reuse in agriculture.
In view of the above, the authors of this study strongly believe that supporting underdeveloped countries, which are most exposed to famine and serious diseases, in the construction of sewage systems, treatment plants to ensure effluents of appropriate quality from a microbiological and physico-chemical point of view and large-scale examples of good practices for the recovery of wastewater in irrigation that are currently implemented in developed countries, will contribute to the sustainability of water resources and the environment, agriculture and human life worldwide.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.U. and V.V.; methodology, N.U. and G.V.; validation, N.U., V.V. and G.V.; formal analysis, G.V.; investigation, N.U.; resources, V.V.; data curation, G.V.; writing—original draft preparation, N.U., V.V. and G.V.; writing—review and editing, N.U.; visualization, V.V.; supervision, V.V. and G.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant of the Romanian Ministry of Research and Innovation CCDI—UEFISCDI, Project INNOVATIVE TECHNOLOGIES FOR IRRIGATION OF AGRICULTURAL CROPS IN ARID, SEMIARID AND SUBHUMID-DRY CLIMATE, project number PN-III-P1-1.2-PCCDI-2017-0254, Contract no. 27 PCCDI/2018, within PNCDI III.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Allen, M.R.; Dube, O.P.; Solecki, W.; Aragon-Durand, F.; Cramer, W.; Humphreys, S.; Kainuma, M.; Kala, J.; Mahowald, N.; Mulugetta, Y.; et al. Framing and Context. In Global Warming of 1.5 °C—An IPCC Special Report on the Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 °C Above Pre-Industrial Levels and Related Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Pathways, in the Context of Strengthening the Global Response to the Threat of Climate Change, Sustainable Development, and Efforts to Eradicate Poverty; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Portner, H.-O., Roberts, D., Skea, J., Shukla, P.R., Pirani, A., Moufouma-Okia, W., Pean, C., Pidcock, R., et al., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/sites/2/2019/05/SR15_Chapter1_Low_Res.pdf (accessed on 17 October 2020).
- Gerten, D.; Lucht, W.; Ostberg, S.; Heinke, J.; Kowarsch, M.; Kreft, H.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Rastgooy, J.; Warren, R.; Schellnhuber, H.-J. Asynchronous exposure to global warming: Freshwater resources and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 034032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNicola, E.; Aburizaiza, O.S.; Siddique, A.; Khwaja, H.A.; Carpenter, D.O. Climate Change and Water Scarcity: The Case of Saudi Arabia. Ann. Glob. Health 2015, 81, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Coping with Water Scarcity—Challenge of the Twenty-First Century, World Water Day; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2007; Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-aq444e.pdf (accessed on 16 September 2020).
- Winpenny, J.; Heinz, I.; Koo-Oshima, S.; Salgot, M.; Collado, J.; Hernandez, F.; Torricelli, R. The Wealth of Waste. The Economics of Wastewater Use in Agriculture; FAO Water Reports 35; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2010; Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/i1629e/i1629e.pdf (accessed on 16 September 2020).
- European Commission (EC). Water Is Too Precious to Waste. 2018. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/water/pdf/water_reuse_factsheet_en.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2020).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Coping with Water Scarcity—An Action Framework for Agriculture and Food Security; FAO Water Reports 38; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2012; Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-i3015e.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Sofroniou, A.; Bishop, S.R. Water Scarcity in Cyprus: A Review and Call for Integrated Policy. Water 2014, 6, 2898–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra-Castro, C.; Lopes, A.R.; Vaz-Moreira, I.; Silva, E.F.; Manaia, C.M.; Nunes, O.C. Wastewater reuse in irrigation: A microbiological perspective on implications in soil fertility and human and environmental health. Environ. Int. 2015, 75, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bixio, D.; Thoeye, C.; De Koning, J.; Joksimovic, D.; Savic, D.; Wintgens, T.; Melin, T. Wastewater reuse in Europe. Desalination 2006, 187, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquarec. Report on Integrated Water Reuse Concepts; Wintgens, T., Hochstrat, R., Eds.; Sustainable Sanitation Alliance: Eschborn, Germany, 2006; Available online: https://www.susana.org/en/knowledge-hub/resources-and-publications/library/details/551.11 (accessed on 2 September 2020).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). The Future of Food and Agriculture. Alternative Pathways to 2050; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018; Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/I8429EN/i8429en.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2020).
- Hofste, R.; Reig, P.; Schleifer, L. 17 Countries, Home to One-Quarter of the World’s Population, Face Extremely High Water Stress; WRI: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Available online: https://www.wri.org/blog/2019/08/17-countries-home-one-quarter-world-population-face-extremely-high-water-stress (accessed on 17 September 2020).
- World Resources Institute. Aqueduct Country Rankings. 2020. Available online: https://www.wri.org/applications/aqueduct/country-rankings/ (accessed on 3 September 2020).
- Lavrnić, S.; Zapater-Pereyra, M.; Mancini, M.L. Water Scarcity and Wastewater Reuse Standards in Southern Europe: Focus on Agriculture. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Resources Institute. Water. Mapping, Measuring, and Mitigating Global Water Challenge. 2020. Available online: https://www.wri.org/our-work/topics/water (accessed on 3 September 2020).
- European Environment Agency (EEA). Is Europe’s Freshwater Use Sustainable? 2017. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/highlights/world-water-day-is-europe (accessed on 14 September 2020).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Irrigation Management—Factsheet; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020; Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-i4591e.pdf (accessed on 13 September 2020).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). The State of the World’s Land and Water Resources for Food and Agriculture, Managing Systems at Risk; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2011; Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/i1688e/i1688e00.pdf (accessed on 13 September 2020).
- Alexandratos, N.; Bruinsma, J. World Agriculture Towards 2030/2050 (The 2012 Revision); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2012; Available online: http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/esa/Global_persepctives/world_ag_2030_50_2012_rev.pdf (accessed on 13 September 2020).
- Siebert, S.; Burke, J.; Faures, J.M.; Frenken, K.; Hoogeveen, J.; Döll, P.; Portmann, F.T. Groundwater use for irrigation—A global inventory. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 1863–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruinsma, J. The resources outlook: By how much do land, water and crop yields need to increase by 2050? In Looking Ahead in World Food and Agriculture: Perspectives to 2050; Conforti, P., Ed.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hertel, T.W.; Liu, J. Implications of water scarcity for economic growth. OECD Environ. Work. Pap. 2016, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolde, E. Greywater reuse systems for toilet flushing in multi-storey buildings—Over ten years experience in Berlin. Urban Water 2000, 1, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, P.T.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Zhou, J.L.; Nguyen, P.D.; Listowski, A.; Wang, X.C. A mini-review on the impacts of climate change on wastewater reclamation and reuse. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 494–495, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, A.; Tsurita, I.; Burnett, K.; Orencio, P.M. A review of the current state of research on the water, energy, and food nexus. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017, 11, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Research Institute. Aqueduct Food. 2020. Available online: https://www.wri.org/applications/Aqueduct/food/#/ (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- World Research Institute. Supporting Agriculture, Environment, and Sustainable Development. 2020. Available online: https://www.wri.org/our-work/topics/food (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- Cossio, C.; Perez-Mercado, L.F.; Norrman, J.; Dalahmeh, S.S.; Vinnerås, B.; Mercado, A.; McConville, J. Impact of treatment plant management on human health and ecological risks from wastewater irrigation in developing countries—Case studies from Cochabamba, Bolivia. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2019, 29, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fraiture, C.; Wichelns, D. Satisfying future water demands for agriculture. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, N.P.; Duchin, F. Feeding Nine Billion People Sustainably: Conserving Land and Water through Shifting Diets and Changes in Technologies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4444–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.I.; Muscolo, A.; Farooq, M.; Ahmad, W. Sustainable use and management of non-conventional water resources for rehabilitation of marginal lands in arid and semiarid environments. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 221, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y. Wastewater irrigation: Past, present, and future. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2017, 6, e1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanjra, M.A.; Blackwell, J.; Carr, G.; Zhang, F.; Jackson, T.M. Wastewater irrigation and environmental health: Implications for water governance and public policy. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2012, 215, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalde-Sanz, L.; Gawlik, B.M. Minimum Quality Requirements for Water Reuse in Agricultural Irrigation and Aquifer Recharge, Towards a Water Reuse Regulatory Instrument at EU Level; JCR Science for Policy Report, EUR 28962 EN; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2017; Available online: https://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/bitstream/JRC109291/jrc109291_online_08022018.pdf (accessed on 4 September 2020).
- Maaß, O.; Grundmann, P. Governing Transactions and Interdependences between Linked Value Chains in a Circular Economy: The Case of Wastewater Reuse in Braunschweig (Germany). Sustainability 2018, 10, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, T.; Jung, M.; Lee, E.; Park, S.; Lee, J.; Jeong, H. Assessing environmental impacts of reclaimed wastewater irrigation in paddy fields using bioindicator. Irrig. Sci. 2013, 31, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emongor, V.; Macheng, B.; Kefilwe, S. Effects of secondary sewage effluent on the growth, development, fruit yield and quality of tomatoes (Lycopersicon lycopersicum (L.) karten). Acta Hortic. 2012, 944, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnacka, K.; Witek-Krowiak, A.; Moustakas, K.; Skrzypczak, D.; Mikula, K.; Loizidou, M. A transition from conventional irrigation to fertigation with reclaimed wastewater: Prospects and challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 130, 109959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drechsel, P.; Mara, D.D.; Bartone, C.R.; Scheierling, S.M. Improving Wastewater Use in Agriculture: An Emerging Priority; World Bank Policy Research Working Paper No. 5412; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bedbabis, S.; Ben Rouina, B.; Boukhris, M.; Ferrara, G. Effect of irrigation with treated wastewater on soil chemical properties and infiltration rate. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 133, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltrán, E.M.; Pablos, M.V.; Torija, C.F.; Porcel, M.Á.; González-Doncel, M. Uptake of atenolol, carbamazepine and triclosan by crops irrigated with reclaimed water in a Mediterranean scenario. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadkhani, M.; Nikaeen, M.; Yadegarfar, G.; Hatamzadeh, M.; Pourmohammadbagher, H.; Sahbaei, Z.; Rahmani, H.R. Effects of irrigation with secondary treated wastewater on physicochemical and microbial properties of soil and produce safety in a semi-arid area. Water Res. 2018, 144, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonigro, A.; Rubino, P.; Lacasella, V.; Montemurro, N. Faecal pollution on vegetables and soil drip irrigated with treated municipal wastewaters. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 174, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldetsadik, D.; Drechsel, P.; Keraita, B.; Itanna, F.; Erko, B.; Gebrekidan, H. Microbiological quality of lettuce (Lactuca sativa) irrigated with wastewater in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia and effect of green salads washing methods. Int. J. Food Contam. 2017, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, A.; Karaolia, P.; Hapeshi, E.; Michael, C.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Long-term wastewater irrigation of vegetables in real agricultural systems: Concentration of pharmaceuticals in soil, uptake and bioaccumulation in tomato fruits and human health risk assessment. Water Res. 2017, 109, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirelli, G.; Consoli, S.; Licciardello, F.; Aiello, R.; Giuffrida, F.; Leonardi, C. Treated municipal wastewater reuse in vegetable production. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 104, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatta, G.; Libutti, A.; Gagliardi, A.; Beneduce, L.; Brusetti, L.; Borruso, L.; Disciglio, G.; Tarantino, E. Treated agro-industrial wastewater irrigation of tomato crop: Effects on qualitative/quantitative characteristics of production and microbiological properties of the soil. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 149, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akponikpè, P.I.; Wima, K.; Yacouba, H.; Mermoud, A. Reuse of domestic wastewater treated in macrophyte ponds to irrigate tomato and eggplant in semi-arid West-Africa: Benefits and risks. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Priyadarshi, M.; Dubey, S. Experimental study on accumulation of heavy metals in vegetables irrigated with treated wastewater. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkhair, K.S. Microbial contamination of vegetable crop and soil profile in arid regions under controlled application of domestic wastewater. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, S83–S92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beneduce, L.; Gatta, G.; Bevilacqua, A.; Libutti, A.; Tarantino, E.; Bellucci, M.; Troiano, E.; Spano, G. Impact of the reusing of food manufacturing wastewater for irrigation in a closed system on the microbiological quality of the food crops. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 260, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libutti, A.; Gatta, G.; Gagliardi, A.; Vergine, P.; Pollice, A.; Beneduce, L.; Disciglio, G.; Tarantino, E. Agro-industrial wastewater reuse for irrigation of a vegetable crop succession under Mediterranean conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 196, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Agrawal, S.B. Effects of Waste Water Irrigation on Physical and Biochemical Characteristics of Soil and Metal Partitioning in Beta vulgaris L. Agric. Res. 2012, 1, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, L.S.; Smith, H.K.; Taylor, G. The potential to improve culinary herb crop quality with deficit irrigation. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 242, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirzel, D.R.; Steenwerth, K.; Parikh, S.J.; Oberholster, A. Impact of winery wastewater irrigation on soil, grape and wine composition. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 180, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petousi, I.; Daskalakis, G.; Fountoulakis, M.; Lydakis, D.; Fletcher, L.; Stentiford, E.; Manios, T. Effects of treated wastewater irrigation on the establishment of young grapevines. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 658, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perulli, G.D.; Gaggia, F.; Sorrenti, G.; Donati, I.; Boini, A.; Bresilla, K.; Manfrini, L.; Baffoni, L.; Di Gioia, D.; Grappadelli, L.C.; et al. Treated wastewater as irrigation source: A microbiological and chemical evaluation in apple and nectarine trees. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 244, 106403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, P.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Thakur, A.; Nayak, A.; Sahu, P.; Ambast, S. Automatic drip irrigation scheduling effects on yield and water productivity of banana. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 257, 108677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrero, F.; Alarcón, J.J. Effects of treated wastewater irrigation on lemon trees. Desalination 2009, 246, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Cortés, V.; Phelps, B.; Van Ryswyk, H.; Srebotnjak, T. Experimental Analysis of Soil and Mandarin Orange Plants Treated with Heavy Metals Found in Oilfield-Produced Wastewater. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmali, A.; Mandi, L.; Loutfi, K.; El Ghadraoui, A.; El Mansour, T.E.; El Kerroumi, A.; Hejjaj, A.; Del Bubba, M.; Ouazzani, N. Agro-physiological responses of Koroneiki olive trees (Olea europaea L.) irrigated by crude and treated mixture of olive mill and urban wastewaters. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 263, 109101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedbabis, S.; Trigui, D.; Ben Ahmed, C.; Clodoveo, M.L.; Camposeo, S.; Vivaldi, G.A.; Ben Rouina, B. Long-terms effects of irrigation with treated municipal wastewater on soil, yield and olive oil quality. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 160, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erel, R.; Eppel, A.; Yermiyahu, U.; Ben-Gal, A.; Levy, G.; Zipori, I.; Schaumann, G.E.; Mayer, O.; Dag, A. Long-term irrigation with reclaimed wastewater: Implications on nutrient management, soil chemistry and olive (Olea europaea L.) performance. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petousi, I.; Fountoulakis, M.; Saru, M.; Nikolaidis, N.P.; Fletcher, L.R.; Stentiford, E.; Manios, T. Effects of reclaimed wastewater irrigation on olive (Olea europaea L. cv. ‘Koroneiki’) trees. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 160, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilpi, S.; Lamb, D.; Bolan, N.; Seshadri, B.; Choppala, G.; Naidu, R. Waste to watt: Anaerobic digestion of wastewater irrigated biomass for energy and fertiliser production. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 239, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Xu, Z.; Cui, Y.; Ma, Y.; Su, J.; Nan, Z. Temporal changes of calcareous soil properties and their effects on cadmium uptake by wheat under wastewater irrigation for over 50 years. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojid, M.; Biswas, S.; Wyseure, G. Interaction effects of irrigation by municipal wastewater and inorganic fertilisers on wheat cultivation in Bangladesh. Field Crop. Res. 2012, 134, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Deshbhratar, P.; Ramteke, D. Effects of sewage wastewater irrigation on soil properties, crop yield and environment. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 103, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Poustie, A.; Verburg, P.; Pagilla, K.; Yang, Y.; Hanigan, D. Trace organic contaminants in field-scale cultivated alfalfa, soil, and pore water after 10 years of irrigation with reclaimed wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campi, P.; Navarro, A.; Palumbo, A.D.; Modugno, F.; Vitti, C.; Mastrorilli, M. Energy of biomass sorghum irrigated with reclaimed wastewaters. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 76, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaganti, V.N.; Ganjegunte, G.; Niu, G.; Ulery, A.; Flynn, R.; Enciso, J.M.; Meki, M.N.; Kiniry, J.R. Effects of treated urban wastewater irrigation on bioenergy sorghum and soil quality. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 228, 105894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, G.C.; Sarkar, A.; Rashid, H.; Shohan, M.H.; Islam, M.; Wang, Q. Assessment of the irrigation feasibility of low-cost filtered municipal wastewater for red amaranth (Amaranthus tricolor L. cv. Surma). Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2015, 3, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ganjegunte, G.; Ulery, A.; Niu, G.; Wu, Y. Effects of treated municipal wastewater irrigation on soil properties, switchgrass biomass production and quality under arid climate. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 99, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorta-Santos, M.; Tejedor, M.; Jiménez, C.; Hernández-Moreno, J.M.; Palacios-Díaz, M.; Diaz, F.J. Evaluating the sustainability of subsurface drip irrigation using recycled wastewater for a bioenergy crop on abandoned arid agricultural land. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 79, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zema, D.A.; Bombino, G.; Andiloro, S.; Zimbone, S.M. Irrigation of energy crops with urban wastewater: Effects on biomass yields, soils and heating values. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 115, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadis, F.; Archontakis, F.; Banias, G.; Achillas, C. Consumers’ Perception of Wastewater Usage in Agriculture: Evidence from Greece. In Agricultural Cooperative Management and Policy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 137–150. [Google Scholar]
- Ungureanu, N.; Vlăduț, V.; Zăbavă, B.Ș.; Andrei, P.; Constantinescu, M. Current state of wastewater use in irrigated agriculture. Ann. Univ. Craiova Agric. Montanology Cadastre Ser. 2018, 48, 417–424. [Google Scholar]
- Global Water Intelligence. Municipal Water Reuse Markets 2010; Media Anal. Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez, B.; Asano, T. Water reclamation and reuse around the world. In Water Reuse: An International Survey: Common Practices and Current Needs in the World; Jimenez, B., Asano, T., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2008; pp. 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, B.; Asano, T. Water Reuse: An International Survey of Current Practice, Issues and Needs; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater, excreta and greywater. In Wastewater Use in Agriculture; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ungureanu, N.; Vlăduț, V.; Dincă, M.; Zăbavă, B.Ș. Reuse of wastewater for irrigation, a sustainable practice in arid and semi-arid regions. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Thermal Equipment, Renewable Energy and Rural Development (TE-RE-RD), Drobeta-Turnu Severin, Romania, 31 May–2 June 2018; pp. 379–384. [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrat, R.; Wintgens, T.; Melin, T.; Jeffrey, P. Assessing the European wastewater reclamation and reuse potential—A scenario analysis. Desalination 2006, 188, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions: Report on the Review of the European Water Scarcity and Droughts Policy. 2012. Available online: https://climate-adapt.eea.europa.eu/metadata/publications/report-on-the-review-of-the-european-water-scarcity-and-drought-policy/11309505 (accessed on 22 October 2020).
- BIO by Deloitte. Optimizing Water Reuse in the EU Public Consultation Analysis Report Prepared for the European Commission (DG ENV). Part I; In Collaboration with ICF and Cranfield University; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2015; Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/water/blueprint/pdf/BIO_Water%20Reuse%20Public%20Consultation%20Report_Final.pdf (accessed on 22 October 2020).
- Lazarova, V. Water Reuse in Europe, Status and Recent Trends in Policy Development. In Proceedings of the Final Conference on the Project LIFE+ ReQpro, Reggio Emilia, Italy, 23 February 2017; Available online: http://reqpro.crpa.it/media/documents/reqpro_www/eventi/20170223_FinalMeeting_RE/Lazarova_LIFE+ReQpro.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- European Commission (EC). Regulation EU 2020/741 of the European Parliament and of the Council, on Minimum Requirements for Water Reuse; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020; Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32020R0741&from=EN (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Norton-Brandão, D.; Scherrenberg, S.M.; Van Lier, J.B. Reclamation of used urban waters for irrigation purposes—A review of treatment technologies. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 122, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamizoulis, G. Setting health based targets for water reuse (in agriculture). Desalination 2008, 218, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichai, F.; Polo-López, M.I.; Ibañez, P.F. Solar disinfection of wastewater to reduce contamination of lettuce crops by Escherichia coli in reclaimed water irrigation. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6040–6050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhrimann, S.; Knoblauch, A.; Stalder, M.; Niwagaba, C.B.; Babu, M.; Kabatereine, N.B.; Halage, A.A.; Utzinger, J.; Cissé, G.; Nauta, M. Disease burden due to gastrointestinal pathogens in a wastewater system in Kampala, Uganda. Microb. Risk Anal. 2016, 4, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNICEF. Pneumonia and Diarrhoea: Tackling the Deadliest Diseases for the World’s Poorest Children. 2012. Available online: https://www.unicef.org/publications/index_65491.html (accessed on 3 September 2020).
- Aziz, R.K.; Khalifa, M.M.; Sharaf, R.R. Contaminated water as a source of Helicobacter pylori infection: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plutzer, J.; Ongerth, J.; Karanis, P. Giardia taxonomy, phylogeny and epidemiology: Facts and open questions. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2010, 213, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotloff, K.L.; Nataro, J.P.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Nasrin, D.; Farag, T.H.; Panchalingam, S.; Wu, Y.; Sow, S.; Sur, D.; Breiman, R.F.; et al. Burden and aetiology of diarrhoeal disease in infants and young children in developing countries (the Global Enteric Multicenter Study, GEMS): A prospective, case-control study. Lancet 2013, 382, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Flaherty, E.; Solimini, A.; Pantanella, F.; De Giusti, M.; Cummins, E. Human exposure to antibiotic resistant-Escherichia coli through irrigated lettuce. Environ. Int. 2019, 122, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, H.-F.; Barker, S.F.; Hamilton, A.J. A probabilistic quantitative microbial risk assessment model of norovirus disease burden from wastewater irrigation of vegetables in Shepparton, Australia. Water Res. 2014, 54, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaas, L.; Gourinat, A.-C.; Urbès, F.; Langlet, J. A 1-Year Study on the Detection of Human Enteric Viruses in New Caledonia. Food Environ. Virol. 2015, 8, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Wichelns, D.; Raschid-Sally, L.; McCornick, P.; Drechsel, P.; Bahri, A.; Minhas, P. The challenges of wastewater irrigation in developing countries. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, E.; Pierre, M.G.; Perrodin, Y. Groundwater contamination by microbiological and chemical substances released from hospital wastewater: Health risk assessment for drinking water consumers. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Omron, A.; El-Maghraby, S.; Nadeem, M.; El-Eter, A.; Al-Mohani, H. Long term effect of irrigation with the treated sewage effluent on some soil properties of Al-Hassa Governorate, Saudi Arabia. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2012, 11, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lu, S.; Jiao, W.; Wang, M.; Chang, A.C. Reclaimed water: A safe irrigation water source? Environ. Dev. 2013, 8, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaoua, S.; Boussaa, S.; El Gharmali, A.; Boumezzough, A. Impact of irrigation with wastewater on accumulation of heavy metals in soil and crops in the region of Marrakech in Morocco. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2019, 18, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Malik, R.N. Human health risk assessment of heavy metals via consumption of contaminated vegetables collected from different irrigation sources in Lahore, Pakistan. Arab. J. Chem. 2014, 7, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hassanin, A.S.; Samak, M.R.; Abdel-Rahman, G.N.; Abu-Sree, Y.H.; Saleh, E.M. Risk assessment of human exposure to lead and cadmium in maize grains cultivated in soils irrigated either with low-quality water or freshwater. Toxicol. Rep. 2020, 7, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, M.; Kiran, B.; Rani, S.; Rani, A.; Kaur, B.; Mittal, N. Heavy metal accumulation in vegetables irrigated with water from different sources. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phogat, V.; Mallants, D.; Cox, J.; Šimůnek, J.; Oliver, D.; Awad, J. Management of soil salinity associated with irrigation of protected crops. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 227, 105845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgallal, M.; Fletcher, L.; Evans, B. Assessment of potential risks associated with chemicals in wastewater used for irrigation in arid and semiarid zones: A review. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 177, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, T.W.; Jiang, B. Soil Salinity and Exchangeable Cations in a Wastewater Irrigated Area, India. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezlit, Y.D.; Smith, R.J.; Raine, S.R. A Review of Salinity and Sodicity in Irrigation. CRC for Irrigation Futures; Irrigation Matters Series; University of Southern Queensland: Toowoomba, Australia, 2010; Available online: https://eprints.usq.edu.au/23259/1/Review_of_salinity_and_sodicity_in_irrigation.pdf (accessed on 21 October 2020).
- Urbano, V.R.; Mendonça, T.G.; Bastos, R.G.; Souza, C.F. Effects of treated wastewater irrigation on soil properties and lettuce yield. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 181, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhas, P.S.; Ramos, T.B.; Ben-Gal, A.; Pereira, L.S. Coping with salinity in irrigated agriculture: Crop evapotranspiration and water management issues. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 227, 105832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyen, Z.; Moore, G.; Wrigley, R.J. Soil salinity and sodicity effects of wastewater irrigation in South East Australia. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 99, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcívar, M.; Zurita-Silva, A.; Sandoval, M.; Muñoz, C.; Schoebitz, M. Reclamation of Saline-Sodic Soils with Combined Amendments: Impact on Quinoa Performance and Biological Soil Quality. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjegunte, G.; Ulery, A.; Niu, G.; Wu, Y. Organic carbon, nutrient, and salt dynamics in saline soil and switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.) irrigated with treated municipal wastewater. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 29, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keraita, B.; Konradsen, F.; Drechsel, P.; Abaidoo, R.C. Effect of low-cost irrigation methods on microbial contamination of lettuce irrigated with untreated wastewater. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2007, 12, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morugán-Coronado, A.; García-Orenes, F.; Cerdà, A. Effect of land management on soil properties in flood irrigated citrus orchards in Eastern Spain. SOIL Discuss. 2015, 2, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, M.Y.; Demirel, K.; Erken, O.; Bahar, E.; Devecirel, M. Emitter clogging and effects on drip irrigation systems performances. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2010, 5, 532–538. [Google Scholar]
- Capra, A.; Scicolone, B. Assessing dripper clogging and filtering performance using municipal wastewater. Irrig. Drain. 2005, 54, S71–S79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capra, A.; Scicolone, B. Recycling of poor quality urban wastewater by drip irrigation systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2007, 15, 1529–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrero, F.; Kalavrouziotis, I.; Alarcón, J.J.; Koukoulakis, P.; Asano, T. Use of treated municipal wastewater in irrigated agriculture—Review of some practices in Spain and Greece. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, M.; Singh, V.P. Global Experiences on Wastewater Irrigation: Challenges and Prospects. Extrem. Chang. Clim. 2016, 72, 289–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.F. Effect of chlorination on emitter clogging and system performance for drip irrigation with sewage effluent. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2010, 26, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Rajput, T. Effect of drip tape placement depth and irrigation level on yield of potato. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 88, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, V.K.; Rajput, T.B.S.; Patel, N. Biometric properties and selected chemical concentration of cauliflower influenced by wastewater applied through surface and subsurface drip irrigation system. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 139, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.; Stine, S.W.; Choi, C.; Gerba, C.P. Comparison of Crop Contamination by Microorganisms during Subsurface Drip and Furrow Irrigation. J. Environ. Eng. 2006, 132, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Water Management Institute. Recycling Realities: Managing Health Risks to Make Wastewater an Asset; Water Policy Briefing 17; IWMI and GWP: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Loufty, N.M. Reuse of wastewater in Mediterranean region, Egyptian experience. In The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Barcelo, D., Petrovic, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chibuike, G.U.; Obiora, S.C.; Chibuike, G.U. Heavy Metal Polluted Soils: Effect on Plants and Bioremediation Methods. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2014, 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).