Abstract
The brewing industry generates, as the primary coproduct, brewers’ spent grain (BSG). In Mexicali, Baja California, Mexico, there are 17 companies that generated 282 tons of BSG by 2016. Cattle feeding is the most common type of disposal for this waste. However, it can be valorized for the production of bioenergy or as a source of added-value products. Therefore, the objective of the present work was to assess the physicochemical properties of the brewers’ spent grain from a local craft brewery, to choose the most appropriate exploitation route. Chemical and morphological analyses were carried out by energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (EDX), scanning electron microscopy, and the higher heating value determination. The results of the proximate analyses were 72.32% moisture, 78.47% volatile matter, 17.48% fixed carbon, and 4.05% ash. The results of the chemical analysis for extractables were 5.23% using organic solvent and 50.25% using hot water. The content determination were 17.13% lignin, 26.80% cellulose, and 37.17% hemicellulose. The results of the ultimate analysis were 43.59% C, 6.18% H, 3.46% N, and 37.22% O. The higher heating value experimentally obtained was 18.70 MJ/kg. Moreover, in the EDX analysis, Ca, P, K, and S were mainly found. It is recommendable to valorize the BSG through the xylitol, bioethanol or biogas production, because of its high moisture, hemicellulose and cellulose content.
1. Introduction
Currently, alcoholic beverage production contributes significantly to the economy of many countries [1]. Along with wine, beer is the alcoholic beverage that has experienced a significant increase in its expansion in terms of historical production, consumption and diffusion worldwide [2]. The impact of the beer industry is such that, in October 2016, the third largest acquisition in history was signed by the two largest beer companies in the world. Anheuser-Busch InBev (AB InBev) and SABMiller merged more than $100 billion US dollars, to operate under the Newbelco name, and are expecting an annual sale of $55 billion [3]. On the other hand, small breweries multiply almost daily in some countries, which are known as craft breweries [2].
In 2016, world beer production reached 195,747.7 million liters. The leading beer producing countries are China, the United States, Brazil and Mexico. Mexico positioned itself in fourth place, producing 5.36% of beer worldwide in 2016, with 10.5 billion liters [4]. In 2016, the Beer Association of Mexico reported 400 formal producers of craft beer in Mexico, which had a production of 6.52 million liters. The main producing states are Jalisco, Nuevo León and Baja California; with national productions of 34%, 15% and 8%, respectively [5]. In Mexicali, Baja California, the beer industry is a sector with approximately 10 years of production. In 2016, this sector was made up of at least 17 breweries, shown in Figure 1.
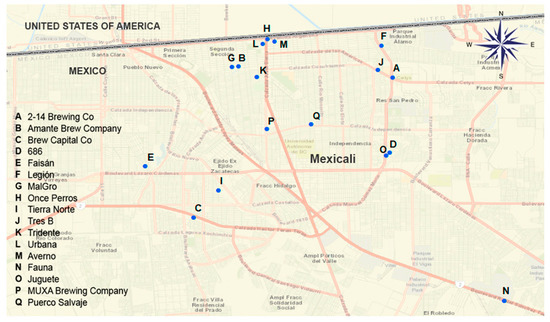
Figure 1.
Location of brewery factories in Mexicali.
The main waste from the beer industry is brewery spent grain (BSG), which represents approximately 85%. Yeast and residual hops are also generated [6]. The BSG constitutes an unconventional waste that must be disposed of in accordance with the environmental regulations of the region. The disposal of this type of waste to the environment causes damage to the ecosystem due to its high content of organic matter [7]. It leads to the search of sustainable alternatives for the disposal of BSG.
During 2016, a survey was carried out in Mexicali, in order to obtain information on the craft beer production processes in the industries already installed; the results focus on the production of BSG as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
BSG (brewers’ spent grain) (dry basis) generation in kg, 2016.
As BSG is rich in protein and fiber, its main application is livestock feed [8]. In Mexicali, BSG is offered to cattle ranches free of charge to feed livestock, mainly, and secondarily, for baking or composting.
Malt is one of the fundamental raw materials for beer production. It provides fermentable sugars and nutrients, as well as the color, taste, and body in beer [9]. However, the use of malt generates a solid waste known as BSG. A total of 1.25–1.30 kg of BSG/kg of malt is generated with a moisture content which varies from 50% to 85%, according to the applied filtering technique. It is estimated to be a waste generation of 14–20 kg of BSG/L of beer [9]. In general, BSG consists of husk, pericarp, seed coat and endosperm, which are rich in cellulose and lignin [6].
BSG comes from the processing of barley grains (Hordeum vulgare), where two stages are distinguished: malting and mashing (Figure 2) [10]. The first stage takes place in a malt house with the grains that meet quality criteria: to be viable, disease-free, with whole husk, among others. Before starting the malting, the grains are cleaned through the removal of foreign bodies (loose straw, different seeds, and dust) and separated according to their size. Malting involves the steeping, germination and kilning of grains. The steeping’s main primary objective is to clean and hydrate the barley grains and takes approximately 40 h. During this time, the grains are mixed with water, which is three times replaced with clean water, with aeration periods. Subsequently, germination begins, being the sprouting of rootlets the most visible sign. During germination, the aleurone layer’s cells generate enzymes to break down the endosperm and release the nutrients, sugars, and free amino nitrogen (FAN) that the embryo needs to develop. During the kilning phase, the “green malt” is dried at 76 °C for pale malts or at 110 °C for darker malts. Finally, the dried rootlets are retired by sifting, and the malt has to be aged at least three weeks before using it in breweries [9].
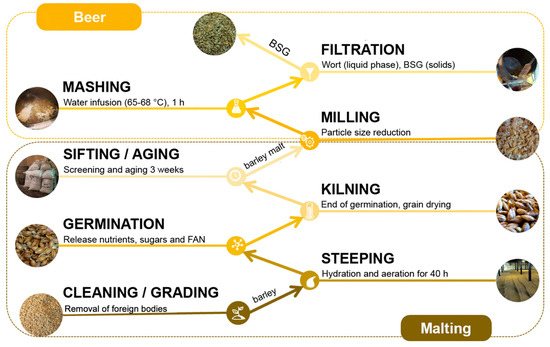
Figure 2.
BSG production of barley grain.
The mashing takes place in the brew-house, where the malt is milled and mixed with pretreated water (for off-odors and flavors and mineral addition) maintaining a temperature from 65 to 68 °C by approximately an hour. The temperature, mashing time, and the option to add other ingredients depends on the kind of beer. During mashing, the starch is converted into fermentable sugars and non-fermentable dextrins by diastase enzymes. As a result of mashing, the sweet must and BSG are generated and separated through lautering. The BSG remains in a manifold, and the must is recirculated and drained [11]. The recovered must is sent to the beer elaboration process, while the BSG is considered as a waste. As the BSG composition varies according to the barley variety, harvest time, malting and mashing techniques, and the type of ingredients in case of adding it during the mashing, it is essential to determine the composition and physicochemical properties of the waste to be valorized and to select the most convenient route of use.
Hence, the investigation of alternative applications of BSG is important from several perspectives, such as valorization of this coproduct, environmental protection and avoiding disposal problems. The BSG can be used for dietary and nutritional applications [12,13,14,15,16]; as a source of high-value bioproducts e.g., xylitol, lactic acid, xylan, carboxylic acid, arabinoxylans, protein, fermentable sugars, and cellulose nanofibers [6,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]; for biotechnological processes [24,25,26] and for bioenergy production such as biomethane, co-combustion, bioethanol, pyrolysis, bio-oil, and biohydrogen [27,28,29,30,31,32,33].
One of the BSG’s main applications is animal nutrition, due to its high protein and fiber content. It is mainly used for cattle feeding, but also, it has been reported for poultry, pigs, and fish feeding [6]. Additionally, BSG has served as a source of dietary fiber (DF) for human food consumption. Arabinoxylan (AX), lignin, and beta-glucans are considered as DF, and their consumption is associated with health benefits [8,13,34].
On the other hand, BSG is a source of high-value bioproducts such as antioxidants, monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, xylitol, arabitol, lactic acid, carboxylic acids, emulsifiers, plasticizers, among others [19,35,36]. The spent grain has also been used in biotechnological processes such as a substrate for microorganism culture and enzyme production [24,37]. Another reported process is as a carrier in immobilized-cell systems and as material adsorbent [35]. Additionally, BSG has been used in paper production, wood-based particle board, bricks and biodegradable films [6,38,39].
To mitigate greenhouse gases (GHGs) and increase the region’s energy autonomy, this proposal serves as a guide to develop projects that convert waste into value-added products such as bioethanol. The basic steps for the production of bioethanol from biomass are: pretreatment, hydrolysis, fermentation and distillation. The bioconversion of lignocellulose to bioethanol is complicated by: (1) the natural resistance of biomass to decomposition; (2) the variety of sugars released when cellulose and hemicellulose are broken, which leads to the search for the organisms that ferment these residues more efficiently; (3) costs of collection and storage of lignocellulosic materials [40]. Among the microorganisms reported for the bioconversion of beer bagasse in bioethanol are: S. cerevisiae [41], S. cerevisiae NRRL YB 2293 [42], Zymomonas mobilis [43], Pichia stipitis, Kluyveromyces marxianus [44], Trametes versicolor [45], among others.
The physicochemical characterization and hydrolysis of the BSG generated in Mexicali is unprecedented. However, there is an interest in the brewing community for an appropriate waste disposal, which does not generate environmental deterioration, as well as in the possible added-value products that can be produced from BSG. Beer bagasse is an abundant material in Mexicali, available throughout the year and at low cost, which can be valorized in a more attractive way by breweries, through the production of energy or as a source of value-added products. Hence, the objective of the present work was to assess the physicochemical properties of the brewers’ spent grain from the brewery industry of Baja California, Mexico, in view of its potential application for bioenergy and high-value bioproducts’ production. Chemical and morphological analyses were carried out by energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and the higher heating value was evaluated.
2. Materials and Methods
BSG samples were provided by Big Bad Brewing Co. The BSG comes from a process in which 85% of 2-row malt and 15% of specialty malts were used. The sample was prepared according to the NREL/TP-510-46620 process [46]. Additionally, a sample of the 2-row malt used in the process was analyzed along with the BSG through SEM.
2.1. Proximate Analysis
By means of the proximate analysis, the contents of humidity, volatile matter, ash and fixed carbon were determined. This analysis is of special importance for the evaluation of the biomass combustion phenomenon [47]. The following analyses of the BSG were performed by triplicate. First, the moisture content (%Moisture) was determined according to the NREL/TP-510-42621 process [48]. For that purpose, 1 g of sample was heated in a muffle at 105 ± 3 °C at a constant weight. Subsequently, the volatile matter percentage (%Volatile Matter) was measured according to the ASTM E872 standard [49]. The sample, free of moisture, was introduced into the muffle at 950 °C, for 7 min in the absence of air. Then, the percentage of ash (%Ash) was determined according to the ASTM E830 standard [50]. The sample, free of moisture, and volatile matter was heated up to 580 °C for 4 h. The obtained ashes were stored for further analysis. Lastly, the percentage of fixed carbon (%Fixed carbon) was calculated by subtracting %Volatile Matter and %Ash out of 100%.
2.2. Chemical Analysis
Through chemical analysis, the composition of extractables, cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin were determined. Cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin are strongly bound by non-covalent forces and covalent crosslinks, resulting in a complex structure [51]. The BSG chemical analyses were carried out by triplicate. They included the determination of the content of extractable in organic solvents and extractable in hot water lignin, holocellulose, cellulose, and hemicellulose.
The process to quantify the extractable in organic solvent compounds (%Ex1) was based on the T 264 cm-07 standard [52]. Using this standard, acetone was selected as a solvent for the extraction. A cellulose thimble with 5 g of sample was placed in a Soxhlet equipment. The solvent boiled for 8 h, securing at least 4 siphons per hour. At the end of the extraction, the sample was dried and the mass difference was measured.
Then, the quantity of extractable water (%Ex2) was determined according to the T 207 cm-99 standard [53]. A moisture-free sample of 4 g and acetone-extractable were placed in an Erlenmeyer flask, and 200 mL of hot water was added. The flask was placed in a boiling water bath and remained at constant volume with a condenser. After 3 h, the content was filtered out of the flask and washed with 200 mL of hot water. Finally, the sample was dried and the mass difference was measured.
The methodology for lignin content determination (%Lig) was based on the ASTM D 1106–96 (2001) standard [54], 1 g of dried sample, free of total extractable (in an organic solvent and hot water), was mixed with 15 mL of 72% H2SO4 at 13 °C. The mixture was stirred at 400 rpm for 1 min and 200 rpm for 2 h, at 19 °C. Next, the mixture was transferred to a 1 L Erlenmeyer flask, and 560 mL of deionized water was added to achieve a dilution of the acid at 3%. The content of the flask was brought to constant-boiling with reflux during 4 h. It was then allowed to cool at room temperature, filtered and washed until reaching neutral pH. Finally, it was dried and the mass difference was measured.
Afterward, the holocellulose content (%Hol) was determined according to the ASTM D1104-56 (1978) standard [55]. In an Erlenmeyer flask were added 2 g of spent grain, free of moisture, and total extractable, 150 mL of distilled water, 0.2 mL acetic acid at 15 °C, and 1 g sodium chlorite. Next, the flask with a cap was placed in a water bath at 75 °C for 5 h, with constant agitation. Each hour, 0.22 mL of acetic acid at 15 °C and 1 g sodium chlorite were added. After 5 h, the flask was placed in a cold water bath, until 10 °C. The content was immediately filtered out of the flask and washed with 500 mL of cold water until the sample lost its yellow coloration. Finally, the sample was dried and the mass difference was measured.
The cellulose content determination (%Cel) was based on the methodology reported by Rowell et al. [56]. In an Erlenmeyer flask, 2 g of dried holocellulose and 10 mL of 17.5% NaOH at 20 °C were added, and the mixture was left to rest for 5 min at 20 °C. Later, 5 mL of 17.5% NaOH at 20 °C were added every 5 min, resulting in 25 mL of total NaOH. After adding the last 5 mL of NaOH, the mixture was left to rest for 30 min at 20 °C. Then, 33 mL of deionized water at 20 °C was added to the mix and left to rest for 60 min. After 105 min passed since the beginning of the process, the flask content was filtered. The waste was washed in the following order: with 100 mL of 8.3% NaOH, deionized water at 20 °C, 15 mL of acetic acid at 10% and deionized water, until reaching a neutral pH. The waste was dried and the mass difference was measured. Finally, the percentage of hemicellulose (%Hem) was measured by difference. The percentage of cellulose (%Cel) was subtracted from the percentage of holocellulose (%Hol).
2.3. Ultimate Analysis
The ultimate analysis quantifies the content of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen of the BSG. It provides useful information about the quality of biomass as a fuel [57]. It was performed in a Thermo Flash-2000 ECHNS-O equipment. The reactor with vanadium oxide as a catalyst was used to determine C, H, and N at 900 °C and O at 1060 °C.
2.4. Higher Heating Value
The heating value of a fuel is the amount of heat generated by the complete combustion of a unit mass of the fuel at standard conditions, 1 atm and 25 °C. Heating value is an important parameter that must be determined in the evaluation of the energy potential of any fuel and to analyze and design bioenergy systems [58]. The process to determine the higher heating value (HHV) was based on the ASTM 711 standard [59]. The prepared sample was analyzed in an oxygen bomb calorimeter IKA C2000, at isoperibolic operation mode and 25 °C of the water bucket. The analysis was carried out in duplicate.
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy
The 2-row malt and the unground dried BSG were analyzed through the SEM JEOL JSM-6360 microscope, with an accelerating voltage of 15 kV and vacuum of 45 Pa. The micrographs were taken at 15X, 25X and 200X.
2.6. Energy Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy Analysis
The BSG ashes were analyzed through the energy dispersive x-ray fluorescence spectroscopy technique. The analysis was carried out in the Shimadzu energy dispersive x-ray fluorescence spectrometer X EDX-7000. The channels used were Al-U at 50 kV and Na-Sc at 15 kV.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proximate Analysis
The proximate analysis experimental results are indicated in Table 2. The tests were performed by triplicate. The relative standard deviation was: 0.33 moisture, 0.35 volatile matter, 0.08 ash, and 0.39 fixed carbon. The table also displays that the obtained results in the current work are similar to the ones reported by others.

Table 2.
Proximate analysis results of BSG.
It was found that the BSG has a moisture content of 77.32%, which is considered high, and 52.94 t/year of BSG dry basis was generated. The high moisture content represents a significant disadvantage if the thermochemical conversion pathway is selected, because it requires energy to dry the biomass [58]. Additionally, an ash content of 4.05% was obtained, which is adequate if the BSG follows the thermochemical pathway, since a high content of ash may cause ignition and combustion problems [51]. The ash content in the spent grain reported by other authors ranks from 3.50% to 5.03%. Lee [26], Machado [61] and Mathias [62] reported a very similar ash content to the value reported in the current work, as is shown in Table 2. Moreover, the volatile matter was of 78.47%, and it is comparable to the one reported by Lee [26] and Becidan [39]. The content of fixed carbon was of 17.48%, which is similar to that reported by Lee [26] and Becidan [39]. The biomass with high volatility presents many advantages as a raw material for combustion. Moreover, high content of volatile matter and fixed carbon increase the higher heating value of any biomass fuels [47].
For thermochemical processes, moisture content is crucial, since a high content can decrease the effectiveness of the process by requiring additional energy to vaporize the water [58]. The desired moisture contents can range from 5% for combustion processes to 30% for gasification [51]. As the reactivity of volatile gases is much higher than the solid matrix, the amount of volatile matter is an important factor in the selection of thermochemical systems (pyrolysis, combustion, gasification) [63]. Ashes have no energy value, and their high content causes ignition and combustion problems in thermochemical processes [51]. However, the ashes can be recovered and used as fertilizer [58]. A high content of volatile matter and fixed carbon increases the calorific value of any biomass fuel [47].
3.2. Chemical Analysis
The chemical analysis results are shown in Table 3 and they were compared with those reported by other authors. The tests were performed by triplicate. The relative standard deviation was: 0.08 lignin, 1.71 cellulose, and 0.30 hemicellulose. The variation between the reported results may be due to the nature of the malt, and the malting and mashing techniques. The analyzed spent grain contains 5.23% of acetone extractable. Among the acetone extractable can be found resins, fatty acids, sterols, waxes and fats [52]. The extractable in hot water was 50.25%, and the main components found were polyphenols, low molecular weight carbohydrates, tannins, gums, and starch [52]. On the other hand, it was found that the spent grain contained 26.80% of cellulose, 37.17% of hemicellulose, and 17.13% of lignin, which results are similar to those reported by other authors, such as Klímek [64] and Machado [61]. The cellulose and hemicellulose are of great interest, because they can be bio-converted to biogas, bioethanol, lactic acid, xylitol, and arabitol, among others. Meanwhile, compounds with antioxidant activities such as ferulic and p-coumaric acids can be extracted from the lignin fraction [44]. The integration of bioethanol and xylitol production from BSG has even been studied, under the concept of bio-refinery [43].

Table 3.
Chemical analysis results of BSG.
3.3. Ultimate Analysis
It was found in the ultimate analysis that the spent grain contains 43.59% carbon, 6.18% hydrogen, 37.22% oxygen, and 3.46% nitrogen as is detailed in Table 4. This analysis is useful for the evaluation of the environmental impact of the biomass and the estimation of its calorific value [47].

Table 4.
Ultimate analysis results of BSG.
3.4. Higher Heating Value
The HHV of BSG dry basis was 18.70 MJ/kg, which is similar to the value reported by Sanna [32] and is within the values reported by other authors, which ranks from 18.55 MJ/kg to 20.83 MJ/kg, as is reported in Table 5. The tests were performed by duplicate. The relative standard deviation was 0.15.

Table 5.
Higher heating value (HHV) results of BSG.
The HHV is a critical parameter in the evaluation of the energy potential of any biomass resource. Other agricultural wastes evaluated have a similar HHV to the spent grain, such as wheat straw with 14.86 MJ/kg [69], sugarcane bagasse with 16.91 MJ/kg [70], corn stover with 17.80 MJ/kg, and walnut shell with 21.60 MJ/kg [71].
Considering the HHV of the BSG dry basis and the BSG generated by the brewery sector of Mexicali, Baja California, Mexico, a total energy content of 989,978 MJ/year was estimated, and its economic exploitation viability can be evaluated in order to recommend its use in productive processes for energy or bioproducts.
3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy
Figure 3 is a micrograph of 2-row malt grain, in which its components can be identified. Figure 4 displays the obtained micrographs of the 2-row malt and BSG. It can be appreciated that the malt was degraded during the mashing. However, it did not happen aggressively, so the endosperm still contains starch. It was also confirmed that the husk, pericarp, aleurone, and testa did not suffer significant changes.
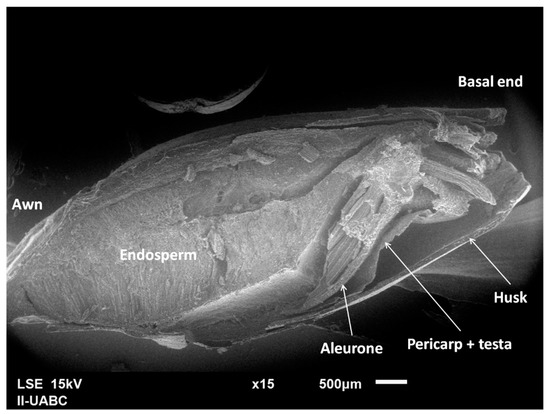
Figure 3.
Micrograph of 2-row malt grain with identified parts.
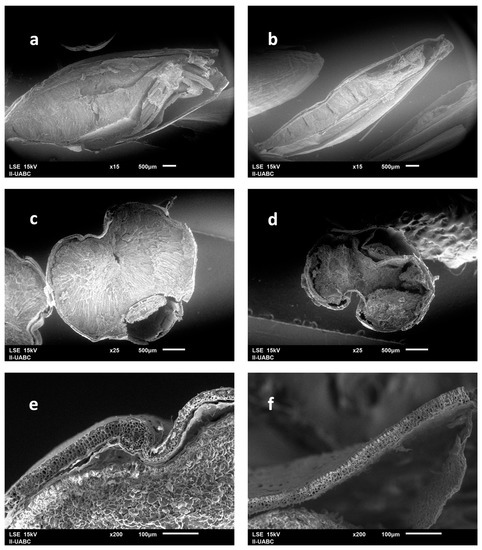
Figure 4.
Comparison of morphology between 2-row malt and BSG: (a) Unprocessed 2-row malt kernel; (b) Cross-section of a malt kernel; (c) Husk and starchy endosperm of 2-row malt; (d) 2-row malt after being macerated; (e) Cross-section of BSG; (f) Husk in BSG.
3.6. Energy Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy Analysis
Table 6 exhibits the energy dispersive x-ray fluorescence spectroscopy analysis of the BSG ashes. The main elements found were: calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sulfur and silicon, and in minor quantity: iron, zinc, copper, manganese, and strontium. The high percentage of calcium is expected, because the water used for the mashing includes calcium. Minerals are a source of elements such as phosphorus, sulfur, copper, iron, zinc, potassium, calcium and sodium, and serve as nutrients for yeasts, promoting and increasing the BSG bioconversion [72].

Table 6.
Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy analysis of BSG ash.
4. Conclusions
The physicochemical characterization of spent grain samples generated in a brewery in Mexicali, Baja California was performed, yielding results that are indicative of the potential reuse of this waste. Despite the spent grain’s high heating value, compared with other types of biomass, it is necessary to reduce its moisture content under 50% to be suitable as biofuel through thermochemical type conversions. Then, it is necessary to valorize the economic viability exploitation of the BSG generated by breweries, whether to produce high-value bioproducts or bioenergetics through biochemical conversion pathways. Since the BSG contains cellulose, starch, and low molecular weight sugars, a feasible option is to use it for bioethanol production, via anaerobic fermentation. Another option that results very attractive is the sweetener xylitol production from BSG, due to its high hemicellulose content. Baja California State is the top leader in the brewery industry in Mexico with almost 100 craft breweries and an economical spill of 90 M USD per year. Half of the enterprises are located in Mexicali, which ensures the volume of raw material for the production of bioenergy or generation of bioproducts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.C. and G.M.; data curation, M.A.C., G.M. and M.C.; formal analysis, D.G.M., C.G. and M.C.; methodology, M.A.C., G.M., B.V.-S. and A.M.; project administration, M.A.C.; visualization, J.R.A. and J.A.L.; writing—original draft, M.A.C., G.M., D.G.M., B.V.-S., J.R.A. and C.G.; writing— review and editing, M.A.C., B.V.-S., J.R.A., C.G., J.A.L. and A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Council on Science and Technology (CONACYT) and the Engineering Institute of the Universidad Autónoma de Baja California for their support in the development of this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Willaert, R. The Beer Brewing Process: Wort Production and Beer Fermentation. In Handbook of Food Products Manufacturing, 1st ed.; Hui, Y.H., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2006; Volume 1, pp. 443–506. [Google Scholar]
- Cabras, I.; Higgins, D.; Preece, D. Brewing, Beers and Pubs: A Global Perspective, 1st ed.; Palgrave McMillan: London, UK, 2016; pp. 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Forbes. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/taranurin/2016/10/10/its-final-ab-inbev-closes-on-deal-to-buy-sabmiller/#24cde60d432c (accessed on 10 July 2017).
- Barth-Hass Group. The Barth Report; Joh. Barth & Sohn GmbH & Co. KG: Nürnberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cerveceros de México. Available online: https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B_0yYb1PC13oNl9Vc3EwaG5IMlU/view (accessed on 11 July 2017).
- Mussato, S.I.; Dragone, G.; Roberto, I.C. Brewers’ spent grain: Generation, characteristics and potentials applications. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 43, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias, T.R.; Moretzsohn, P.P.; Camporese, E.F. Solid wastes in brewing process: A review. J. Brew. Distil 2014, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K.M.; Steffen, E.J.; Arendt, E.K. Brewers’ spent grain: A review with an emphasis on food and health. J. Inst. Brew. 2016, 122, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallet, J. Malt: A Practical Guide from Field to Brewhouse, 1st ed.; Brewers Publications: Boulder, CO, USA, 2014; pp. 100–120. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, M.; Abu-Ghannam, N.; Gallaghar, E. Barley for brewing: Characteristic changes during malting, brewing and applications of its by-products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. 2010, 9, 18–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.J. How to Brew: Everything You Need to Know to Brew Beer Right the First Time, 1st ed.; Brewers Publications: Boulder, CO, USA, 2006; pp. 1–347. [Google Scholar]
- Öztürk, S.; Özboy, Ö.; Cavidoğlu, İ.; Köksel, H. Effects of brewer’s spent grain on the quality and dietary fibre content on cookies. J. Inst. Brew. 2002, 108, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojceska, V.; Ainsworth, P.; Plunkett, A.; İbanoğlu, S. The recycling of brewer’s processing by-product into ready-to-eat snacks using extrusion technology. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 47, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Du, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Jin, Y. Optimization of brewer’s spent grain-enriched biscuits processing formula. J. Food Process. Eng. 2014, 37, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burçin Özvural, E.; Vural, H.; Gökbulut, İ.; Özboy-Özbaş, Ö. Utilization of brewer’s spent grain in the production of Frankfurters. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2009, 44, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.S.; Choi, Y.S.; Hyun-Wook, K.; Hwang, K.E.; Song, D.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, C.J. Effects of replacing pork back fat with brewer’s spent grain dietary fiber on quality characteristics of reduced-fat chicken sausages. Korean J. Food Sci. An. 2014, 34, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejin, J.; Radosavljević, M.; Kocić-Tanackov, S.; Djukić-Vuković, A.; Mohović, L. Lactic acid fermentation of brewer’s spent grain hydrolysate by Lactobacillus rhamnosus with yeast extract addition and pH control. J. Inst. Brew. 2017, 123, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, C.; Kemppainen, K.; Kutti, L.; Varhimo, A.; Asikainen, S.; Grönroo, A.; Määttänen, M.; Buchert, J.; Harlin, A. Extraction of xylan from wood pulp and brewer’s spent grain. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 70, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wan, C. Carboxylic acid production from brewer’s spent grain via mixed culture fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 182, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, S.F.; Gullón, B.; Gullón, P.; Ferreira, S.; Maia, C.J.; Alonso, J.L.; Domingues, F.C.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Evaluation of the prebiotic potential of arabinoxylans from brewer’s spent grain. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2014, 98, 9365–9373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.S.; Yin, G.M.; He, Y.Z.; Hu, S.Q.; Li, B.; Li, L. Recovery of protein from brewer’s spent grain by ultrafiltration. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 48, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luft, L.; Confortin, T.; Todero, I.; da Silva, J.; Tovar, L.; Kuhn, R.; Jahn, S.; Treichel, H.; Mazutti, M. Ultrasound technology applied to enhance enzymatic hydrolysis of brewer’s spent grain and its potential for production of fermentable sugars. Waste Biomass Valoris. 2018, 10, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.K.; Gregor, T.; Wimmer, R. Utilising brewer’s spent grain as a source of cellulose nanofibres following separation of protein-based biomass. Bioresources 2017, 12, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łaba, W.; Piegza, M.; Kawa-Rygielska, J. Evaluation of brewer’s spent grain as a substrate for production of hydrolytic enzymes by keratinolytic bacteria. J. Chem. Technol. Biot. 2017, 92, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordialik-Bogacka, E. Saccharomyces pastorianus immobilized on brewer’s spent grain system for lead ion biosorption. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2014, 96, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Yang, H.J.; Song, K.B. Preparation and characterization of brewer’s spent grain protein-chitosan composite films. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2015, 52, 7549–7555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tao, Y.; Termudo, M.; Bijl, H.; Kloek, J.; Ren, N.; Van Lier, J.B.; de Kreuk, M. Biomethanation from enzymatically hydrolyzed brewer’s spent grain: Impact of rapid increase in loadings. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 190, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochmann, G.; Drosg, B.; Fuchs, W. Anaerobic digestion of thermal pretreaded brewers’ spent grain. Environ. Prog. Sustain. 2015, 34, 1092–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celaya, A.M.; Lade, A.T.; Goldfarb, J.L. Co-combustion of brewer’s spent grains and Ilinois No. 6 coal: Impact of blend ratio on pyrolysis and oxidation behavior. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 129, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.; Smart, K.A.; James, S.; Cook, D.J. Bioethanol production from brewers spent grains using a fungal consolidated bioprocessing (CBP) approach. Bioenerg. Res. 2017, 10, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.S.; Brammer, J.G.; Hornung, A.; Steele, A.; Poulston, S. The intermediate pyrolysis and catalytic steam reforming of brewers spent grain. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2011, 103, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, A.; Li, S.; Linforth, R.; Smart, K.A.; Andrésen, J.M. Bio-oil and bio-char from low temperature pyrolysis of spent grains using activated alumina. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 10695–10703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zang, L. Enhancement of biohydrogen production from brewer’s spent grain by calcined-red mud pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 209, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, J.; Procopio, S.; Becker, T. Brewer’s spent grain: Source of value-added polysaccharides for the food industry in reference to the health claims. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 241, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiros, C.; Christakopoulos, P. Biotechnological potential of brewers spent grain and its recent applications. Waste Biomass Valoris. 2012, 3, 2130–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fărcaş, A.; Socaci, S.; Francisc, D.; Tofana, M.; Mudura, E.; Diaconeasa, Z. Volatile profile, fatty acids composition and total phenolics content of brewers’ spent grain by-product with potential use in the development of new functional foods. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 64, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, R.P.; Junior, N.A.; Pereira, N., Jr.; Bon, E.P.; Coelho, R.R. Brewer’s spent grain and corn steep liquor as substrates for cellulolytic enzymes production by Streptomyces malaysiensis. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 48, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K. Anaerobic Digestion of Brewer’s Spent Grain in a Novel Plug Flow Reactor System. Master’s Thesis, The University of Georgia, Athens, GA, USA, 2006. Available online: https://athenaeum.libs.uga.edu/handle/10724/26687 (accessed on 22 August 2017).
- Becidan, M.; Skreyberg, Ø.; Hustad, J.E. Products distribution and gas release in pyrolysis of thermally thick biomass residues samples. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2007, 78, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balat, M. Production of bioethanol from lignocellulosic materials via the biochemical pathway: A review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 858–875. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, S.; Smart, K.; Cook, D. A comparison of dilute acid- and alkali-catalyzed hydrothermal pretreatments for bioethanol production from brewers’ spent grains. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2018, 72, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, R.; Soccol, C.R.; Souza, L.P.; Lorenci, A.; Faraco, V. Second Generation Bioethanol Produnction from Brewers’ Spent Grain. Energies 2015, 8, 2575–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávila, J.; Rosenberg, M.; Cardona, C. A biorefinery approach for the production of xylitol, ethanol and polyhydroxybutyrate from brewer’s spent grain. AIMS Agric. Food 2016, 1, 52–66. [Google Scholar]
- White, J.S.; Yohannan, B.K.; Walker, G. Bioconversion of brewer’s spent grains to bioethanol. FEMS Yeast Res. 2008, 8, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Uchii, A.; Kanawaku, T.; Yanase, H. Bioconversion of xylose, hexoses and biomass to ethanol by a new isolate of the white rot basidiomycete Trametes versicolor. Springer Plus 2014, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Preparation of Samples for Compositional Analysis. National Renewable Energy Laboratory. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/docs/gen/fy08/42620.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2017).
- Saidur, R.; Abdelaziz, E.A.; Demirbas, A.; Hossain, M.S.; Mekhilef, S. A review of biomass as a fuel for boilers. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 2262–2289. [Google Scholar]
- Determination of Total Solids in Biomass and Total Dissolved Solids in Liquid Process Samples. National Renewable Energy Laboratory. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/docs/gen/fy08/42621.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2017).
- American Society for Testing and Materials ASTM International. Standard Test Method for Volatile Matter in the Analysis of Particulate Wood Fuels; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2006; pp. E872–E882. [Google Scholar]
- American Society for Testing and Materials ASTM International. Standard Test Method for Ash in the Analysis Sample of Refuse Derived Fuel; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004; pp. E830–E887. [Google Scholar]
- Mariusz, Z.; Pawlowski, A. Biomass for fuels–classification and composition. In Biomass for Biofuels, 1st ed.; Bulkowska, K., Gusiatin, Z.M., Klimiuk, E., Pawlowski, A., Pokoj, Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2016; pp. 15–36. [Google Scholar]
- Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry. Preparation of Wood for Chemical Analysis Test Method T264 Cm-07; TAPPI: Peachtree Corners, GA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry. Water Solubility of Wood and Pulp Test Method T207 cm-99; TAPPI: Peachtree Corners, GA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- American Society for Testing and Materials ASTM International. D 1106-96 Standard Test Method for Acid-Insoluble Lignin in Wood; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- American Society for Testing and Materials ASTM International. D 1104-56 Method of Test for Hollocelulose in Wood; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Rowell, R.M.; Pettersen, R.; Tshabalala, M.A. Cell Wall Chemistry. In Handbook of Wood Chemistry and Wood Composites, 1st ed.; Rowell, R.M., Ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 33–74. [Google Scholar]
- Sadhukhan, J.; Siew, K.; Martinez, E. Biorefineries and Chemical Processes. Design, Integration and Sustainability Analysis, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: London, UK, 2014; pp. 110–115. [Google Scholar]
- Nhuchhen, D.R.; Abdul, P.S. Estimation of higher heating value of biomass from proximate analysis: A new approach. Fuel 2012, 99, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society for Testing and Materials ASTM. International Standard Test Method for Gross Calorific Value of Refuse-Derived Fuel by the Bomb Calorimeter; ASTM E711: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Buffington, J. The Economic Potential of Brewer’s Spent Grain (BSG) as a Biomass Feedstock. Adv. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 4, 308–318. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, R.M.; Rodrigues, R.A.; Henriques, C.M.; Gameiro, L.F.; Ismael, M.R.; Reis, M.T.; Freire, J.P.; Carvalho, J.M. Dewatering of brewer’s spent grain using an integrated membrane filter press with vacuum drying capabilities. Sep. Sci Technol. 2016, 51, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias, T.R.; Alexandre, V.M.; Cammarota, M.C.; de Mello, P.P.; Sérvulo, E.F. Characterization and determination of brewer’s solid wastes composition. J. Inst. Brew. 2015, 121, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Q. Sustainable mechanisms of biochar derived from brewer’s spent grain and sewage sludge for ammonia-nitrogen capture. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 3927–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klímek, P.; Wimmer, R.; Mishra, P.K.; Kúdela, J. Utilizing brewer’s-spent-grain in wood-based particleboard manufacturing. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 141, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, G.S.; Kaur, S.; Brar, S.K. In-vitro decoloration of recalcitrant dyes through an ecofriendly approach using laccase from Trametes versicolor grown on brewer’s spent grain. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2012, 72, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiros, C.; Christakopoulos, P. Enhanced ethanol production from brewer’s spent grain by a fusarium oxysporum consolidated system. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2009, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Russ, W.; Mörtel, H.; Meyer-Pittroff, R. Application of spent grains to increase porosity in bricks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2005, 19, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weger, A.; Binder, S.; Franke, M.; Hornung, A.; Rub, W.; Mayer, W. Solid biofuel production by mechanical pre-treatment of brewer’s spent grain. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2014, 37, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, G.; Coronado, M.; Torres, R.; Jaramillo, B.; García, C.; Stoycheva, M.; Vázquez, A.; León, J.; Lambert, A.; Valenzuela, E. Higher heating value determination of wheat straw from Baja California, México. Energy 2016, 109, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turn, S.Q.; Jenkins, B.M.; Jakeway, L.A.; Blevins, L.G.; Williams, R.B.; Rubenstein, G.; Kinoshita, C.M. Test results from sugar cane bagasse and high fiber cane co-fired with fossil fuels. Biomass Bioenerg. 2006, 30, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, S.; Ayanoglu, A. Determination of higher heating values (HHVs) of biomass fuels. Ener. Educ. Sci. Tech. A 2012, 28, 749–758. [Google Scholar]
- White, C.; Zainasheff, J. Yeast: The Practical Guide to Beer Fermentation, 1st ed.; Brewers Publications: Boulder, CO, USA, 2010; pp. 77–91. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).