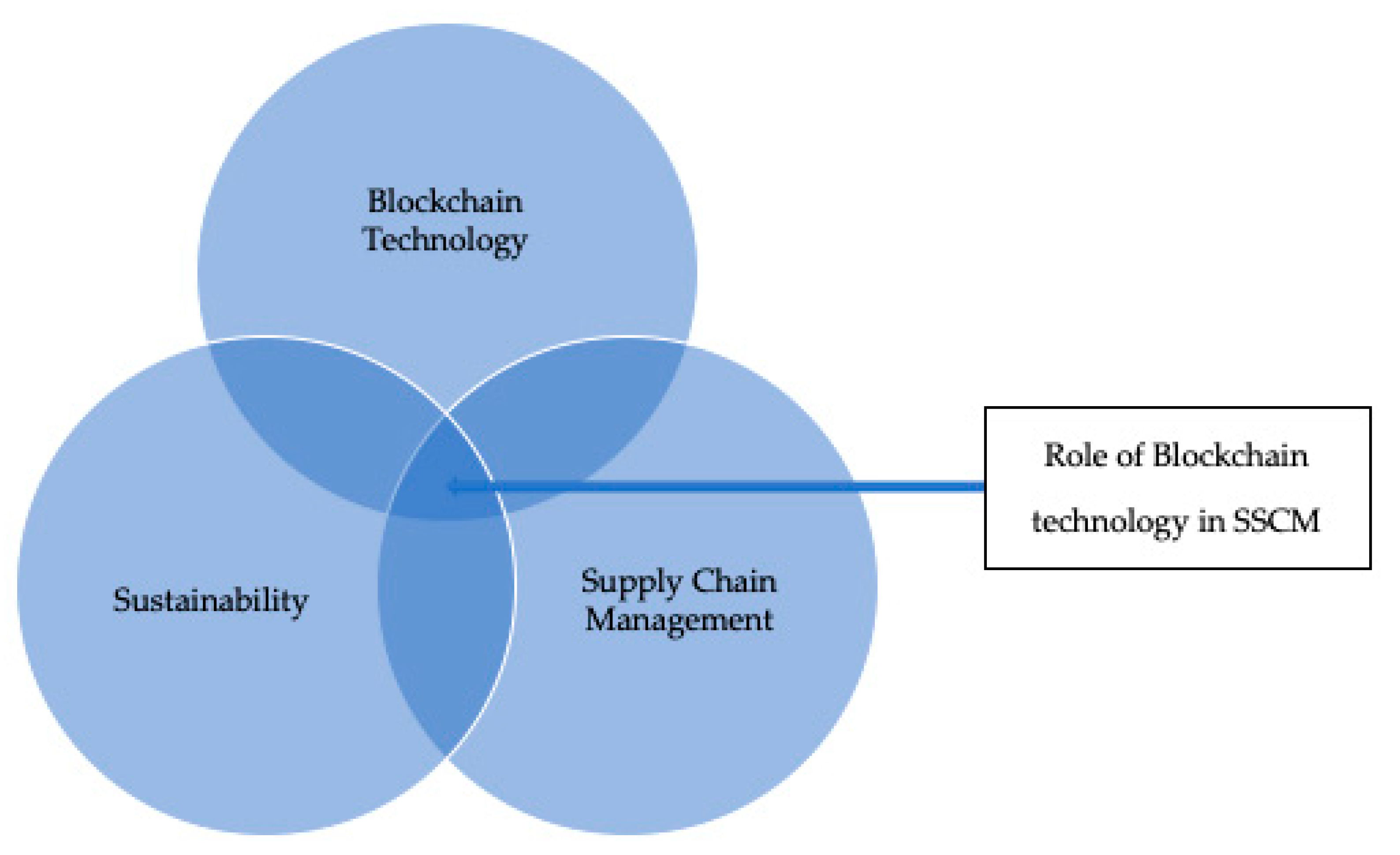
Blockchain Technology for Sustainable Supply Chain Management: A Systematic Literature Review and a Classification Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
- What: What are the key findings of this literature review?
- Who: Identify researchers in the area of our research interest and the most active researchers.
- Where: Identify the journals that have published research in the area of our research interest.
- When: Identify the span of time for which research has been conducted in the area of our research interest.
- How: How is research in this area going to change the way business is conducted? Identify the new business models in this area.
- Why: Why is it important for researchers to conduct research in this area? Why is it necessary to further examine this research area if it has already been studied in great detail? Identify the research gaps.
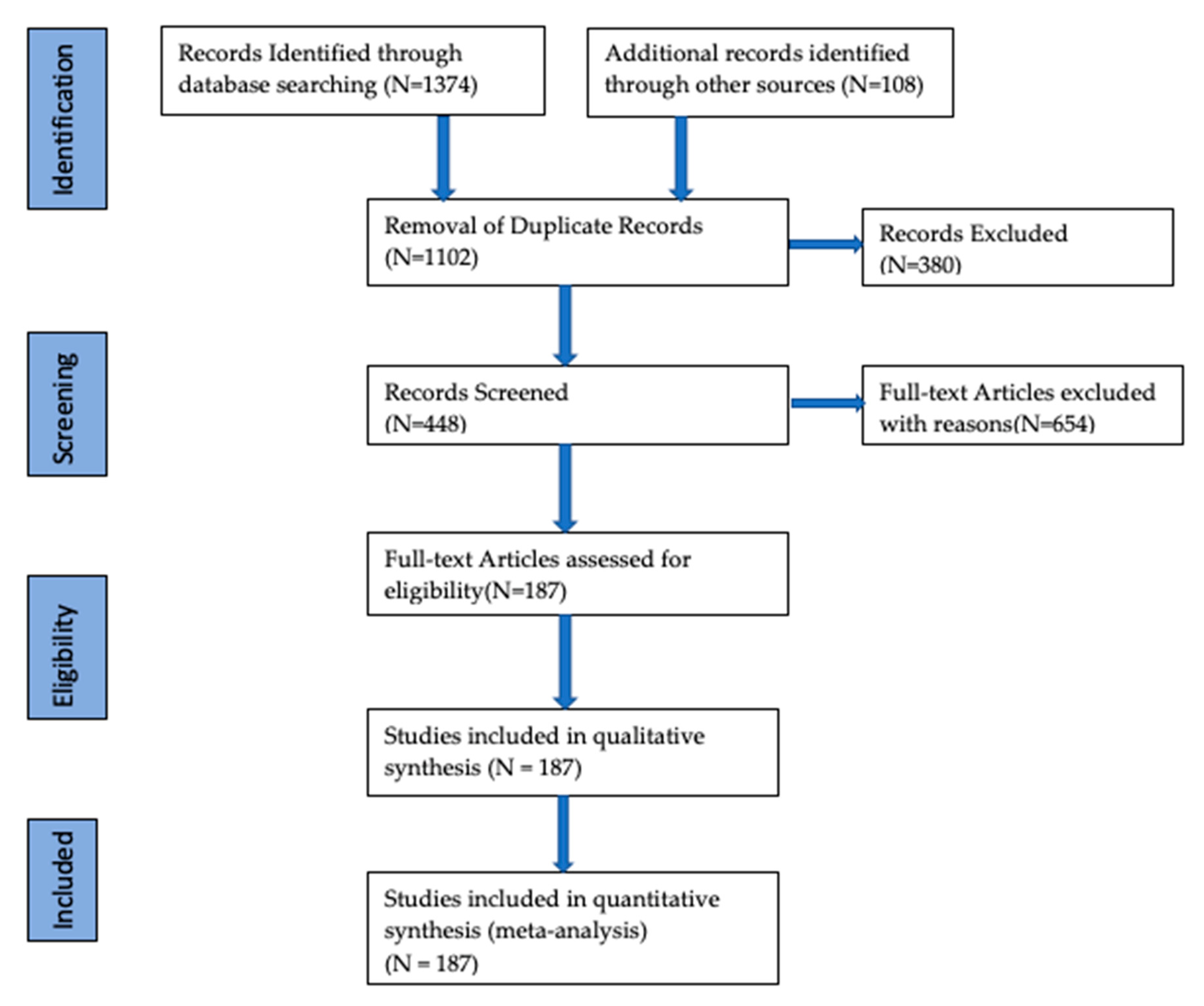
2. Research Methodology
- Introduces the researcher to the technology from a particular perspective;
- Introduces the researcher to the core offering or benefit of the technology;
- Raises the awareness of the researcher about early experimentation or adoption of the technology;
- Helps the researcher to assess the impact of the new technology;
- Helps the researcher or possibly a budding entrepreneur or a seasoned manager learn about the business environment in which the technology operates and how the technology may adopt to the business environment through sound business models;
- Helps the researcher/entrepreneur/manager learn about the key use cases or the applicability of the technology in the business;
- Helps the researcher/entrepreneur/manager understand how the technology is leading to sustainable development by creating sustainable practices in the business;
- Helps the researcher/entrepreneur/manager understand the state of art in research and business of the technology today;
- Helps the researcher/entrepreneur/manager understand big global success stories that have happened based on the technology.
- (a)
- INTRODUCTORY: This level consists of introductory articles that create awareness of the various aspect of the emerging technology. It may take a look at the technology from various perspectives. It may also delve into the hype behind this new technology.
- (b)
- BENEFITS: This level consists of articles on the benefits of using blockchain. They study the primary reason the technology should be further researched and investigate the use cases. In short, this level answers the question of why blockchain technology should be given attention.
- (c)
- EARLY EXPERIMENTATION AND ADOPTION: This level consists of articles describing early experimentation and lessons learned from them. They examine the growth factors and barriers. In short, this level identifies the key use cases and the experiments conducted in this regard.
- (d)
- IMPACT ASSESSMENT: This level consists of articles assessing the long-term impact of blockchain technology. They may be based on the success and failure stories from the previous level of research articles.
- (e)
- BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT: This level consists of articles on the business environment in which blockchain technology will have to operate. They may identify legal and technical challenges. They may also identify the business models that might be successful in such a business environment.
- (f)
- APPLICABILITY TO THE BUSINESS TODAY: This level consists of articles identifying how technology is being used for influencing business in today’s environment.
- (g)
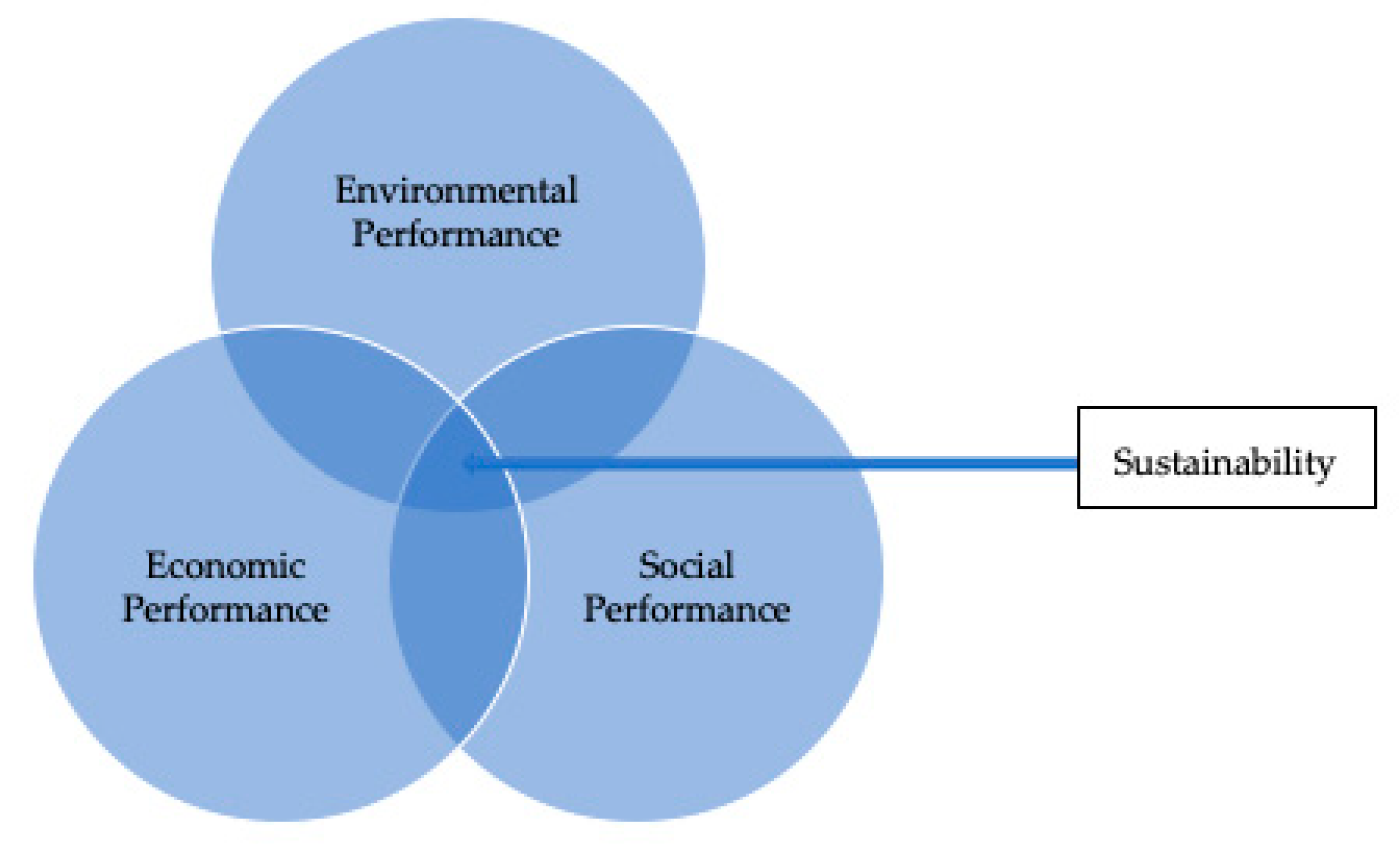
- CREATION OF SUSTAINABLE BUSINESS: This level consists of articles on blockchain technology’s advantages, limitations, and scope. They look at the sustainability (environmental, social, and economic performance) aspect of the businesses based on this new technology.
- (h)
- STATE-OF-THE-ART IN BUSINESS: This level comprises articles studying the current state of the evolution of blockchain technology. They examine the technology’s maturity through the lens of having clear standards and policies. They also look at the performance and research gaps if any.
- (i)
- BIG GLOBAL SUCCESS STORIES: This level comprises articles on the globally relevant examples of the successful applications of this new technology.
3. Results: Development of a Classification Framework
3.1. ETLCL 1: INTRODUCTORY
3.1.1. Historical/Futuristic
3.1.2. Multidisciplinary
3.1.3. Maturity
3.1.4. Socio-Technical
3.2. ETLCL 2: BENEFITS
3.2.1. Traceability
3.2.2. Transparency
3.2.3. Trust
3.2.4. Digital Identity
3.2.5. Frictionless Collaboration
3.2.6. Anti-Counterfeiting
3.3. ETLCL 3: EARLY EXPERIMENTATION AND ADOPTION
3.3.1. Growth Factors and/or Barriers
3.3.2. Assessment and/or Customization
3.3.3. Cryptocurrencies
3.3.4. Review
3.4. ETLCL 4: IMPACT ASSESSMENT
3.4.1. Forecasting
3.4.2. Disruption/Digital Transformation
3.4.3. Industry 4.0
3.5. ETLCL 5: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT
3.5.1. Business Model
3.5.2. Legal and Governance
3.5.3. Policy and Regulation
3.5.4. Sharing Economy
3.5.5. Theory
3.6. ETLCL 6: APPLICABILITY TO THE CURRENT BUSINESS SCENARIO
3.6.1. ICO
3.6.2. Risk Management
3.6.3. Smart Contracts
3.6.4. Modeling/Pilot
3.7. ETLCL 7: CREATION OF SUSTAINABLE BUSINESS
3.7.1. Advantages
3.7.2. Limitations/Barriers
3.7.3. Performance
3.7.4. Environment
3.7.5. Social Innovation/Financial Inclusion
3.7.6. Supply Chain Finance
3.7.7. Sustainable Development Goals
3.8. ETLCL 8: STATE-OF-THE-ART IN BUSINESS
3.8.1. Accounting/Auditing
3.8.2. Launched Projects
3.8.3. Research Gap
3.8.4. Risk
3.8.5. Standards
3.8.6. Trends
4. Discussion in Context of Research Questions
4.1. Research Question 1: WHAT
4.2. Research Question 2: WHO
4.3. Research Question 3: WHERE
4.4. Research Question 4: WHEN
4.5. Research Question 5: HOW
- Creation of a blockchain architecture that can be used by others to develop applications. It will work by promoting itself as a technical or market standard over which innovations can be developed.
- Displacement of incumbents from value chains, such as blockchain-based car rental platform that may displace companies like Uber and Ola.
- Creating firm-specific value for all partners of the value chain by enhancing value-chain efficiency.
- Address and resolve long-standing issues of contemporary business practices like traceability issues.
- Development of blockchain solutions for pre-existing business practices.
4.6. Research Question 6: WHY
- (a)
- How to theoretically evaluate the benefits of blockchain technology-based applications in SSCM?
- (b)
- What tradeoff considerations must be evaluated while reflecting on the adoption of blockchain technology for SSCM?
- (c)
- What changes in accounting practices would ensure that they account for externalities?
- (a)
- What activities are necessary to integrate existing legacy systems into the blockchain networks?
- (b)
- How can blockchain service providers gain traction from multiple actors of the supply chain?
- (c)
- Is the lack of governance structure a barrier to the evolution of blockchain-based supply chains?
- (d)
- How will SCM theories evolve to account for blockchain-based supply chains? Will it require new theories? Will it essentially require multidisciplinary teams to come up with a new theory?
- (e)
- How does stakeholder behavior change when blockchain-based information management systems manage data?
- (f)
- Can blockchain technology help build information management systems that address all three pillars of sustainability simultaneously?
- (g)
- How to determine the need to use blockchain for an SSCM project? What are the information management systems for which a firm should use blockchain-based distributed ledgers? Which systems should remain in silos of individual organizations (traditional databases)?
5. Conclusions
5.1. Theoretical Implications
5.2. Practical Implications
5.3. Limitations and Scope for Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Casino, F.; Dasaklis, T.K.; Patsakis, C. A systematic literature review of blockchain-based applications: Current status, classification and open issues. Telemat. Inf. 2019, 36, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, J.H.; Davies, P.B. Understanding blockchain technology for future supply chains: A systematic literature review and research agenda. Suppl. Chain Manag. Int. J. 2019, 1, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackius, N.; Petersen, M. Blockchain in Logistics and Supply Chain: Trick or Treat? In Proceedings of the Hamburg International Conference of Logistics. Digitalization in Supply Chain Management and Logistics: Smart and Digital Solutions for an Industry 4.0 Environment, Berlin, Germany, October 2017; p. 16. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, C.; Cai, Y.; Yu, Y.T.; Tse, T.H. 5W+1H pattern: A perspective of systematic mapping studies and a case study on cloud software testing. J. Syst. Softw. 2016, 116, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, S. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. Cryptogr. Mail. List 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, C.; Rogers, D. A Framework of Sustainable Supply Chain Management: Moving Toward New Theory. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2008, 38, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, P. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta Analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaser, B.G.; Strauss, A.L. The Discovery of Grounded Theory: Strategies for Qualitative Research; Aldine Transactions: A Division of Transaction Publishers; Aldine: Chicago, IL, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Tate, M. A Descriptive Literature Review and Classification of Cloud Computing Research. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2012, 31, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heder, M. From NASA to EU: The evolution of the TRL scale in public sector innovation. Innov. J. Public Sect. Innov. J. 2017, 22, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, V. A Brief History of Blockchain. In Harvard Business Review; Harvard Business Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Firdaus, A.; Ab Razak, M.F.; Feizollah, A.; Hashem, I.A.T.; Hazim, M.; Anuar, N.B. The rise of “blockchain”: Bibliometric analysis of blockchain study. Scientometrics 2019, 120, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, L.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Misra, S.K.; Rana, N.P.; Raghavan, V.; Akella, V. Blockchain research, practice and policy: Applications, benefits, limitations, emerging research themes and research agenda. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 49, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, J.; Camarinha-Matos, L.M. Approaches for resilience and antifragility in collaborative business ecosystems. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 151, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Hughes, L.; Ismagilova, E.; Aarts, G.; Coombs, C.; Crick, T.; Galanos, V. Artificial Intelligence (AI): Multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 101994, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanson, M.; Bogner, A.; Bilgeri, D.; Fleisch, E.; Wortmann, F. Blockchain for the IoT: Privacy-Preserving Protection of Sensor Data. J. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2019, 20, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnson, P. Blockchain coming of age. Suppl. Chain Manag. Rev. 2017, 21, 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenberg, A.J.; King, L.J. Blockchain in context. Inf. Syst. Front. 2020, 22, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virto, L.R. A preliminary assessment of the indicators for Sustainable Development Goals(SDG) 14 “Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development”. Mar. Policy 2018, 98, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, A.; Xuan, D.T.; Cottrill, K. Is blockchain the missing link in the Halal Supply Chain. Suppl. Chain Manag. Rev. 2018, 22, 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Montecchi, M.; Plangger, K.; Etter, M. It’s real, trust me! Establishing supply chain provenance using blockchain. Bus. Horizons 2019, 62, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, R.V.; Harsh, H.O.; Ray, P.; Babu, A.K. Food quality traceability prototype for restaurants using blockchain and food quality data index. J. Cleaner Prod. 2019, 240, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnke, K.; Janssen, M.F.W.H.A. Janssen Boundary conditions for traceability in food supply chains using blockchain technology. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 101969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, T.K.; Pal, R. Traceability in Textile and Clothing Supply Chains: Classifying Implementation Factors and Information Sets via Delphi study. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheem, D.; Shishaev, M.; Dikovitsky, V. Food System Digitalization as a Means to Promote Food and Nutrition Security in the Barents Region. Agriculture 2019, 9, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violino, S.; Pallottino, F.; Sperandio, G.; Figorilli, S.; Antonucci, F.; Ioannoni, V.; Fappiano, D.; Costa, C. Are the Innovative Electronic Labels for Extra Virgin Olive Oil Sustainable, Traceable, and Accepted by Consumers? Foods 2019, 8, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violino, S.; Pallottino, F.; Sperandio, G.; Figorilli, S.; Ortenzi, L.; Tocci, F.; Vasta, S.; Imperi, G.; Costa, C. A Full Technological Traceability System for Extra Virgin Olive Oil. Foods 2020, 9, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Zhang, C.; Gong, Y.; Brown, S.; Li, Z. A Content-Analysis Based Literature Review in Blockchain Adoption within Food Supply Chain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figorilli, S.; Antonucci, F.; Costa, C.; Pallottino, F.; Raso, L.; Castiglione, M.; Pinci, E.; Vecchio, D.D.; Colle, G.; Proto, A.R.; et al. A Blockchain Implementation Prototype for the Electronic Open Source Traceability of Wood along the Whole Supply Chain. Sensors 2018, 18, 3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; An, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, H.; Xia, L.; Sun, X.; Guo, Y. State-of-the-Art Internet of Things in Protected Agriculture. Sensors 2019, 19, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treiblmaier, H.; Rejeb, A.; Strebinger, A. Blockchain as a Driver for Smart City Development: Application Fields and a Comprehensive Research Agenda. Smart Cities 2020, 3, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigini, D.; Conti, M. NFC-Based Traceability in the Food Chain. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumblauskas, D.; Mann, A.; Dugan, B.; Rittmer, J. A blockchain use case in food distribution: Do you know where your food has been? Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 102008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, M.; Won, Y. A study on the transparent price tracing system in supply chain management based on blockchain. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, W.L.; Ellams, D.; Han, S.; Tyler, D.; Boiten, V.J.; Paco, A.; Moora, H.; Balogun, A.-L. A review of the socio-economic advantages of textile recycling. J. Cleaner Prod. 2019, 218, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Azzi, R.; Chamoun, R.K.; Sokhn, M. The power of a blockchain-based supply chain. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 135, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, M.; Yik, S. Precision Livestock Farming in Swine Welfare: A Review for Swine Practitioners. Animals 2019, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Pena, M.; Fraga, F.J.A.; Sotano, A.J.S.; Batista, M. Shipbuilding 4.0 Index Approaching Supply Chain. Materials 2019, 12, 4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, T.; Lee, J.; Ryu, D. Blockchain Technology and Manufacturing Industry: Real-Time Transparency and Cost Savings. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.A.; Oliver, M.; Ramalhinho, H. Challenges for Connecting Citizens and Smart Cities: ICT, E-Governance and Blockchain. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapscott, D.; Euchner, J. Blockchain and the Internet of Value. Res. Technol. Manag. 2019, 62, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrill, K. The Benefits of Blockchain: Fact or wishful thinking. Suppl. Chain Manag. Rev. 2018, 22, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Cottrill, K. Can we trust the “trust machine?”. Suppl. Chain Manag. Rev. 2018, 22, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, N.; Al-Jaroodi, J.; Jawhar, I. Cyber-Physical Systems Forensics: Today and Tomorrow. J. Sensor Actuat. Netw. 2020, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainelli, M. Blockchain Will Help Us Prove Our Identities in a Digital World. In Harvard Business Review; Harvard Business Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Radell, C.; Schannon, D. Digital Procurement: The Benefits go far beyond the efficiency. Supply Chain Management Review, 6 March 2019; 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Meraviglia, L. Technology and counterfeiting in the fashion industry. Bus. Horizons 2018, 61, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyal, A.A.; Junejo, A.Z.; Zawish, M.; Ahmed, K.; Khalil, A.; Soursou, G. Applications of Blockchain Technology in Medicine and Healthcare: Challenges and Future Perspectives. Cryptography 2019, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bublitz, F.M.; Oetomo, A.; Sahu, K.S.; Kuang, A.; Fadrique, L.X.; Velmovitsky, P.E.; Nobrega, R.M.; Morita, P.P. Disruptive Technologies for Environment and Health Research: An Overview of Artificial Intelligence, Blockchain, and Internet of Things. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visconti, R.M.; Morea, D. Healthcare Digitalization and Pay-For-Performance Incentives in Smart Hospital Project Financing. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polenzani, B.; Riganelli, C.; Marchini, A. Sustainability Perception of Local Extra Virgin Olive Oil and Consumer’s Attitude: A New Italian Perspective. Sustainability 2020, 12, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalan, T. Born Global on Blockchain. Rev. Int. Bus. Strategy 2018, 28, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.-W.; Leong, L.-Y.; Hew, J.-J.; Tan, G.W.-H.; Ooi, K.-B. Time to seize the digital evolution: Adoption of blockchain in operations and supply chain management among Malaysian SMEs. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 101997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldo, J. A hitchhiker’s guide to the blockchain universe. Commun. ACM 2019, 62, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viniak, V. Beyond Cryptocurrency: Blockchain as a value creator and connector. Supply Chain Management Review, 8 January 2019; 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Queiroz, M.M.; Wamba, S.F. Blockchain adoption challenges in supply chain: An empirical investigation of main drivers in India and USA. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 46, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Arha, H. Understanding the blockchain technology adoption in supply chains-Indian context. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 57, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, S.; Majumdar, A.; Monahan, S. Unlocking blockchain’s potential in your supply chain. Suppl. Chain Manag. Rev. 2018, 22, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Casey, M.J.; Wong, P. Global Supply Chains are about to Get Better, Thanks to Blockchain. In Harvard Business Review; Harvard Business Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, B.; Gupta, R. Analysis of barriers to implement blockchain in industry and service sectors. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 136, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogataj, D.; Bogataj, M. NPV approach to material requirements planning theory-a 50-year review of these research achievements. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 57, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, K.; Swanson, D. The Supply Chain Has No Clothes: Technology Adoption of Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency. Logistics 2018, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gausdal, A.H.; Czachorowski, K.V.; Solesvik, M.Z. Applying Blockchain Technology: Evidence from Norwegian Companies. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldarelli, G.; Rossignoli, C.; Zardini, A. Overcoming the Blockchain Oracle Problem in the Traceability of Non-Fungible Products. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iansiti, M.; Lakhani, K.R. The Truth About Blockchain. In Harvard Business Review; Harvard Business Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Saadatmand, F.; Lindgren, R.; Schultze, U. Configurations of platform organizations: Implications for complementor engagement. Res. Policy 2019, 48, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeck, D.; Sternberg, H.; Hofmann, E. Distributed ledger technology in supply chains: A transaction cost perspective. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 58, 2124–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, A.B.; Risius, M.; Beck, R. A Ten-Step Decision Path to Determine when to use blockchain technologies. MIS Q. Exec. 2019, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.-M. Blockchain technology supported platforms for diamond authentication and certification in luxury supply chains. Trans. Res. Part E 2019, 128, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berke, A. How Safe are Blockchains? It Depends. In Harvard Business Review; Harvard Business Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Boone, T.; Ganeshan, R.; Jain, A.; Sanders, N.R. Forecasting sales in the supply chain: Consumer analytics in the big data era. Int. J. Forecast. 2019, 35, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelis, J.; Silva, E.R.d. Blockchain adoption: A value driver perspective. Bus. Horizons 2019, 62, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alt, R. Electronic markets and current general research. Electron. Markets 2018, 28, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrovnik, M.; Herold, D.M.; Furst, E.; Kummer, S. Blockchain for and in Logistics: What to Adopt and Where to Start. Logistics 2018, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, P.; Sinn, F.; Herden, T.T. Examples from Blockchain Implementations in Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Exploring the Mindful Use of a New Technology. Logistics 2018, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klarin, A. The decade-long cryptocurrencies and the blockchain rollercoaster: Mapping the intellectual structure and charting future directions. Res. Int. Bus. Fin. 2020, 51, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derks, J.; Gordijn, J.; Siegmann, A. From chaining blocks to breaking even: A study on the profitability of bitcoin mining from 2012 to 2016. Electr. Markets 2018, 28, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuen, D.L.K. Fintech and Alternative Investment. J. Alter. Investig. 2018, 22, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Chan, H.-L.; Siqin, T. Demand forecasting in retail operations for fashionable products: Methods, practices, and real case study. Ann. Operat. Res. 2020, 291, 761–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vial, G. Understanding digital transformation: A review and a research agenda. J. Strategic Inf. Syst. 2019, 28, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoef, P.C.; Broekhuizen, T.; Bart, Y.; Bhattacharya, A.; Dong, J.Q.; Fabian, N.; Haenlein, M. Digital transformation: A multidisciplinary reflection and research agenda. J. Bus. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, G.; Tricarico, L. “May the Force move you”: Roles and actors of information sharing devices in urban mobility. Cities 2019, 88, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapscott, D.; Tapscott, A. How blockchain will change organizations. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2017, 58, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Partida, B. Blockchain’s great potential. Suppl. Chain Manag. Rev. 2018, 22, 51–53. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, T.; Kuhn, M.; Hartmann, E. Blockchain technology enabling the Physical Internet: A synergetic application framework. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 136, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morkunas, V.J.; Paschen, J.; Boon, E. How blockchain technologies impact your business model. Bus. Horizons 2019, 62, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.; Park, A.; Kietzmann, J.; Archer-Brown, C. Beyond bitcoin: What blockchain and distributed ledger mean for firms. Bus. Horizons 2019, 62, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, J.L.; Sawaya, W.J. Tortoise, not the hare: Digital transformation of supply chain business processes. Bus. Horizons 2019, 62, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattu, V.K.; Nanda, A.; Chattu, S.K.; Kadri, S.M.; Knight, A.W. The Emerging Role of Blockchain Technology Applications in Routine Disease Surveillance Systems to Strengthen Global Health Security. Big Data Cognit. Comput. 2019, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treiblmaier, H. Combining Blockchain Technology and the Physical Internet to Achieve Triple Bottom Line Sustainability: A Comprehensive Research Agenda for Modern Logistics and Supply Chain Management. Logistics 2019, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Liu, S.; Lopez, C.; Lu, H.; Elgueta, S.; Chen, H.; Boshkoska, B.M. Blockchain technology in agri-food value chain management: A synthesis of applications, challenges and future research directions. Comput. Ind. 2019, 109, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Qiu, H.; Bi, Y.; Chang, S.-H.; Lam, A.L. Analysis of coordination mechanism of supply chain management information system from the perspective of blockchain. Inf. Syst. E Bus. Manag. 2019, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.S.; Veelenturf, L.P. The strategic role of logistics in the industry 4.0 era. Trans. Res. Part E 2019, 129, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srai, J.S.; Lorentz, H. Developing design principles for the digitalisation of purchasing and supply management. J. Purchas. Suppl. Manag. 2019, 25, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schniederjans, D.G.; Curado, C.; Khalajhedayati, M. Supply chain digitisation trends: An integration of knowledge management. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 220, 107439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Pena, M.; Sotano, A.J.S.; Perez-Fernandez, V.; Abad, F.J.; Batista, M. Achieving a sustainable shipbuilding supply chain under I4.0 perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prockl, G.; Bhakoo, V.; Wong, C. Supply chains and electronic markets—Impulses for value co-creation across the disciplines. Electr. Markets 2017, 27, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, M. The future of manufacturing industry: A strategic roadmap toward Industry 4.0. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2018, 29, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandner, P.; Lange, A.; Schulden, P. The Role of the CFO of an Industrial Company: An Analysis of the Impact of Blockchain Technology. Future Int. 2020, 12, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, S.H.; Silva, H.R.O.; Silva, M.T.d.; Goncalves, R.F.; Sacomano, J.B. Industry 4.0 and Sustainability Implications: A Scenario-Based Analysis of the Impacts and Challenges. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weking, J.; Mandalenakis, M.; Hein, A.; Hermes, S.; Bohm, M.; Krcmar, H. The impact of blockchain technology on business models—A taxonomy and archetypal patterns. Electr. Markets 2020, 30, 285–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.-M.; He, Y. Peer-to-peer collaborative consumption for fashion products in the sharing economy: Platform operations. Trans. Res. Part E 2019, 126, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.-M.; Feng, L.; Li, R. Information disclosure structure in supply chains with rental service platforms in the blockchain technology era. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 221, 107473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felin, T.; Lakhani, K. What problems will you solve with blockchain? MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2018, 60, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, A.Y.L.; Lim, E.T.K.; Hua, X.; Zheng, S.; Tan, C.-W. Business on Chain: A comparative case study of five blockchain-inspired business models. J. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2019, 20, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, R.; Iorfida, C.; Li, Y.; Manerba, D.; Musso, S.; Perboli, G.; Tadei, R.; Yuan, S. Sustainable and De-Stressed International Supply-Chains through the SYNCHRO-NET Approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahdeaho, O.; Hilmola, O.-P. Business Models Amid Changes in Regulation and Environment: The Case of Finland-Russia. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaio, A.D.; Boccia, F.; Landriani, L.; Palladino, R. Artificial Intelligence in the Agri-Food System: Rethinking Sustainable Business Models in the COVID-19 Scenario. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werbach, K. Trust, But Verify: Why the Blockchain Needs the Law. Berkeley Technol. Law J. 2018, 33, 65. [Google Scholar]
- Sulkowski, A. Blockchain, business supply chains, sustainability, and law: The future of governance, legal frameworks, and lawyers. Del. J. Corp. Law 2019, 43, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkis, J.; Zhu, Q. Environmental sustainability and production: Taking a road less travelled. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murck, P. Who Controls the Blockchain? In Harvard Business Review; Harvard Business Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Finck, M.; Moscon, V. Copyright Law on blockchains: Between new forms of rights administration and digital rights management 2.0. IIC Int. Rev. Intell. Property Compet. Law 2019, 50, 77–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkov, I.; Trump, B.D.; Poinsatte-Jones, K.; Florin, M.-V. Governance Strategies for a Sustainable Digital World. Sustainability 2018, 10, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, P. Regulatory issues in blockchain technology. J. Fin. Regul. Compl. 2017, 25, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorun, C.; Diels, J. Consumer Protection Technologies: An investigation into the potentials of new digital technologies for consumer policy. J. Consum. Policy 2020, 43, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholl, H.J.; Bolivar, M.P.R. Regulation as both enabler of technology use and global competitive tool: The Gibraltar case. Govern. Inf. Quart. 2019, 36, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerwe, O.; Silva, R. Clarifying the sharing economy: Conceptualization, Typology, Antecedents and Effects. Acad. Manag. Perspect. 2020, 34, 65–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Singgih, M.; Wang, J.; Rit, M. Making sense of blockchain technology: How will it transform supply chains? Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 211, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treiblmaier, H. The impact of the blockchain on the supply chain: A theory based research framework and a call for action. Suppl. Chain Manag. Int. J. 2018, 23, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.G.; Wagner, S.M. Blockchain and supply chain relations: A transaction cost theory perspective. J. Purchas. Suppl. Manag. 2019, 25, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummer, S.; Herold, D.M.; Dobrovnik, M.; Mikl, J.; Schafer, N. A Systematic Review of Blockchain Literature in Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Identifying Research Questions and Future Directions. Future Int. 2020, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D. The ever-evolving business ecosystem. Bus. Horizons 2018, 61, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, I.H.Y.; Greene, E.F. The Marriage of Technology, Markets and Sustainable (and) Social Finance: Insights from ICO markets for a new regulatory framework. Eur. Bus. Organ. Law Rev. 2019, 20, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Tsai, P.-H.; Wang, J.-L. Improving Financial Service Innovation Strategies for Enhancing China’s Banking Industry Competitive Advantage during the Fintech Revolution: A Hybrid MCDM Model. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N. Managing interactive collaborative mega project supply chains under infectious risks. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 218, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, F.; Qi, E. Research on Risk Avoidance and Coordination of Supply Chain Subject based on blockchain technology. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viriyasitavat, W.; Xu, L.D.; Bi, Z.; Sapsomboon, A. Blockchain-based business process management (BPM) framework for service composition in Industry 4.0. J. Intell. Manuf. 2020, 31, 1737–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, R.; Manerba, D.; Bruno, G.; Tadei, R. Synchromodal logistics: An overview of critical success factors, enabling technologies, and open research issues. Trans. Res. Part E 2019, 129, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eenmaa-Dimitrieva, H.; Schmidt-Kessen, M.J. Creating markets in no-trust environments: The law and economics of smart contracts. Comput. Law Secur. Rev. 2019, 35, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.E.; Chen, Y.-C.; Lu, M.-F. Supply chain re-engineering using blockchain technology: A case of smart contract based tracking process. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 144, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, D.-Y.; Wang, X. Applications of Blockchain Technology to Logistics Management in Integrated Casinos and Entertainment. Informatics 2018, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmeron-Manzano, E.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. The Role of Smart Contracts in Sustainability: Worldwide Research Trends. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Sarkis, J. Expanding Green Supply Chain Performance Measurement through Emergy Accounting and Analysis. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 225, 107576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Sharma, R. Modeling the blockchain enabled traceability in agriculture supply chain. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 101967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamchandani, A.; Srivastava, S.K.; Srivastava, R.K. Perception-based model for analyzing the impact of enterprise blockchain adoption on SCM in the Indian service industry. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 102019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helo, P.; Hao, Y. Blockchains in operations and supply chains: A model and reference implementation. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 136, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forger, G. Nextgen Supply Chain Awards. Supply Chain Management Review, 13 April 2020; 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, S.; Singh, S.P. Blockchain critical success factors for sustainable supply chain. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 152, 104505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phang, D.C.W.; Wang, K.; Wang, Q.; Kauffman, R.J.; Naldi, M. How to derive causal insights for digital commerce in China? A research commentary on computational social science methods. Electr. Commer. Res. Appl. 2019, 35, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolakis, W.; John, L.; Krishnan, H. How Blockchain Can Shape Sustainable Global Value Chains: An Evidence, Verifiability, and Enforceability (EVE) Framework. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, G.; Dhaigude, A.S. A conceptual model of sustainable supply chain management in small and medium enterprises using blockchain technology. Cogent. Econ. Fin. 2019, 7, 1667184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshetri, N. Blockchain’s roles in meeting key supply chain management objectives. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2018, 39, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurzawska, A. Towards responsible and sustainable supply chains-innovation, multi-stakeholder approach and governance. Philo. Manag. 2020, 19, 267–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudenreich, B.; Schaltegger, S. Developing sufficiency-oriented offerings for clothing users: Business approaches to support consumption reduction. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 247, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filimonau, V.; Naumova, E. The blockchain technology and the scope of its application in hospitality operations. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 87, 102383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.; Catalani, C. What Blockchain Can’t Do? In Harvard Business Review; Harvard Business Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Saberi, S.; Kouhizadeh, M.; Sarkis, J.; Shen, L. Blockchain technology and its relationships to sustainable supply chain management. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 57, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimba, P.; Tran, A.B.; Weber, I.; Staples, M.; Ponmarev, A.; Xu, X. Quantifying the cost of distrust: Comparing blockchain and cloud services for business process execution. Inf. Syst. Front. 2020, 22, 487–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prufer, J. Trusting privacy in the cloud. Inf. Econ. Policy 2018, 45, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.; Tavalaei, M.M.; Ozalp, H. Blockchain based platforms: Decentralized infrastructures and its boundary conditions. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 146, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Song, M.; Ai, B.; Ming, Y. Blockchain technology and enterprise operational capabilities: An empirical test. Int.J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 101946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacity, M.C. Addressing Key Challenges to making enterprise blockchain applications a reality. MIS Quart. Execut. 2018, 17, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, T.-M.; Luo, S. Data quality challenges for sustainable fashion supply chain operations in emerging markets: Roles of blockchain, government sponsors and environment taxes. Trans. Res. Part E 2019, 131, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaio, A.D.; Varriale, L. Blockchain technology in supply chain management for sustainable performance: Evidence from the airport industry. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 102014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sener, A.; Barut, M.; Oztekin, A.; Avcilar, M.Y.; Yildirim, M.B. The role of information usage in a retail supply chain: A causal data mining and analytical modeling approach. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 99, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizot, M.; Junior, P.P.A.; Trojan, F.; Magacho, C.S.; Thesari, S.S.; Goffi, A.S. Analysis of Evaluation methods of sustainable supply chain management in production engineering journals with high impact. Sustainability 2020, 12, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Gawankar, S.A. Achieving sustainable performance in a data-driven agriculture supply chain: A review for research and applications. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 219, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-S.; Shin, N. The Impact of Blockchain Technology Application on supply chain partnership and performance. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Gunasekaran, A.; Childe, S.J.; Papadopoulos, T.; Luo, Z.; Roubaud, D. Upstream supply chain visibility and complexity effect on focal company’s sustainable performance: Indian manufacturer’s perspective. Ann. Operat. Res. 2020, 290, 343–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejeb, A.; Keogh, J.G.; Treiblmaier, H. Leveraging the Internet of Things and Blockchain Technology in Supply Chain Management. Future Int. 2019, 11, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahkani, M.J.; Wang, S.; Urbanski, M.; Egorova, M. Sustainable B2B E-Commerce and Blockchain-Based Supply Chain Finance. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouhizadeh, M.; Sarkis, J. Blockchain Practices, Potentials, and Perspectives in Greening Supply Chains. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinder, M. Making Cryptocurrencies More Environmentally Sustainable. In Harvard Business Review; Harvard Business Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouhizadeh, M.; Sarkis, J.; Zhu, Q. At the Nexus of Blockchain Technology, the Circular Economy, and Product Deletion. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujicic, S.; Hasanspahic, N.; Car, M.; Campara, L. Distributed Ledger Technology as a Tool for Environmental Sustainability in the Shipping Industry. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Shu, Z.; Liu, X. Blockchain Enhanced Emission Trading Framework in Fashion Apparel Manufacturing Industry. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.Q.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Kang, K.; Costa, F. A Blockchain-Based Framework for Green Logistics in Supply Chains. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuetz, S.; Venkatesh, V. Blockchain, adoption and financial inclusion in India: Research opportunities. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 101936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kumar, V.; Karam, E. New-age technologies-driven social innovation: What, how, where, and why? Ind. Market. Manag. 2020, 89, 499–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Hao, Z.; Wang, F.; Li, H. Innovative Blockchain-Based Approach for Sustainable and Credible Environment in Food Trade: A Case Study in Shandong Province, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Li, S. The role of supply chain finance in improving the competitive advantage of online retailing enterprises. Electr. Commer. Res. Appl. 2019, 33, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.E.; Luo, H.L.; Chen, Y. Blockchain-Enabled Trade Finance Innovation: A Potential Paradigm Shift on Using Letter of Credit. Sustainability 2020, 12, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franca, A.S.L.; Neto, J.A.; Goncalves, R.F.; Almeida, C.M.V.B. Proposing the use of blockchain to improve the solid waste management in small municipalities. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Torres, S.; Albareda, L.; Rey-Garcia, M.; Seuring, S. Traceability for sustainability-literature review and conceptual framework. Suppl. Chain Manag. Int. J. 2019, 24, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Vasarhelyi, M.A. Toward Blockchain-Based Accounting and Assurance. J. Inf. Syst. 2017, 31, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyne, J.G.; McMickle, P.L. Can Blockchains Serve an Accounting Purpose? J. Emerg. Technol. Acc. 2017, 14, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-S.; Lirn, T.-C. Revisiting the resource-based view on logistics performance in the shipping industry. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Log. Manag. 2017, 47, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodside, J.M.; Augustine, F.K., Jr.; Giberson, W. Blockchain technology adoption, status and strategies. J. Int. Technol. Inf. Manag. 2017, 26, 65–93. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Jia, F.; Schoenherr, T.; Gong, Y.; Chen, L. Cross-border e-commerce firms as supply chain integrators: The management of three flows. Ind. Market. Manag. 2020, 89, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, J.-H.; Liao, Y.-C.; Chong, B.; Liao, S.-w. Governance on the Drug Supply Chain via Gcoin Blockchain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Liu, R.; Shan, Z. Is Blockchain a Silver Bullet for Supply Chain Management? Technical Challenges and Research Opportunities. Decis. Sci. 2020, 51, 8–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flak, J. Technologies for Sustainable Biomass Supply-Overview of Market Offering. Agronomy 2020, 10, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cai, T.; He, W.; Chen, L.; Zhao, G.; Zou, W.; Guo, L. A Blockchain-Driven Supply Chain Finance Application for Auto Retail Industry. Entropy 2020, 22, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazaitis, A. Breaking the Chains of Open Innovation: Post-Blockchain and the Case of Sensorica. Information 2020, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unerman, J.; Bebbington, J.; O’Dwyer, B. Corporate reporting and accounting for externalities. Acc. Bus. Res. 2018, 48, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Tonnissen, S.; Teuteberg, F. Analysing the impact of blockchain technology for operations and supply chain management: An explanatory model drawn from multiple case studies. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 101953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, R.; Mark, S.; Aitken, J. Blockchain Technology: Implications for operations and supply chain management. Suppl. Chain Manag. Int. J. 2019, 24, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Melynk, S.A.; Speier-Pero, C.; Connors, E. Blockchain is vastly overrated; supply chain cyber security is vastly underrated. Supply Chain Management Review, 1 May 2019; 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Guadamuz, A. All watched over by machines of loving grace: A critical look at smart contracts. Comput. Law Secur. Rev. 2019, 35, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Awrey, D.; Zwieten, K.V. The Shadow Payment System. J. Corp. Law 2018, 43, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Freund, A.; Stanko, D. The Wolf and the Caribou: Coexistence of Decentralized Economies and Competitive Markets. J. Risk Fin. Manag. 2018, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grody, A.D. Rebuilding financial industry infrastructure. J. Risk Manag. Fin. Inst. 2018, 11, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Tijan, E.; Aksentijevic, S.; Ivanic, K.; Jardas, M. Blockchain technology implementation in logistics. Sustainability 2019, 1185, 13. [Google Scholar]
- McCrea, B. 7 Supply chain financing trends to watch. Supply Chain Management Review, 6 March 2019; 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Google. Google Scholar Metrics. Available online: https://scholar.google.co.in/intl/en/scholar/metrics.html#metrics (accessed on 27 May 2020).
| Level | TRL in Europe | ETLCL |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Observation of basic principles | INTRODUCTORY |
| 2 | Formulation of the technology concept | BENEFITS |
| 3 | Experimental proof of concept | EARLY EXPERIMENTATION AND ADOPTION |
| 4 | Validation of technology in a lab | IMPACT ASSESSMENT |
| 5 | Validation of technology in a relevant environment | BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT |
| 6 | Demonstration of technology in an operational environment | APPLICABILITY TO THE BUSINESS TODAY |
| 7 | Demonstration of system prototype in an operational environment | CREATION OF SUSTAINABLE BUSINESS |
| 8 | Completion and certification of a system complete | STATE-OF-THE-ART IN BUSINESS |
| 9 | Verification of the actual system in an operational environment | BIG GLOBAL SUCCESS STORIES |
| Classification | Sub-Classification | Relevant References |
|---|---|---|
| ETLCL 1: INTRODUCTORY | Historical/Futuristic | [11,12,13] |
| Multidisciplinary | [14,15,16] | |
| Maturity | [17] | |
| Socio-Technical | [18] | |
| ETLCL 2: BENEFITS | Traceability | [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32] |
| Transparency | [33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40] | |
| Trust | [41,42,43,44] | |
| Digital Identity | [45] | |
| Frictionless Collaboration | [46] | |
| Anti-Counterfeiting | [47,48,49,50,51] | |
| ETLCL 3: EARLY EXPERIMENTATION AND ADOPTION | Growth Factors and/or Barriers | [52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64] |
| Assessment and/or Customization | [2,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75] | |
| Cryptocurrencies | [76,77,78] | |
| Review | [1] | |
| ETLCL 4: IMPACT ASSESSMENT | Forecasting | [79] |
| Disruption/Digital Transformation | [80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90] | |
| Industry 4.0 | [91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100] | |
| ETLCL 5: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT | Business Model | [101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108] |
| Legal and Governance | [109,110,111,112,113,114] | |
| Policy and Regulation | [115,116,117] | |
| Sharing Economy | [118] | |
| Theory | [119,120,121,122] | |
| ETLCL 6: APPLICABILITY TO THE BUSINESS TODAY | ICO | [123,124] |
| Risk Management | [125,126,127] | |
| Smart Contracts | [128,129,130,131,132,133] | |
| Modeling/Pilot | [134,135,136,137,138] | |
| ETLCL 7: CREATION OF SUSTAINABLE BUSINESS | Advantages | [139,140,141,142,143,144,145,146] |
| Limitations/Barriers | [147,148,149,150,151,152,153,154] | |
| Performance | [155,156,157,158,159,160,161,162] | |
| Environment | [163,164,165,166,167,168] | |
| Social Innovation/Financial Inclusion | [169,170,171] | |
| Supply Chain Finance | [172,173] | |
| Sustainable Development Goals | [174,175] | |
| ETLCL 8: STATE-OF-THE-ART IN BUSINESS | Accounting/Auditing | [176,177] |
| Launched Projects | [178,179,180,181,182,183,184,185] | |
| Research Gap | [186,187,188] | |
| Risk | [189,190,191,192] | |
| Standards | [193] | |
| Trends | [194,195] |
| ETLCL 1 | 8 |
| ETLCL 2 | 33 |
| ETLCL 3 | 29 |
| ETLCL 4 | 22 |
| ETLCL 5 | 22 |
| ETLCL 6 | 16 |
| ETLCL 7 | 37 |
| ETLCL 8 | 20 |
| ETLCL 9 | 0 |
| Historical/Futuristic | 3 |
| Multidisciplinary | 3 |
| Maturity | 1 |
| Socio-Technical | 1 |
| Traceability | 14 |
| Transparency | 8 |
| Trust | 4 |
| Digital Identity | 1 |
| Frictionless Collaboration | 1 |
| Anti-Counterfeiting | 5 |
| Growth Factors and/or Barriers | 13 |
| Assessment and/or Customization | 12 |
| Cryptocurrencies | 3 |
| Review | 1 |
| Forecasting | 1 |
| Disruption / Digital Transformation | 11 |
| Industry 4.0 | 10 |
| Business Model | 8 |
| Legal and Governance | 6 |
| Policy and Regulation | 3 |
| Sharing Economy | 1 |
| Theory | 4 |
| ICO | 2 |
| Risk Management | 3 |
| Smart Contracts | 6 |
| Modeling/Pilot | 5 |
| Advantages | 8 |
| Limitations/Barriers | 8 |
| Performance | 8 |
| Environment | 6 |
| Social Innovation/Financial Inclusion | 3 |
| Supply Chain Finance | 2 |
| Sustainable Development Goals | 2 |
| Accounting/Auditing | 2 |
| Launched Projects | 8 |
| Research Gap | 3 |
| Risk | 4 |
| Standards | 1 |
| Trends | 2 |
| Citations | Authors (Year) | Title | Journal | Classification | Sub-Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 326 | Kshetri, Nir (2018) | Blockchain’s roles in meeting key supply chain management objectives | International Journal of Information Management | ETLCL 7: CREATION OF SUSTAINABLE BUSINESS | Advantages |
| 202 | Francisco, Kristoffer (2018) | The Supply Chain Has No Clothes: Technology Adoption of Blockchain for Supply | Logistics | ETLCL 3: EARLY EXPERIMENTATION AND ADOPTION | Growth Factors and/or Barriers |
| 193 | Saberi, Sara (2019) | Blockchain technology and its relationships to sustainable supply chain management | International Journal of Production Research | ETLCL 7: CREATION OF SUSTAINABLE BUSINESS | Limitations or Barriers |
| 179 | Casino, Fran (2019) | A systematic literature review of blockchain-based applications: Current status, classification and open issues | Telematics and Informatics | ETLCL 3: EARLY EXPERIMENTATION AND ADOPTION | Review |
| 171 | Dai, Jun (2017) | Towards Blockchain-based accounting and assurance | Journal of Information Systems | ETLCL 8: STATE OF ART IN BUSINESS | Accounting or Auditing |
| 170 | Tapscott, Don (2017) | How Blockchain will change Organizations | MIT Sloan Management Review | ETLCL 4: IMPACT ASSESSMENT | Disruption or Digital Transformation |
| 150 | Ghobakhloo, Morteza (2018) | The future of manufacturing industry: a strategic roadmap toward Industry 4.0 | Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management | ETLCL 4: IMPACT ASSESSMENT | Industry 4.0 |
| 104 | Werbach, Kevin (2018) | Trust, but verify: Why Blockchain needs the law | Berkeley Technology Law Journal | ETLCL 5: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT | Legal and Governance |
| 104 | Casey, Michael J. (2017) | Global Supply Chains are about to get better, Thanks to blockchain | Harvard Business Review | ETLCL 3: EARLY EXPERIMENTATION AND ADOPTION | Growth Factors and/or Barriers |
| Barrier Category | Adoption Barrier |
|---|---|
| Inter-organizational Barriers | Customer’s level of awareness and tendency with regard to the blockchain technology and the sustainability aspects |
| Collaboration-, communication-, and coordination-related problems in a supply chain which needs to be digitized | |
| Lack of information disclosure policy or policy-implementation challenges between partners in the supply chain | |
| Barriers in integrating sustainable practices based on a new technology like blockchain technology across all partners of the supply chain | |
| Cultural differences inherent in big, medium, and small supply chain partners | |
| Intra-organizational Barriers | Constraints of financial nature |
| Absence of top-level management’s commitment and support | |
| The flexibility to introduce new organizational policies for using the blockchain technology which may have no relevant policies in place to begin with | |
| Absence of knowledge and expertise in current workforce | |
| Challenges associated with bringing a transformation in the organizational culture | |
| Inertia of legacy systems causing unwillingness to adapt to new systems | |
| Lack of technological tools for implementation of new solutions in the sustainable supply chains | |
| System-Related Barriers | Security and related issues |
| Blockchain technology may not be easily accessible | |
| Negative public perception can lead to lower adoption intention for blockchain technology | |
| Immutability property of blockchain technology may be viewed as both a virtue and a vice | |
| Blockchain technology is an evolving technology, so blockchain based solutions as they exist till today are immature | |
| External Barriers | Absence of a regulatory framework and governmental policies in most geographies |
| Amidst the market competition, blockchain technology adds to the uncertainty of doing business | |
| Absence of external stakeholders in the onboarding process for the blockchain technology | |
| Commitment of the industry in ethical and safe practices may be lacking or be limited | |
| The rewards and encouragement programs associated with using blockchain technology may not be substantial |
| First Author | Title | Journal | Classification | Sub-Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Choi, Tsan-Ming | Blockchain-technology-supported platforms for diamond authentication and certification, in luxury supply chains | Transportation Research Part E | ETLCL 3: EARLY EXPERIMENTATION AND ADOPTION | Assessment and or customization |
| Data quality challenges for sustainable fashion supply chain operations in emerging markets: Roles of blockchain, government sponsors and environment taxes | Transportation Research Part E | ETLCL 7: CREATION OF SUSTAINABLE BUSINESS | Limitations and Barriers | |
| Information disclosure structure in supply chains with rental service platforms in the blockchain technology era | International Journal of Production Economics | ETLCL 5: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT | Business Model | |
| Peer-to-peer collaborative consumption for fashion products in the sharing economy: Platform Operations | Transportation Research Part E | ETLCL 5: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT | Business Model | |
| Kamble, Sachin | Modeling the blockchain-enabled traceability in agriculture supply chain | International Journal of Information Management | ETLCL 6: APPLICABILITY TO THE BUSINESS TODAY | Modeling or Pilot |
| Achieving sustainable performance in a data-driven agriculture supply chain: A review for research and applications | International Journal of Production Economics | ETLCL 7: CREATION OF SUSTAINABLE BUSINESS | Performance | |
| Understanding the blockchain technology adoption in supply chains-Indian context | International Journal of Production Research | ETLCL 3: EARLY EXPERIMENTATION AND ADOPTION | Growth factors and or barriers | |
| Treiblmaier, Horst | The impact of the blockchain on the supply chain: A theory based research framework and a call for action | Supply Chain Management: An International Journal | ETLCL 5: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT | Theory |
| Combining Blockchain Technology and the Physical Internet to Achieve Triple Bottom Line Sustainability: A Comprehensive Research Agenda for Modern Logistics and Supply Chain Management | Logistics | ETLCL 4: IMPACT ASSESSMENT | Disruption/ Digital Transformation | |
| Blockchain as a Driver for Smart City Development: Application Fields and a Comprehensive Research Agenda | Smart Cities | ETLCL 2: BENEFITS | Traceability | |
| Chang, Shuchih Ernest | Supply chain re-engineering using blockchain technology: A case of smart contract-based tracking process | Technological Forecasting and Social Change | ETLCL 6: APPLICABILITY TO THE BUSINESS TODAY | Smart Contracts |
| Blockchain-enabled trade finance innovation: A potential paradigm shift on using letter of credit | Sustainability | ETLCL 7: CREATION OF SUSTAINABLE BUSINESS | Supply Chain Finance | |
| Cottrill, Ken | Can we trust the “trust machine?” | Supply Chain Management Review | ETLCL2: BENEFITS | Trust |
| The Benefits of Blockchain: Fact or wishful thinking | Supply Chain Management Review | ETLCL2: BENEFITS | Trust | |
| Giusti, Riccardo | Sustainable and De-Stressed International Supply-Chains Through the SYNCHRO-NET Approach | Sustainability | ETLCL 5: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT | Business Model |
| Synchromodal logistics: An overview of critical success factors, enabling technologies, and open research issues | Transportation Research Part E | ETLCL 6: APPLICABILITY TO THE BUSINESS TODAY | Smart Contracts | |
| Kouhizadeh, Mahtab | Blockchain Practices, Potentials, and Perspectives in Greening Supply Chains | Sustainability | ETLCL 7: CREATION OF SUSTAINABLE BUSINESS | Environment |
| At the Nexus of Blockchain Technology, the Circular Economy, and Product Deletion | Applied Sciences | ETLCL 7: CREATION OF SUSTAINABLE BUSINESS | Environment | |
| Ramirez-Pena, Magdalena | Shipbuilding 4.0 Index Approaching Supply Chain | Materials | ETLCL 2: BENEFITS | Transparency |
| Achieving a sustainable shipbuilding supply chain under I4.0 perspective | Journal of Cleaner Production | ETLCL 4: IMPACT ASSESSMENT | Industry 4.0 | |
| Tapscott, Don | Blockchain and the Internet of Value | Research-Technology Management | ETLCL2: BENEFITS | Trust |
| How Blockchain will change organizations | MIT Sloan Management Review | ETLCL 4: IMPACT ASSESSMENT | Disruption or Digital Transformation | |
| Vaio, Assunta Di | Artificial Intelligence in the Agri-Food System: Rethinking Sustainable Business Models in the COVID-19 Scenario | Sustainability | ETLCL 5: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT | Business Model |
| Blockchain technology in supply chain management for sustainable performance: Evidence from the airport industry | International Journal of Information Management | ETLCL 7: CREATION OF SUSTAINABLE BUSINESS | Performance | |
| Violino, Simona | Are the Innovative Electronic Labels for Extra Virgin Olive Oil Sustainable, Traceable, and Accepted by Consumers? | Foods | ETLCL 2: BENEFITS | Traceability |
| A Full Technological Traceability System For Extra Virgin Olive Oil | Foods | ETLCL 2: BENEFITS | Traceability | |
| Wang, Yingli | Understanding Blockchain Technology for Future Supply Chains: A Systematic Literature Review and Research Agenda | Supply Chain Management: an International Journal | ETLCL 3: EARLY EXPERIMENTATION AND ADOPTION | Assessment and or customization |
| Making sense of blockchain technology: How will it transform supply chains | International Journal of Production Economics | ETLCL 5: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT | Theory |
| h5 Index | h5 Median | Journal | Number of Papers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 78 | 113 | Sustainability | 26 |
| 67 | 113 | International Journal of Information management | 13 |
| 6 | 11 | Supply Chain Management Review | 11 |
| 61 | 104 | Harvard Business Review | 8 |
| 53 | 99 | Business Horizons | 7 |
| 89 | 126 | International Journal of Production Economics | 6 |
| 63 | 90 | International Journal of Production Research | 6 |
| 132 | 166 | Journal of Cleaner Production | 5 |
| 53 | 72 | Transportation Research Part E | 5 |
| 27 | 41 | Electronic Markets | 4 |
| NA | NA | Logistics | 4 |
| 46 | 77 | Supply Chain Management: an international journal | 4 |
| 58 | 77 | Computers and Industrial Engineering | 3 |
| 27 | 39 | Future Internet | 3 |
| 85 | 117 | International Journal of Environment Research and Public Health | 3 |
| 74 | 96 | Technological Forecasting and Social Change | 3 |
| 46 | 68 | Annals of Operations Research | 2 |
| 26 | 41 | Computer Law and Security Review | 2 |
| 35 | 59 | Electronic Commerce Research and Applications | 2 |
| NA | NA | Foods | 2 |
| 66 | 94 | Industrial Marketing Management | 2 |
| 42 | 57 | Information Systems Frontiers | 2 |
| 96 | 131 | Journal of Business Research | 2 |
| 31 | 49 | Journal of Purchasing and Supply Management | 2 |
| 35 | 63 | Journal of the Association for Information Systems | 2 |
| 22 | 54 | MIS Quarterly Executive | 2 |
| 37 | 64 | MIT Sloan Management Review | 2 |
| 104 | 151 | Sensors | 2 |
| 45 | 84 | Academy of Management Perspectives | 1 |
| 27 | 41 | Accounting and Business Research | 1 |
| 29 | 40 | Agriculture | 1 |
| 29 | 51 | Agronomy | 1 |
| 30 | 43 | Animals | 1 |
| 53 | 68 | Applied Sciences | 1 |
| 24 | 35 | Berkeley Technology Law Journal | 1 |
| NA | NA | Big Data and Cognitive Computing | 1 |
| 51 | 70 | Cities | 1 |
| 16 | 24 | Cogent Economics and Finance | 1 |
| 70 | 130 | Communications of ACM | 1 |
| 45 | 79 | Computers in Industry | 1 |
| NA | NA | Cryptography | 1 |
| 26 | 34 | Decision Sciences | 1 |
| NA | NA | Delaware Journal of Corporate Law | 1 |
| 58 | 84 | Entropy | 1 |
| 12 | 16 | European Business Organization Law Review | 1 |
| 58 | 107 | Government Information Quarterly | 1 |
| 12 | 15 | International Review of Intellectual Property and Competition Law | 1 |
| NA | NA | Informatics | 1 |
| NA | NA | Information | 1 |
| 19 | 29 | Information Economics and Policy | 1 |
| 26 | 40 | Information Systems and e-Business Management | 1 |
| 73 | 102 | International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health | 1 |
| 44 | 65 | International Journal of Forecasting | 1 |
| 68 | 93 | International Journal of Hospitality Management | 1 |
| 38 | 54 | International Journal of Physical Distribution and Logistics Management | 1 |
| 21 | 32 | Journal of Consumer Policy | 1 |
| NA | NA | Journal of Emerging Technologies in Accounting | 1 |
| 11 | 14 | Journal of Financial Regulation and Compliance | 1 |
| 23 | 31 | Journal of Information Systems | 1 |
| 41 | 56 | Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing | 1 |
| 10 | 14 | Journal of International Technology and Information Management | 1 |
| 34 | 42 | Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management | 1 |
| 23 | 27 | Journal of Marine Science and Engineering | 1 |
| 18 | 24 | Journal of Risk and Financial Management | 1 |
| 11 | 14 | Journal of Risk Management in Financial Institutions | 1 |
| 19 | 26 | Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks | 1 |
| 35 | 57 | Journal of Strategic Information Systems | 1 |
| 49 | 73 | Marine Policy | 1 |
| NA | NA | Materials | 1 |
| 8 | 9 | Philosophy of Management | 1 |
| 35 | 47 | Research in International Business and Finance | 1 |
| 87 | 128 | Research Policy | 1 |
| 25 | 57 | Research-Technology Management | 1 |
| 61 | 86 | Resources, Conservation and Recycling | 1 |
| NA | NA | Review of International Business and Strategy | 1 |
| 57 | 84 | Scientometrics | 1 |
| NA | NA | Smart Cities | 1 |
| 52 | 88 | Telematics and Informatics | 1 |
| 12 | 17 | The Journal of Alternative Investments | 1 |
| 18 | 29 | The Journal of Corporation Law | 1 |
| Year | Number of publications |
| 2015 | 0 |
| 2016 | 0 |
| 2017 | 16 |
| 2018 | 41 |
| 2019 | 78 |
| Early 2020 | 52 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paliwal, V.; Chandra, S.; Sharma, S. Blockchain Technology for Sustainable Supply Chain Management: A Systematic Literature Review and a Classification Framework. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7638. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187638
Paliwal V, Chandra S, Sharma S. Blockchain Technology for Sustainable Supply Chain Management: A Systematic Literature Review and a Classification Framework. Sustainability. 2020; 12(18):7638. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187638
Chicago/Turabian StylePaliwal, Vineet, Shalini Chandra, and Suneel Sharma. 2020. "Blockchain Technology for Sustainable Supply Chain Management: A Systematic Literature Review and a Classification Framework" Sustainability 12, no. 18: 7638. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187638
APA StylePaliwal, V., Chandra, S., & Sharma, S. (2020). Blockchain Technology for Sustainable Supply Chain Management: A Systematic Literature Review and a Classification Framework. Sustainability, 12(18), 7638. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187638







