Abstract
Intelligent traffic control at urban intersections is vital to ensure efficient and sustainable traffic operations. Urban road intersections are hotspots of congestion and traffic accidents. Poor traffic management at these locations could cause numerous issues, such as longer travel time, low travel speed, long vehicle queues, delays, increased fuel consumption, and environmental emissions, and so forth. Previous studies have shown that the mentioned traffic performance measures or measures of effectiveness (MOEs) could be significantly improved by adopting intelligent traffic control protocols. The majority of studies in this regard have focused on mono or bi-objective optimization with homogenous and lane-based traffic conditions. However, decision-makers often have to deal with multiple conflicting objectives to find an optimal solution under heterogeneous stochastic traffic conditions. Therefore, it is essential to determine the optimum decision plan that offers the least conflict among several objectives. Hence, the current study aimed to develop a multi-objective intelligent traffic control protocol based on the non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm II (NSGA-II) at isolated signalized intersections in the city of Dhahran, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The MOEs (optimization objectives) that were considered included average vehicle delay, the total number of vehicle stops, average fuel consumption, and vehicular emissions. NSGA-II simulations were run with different initial populations. The study results showed that the proposed method was effective in optimizing considered performance measures along the optimal Pareto front. MOEs were improved in the range of 16% to 23% compared to existing conditions. To assess the efficacy of the proposed approach, an optimization analysis was performed using a Synchro traffic light simulation and optimization tool. Although the Synchro optimization resulted in a relatively lower signal timing plan than NSGA-II, the proposed algorithm outperformed the Synchro optimization results in terms of percentage reduction in MOE values.
Keywords:
traffic engineering; optimization; signalized intersections; congestion; MOEs; NSGA-II; Synchro 1. Introduction
Urban traffic congestion has become a global challenge in road transport networks. It has severe negative consequences on the urban economy, traffic operations, safety, and sustainable development [1,2]. Further repercussions include excessive vehicle delays, increased fuel consumption, high vehicular emissions, and increased drivers’ anxiety [3,4]. Traffic congestion could be recurrent, resulting from periodic traffic fluctuations, or it may be non-recurrent, arising due to unforeseen conditions, such as traffic incidents, unanticipated weather conditions, special events, and so forth [5]. Aggressive and unanticipated driving behavior also results in unsustainable travel patterns [6,7]. Road transport is the backbone of countries’ economies; however, the socio-economic costs associated with traffic congestion are also enormous. According to US national transport statistics, transport sector fuel consumption is estimated to be about 70 percent of total oil consumption [8]. Burning such a massive amount of fuel has brought severe negative environmental concerns. Previous studies show that traffic congestion brought huge losses worth 160 billion dollars in 2014, and it further produced 560 billion pounds of dangerous CO2 emissions for the environment in 2011 [9,10]. Likewise, in Europe, congestion accounts for approximately 1% of the entire gross domestic product [11]. Similarly, a previous study estimated that a few major Chinese cities have cumulatively suffered a huge daily economic loss worth $ 1 billion due to traffic congestion [12].
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) and surrounding gulf states have witnessed a rapid increase in road traffic congestion, particularly after the oil bang in the early 1970s. KSA, in particular, has experienced miserable urban traffic congestion in major urban metropolitans, such as Riyadh, Makkah, Madinah, and Dammam, due to a lack of intra-city public transport infrastructure and services [13]. The lack of such services for commuters within the cities has encouraged increased auto-ownership, which is one of the significant factors responsible for high traffic congestion. Such unsustainable travel patterns over the years have led to increased travel costs, extreme traffic congestion, and alarming environmental emissions in the country [13]. It was reported that the cost incurred by traffic congestion in the city of Riyadh is around $ 8 billion, which is an alarming situation [14]. The rapid rate of motorization has also increased the rate of traffic accidents and associated fatalities along highways in KSA [15,16].
Globally, different countermeasures have been proposed and implemented successfully to tackle congestion, particularly during peak hours. Recent studies reported that increasing supply (expanding transport infrastructure) has marginal and temporary benefits to alleviate traffic congestion since it is commonly observed that demand (traffic) tends to increase sharply as the transportation network is expanded [17,18]. Additionally, existing infrastructure in highly dense urban areas puts restraints or limits on the full-scale renovation or development of existing and new facilities [19]. The provision of various types of modern roundabout bike-sharing systems is also considered to reduce congestion and enhance sustainable mobility in urban metropolitans. For example, a study conducted by Tollazzi et al. reported that the adoption of various types of two-level roundabouts could significantly improve throughput and safety, particularly at the intersection with space limitations [20]. Another study utilized a calibrated E. Macioszek model to evaluate the capacity of roundabouts in the city of Tokyo and the surroundings in Japan [21]. It was found that roundabout entry capacity is significantly influenced by the distribution of vehicle headways and various geometrical factors at intersections. The error rate of the model ranged between 2.2% to 9.4%. However, roundabouts are useful for low to medium flow conditions. In their study, Macioszek et al. reported that the adjustment of bike-sharing facilities to user’s expectations could significantly improve the long-term goals of sustainable urban mobility [22]. In another study, Song et al. reported that the presence of bike-sharing has great prospects for boosting bicycle accessibility, thus, ensuring green and sustainable urban transportation [23]. Congestion pricing, travel demand management (TDM), proactive traffic prediction, and network optimizations have also proved beneficial in mitigating traffic congestion effectively [24,25,26,27].
Intersections are hotspots for traffic congestions in urban areas, especially during rush hours. Congestion at intersections is also associated with a significantly large proportion of total accidents and fatalities [28]. Intersections are vital components of the urban transport network. Ensuring the efficient operation of intersections could lead to a smooth and safe flow on city-wide urban corridors [29]. Alternatively, poor traffic flow management at the intersection would cause chaos in the city. Therefore, intelligent traffic control at the intersection is essential and inevitable. Traffic flow at intersections could either be stop-controlled or signal-controlled. The former is deployed when traffic volumes are low, while for heavy urban traffic, signalized traffic control through signals is preferred. For signalized intersections, the flow may be regulated using either a fixed-time control scheme or traffic actuated scheme, which is based on dynamic traffic demand. A system based on a fixed control paradigm is not very effective since traffic demand is likely to vary during different times of the day. Alternatively, several methods exist for actuating traffic lights at intersections. The operational performance at the signalized intersection could be assessed using various traffic performance measures—also known as measures of effectiveness (MOEs). Some of the commonly used MOEs for evaluating the intersection level of service (LOS) include average vehicle delays, number of stops, travel time, throughput and traffic capacity, queue lengths, average fuel consumption, and total vehicular emissions (such as CO, NOx, HC), etc. Recently, numerous studies have been conducted to optimize these MOEs at intersections as well as at network levels [30,31,32,33].
Among various MOEs, average vehicle delay, indicating the extra time spent by vehicles to clear the intersection, is the most common measure to assess the operational performance of signalized intersections. Additionally, it is the most used criterion for establishing intersection LOS. Mathematical formulations for estimating delay estimates at signalized intersections have evolved over the years. Beckmann et al. first proposed intersection delay formulation based on the queuing theory [34]. Their work was extended by Webster et al. based on the saturation flow rate and queuing to simplify the determination of lane group capacity and estimation of phase-related delay prediction [35]. The formulae presented by researchers are presented in Equation (1). Later on, Akçelik et al. proposed a movement-related delay estimation for oversaturated traffic conditions [36]. The average vehicle delay for all phases of the intersection could then be computed (shown in Equation (2)) after calculating the phase-related delay estimates from the previous equation.
where di is the phase-related vehicle delay (sec./veh), D is the average intersection delay, C denotes the cycle length, Xi is the green time ratio (g/C) for ith phase, Si represents the saturation flow rate for ith phase, and qi is actual the traffic flow arriving in ith phase.
Another important MOE to determine the intersection LOS is the number of vehicular stops. Frequent stop-and-go traffic could seriously hamper intersection capacity. Studies have shown that vehicle delay tends to increase with a decrease in the number of stops, particularly at larger cycle lengths [37]. Akçelik et al. were the pioneers in the development of a mathematical formula for the number of stop estimations [38] across intersections. Rakha et al. conducted a detailed review study of state-of-the-art models for estimating the number of stop signalized intersections under unsaturated and oversaturated conditions [39]. The number of stop estimates at the signalized intersection has a significant bearing on the fuel energy consumption of vehicles and emissions. The majority of pioneer models dedicated to finding the number of stops do not account for partial stops that may happen on intersection approaches and in unsaturated traffic conditions. The number of stops during the ith phase and the total number of stops at the intersection could be determined using Equations (3) and (4), respectively [40].
where Ri is the number of stops at the intersection approach during the ith phase, H denotes the total number of vehicle stops at an intersection, and yi is the ratio of vehicles arriving in ith phase to corresponding saturation flow (q/S). Other variables (C, qi, Xi) are the same as used in the preceding equations.
Increased fuel consumption and vehicular emission at urban road intersections are other major concerns in transportation economics. The emissions produced are proportional to fuel consumption during the journey. It is reported that the vehicle’s fuel consumptions and emissions are usually higher near intersections compared to other street segments. Fuel consumption is affected by several factors, such as vehicle speed, vehicle type, vehicle age, acceleration or deceleration, delay, number of stops made, road gradient, traffic, and weather conditions [41,42,43]. Fuel economy is critical because of both environmental and energy conservation concerns. Studies have shown that fuel economy and emissions could be significantly reduced by improving vehicle standards as well as the optimization of traffic management systems [44,45]. Among vehicular emissions, carbon monoxide (CO), nitrous oxide (NOx), and hydrocarbons (HC) constitute a significant proportion of total emissions. Several emission estimation models are available to determine the precise quantity of each emission type [46]. Existing traffic energy (fuel consumption) and emission models are broadly micro models studying the energy consumption and emissions for individual vehicle and macro models, which consider it from macroscopic perspectives [47]. Estimation models for fuel consumption and emissions have evolved substantially over the years. The following mathematical formulae have been widely used as objective functions for fuel energy and vehicular emissions from signal control optimization perspectives [37,48,49].
where FC indicates the average fuel consumption during one signal cycle, ri is the effect red time of ith phase, t0i is the time from the start of green indication during each phase, xi is the degree of approach saturation, and fa, fb, fc are the coefficients for fuel consumption rates. All other parameters are the same used in previous equations. Vehicle emissions (CO and NOx) are generally computed using the following relations:
where ECO is carbon monoxide emissions, ENO denotes nitrogen oxide emissions, Di is the average delay of each vehicle at ith phase, EFPCU is standard car unit emission factor, and qi is the same as mentioned in Equation (1). Alternatively, vehicle exhaust (CO and NO) may be calculated using the following relationship [49]:
A thorough review of the existing literature revealed that different methods and control strategies have been proposed for promoting smooth and efficient traffic operations through signalized intersections in urban metropolitans. The majority of previous studies have approached signal control optimization problems from mono or bi-objective (delay, stops, queue, emissions, etc.) perspectives in a highly simplified scenario of lane-based homogenous traffic configuration. Furthermore, recent studies are increasingly inclined to use traffic simulation for studying field traffic data without appropriate validation. However, field traffic has non-linear, stochastic, and intricate characteristics. Due to the complexity of real-time traffic flow at a signalized intersection, the adoption of multi-objective optimization is often inevitable. Decision-makers often have to deal with multiple conflicting objectives to find an optimal solution. Traffic engineers are not concerned with knowing the best solution based on a single objective at all costs. It is likely that an indented improvement in one of the objectives will result in the deterioration of another objective. It is, therefore, vital to establish a reasonable trade-off among various conflicting objectives simultaneously and to identify an optimal plan (Pareto front) that provides minimum objective conflict.
In this study, a real-world traffic control problem was solved through the application and validation of a multi-objective-based metaheuristic. Specifically, we aimed to develop a non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA-II)-based multi-objective optimization framework for intelligent traffic control on-field/real-world network data. Four optimization objectives—i.e., average vehicle delay (sec./vehicle), the number of vehicular stops, average fuel consumption (liter/hr.), and vehicle emissions (CO and NO) were considered simultaneously to yield an optimal Pareto front. A detailed comparative analysis is presented to evaluate the performance of the proposed NSGA-II algorithm in terms of the percentage improvement in various field MOEs with reference to the existing traffic control scheme. A validation analysis by traffic simulation and optimization software (Synchro) demonstrated the adequacy and robustness of the proposed method.
The rest of this paper is structured as follows. Section 2 provides a detailed literature review on signal control optimization. Section 3 presents a description of the study area and field data collection. Section 4 discusses optimization methodologies based on NSGA-II and Synchro. Section 5 presents the results and discussions in detail. Finally, Section 6 summarizes key conclusions from the current study and provides prospects for future research studies.
2. Related Work
Methods used for traffic light control at signalized intersections play a pivotal role in determining the quality of operating conditions. Studies conducted in the past have focused on optimizing the signal cycle length, intersection phasing sequence, and offset to enhance certain MOEs, such as average vehicle delay, travel time, number of stops, queue length, fuel consumption, emissions, etc. Delay at intersections is the most common optimization objective addressed by previous studies [31,50,51]. Regression and probability-based methods were initially proposed to approach the problem of traffic light optimization [52,53]. However, these methods did not provide reliable results for oversaturated and undersaturated intersection traffic conditions. Consequently, approaches based on adaptive traffic control were proposed to mitigate the issues of congested and transient traffic flow [54,55]. Among the different models used for traffic light setting, Transport and Road Research Laboratory (TRRL), Australian Road Research Board (ARRB), and Highway Capacity Manual (HCM) are widely used [31]. With rapid advances in information and communication technologies (such as 5G, Internet of Things (IoT), Dedicated Short Range Communication (DRSC), etc.), methods based on simulation and various metaheuristics have been increasingly used for dynamic traffic control through urban networks. These control methods are believed to be more efficient, robust, and realistic for capturing the stochastic, non-linear, and heterogeneous characteristics of traffic flow through signalized intersections [56]. However, heuristic-based studies in the past have mostly dealt with signal control optimization problems from the perspectives of mono-objective or bi-objective solutions without catering for multiple objectives simultaneously. Some popular heuristic techniques used for intelligent traffic control through signalized intersections include genetic algorithms (GA), ant colony optimization (ACO), differential evolution (DE), artificial immune system (AIS), reinforcement learning (RL), and different machine learning algorithms [57,58,59,60,61,62,63].
Linear programming and fuzzy logic were mostly explored for intersection optimization before early 2000, primarily due to the absence of powerful simulation tools and low computational efficiencies [64,65]. A recent study proposed a kinematic wave theory-based method for flow optimization at signalized intersections and found that the signal timing plan obtained could significantly improve average vehicle delay and LOS conditions [66]. The efficiency of GA was explored for delay optimization through signalized intersections under varying flow scenarios [58]. It was revealed that the proposed method yielded a systemic and robust signal timing plan to minimize the delay. Another recent study compared the performance of GA and DE for delay optimization at a signalized intersection and found that GA outperformed DE by reducing delay estimated in the range of 15% to 35% [31]. Putha et al. used ACO and GA for optimizing flow in oversaturated intersection networks, and found that ACO provided relatively robust optimization outputs [57]. Liu et al. suggested a novel DE-based bacterial foraging optimization (DEBFO) for optimizing delay and compared the performance of the proposed method with GA. It was revealed that DEBFO resulted in a 5.6% and 28.3% reduction in average vehicle delay compared to GA and the existing pre-timed traffic control scheme, respectively. Ma and Nakamura developed an analytical framework to achieve the optimized cycle timing of isolated intersections considering vehicle exhaust emissions as an objective function [67]. The immune network algorithm (INA) is another notable technique recently used for the signal control optimization problem. For example, INA was used to optimize delay, throughput, and queue at signalized intersection MOE outputs from an optimized signal scheme that outperformed the existing pre-timed and adaptive traffic control [59]. The adequacy of the proposed method was further validated using the microscopic traffic simulation tool VISSIM.
To overcome the limitations of mono-objective optimization methods and linear programming, Zhao et al. proposed a non-dominated sorting artificial bee colony (ABC) multi-objective algorithm for optimizing delay and vehicle stops at unsaturated isolated signalized intersections [68]. It was found that the suggested method could efficiently solve the Pareto front by improving the stops and delay simultaneously. A multi-objective particle swarm algorithm was employed by Jia et al. for signal timing optimization with three optimization goals—i.e., per capita delay, capacity, and automobile exhaust emissions—in the city of Jinzhou, China [69]. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithm was demonstrated by comparing it with other state-of-the-art algorithms. Ding et al. established a bi-objective model for optimization, with the primary objective of reducing platoon delays and reducing harmful emissions along urban arterial roads [42]. Hajbabaie et al. developed a bi-level optimization framework for simultaneous signal timing optimization and traffic distribution in urban transport networks, taking into account over-saturated scenarios and various driver behaviors [70]. The proposed method greatly enhanced network performance, increasing the number of completed trips by 20%, and further reduced the optimized delay estimates by over 25%.
Yang and Luo [26] used a GA based optimization, with several inheriting principles of the simulated annealing (SA) process to reduce the overall delay at an isolated intersection for both transit vehicles and general vehicles [71]. Yuri et al. and Ceylan et al. also explored the applicability of DE for intersection optimization [72,73]. Delay and queue length were the optimization objectives. Both studies showed the adequacy of the proposed methods. Robertson et al. investigated signal timing optimization to minimize stops and delays in urban city traffic and found that considered MOEs were significantly enhanced [74]. Rakha et al. conducted a microscopic-based simulation study in a highly simplified scenario to investigate the impact of signal coordination and optimization on fuel energy consumption and emissions [75]. The results demonstrated that an effective signal control scheme could minimize air pollution by up to 50%. Dissanayake et al. also used GA to optimize signal timing and performed comparative experiments under the same geometry and traffic conditions on different simulation platforms [76]. It was reported that GA yielded a robust traffic light setting, thereby substantially improving the throughput and travel time.
Mingwei et al. utilized multi-objective-based GA to solve signal control optimization at an isolated signalized intersection near Shanghai Ocean University, China [77]. Vehicular stops, average vehicle delay, and fuel consumption were the objective functions. It was found that the signal timing plan yielded by the proposed algorithm improved the considered MOEs significantly compared to existing conditions. Sun et al. used non-dominated sorting genetic algorithms (NGSA and NSGA-II) for intelligent traffic control through signalized intersections [78]. It was found that NSGA-II resulted in the more robust spread of signal timing design along the Pareto front with high convergence speed. Li et al. also examined the efficiency of NSGA-II for signal control optimization from the perspectives of intersection throughput and average queue ratio [79]. The NSGA-II results were validated on the traffic simulation platform VISSIM. To assess the benefits of signal timing optimization from an emissions and delay reduction viewpoint, Lv et al. proposed motor vehicle emission simulation (MOVES) models coupled with an optimization analysis using GA [80]. This study reported approximately an 11% reduction in emissions at the cost of increasing the delay by 14.8%. Kwak et al. proposed a novel GA-based optimizer (VT-Micro model) to investigate the impact of urban traffic setting on fuel consumption and vehicle exhaust emissions [49]. The results were compared with microscopic traffic simulator TRANSIM. The study results indicated that the proposed method reduced fuel consumption in the range of 8%–20%, and vehicular emissions by over 20%. In another study, Deng et al. suggested microscopic traffic simulation-based bi-objective arterial offset optimization, considering delay and emissions for vehicles platoon [42]. It was noted that delays and emissions were improved by 20% and 7%, respectively. Kou et al. utilized genetic algorithm-based multi-objective optimization to adjust the signal time setting under multiple scenarios, considering delay, stops, and emissions as optimization objectives [37]. The optimal Pareto front was solved using reasonable trade-off among various competing objectives. It was noted that the proposed optimization algorithm yielded a significant reduction in average vehicle delay and emission than the results obtained using HCM methods. Table 1 provides a summary of previous studies for signal control optimization methods along with considered optimization objectives.

Table 1.
Summary of selected literature for signal control optimization.
3. Selection of Study Area and Data Collection
The city of Dhahran was chosen as an area of study (Figure 1). It is one of the key cities of Eastern Province, KSA. It has a total population of about 0.3 million and is located over an area of approximately 100 square kilometers [96]. A large proportion of Dhahran’s population comprises expatriates from different cultural backgrounds, thus, generating diverse road user populations. The primary source of trip productions/attractions in the city includes various public/private businesses, commercial activities, academic institutions, and, notably, ARAMCO, which is the world’s largest oil processing facility. The city’s residents are mostly dependent on their private vehicles or taxis for commuting within the city since no public transport infrastructure/services are available. Therefore, the number of registered vehicles and auto-ownership has increased rapidly over the past few years, which is one of the main sources of traffic congestion in the city. The city also faces alarming environmental threats due to traffic congestion. Traffic congestion, particularly at the signalized intersection during rush hours, has also led to low travel speed and increased travel costs. Estimates have warned about more intense and miserable traffic operating conditions in the near future in the absence of appropriate countermeasures and planned development. Therefore, it is exciting as well as challenging to study the city’s traffic.
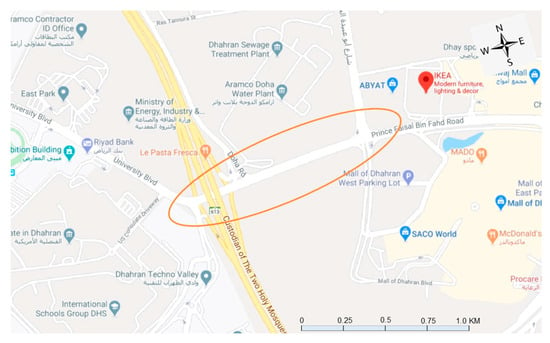
Figure 1.
Study area (from google street maps).
The data used in this study were acquired from two four-leg signalized intersections in the study area, which are located in mixed commercial and residential zones. Intersection-I is located at the crossing of King Saud Street with Faisal-Bin-Fahd Road, whereas Intersection-II is located near the US consulate at the crossing of the Dhahran Tech Valley route with Faisal-Bin-Fahd Road. Traffic flow at both intersections is regulated using a pre-timed traffic control scheme. Essential field data were collected on different parameters, such as traffic volume, phases sequence, signal control, travel speed, saturation flow, rate, queue lengths, and vehicle classification, etc. [31]. Trained observers were deployed to collect all the necessary data using standard protocols carefully. Volume data were obtained during evening peak periods for two hours, which is deemed appropriate for optimization studies. For collecting signal control data, manual methods were employed. Trained observers were deployed at both intersections to collect traffic volumes, signal control, and road inventory data. Approximately 3% of the total number of vehicles recorded were buses and other heavy vehicles, while the remaining were classified as passenger cars. Intersection-I and II have cycle lengths of 160 sec and 220 sec, respectively. Data on individual green splits during each phase were also recorded. Traffic volume, signal control, and phases scheme data collected from the field for both the intersections are shown in Table 2. The data collected were transferred to TRANSYT 7F software for a detailed analysis of various MOEs in existing conditions. In addition, existing road inventory data were also collected, which is a vital input variable for traffic simulation with Synchro.

Table 2.
Traffic volume, phases sequence, and signal control data collected from intersections.
4. Methodology
4.1. NSGA-II
The non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm II (NSGA-II) was used for the signal control optimization problem to achieve an optimal combination of considered objectives along the Pareto front [97]. The Pareto front refers to the plan/front of compromised yet acceptable solutions to all the objectives. Like other metaheuristics, NSGA-II is a popular non-domination and population-based optimization method inspired by natural selection to yield an optimal solution for a set of objective functions. NSGA-II belongs to the family of multi-objective algorithms and is an extended version of NSGA proposed initially by Deb et al. in 2002 [98]. NGSA-II is similar to simple genetic algorithms and NGSA in terms of application genetic operators, such as crossover and mutation operators. However, NGSA-II is more efficient compared to its predecessor algorithms, since the algorithm tends to spread more swiftly and appropriately when a specific non-dominated front is encountered [99]. NSGA-II was selected for multi-criteria signal control optimization because it produces a better spread of the optimal signal design plan on the true Pareto front at a high convergence speed, which results in reduced vehicle operating costs [1,2]. The strength of NSGA-II lies in its robust elitist strategy, emphasis on non-dominated solutions, fast running speed, and its explicit diversity preserving mechanism. Another motivation for choosing NSGA-II for the current study was that the proposed algorithm is based on the strategy for preserving diversity in the population mix, which requires no parameter fix. Furthermore, NSGA-II outperforms earlier heuristics from the same family because of the intrinsic elitist principle in its architecture [98]. In addition to conventional genetic operators, NGSA-II has two unique and specialized mechanisms and multi-objective operators—i.e., non-dominated sorting and crowding distance. Non-dominated sorting involves portioning and sorting the population into distinct fronts (such as F1, F2, etc.) before performing a selection (based on the individual’s non-domination), where each of these fronts indicates an approximated Pareto front. Non-dominated individuals obtained from the first rank, which are the ones only dominated by the first front, constitute the second rank and so on, while crowding distance establishes ranking among members of the Pareto front that are dominated by each other. The crowding distance mechanism, in particular, is vital to preserving the diversity of solution [100]. Once an optimal Pareto front for conflicting objectives is achieved, the solution for any particular can no longer be improved, but at the cost of worsening another objective.
The selection of an appropriate method for aggregating conflicting and competing objectives is a very challenging and critical task. Three methods are widely used to achieve this goal: a) weighted sum method, b) goal programming, and c) the ε-constraint method [101]. The weighted sum method is aimed at assigning different weight coefficients (w1, w2, w3, etc.) to formulate a scalar optimization problem. The summation of weights assigned to each objective function must equate to unity. The goal programming method allows decision-makers to assign goals or targets for each objective to be achieved. These goals may be incorporated as constraints to the optimization problem. The objective function then tends to minimize the absolute deviations from the assigned targets associated with each objective. Lastly, the ε-constraint method assigns priority to one primary objective and considers all other objectives as constraint conditions within fixed allowable limits εi. However, this method has received criticism, as it is very time consuming and, furthermore, the solution is almost impossible when the constraint bounds are too low. In this study, the weighted sum method was used for the aggregation of the objective function with no bias toward any specific objective by assigning approximately proportional weights to each objective. The generic formula for the current signal control problem optimization using NSGA-II is presented in Equation (8):
where F(x) is the combined objective function to be optimized, which consists of a vector of green time for individual phase, f1(y) indicates objective function with respect to delay, f2(y) denotes objective function with respect to the number of stops, f3(y) is the objective function for fuel consumptions, and f4(y) is the objective function corresponding to total emissions, while w1,w2,w3,w4 represents the weights assigned to each objective function. In the constraint conditions, i represents a movement for each phase or direction of travel; gi is the green splits allocated to each phase, also known as decision variables, li is the lost time per phase, while C indicates the intersection cycle length.
A typical NSGA-II optimization search process is accomplished in various steps, including: (i) chromosome encoding and population initialization based on problem range and constraint conditions; (ii) the non-dominated sorting of the initial population; (iii) the assignment of crowding distance to the individual front once sorting is established; (iv) conducting a tournament for the selection of best individuals using the crowding comparison operator; (v) the application of genetic operators, such as simulated binary crossover and polynomial mutation to yield offspring; and (vi) the recombination and selection of population successively to yield the best Pareto front or until the stopping criteria is satisfied. The flow chart for the proposed algorithm molded based on the present optimization problem is shown in Figure 2. Table 3 provides range and values for different algorithm parameters along with the list of decision variables and suitable constraint conditions considered during the current study. The constraint limits for green splits, cycle length, and lost time were adopted from a couple of former studies [31,95]. The NSGA-II signal optimization program was developed and solved on the MATLAB interface (version R2019a).
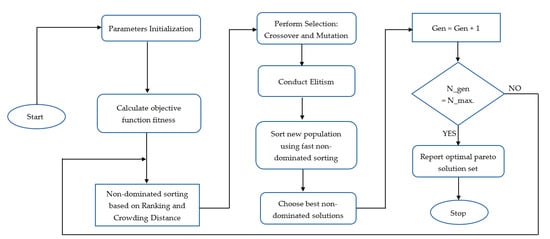
Figure 2.
Flow chart for proposed non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm II (NSGA-II) algorithm.

Table 3.
Experimental configuration for algorithm parameters.
4.2. Traffic Simulation Using Synchro
To assess the adequacy and robustness of the proposed algorithm, Synchro software (version 10) was used. Synchro is a macroscopic traffic simulation and optimization tool and is widely used for the performance analysis of signalized intersections, as well as roundabouts. Synchro is gaining rapid acceptance among transportation specialists and decision-makers because of its friendly user interface and easy to understand traffic simulations. The software is based on the Highway Capacity Manual (HCM, 2010) for analyzing signalized intersections. Synchro offers flexibility to collect detailed information on various traffic performance measures, such as vehicle delay, the number of stops, travel time, throughput, fuel consumption, emissions, etc., either for an isolated intersection or network level [102]. Moreover, this traffic simulation package allows the implementation of an intersection capacity utilization (ICU) method to yield intersection capacity. In addition to the HCM and ICU methods, these tools also provide the “Synchro percentile delay” method for evaluating signalized intersections. The software is capable of optimizing cycle lengths, green splits, offsets, and phase sequences to improve desired MOEs. The optimization routine with Synchro permits users to assign weights to specific phases, thus, giving multiple options while developing optimized signal timing plans. When optimizing cycle lengths, the software attempts to find the shortest cycle length that is capable of clearing the critical percentile of traffic throughput [103]. Optimization is performed through a semi-exhaustive search mechanism. Traffic simulations for Synchro are run in SIMTraffic (a microscopic traffic simulation software) coupled with it. Therefore, any coding error or warning in Synchro must be reviewed and subsequently corrected before initiating SimTraffic simulations. One inherent disadvantage of using Synchro is that it cannot accurately model oversaturated traffic conditions [104]. For the current study, all the essential data collected from the field, as well as road inventory data, were carefully incorporated into Synchro. Performance measures that were previously chosen for NSGA-II simulations were selected during the optimization process to compare the performance between the two approaches from existing pre-timed signal control scenarios. For signal coordination, Intersection-I was activated as a “master intersection” from the simulation setup.
5. Results and Discussions
5.1. Convergence of NSGA-II Curves
Figure 3 presents the convergence curves of NSGA-II objective functions against the number of iterations for the different initial populations. The objective function indicates average vehicle delay (Figure 3a), the number of stops (Figure 3b), average fuel consumption (Figure 3c), and emissions (Figure 3d). The proposed algorithms were tested for the different initial populations because a low initial chromosome population could easily exhibit premature convergence due to chromosome recessiveness or dominance in search for solution space [105], whereas in the case of a very large initial population size, the algorithm tends to perform poorly while searching for the best chromosomes in every generation in solution space [105]. Therefore, the simulations were performed at three different population sizes—i.e., 30, 50, and 100—to determine the best candidate population.
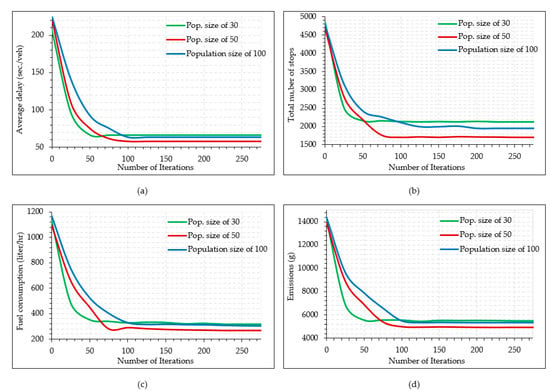
Figure 3.
Convergence of NSGA-II curves: (a) delay evolution; (b) stops evolution; (c) Fuel Consupmtion (FC) evolution; (d) emissions evolution.
A close evaluation of the NSGA-II curves presented revealed that all the curves initially tended to converge rapidly to the corresponding minimum objective functions. However, after attaining a steady value for respective objective functions, they became flat as the number of generations further increased. Considering the effect of initial population size, it is interesting to note that the convergence curves for the initial population size of 30 for all the objective functions converged considerably fast (between 30 to 50 iterations), as anticipated. Curves with an initial population size of 50 converged to minimum objective functions at the maximum number of generations ranging between 30 to 90, while those having an initial population size of 100 converged at a number of iterations beyond 100 for nearly all the scenarios. However, the solution quality (minimum fitness value of the objective function) obtained for the initial population size of 50 was slightly better compared to those yielded by an initial population of 30 and 100. Although the objective function evolution curves for 30 and 100 initial population size converged at widely different iterations, ultimately, they performed almost similarly as far as the final solutions were concerned. The convergence patterns for NSGA-II shown above are consistent with previous studies [106,107]. A study recently conducted in the study area compared the performance of GA and DE for delay optimization and concluded that although DE converged much faster than GA, the solution quality from GA was more robust [31]. It is worth noting that Figure 3 presents the typical plots developed for Intersection-I only. Similar plots were also developed for Intersection-II. For Intersection-I, the minimum function fitness values obtained were: 57.9 for average vehicle delay (sec./veh.), 1698 for the number of stops; 304.8 for average fuel consumption (liter/hr.); and 5624 for CO emissions (g). The optimal objective function values for Intersection-II are provided in subsequent sections. It took, on average, 0.45 to 0.60 sec for the NGSA-II MATLAB code/program to execute and yield the final solution.
5.2. NSGA-II Versus Synchro Optimized Signal Timing Plan
Table 4 shows the optimized signal timing plan for NGSA-II and using Synchro at both intersections. The optimized intersection cycle lengths and corresponding green splits (gI, gII, gIII, and gIV) for each phase are shown. Green splits indicate the decision variables that were constrained to having values within the acceptable range to yield the optimal Pareto front for the considered objective functions. As evident from the above table, the distribution of optimized green splits for each phase from both NSGA-II and Synchro was well intuitive and proportionate based on the approaching traffic volume during each phase. To ensure safety and smooth and efficient operations at intersections, the time allocated for intersection clearance was kept the same as existing conditions. It may be noted from Table 4 that the cycle length for Intersection-I reduced by approximately one-fourth and about one-third using NSGA-II and Synchro, respectively. Similarly, for Intersection-II, the reduction in signal cycle length was around 25% for NSGA-II, and slightly above 37% using Synchro. Table 4 also provides a percentage deviation in individual green splits for both methods from the existing pre-timed signal control scheme. Although the percentage reduction in the optimized signal timing plan (cycle length and splits) using Synchro was more pronounced, the optimized signal control settings obtained from NSGA-II yielded robust and more acceptable traffic performance measures, such as average delay, stops, fuel consumption, and emissions. A previous study considering mono-objective delay optimization conducted in the study area suggested that the intersection cycle lengths were reduced by approximately 32% using GA and over 40% with DE [31]. Thus, it is obvious and intuitive that a multi-objective optimization problem (such as the NSGA-II adopted for the current study) will have significantly different intersection optimization plans since it accounts for several conflicting objectives simultaneously.

Table 4.
Comparison of signal timing plan for NSGA-II vs. Synchro.
5.3. Comparison of MOEs with Existing Conditions
Table 5 provides a detailed comparison for different MOEs for existing conditions, with the optimized MOE estimates obtained using NSGA-II and Synchro. Existing pre-timed signal-controlled schemes are poorly designed at both intersections and are not capable of handling dynamic traffic demand, particularly during rush hours, causing excessive vehicle delays, frequent stops, long queues, increased fuel consumption, and vehicular emissions. The operating conditions at Intersection-II, in particular, could quickly turn down LOS (level of service) F conditions in the near future, if signal control strategy and intersection configuration are not reviewed. It is clear from the results presented in the table below that multi-objective signal optimization using NSGA-II could significantly improve various traffic performance measures. Although signal timing optimization using Synchro also witnessed some improvements in the considered MOEs, NSGA-II yielded a more robust optimization plan by providing more desirable MOE values. Figure 4 presents more illustrative graphs for the percentage reduction in various traffic performance measures. It is evident from the plot that NSGA-II reduced the average vehicle delay by approximately 18% and 23% at Intersection-I and II, respectively. The corresponding values for optimized delay at both intersections were less than 14% using Synchro. Similarly, the number of stops on average were decreased by 17% using both methods. Likewise, with NSGA-II, average fuel consumption was enhanced by almost 23% and roughly 12% with Synchro optimization. Likewise, vehicular emissions, including CO and NOx, were reduced on average by over 17.5% and 13% using NSGA-II and Synchro, respectively. Previous studies have shown the robust performance of NSGA-II for a wide range of applications across diverse disciplines [108,109]. Thus, it is evident from the results of the current study that proposed multi-objective-based NSGA-II optimization for real-time adaptive signal control outperformed the Synchro optimization analysis.

Table 5.
Measures of effectiveness (MOEs) comparison with existing conditions.
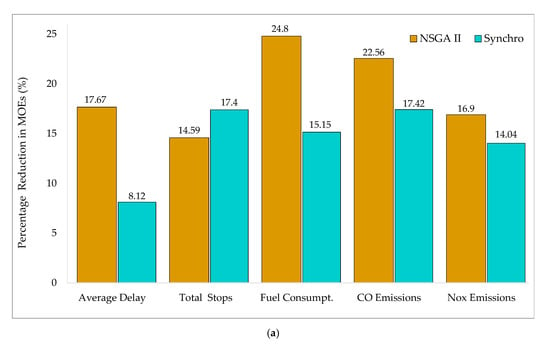
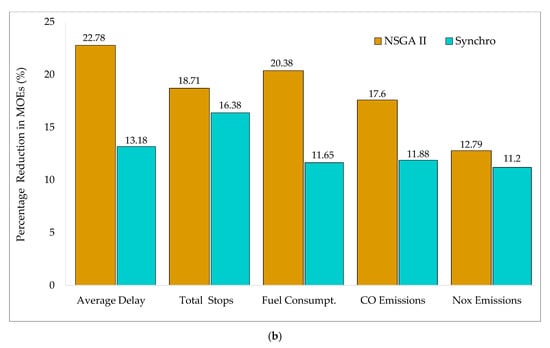
Figure 4.
Percentage reduction in field MOEs: (a) Intersection-I; (b) Intersection-II.
6. Conclusions and Future Prospects
This study aimed to optimize traffic flow at isolated signalized intersections using multi-objective NSGA-II-based optimization in the city of Dhahran, KSA. A thorough review of the existing literature on the current topic suggests that previous studies have mainly focused on mono-objective or bi-objective-based optimization for homogenous and lane-based traffic scenarios. However, field traffic conditions are frequently non-linear, heterogeneous, and stochastic. Furthermore, earlier studies have demonstrated that objectives based on a single MOE usually conflict with other MOEs. It is likely that an improvement in one of the objectives will result in the deterioration of another objective. Traffic engineers are not concerned with knowing the best solution based on a single objective at all costs.
In this study, we proposed NSGA-II-based multi-objective optimization considering four different objectives (MOEs) concurrently, including average vehicle delay, number of stops, average fuel consumption, and vehicular emissions. The optimum MOE estimates along the Pareto front were obtained by optimizing green splits in response to dynamic traffic demand. The proposed algorithm yielded an intelligent signal timing plan at both intersections. The study results indicated that the proposed method was effective in improving the MOE values by a significant proportion compared to existing conditions. The average vehicle delay was improved by over 19%, whereas the number of stops were reduced by approximately 16% compared to current traffic situations. Similarly, there was a 22.5% reduction in average fuel consumption and about a 17% decrease in total vehicular emissions. To evaluate the efficacy of the proposed approach, an optimization analysis was performed using the Synchro traffic light simulation and optimization tool, considering the same MOEs, traffic, and network configuration. The reduction in cycle length and associated green splits from Synchro were more pronounced compared to the NSGA-II results. However, NSGA-II outperformed Synchro optimization in terms of average percentage reduction for considered MOE values, which demonstrated the robustness and superior performance of the proposed methods.
To conclude, we can argue that in order to promote sustainable traffic operations, particularly in the study area, traffic control at the signalized intersection should be based on intelligent multi-objective heuristics rather than a traditional fixed-time control strategy or mono-objective-based signal design. The findings of this study could provide useful guidance to traffic engineers, policy, and decision-makers to mitigate traffic congestion in urban areas. The limitations of the current study could be considered in future studies. First, the applicability of NSGA-II for network optimization should be explored. Second, the effect of mixed traffic flow and the road–vehicle collaborative environment could also be considered in forthcoming studies. Similarly, it is recommended to consider additional MOEs, such as traffic throughput, queue length, etc. Additionally, studies could also focus on the impact of non-motorized modes to solve similar optimization problems. Finally, more efficient computational techniques should be explored.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.-T., A.J. and H.M.A.-A.; methodology, A.J. and M.Z.; software, A.J. and M.Z.; validation, M.A.-T., M.A.A.-S. and H.M.A.-A.; formal analysis, H.M.A.-A. and M.Z.; investigation, A.J. and M.Z.; resources, M.A.A.-S. and H.M.A.-A.; data curation, A.J.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A.-T. and A.J.; writing—review and editing, M.A.A.-S. and H.M.A.-A.; visualization, M.A.-T. and M.Z.; supervision, M.A.A.-S. and H.M.A.-A.; project administration, H.M.A.-A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate and acknowledge the support provided by King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals (KFUPM) for providing all the essential resources to conduct this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, S.; Triantis, K.P.; Sarangi, S. A framework for evaluating the dynamic impacts of a congestion pricing policy for a transportation socioeconomic system. Transp. Res. Part A: Policy Pract. 2010, 44, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavta, K.; Goswami, A. Traffic Congestion Mitigation: A Research Review of Supply and Demand Approaches. In Proceedings of the Transportation Research Board 97th Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 7–11 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Emo, A.K.; Matthews, G.; Funke, G.J. The slow and the furious: Anger, stress and risky passing in simulated traffic congestion. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2016, 42, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcocchio, J.C.; Levinson, H.S. The costs and other consequences of traffic congestion. In Road Traffic Congestion: A Concise Guide; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 159–182. [Google Scholar]
- Zahid, M.; Chen, Y.; Jamal, A. Freeway Short-Term Travel Speed Prediction Based on Data Collection Time-Horizons: A Fast Forest Quantile Regression Approach. Sustainability 2020, 12, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.; Chen, Y.; Jamal, A.; Al-Ahmadi, H.M.; Al-Ofi, A.K. Adopting Machine Learning and Spatial Analysis Techniques for Driver Risk Assessment: Insights from a Case Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahid, M.; Chen, Y.; Khan, S.; Jamal, A.; Ijaz, M.; Ahmed, T. Predicting Risky and Aggressive Driving Behavior among Taxi Drivers: Do Spatio-Temporal Attributes Matter? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Transportation. Fuel Cost and Consumption; Bureau of Transportation Statistics: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Economist, T. The Cost of Traffic Jams; The Economist: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Schrank, D.; Eisele, B.; Lomax, T.; Bak, J. 2015 Urban Mobility Scorecard; The Texas A&M Transportation Institute and Inrix: College Station, TX, USA, 2015; Volume 9, p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Schrank, D.; Lomax, T.; Eisele, B. 2012 Urban Mobility Report; Texas Transportation Institute: College Station, TX, USA, 2012; Available online: http://mobility.tamu.edu/ums/report (accessed on 25 July 2020).
- Levy, J.I.; Buonocore, J.J.; von Stackelberg, K. The Public Health Costs of Traffic Congestion; Harvard Center for Risk Analysis: Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dano, U.L.; AlQahtany, A.M. Issues undermining public transport utilization in Dammam city, Saudi Arabia: An expert-based analysis. J. Sustain. Sci. Manag. 2019, 14, 155–169. [Google Scholar]
- Sibai, A. AI Bottleneck Traffic Creates a Heavy Loss of SR 81 Billion; The Saudi Gazette: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jamal, A.; Rahman, M.T.; Al-Ahmadi, H.M.; Mansoor, U. The Dilemma of road safety in the eastern provice of Saudi Arabia: Consequences and Prevention strategies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T.; Jamal, A.; Al-Ahmadi, H.M. Examining Hotspots of Traffic Collisions and their Spatial Relationships with Land Use: A GIS-Based GeographicallyWeighted Regression Approach for Dammam, Saudi Arabia. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, F.; De Croix, G.; Keskin, N.B. Competition between two-sided platforms under demand and supply congestion effects. Available SSRN 3250224 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.M.; Rao, K.R. Measuring urban traffic congestion—A review. Int. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2012, 2, 286–305. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, I.; Jamal, A.; Subhan, F. Public perception of autonomous car: A case study for Pakistan. Adv. Transp. Stud. 2019, 49, 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Tollazzi, T.; Guerrieri, M.; Jovanović, G.; Renčelj, M. Functions, Capacities, and Traffic Safety Characteristics of Some Types of Two-Level Roundabouts. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macioszek, E. Roundabout Entry Capacity Calculation—A Case Study Based on Roundabouts in Tokyo, Japan, and Tokyo Surroundings. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macioszek, E.; Świerk, P.; Kurek, A. The Bike-Sharing System as an Element of Enhancing Sustainable Mobility—A Case Study based on a City in Poland. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Qi, H.; Zhang, Y. Impact Evaluation of Bike-Sharing on Bicycling Accessibility. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbuLibdeh, A. Traffic congestion pricing: Methodologies and equity implications. Urban Transp. Syst. 2017, 203–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantsuji, T.; Fukuda, D.; Zheng, N. Simulation-based joint optimization framework for congestion mitigation in multimodal urban network: A macroscopic approach. Transportation 2019, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisetjindawat, W.; Derrible, S.; Kermanshah, A. Modeling the effectiveness of infrastructure and travel demand management measures to improve traffic congestion during typhoons. Transp. Res. Rec. 2018, 2672, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.; Chen, Y.; Jamal, A.; Memon, Q.M. Short Term Traffic State Prediction Via Hyperparameter Optimization Based Classifiers. Sensors 2020, 20, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albalate, D.; Fageda, X. Congestion, Road Safety, and the Effectiveness of Public Policies in Urban Areas. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.; Coelho, M.C.; Rouphail, N.M. Assessing the impact of closely-spaced intersections on traffic operations and pollutant emissions on a corridor level. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 54, 304–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, C.M.; Bullock, D.M. Optimization of Traffic Signal Offsets with High Resolution Event Data. J. Transp. Eng. Part A Syst. 2020, 146, 04019076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, A.; Rahman, M.T.; Al-Ahmadi, H.M.; Ullah, I.M.; Zahid, M. Intelligent Intersection Control for Delay Optimization: Using Meta-Heuristic Search Algorithms. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.K.; Liu, Y. Optimization of signalized network configurations using the Lane-based method. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, G.; Pang, S.-S.; Yang, X.; Tian, J. Signal timing of intersections using integrated optimization of traffic quality, emissions and fuel consumption: A note. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2004, 9, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, M.; McGuire, C.B.; Winsten, C.B. Studies in the Economics of Transportation; RAND: Santa Monica, CA, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, F.V. Traffic Signal Settings; Department of Scientific and Industrial Research: London, UK, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Akcelik, R. Traffic Signals: Capacity and Timing Analysis; Australian Road Research Board: Vermont South, Australia, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Kou, W.; Chen, X.; Yu, L.; Gong, H. Multiobjective optimization model of intersection signal timing considering emissions based on field data: A case study of Beijing. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2018, 68, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçelik, R. Time-Dependent Expressions for Delay, Stop Rate and Queue Length at Traffic Signals; Australian Road Research Board: Vermont South, Australia, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Rakha, H.; Kang, Y.-S.; Dion, F. Estimating vehicle stops at undersaturated and oversaturated fixed-time signalized intersections. Transp. Res. Rec. 2001, 1776, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Fang, Z.; Dong, H.; Liu, J.; Pan, S. Data analysis with multi-objective optimization algorithm: A study in smart traffic signal system. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 15th International Conference on Software Engineering Research, Management and Applications (SERA), London, UK, 7–9 June 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 307–310. [Google Scholar]
- Shafabakhsh, G.; Taghizadeh, S.A.; Kooshki, S.M. Investigation and sensitivity analysis of air pollution caused by road transportation at signalized intersections using IVE model in Iran. Eur. Transp. Res. Rev. 2018, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Chen, X.; Yu, L.; Wang, X. Arterial Offset Optimization Considering the Delay and Emission of Platoon: A Case Study in Beijing. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphail, N.M.; Frey, H.C.; Colyar, J.D.; Unal, A. Vehicle emissions and traffic measures: Exploratory analysis of field observations at signalized arterials. In Proceedings of the 80th Annual Meeting of the Transportation Research Board, Washington, DC, USA, 7–11 January 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kodjak, D. Policies to reduce fuel consumption, air pollution, and carbon emissions from vehicles in G20 nations. Int. Counc. Clean Transp. 2015, 28, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Shaheen, S.A.; Lipman, T.E. Reducing greenhouse emissions and fuel consumption. IATSS Res. 2007, 31, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, E.; Bektaş, T.; Laporte, G. A comparative analysis of several vehicle emission models for road freight transportation. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2011, 16, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaassdorff, C.; Smit, R.; Borge, R.; Hickman, M. Comparison of microscale traffic emission models for urban networks. In Proceedings of the 23rd Biennial International Clean Air and Environment Conference—The critical Atmosphere, Brisbane, Australia, 15–18 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, T.-Y. A fuel-based signal optimization model. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2013, 23, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.; Park, B.; Lee, J. Evaluating the impacts of urban corridor traffic signal optimization on vehicle emissions and fuel consumption. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2012, 35, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Zhang, Y.; Sadollah, A.; Su, R. Optimizing urban traffic light scheduling problem using harmony search with ensemble of local search. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 48, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakariya, A.Y.; Rabia, S.I. Estimating the minimum delay optimal cycle length based on a time-dependent delay formula. Alex. Eng. J. 2016, 55, 2509–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.-J. New optimal cycle length formulation for pretimed signals at isolated intersections. J. Transp. Eng. 2004, 130, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.D.; Li, J.-M. Short or long—Which is better? Probabilistic approach to cycle length optimization. Transp. Res. Rec. 2007, 2035, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.-H.; Lin, J.-T. Optimal signal timing for an oversaturated intersection. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2000, 34, 471–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Peng, X.; Li, L.; Li, Z. A fast signal timing algorithm for individual oversaturated intersections. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2010, 12, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Head, K.L.; Ding, J. Heuristic Algorithm for Priority Traffic Signal Control. Transp. Res. Rec. 2011, 2259, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putha, R.; Quadrifoglio, L.; Zechman, E. Comparing Ant Colony Optimization and Genetic Algorithm Approaches for Solving Traffic Signal Coordination under Oversaturation Conditions. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2012, 27, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foy, M.D.; Benekohal, R.F. Signal timing determination using genetic algorithms. Transp. Res. Rec. 1993, 1365, 108–115. [Google Scholar]
- Louati, A.; Darmoul, S.; Elkosantini, S.; ben Said, L. An artificial immune network to control interrupted flow at a signalized intersection. Inf. Sci. 2018, 433, 70–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Du, X.; Wang, G.; Han, Z. A Deep Reinforcement Learning Network for Traffic Light Cycle Control. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, E.; AKGÜNGÖR, A.P. Delay estimation models for signalized intersections using differential evolution algorithm. J. Eng. Res. 2017, 5, 16–29. [Google Scholar]
- El-Tantawy, S.; Abdulhai, B.; Abdelgawad, H. Design of Reinforcement Learning Parameters for Seamless Application of Adaptive Traffic Signal Control. J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2014, 18, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gora, P.; Mozejko, M.; Brzeski, M.; Karnas, K.; Przybyszewski, P.; Klemenko, A.; Kochanski, A.; Dryja, H.; Kukawska, M.; Kopczyk, D. Solving Traffic Signal Setting Problem Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th International Conference on Models and Technologies for Intelligent Transportation Systems (MT-ITS), Cracow, Poland, 5–7 June 2019; IEEE: Cracow, Poland, 2019; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Pandit, K.; Ghosal, D.; Zhang, H.M.; Chuah, C. Adaptive Traffic Signal Control with Vehicular Ad hoc Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2013, 62, 1459–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, S.; Chand, S. Adaptive Traffic Signal Control Using Fuzzy Logic. In Proceedings of the First IEEE Regional Conference on Aerospace Control Systems, Westlake Village, CA, USA, 25–27 May 1993; pp. 122–126. [Google Scholar]
- Nesmachnow, S.; Massobrio, R.; Arreche, E.; Mumford, C.; Olivera, A.C.; Vidal, P.J.; Tchernykh, A. Traffic lights synchronization for Bus Rapid Transit using a parallel evolutionary algorithm. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Nakamura, H. Cycle length optimization at isolated signalized intersections from the viewpoint of emission. In Traffic and Transportation Studies 2010; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 2010; pp. 275–284. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; He, R.; Su, J. Multi-objective optimization of traffic signal timing using non-dominated sorting artificial bee colony algorithm for unsaturated intersections. Arch. Transp. 2018, 46, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Lin, Y.; Luo, Q.; Li, Y.; Miao, H. Multi-objective optimization of urban road intersection signal timing based on particle swarm optimization algorithm. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 1687814019842498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajbabaie, A.; Benekohal, R.F. Traffic signal timing optimization: Choosing the objective function. Transp. Res. Rec. 2013, 2355, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Luo, D. Acyclic Real-Time Traffic Signal Control Based on a Genetic Algorithm. Cybern. Inf. Technol. 2013, 13, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, H. Optimal Design of Signal Controlled Road Networks Using Differential Evolution Optimization Algorithm. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013, 696374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Srinivasan, D.; Lu, X.; Sun, Z.; Zeng, W. Type-2 fuzzy multi-intersection traffic signal control with differential evolution optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 7338–7349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.I.; Lucas, C.F.; Baker, R.T. Coordinating Traffic Signals to Reduce Fuel Consumption; Traffic Engineering Department Transport and Road Research Laboratory: Crowthorne, Berkshire, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Rakha, H.; Van Aerde, M.; Ahn, K.; Trani, A. Requirements for Evaluating Traffic Signal Control Impacts on Energy and Emissions Based on Instantaneous Speed and Acceleration Measurements. Transp. Res. Rec. 2000, 1738, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, D.T.; Senanayake, S.M.R.; Divarathne, H.K.D.W.M.M.R.; Samaranayake, B.G.L.T. Real-time dynamic traffic light timing adaptation algorithm and simulation software. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Industrial and Information Systems (ICIIS), University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, 28–31 December 2009; IEEE: Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, 2009; pp. 563–567. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Oeda, Y.; Sumi, T. Multi-Objective Optimization of Intersection Signal Time Based on Genetic Algorithm. Mem. Fac. Eng. Kyushu Univ. 2018, 78, 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Benekohal, R.F.; Waller, S.T. Multiobjective traffic signal timing optimization using non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE IV2003 Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Proceedings (Cat. No. 03TH8683), Columbus, OH, USA, 9–11 June 2003; pp. 198–203. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yu, L.; Tao, S.; Chen, K. Multi-Objective Optimization of Traffic Signal Timing for Oversaturated Intersection. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013, 182643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zietsman, J. Investigating Emission Reduction Benefit From Intersection Signal Optimization. J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2013, 17, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Abdulhai, B.; Shalaby, A.; Chung, E.-H. Real-time optimization for adaptive traffic signal control using genetic algorithms. J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2005, 9, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.M.; Sharma, A. Multiobjective plan selection optimization for traffic responsive control. J. Transp. Eng. 2006, 132, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guangwei, Z.; Albert, G.; Sherr, L.D. Optimization of adaptive transit signal priority using parallel genetic algorithm. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2007, 12, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yan, X.; Wu, C. Optimization Model for Traffic Signal Control with Environmental Objectives. In Proceedings of the 2008 Fourth International Conference on Natural Computation, Jinan, China, 18–20 October 2008; IEEE: Jinan, China, 2008; pp. 530–534. [Google Scholar]
- Salkham, A.; Cunningham, R.; Garg, A.; Cahill, V. A Collaborative Reinforcement Learning Approach to Urban Traffic Control Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence and Intelligent Agent Technology, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 9–12 December 2008; IEEE: Sydney, Australia, 2008; pp. 560–566. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Huang, S.; Liu, X. Urban Area Traffic Signal Timing Optimization Based on Sa-PSO. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computational Intelligence, Sanya, China, 23–24 October 2010; IEEE: Sanya, China, 2010; pp. 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Chen, Z. Multiobjective optimization of HEV fuel economy and emissions using the self-adaptive differential evolution algorithm. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2011, 60, 2458–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Hou, Z. Ant colony algorithm for traffic signal timing optimization. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2012, 43, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, B.; Elkosantini, S.; Darmoul, S. Traffic Control at Intersections Using Artificial Immune System Approach. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference of Modeling, Optimization and Simulation—MOSIM’12, Bordeaux, France, 6–8 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Cai, M. Intersection signal control multi-objective optimization based on genetic algorithm. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2014, 1, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökçe, M.A.; Öner, E.; Işık, G. Traffic signal optimization with Particle Swarm Optimization for signalized roundabouts. SIMULATION 2015, 91, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.; Zhang, J.-F.; Zhou, Z.-M. Multi-objective traffic signal control model for traffic management. Transp. Lett. 2015, 7, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğan, E.; Akgüngör, A.P. Optimizing a fuzzy logic traffic signal controller via the differential evolution algorithm under different traffic scenarios. Simulation 2016, 92, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adacher, L.; Gemma, A. A robust algorithm to solve the signal setting problem considering different traffic assignment approaches. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 2017, 27, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakici, Z.; Murat, Y.S. A Differential Evolution Algorithm-Based Traffic Control Model for Signalized Intersections. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Interior, M. Statistical Yearbook; General Authority of Statistics: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Seshadri, A. NSGA-II: A multi-objective optimization algorithm. MAT-Lab Cent. Implementierung 2009. Available online: http://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/10429 (accessed on 8 September 2020).
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmerich, M.T.; Deutz, A.H. A tutorial on multiobjective optimization: Fundamentals and evolutionary methods. Nat. Comput. 2018, 17, 585–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, X.; Yu, X. Improved Crowding Distance for NSGA-II. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.12667. [Google Scholar]
- Gunantara, N. A review of multi-objective optimization: Methods and its applications. Cogent Eng. 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.-Y.; Chen, S.-K.; GUO, J.; BAI, L.; CHANG, C. Timing Optimization and Simulation on Signalized Intersection by Synchro. J. North. Jiaotong Univ. 2004, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Synchro. Trafficware Synchro Software User Guide 2019; Synchro Software Ltd.: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Benekohal, R.F.; Elzohairy, Y.M.; Saak, J.E. Comparison of delays from Highway Capacity software, Synchro, PASSER II and IV, and CORSIM for urban arterials. Transp. Res. Rec. 2002, 1802, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.M.; Kim, Y.B.; Oh, C.H. A study on the convergence of genetic algorithms. Comput. Ind. Eng. 1997, 33, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poles, S.; Fu, Y.; Rigoni, E. The effect of initial population sampling on the convergence of multi-objective genetic algorithms. In Multiobjective Programming and Goal Programming; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 123–133. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdani, T.M.; Won, J.-M.; Alimi, A.M.; Karray, F. Multi-objective feature selection with NSGA II. In Proceedings of the International conference on adaptive and natural computing algorithms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 240–247. [Google Scholar]
- Monsef, H.; Naghashzadegan, M.; Jamali, A.; Farmani, R. Comparison of evolutionary multi objective optimization algorithms in optimum design of water distribution network. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2019, 10, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branke, J.; Goldate, P.; Prothmann, H. Actuated traffic signal optimization using evolutionary algorithms. In Proceedings of the 6th European Congress and Exhibition on Intelligent Transport Systems and Services, Aalborg, Denmark, 18–20 June 2007; pp. 203–225. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).