Abstract
Atmospheric plastic pollution is now a global problem. Microplastics (MP) have been detected in urban atmospheres as well as in remote and pristine environments, showing that suspension, deposition and aeolian transport of MP should be included and considered as a major transport pathway in the plastic life cycle. This work reports an up to date review of the experimental estimation of deposition rate of MP in rural and urban environment, also analyzing the correlation with meteorological factors. Due to the limitations in sampling and instrumental methodology, little is known about MP and nanoplastics (NP) with sizes lower than 50 µm. In this review, we describe how NP could be transported for longer distances than MP, making them globally present and potentially more concentrated than MP. We highlight that it is crucial to explore new methodologies to collect and analyze NP. Future research should focus on the development of new technologies, combining the existent knowledge on nanomaterial and atmospheric particle analysis.
1. Introduction
The global plastic production has increased dramatically in the past 40 years, reaching 359 million tons in 2018 [1]. The life service of plastic products is variable, from less than 1 year to more than 50 years; therefore, the annual plastic waste is not necessarily correlated to the production in a specific time range [1]. Waste mismanagement and unauthorized dumping lead to the release of plastic in the environment and, because of its long environmental lifetime, plastic is easily accumulated in various environmental matrices [2]. Plastic pollution in marine and terrestrial environments has been widely reported since the 70 s [3,4,5] and it is currently a demographic, societal and economic problem [6].
Based on their size, plastic debris can be categorized into five classes: (i) megaplastics (>50 cm), (ii) macroplastics (5–50 cm), (iii) mesoplastics (0.5–5 cm), (iv) microplastics, MP, (1 µm–5 mm) and (v) nanoplastics, NP, (<1 µm) [7]. However, there is not a general consensus on the boundary between MP and NP; recently, Hartmann et al. proposed a definition of NP for plastic particles smaller than 1 µm and a further subdivision between nanoplastics (<100 nm) and submicron-plastics (between 100 nm and 1 µm), to match the accepted definition of nanomaterials [8]. The same study propose to define plastics between 1 and 10 mm as milliplastics or to extend the definition of mesoplastics to this range. On the basis of their origin, MP are classified into primary and secondary. Primary MP are tiny particles designed for commercial use, such as plastic microbeads in personal care products or in turf pitches, as well as microfibers shed from clothing and other textiles, such as fishing nets; while, secondary MP are produced in the environment by degradation and mechanical abrasion of larger plastic debris [9]. Although primary NP have also been detected in facial cleansers [10], NPs are mainly the unwanted product of degradation of larger plastics [11].
Moreover, MP have been further classified based on their shape as microbeads, pellets, fibers, foam and fragments. Microbeads are synthetized by emulsion, suspension and dispersion polymerization and can generally be associated with spherical form [12]. Pellets are industrial raw material for manufacturing of larger products and they can be released unintentionally in the environment during manufacturing and transport. They are small granules, generally with shape of cylinder or a disk [13]. Synthetic fibers have generally cylindrical shape with average diameter of 10–20 µm and length up to few mm and they are generated from wear of textile material. Foams and fragments are mainly of secondary origin; they are produced by mechanical abrasion of larger plastic products and they have generally an irregular shape [14]. Shape and size have a crucial impact on the transport of MP in many environmental matrices, like atmosphere and soil; therefore, transport through the environmental compartments might be peculiar for the different types of MP [15,16,17].
Due to their environmental persistence and potential health effect, MP pollution has attracted much attention recently from the research community and the authorities; indeed, the European Commission is evaluating to restrict intentional uses of MP. Several scientific works in the last decade show the presence of MP in soil, freshwater and oceans [14,18,19,20]. Recently, MP occurrence was also shown in the atmospheric environment, with measurements in particulate matter and in wet and dry deposition [21,22]. However, the research activity on NP is still at a preliminary state, due to the difficulties in sampling and detection. Only few works reveal NP occurrence in marine environments [23,24] while, at the present time, no evidence is reported for the atmosphere.
The goal of this work is to give an overarching and critical point of view on research findings and current knowledge on MP and NP in the atmosphere. The aim is to embed the atmospheric transport, transformation and degradation of MP and NP within the concept of plastic cycle introduced by Horton and Dixon [25] and further developed by Bank and Hansson [26]. After the introduction of this concept, three main scientific issues are covered in this work. The first one is a general overview and comparison of sampling methodology and analytical techniques commonly used for the detection of MP in the atmosphere, as well as future developments for the analysis of NP. The second one is related to MP occurrence and concentration, to evaluate the importance of atmospheric transport as a source in other matrices. The third one is focused on the estimation of the atmospheric concentration of NP. This latter is crucial to assess the environmental impact of NP. Indeed, NP have high surface-to-volume ratio [27] that affects their reactivity and the way they can adsorb other types of pollutants.
2. Discussion
2.1. The Plastic Cycle
Research on microplastics is currently focusing on separate environmental compartments, such as soil, vegetation, water bodies (freshwater and sea) and atmosphere. Nonetheless, these compartments are linked and the transport of MP and NP is made more complex by chemodynamics, intended as the dynamic changes that take place in the environment because of interaction between MP, NP and natural compounds [28]. For example, water microalgae are able to grow on MP particles, leading to an increase in the density and facilitating their sinking in sediments, with a transit from water bodies to soil [29]. On the other hand, the comb-out effect is responsible for the deposition of atmospheric MP on the canopy [30], probably facilitated by the wax layer on leaves, which is able to trap hydrophobic pollutants [31]. The study from Scheurer and Bigalke [32] shows that 90% of Swiss floodplain soils contain MP, and the main result is that the mesoplastic concentration is correlated with the presence of bigger plastic waste, while MP were found also in soil not affected by human activity. The authors suggest that the presence in remote unsettled high mountain areas and the dominance of small MP (<500 μm diameter) particles, indicate that MP enter soils via diffuse aeolian transport.
The boundaries between compartments are thus blurred and permeable, the occurrence and abundance of MP and NP depend on the interactions and connections with the adjacent environments. Therefore, Horton and Dixon [25] and Bank and Hansson [26] have introduced the concept of “Plastic Cycle” to indicate the biogeochemical cycle of plastics between environmental compartments and stressing the global nature of this ubiquitous problem [26]. However, in the “Plastic Cycle” model the fate and transport of plastic only include the transfer from lands to oceans, considering mainly a unidirectional flow. The “Plastic Cycle” model is mainly developed for large plastic debris (meso- and macroplastics). Therefore, it does not consider the possible transfer from seas to soils and, most importantly, it does not evaluate the atmospheric transport, which could be relevant for MP and NP. Atmospheric transport of MP is poorly understood, but recent studies have shown that it is likely to be a crucial transport pathway [33,34,35]. Even less is known about transport and sources of NP; however, due to their small size it is plausible to assume that NP could derive from similar sources compared to MP, and that atmospheric transport of NP may be comparable to MP transport. Atmospheric dynamics include suspension, transport and deposition of MP and NP. The main sources are urban, industrial and agricultural activities [21,22,36,37] and traffic [38,39,40], while secondary sources, like erosion of contaminated soils [41] and suspension of MP from the ocean during bubble bursting [42], should also be taken into account. Figure 1 reports the main sources and transport pathways of MP and NP. Once in the atmosphere, plastic particles are transported following air masses movements [17,43] and could act as ice nuclei, facilitating the formation of ice crystals [44]. The atmospheric oxidant capacity probably has a key role in their transformation, since MP and NP are exposed to sunlight [45], gas-phase oxidants (ozone, hydroxyl and nitrate radicals) [46,47,48,49] and aqueous phase oxidants (hydroxyl and nitrate radicals) [50] with higher concentrations compared to soil and water bodies. However, little is known about the fate and transformation of MP in the atmosphere. MP and NP shape and dimensions influence their deposition, and therefore their residence time in the atmosphere. The deposition is potentially accelerated by scavenging such as precipitations [33,34] and comb-out effect [30].
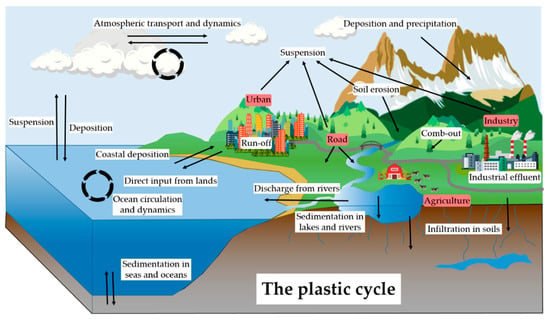
Figure 1.
Conceptual model of the biogeochemical cycle of plastic. Red boxes represent sources and white boxes represent transport factors and mechanisms. Arrows represent transport pathways.
In our view, the concept of the plastic cycle may indicate the continuous and complex movement of plastic materials between a wide range of environmental matrices, also potentially affecting the biota, including in humans. MP and NP are contaminating even the most remote areas of our planet and atmospheric dynamic is one of the key processes to understand the global MP and NP pollution. In addition, mechanical and chemical degradation lead to the fractionation of MP, which induces a continuous change in the contaminants’ characteristics, in particular, their size distribution strongly influences their fate in the environment.
2.2. Critical Review on Sampling Methodology and Analysis
2.2.1. Sampling
To the best of our knowledge no standard operation protocols (SOPs) have been released for MP and NP analysis in the environment. Conversely, the sampling methodologies of MP in seawater and freshwater have been extensively discussed [51,52]. The debate for airborne MP is still open: the sampling methodology is different from one study to another, making comparisons difficult. Concerning outdoor sampling, two main methods have been used, based on passive and active collection. The main difference is that the active method allows the determination of the concentration in the air; this information could be further used for exposure studies. Instead, the passive method estimates the flux from atmospheric deposition to establish a mass balance. These methods have been applied with some differences in each study, without defining a standardized procedure. Passive sampling is generally carried out using a rain samples collector (a sampling bottle for collecting the rain) or a particulate fallout collector (a funnel). In order to avoid contaminations, the funnel is often made from stainless steel and the bottle from glass. After collection, the funnel is rinsed with ultrapure water to remove the particles adhering to the surface, as described, for instance, in Allen et al. [33] and Klein and Fischer [30]. A passive sampler has been developed to collect representative samples of dry and wet atmospheric particulate fallout for subsequent analysis by NILU (Norwegian Institute for Air Research, Particulate Fallout Collector (p.no. 9721)). Besides, the active collection requires a pump for aspiration of air through filters with well-defined mesh, as usually performed for atmospheric particulate matter [53,54] and as described for airborne MP [37,42,55]; sampling devices with sequential filters with decreasing mesh size are also available (cascade impactor). Commonly, to avoid contaminations, sampling is performed using quartz fiber or polytetrafluoroethylene filters. Although both sampling methods present pros and cons, the active sampling requires lower sampling time, it is less affected by meteorological conditions and sampling can be reported for a certain volume of air, leading to an easier comparison of measurements obtained in different sites. Moreover, it is not affected by resuspension of the MP. On the other side, passive sampling is important to estimate wet and dry deposition that can be used in theoretical models to gauge the importance of MP and NP’ atmospheric transport. However, passive sampling is carried out for long periods, generally of the order of weeks, and resuspension of the particles deposited on the sampler should be evaluated, especially for dry conditions and high wind speed.
2.2.2. Purification
Both active and passive collection are not specific for MP; therefore, they need to be separated from the other particulate matter. Separation is often achieved taking advantage of the lower density of MP, by washing the filters with NaI or ZnCl2 solutions, as described in Prata et al. [56]; other salts have been used for MP in seawater, freshwater and sediments [51]. This step can be preceded or followed by the digestion of unwanted material attached to MP by treatment with H2O2, Fenton reaction or enzymatic digestion. Other aggressive chemicals such as KOH, HNO3, H2SO4 or HClO4 have been used for other environmental matrices [51], but, to our knowledge, in atmospheric deposition studies only NaClO [30] or H2O2 have been used [33]. The unwanted material is composed of organic and inorganic matter, including also dust and biofilm, and can interfere with the identification of MP in the further steps. Density separation and sample treatment increase the potential loss of sample and can damage the plastic particles, especially the ones with smaller sizes. Indeed, both hydrogen peroxide and the Fenton reaction produce hydroxyl radicals, which were shown to react efficiently with some NP [50]. For this reason, separation and purification steps have not been employed in several studies, however this might increase the difficulties in the detection and the identification of MP [34,37,42,55].
It is worth noting that these sampling methodologies and treatments have been applied successfully to airborne MP, while NP analysis requires improvement in both sampling and sample treatment.
2.2.3. Analysis
Analysis of MP can be performed via spectroscopic or spectrometric techniques. Both approaches are generally applied for the analysis of MP in different environmental matrices like sediments, freshwater and seawater, but, to our knowledge, only spectroscopic techniques have been applied for the analysis of MP in the atmosphere.
Distinct MP identification (particle by particle) is commonly performed using vibrational spectroscopy, such as FT-IR (Fourier transform infrared) or Raman spectroscopy. For MP analysis, FT-IR can be applied in reflection and transmission modes, or as ATR-FT-IR (attenuated total reflection-FT-IR). Spectroscopic techniques have the great advantage to be non-destructive, even though they are suitable only to identify MP larger than 100 µm, with a loss of information on smaller particles. They require extensive sampling preparation, like density separation and matrix digestion, because the IR beam is not able to reach the MP that are covered by natural organic and inorganic matter. Additionally, a sufficient amount of plastic is required to obtain significant results, due to the point-by-point analysis characteristic of spectroscopic techniques. Moreover, spectroscopic techniques are not applicable, for example, to MP deriving from tire wear, which potentially represent a huge fraction of atmospheric MP in the coarse mode. Indeed, filler components of tire wear, such as black carbon, completely absorb IR radiation, preventing the identification of these MP [57].
A different analytical approach is the identification of MP using spectrometric methods: for instance, py-GC-MS (pyrolysis-gas chromatography mass spectrometry) is a destructive thermoanalytical method successfully applied for the analysis of seawater MP and NP [58,59]. Ter Halle et al. analyzed seawater plastic debris of LDPE (low density polyethylene), HDPE (high density polyethylene), PVC (polyvinylchloride), PET (polyethylenterephthalate), PS (polystyrene), and PP (polypropylene) of mesoplastics, MP and NP. [23] In this case, for the analysis of the colloidal fraction (NP and MP < 50 µm), seawater was concentrated by ultrafiltration, using 10 kDa poly(ether sulfone) membrane and pushing the samples through the membranes using N2. The extract was lyophilized and analyzed by py-GC-MS; spectra were compared to pyrolysis pattern of pure LDPE, HDPE, PVC, PET, PS and PP, allowing the first determination of NP composition in seawater. A spectrometric approach was also used by Eisentraut et al. [57] on MP and tire wear micro particles, with the difference that the sample was not purified before the analysis (minimal sample preparation). In this case, decomposition of MP was achieved by heating in a thermogravimetric analyzer, adsorption and pre-concentration of the products on a thermal desorption unit and cryofocusing before the analysis with GC-MS. Although py-GC-MS is a powerful technique to determine the chemical composition of the mixture of MP, and it is the only available technique to analyze NP, the quantification of the number of MP and NP is not possible with this technique.
The identification of plastics is usually carried out comparing the spectra with standard compounds and polymers. Often the support of libraries is also used; for example, for the GC-MS analysis the National Institute of Science and Technology (NIST05 and NIST05s) library may be used [23]. The free library SpectraBaseTM or Nicodom FTIR Spectra Libraries could be used to identify plastics analyzed by IR and Raman spectroscopy. Moreover, a list of representative absorption bands to identify plastics by FT-IR can be found in literature [60].
Käppler et al. [61] carried out a comparison of the spectroscopic and spectrometric approaches for the analysis of MP (particles and fibers) isolated from river sediments. They have found that both methods are able to distinguish between plastic and non-plastic debris, showing a useful complementarity to identify and characterize MP.
The main advantages and disadvantages of spectrometric and spectroscopic approaches are summarized in Table 1. All these factors should be taken into account when choosing the approach: in particular, if the goal of the analysis is the determination of the shape and size of MP, spectroscopic techniques should be preferred, while for the analysis of the composition, spectrometric techniques are more advantageous, especially for smaller particles.

Table 1.
Advantages and disadvantages of spectrometric and spectroscopic approaches. The arrow indicates the cost of the two different categories, considering the initial price of the instrument, the maintenance and consumables.
2.3. Occurrence of Microplastics in the Atmospheric Deposition
Two interesting review articles from Chen et al. [62] and Zhang et al. [63] (2020) have focused their attention on the occurrence and abundance of MP in the urban environment, with particular emphasis on the sampling methodology, sample purification and analysis. They both sum up the recent studies in urban and remote environments, reporting that the majority of MP in cities (Paris (France), Dongguan, Shanghai, Yantai (China) and Nottingham (UK)) are represented by fibers. The only exception is MP in Hamburg (Germany), where most of the detected MP (90–95%) were fragments. The characteristics of MP in the mentioned studies are reported in Table 2. Both reviews categorize MP on the basis of their shape, size, color and composition, showing the extreme variability of MP in the atmosphere, mainly due to the myriad of sources and to the different methodologies used for sampling and analysis.

Table 2.
Characteristics of microplastics (MP) in atmospheric wet and dry deposition in remote and urban areas.
As mentioned in Section 2.1, a crucial reason for MP spreading worldwide is the atmospheric transport: atmosphere is an extremely dynamic compartment and MP have been detected in the most remote areas of the Earth, including the polar region [64] and the Tibetan plateau’s rivers and lakes [65,66]. In particular, the Tibetan plateau is also known as the “Third Pole”, hosting a huge number of glaciers and lakes and being situated far from urban, industrial and agricultural activities. The detection of MP in glacial snow raises the question of the importance of long-distance atmospheric transport in such remote areas.
Occurrence of MP was also reported for other remote sites. Allen et al. [33] report five month analysis of wet and dry deposition in the pristine region of Pyrenees mountains, characterized by a local vicinity scarcely populated and a lack of anthropogenic sources. MP fragments, films and fibers, with respective proportions of 68%, 20% and 12%, were found and analyzed by µRaman spectroscopy, showing the presence of different kind of polymers, like PS, polyethylene (PE) and, in minor quantity, polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene terephthalate (PET), as reported in Table 2. A strong positive correlation between the number of MP and wind speed was found, while the correlation with the amount of precipitations and their duration is less clear. The authors suggest that MP deposition is probably more affected by the intensity of precipitation than by the duration.
Bergmann et al. [34] report MP contamination in snow from the Alps (Davos, Tschuggen and (Switzerland) and Bavaria (Germany)), from ice floes in the Artic and from Svalbard. They compared their results with the ones obtained for analysis of snow samples collected in Bremen (Germany) and from the Isle of Heligoland (North Sea, Germany). MP are mainly found as fragments and pellets compared to fibers. The authors did not investigate deeply the correlation of wind speed, direction, rain and snow event with MP concentration, largely because snow was not freshly deposited for all the samples. Nevertheless, the remoteness of the sampling sites, especially concerning the Artic region, strongly suggests that long-range atmospheric transport is responsible for MP occurrence.
Liu et al. [55] and Wang et al. [42] investigated atmospheric MP over the west Pacific Ocean and the South China Sea and the east Indian Ocean, respectively. Their results show a lower concentration of MP in aerosol over open ocean, compared to the concentration measured in urban sites (Table 2). However, they carefully estimate that, once in the atmosphere, suspended MP are transported passively by complex two- and three-dimensional physical winds, resulting in a large variability over the land and surface ocean. In particular, Wang et al. [42] performed a statistical analysis and highlight that four meteorological factors limit the distribution of MP: (i) wind speed is needed for MP transport, (ii) gust velocity is necessary to suspend MP from the ground or the sea surface, (iii) humidity and (iv) low pressure (strong turbulence) have an important effect on MP transport. They also infer that the atmospheric MP over the ocean might originate not only from the adjacent continent but also from the adjacent oceanic atmosphere polluted by other continental MP emissions.
The recent work from Evangeliou et al. [67] models the global transport of MP produced by road traffic (tire and brake wear particles) to remote regions, such as the Arctic Ocean, considering particles of 10 and 2.5 µm. These dimensions are chosen based on the distribution of aerosol particles in the atmosphere, which are divided in coarse mode (2.5–10 µm, particulate matter (PM) 10) and fine mode (<2.5 µm, PM 2.5), on the basis of their interaction with lungs. They are in the lower range of the definition of MP and most of the studies presented here show instrumental limitations for the detection of particles lower than 10 µm in size. They show that atmospheric transport of MP is an underestimated hazard to terrestrial and marine ecosystems, and it affects air quality on a global scale.
In our opinion, the results reported for urban and remote sites show two main differences: the first one is the abundance of fragments that, with the exception of the city of Hamburg, are dominant in remote environments. This could be related to the size, since fragments are usually smaller than fibers and can be easily suspended by winds and gusts. In addition, during atmospheric transport, larger MP fragments might be degraded into smaller particles by mechanical processes and reactivity: this could explain the larger presence of fibers near the sources (in particular in urban environments) and of fragments in remote sites. The second difference between urban and remote sites is the importance of meteorological conditions; wind speed, gust velocity, humidity and pressure are crucial in long-range transport. For urban sites, it has been observed that minimum wind speed and atmospheric wet deposition are responsible for the highest deposition rate [21,35]. During temperature inversion episodes, MP could be blocked in the lower troposphere, creating an episode of pollution and decreasing the spreading [62]. However, it is difficult to compare different measurements performed with different sampling methodologies and analyses. Standardized sampling, analysis methods and more experimental data are needed to understand the importance of atmospheric dynamic on MP transport to remote sites.
2.4. Microplastics Degradation
In the environment, MP may undergo physical and (bio)chemical degradation processes. Among the physical factors that induce deterioration of plastics, the weathering and the mechanical breakdown are the main ones. A recent study from El Hadri et al. [70] reports a top-down method, based on mechanical degradation, to obtain NP from MP under laboratory conditions. The size distribution, morphology and surface charge of the resulting NP are analyzed and the authors found that they are highly polydispersed with different shapes and negatively charged surfaces. However, this study has been performed using a planetary ball mill, which is probably not representative of environmental conditions.
Although plastic is often defined as an almost inert material, it is composed of a carbon skeleton that is sensitive to oxidation, UV radiation or microbiological activity [27,71,72,73]. For this reason, plastic degradation is not likely to stop at the micrometric size.
When a plastic piece is degraded, the exposed area increases drastically and so does the surface reactivity [27]. MP and NP in the atmosphere are exposed to sunlight and photogenerated oxidants, such as hydroxyl radical (•OH) or ozone (O3). The main abiotic degradation process of plastics is photo-initiated oxidation, which leads to polymer chain scission, branching and formation of polymer fragments as well as volatile compounds [74,75]. This process consists of a complex series of radical reactions initiated by the breaking of covalent bonds in the main polymer chain; consequentially free radicals are formed, which can react with oxygen forming a peroxy-radical species. The reactive species formed in the polymer during this process might react not only with oxygen, but also with other compounds such as nitrogen oxides. However, until now, only a limited number of studies investigated the reactivity of MP and NP towards atmospheric oxidants and further studies are needed to understand the fate of these plastics in the air. For example, Vicente et al. [46] report the formation of degradation products by oxidation of PS nanoparticles in the presence of O3, while our previous study [50] estimates the reactivity constant between PS nanoparticles and •OH. To date, the effect of chemical degradation on plastic has only been studied for macro and mesoplastics, with special attention to plastic films, while little is known for MP and NP.
2.5. Smaller the Size, Higher the Occurrence? Nanoplastics
As explained previously, plastic pollution represents a current global threat. MP are ubiquitous, due to their migration through environmental compartments. However, little is known about the smallest plastic debris, NP, since their size is below the instrumental limit of detection of the techniques currently used for MP (µFT-IR and µRaman). NP have been detected in the ocean [23] and in soil [76], although, to the best of our knowledge, there is not any study that reports their concentration in a specific environment.
NP have some analogies with MP but also some peculiar differences. Although the chemical composition is the same, as evidenced by py-GC-MS (pyrolysis gas chromatography mass spectrometry) identification of characteristic polymer signals by Ter Halle et al. [23], the categorization in different shapes has to be revised. In fact, considering that fibers have an average diameter of 10–20 µm and length of 100–5000 µm, they can mainly break down in fibers with shorter lengths until they reach the shape of fragments, with almost the same diameter in each direction. This process leads to the formation of particles still classified in the range of MP. It is mostly unlikely that fibers break down in the sense of the length. For this reason, presumably, NP do not have the shape of fibers, but could be fragments, spheres and granules: the latter are defined as pieces of plastic manufactured as raw material for larger plastic products. Contrarily to what is observed for MP, which are susceptible to vertical motion because of their density, in the aquatic environment NP have a colloidal behavior, due to their size, and they undergo Brownian motion. Another difference is the interaction with biota: microbial cell can grow on MP, forming a biofilm [77], while NP have the same or even lower size than a microbial cell [78]. For this reason, they can be incorporated into the microorganism cells, but it is difficult to imagine that they can serve as a support for microorganism growth. However, they can be coated with an eco-corona, composed by natural organic matter. The eco-corona could be important to evaluate the toxicity of NP [27,79,80,81], although its structure and composition is not yet completely characterized. Some of the studies report that eco-corona is composed by humic acids, while some others describe it as proteinaceous material. This coating could have an effect on the density of NP making them sink in the aqueous phase, despite the low density of plastic polymers. The eco-corona can also have an impact on the aggregation of NP, but research in this field is still needed [82].
To our knowledge, no evidence of NP in the atmosphere has been reported until now. Nevertheless, due to their low weight and small size, they are highly susceptible to suspension by wind.
The works from Allen et al. [33] and Klein and Fischer [30] report the number of fragments deposed (# m−2 d−1) as a function of the size of the fragments. They both observed that the number of fragments increased as the size decreased. The insert in Figure 2 shows the data reported in the two studies: we have fitted both datasets using the power law equation y = axb, where y is the number of particles deposed (# m−2 d−1) and x is the size (µm). The parameters a and b obtained are reported in Table 3.
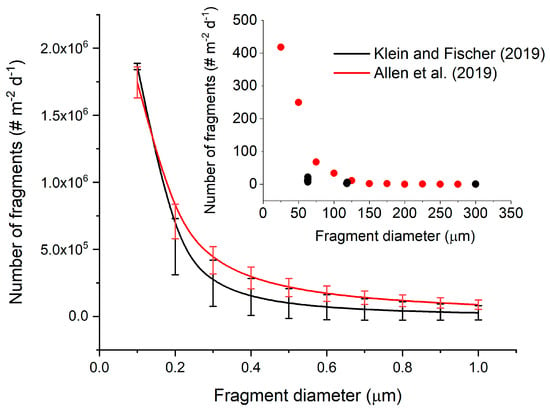
Figure 2.
Theoretical deposition of nanoplastics (NP) as a function of particle size calculated using the extrapolation of the fit of experimental data presented on the insert. Insert: number of fragments reported in the study from Allen et al. [33] and Klein and Fischer [30].

Table 3.
Parameters obtained for the fit of the datasets reported in the study from Allen et al. [33] and Klein and Fischer [30]. Equation y = axb.
The equation obtained allows an estimation of the potential deposition of NP, as shown in Figure 2. Following this extrapolation, the number of NP increases quickly with the decrease in size, leading to a deposition of hundreds of thousands of fragments of sizes lower than 1 µm. These results clearly indicate that NP are potentially present in the atmosphere and in huge concentrations. However, this extrapolation is only a theoretical assumption because the deposition and the settling velocity are related to the size and the density of the NP particle.
Once in the atmosphere, NP would not undergo the same deposition process occurring for MP. For instance, in the absence of wind, the settling velocity of a particle can be calculated by applying Archimedes’ law. The weight of the object (W) is given by the sum of the buoyancy force acting on the object (Fb) and the drag force (D), as reported in Equation (1).
If we consider a spherical object of diameter (d) and density (ρs), W can be expressed as in Equation (2) (g = gravitational acceleration).
While Fb is expressed by Equation (3), with the density of the fluid indicated by ρ.
The drag force can be expressed by Equation (4), where Cd is the drag coefficient, vs. is the settling velocity and A is the projected area of the sphere.
Substituting Equations (2)–(4) in Equation (1), vs. for a spherical particle can be calculated following Equation (5).
While, for a non-spherical particle of equivalent diameter de and projected area Ap, Equation (6) can be used.
The settling velocity is thus proportional to the size and the density of the particle. Considering a spherical particle (Cd = 0.47) of PS, with ρs = 1060 kg m−3, suspended in air (ρ = 1.225 kg m−3 at 15 °C), applying Equation (6) we can easily calculate the settling velocity vs. as a function of the diameter d. In the absence of vertical uplift and turbulence, the PS particle falls down. If we consider the time needed to descend by 1 km and we consider a constant horizontal wind, we can have a brief look at the distance travelled by the particle as a function of its size. Figure 3 reports the simulation for PS particles of different diameters, in the range of MP and NP, in the presence of horizontal wind between 1 (light air in the Beaufort scale) and 13 m s−1 (strong breeze). It is clear that smaller particles are transported for longer distances and fresh breeze is able to transport particles with diameter of 100 nm for 200 km. Polymers with lower density compared to PS (for example PE and PP) could even be transported for longer distances. This is only a simplified schema that does not take into account the vertical uplift of air masses and the gust speed. However, these calculations provide a first approximation on travelling distances of NP and MP in the atmosphere and could contribute to an assessment of the importance of atmospheric transport of NP.
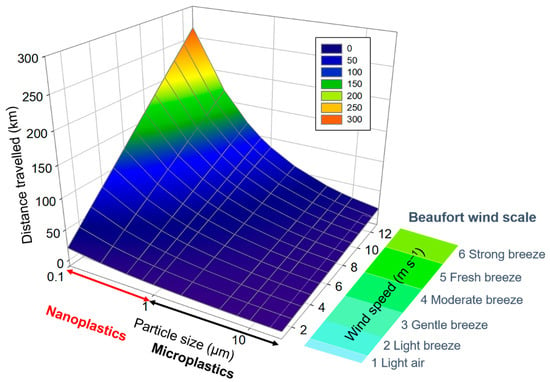
Figure 3.
Horizontal distance travelled by a particle falling vertically for 1 km in the presence of constant horizontal wind between 1 and 13 m s−1. The diagram has been plotted using SigmaPlot (Systat Software, San Jose, CA, USA).
Few studies give an estimation of the distance travelled by MP. Wang et al. [42] use the back-trajectory calculation, which includes localized updraft, convective mixing and advection, to evaluate the origin of MP, and they assess that one of the main sources of MP over the South China Sea and east Indian Ocean is related to the continent. They estimate that MP are transported for distances of 1000 km: this value clearly indicates that atmospheric turbulence plays a crucial role in the long-range transport. With the same approach, Allen et al. [33] calculated that the MP source area was 60 km to the east, 75 km to the west and south, and 95 km to the north of the site, showing results in agreement with the simplified model presented. Bergmann et al. [34] compared the transport of MP to the Artic with the transport of large dust particles and mercury: both are transported over distances of 3500 km from the Sahara to the North Atlantic. Evangeliou et al. [67] presented the first global simulation of atmospheric transport of MP produced by road traffic (tire and brake wear particles), suggesting high transport efficiency of these particles to remote regions, such as the Arctic Ocean. However, they do not report a numeric estimation of the transport and they only assess that smaller particles have higher speed.
According to the simulation presented, NP are susceptible to undergo long-range transport more efficiently than MP. However, since MP have also been detected in remote and pristine environments, we can affirm with some certainty that NP have also reached the most remote areas of the globe. Concerning the upper troposphere, no measurements of MP have been performed in the free troposphere, even if Gateuille et al. [83] have collected MP by deposition in the Alps region at 2100 m a.s.l. (above sea level). More measurements in the free troposphere are needed to understand the transport of MP and NP and the vertical distribution profile.
3. Conclusions and Environmental Implications
The atmospheric transport of MP causes their presence in both remote and pristine environments and plastic pollution is now a global problem: suspension, deposition and aeolian transport of MP should be included and considered as a major transport pathway in the biogeochemical cycle of plastic.
If the research on MP in atmospheric particles and fallout is growing by leaps and bounds, little is known about NP. Nevertheless, this study shows that NP could be transported on longer distances than MP, making them globally present and potentially more concentrated than MP. However, experimental data are needed to estimate their importance in urban and remote environments: this information on fluxes is fundamental to develop and constrain theoretical models.
Besides, until now MP and NP have been considered as inert particles while recent studies show that they can react and interact with light and oxidants, like ozone and hydroxyl radicals [46,50]. Their degradation in the gaseous and aqueous phase releases a myriad of organic compounds from short chain carboxylic acids to aromatic and aliphatic compounds with different functional groups, with a potential non-negligible impact on the composition and concentration of the carbon pool in the gaseous and aqueous phase. More investigations on the fate of MP and NP in the environment could provide an insight into the effect on the biogeochemical cycle of carbon.
Sampling and detection are the main issues in MP and NP analysis. Wet and dry deposition of MP are evaluated using completely different methodologies and standard operating procedures (SOP) should be defined univocally, in order to be able to compare the deposition rate or the MP concentration for different particles. Concerning NP, there are no studies reporting a potential sampling method that could be applied to atmospheric samples. Due to their size, spectroscopic analysis is not suitable. In our view, the best option would be the development of a spectrometric detection method to analyze the composition, coupled to a more traditional SMPS (scanning mobility particle sizer), to detect the particle dimensions.
It is crucial to explore new methodologies to collect and analyze NP. Research should focus on the development of new technologies, combining the existent knowledge on nanomaterial and atmospheric particle analysis.
Author Contributions
A.B. and M.P.: writing—review and editing, M.P.: writing—review and editing, funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We acknowledge funding from the University of Helsinki (Three-Year Research Grants), the ERC Projects 692891-DAMOCLES. Open access funding provided by University of Helsinki.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- PlasticsEurope. Plastics the Facts—2019; PlasticsEurope: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.C.; Tse, H.F.; Fok, L. Plastic waste in the marine environment: A review of sources, occurrence and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrell, T.R. Accumulation of plastic litter on beaches of Amchitka Island, Alaska. Mar. Environ. Res. 1980, 3, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, P.G. Plastics packaging and coastal pollution. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 1972, 3, 35–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cundell, A.M. Plastics in the marine environment. Environ. Conserv. 1974, 1, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.F.; Pinto da Costa, J.; Duarte, A.C. “Sampling of micro(nano)plastics in environmental compartments: How to define standard procedures?”. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 1, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.; Nash, R. Microplastics: Finding a consensus on the definition. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2019, 138, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, N.B.; Hüffer, T.; Thompson, R.C.; Hassellöv, M.; Verschoor, A.; Daugaard, A.E.; Rist, S.; Karlsson, T.; Brennholt, N.; Cole, M.; et al. Are we speaking the same language? recommendations for a definition and categorization framework for plastic debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kershaw, P.; Rochman, C. Sources, fate and effects of microplastics in the marine environment: Part 2 of a global assessment. In Reports and Studies-IMO/FAO/Unesco-IOC/WMO/IAEA/UN/UNEP Joint Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Environmental Protection (GESAMP) Eng No. 93; International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, L.M.; Yousefi, N.; Tufenkji, N. Are there nanoplastics in your personal care products? Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimi, O.S.; Farner Budarz, J.; Hernandez, L.M.; Tufenkji, N. Microplastics and nanoplastics in aquatic environments: Aggregation, deposition, and enhanced contaminant transport. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1704–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environment and Climate Change Canada. Microbeads—A Science Summary; Department of the Environment: Gatineau, QC, Canada, 2015.
- Kooi, M.; Reisser, J.; Slat, B.; Ferrari, F.F.; Schmid, M.S.; Cunsolo, S.; Brambini, R.; Noble, K.; Sirks, L.-A.; Linders, T.E. The effect of particle properties on the depth profile of buoyant plastics in the ocean. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Huang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, F.; Chen, H.; Quan, G.; Yan, J.; Li, T. Environmental occurrences, fate, and impacts of microplastics. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 184, 109612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Powell, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, P. Microplastics as contaminants in the soil environment: A mini-review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Yang, X.; Chen, L.; Chao, J.; Teng, J.; Wang, Q. Microplastics in soils: A review of possible sources, analytical methods and ecological impacts. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, T.; Kang, S.; Sillanpää, M. Importance of atmospheric transport for microplastics deposited in remote areas. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anbumani, S.; Kakkar, P. Ecotoxicological effects of microplastics on biota: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 14373–14396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Mohamed Nor, N.H.; Hermsen, E.; Kooi, M.; Mintenig, S.M.; De France, J. Microplastics in freshwaters and drinking water: Critical review and assessment of data quality. Water Res. 2019, 155, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Busquets, R.; Campos, L.C. Assessment of microplastics in freshwater systems: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Mirande, C.; Mandin, C.; Guerrouache, M.; Langlois, V.; Tassin, B. A first overview of textile fibers, including microplastics, in indoor and outdoor environments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Tan, Z.; Zhan, Z.; Tan, X.; Chen, Q. Characteristic of microplastics in the atmospheric fallout from Dongguan city, China: Preliminary research and first evidence. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 24928–24935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Halle, A.; Jeanneau, L.; Martignac, M.; Jardé, E.; Pedrono, B.; Brach, L.; Gigault, J. Nanoplastic in the North Atlantic subtropical gyre. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13689–13697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, R.; Weder, C.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Emergence of nanoplastic in the environment and possible impact on human health. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1748–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, A.A.; Dixon, S.J. Microplastics: An introduction to environmental transport processes. WIREs Water 2018, 5, e1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bank, M.S.; Hansson, S.V. The Plastic Cycle: A novel and holistic paradigm for the anthropocene. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7177–7179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattsson, K.; Jocic, S.; Doverbratt, I.; Hansson, L.-A. Nanoplastics in the aquatic environment. In Microplastic Contamination in Aquatic Environments; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 379–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibodeaux, L.J. Environmental Chemodynamics: Movement of Chemicals in Air, Water, and Soil, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lagarde, F.; Olivier, O.; Zanella, M.; Daniel, P.; Hiard, S.; Caruso, A. Microplastic interactions with freshwater microalgae: Hetero-aggregation and changes in plastic density appear strongly dependent on polymer type. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 215, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, M.; Fischer, E.K. Microplastic abundance in atmospheric deposition within the Metropolitan area of Hamburg, Germany. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleiman, M.; de Sainte Claire, P.; Richard, C. Heterogeneous photochemistry of agrochemicals at the leaf surface: A case study of plant activator Acibenzolar-S-methyl. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7653–7660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurer, M.; Bigalke, M. Microplastics in Swiss floodplain soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3591–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Phoenix, V.R.; Le Roux, G.; Durántez Jiménez, P.; Simonneau, A.; Binet, S.; Galop, D. Atmospheric transport and deposition of microplastics in a remote mountain catchment. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, M.; Mützel, S.; Primpke, S.; Tekman, M.B.; Trachsel, J.; Gerdts, G. White and wonderful? Microplastics prevail in snow from the Alps to the Arctic. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Saad, M.; Mirande, C.; Tassin, B. Synthetic fibers in atmospheric fallout: A source of microplastics in the environment? Mar. Poll. Bull. 2016, 104, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, S.; Moore, F.; Akhbarizadeh, R. Microplastic pollution in deposited urban dust, Tehran metropolis, Iran. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 20360–20371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Fang, T.; Xu, P.; Zhu, L.; Li, D. Source and potential risk assessment of suspended atmospheric microplastics in Shanghai. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 675, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, S.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Delshab, H.; Soltani, N.; Sorooshian, A. Investigation of microrubbers, microplastics and heavy metals in street dust: A study in Bushehr city, Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Turner, A.; Kelly, F.J.; Dominguez, A.O.; Jaafarzadeh, N. Distribution and potential health impacts of microplastics and microrubbers in air and street dusts from Asaluyeh County, Iran. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, F.; Dietze, V.; Baum, A.; Sauer, J.; Gilge, S.; Maschowski, C.; Gieré, R. Tire abrasion as a major source of microplastics in the environment. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2014–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Riksen, M.J.; Sirjani, E.; Sameni, A.; Geissen, V. Wind erosion as a driver for transport of light density microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, C.; Liu, K.; Zhu, L.; Song, Z.; Li, D. Atmospheric microplastic over the South China Sea and East Indian Ocean: Abundance, distribution and source. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Ulke, J.; Font, A.; Chan, K.L.A.; Kelly, F.J. Atmospheric microplastic deposition in an urban environment and an evaluation of transport. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, M.; Ariya, P.A. Ice nucleation of model nanoplastics and microplastics: A novel synthetic protocol and the influence of particle capping at diverse atmospheric environments. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2019, 3, 1729–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandon, J.; Goldstein, M.; Ohman, M.D. Long-term aging and degradation of microplastic particles: Comparing in situ oceanic and experimental weathering patterns. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2016, 110, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, J.S.; Gejo, J.L.; Rothenbacher, S.; Sarojiniamma, S.; Gogritchiani, E.; Wörner, M.; Kasper, G.; Braun, A.M. Oxidation of polystyrene aerosols by VUV-photolysis and/or ozone. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2009, 8, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, M.R.; Mitchell, S.A.; Bradley, R.H. Surface studies of low molecular weight photolysis products from UV-ozone oxidised polystyrene. Surf. Sci. 2005, 581, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R.J.; Fischer, D.A.; Lenhart, J.L. Systematic oxidation of polystyrene by ultraviolet-ozone, characterized by near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure and contact angle. Langmuir 2008, 24, 8187–8197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; He, Q.; Wang, C.; Sun, S. Surface modification of polystyrene microsphere using ozone treatment. Ferroelectrics 2018, 530, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, A.; Sordello, F.; Ehn, M.; Vione, D.; Passananti, M. Degradation of nanoplastics in the environment: Reactivity and impact on atmospheric and surface waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prata, J.C.; da Costa, J.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Methods for sampling and detection of microplastics in water and sediment: A critical review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, F.; Kochleus, C.; Bänsch-Baltruschat, B.; Brennholt, N.; Reifferscheid, G. Sampling techniques and preparation methods for microplastic analyses in the aquatic environment—A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmi, A.; Wiedensohler, A.; Laj, P.; Fjaeraa, A.-M.; Sellegri, K.; Birmili, W.; Weingartner, E.; Baltensperger, U.; Zdimal, V.; Zikova, N.; et al. Number size distributions and seasonality of submicron particles in Europe 2008–2009. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 5505–5538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parshintsev, J.; Ruiz-Jimenez, J.; Petäjä, T.; Hartonen, K.; Kulmala, M.; Riekkola, M.-L. Comparison of quartz and Teflon filters for simultaneous collection of size-separated ultrafine aerosol particles and gas-phase zero samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 3527–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wu, T.; Wang, X.; Song, Z.; Zong, C.; Wei, N.; Li, D. Consistent transport of terrestrial microplastics to the ocean through atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10612–10619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; Castro, J.L.; da Costa, J.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Cerqueira, M.; Rocha-Santos, T. An easy method for processing and identification of natural and synthetic microfibers and microplastics in indoor and outdoor air. MethodsX 2020, 7, 100762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisentraut, P.; Dümichen, E.; Ruhl, A.S.; Jekel, M.; Albrecht, M.; Gehde, M.; Braun, U. Two birds with one stone—Fast and simultaneous analysis of microplastics: Microparticles derived from thermoplastics and tire wear. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermabessiere, L.; Himber, C.; Boricaud, B.; Kazour, M.; Amara, R.; Cassone, A.-L.; Laurentie, M.; Paul-Pont, I.; Soudant, P.; Dehaut, A.; et al. Optimization, performance, and application of a pyrolysis-GC/MS method for the identification of microplastics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 6663–6676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühn, S.; van Oyen, A.; Booth, A.M.; Meijboom, A.; van Franeker, J.A. Marine microplastic: Preparation of relevant test materials for laboratory assessment of ecosystem impacts. Chemosphere 2018, 213, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.R.; Horgen, F.D.; Orski, S.V.; Rodriguez, C.V.; Beers, K.L.; Balazs, G.H.; Jones, T.T.; Work, T.M.; Brignac, K.C.; Royer, S.-J.; et al. Validation of ATR FT-IR to identify polymers of plastic marine debris, including those ingested by marine organisms. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2018, 127, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Käppler, A.; Fischer, M.; Scholz-Böttcher, B.M.; Oberbeckmann, S.; Labrenz, M.; Fischer, D.; Eichhorn, K.-J.; Voit, B. Comparison of μ-ATR-FTIR spectroscopy and py-GCMS as identification tools for microplastic particles and fibers isolated from river sedimnts. Anal. Bioanal. Chem 2018, 410, 5313–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Feng, Q.; Wang, J. Mini-review of microplastics in the atmosphere and their risks to humans. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, S.; Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Gao, T.; Sillanpää, M. Atmospheric microplastics: A review on current status and perspectives. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 203, 103118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeken, I.; Primpke, S.; Beyer, B.; Gütermann, J.; Katlein, C.; Krumpen, T.; Bergmann, M.; Hehemann, L.; Gerdts, G. Arctic sea ice is an important temporal sink and means of transport for microplastic. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Su, J.; Xiong, X.; Wu, X.; Wu, C.; Liu, J. Microplastic pollution of lakeshore sediments from remote lakes in Tibet plateau, China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Yin, L.; Li, Z.; Wen, X.; Luo, X.; Hu, S.; Yang, H.; Long, Y.; Deng, B.; Huang, L. Microplastic pollution in the rivers of the Tibet Plateau. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangeliou, N.; Grythe, H.; Klimont, Z.; Heyes, C.; Eckhardt, S.; Lopez-Aparicio, S.; Stohl, A. Atmospheric transport is a major pathway of microplastics to remote regions. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Tian, C.; Luo, Y. Various forms and deposition fluxes of microplastics identified in the coastal urban atmosphere. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 3902–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, T.; Johnson, M.; Nathanail, P.; MacNaughtan, W.; Gomes, R.L. Freshwater and airborne textile fibre populations are dominated by ‘natural’, not microplastic, fibres. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hadri, H.; Gigault, J.; Maxit, B.; Grassl, B.; Reynaud, S. Nanoplastic from mechanically degraded primary and secondary microplastics for environmental assessments. NanoImpact 2020, 17, 100206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, J.P.; Santos, P.S.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. (Nano) plastics in the environment–sources, fates and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, A.L.; Kawaguchi, S.; King, C.K.; Townsend, K.A.; King, R.; Huston, W.M.; Nash, S.M.B. Turning microplastics into nanoplastics through digestive fragmentation by Antarctic krill. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.; Sinclair, C.J.; Bradley, E.L.; Boxall, A.B. Effects of environmental conditions on latex degradation in aquatic systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiero, A. Plastics in the Environment; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gewert, B.; Plassmann, M.M.; MacLeod, M. Pathways for degradation of plastic polymers floating in the marine environment. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, R.R.; Nizzetto, L. Fate and occurrence of micro(nano)plastics in soils: Knowledge gaps and possible risks. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 1, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberbeckmann, S.; Löder, M.G.J.; Labrenz, M. Marine microplastic-associated biofilms—A review. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, P.A.; Angert, E.R. Small but mighty: Cell size and bacteria. CSH Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a019216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadare, O.O.; Wan, B.; Guo, L.-H.; Xin, Y.; Qin, W.; Yang, Y. Humic acid alleviates the toxicity of polystyrene nanoplastic particles to Daphnia Magna. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 1466–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, F.; Lynch, I. Secreted protein eco-corona mediates uptake and impacts of polystyrene nanoparticles on Daphnia magna. J. Proteom. 2016, 137, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, J.; Stoll, S.; Slaveykova, V.I. Influence of nanoplastic surface charge on eco-corona formation, aggregation and toxicity to freshwater zooplankton. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-S.; Le, C.; Chiu, M.-H.; Chin, W.-C. The impact of nanoplastics on marine dissolved organic matter assembly. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gateuille, D.; Dusaucy, J.; Gillet, F.; Gaspéri, J.; Dris, R.; Tourreau, G.; Naffrechoux, E. Microplastic Contamination in Remote Alpine Lakes; EGU, Sharing geoscience online: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
