Abstract
Obtaining the reverberation time of a multipurpose building is most effective when accurate data is used to simulate the building. Therefore, this study proposes a method of measuring the sound absorption coefficient that is close to the sound absorption performance of the conditions in which building materials are actually used. In addition, a sufficient diffusivity evaluation method for sound absorption coefficient measurement in a reverberation chamber is proposed, to address the sound absorption performance difference caused by internal diffusion of the reverberation chamber. When the sound absorption performance was evaluated after installing the specimen under the condition of minimized edge effect, the result obtained should closely match the sound absorption performance of the specimen surface. The sound absorption performance of the specimen () with minimized edge effect and the sound absorption performance on the specimen surface were proposed as an evaluation indicator of agreement between the values. Experimental results show that diffusion inside the reverberation chamber is enhanced when < 0.02, for which sufficient diffusion can be assumed inside the reverberation chamber. In addition, to verify the validity of the proposed evaluation indicator, we investigated the relationship with the objective diffusion evaluation indicator for diffuse field configuration in the reverberation chamber, such as relative standard deviation of decay rate () and Np values. The results of this study are expected to contribute to a more accurate estimation of the sufficient diffusion condition in the reverberation chamber, in evaluating the sound absorption performance of the material, and that inside the reverberation chamber.
1. Introduction
The sound absorption characteristics of various finishing materials or vegetation used inside and outside a building are important factors determining the sound environment of the space. The sound absorbing characteristics of these materials are measured by random incidence based on the Sabine reverberation formula given in ISO 354 (2003) or ASTM C423 (2017). In particular, the sound absorption performance of vegetation materials is an important factor in analyzing sound propagation outside the building and predicting sound environment through scale modeling [1,2]. In addition, the outdoor sound propagation is affected by the sound absorption of the irregular shape of the building as well as the sound absorption by vegetation, which shortens the reverberation time of the space [3]. Therefore, for proper understanding of these phenomena, it is necessary to accurately analyze the sound absorption performance of the building materials to be used. The underlying assumption is that the reverberation chamber, which is the measurement space of this study, is a diffuse sound field [4,5,6]. The diffusion state inside the reverberation chamber varies according to the shape of the reverberation chamber and the size of the space [7,8]. Moreover, it is not straightforward to estimate the precise sound absorption performance of the specimen because it is difficult to ensure sufficient diffuse sound field conditions inside the reverberation chamber when measuring the sound absorption coefficient of specimens with high sound absorption performance [9]. Therefore, a reverberation chamber design with no parallel planes has been proposed to avoid the occurrence of a room mode formed in the reverberation chamber and ensure sufficient diffusion [10,11]. ISO 354 [12] also specifies achieving a sufficiently diffuse sound field by increasing the installation area of the diffusion plate by 5 m2 until there is no further enhancement of the sound absorption performance of the specimen. Many other international standards describe the installation dimension of the reverberation chamber [13,14,15,16]. However, even if a diffusion plate is installed according to these procedures, it has been reported that there are still significant differences between sound absorption performance data from different laboratories [17,18], and the reason is assumed to be that the diffusion states of the reverberation chambers are different from each other [19]. The sound absorption coefficient error between these different reverberation chambers is an important factor in determining the sound absorption characteristics of various materials not only indoors but also outside the building. In addition, accurate measurement of sound absorption performance characteristics is an important research subject, because the required sound absorption performance of the building materials is determined in the design stage of the building through scale modeling or simulation analysis [20].
Previous studies have shown that the addition of a diffusion plate following the ISO 354 measurement procedure does not always provide an optimal diffuse field due to the additional sound absorption and the occupancy of the spatial volume of the diffusion plate [21]. Therefore, to evaluate the sound absorption performance of the specimen surface more accurately, it is necessary to investigate a measurement method to quantitatively determine whether sufficient diffusion occurs in the reverberation chamber. Previous studies on the diffuse field in the reverberation chamber [22,23,24] show the limitations in accurately defining the sufficient diffusion state of the reverberation chamber and evaluating the extent of diffusion. Davy et al. argued that the standard deviation of the reverberation time according to the location of the microphone in the reverberation chamber can be used as an indicator for evaluating the diffusion of the space. In their report, the ratio of the standard deviation of the measured reverberation time to the theoretical reverberation time was defined as “diffuse field factor,” and they proposed that the factor can evaluate the diffusion in the chamber [8]. As a result, the inside of the space is in diffusion state when the standard deviation of the measured reverberation time is smaller than the standard deviation of the theoretical reverberation time. They further argued that the indicator had limitations in assessing the small effects from changes in indoor diffusivity.
However, Vorlander reported that when there are many diffusers in the chamber, the peak level of the impulse response decreases in the time domain and the density of the peak level increases [25]. In this regard, Jeon et al. proposed the number of peaks (Np) of the impulse response as a method for evaluating the indoor diffusivity according to the surface type inside a chamber [26], and it was verified that when the diffusion plate was installed on the surface of the chamber inside, a higher Np was observed in the high frequency domain. As a result, the indoor diffusivity can be evaluated using the Np values. However, these previous studies emphasize the evaluation of diffusivity but do not provide clear solutions for the evaluation of optimal diffusion conditions inside the reverberation chamber. Although the extent of improvement of diffusion in specific conditions can be evaluated, there is little research on accurate evaluation of diffusivity of the reverberation chamber required to evaluate the sound absorption coefficient. Therefore, in this study, we have investigated a method to quantitatively evaluate the diffusivity necessary for sound absorption coefficient measurement in a reverberation chamber. For this purpose, we first define the concept of sufficient diffusion within the reverberation chamber and propose a new evaluation indicator, , where is the sound absorption coefficient of the infinite plate, and is the sound absorption coefficient of the specimen, which has an almost negligible edge effect. Based on proposed in the previous studies, was obtained, and for the calculation of , we have proposed and verified a specimen installation method that produces minimal edge effect of the specimen. Finally, the proposed evaluation indicator was validated by the analysis of correlation between , the proposed evaluation indicator, and Srel and Np values, the proposed diffusion evaluation indicators presented in previous studies.
2. Diffusivity Evaluation Method
2.1. Definition of Sufficient Diffusion
For the diffusivity evaluation of the reverberation chamber, it is not possible to determine which evaluation indicator accurately represents the indoor diffusivity among the many evaluation scales proposed in previous studies [27]. Although much research has been done to date, there are no adequate measures for the evaluation because there is no consensus on the definition of sufficient diffusion in the reverberation chamber. Therefore, in this study, we defined sufficient diffusion in the reverberation chamber as "the state in which the effect of indoor diffusivity on the sound absorption performance evaluation of the specimen is minimized" and performed an experiment on the evaluation method. In other words, this study does not present another measure to evaluate the diffusivity but differs from the previous studies in the sense that the study aims to measure how sound absorption performance of the specimen is affected by the indoor diffusion state. The experimental procedure for the evaluation is as follows. It is clear that when a specimen with a high sound absorption performance is installed inside the reverberation chamber, it is a non-diffuse state. If the inside of the reverberation chamber is in the perfect diffusion state and the size of the specimen is infinitely large such that no additional sound absorption occurs due to the edge effect, the sound absorption coefficient value () of the specimen measured under these conditions will be the sound absorption performance of the specimen surface. In other words, when the sound absorption coefficient is measured for an infinitely large specimen in a laboratory with a good diffuse field condition, a sound absorption coefficient value that is close to the sound absorption performance of the specimen surface can be measured.
2.2. Minimizing Edge Effect and Measuring Sound Absorption Performance of the Specimen Surface
2.2.1. Minimization of Edge Effect
As argued in Section 2.1, in order to determine if the chamber has reached a sufficient diffusion state by installing the diffusion plate inside the reverberation chamber and enhancing the diffuse field, the experiment has to be conducted for an infinitely large specimen for which there is no edge effect. However, this is impossible practically. As the measurement of the sound absorption coefficient is performed for a specimen with finite size, the edge effect occurs depending on the relative ratio of the edge length to the area of the specimen. The edge effect is a diffraction phenomenon that occurs when sound is incident on the discontinuous acoustic impedance surface existing on the edge and boundary of the specimen [28]. Thus, when the border of a reflective material higher than the specimen height is placed on the edge of the specimen, the sound absorbed by the side of the specimen can be minimized and the sound absorption performance of the sound incident on the front face can be measured. Kawakami proposed a method to minimize the edge effect during sound absorption coefficient measurement by applying a border of reflective material to the edge of the specimen [29]. Therefore, in this study, we also propose a method of measuring the sound absorption coefficient by installing a border higher than the specimen surface on the specimen edge to minimize the edge effect. The optimal height of the borders was determined by evaluating the sound absorption performance by increasing the height by 50 mm intervals on the specimen surface, as shown in Figure 1. The borders were installed at a height of 150 mm to obtain the sound absorption performance value closest to that of the specimen surface which has 50 mm thickness. If the border height is not sufficiently high, the edge effect will not disappear, so the absorption coefficient is high. On the other hand, if the border is too high, sound incidence to the specimen surface will be blocked by the border, therefore the sound absorption coefficient becomes lower.
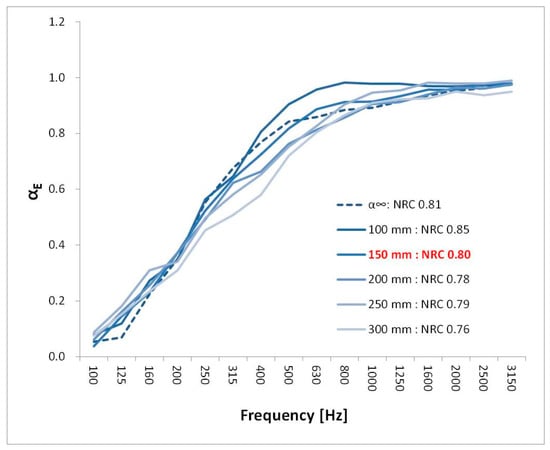
Figure 1.
Sound absorption performance for different border heights.
Next, we conducted an experiment to verify whether edge effects can be minimized when a border is installed, as shown in Figure 2. When the size of the specimen is small, the sound absorption performance is high owing to the edge effect, because the edge length is large compared to the area. If the edge effect is minimized by installing a border on the edge of the specimen, a similar sound absorption coefficient value should be obtained, regardless of the specimen size.
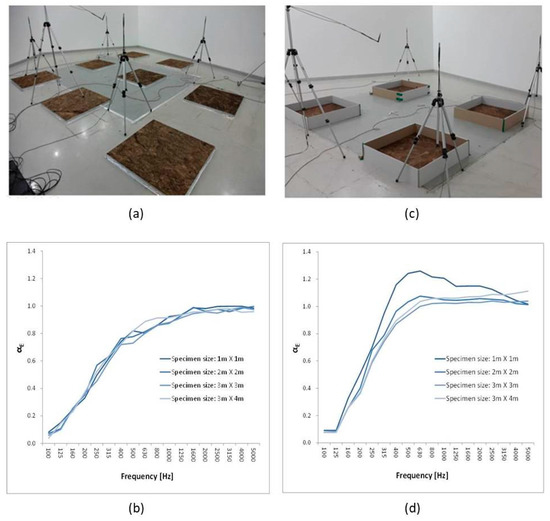
Figure 2.
Test results of sound absorption performance with border installed. (a) specimen without border; (b) specimen with border; (c) sound absorption according to specimen size (without border); (d) sound absorption according to specimen size (with border).
Figure 2 illustrates the experiment in which the sound absorption coefficient was compared and evaluated. The experiment was categorized into two cases: one case in which borders were installed on the sides of the specimen and the other case without borders installed. Specimens with sizes of 1 × 1, 2 × 2, 3 × 3, and 3 × 4 m2 were measured. The installation height of the border was 150 mm from the specimen surface, and a diffusion plate was installed. Figure 2a,b depicts the case in which borders were not installed on the sides of the specimen. In this case, the sound absorption coefficient of different sizes of samples was measured. The results revealed that the smaller the size of the specimen, the higher the sound absorption coefficient, owing to the edge effect. Figure 2c,d depicts the case in which borders were installed on the sides of the specimen. Here, the results revealed that an almost uniform sound absorption coefficient was obtained regardless of the specimen size.
No linear correlation was observed between the specimen size and the sound absorption coefficient. The experimental results demonstrated that the sound absorption performance of the specimen surface with a minimal edge effect can be measured more precisely when a border with a height of 150 mm made of reflective material was placed on the sides of the specimen. Therefore, it is expected that the use of the specimen installation method proposed in this study (Figure 3a) may reduce the deviation in the sound absorption performance test results between different test laboratories, in comparison with the specimen installation method recommended in the existing international standards (Figure 3b).
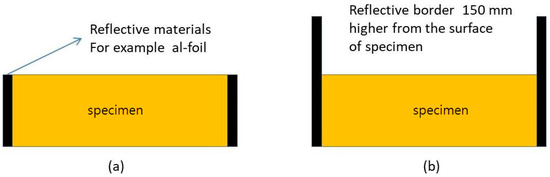
Figure 3.
Specimen installation method, existing international standards (a), and supposed method in this study (b).
2.2.2. Extrapolation of Sound Absorption Coefficient of Infinite Plate
To evaluate , the sound absorption coefficient of an infinitely large specimen corresponding to the sound absorption performance of the specimen surface needs to be evaluated. However, because such measurements are not possible in practice, we deduced based on the experimental method proposed by Kosten [30]. Kosten argued that the sound absorption coefficient ( of the specimen measured in a reverberation chamber with a sufficient diffuse field is equivalent to the sum of the edge effect and the sound absorption performance () of the specimen surface, and the linear correlation between these indicators was verified by Gompertz [31], Wolde [32], and Lauriks [33]. Therefore, if the reverberation chamber has sufficient diffusion, the specimen is installed in such a manner as to minimize the edge effect (), and then, the sound absorption performance () is evaluated. is expected to be similar to ; otherwise, it can be assumed that the diffusion condition of the reverberation chamber affects the sound absorption performance of the specimen. To verify this, the sound absorption performance of the specimen surface was measured by the following method and the calculation procedure is defined in Equation (1).
Here, is the edge effect constant and is the relative edge length.
If the relative edge length of the sample and the sound absorption rate linearly correlated, supposing the sound absorption coefficient is assumed as the Y-axis and the E value is the X-axis, and the correlation between the two parameters is expressed as the first equation, the slope of the first equation becomes the value.
2.3. Specimen Design and Measurement Conditions
In Equation (2), when the specimen area is infinitely large and the sum of the total edge length (E) of the specimen is divided by the area, the obtained value becomes 0. Thus, it can be concluded that the sound absorption performance of an infinitely large specimen () has the same value as the sound absorption performance of the specimen surface without the edge effect. However, to measure in a laboratory, its value can only be obtained by inference. In other words, the specimen size can be gradually increased, as presented in Table 1, and the sound absorption performance can be measured. Then, based on the results, can be deduced through the linear equation, Equation (1). The specimens to be measured were constructed from glass fiber (density = 24 kg/m3, thickness = 50 mm), which has a high sound absorption performance, with areas from 0.25 to 16 m2, as specified in Table 1. To obtain the value of for which the value of E converges to 0 for each frequency band, multiple specimens of various sizes with a minimum length of 0.5 m were installed on the floor. Measurements were performed in a five-sided Kumgang chemical company reverberation chamber with no parallel faces. Its volume and surface area were 246.4 m3 and 234.5 m2, respectively. In addition, for the indoor diffusion, a diffuser made of polycarbonate material was installed with a surface density of 5.4 kg/m2 and an area of 50 m2 including the front and rear areas, which was approximately 25% of the total surface area of the reverberation chamber. In the ISO 354, more than one diffuser with different sizes are recommended, and 15–25% of the total surface area is required for sufficient indoor diffusion, and the installed diffuser area of the laboratory in which the previous study [30] was conducted accounted for 23% of the total surface area.

Table 1.
Test specimen dimensions.
3. Results
3.1. Sound Absorption Coefficient of Infinite Plate
As presented in Table 1, the sound absorption coefficient was measured by increasing the specimen size. The results revealed that, as in Figure 4, as the area of the specimen decreased, i.e., as the value of E increased, the value of the sound absorption coefficient increased linearly. Because the edge length is relatively larger than the specimen area, the sound absorption caused by the edge effect is greater than that on the specimen surface. If the same size is smaller than 4m2, sound absorption coefficient should be higher than one because of edge effect and this is the same result with previous study about edge effect. Previous study summarized the reasons why the sound absorption coefficient can exceed the unit. Edge diffraction which produces edge effect, non-diffuseness in chamber, and sabine formulation should not be applied when the mean absorption is higher than 0.4 [34].
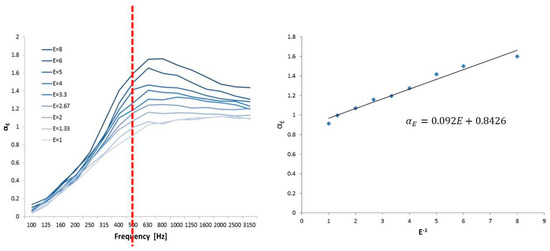
Figure 4.
Results of sound absorption performance for different relative edge lengths (E).
The E values and regression equations of the sound absorption performance () for each frequency band were obtained from the data given in Figure 4, and the results are presented in Table 2. If the relative edge length of the sample and the sound absorption rate linearly correlated, supposing the sound absorption coefficient is assumed as the Y-axis and the E value is the X-axis, and the correlation between the two parameters is expressed as the first equation, the slope of the first equation becomes the value.

Table 2.
Extrapolated equation between and relative edge length (E).
On the other hand, the E value of an infinitely large specimen can be zero because the denominator is infinitely large relative to the numerator. Therefore, when E is 0 in the regression equation, is the sound absorption performance of an infinitely large specimen. The y-intercept of the regression equation for each frequency, shown in Table 2, indicates the sound absorption performance of the infinite plate (), and the gradient corresponds to the edge effect constant (). In the existing standard specifications [11,12], various mounting methods for finishing the edges of the specimen with a reflective material are specified. However, because these methods cannot minimize the edge effect, there is a limitation in measuring the sound absorption performance of the specimen surface. In particular, there is a sizeable difference in the installation area between the minimum installation area recommended by ISO 354 (10 m2) and that stipulated in ASTM C 423 (6.69 m2). This is a factor that increases the differences in the measurement results as different edge effects arise depending on the width and length of the specimen. The measurement results presented in Table 2 indicate that the sound absorption coefficient increased by 0.07–0.09 due to the edge effects, although the sound absorption coefficient was evaluated for specimens with sizes of 10–12 m2 which is the size recommended by the international standards. Therefore, it is necessary to improve the installation method of the specimen so that the values can be evaluated with the minimized edge effect.
3.2. Comparison between and
In this study, sufficient diffusion inside the reverberation chamber is defined as the state with minimized effect on the sound absorption coefficient measurement of the specimen. To quantitatively determine this condition, the sound absorption performance of the infinite plate () was deduced, as described in Section 3.1. In Section 3.2, the sound absorption performance of the specimen with minimal edge effect () is measured. If the difference between and is large despite the sound absorption performance being evaluated with the minimized edge effect, we can conclude that sufficient diffusion was not achieved inside the reverberation chamber. Therefore, the value of was analyzed to determine whether sufficient diffusion was achieved in the reverberation chamber during this experiment. To evaluate the effect of the diffusion condition change in the reverberation chamber on the sound absorption coefficient measurement, the above experiment was repeated with no diffusion plate installed. In addition, the same experiment was conducted in the reverberation chamber with a diffusion plate installed, and a comparative analysis was performed.
(With and without Diffuser)
The experiment was conducted in the KCC reverberation chamber with an installed diffusion plate, which was equivalent to 25% of the total surface area and was installed based on the ISO 354 diffusion plate installation method. Number of each type of diffuser is shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Number of each type of diffuser.
As given in Figure 5b, of glass wool (density = 24 kg/m3, thickness = 50 mm) was estimated to be 0.94 (NRC: Noise Reduction Coefficient), measured without a border installed at the edge of the specimen. The sound absorption performance deduced as the sound absorption performance of the specimen surface was NRC 0.81, indicating a large difference from the NRC 0.94. However, the sound absorption performance () with the minimized edge effect, was evaluated to be NRC 0.80, and the value was similar to the sound absorption performance of the specimen surface. Therefore, it can be concluded that the reverberation chamber in which the experiment was conducted had sufficient diffusion to measure the sound absorption performance.
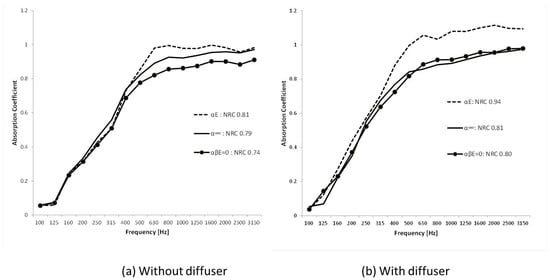
Figure 5.
Comparison between and : (a) without diffuser, and (b) with diffuser.
Next, the same experiment was repeated with all the diffusion plates removed from the reverberation chamber to check if this caused the value of to change. The value was 0.01 when the diffusion plate was installed inside the chamber; however, the value of increased to 0.05 when the diffusion plate was removed. In particular, the difference was 0.05–0.1 at 500 Hz or higher. Therefore, by analyzing the value of , we expect that it can be used as an indicator to determine whether adequate diffusion is available for the evaluation of the sound absorption performance in the reverberation chamber. The effect of the diffuse field condition on the sound absorption performance can be defined as , and the comprehensive results of the above experiment are depicted in Figure 6. The majority of porous sound absorbing materials, including glass wool used in the test, exhibit a low sound absorption performance in the frequency range below 250 Hz; therefore, the sound absorption performance does not change much with respect to the diffusion conditions. The value was 0.05 or higher when the diffusion plates were not installed, and the value decreased to 0.02 or lesser when the diffuse field was improved by installing a diffusion plates. When the value of is close to 0, it indicates that the diffusion conditions are optimal, and it is difficult to determine the minimum value to provide sufficient diffusion. However, considering that the standard measurement uncertainty for the sound absorption coefficient in the KCC reverberation chamber is NRC 0.02, if is 0.03 or greater, then we can determine that the value of is significant. Therefore, when , we can conclude that sufficient diffusion has been achieved for the sound absorption coefficient measurement inside the chamber.
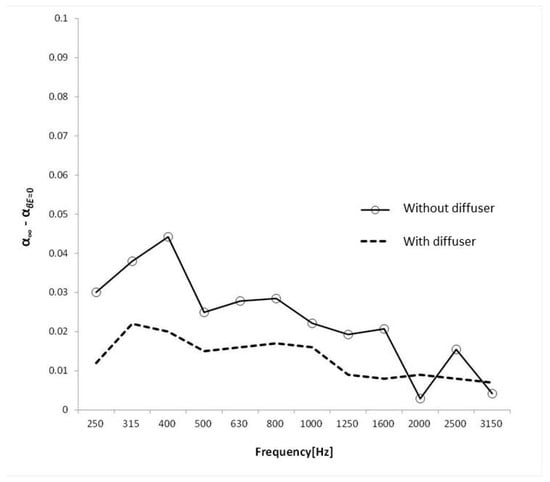
Figure 6.
value according to the diffuse field conditions.
4. Discussion
4.1. Sound Absorption Performance of Finishing Materials in Predicting the Reverberation Time of Buildings
Ray tracing is the most commonly used simulation method to estimate the reverberation time of indoor spaces such as large concert halls, conference rooms and auditoriums. After modeling the shape of the building, the sound absorption performance for each frequency band, typically measured by ISO 354 or ASTM C 423, of the finishing material is input. However, because the minimum installation area of the specimens recommended by the two standards is different, the effect of the edge effect on sound absorption is not constant. According to a recent study [35], for high-performance sound absorption materials, the installation area of the specimen can cause a large deviation in the measured sound absorption performance. Thus, the sound absorption performance of a finishing material sample obtained by the conventional measurement method may be different from the sound absorption performance when installed in an actual building. In addition, ceiling and wall surfaces to which finishing materials are applied may have an area of 100 m2 or larger. The edge effect occurring under this condition is smaller than the edge effect occurring in laboratories where the evaluation is performed on specimens of perhaps 10 m2. Therefore, when estimating the reverberation time of a large space, when the total area of the finishing material applied to the ceiling, floor, and wall is much larger than the area measured in the laboratory, more accurate estimation will be achieved by inputting the sound absorption performance value evaluated under conditions that minimize the edge effect. The average sound absorption coefficient of the specimens used in this study was 0.90 and the edge effect constant was in the range between 0.05 and 0.1. According to Equation (1), when the relative edge length (sum of edge length/area) is 1, additional sound absorption corresponding to 0.05 to 0.1 may occur due to the edge effect. Therefore, if the area of the sound absorbing material used in the actual building is large and the relative edge length is less than 0.5, more accurate prediction may be achieved when we use rather than in Equation (1). However, estimating the value for all specimens is very expensive and time-consuming. In this regard, we propose the use of because it has the closest value. Therefore, we argue that a standardized specimen installation method is needed to evaluate , and a method of installing a border at the edge of the specimen is necessary.
4.2. Relative Standard Deviation of Decay Rate
In ASTM C 423, the relative standard deviation of the decay rate () is proposed as an evaluation metric to achieve sufficient diffusion in an indoor space. This standard provides the maximum allowable value of for each frequency band and recommends that the value measured by each microphone should be within this allowable range. However, when using this evaluation indicator, a large deviation in the sound absorption performance of each measurement site occurs even though diffusion within the allowable range is ensured within the reverberation chamber. Therefore, this study proposed as an evaluation method to quantitatively determine sufficient diffusion. In this experiment, to validate values, we compared the correlation of frequency bands with the diffuse field evaluation indicator proposed by ASTM C 423. ASTM C 423 specifies the maximum allowable displacement of the decay rate depending on the location of the microphone. The decay rate can be calculated as follows.
Here, represents the decay rate measured at the i-th microphone, represents the reverberation time at the i-th position, and is the air attenuation coefficient calculated according to ISO 9613-1.
Therefore, the standard deviation of decay rate between the positions of the microphones in the 1/3 octave band frequency band can be calculated by Equation (4).
Here, represents the standard deviation of decay rate, is the number of microphones, and denotes the decay rate averaged over all microphones.
Finally, the relative standard deviation of decay rate ( was calculated as and the calculation results for in three different diffuse field conditions are shown in Figure 7.
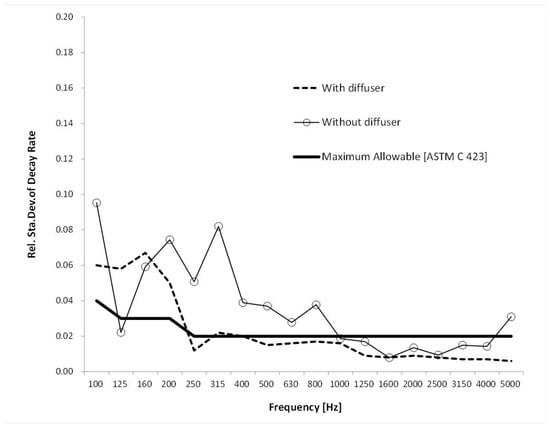
Figure 7.
Relative standard deviation of decay rate () for different diffuse field conditions.
The thick solid line in Figure 7 represents the maximum allowable value of the microphone for each frequency band specified in the ASTM standard. In a KCC reverberation chamber without a diffusion plate, the value exceeds the allowable range values in the standards, and the deviation is within the allowable range of 1000–4000 Hz. However, when the diffusion plate was installed, the value was within the allowable range over the entire frequency range of 250–5000 Hz, confirming that the diffusion inside the chamber is improved by installing the diffusion plate.
4.3. Correlation between and
To verify the value of proposed in this study, a correlation analysis was performed with the value. The results indicated that the frequency band of 100–200 Hz was not in the allowable range of the standard. Therefore, the correlation analysis was performed in the range of 250–5000 Hz, which was within the allowable range in the standard, and the result is shown in Figure 8. Because the value is a relative standard deviation of the reverberation time at each microphone position, the lower the value, the better the diffusion condition in the corresponding frequency band. It was also verified that the lower the value of , the better the diffusion condition. Figure 8 shows that there is a linear correlation between these indicators, so the value of can be used as an indicator to evaluate the diffusion condition inside the reverberation chamber. The advantage of using as an indicator of diffusivity in chamber is that we can determine the optimum status of sufficient diffusion in room, whereas the existing indicator only shows the maximum allowable value in room.
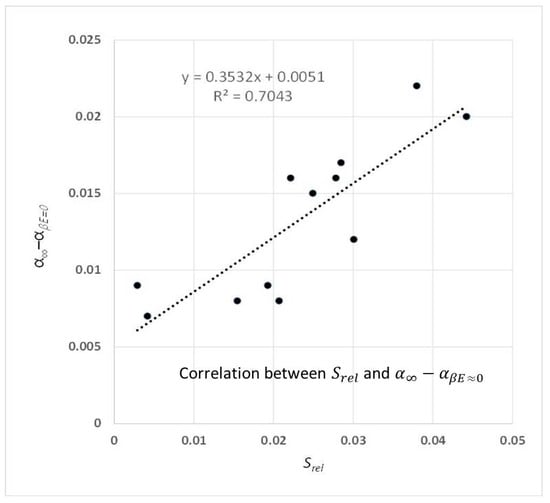
Figure 8.
Correlation analysis of decay rate () for different diffuse field conditions.
4.4. Number of Peaks
To verify the value, the value of number of peaks (Np), another diffusion indicator, was analyzed. The Np value was measured while increasing the number of diffusion plates installed in the reverberation chamber, and the correlation between the value of and the Np value according to the diffusion plate condition was examined. The installation area of the diffusion plate to total surface area of reverberation chamber was gradually increased to 6%, 11%, 15%, and 19%. The relative diffusivity index was defined as the relative value of Np when the proportion of diffusion plate area to surface area was increased between 0% and 19%. Consequently, Figure 9 shows that the Np value gradually increased as more diffusion plates were installed, and the rising curve showed a slow trend with installation over 19% of the total surface area of reverberation chamber. The value of was also 0.05 when the diffusion plate was not installed, but it decreased to 0.01 when the installation area became 19% of the total. Therefore, it can be verified again that the diffusion condition inside the chamber can be improved as the value of is minimized.
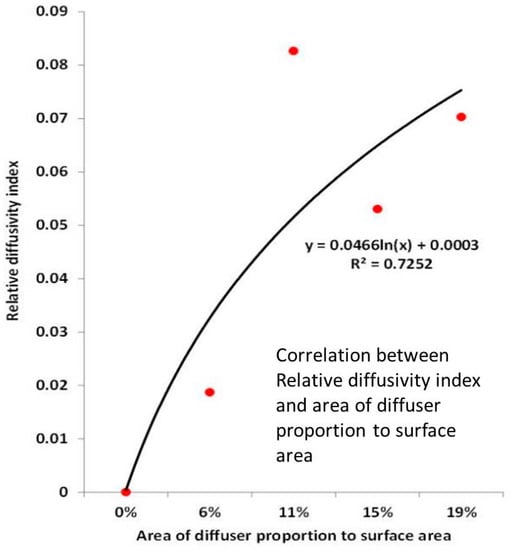
Figure 9.
Measurement of Relative diffusivity index.
5. Conclusions
In order to accurately model reverberation time in large spaces such as auditoriums, conference halls, and gymnasiums, accurate measurement of sound absorption performance of building materials is required. In addition, reducing the deviation between measurement results from different laboratories is also very important. Otherwise, manufacturers of sound-absorbing materials will continue searching for measurement institutions that provide potentially inaccurate but numerically better sound absorption performance results. There are many reasons for the large spread in results of sound absorption performance between laboratories. A recent study [36] showed the volume and shape of the reverberation chamber, type and area diffuser, the edge-effect, and the installation area of the sample are the major factors that influence the results. But the most influential factor in the deviation of data obtained between laboratories is the different diffusion conditions in their reverberation chambers. In this regard, this study investigated an evaluation method to determine whether sufficient diffusion conditions are implemented for the evaluation of sound absorption performance inside a reverberation chamber. Most previous studies investigated the development of an evaluation indicator of diffusivity, but this study quantitatively calculated the effect of diffusion conditions on the sound absorption performance of the specimen evaluated in the reverberation chamber and determined the diffusivity within the chamber. The factors affecting the sound absorption coefficient measured by the international standard are the sound absorption of the specimen surface, the edge effect, and the diffusion conditions inside the reverberation chamber. If we assume the conditions to be the realization of sufficient diffusion inside the chamber and the minimization of edge effects, the value of sound absorption coefficient () measured at this time should be almost identical to the value of the sound absorption coefficient () of the specimen surface. To verify this, we demonstrated that almost no edge effect occurred when a border of 150 mm from the specimen surface was installed on the edge of the specimen and compared the measured sound absorption coefficient value with that of the specimen surface. As a result, the NRC value difference between and was 0.02 when the diffusion plate was installed, but it increased to 0.05 without the diffusion plate. In other words, the difference between and decreases as the diffusion becomes sufficient, whereas when the diffusion is insufficient, the difference between and increases. Additionally, it exhibits a high correlation with and Np, the existing diffusion evaluation indicators. Therefore, if the value of and is 0.02 or less by the evaluation method proposed in this study, it may be possible to quantitatively determine whether sufficient diffusion is ensured in the reverberation chamber. Finally, to reduce the data deviation between test sites, we proposed a method of installing a border comprising a reflective material with a height that is 150 mm higher than the specimen height at the edge of the specimen. As the edge effect varies depending on the installation area or the ratio of the width and length of the specimen, this may also cause a large measurement deviation between the test sites. Therefore, an installation method that can measure the sound absorption performance of a specimen surface by minimizing the edge effect needs to be supplemented to the ISO or ASTM standard measurement methods. For the expansion of the evaluation index proposed in this study, further study under different conditions is required. Furthermore, additional experiments will be required for different types and thicknesses of sound absorbing materials. In future research, we will investigate the deviation of measurement results between the test laboratories after diffusion plate installation in the reverberation chambers according to the method proposed in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.H.K.; Writing-original draft, K.H.K.; Examination-identification, J.Y.J.
Funding
This research was supported by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation(NRF) and funded by the Korean government(MSIT) [grant number 2019M3E5D1A01069363].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.” Authors must identify and declare any personal circumstances or interest that may be perceived as inappropriately influencing the representation or interpretation of reported research results. Any role of the funders in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results must be declared in this section. If there is no role, please state “The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Picaut, J.; Simon, L. A scale model experiment for the study of sound propagation in urban areas. Appl. Acoust. 2001, 62, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornikx, M.; Forssén, J. A scale model study of parallel urban canyons. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2008, 94, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, R. Role of multiple reflections and reverberation in urban noise propagation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1974, 55, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morfey, C. Dictionary of Acoustics; Academic Press: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, T.J. Diffusion in reverberation rooms. J. Sound. Vib. 1971, 16, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, R.; Grewal, A. Reverberation rooms and spatial uniformity. Can. Acoust. Acoust. Can. 2008, 36, 28–29. Available online: https://jcaa.caa-aca.ca/index.php/jcaa/article/view/2021 (accessed on 22 November 2019).
- Park, H.; Jeon, J.Y. The effects of light equipment on the acoustic characteristics of a TV studio. Build. Environ. 2017, 120, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, E.; Sakamoto, S.; Tachibana, H. Effects of room shape and diffusing treatment on the measurement of sound absorption coefficient in a reverberation room. Acoust. Soc. Japan 2004, 25, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercammen, M.L.S. How to Improve the Accuracy of the Absorption measurement in the Reverberation Chamber. In Proceedings of the NAG-DAGA 2009, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 23–26 March 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sute, K.; Koyasu, M. On the New Reverberation Chamber with Nonparallel Walls (Studies on the Measurement of Absorption Coefficient by the Reverberation Chamber Method, II). J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1959, 1, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C 423-09a. Standard Test Method for Sound Absorption and Sound Absorption Coefficients by the Reverberation Room Method; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 354: 2003(E). Acoustics—Measurement of Sound Absorption in a Reverberation Room; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM Standard E596. Standard Test Method for Laboratory Measurement of Noise Reduction of Sound-Isolating Enclosures; Annual Book of ASTM Standards; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO Standard 17497-1. Acoustics—Sound-Scattering Properties of Surfaces—Part 1: Measurement of the Random-Incidence Scattering Coefficient in a Reverberation Room; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM Standard E492. Standard Test Method for Laboratory Measurement of Impact Sound Transmission through Floor-Ceiling Assemblies Using the Tapping Machine; Annual Book of ASTM Standards; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM Standard E90. Acoustics—Standard Test Method for Laboratory Measurement of Air-Borne Sound Transmission Loss of Building Partitions and Elements; Annual Book of ASTM Standards; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercammen, M. Improving the accuracy of sound absorption measurement according to ISO 354. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Room Acoustics, Melbourne, Australia, 29–31 August 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cops, A.; Vanhaecht, J.; Leppens, K. Sound absorption in a Reverberation Room: Causes of discrepancies on Measurement Results. Appl. Acoust. 1995, 46, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, M.; Vercammen, M.; Jeong, C.H. Effects of different diffuser types on the diffusivity in reverberation chambers. In Proceedings of the EuroNoise 2015, Maastrict, The Netherlands, 31 May 2015–3 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, H.; Kim, H.; Jeon, J. Scale-model method for measuring for noise reduction in residential buildings by vegetation. Build. Environ. 2015, 86, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, D.T.; Müller-Trapet, M.; Adelgren, J.; Vorländer, M. Comparison of hanging panels and boundary diffusers in a reverberation chamber. Build. Acoust. 2014, 21, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, D.T.; Müller-Trapet, M.; Adelgren, J.; Vorländer, M. Effect of boundary diffusers in a reverberation chamber: Standardized diffuse field quantifiers. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 135, 1898–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lautenbach, M.R.; Vercammen, M.L. Can we use the standard deviation of the reverberation time to describe diffusion in a reverberation chamber? In Proceedings of the Meetings on Acoustics, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2–7 June 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davy, J.L.; Dunn, I.P. The variance of decay rates in a reverberation rooms. Acta Acust. United Acust. 1979, 43, 12–25. [Google Scholar]
- Vorlander, M. Auralization; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 1–335. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, J.Y.; Jang, H.S.; Kim, Y.H. Influence of wall scattering on the early fine structures of measured room impulse responses. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 137, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mee, D.J.; Vallis, J. Improving Sound Diffusion in a Reverberation Chamber. In Proceedings of the Acoustics 2015 Hunter Valley, Pokolbin, Australia, 15–18 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tomasson, S.I. On the absorption coefficient. Acta Acust. United Acust. 1980, 44, 265–273. [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami, F.; Saka, T. Deep-well approach for canceling the edge effect in random incident absorption measurement. J. Acoust. Soc. Jpn. E 1998, 19, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kosten, C.W. International comparison measurements in the reverberation room. Acta Acust. United Acust. 1960, 10, 400–411. [Google Scholar]
- Gomperts, M.C. Do the classical reverberation formulae still have a right for existence? Acta Acust. United Acust. 1965, 16, 255–268. [Google Scholar]
- Ten Wolde, T. Measurements on the edge-effect in reverberation rooms. Acta Acust. United Acust. 1967, 17, 207–212. [Google Scholar]
- Lauriks, W.; Cops, A.; Belien, P. The influence of edge-effect on the statistical absorption coefficient. Acustica 1990, 70, 155–159. [Google Scholar]
- Scrosati, C.; Scamoni, F.; Depalma, M.; Granzotto, N. On the diffusion of the sound field in a reverberation room. In Proceedings of the 26th International Congress on Sound and Vibration, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–11 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vercammen, M. On the revision of ISO 354, measurement of the sound absorption in the reverberation room. In Proceedings of the ICA 2019 AACHEN, Aachen, Germany, 9–13 September 2019; pp. 3991–3996. [Google Scholar]
- Scrosati, C.; Annesi, D.; Barbaresi, L.; Baruffa, R.; D’angelo, F.; de Napoli, G.; Depalma, M.; di Bella, A.; di Filippo, S.; D’oraZzio, D.; et al. Design Principles of the Italian Round Robin Test on Reverberation Rooms. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Congress on Acoustics, Aachen, Germany, 9–13 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).