Maintenance Cost Estimation in PSCI Girder Bridges Using Updating Probabilistic Deterioration Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
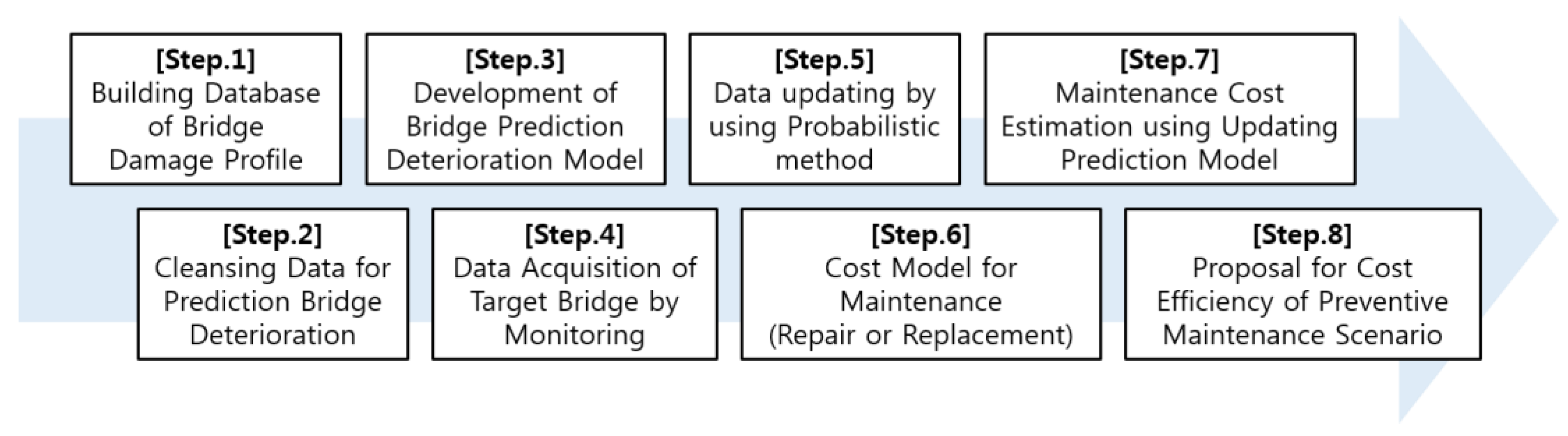
2. Bridge Deterioration Model
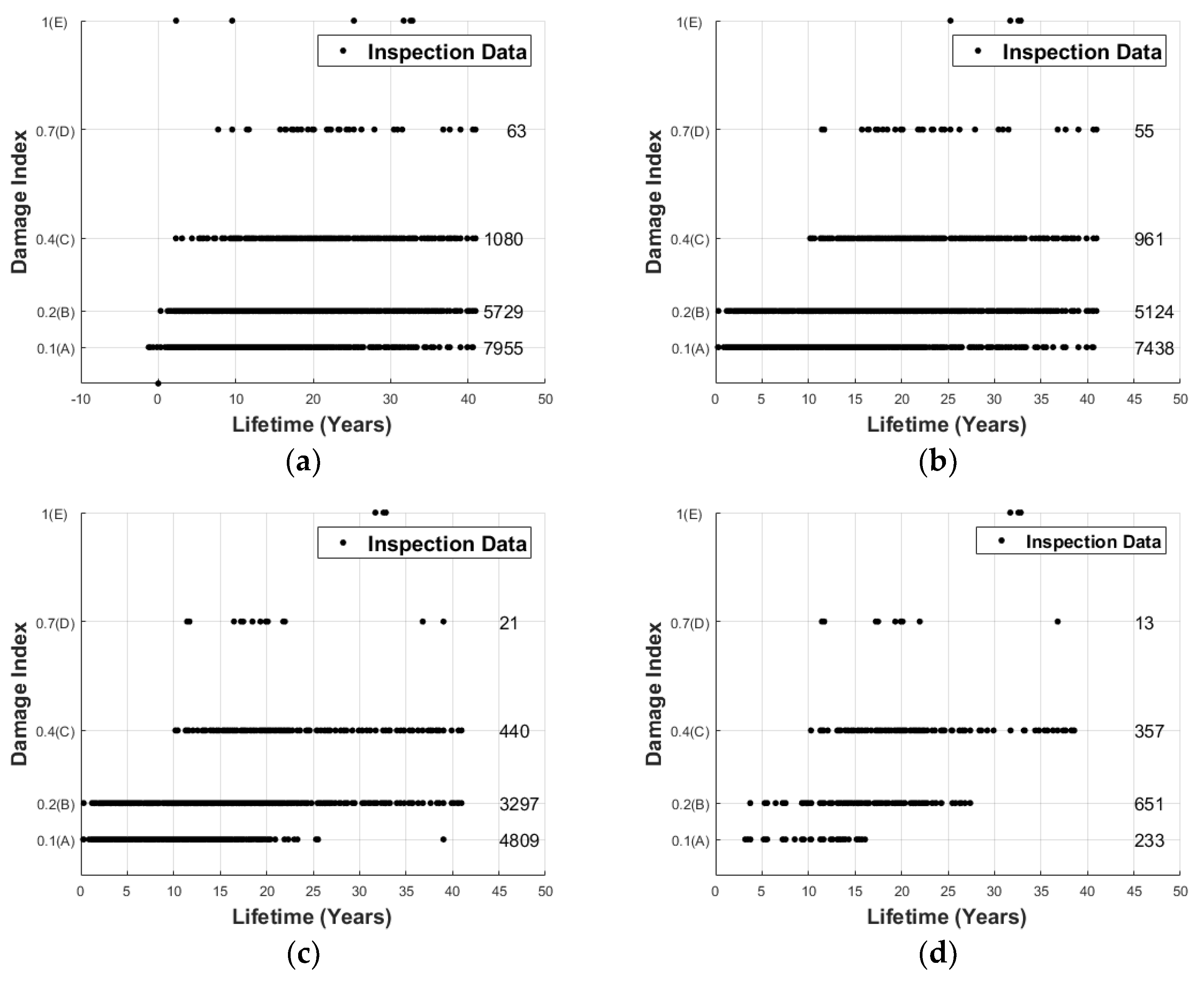
2.1. Cleansing Data for Prediction of Bridge Deterioration
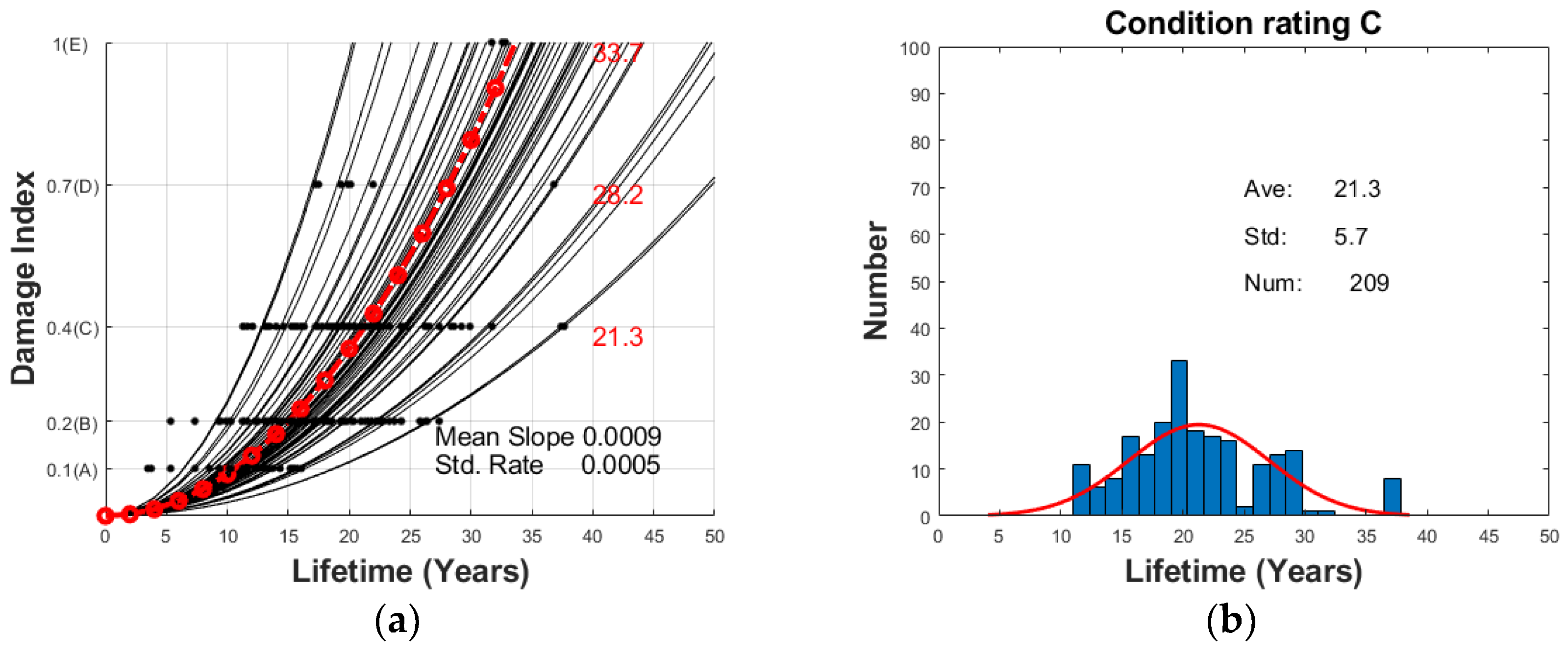
2.2. The Regression Analysis for Each State Condition History Data
3. Prediction of Bridge Deterioration Progress Based on the Particle Filtering
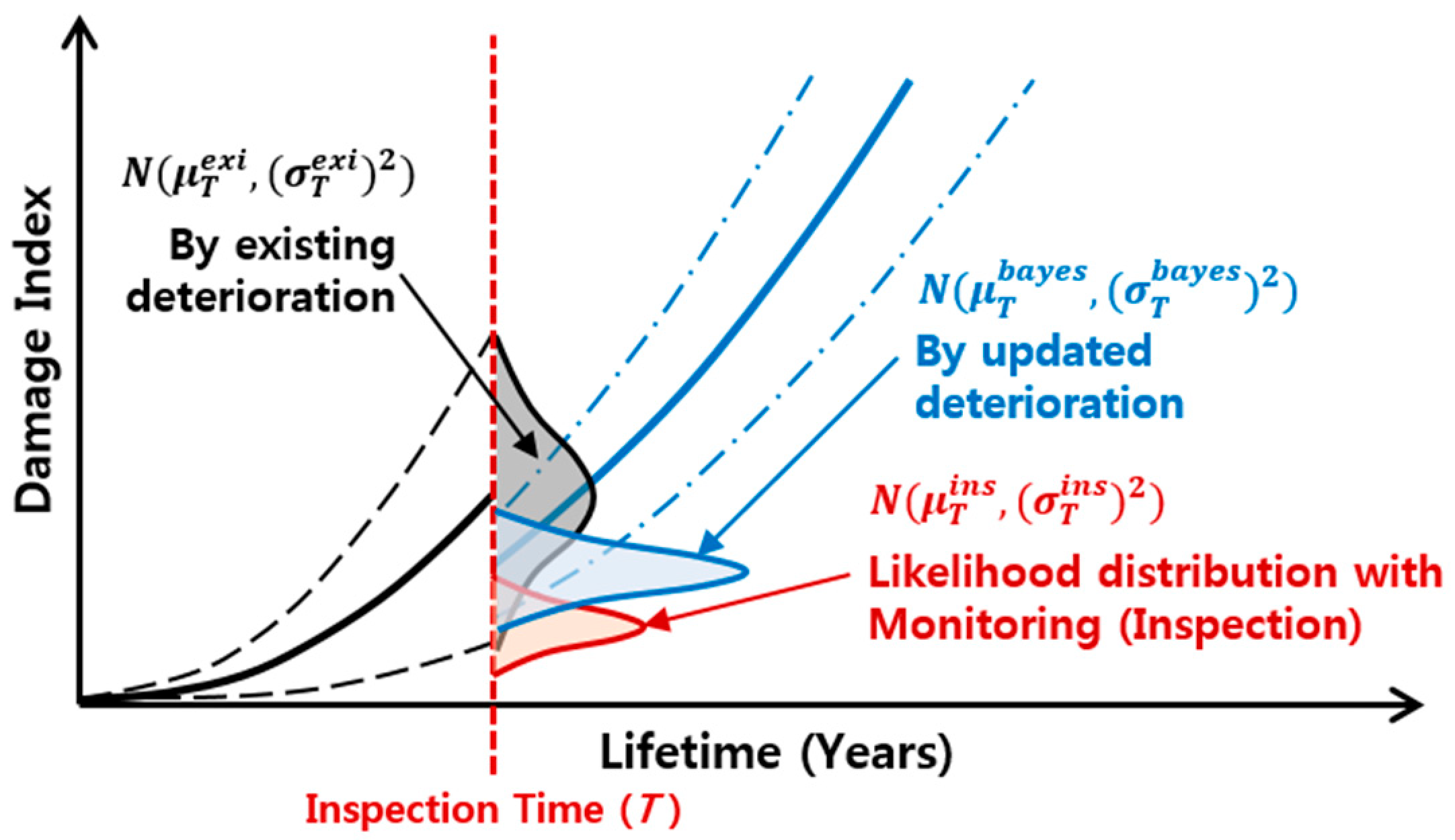
3.1. General Bayesian Updating
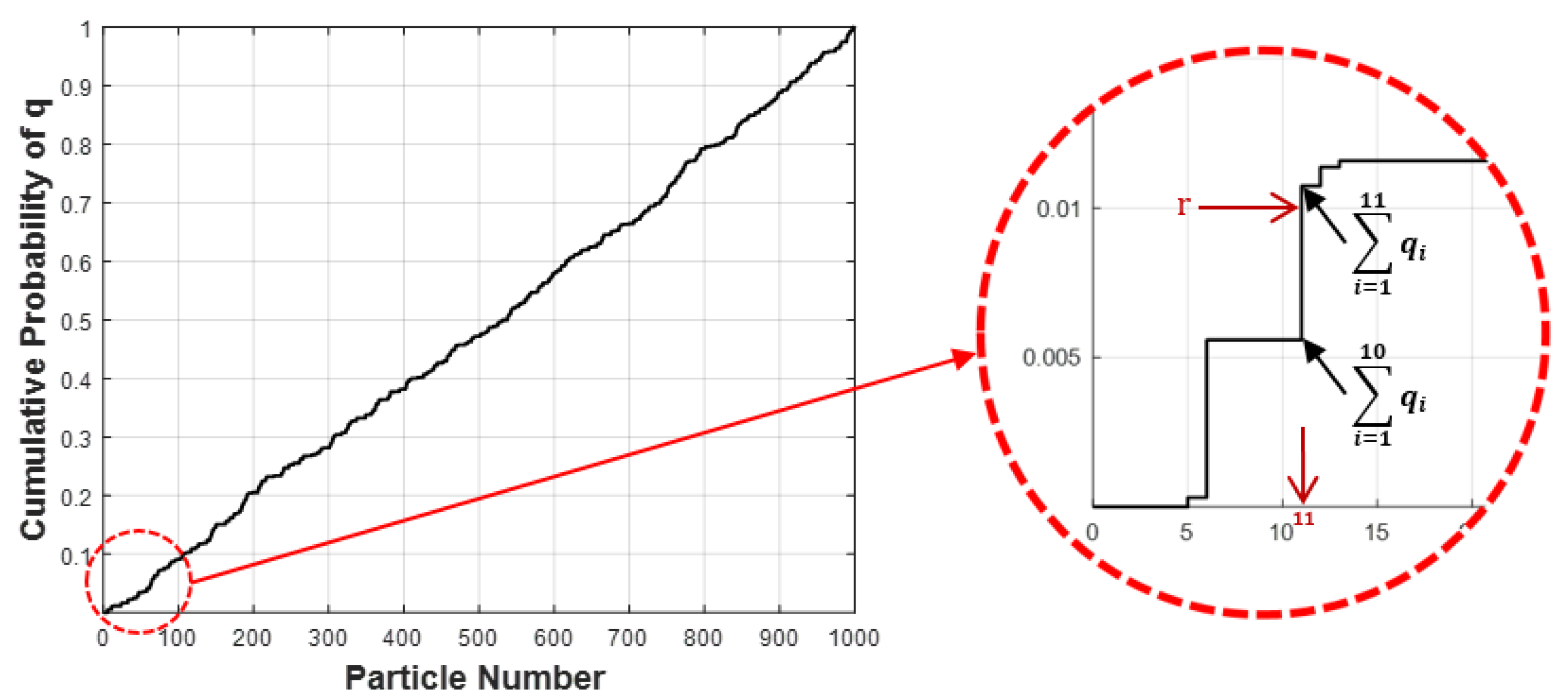
3.2. Particle Filtering Technique
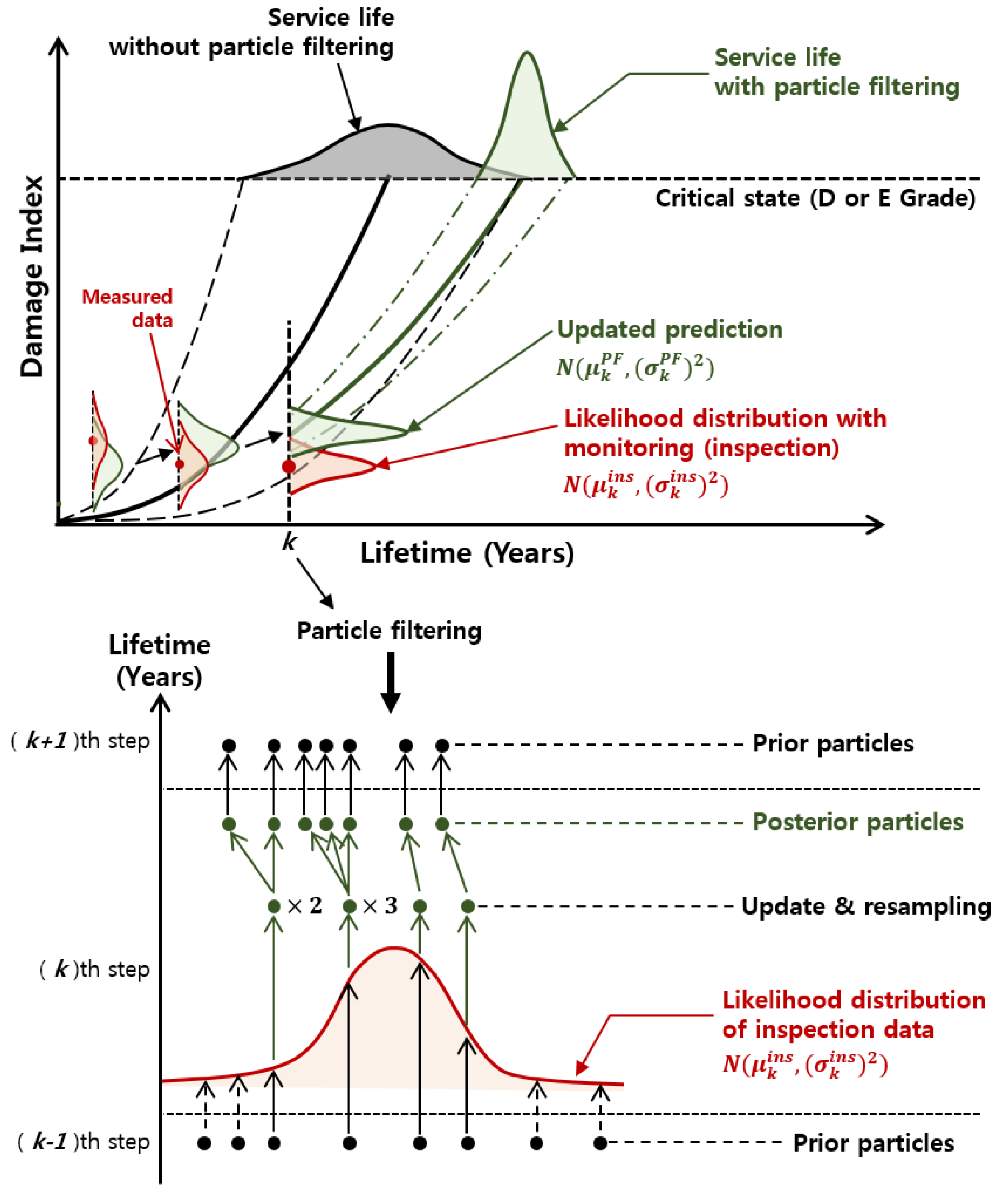
3.3. Particle Filtering Model for Prediction of Bridge Deterioration
3.4. Application of Particle Filtering Model
4. Preventive Maintenance Scenario for Operational Stage Bridge
4.1. Preventive Maintenance
4.2. Maintenance Cost Model
5. Effects of Proposed Method
5.1. Mokdo Bridge and Input Parameters
5.2. Maintenance Cost Model Applied to the Target PSCI Girder Bridge
5.3. Discussions Based on the Results of the Maintenance Cost
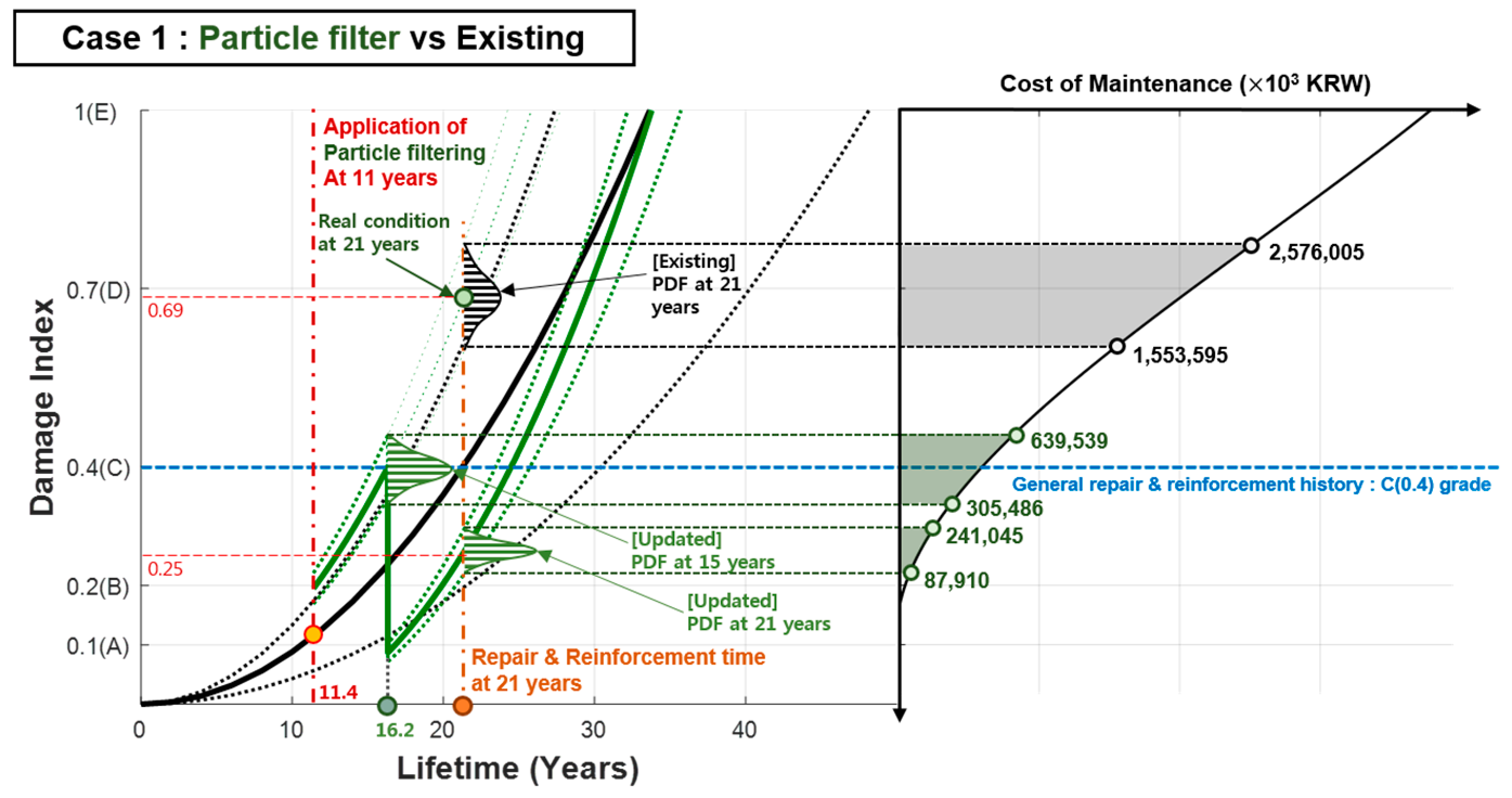
5.3.1. Case 1: Updated Mean State () < Existing Mean State ()
5.3.2. Case 2: Comparison to the Bayesian Updating Model
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- This study proposed potential maintenance scenarios (Case 1 and 2) by considering the particle filtering update based on big data using the monitoring technologies in the operational stage of the bridge that is currently in use and applying it to the specific element of the Mokdo Bridge (PSCI girder) so as to determine the cost saving because of the update for the existing deterioration model based on the general maintenance level setting (C rating). It was analyzed that such cost saving can be attributed to the increase in the maintenance cost (Figure 10), where the acceleration trend of the cubic polynomial curve was reflected more as the rating of the PSCI girder fell (D, E grade).
- (2)
- According to the example in (Section 5.3) for calculating the maintenance cost, which was considered in this study, the maintenance level of the bridge (rating) was set to C rating (0.4), and the particle filter update was performed for a specific time (eleven years). Case 1 showed a steeper slope when compared to that of the existing deterioration model, resulting in approximately 50% of the maintenance cost-saving effect. This was because the proposed model detected damage types, such as pre-stressed tendon, which could be difficult to detect using the existing visual inspection and nondestructive inspection, and allowed for the early prediction of posterior damages and the subsequent one-time preventive repair and reinforcement.
- (3)
- The proposed preventive bridge maintenance scenario using the particle filtering estimation broke away from the current maintenance system, where maintenance action is performed after the damages were detected by the inspection of almost D rated (0.69) bridges and where the condition of the maintenance target structures was accurately predicted. Thus, we presented the potential application of the proposed model for establishing a maintenance decision-making process, including the determination of the optimal repair and reinforcement period. It is expected that the particle filtering update-based maintenance scenario using monitoring technologies, which was proposed in this study, could save a considerable amount of repair and reinforcement cost when compared to the existing labor-based maintenance strategies, which could not determine the causes of early deterioration.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lake, N.; Seskis, J. Bridge Management Using Performance Models; Technical Report; Austroads: Sydney, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Emotoa, H.; Takahashib, J.; Widyawatic, R.; Miyamoto, A. Performance evaluation and remaining life prediction of an aged Bridge by J-BMS. Procedia Eng. 2014, 95, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thompson, P.D.; Small, E.P.; Johnson, M.; Marshall, A.R. The Pontis Bridge Management System. Struct. Eng. Int. 2018, 8, 303–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, M.P.; Frangopol, D.M. Condition Prediction of Deteriorating Concrete Bridges using Bayesian Updating. J. Struct. Eng. 1999, 125, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonta, D.; Zandonini, R.; Bortot, F. A reliability-based bridge management concept. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2007, 3, 215–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catbas, F.N. Structural health monitoring: Applications and data analysis. In Structural Health Monitoring of Civil Infrastructure Systems; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Castel, A.; Francois, R. The corrosion pattern of reinforcement and its influence on serviceability of reinforced concrete members in chloride environment. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Zhang, Z.; Salah, U.K. Reliability Data Update Method with Gamma Distribution. In Proceedings of the 2011 Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference, Wuhan, China, 25–28 March 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Orcesi, A.D.; Frangopol, D.M. Bridge Performance Monitoring Based on Traffic Data. J. Eng. Mech. 2013, 139, 1508–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.; Neves, L.; Matos, J.; Soares, J.S. A degradation and maintenance model: Application to Portuguese context. In Proceedings of the 7th International IABMAS Conference on Bridge Maintenance, Safety, Management, Resilience and Sustainability, Shanghai, China, 7–11 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Agency for Infrastructure Technology Advancement (KAIA). Large-Scale Infrastructure Monitoring and Management Using Unmanned Inspection Units; KAIA: Anyang-Si, Korea, 2016.
- Zampieri, P.; Curtarello, A.; Pellegrino, C.; Maiorana, E. Fatigue strength of corroded bolted connection. Frat. Ed Integr. Structturale 2018, 12, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Lee, M.K. Demand Forecasting in the Early Stage of the Technology’s Life Cycle Using a Bayesian Update. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Huh, S.Y. Forecasting Long-Term Crude Oil Prices Using a Bayesian Model with Informative Priors. Sustainability 2017, 9, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadollahi, P.; Huang, Y.; Li, J. Bayesian Finite Element Model Updating and Assessment of Cable-Stayed Bridges Using Wireless Sensor Data. Sensors 2018, 18, 3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Choi, Y.R.; Ann, H.; Kong, J.S. The Preventive Maintenance Strategy in Operation Stage of Bridge using Bayesian Inference. J. Korea Soc. Civ. Eng. 2019, 39, 135–146. [Google Scholar]
- Technical Report; Guideline and Commentary of Safety Inspection and In-Depth Safety Inspection for Structures-Bridge; Korea Infrastructure Safety & Technology Corporation (KISTEC): Seoul, Korea, 2017.
- Ang, A.; Tang, W. Probability Concepts in Engineering: Emphasis on Applications in Civil and Environmental Engineering, 2nd ed.; Willey: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 346–365. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, D. Optimal State Estimation: Kalman, H-Infinity, and Nonlinear Approaches; John Willey & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 461–483. [Google Scholar]
- Dowd, M.; Joy, R. Estimating behavioral parameters in animal movement models using a state-augmented particle filter. Ecology 2011, 92, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Zi, G.; Mun, S.; Kong, J.S.; Choi, J.H. Probabilistic prognosis of fatigue crack growth for asphalt concretes. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2015, 141, 212–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, M.C.; Lee, S.J.; Cha, K.; Zi, G.; Kong, J.S. Probabilistic model forecasting for rail wear in seoul metro based on Bayesian theory. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2019, 96, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, H. Bridge Life-Span Extension Using ICT, Partial Replacement and Low-Carbon Materials; Technical Report; Korea Agency for Infrastructure Technology Advancement (KAIA): Anyang, Korea, 2018.
- Frangopol, D.M.; Neves, L. Structural Performance Updating and Optimization with Conflicting Objectives under Uncertainty. ASCE J. Struct. Eng. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.W.; Park, K.H.; Kwang, J.K.; Kong, J.S.; Park, D.H. Study on Bayesian Probability Model for Estimation of Bridges Performance. In Proceedings of the 2010 Korean Society of Civil Engineers Conference, Incheon, Korea, 20–22 October 2010; pp. 1345–1348. [Google Scholar]
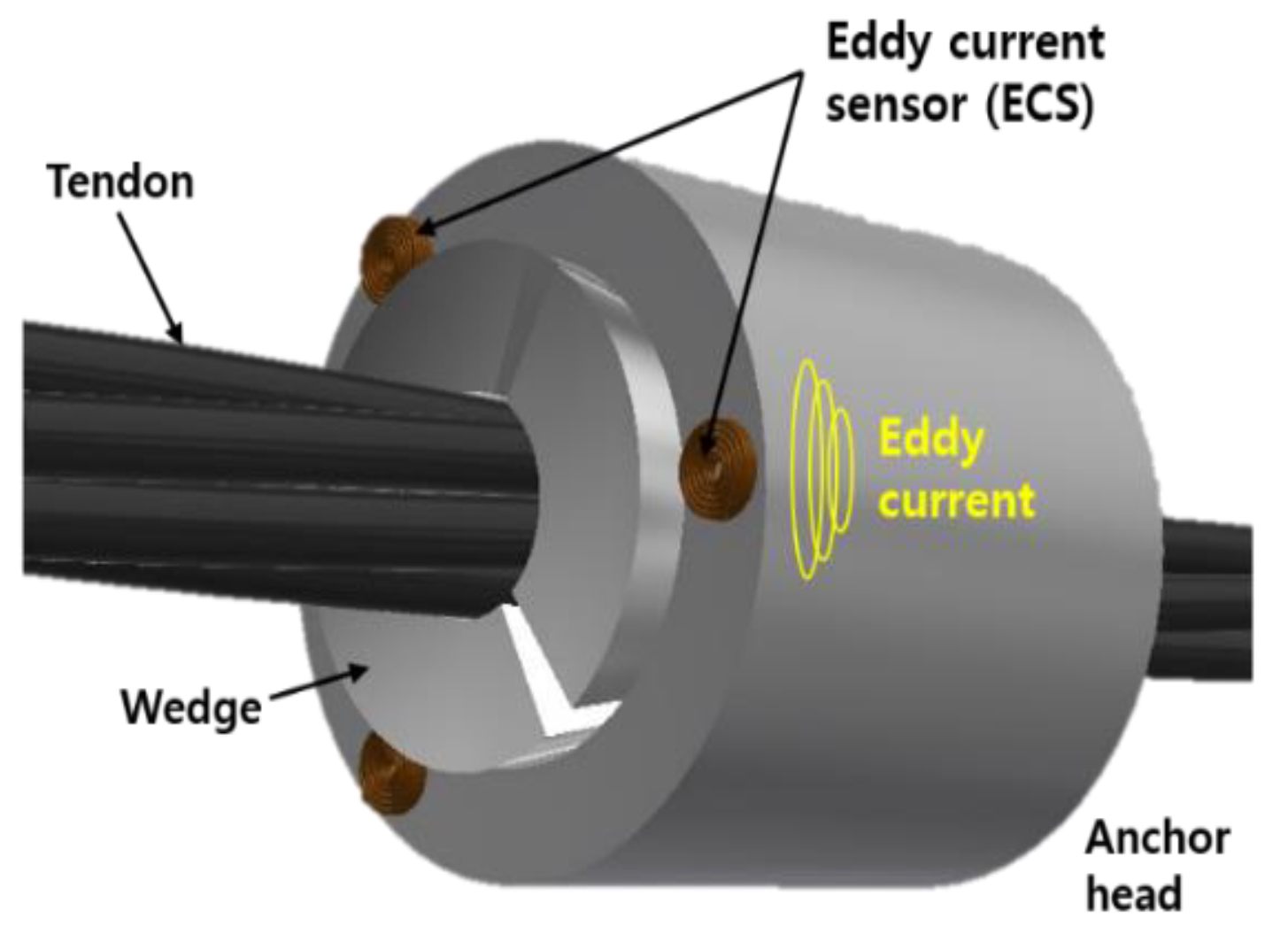
- Kim, J.-M.; Lee, J.; Sohn, H. Automatic measurement and warning of tension force reduction in a PT tendon using eddy current sensing. NDT E Int. 2017, 87, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-M.; Lee, J.; Sohn, H. Detection of tension force reduction in a post-tensioning tendon using pulsed-eddy-current measurement. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2018, 65, 129–139. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, Y.K. Developing Bridge. Management System considering Life-Cycle Cost and Performance of Bridges; Technical Report; Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs (MLTMA): Gwacheon, Korea, 2008.


| Condition Rating | A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range of damage index (x) | |||||
| Representative Damage index (x) | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 1.0 |
| Division | Using Particle Filtering | Using Bayesian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean D.I * | 95% CI * of D.I * Lower/Upper | RE | Mean D.I * | 95% CI * of D.I * Lower/Upper | RE | |
| Geomyul | 0.36 | 0.301/0.411 | 10.9% | 0.35 | 0.271/0.423 | 13.2% |
| Ha | 0.39 | 0.350/0.433 | 2.1% | 0.42 | 0.325/0.512 | 4.7% |
| Hwangun | 0.33 | 0.272/0.400 | 17.0% | 0.30 | 0.232/0.363 | 25.7% |
| Jangseon | 0.34 | 0.278/0.405 | 14.7% | 0.31 | 0.239/0.375 | 23.2% |
| Mokdo | 0.35 | 0.287/0.405 | 13.4% | 0.28 | 0.217/0.349 | 29.2% |
| Hwangjeon | 0.39 | 0.322/0.458 | 2.5% | 0.35 | 0.276/0.432 | 11.6% |
| Division | Quantity | Division | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
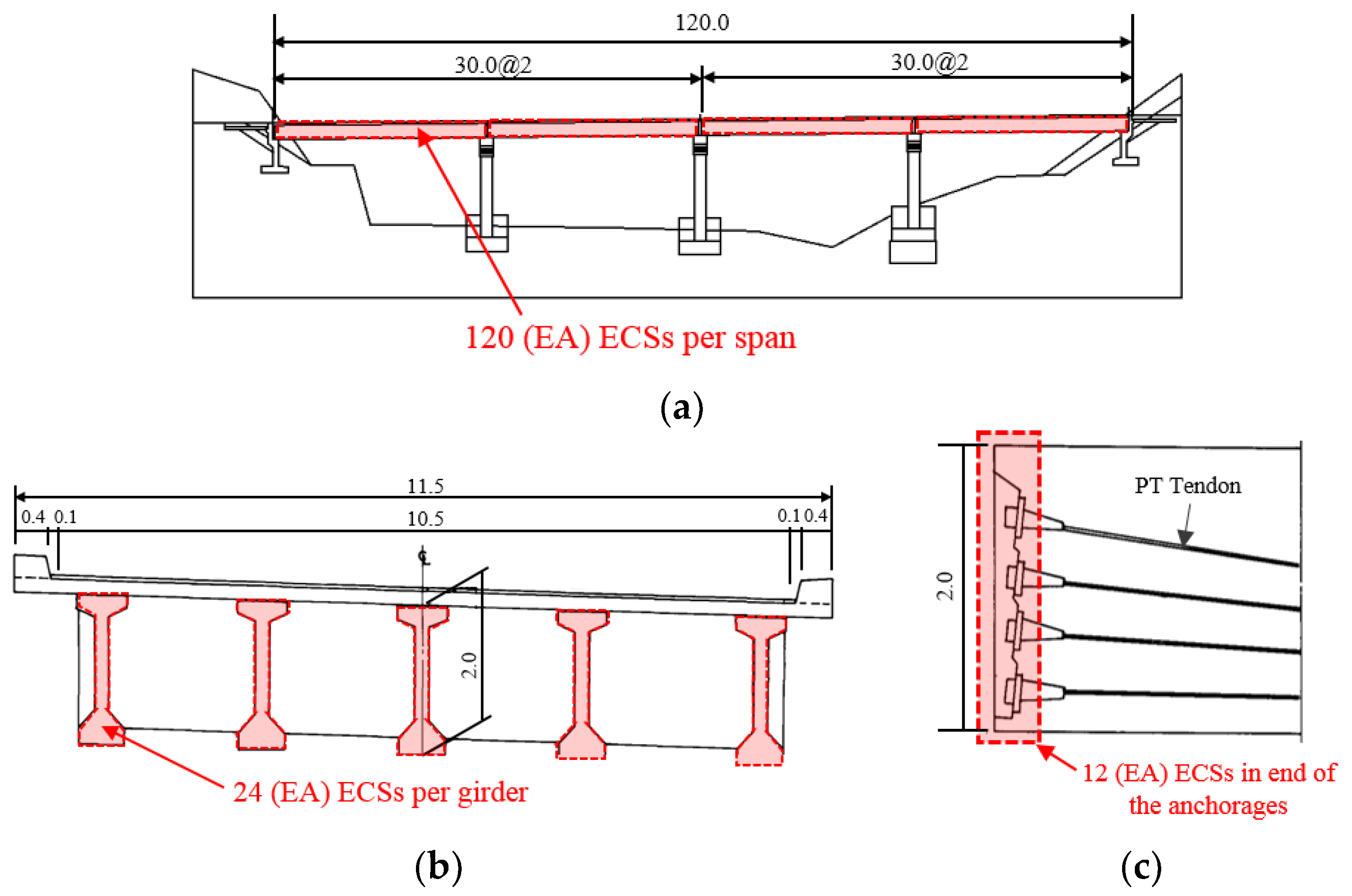
| Bridge Type | PSCI girder | Number of Girder | 5 |
| Design Load | DB-24 * | Number of Lane | 2 |
| Number of Span | 4 | Span Length (m) | 30 |
| Completion Date | 1998.12.01 | Total Span Length (m) | 120(4@30) |
| PC Tendon (EA) | 80(5@4@4) | Effectiveness Width (m) | 10.5 |
| Division | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Cost of unit of ECS sensor including installation (KRW) | 400,000 |
| The number of ECS (EA) | 480 |
| Probability of misclassification using ECS (%) | 5 |
| Division | Regular Inspection | Precise Inspection | Precise Safety Diagnosis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Existing | ECSs | Existing | ECSs | Existing | ECSs | |
| One-time Inspection Cost ( KRW) | 3437 | 16,152 | 48,463 | 26,450 | ||
| Inspection Time | Once every six months | Once every two years | (First time in 10 years) Once every five years | |||
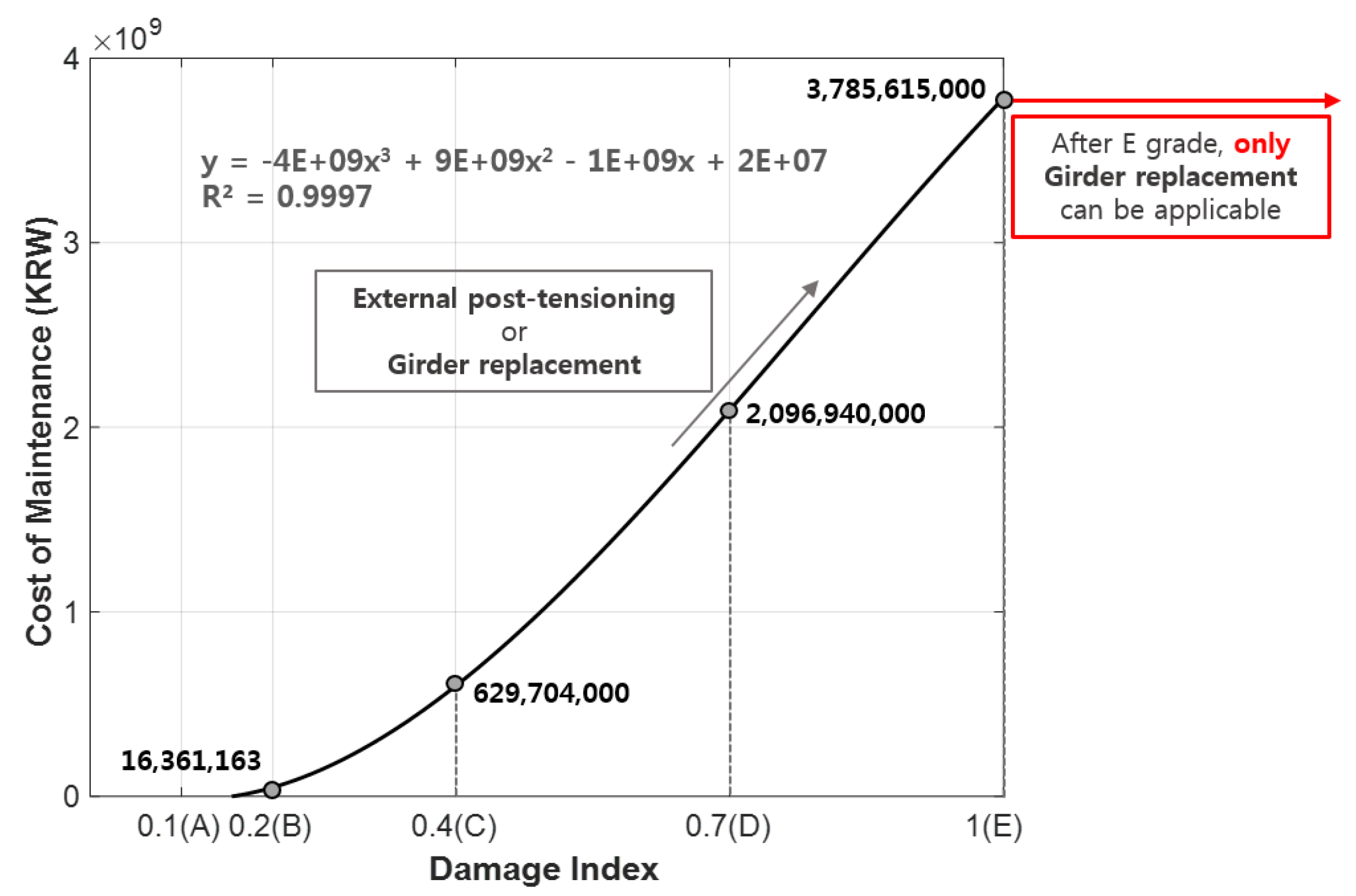
| Representative Damage Type | Representative Application Method | Unit Cost (KRW) | Application Grade | Application Frequency Rate (%) | Cost of Maintenance by Rating (KRW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exposed, corroded tendons | Filling method (Grouting) | 173,134 | B(0.2) | 62.0 | 16,361,000 |
| C(0.4) | 29.5 | 629,704,000 | |||
| External post-tensioning | 2,837,937 | C(0.4) | 16.0 | ||
| D(0.7) | 22.0 | 2,096,940,000 | |||
| tendon fractures | Girder replacement | 7,969,380 | D(0.7) | 25.0 | |
| E(1) | 100.0 | 3,785,615,000 |
| Division | Cost (Unit: KRW) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inspection | Repair and Reinforcement | Rehabilitation (Failure) | Total Maintenance | |
| Existing Scenario | 334,952,646 | 1,663,780,152 | 1,013,611 | 1,999,746,409 |
| PF Scenario | 470,106,591 | 530,423,653 | 9.93 | 1,000,530,244 |
| Division | Cost (Unit: KRW) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inspection | Repair and Reinforcement | Rehabilitation (Failure) | Total Maintenance | |
| Bayesian Scenario | 434,373,456 | 911,667,506 | 2.45 | 1,346,040,961 |
| PF Scenario | 525,544,859 | 1.01 | 959,918,315 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.H.; Choi, Y.; Ann, H.; Jin, S.Y.; Lee, S.-J.; Kong, J.S. Maintenance Cost Estimation in PSCI Girder Bridges Using Updating Probabilistic Deterioration Model. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6593. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236593
Lee JH, Choi Y, Ann H, Jin SY, Lee S-J, Kong JS. Maintenance Cost Estimation in PSCI Girder Bridges Using Updating Probabilistic Deterioration Model. Sustainability. 2019; 11(23):6593. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236593
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jin Hyuk, Yangrok Choi, Hojune Ann, Sung Yeol Jin, Seung-Jung Lee, and Jung Sik Kong. 2019. "Maintenance Cost Estimation in PSCI Girder Bridges Using Updating Probabilistic Deterioration Model" Sustainability 11, no. 23: 6593. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236593
APA StyleLee, J. H., Choi, Y., Ann, H., Jin, S. Y., Lee, S.-J., & Kong, J. S. (2019). Maintenance Cost Estimation in PSCI Girder Bridges Using Updating Probabilistic Deterioration Model. Sustainability, 11(23), 6593. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236593






