Assessing the Moderating Effect of Corruption on the E-Government and Trust Relationship: An Evidence of an Emerging Economy
Abstract
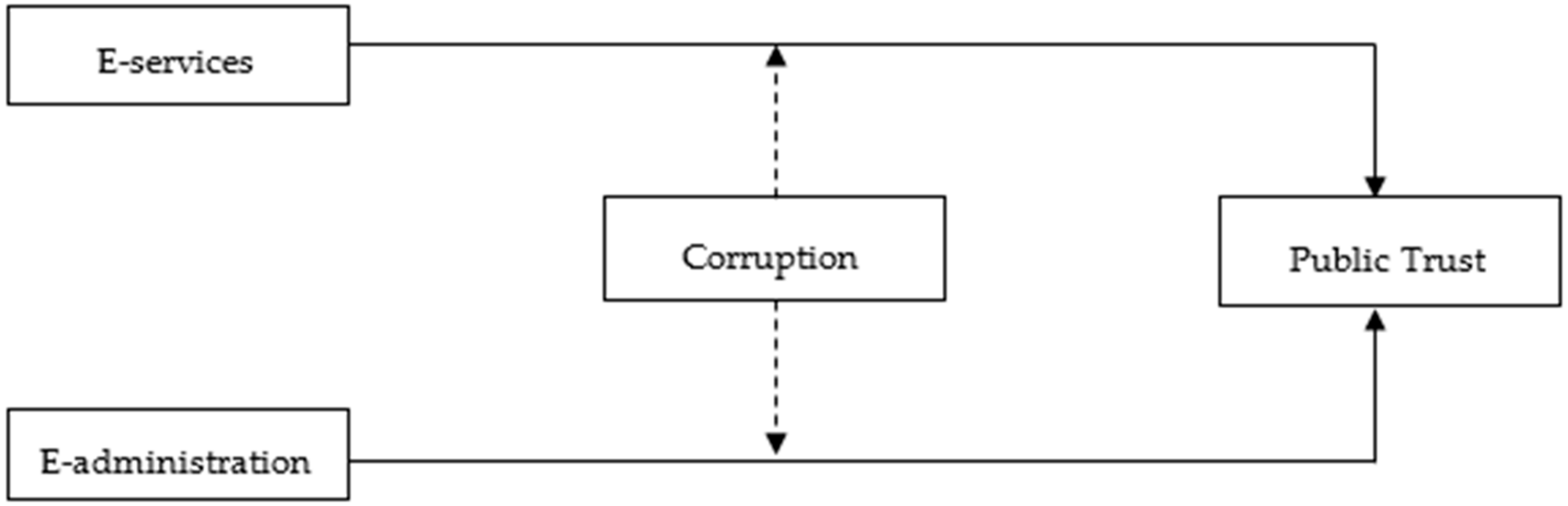
1. Introduction
- What is the influence of e-government in building public trust in local-self-government?
- To what magnitude does corruption moderate the influence of e-government practices in building public trust?
2. Literature Review and Hypotheses Development
2.1. E-Government
2.2. E-Government and Public Trust
2.3. Moderating Effect of Corruption on the Relationship between E-Government and Public Trust
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Research Design and Data Collection
3.2. Measures
4. Results
4.1. Common Method Bias (CMB)
4.2. Measurement Model
4.3. Regression Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Practical Implications
7. Future Research Direction
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clark, J.R.; Lee, D.R. The optimal trust in government. East. Econ. J. 2001, 27, 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Shi, T. Media effects on political confidence and trust in the People’s Republic of China in the post-Tiananmen period. East Asia 2001, 19, 84–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, G.S.; Popovski, V. Building Trust in Government: Innovations in Governance Reform in Asia; United Nations University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Hu, W. Determinants of public trust in government: Empirical evidence from urban China. Int. Rev. Adm. Sci. 2017, 83, 358–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.A.; Knotts, H.G.; Brennan, K.M. The importance of trust in government for public administration: The case of zoning. Public Adm. Rev. 2008, 68, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. Public trust in government in Japan and South Korea: Does the rise of critical citizens matter? Public Adm. Rev. 2010, 70, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, S.; Watts, V.; McCormick, A.K.H.G.; Young, S. Building and maintaining trust in a community-based participatory research partnership. Am. J. Public Health 2008, 98, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.H.; Listhaug, O. Policy preferences and political distrust: A comparison of Norway, Sweden and the United States. Scand. Political Stud. 1998, 21, 161–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, M.; Stoker, L. Political trust and trustworthiness. Annu. Rev. Political Sci. 2000, 3, 475–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nye, J.S.; Zelikow, P.; King, D.C. Why People Don’t Trust Government; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bok, D.C. The Trouble with Government; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Diamond, L. Building trust in government by improving governance. In Proceedings of the 7th Global Forum on Reinventing Government: “Building Trust in Government” Sponsored by the United Nations Session V: Elections Parliament, and Citizen Trust Vienna, Vienna, Austria, 26 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tolbert, C.J.; Mossberger, K. The effects of e-government on trust and confidence in government. Public Adm. Rev. 2006, 66, 354–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M. E-government, GIS and good governance. Public Manag. 2013, 95, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Das, J.; DiRienzo, C.; Burbridge, J. Global e-government and the role of trust: A cross country analysis. Appl. Technol. Integr. Gov. Organ. 2010, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chhabra, S.; Jaiswal, M. E-Government Organizational Performance Framework: Case Study of Haryana State in India. In Social and Organizational Developments through Emerging E-Government Applications: New Principles and Concepts: New Principles and Concepts; Information Science Reference: Hersheyn, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 144–165. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Mayahi, I.; Mansoor, S. UAE e-goverment: SWOT analysis and TOWS matrix. In Proceedings of the 2012 Tenth International Conference on ICT and Knowledge Engineering, Bangkok, Thailand, 21–23 November 2012; pp. 201–204. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Williams, M.D.; Rana, N.P.; Williams, J. Reflecting on e-government research: Toward a taxonomy of theories and theoretical constructs. Int. J. Electron. Gov. Res. 2011, 7, 64–88. [Google Scholar]
- Alghamdi, I.A.; Goodwin, R.; Rampersad, G. E-government readiness assessment for government organizations in developing countries. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2011, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN. United Nations E-Government Survey 2012: E-Government for the People; Division for Public Administration and Development: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, C. Fundamental of Development Administration; Scholar Press: Selangor, Malaysia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, S.C.; Teo, T. Citizen trust development for e-government adoption: Case of Singapore. In Proceedings of the 9th Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems: I.T. and Value Creation, PACIS 2005, Bangkok, Thailand, 7 July–10 July 2005; pp. 721–734. [Google Scholar]
- Spremić, M.; Šimurina, J.; Jaković, B.; Ivanov, M. E-government in transition economies. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2009, 53, 518–526. [Google Scholar]
- Ojo, A.K.; Janowski, T.; Estevez, E. Determining Progress Towards e-Government: What are the core indicators? In Proceedings of the ECEG, Antwerp, Belgium, 16–17 June 2005; pp. 312–322. [Google Scholar]
- Han, R.; Jia, L. Governing by the Internet: Local governance in the digital age. J. Chin. Gov. 2018, 3, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzardi, R.; Calcopietro, C.; Ivanovic, E.F. New-Economy Sector Study Electronic Government and Governance: Lessons for Argentina. New-Economy Sector Study: Electronic Government and Governance-Lessons from Argentina Retrieved. 2002. Available online: http://documents. worldbank. org/curated/en/527061468769894044/pdf/266390WP0E1Gov1gentina1Final1Report. pdf (accessed on 25 June 2019).
- Abdullah, A.; Rogerson, S.; Fairweather, N.B.; Prior, M. The motivations for change towards e-government adoption: Case studies from Saudi Arabia. In Proceedings of the E-Government Workshop, London, UK, 11 September 2006; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Zoubi, M.I.; Sam, T.L.; Eam, L.H. Analysis of e-government adoption and organization performance in the Jordan businesses sector. Acad. Res. Int. 2011, 1, 334. [Google Scholar]
- Jalali, F.; Khorasani, F. The relationship between e-government and the public trust among the citizens in district 5, Tehran. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2012, 4, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar]
- Bankole, F.O.; Bankole, O.O.; Brown, I. Mobile banking adoption in Nigeria. Electron. J. Inf. Syst. Dev. Ctries. 2011, 47, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampen, J.K.; De Walle, S.V.; Bouckaert, G. Assessing the relation between satisfaction with public service delivery and trust in Government. The impact of the predisposition of citizens toward Government on evalutations of its performance. Public Perform. Manag. Rev. 2006, 29, 387–404. [Google Scholar]
- Bouckaert, G.; Van de Walle, S. Comparing measures of citizen trust and user satisfaction as indicators of ‘good governance’: Difficulties in linking trust and satisfaction indicators. Int. Rev. Adm. Sci. 2003, 69, 329–343. [Google Scholar]
- Cegarra-Navarro, J.G.; Pachón, J.R.C.; Cegarra, J.L.M. E-government and citizen’s engagement with local affairs through e-websites: The case of Spanish municipalities. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2012, 32, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeks, R. Understanding and measuring eGovernment: International benchmarking studies. In Proceedings of the UNDESA Workshop, “E-Participation and E-Government: Understanding the Present and Creating the Future”, Budapest, Hungary, 27–28 July 2006; pp. 27–28. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, E.W.; Hinnant, C.C. Internet use, transparency, and interactivity effects on trust in government. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Big Island, HI, USA, 6–9 January 2003; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, E.W.; Hinnant, C.C.; Moon, M.J. Linking citizen satisfaction with e-government and trust in government. J. Public Adm. Res. Theory 2004, 15, 371–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent, M.; Vandebeek, C.A.; Gemino, A.C. Building citizen trust through e-government. Gov. Inf. Q. 2005, 22, 720–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quah, J.S. Curbing Asian corruption: An impossible dream? Curr. Hist. N.Y. Phila. 2006, 105, 176. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.W. E-government and corruption: A cross-country survey. World Political Sci. 2014, 10, 217–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullan, M. A theory of corruption. Sociol. Rev. 1961, 9, 181–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiden, G.E.; Dwivedi, O.; Jabbra, J.G. Where Corruption Lives; Kumarian Press: Bloomfield, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Rose-Ackerman, S. Corruption: A Study in Political Economy; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Tu, W. Corruption tolerance and its influencing factors—The case of China’s civil servants. J. Chin. Gov. 2017, 2, 307–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertot, J.C.; Jaeger, P.T.; Grimes, J.M. Using ICTs to create a culture of transparency: E-government and social media as openness and anti-corruption tools for societies. Gov. Inf. Q. 2010, 27, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, D.C.; Eom, T.H. E-government and anti-corruption: Empirical analysis of international data. Int. J. Public Adm. 2008, 31, 298–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupu, D.; Lazăr, C.G. Influence of e-government on the level of corruption in some EU and non-EU states. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2015, 20, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.J.; Jalal, A. An empirical analysis of the relationship between e-government and corruption. Int. J. Digit. Account. Res. 2012, 12, 145–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameel, A.; Asif, M.; Hussain, A. Good Governance and Public Trust: Assessing the Mediating Effect of E-Government in Pakistan. Lex Localis J. Local Self Gov. 2019, 17, 299–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbahnasawy, N.G. E-government, internet adoption, and corruption: An empirical investigation. World Dev. 2014, 57, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimicopoulos, M.G.; Kyj, L.; Sormani, N.; Bertucci, G.; Qian, H. Public Governance Indicators: A Literature Review. 2007. Available online: https://publicadministration.un.org/publications/content/PDFs/E-Library%20Archives/2007%20Public%20Governance%20Indicators_a%20Literature%20Review.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- Clausen, B.; Kraay, A.; Nyiri, Z. Corruption and confidence in public institutions: Evidence from a global survey. World Bank Econ. Rev. 2011, 25, 212–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.H.; Choi, B.D. E-government to combat corruption: The case of Seoul metropolitan government. Int. J. Public Adm. 2004, 27, 719–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciborra, C.; Navarra, D.D. Good governance, development theory, and aid policy: Risks and challenges of e-government in Jordan. Inf. Technol. Dev. 2005, 11, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Teo, T.S.; Lim, V.K. Examining the relationships among e-government maturity, corruption, economic prosperity and environmental degradation: A cross-country analysis. Inf. Manag. 2013, 50, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, B. Good governance, administrative reform and socio-economic realities: A South Pacific perspective. Int. J. Soc. Econ. 1999, 26, 354–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dion, M. What is corruption corrupting? A philosophical viewpoint. J. Money Laund. Control 2010, 13, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, Y.; Gupta, S.; Zhao, L. What motivates customers to participate in social commerce? The impact of technological environments and virtual customer experiences. Inf. Manag. 2014, 51, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Lederer, A.L. An instrument for measuring the business benefits of e-commerce retailing. Int. J. Electron. Commer. 2003, 7, 65–99. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, M.N. Research Methods for Business Students, 5/e; Pearson Education India: Noida, India, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Salminen, A.; Ikola-Norrbacka, R. Trust, good governance and unethical actions in Finnish public administration. Int. J. Public Sect. Manag. 2010, 23, 647–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Qing, M.; Hwang, J.; Shi, H. Ethical Leadership, Affective Commitment, Work Engagement, and Creativity: Testing a Multiple Mediation Approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, M.; Asif, M.; Hussain, A.; Jameel, A. Exploring the impact of ethical leadership on job satisfaction and organizational commitment in public sector organizations: The mediating role of psychological empowerment. Rev. Manag. Sci. 2019, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Mena, J.A. An assessment of the use of partial least squares structural equation modeling in marketing research. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2012, 40, 414–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwel, S.; Lingqiang, Z.; Asif, M.; Hwang, J.; Hussain, A.; Jameel, A. The Influence of Destination Image on Tourist Loyalty and Intention to Visit: Testing a Multiple Mediation Approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drost, E.A. Validity and reliability in social science research. Educ. Res. Perspect. 2011, 38, 105. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.; Sahito, N.; Thi Nguyen, T.V.; Hwang, J.; Asif, M. Exploring the Features of Sustainable Urban Form and the Factors that Provoke Shoppers towards Shopping Malls. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Jameel, A.; Hussain, A.; Hwang, J.; Sahito, N. Linking Transformational Leadership with Nurse-Assessed Adverse Patient Outcomes and the Quality of Care: Assessing the Role of Job Satisfaction and Structural Empowerment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Asif, M.; Jameel, A.; Hwang, J.; Sahito, N.; Kanwel, S. Promoting OPD Patient Satisfaction through Different Healthcare Determinants: A Study of Public Sector Hospitals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Jameel, A.; Sahito, N.; Hwang, J.; Hussain, A.; Manzoor, F. Can Leadership Enhance Patient Satisfaction? Assessing the Role of Administrative and Medical Quality. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Asif, M.; Jameel, A.; Hwang, J. Measuring OPD Patient Satisfaction with Different Service Delivery Aspects at Public Hospitals in Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobucci, D.; Schneider, M.J.; Popovich, D.L.; Bakamitsos, G.A. Mean centering, multicollinearity, and moderators in multiple regression: The reconciliation redux. Behav. Res. Methods 2017, 49, 403–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, J.A.; DeGeest, D.; Li, A. Tackling the problem of construct proliferation: A guide to assessing the discriminant validity of conceptually related constructs. Organ. Res. Methods 2016, 19, 80–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, B.B.; Sakakibara, S.; Schroeder, R.G.; Bates, K.A.; Flynn, E.J. Empirical research methods in operations management. J. Oper. Manag. 1990, 9, 250–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, F.; Wei, L.; Hussain, A.; Asif, M.; Shah, S.I.A. Patient Satisfaction with Health Care Services; An Application of Physician’s Behavior as a Moderator. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, F.; Wei, L.; Asif, M.; Haq, M.Z.u.; Rehman, H.u. The Contribution of Sustainable Tourism to Economic Growth and Employment in Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Trust in Government, Policy Effectiveness and the Governance Agenda. Government at a Glance; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Anello, E. Ethical Infrastructure for Good Governance in the Public Pharmaceutical Sector; World Health Organisation Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
| Constructs | Items | Loadings | Cronbach’s Alpha | Composite Reliability | Average Variance Extracted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-services | 0.954 | 0.944 | 0.685 | ||
| Through browsing the Local government website, I can identify the required documents to complete the e-service. (e.g. local taxation, online fee) | ES1 | 0.947 | |||
| Through browsing the Local government website, I can have an idea of how the procedure of e-service will take place. | ES2 | 0.702 | |||
| I can track my e-service status by using the Local government online tracking functionality service. | ES3 | 0.607 | |||
| I can pay the Local e-service fees online. | ES4 | 0.635 | |||
| It is easy to conduct my Local e-service at any time. | ES5 | 0.984 | |||
| Local government information is easy to understand. | ES6 | 0.833 | |||
| Local government websites are regularly updated. | ES7 | 0.816 | |||
| My Local government regularly announces new services online. | ES8 | 0.970 | |||
| E-administration | 0.963 | 0.960 | 0.728 | ||
| Completing my transactions through e- administration procedures are better than doing it manually. | EA1 | 0.771 | |||
| Paperless e- administration reduces my administrative costs in Local government. | EA2 | 0.831 | |||
| Local government e-administration facilitates the procedure of my transactions among different administrative departments. | EA3 | 0.917 | |||
| E- Administration reduces the conflicting information in my transactions among different departments. | EA4 | 0.940 | |||
| Automated e-administration in Local government gives me prompt service. | EA5 | 0.827 | |||
| Doing transactions through e- administration minimizes Corruption actions in Local government. | EA6 | 0.723 | |||
| Doing transactions through e-administration avoids favoritism in Local government. | EA7 | 0.914 | |||
| Doing transactions through e- administration minimizes processing time. | EA8 | 0.913 | |||
| E- Administration provides more efficient Local governmental services. | EA9 | 0.816 | |||
| Public trust | 0.939 | 0.937 | 0.682 | ||
| Local government services are provided on time. (E.g. local taxation, online fee, etc.). | PT1 | 0.759 | |||
| The quality of Local government services is good. | PT2 | 0.870 | |||
| The behavior of the Local service provider is friendly and problem-solving. | PT3 | 0.852 | |||
| The political party continues the previous Local government program when came into authority. | PT4 | 0.885 | |||
| Local government public service providers are honest and fair. | PT5 | 0.810 | |||
| The promise made by Local government politicians is kept or fulfilled. | PT6 | 0.779 | |||
| Information about Local government service increases your satisfaction with the service. | PT7 | 0.817 | |||
| Local government politicians are more trustworthy as compare to the national level. | PT8 | 0.823 | |||
| Corruption | 0.933 | 0.928 | 0.617 | ||
| Corruption decrease your satisfaction with the quality of services | C1 | 0.816 | |||
| Corruption leads to low confidence in government to solve problem | C2 | 0.847 | |||
| Corruption leads to less information about government actions | C3 | 0.787 | |||
| Corruption decrease the importance of laws and regulation | C4 | 0.812 | |||
| Local government is more corrupted as compare to national | C5 | 0.713 | |||
| Corruption decrease the outcome of accountability | C6 | 0.770 | |||
| Corruption leads to low trust in government | C7 | 0.763 | |||
| Corruption decrease the outcome of accountability | C8 | 0.769 |
| Outcome Variable: Public Trust | Standardized Estimates | 95.0% CI | Collinearity Statistics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | SE | t | Sig. | Lower Bound | Upper Bound | Tolerance | VIF | |
| E-Administration | 0.178 | 0.038 | 4.684 | 0.012 | 0.131 | 0.243 | 0.672 | 1.487 |
| E-Services | 0.241 | 0.042 | 5.738 | 0.000 | 0.174 | 0.297 | 0.725 | 1.379 |
| Model summary | R = 0.610; R2 = 0.372; F = 74.33; p = 0.00; Durbin-Watson (DW) = 1.779 | |||||||
| Outcome Variable: Public Trust | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3 | |||||||
| β | SE | t | β | SE | t | β | SE | t | |
| E-Service | 0.213 *** | 0.025 | 8.520 | 0.231 *** | 0.024 | 9.625 | 0.113 *** | 0.032 | 3.531 |
| Corruption | 0.147 *** | 0.031 | 4.742 | −0.317 *** | 0.076 | −4.171 | |||
| E-Service × Corruption | 0.129*** | 0.018 | 7.167 | ||||||
| Δ R2 | 0.127 | 0.174 | 0.246 | ||||||
| F Change | 79.480 | 55.664 | 53.743 | ||||||
| Outcome Variable: Public Trust | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3 | |||||||
| β | SE | t | β | SE | t | β | SE | t | |
| E-administration | 0.290 *** | 0.033 | 8.788 | 0.287 *** | 0.033 | 8.697 | 0.196 *** | 0.034 | 5.765 |
| Corruption | 0.139 *** | 0.032 | 4.344 | −0.357 *** | 0.078 | −4.578 | |||
| E-Administration × Corruption | −0.059 *** | 0.008 | −7.375 | ||||||
| Δ R2 | 0.287 | 0.319 | 0.407 | ||||||
| F Change | 75.231 | 45.163 | 51.815 | ||||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jameel, A.; Asif, M.; Hussain, A.; Hwang, J.; Sahito, N.; Bukhari, M.H. Assessing the Moderating Effect of Corruption on the E-Government and Trust Relationship: An Evidence of an Emerging Economy. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6540. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236540
Jameel A, Asif M, Hussain A, Hwang J, Sahito N, Bukhari MH. Assessing the Moderating Effect of Corruption on the E-Government and Trust Relationship: An Evidence of an Emerging Economy. Sustainability. 2019; 11(23):6540. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236540
Chicago/Turabian StyleJameel, Arif, Muhammad Asif, Abid Hussain, Jinsoo Hwang, Noman Sahito, and Mussawar Hussain Bukhari. 2019. "Assessing the Moderating Effect of Corruption on the E-Government and Trust Relationship: An Evidence of an Emerging Economy" Sustainability 11, no. 23: 6540. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236540
APA StyleJameel, A., Asif, M., Hussain, A., Hwang, J., Sahito, N., & Bukhari, M. H. (2019). Assessing the Moderating Effect of Corruption on the E-Government and Trust Relationship: An Evidence of an Emerging Economy. Sustainability, 11(23), 6540. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236540








