Abstract
Accurate, year-by-year crop distribution information is a key element in agricultural production regulation and global change governance. However, due to the high sampling costs and insufficient use of historical samples, a supervised classifying method for sampling every year is unsustainable for mapping crop types over time. Therefore, this paper proposes a method for the generation and screening of new samples for 2018 based on historical crop samples, and then it builds a crop mapping model for that current season. Pixels with the same crop type in the historical year (2013–2017) were extracted as potential samples, and their spectral features and spatial information in the current year (2018) were used to generate new samples based on clustering screening. The research result shows that when the clustering number is different, the number and structure of new generated sample also changes. The sample structure generated in Luobei County was not balanced, with the ‘other crop’ representing less than 3.97%, but the structure of southwest Hulin City was more balanced. Based on the newly generated samples and the ground reference data of classified year, the classification models were constructed. The average classification accuracies of Luobei County in 2018 based on new generated samples and field samples were 69.35% and 77.59%, respectively, while those of southwest Hulin City were 80.44% and 82.94%, respectively. Combined with historical samples and the spectral information of the current year, this study proposes a method to generate new samples. It can overcome the problem of crop samples only being collected in the field due to the difficulty of visual interpretation, effectively improve the use of historical data, and also provide a new idea for sustainable crop mapping in many regions lacking seasonal field samples.
1. Introduction
Medium-high resolution crop mapping at regional scales can provide basic data for the more precise regulation of agricultural production and global change governance [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], and it is an important support for implementing sustainable agriculture [8]. At present, crop classification based on remote sensing data mainly adopts the strategy of supervised classification [9,10,11], which means that sample data must be used for the model training. Crop samples are difficult to obtain by visual interpretation, so they can only be collected in the field. However, due to the limitations of severe weather, field sampling safety, accessibility, time, and cost, it is difficult to collect sufficient and reliable ground samples. In addition, in existing crop classification studies, seasonal samples are often only used for crop classification in the current season, and they are rarely used for the next season or even the next few seasons, resulting in a low utilization rate of historical data [1,6,8]. The difficulty of sampling and the low utilization of historical data have led to the high cost of year-by-year mapping. At the same time, after collecting data every year, it is necessary to carry out complex operations such as data preprocessing, and the final crop map is often obtained after the harvest, which leads to a lag of crop mapping and its guiding role for farming being greatly weakened. Therefore, it is difficult to meet the demand for crop mapping by sampling every year. The question of how to sustainably carry out crop classification based on historical data has become a research hotspot.
There are three main methods for classifying crops based on historical data: One is to reuse the spectral curve, the second is to reuse the training model, and the third is to generate “training samples.”
Reusing spectral curves is a method for classification based on the fact that the spectral similarity of the same crop is greater than that of different crops between years [12]. The spectral curves of inter-annual crops are often extracted from historical samples and image data, and the similarity between pixels and curves is calculated to classify crops in the current season. Examples include using the initial fitting curve based on the simple interpolation method [13], using the smoothing curve through wavelet and Savitzky–Golay (S–G) filters [14,15,16], using Roy’s [17] use of linear and nonlinear harmonic functions to fit a normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) curve, and the evaluation of the optimal time phase number of curves fitted by different functions. However, the function in Roy’s [17] paper has more than five parameters, and the effective observation requires three times of the parameters; as such, at least 15 time-phase images are required, which is difficult to satisfy for large-scale mapping and even small-area mapping in many areas. Therefore, many scholars use the asymmetric double-sigmoid function method proposed by Soudani [18] to fit the crop curve for classification [19,20,21,22]. In addition, machine learning algorithms are gradually being applied to the fitting of spectral curves [23]. However, due to environmental factors such as moisture, light, temperature, crop varieties, the inter-annual variation of planting time, and regional differences, the growth and spectral curves of the same crops are inconsistent, which affects the accuracy of identifying crop types based on spectral similarity.
Reusing a training model involves classifying multiple times using a constructed classification model. It is necessary to train a model with a strong inter-annual generalization ability, based on multi-year historical samples, to classify seasonal crops. For example, in terms of county and provincial scales, Zhong [24,25] implemented a method of multi-time classification by one time training based on historical data in Doniphan County, Kansas and Paraná, Brazil, which reduced sampling cost and improved the classification efficiency; Muhammad [26] trained a classification model by using the ground reference data of adjacent years and then classified other years, and they finally obtained the main crop classification results from 2005 to 2013 in Kansas, with an accuracy of 74.4%–81.9%; Cai [27] used CDL (Cropland Data Layer) and Landsat data to train a model based on historical samples by the deep neural network (DNN) method and then applied it to the classification of seasonal crops in the American corn belt to achieve a better classification accuracy. On multi-state and even national scales, based on the idea of time-migration, Wang [28] used random forest classifiers to achieve crop mapping in nine states in the Midwestern United States; dos Santos Luciano AC [29], based on the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform, used a multi-year historical data training model to identify the sugarcane distribution in Brazil from 2009 to 2016, with an average precision of 91%. However, this method generally requires a balance of image information between years. Due to the influence of cloud and shadow, it is difficult to achieve the balance of inter-annual images when there are a large number of historical years. Currently, the basic method is to complement the image by interpolation, although a decline in data quality is caused by this method, which then affects the subsequent classification.
The generation of “training samples” is the method that uses historical data to create the current year’s samples and then constructs the classification model. According to the auxiliary information, such as the stability of the crop planting structure, the pixels with unchanged crop type in the historical year are extracted as the “training samples” for the crops in the current season. Then, based on this sample, the current year is classified. For example, Hao [30] used the historical year CDL data of Kansas in the United States to extract hypothetical samples based on the Artificial Antibody Network (ABNet) method to screen hypothetical samples, and obtained “training samples” to classify the current crops with an overall accuracy of 90%.
These seasonal crop classification methods based on historical samples focus on the use of historical information, but they lack an effective use of information in the current year. Due to environmental differences such as inter-annual light and warmth, as well as differences in crop varieties [31], relatively stable classification features such as the spectral curves of the same crops, phenological characteristics, and the statistical parameters of key phases will continue to fluctuate during the inter-annual period; in particular, the generated training samples are prone to a large amount of noise, which reduces classification accuracy, and it is necessary to further improve the purity of the generated samples by combining auxiliary information. In addition, most of the “training samples” generated at present are based on CDL data, but in regions lacking CDL data, the effectiveness of this method remains to be verified. From the above analysis, it can be concluded that if the newly generated samples can be screened based on historical samples and combined with auxiliary information such as local planting structures and the spectral characteristics of the classification year; this can create an improved way to use historical samples for crop classification in the current season.
Therefore, based on China’s GF-1 data, which is a remote sensing satellite launched by the Chinese government in 2013, this study takes the crop planting areas in Luobei County and Hulin City in Heilongjiang Province of China as examples (no CDL data, only a small number of historical samples). First, using information of historical crop planting structure and the current year’s spectral data, we explore new samples’ generation and screening methods based on spatial clustering analysis; second, using the newly generated samples to build a seasonal crop classification model, we perform the classification and provide a new method for crop classification when there are a lack of sample data in the classified year.
2. Materials
2.1. Study Area
In this paper, two study areas in Heilongjiang Province of China were selected, namely Luobei County of Hegang City and the southwest of Hulin City. The length was about 60 km from east to west and 50 km from north to south, with a total area of about 3000 km2. Luobei County is located in the east of Hegang City, between 130°36′18″–131°22′26″ E and 47°17′38″–47°44′56″ N based on WGS84, and it belongs to the cold temperate continental monsoon climate [32]. The south is low-lying and boggy, with an annual average temperature of 1.57 °C, a frost-free period of 128 days, and an annual precipitation of 549.1 mm. The southwest of Hulin City is located in the southeastern plain area, with the ground span of 132°25′1.2″–133°12′18″ E, 45°35′24″–46°1′22.7″ N based on WGS84, and it belongs to the middle temperate continental monsoon climate, which is a mild and humid climate area in the Sanjiang Plain [33]. Spring is windy and dry, summer is short and rainy, autumn is waterlogging with early frost, and winter is cold and long. The annual average temperature is 3.5 °C, the annual average relative humidity is 70%, and the annual average precipitation is 566.2 mm. The precipitation is mainly concentrated in June, July and August, accounting for 53% of the annual total precipitation. The sunshine is about 2274.0 h, and the frost-free period is 141 days. Most of the melting of the snow occurs at the end of February, and the freezing period is about 180 days.
The planting calendars in the study area are relatively stable with little inter-annual differences. The growing season of the main crops is basically from March to October, among which maize is sown from late April to early May, matures in September, and is harvested around October; rice is sown in April and ripens in September, later than the maturation date of maize; and the growth period of other crops or melons is basically from March to October.
The reasons for the selection of the study area are as follows: First, Heilongjiang Province is an important major grain-producing area in China, and the selected area is located in the major grain-producing counties of Heilongjiang, with less interference. Second, the selection of two regions can better verify the feasibility of this method and allow for the comparison of regional differences.
2.2. Data Sources
2.2.1. Remote Sensing Data
In view of the characteristics of many acquisition years, the large coverage area and the high spatial and temporal resolution of images required by this study, the Chinese GF-1 satellite launched on 26 April 2013 was selected. The four wide-width multispectral cameras (called WFV) on the GF-1 satellite can reach a width of 800 km and generate four bands, including blue (0.45–0.52 μm), green (0.52–0.59 μm), red (0.63–0.69 μm), and near-infrared (0.77–0.89 μm) bands, which can meet the calculation of a common vegetation index. The spatial resolution is 16 m, and the revisit period is 4 days; with this high spatial and temporal resolution, the satellite can obtain more remote sensing images of the key growth periods of cloudless crops. In this paper, GF-1 WFV data in the growing season of maize and rice (April–September) with the percentage of cloud less than 10% were selected as remote sensing data sources. The data were derived from the China Centre for Resource Satellite Data and Application (CRESDA) and were the level-one product (L1). Taking 2013–2017 as the historical years and 2018 as the year to be classified and obtaining the multi-temporal GF-1 WFV data during the growth period of 2013–2018, Figure 1 lists the details of these scenes. As can be seen from Figure 1, the inter-annual imbalance of cloudless images is very obvious. The number of images in Luobei County has at least 9 phases in 2013 and up to 15 phases in 2015; the number of images in the southwest of Hulin was less than that in Luobei County, with a minimum of 7 temporal phases appearing in 2016 and a maximum of 11 temporal phases appearing in 2015.
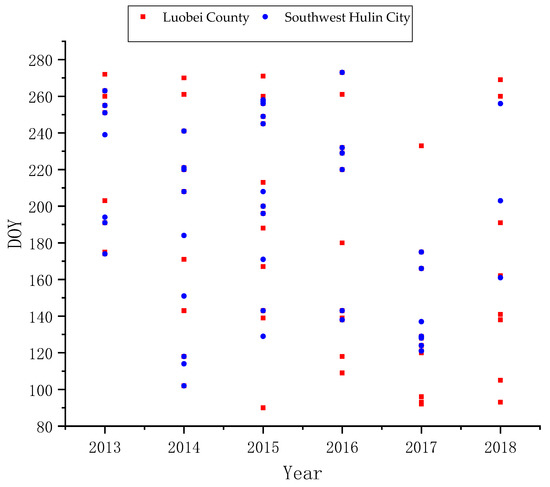
Figure 1.
Description of GF-1 data used in this study.
2.2.2. Field Sample Data
In order to obtain the main types of crop mapping in the study area, a ground-based field survey was conducted in 2013–2018. The latitude and longitude coordinates of the labels were measured using a handheld GPS (global positioning system) based on the principle of wide area difference, named MM9, and the vegetation types and photographs were recorded. The year with the largest number of samples in Luobei County of Hegang City was 2014, with a total of 553 samples, and the lowest number was 237 samples in 2018; the largest sample size in the southwest of Hulin City was 455 in 2017, and the year with the lowest number was also 2018, with a total of 206. Due to the large plot of Heilongjiang, most of the sampling was carried out along the roadside of the field, which can help to save costs as much as possible. The sample size and spatial distribution are shown in Table 1 and Figure 2, respectively.

Table 1.
Statistics on the ground reference samples.
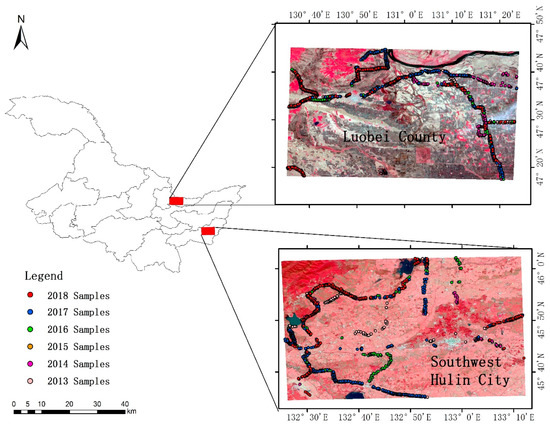
Figure 2.
Study area and the distribution of ground reference samples.
3. Methods
The research workflow is shown in Figure 3 and can be divided into five parts: Data preprocessing, historical year classification, potential sample extraction and sample screening, current year classification, and accuracy assessment. First, the GF-1 WFV automatic processing and sharing platform developed by our team was used to preprocess the images and sample data. Second, the random forest classifier was used to classify 10 times per year from 2013 to 2017 to obtain the classification results of historical years. In the third step, according to the result of the second step, the pixels with the same type in all historical years were extracted as potential samples, and the new samples were generated based on spectral similarity by spatial k-means clustering. The fourth step was to classify 2018 based on the new generated samples and current year samples and to obtain two classification results. Finally, the accuracy of the two classification results was verified to verify the feasibility of the proposed method.
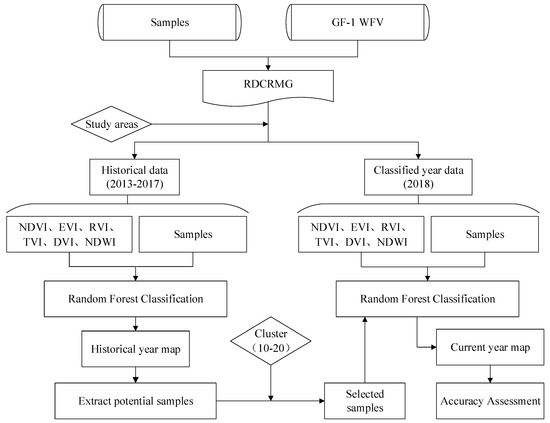
Figure 3.
Workflow of this study.
3.1. Data Preprocessing
Both the GF-1 images and the field samples were stored using the Raster Dataset Clean and Reconstitution Multi-Grid (RDCRMG) grid system developed by China Agricultural University [34]. The RDCRMG is a multisource raster data organization and management logic framework that is similar to the Military Grid Reference System (MGRS) data organization framework [11]. Currently, the implementation of the RDCRMG is mainly based on code and includes some basic functionality based on the graphical user interface (GUI), such as the preprocessor. According to the RDCRMG system, three levels of square grids (100, 10, and 1 km) with different grid sizes, strictly nested relationships, and specific codes are used as consistent RS image partition units. The GF-1/WFV L1 product does not provide geometric correction, so it cannot be directly used for crop classification. The GF-1 WFV automated processing and sharing platform developed by our team can achieve automated pre-processing, including traditional radiation calibration, atmospheric correction and orthorectification, as well as cloud detection, geometric registration, projection conversion, clipping and cleaning based on the RDCRMG [34]. In order to best preserve the original spectral characteristics of each pixel, the nearest neighbor sampling method was used in the geometric registration and atmospheric correction, with a 6-S radiative transfer model. The sample data in the RDCRMG underwent the following steps: Rasterization, project conversion, clipping, and cleaning.
3.2. Historical Year Crop Classification and Sampling Procedures
The main crops in Heilongjiang Province are maize, rice and soybean, but the field survey showed that the main crops in the study area were maize and rice, with few other crops. Therefore, the final classification categories were maize, rice, and other.
The quality of the training and test data directly affects the results of the supervised classification. There are several sampling strategies available, including single pixel, seed, and block or polygon. In areas that are spectrally homogeneous, single-pixel training can obtain better classification results [35]. Due to the large size of the plots in Heilongjiang Province and the strong homogeneity of the spectrum in the same plot, the single-pixel random sampling method was adopted in this paper, and the collected samples were divided into training and test samples according to the ratio of 2:1. All samples were sourced from the field survey to ensure the accuracy of the samples.
3.3. Classification Feature Selection and Calculation
Considering the differences in phenology, seasonal differences, as well as the significance and anti-saturation degree of different vegetation indexes (VIs), the commonly used VIs can be divided into four categories. (1) To reflect the comprehensive change in crop growth: The normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) and the enhanced vegetation index (EVI). (2) To reflect crop greenness: The triangle vegetation index (TVI), the ratio vegetation index (RVI), and the green normalized difference vegetation index (GNDVI). (3) To reflect crop soil background: The difference vegetation index (DVI) and the soil regulation vegetation index (SAVI). (4) To reflect the canopy moisture content of crops: The normalized difference water index (NDWI). Among them, several vegetation indexes are strongly correlated [36]. Therefore, six vegetation indexes with weak correlation coefficients, namely the NDVI, the EVI, the RVI, the TVI, the DVI and the NDWI, were selected in this paper. The formula is as follows:
where NIR, R, G, and B are the reflectance values of the near-infrared, red, green, and blue spectral bands, respectively.
NDVI = (NIR − R)/(NIR + R)
EVI = 2.5 ∗ (NIR − R)/(NIR + 6R − 7.5B + 1)
RVI = NIR/R
TVI = 60 ∗ (NIR − G) − 100 ∗ (R − G)
DVI = NIR − R
NDWI = (G − NIR)/(G + NIR)
Time series NDVIs can effectively reflect changes in crop growth period. Figure 4 shows the time-series curves of six VIs during the growth periods of maize and rice in Luobei County, Hegang City in 2015. As can be seen from Figure 4, the growth period of maize and rice was very close, and each vegetation index curve had a high similarity. However, it can be seen that the NDVI and the NDWI differed greatly in the early growth stage, but there was almost no difference in the middle and late stages; this may be due to the fact that the NDVI reached saturation in the middle and late growth stages and could not respond to biomass very well. NDWI is sensitive to water, so the paddy field filled with water in May made the NDWI of the rice field and the maize field different. The difference in the RVI is obvious in the middle growth stage. This is because the RVI is very sensitive when the vegetation coverage is high, and the sensitivity is significantly reduced when the vegetation coverage is less than 50%. Therefore, when the vegetation biomass was high in the middle growth period, the RVI distinguished between corn and rice more significantly. The TVI, the DVI and the EVI were different in the whole growth period, and these vegetation indexes could effectively reflect the differences in biomass and eliminate the influence of background values such as soil.
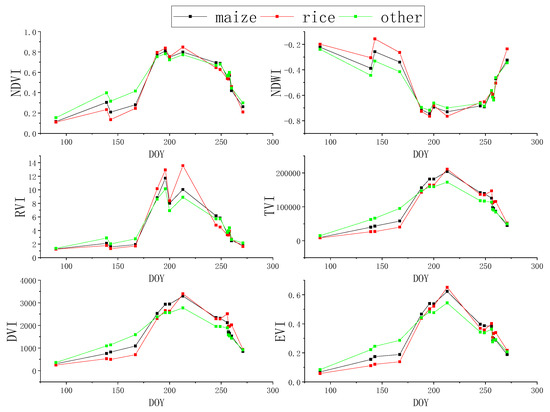
Figure 4.
Time-series vegetation index (VI) curves of different vegetation types during the growth period.
3.4. Random Forest Classification
Random forest (RF) is an integrated algorithm which belongs to the bagging type. By combining multiple weak classifiers, the final result is obtained by voting, which gives the overall model result a higher precision and generalization ability. The classification and regression trees (CART) decision tree is used as a weak classifier in the random forest algorithm. When training the model, multiple trees are generated, and the features selected by each tree are only a few of the features selected at random [37].
Because of its strong randomness, the random forest algorithm can achieve better generalization and anti-overfit ability, meaning that it is generally not necessary to do additional pruning. At the same time, random forests can process high-dimensional data well, and this method has significant advantages when there are many samples and features. In this paper, a large number of samples was generated in the process of using historical data, and the use of six time series VIs led to a large number of features. Therefore, the random forest method was adopted for classification and identification, and a total of 150 trees were generated. The number of features of each tree was the square root of the number of input features, and the sample size selected for each tree was the same as the number of training sets.
3.5. New Sample Generation and Screening
In this study, the classification results of maize and rice from 2013 to 2017 were generated first. On this basis, new samples were extracted and screened, and then the classification map was constructed for the years with insufficient ground data.
The more stable the planting structure is, the smaller the inter-annual change in crop types in each plot is. This paper used this idea to design a new sample extraction and screening method, as shown in Figure 5. First, the classification results of historical years were superimposed to calculate the occurrence frequency of different crop types for each pixel. When the crop type of a pixel remained unchanged from 2013 to 2017, that is the occurrence frequency was 50 times (10 classification results per year for a total of five years), then the pixel was extracted as a “potential sample,” and given the label of this crop type. Then, according to the spectral characteristics and spatial information of the current year (2018), the potential samples were clustered. Next, the proportion of maize, rice and other in each cluster item was calculated, and the crop type with the largest proportion—one exceeding 0.67—was selected as the label of this cluster item so that all the items were divided into corn, rice or other, and the clustering result was divided into three groups. Finally, the clustering results with the three categories were superimposed with the “potential samples,” and the pixels with the same labels were extracted as the new samples that were finally used for the current year’s classification. The number of clusters was repeated from 3 to 20. If no crop class accounted for more than 0.67 in an experiment, the results of this clustering were not used. Meanwhile, the effects of the number of clusters on the structure and classification accuracy of newly generated samples were compared. This method not only made use of the stable planting structure of local crops but also took into account the spectral features of the current year. It integratds the empirical data and remote sensing data to generate new samples sustainably and conduct crop classification for the current year on this basis.
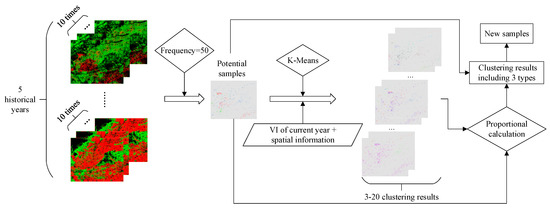
Figure 5.
Process of new sample generation and screening.
3.6. Accuracy Assessment
One third of the field samples of corn, rice and other of every year were used as verification samples, and the specific quantity is shown in Table 2. Then the confusion matrix and F-score were used to assess the classification results. By constructing a confusion matrix, five accuracy assessment indexes could be obtained: Overall accuracy (OA), producer accuracy (PA), user accuracy (UA), kappa coefficient (K) and F-Score. Kappa analysis provided a measure of the magnitude of agreement between the predicted and actual class membership [38]. A kappa value of 0 represents a total random classification, while a kappa value of 1 corresponds to a perfect agreement between the reference and classification data. The calculation formula for each indicator is as follows:
where TP and FN, respectively, refer to the true category of samples as positive examples and the model prediction results as positive examples and negative examples. TN and FP refer to the negative examples of the true category of samples, which are predicted by the model as negative examples and positive examples. N is the total number of real samples.

Table 2.
Statistics on the validate reference samples.
4. Results
4.1. Classification Results of Historical Years and Potential Sample Extraction
The RF classifier was classified using 150 CART trees. The number of features in 2013–2017 varied according to the phase, and the number of phases was positively correlated with the classification accuracy. In general, the number of time phases in Luobei County of Hegang City was higher than that in southwest Hulin City, and the accuracy of the former was generally higher than that of the latter, as shown in Table 3. The number of features of Luobei County in Hegang City was 54–90, among which the number of features was the highest in 2015. It is also reflected in Table 3 that the F-Score of maize and rice reached the maximum in 2015. The feature number of southwest Hulin City was the lowest at 36 in 2016 and the highest at 66 in 2015. The overall accuracy of 2015 and the F-Scores of maize and rice all reached their maximum value in Table 3, which also indicates that feature number and time phase number have a certain influence on classification accuracy.

Table 3.
Accuracy of historical years’ classification.
The classifications and accuracy verifications were carried out 10 times in each historical year for the two regions, which eliminated the contingency of results that may have resulted from one classification and simultaneously extended the validation sample size to prevent deviations in verification results due to too few verification samples. The result in Table 3 shows that the average classification accuracy was about 80%, of which the highest appeared in the 2015 classification of southwest Hulin City and was 92.45%. The better the classification results of historical years are, the higher the accuracy of using them to extract samples are. The experiments of historical years in this paper meet the basic requirements of classification accuracy and have the conditions to extract samples from them.
4.2. Effect of Clustering Number on New Sample Structure and Classification Accuracy
The potential samples were extracted from the classification results of the historical years 2013–2017. However, these samples were obtained based on the assumption that the crop types of pixels remain unchanged every year, i.e., that the regional planting structure was stable. However, there are uncertainties, and this uncertainty can be reduced by combining the spectral consistency information of crops in the current year. Therefore, this study introduces the idea of clustering, based on the spectral features of the current year and then screening potential samples to improve the purity of the sample. Multiple clustering is carried out on the potential samples. The clustering method is k-means, and the number of clustering is 3–20. By calculating the ratio of clustering items to categories, it was found that only when a type has at least 10 clustering items does it meet the maximum selection ratio, and maize, rice and the other three types can be assigned to each pixel. When the clustering number is 10–20, the final classification accuracy presents a steady trend, so the results of clusters with 10–20 items were finally selected for analysis. The proportion of samples obtained after screening is shown in Table 4. It can be seen that the sample structure in southwest Hulin City was more uniform than that in Luobei County, with their lowest values at 8.95% and 3.44%, respectively. In addition, the proportion of maize samples in southwest Hulin City was relatively low, the proportion of other samples in Luobei County was relatively low, and the highest proportion of this type was only 3.97%.

Table 4.
Proportion of all types of samples.
According to the statistics of sample sizes of different clusters, it was found that the sample size changes when the clustering number is different. The sample size of Luobei County in Hegang City was the lowest at 1,892,129 pixels and the highest at 2,180,153 pixels when the clustering number was 19. Meanwhile, the sample size in southwest Hulin was at least 125,719 and the maximum number was 147,515 pixels when the number of clusters was 20. The sample size of the two regions varied greatly, mainly because the crop planting information in Luobei County was more stable and the planting mode in the past five years was basically unchanged, so the sample size obtained by superposition was large. The distribution of crops in southwest Hulin City in 2013 was quite different from that of other years. Therefore, when the data of five years were superimposed, fewer samples were extracted. The distribution of the new sample generated is shown in Figure 6. In addition to reflecting the difference in quantity between the two regions, it can be seen that there were significant differences in the sample structure between Luobei County and southwest Hulin City, which is similar to the statistical results in Table 4.
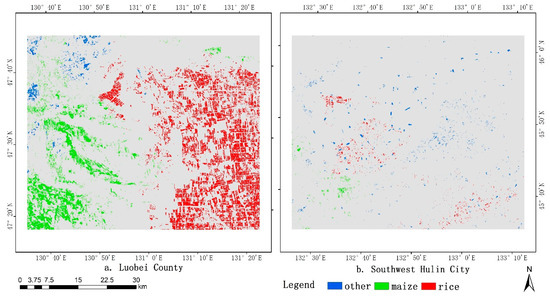
Figure 6.
Distribution map of the new sample.
Using the sample in Figure 6 for classification, the accuracy is shown in Figure 7. It can be seen that when the sample structure is out of balance, the overall accuracy of the classification is reduced, so the accuracy of Luobei County in Figure 7 was generally lower than that of southwest Hulin City. Meanwhile, in the southwest of Hulin City, when the proportion of maize samples was less than 10%, the accuracy was greatly affected. When the clustering number was 14 or 15, the proportion of maize was 9.08% or 8.95%, respectively, leading to a low value of classification accuracy.
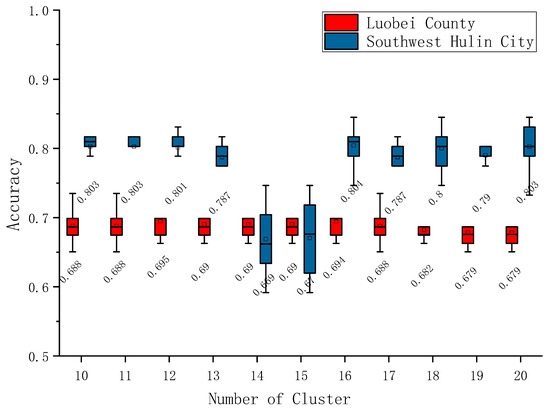
Figure 7.
The effect of clustering number on accuracy.
4.3. Accuracy Assessment and Analysis
The classification result of the newly generated sample was verified 10 times. The sample used for each accuracy verification was one third of the randomly assigned samples in the field, which was consistent with the verification sample for classification in the current year. The overall accuracy verification results are shown in Table 5. From this table, we can see that the accuracy of southwest Hulin City was higher than that of Luobei County. The accuracy of Hulin City based on the current year’s sample and historical data was 82.94% and 80.44%, respectively. Though the results based on historical data were still lower than the classification accuracy of the current year, the classification accuracy could meet the basic requirements in the years lacking samples, and the user accuracy and producer accuracy of corn and rice reached a high level. The classification accuracy of Luobei County based on the samples of the current year was 77.59%, while the classification accuracy based on historical data was only 69.35%, and the ‘other’ type were misclassified into maize, which shows a strong relationship with the fact that the proportion of the ‘other’ type is too small. The imbalance of the sample structure led to a decline in accuracy.

Table 5.
Confusion matrix.
The construction of a confounding matrix based on field samples is a traditional accuracy assessment method. However, due to the small sample size, it is not comprehensive to evaluate classification accuracy only by considering the data in the confounding matrix. Therefore, it is necessary to evaluate the classification results by combining crop mapping. The crop map in the southwest of Hulin City is shown in Figure 8. In this figure, a is based on the classification results of the current year’s samples and b is the distribution of crops with historical data. The maps are superimposed with false color images in the area. It can be seen that both methods could better distinguish water and forests from maize and rice, but the magnified area shows that the misclassification of buildings and roads as maize was more serious based on the classification of samples in the current year, and there was also a phenomenon of misclassifying rice into corn. However, buildings could be better distinguished when classification was based on historical data, and the outline of rice plots was also clear. This also suggests that when basing on historical data, the classification performed slightly worse in terms of overall accuracy based on the real samples, but on the feature map, this method could achieve a better classification effect. This may be due to the fact that the sample size generated by historical data was greater than the field samples taken; while there were some errors in these data, the random forest algorithm had some fault tolerance, so a better map was obtained.
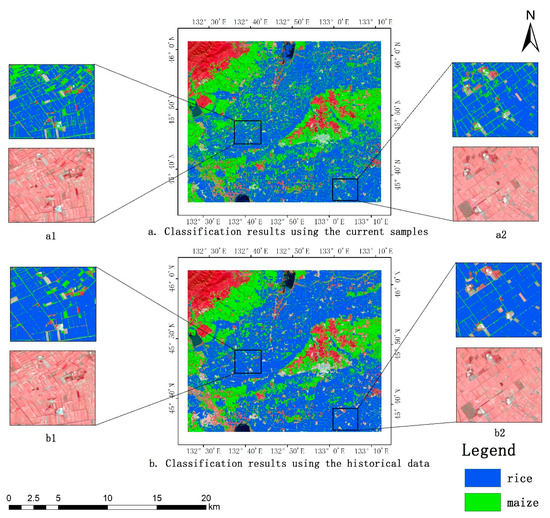
Figure 8.
Crop mapping in southwest Hulin City.
5. Discussion
The method proposed in this study involves selecting pixels with unchanged crop type for five years as potential samples, according to historical samples and classification results (2013–2017), and then producing new samples by the superposition of pixel spectral information in the year to be classified (2018) before finally constructing the classification model. Different from Hao [30]’s spectral curve screening method based on historical data, this paper screened potential samples based on the clustering of the current year’s spectral features and spatial information. Due to differences in inter-annual environment, inter-annual spectral curves of the same crop can be inconsistent, and the application of the classified year’s data to this link can avoid the influence caused by differences in spectral curves. Additionally different from Hao [30] is that the method proposed in this study can be widely used to most of the world without CDL data, which are only abundant in the USA. Therefore, this method can provide a new idea of classification for regions lacking samples in classified year and save the expensive financial and labor cost of sampling, which is of great significance for sustainable crop mapping.
Compared with the method of reusing the spectral curve, our method can avoid the influence of environmental factors on spectral curve differences in the same crop. Compared with the method of reusing the training model, our method does not need a balance of image information between years, which is difficult to satisfy in most areas due to cloud and shadow. Compared with the method of generating “training samples” based on historical information, our method uses both the spectral information of historical samples and the current year to ensure that the generated samples are more accurate. However, the new generated samples in this paper were large and beyond the requirements of classification, and they contained a lot of noise. If the membership degree of each cluster pixel is used to constrain samples screening, the purity of new samples should be improved, and the number of new samples can be reduced.
6. Conclusions
In order to improve the utilization efficiency of historical samples, reduce the dependence of crop distribution mapping on year-by-year sampling, and produce crop distribution maps sustainably at a lower cost, a new method for generating and screening new crop samples based on historical data was proposed and used for current season crop classification in this paper. The basic idea is to obtain potential samples by extracting pixels with the same crop type in all historical years, clustering each pixel with the spectral features and position information of the current year, superimposing with potential samples, and filtering to generate new samples.
Through the research in Luobei County and the southwest of Hulin City, Heilongjiang Province, the results showed that: First, a large number of samples were generated based on historical data combined with the spectral data and location information clustering method of the current year. When the number of clusters was different, the number and structure of new generated sample changed. Luobei County generated a sample size of 1,892,129–2,180,153 pixels, and the sample size of southwest Hulin City was 125,719–147,515 pixels. Due to the stable crop structure from 2013 to 2017, more new samples were generated in Luobei County, but the sample structure generated by this county was not balanced, with the maximum of the ‘other crop’ being only 3.97%. Meanwhile, the structure of southwest Hulin City was relatively balanced. The new sample clustering screening criteria with a relatively stable classification accuracy can be obtained as follows: The type with the largest proportion in each cluster term should be greater than 0.67, and the type with the smallest proportion in the final sample should account for at least 15%. Second, it is feasible to map crop types based on the generated new samples. The classification accuracies based on the new generated samples and the field samples in Luobei County were 69.35% and 77.59%, respectively, while those in southwest Hulin City were 80.44% and 82.94%, respectively, which basically meets the mapping requirements.
This study proposed a method of generating high-purity samples combined with historical samples and spectral information of the current year. This method overcomes the problem of crop samples only being collected in the field because they are difficult to visually interpret. The proposed method effectively improves the utilization efficiency of historical data and provides a new idea for sustainable crop mapping in many areas lacking crop samples.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.L.; methodology, L.Z.; software, D.L. and Q.X.; validation, L.Z.; formal analysis, L.Z.; investigation, L.Z. and D.L.; resources, C.Z.; data curation, N.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, L.Z.; writing—review and editing, Z.L. and X.Z.; visualization, T.R.; project administration, S.L.; funding acquisition, Z.L.
Funding
This research was funded by National Key Research and Development Plan of China, grant number 2018YFD0100803.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hao, P.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, L.; Niu, Z.; Shakir, M. Feature Selection of Time Series MODIS Data for Early Crop Classification Using Random Forest: A Case Study in Kansas, USA. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 5347–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doraiswamy, P.C.; Hatfield, J.L.; Jackson, T.J.; Akhmedov, B.; Prueger, J.; Stern, A. Crop condition and yield simulations using Landsat and MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haboudane, D.; Miller, J.R.; Tremblay, N.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Dextraze, L. Integrated narrow-band vegetation indices for prediction of crop chlorophyll content for application to precision agriculture. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; Biradar, C.M.; Noojipady, P.; Dheeravath, V.; Li, Y.; Velpuri, M.; Gumma, M.; Gangalakunta, O.R.P.; Turral, H.; Cai, X.; et al. Global irrigated area map (GIAM), derived from remote sensing, for the end of the last millennium. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 3679–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ma, H.; Su, W.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Fan, J.; Wu, W. Jointly Assimilating MODIS LAI and ET Products Into the SWAP Model for Winter Wheat Yield Estimation. IEEE J.-Stars. 2015, 8, 4060–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Potapov, P.V.; Krylov, A.; King, L.; Di Bella, C.M.; Hudson, A.; Khan, A.; Adusei, B.; Stehman, S.V.; Hansen, M.C. National-scale soybean mapping and area estimation in the United States using medium resolution satellite imagery and field survey. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudorff, B.F.T.; Sugawara, L.M.; Adami, M.; Freitas, R.M.; Aguiar, D.A.; Mello, M.P. Remote Sensing Time Series to Evaluate Direct Land Use Change of Recent Expanded Sugarcane Crop in Brazil. Sustainability 2012, 4, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Csillik, O. Sentinel-2 cropland mapping using pixel-based and object-based time-weighted dynamic time warping analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardlow, B.D.; Egbert, S.L.; Kastens, J.H. Analysis of time-series MODIS 250 m vegetation index data for crop classification in the U.S. Central Great Plains. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 290–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, D.; Moran, E.; Batistella, M.; Dutra, L.V.; Sanches, I.D.; Bicudo Da Silva, R.F.; Huang, J.; Barreto Luiz, A.J.; Falcao De Oliveira, M.A. Mapping croplands, cropping patterns, and crop types using MODIS time-series data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2018, 69, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Liu, D.; Feng, Q.; Xiong, Q.; Zhang, L.; Ren, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, D.; Huang, J. Large-Scale Crop Mapping Based on Machine Learning and Parallel Computation with Grids. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.C.; Kastens, J.H.; Coutinho, A.C.; Victoria, D.D.C.; Bishop, C.R. Classifying multiyear agricultural land use data from Mato Grosso using time-series MODIS vegetation index data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 130, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, R.; Sankey, T.T.; Congalton, R.G.; Yadav, K.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Ozdogan, M.; Sánchez Meador, A.J. MODIS phenology-derived, multi-year distribution of conterminous U.S. crop types. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Wardlow, B.D.; Gitelson, A.A.; Verma, S.B.; Suyker, A.E.; Arkebauer, T.J. A Two-Step Filtering approach for detecting maize and soybean phenology with time-series MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2146–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huffman, T.; Shang, J.; Qian, B.; Dong, T.; Zhang, Y. Identifying Major Crop Types in Eastern Canada Using a Fuzzy Decision Tree Classifier and Phenological Indicators Derived from Time Series MODIS Data. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 42, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Blackburn, G.A.; Yan, J.; Liu, J. Mapping crop phenology using NDVI time-series derived from HJ-1 A/B data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2015, 34, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Yan, L. Robust Landsat-based crop time series modelling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 110810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soudani, K.; le Maire, G.; Dufrêne, E.; François, C.; Delpierre, N.; Ulrich, E.; Cecchini, S. Evaluation of the onset of green-up in temperate deciduous broadleaf forests derived from Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2643–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Hawkins, T.; Biging, G.; Gong, P. A phenology-based approach to map crop types in the San Joaquin Valley, California. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 7777–7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Gong, P.; Biging, G.S. Phenology-based Crop Classification Algorithm and its Implications on Agricultural Water Use Assessments in California’s Central Valley. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2012, 78, 799–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Yang, P.; Tang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, Z.; Shibasaki, R. Characterizing Spatial Patterns of Phenology in Cropland of China Based on Remotely Sensed Data. Agric. Sci. China 2010, 9, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Cheng, T.; Yao, X.; Deng, X.; Tian, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Y. Detection of rice phenology through time series analysis of ground-based spectral index data. Field Crops Res. 2016, 198, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, P.; Wang, L.; Zhan, Y.; Niu, Z. Using Moderate-Resolution Temporal NDVI Profiles for High-Resolution Crop Mapping in Years of Absent Ground Reference Data: A Case Study of Bole and Manas Counties in Xinjiang, China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2016, 5, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Gong, P.; Biging, G.S. Efficient corn and soybean mapping with temporal extendability: A multi-year experiment using Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Hu, L.; Yu, L.; Gong, P.; Biging, G.S. Automated mapping of soybean and corn using phenology. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2016, 119, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, L.; Hao, P.; Niu, Z. Major crops classification using time series MODIS EVI with adjacent years of ground reference data in the US state of Kansas. Optik 2016, 127, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Guan, K.; Peng, J.; Wang, S.; Seifert, C.; Wardlow, B.; Li, Z. A high-performance and in-season classification system of field-level crop types using time-series Landsat data and a machine learning approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Azzari, G.; Lobell, D.B. Crop type mapping without field-level labels: Random forest transfer and unsupervised clustering techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 222, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciano, A.C.D.S.; Picoli, M.C.A.; Rocha, J.V.; Franco, H.C.J.; Sanches, G.M.; Leal, M.R.L.V.; le Maire, G. Generalized space-time classifiers for monitoring sugarcane areas in Brazil. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 215, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, P.; Wang, L.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, C.; Niu, Z.; Wu, M. Crop classification using crop knowledge of the previous-year: Case study in Southwest Kansas, USA. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 49, 1061–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, X.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, D. The Layout of Maize Variety Test Sites Based on the Spatiotemporal Classification of the Planting Environment. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Song, K.; Zhang, B.; Li, F.; Ren, C. Process of Transformation from Wetland to Farmland and Driving Mechanism Analysis in Luobei County of Sanjiang Plain. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2009, 11, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lei, G. An Evaluation Study on Comprehensive Benefits of Land Use of Jixi Coal City in Heilongjiang Province. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 19, 176–179. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, S.; Liu, D.; Yao, X.; Tang, H.; Xiong, Q.; Zhuo, W.; Du, Z.; Huang, J.; Su, W.; Shen, S.; et al. RDCRMG: A Raster Dataset Clean & Reconstitution Multi-Grid Architecture for Remote Sensing Monitoring of Vegetation Dryness. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1376. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.M.; Stow, D. The effect of training strategies on supervised classification at different spatial resolutions. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2002, 68, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Tong, L.; Liu, Z.; Qiao, M.; Liu, D.; Huang, J. Identification method of seed maize plot based on multi-temporal GF-1 WFV and kompsat-3 texture. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2019, 50, 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Feng, Q.; Gong, J.; Zhou, J.; Liang, J.; Li, Y. Winter wheat mapping using a random forest classifier combined with multi-temporal and multi-sensor data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2018, 11, 783–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsumi, K.; Yamashiki, Y.; Canales Torres, M.A.; Taipe, C.L.R. Crop classification of upland fields using Random forest of time-series Landsat 7 ETM+ data. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 115, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).