Spatiotemporal Variation of Annual Runoff and Sediment Load in the Pearl River during 1953–2017
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Trend and Abrupt Changes Analysis
2.2.2. Periodicity Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Trends in Annual Runoff and Sediment Load
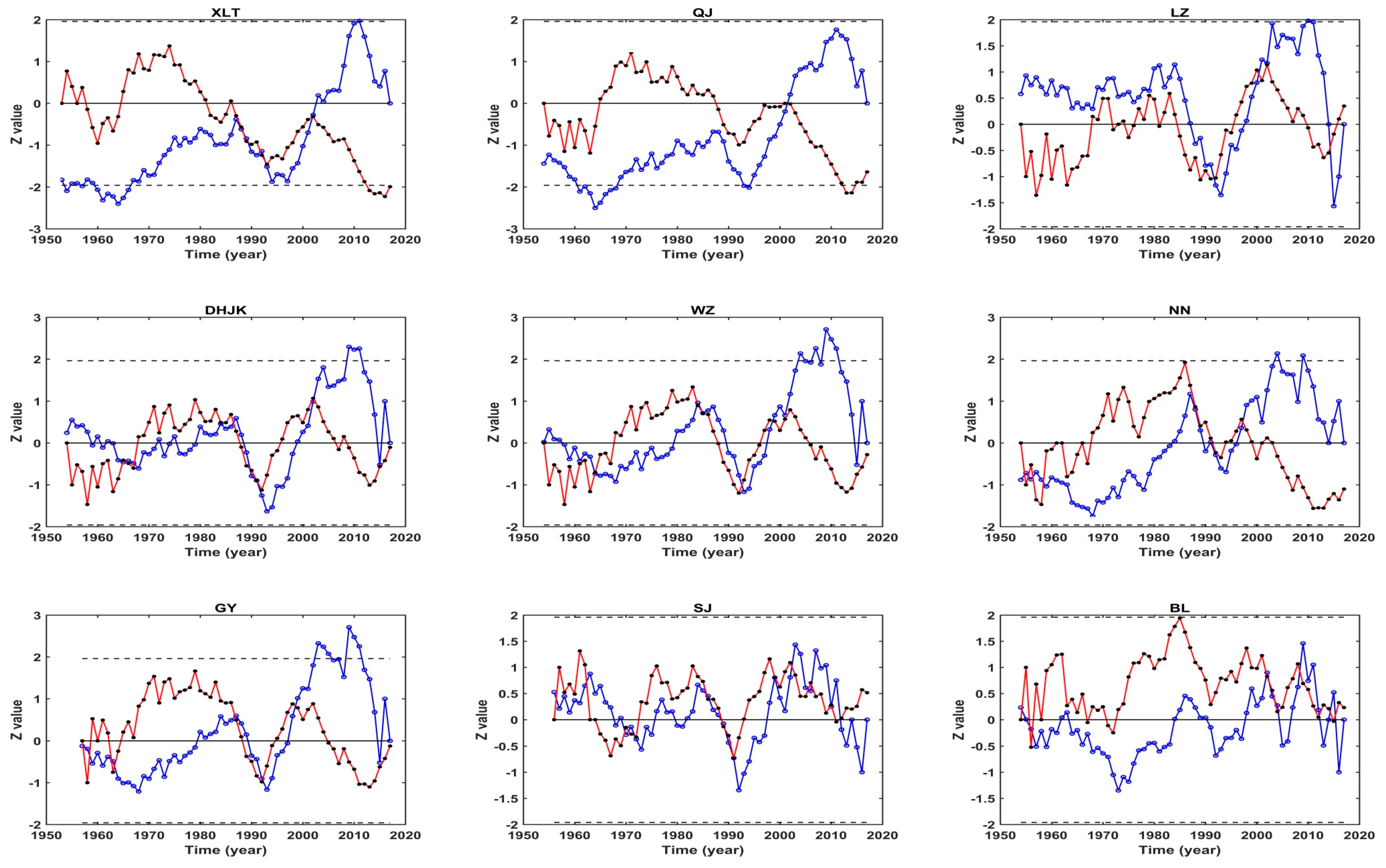
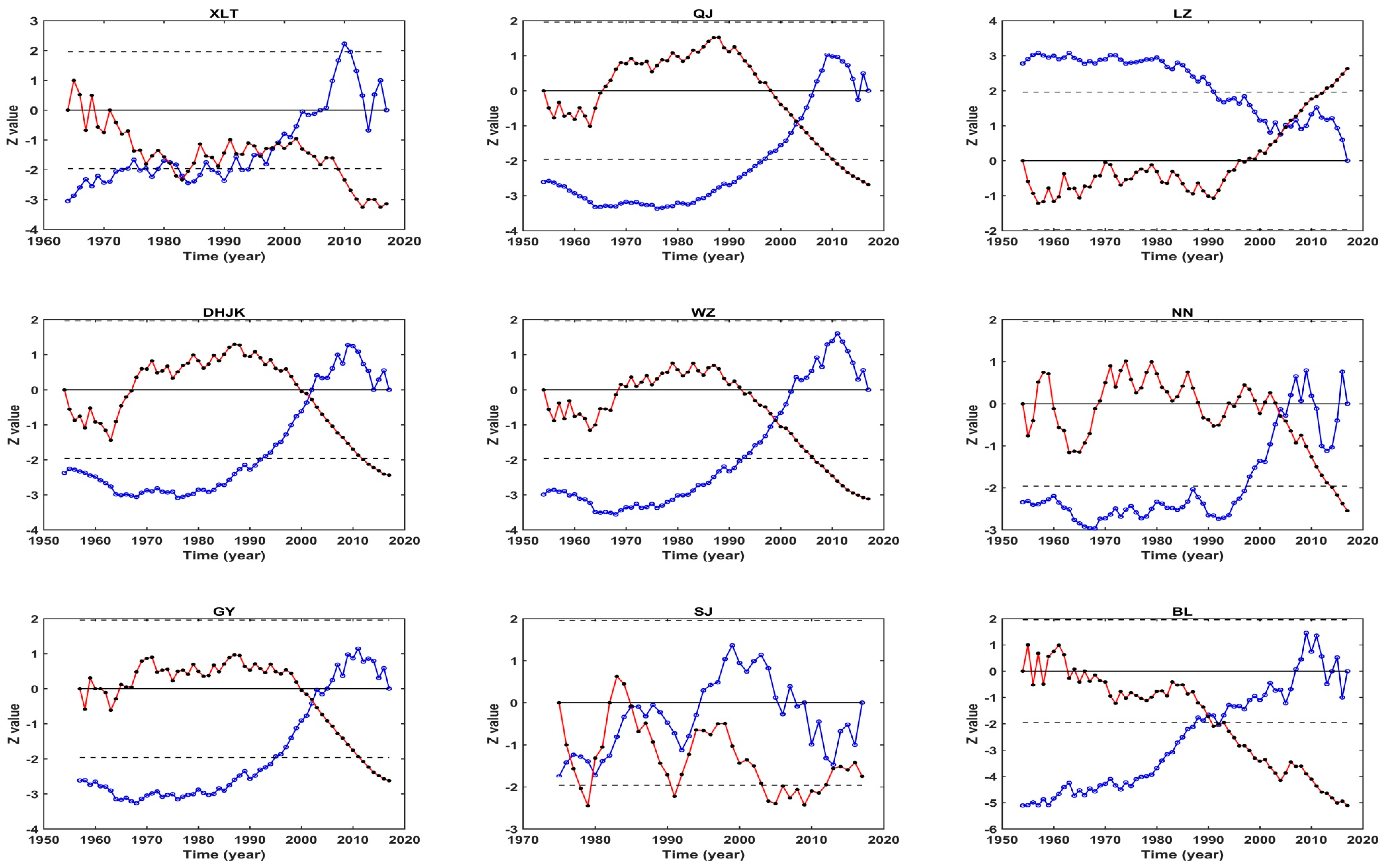
3.2. Abrupt Changes of Annual Runoff and Sediment Load
3.3. Periodicity of Annual Runoff and Sediment Load
4. Discussion
4.1. Rationality of the Study and Comparison with Other Literatures
4.2. Multiple Influential Factors and Implications
4.3. Possible Future Changes and Outlooks
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, L.; Singh, V.P.; Guo, S.L.; Zhou, J.Z.; Zhang, J.H. Copula-based method for multisite monthly daily streamflow simulation. J. Hydrol. 2015, 528, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peckham, S.D. Fluvial landscape models and catchment-scale sediment transport. Glob. Planet Chang. 2003, 39, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E.; Fang, D. Recent trends in the suspended sediment loads of the world’s rivers. Glob. Planet Chang. 2003, 39, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M. River sediments. Philos. Trans. A. Math Phys. Eng. Sci. 2012, 370, 2093–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Guo, S.L.; Hong, X.J.; Chang, F.J. Systematic impact assessment on inter-basin water transfer projects of the Hanjiang River Basin in China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 553, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Yun, H.; An, L. Key drivers of changes in sediment loads of rivers. Adv. Sci. Technol. Water Resour. 2017, 37, 1–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fryirs, K. (Dis)Connectivity in catchment sediment cascades: A fresh look at the sediment delivery problem. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2013, 38, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E. Tracing suspended sediment sources in catchments and river systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 344, 159–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.J.; Mu, X.M.; Strehmel, A.; Tian, P. Temporal Variation of Streamflow, Sediment Load and Their Relationship in the Yellow River Basin, China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliman, J.D.; Farnsworth, K.L.; Jones, P.D.; Xu, K.H.; Smith, L.C. Climatic and anthropogenic factors affecting river discharge to the global ocean, 1951–2000. Glob. Planet Chang. 2008, 62, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E. Human impact on land-ocean sediment transfer by the world’s rivers. Geomorphology 2006, 79, 192–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvitski, J.P.M.; Vorosmarty, C.J.; Kettner, A.J.; Green, P. Impact of humans on the flux of terrestrial sediment to the global coastal ocean. Science 2005, 308, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Chen, S.L.; Dong, P. Temporal variation of sediment load in the Yellow River basin, China, and its impacts on the lower reaches and the river delta. Catena 2010, 83, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.Y.; Ni, J.R.; Borthwick, A.G.L.; Yang, L. A preliminary estimate of human and natural contributions to the changes in water discharge and sediment load in the Yellow River. Glob. Planet Chang. 2011, 76, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.L.; Mu, X.M.; Zhao, G.J.; Shao, H.B.; Gao, P. Dynamic changes of sediment load in the middle reaches of the Yellow River basin, China and implications for eco-restoration. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.A.; Fu, B.J.; Piao, S.L.; Lu, Y.H.; Ciais, P.; Feng, X.M.; Wang, Y.F. Reduced sediment transport in the Yellow River due to anthropogenic changes. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.P.; Xu, Z.X.; Yao, W.Y.; Jin, S.Y.; Xiao, P.Q.; Ran, D.C. Assessing the effects of changes in land use and climate on runoff and sediment yields from a watershed in the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.M.; Xu, M.Z.; Jiang, E.H.; Wang, G.H.; Hu, H.C.; Liu, X. Temporal variations of runoff and sediment load in the upper Yellow River, China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Belkin, I.M. Temporal variation in the sediment load of the Yangtze river and the influences of human activities. J. Hydrol. 2002, 263, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.B.; Lu, X.X.; Yang, S.L.; Cai, A.M. A preliminary estimate of human and natural contributions to the decline in sediment flux from the Yangtze River to the East China Sea. Quat. Int. 2008, 186, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, L.C.; Zeng, C.F.; Wang, D.; Liu, D.F.; Wu, X.T. Variations of Runoff and Sediment Load in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River, China (1950–2013). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.F.; Yang, S.L.; Xu, K.H.; Milliman, J.D.; Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, C.Y. Human impacts on sediment in the Yangtze River: A review and new perspectives. Glob. Planet Chang. 2018, 162, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.K.; Rhoads, B.L.; Wang, D.; Wu, J.C.; Zhang, X. Impacts of large dams on the complexity of suspended sediment dynamics in the Yangtze River. J. Hydrol. 2018, 558, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Lai, C.; Lin, W.; Chen, X. Observed changes in precipitation extremes across 11 basins in China during 1961–2013. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 2866–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.R.; Lu, X.X.; Higgitt, D.L.; Chen, C.T.A.; Han, J.T.; Sun, H.G. Recent changes of water discharge and sediment load in the Zhujiang (Pearl River) Basin, China. Glob. Planet Chang. 2008, 60, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Mu, S.S.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chen, K.M. Temporal variation of suspended sediment load in the Pearl River due to human activities. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2011, 26, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Bulletin of First National Census for Water. 2013. Available online: www.mwr.gov.cn (accessed on 1 January 2013).
- Peitong, N.; Ping, W.; Jianyu, L. Study on Variation of Annual Water Discharge and Sediment Load in Pearl River Delta. Pearl River 2016, 37, 19–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Wang, Z.; Guo, S.; Liao, W.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, X. Scenario-based projections of future urban inundation within a coupled hydrodynamic model framework: A case study in Dongguan City, China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 547, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Chen, T.; Yang, N.; Qu, L.; Li, M.; Chen, D. Spatial and temporal distribution of rainfall and drought characteristics across the Pearl River basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y.; Becker, S.; Zhang, Z.X.; Chen, Y.D.; Coulibaly, M. Trends and abrupt changes of precipitation maxima in the Pearl River basin, China. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2009, 10, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.J.; Chen, J.F.; Lu, W.X.; Chen, X.H.; Lian, Y.Q. Spatiotemporal characteristics of precipitation changes in the Pearl River Basin, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 123, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.X.; Wang, S.J.; Yan, M.; He, L.; Zhang, L. Spatial variation of scale effects of specific sediment yield in Zhujiang (Pearl River) basin. Quat. Int. 2014, 336, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y.; Chen, X.H.; Lu, X.X. Abrupt changes in the discharge and sediment load of the Pearl River, China. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 1495–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y.; Chen, Y.Q.D.; Jiang, J.M. Abrupt behaviors of the streamflow of the Pearl River basin and implications for hydrological alterations across the Pearl River Delta, China. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Chen, J. A wavelet perspective on variabilities of hydrological processes in conjunction with geomorphic analysis over the Pearl River basin in South China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 392–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests Against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George Kendall, M. Rank Correlation Methods; Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Kahya, E.; Kalayci, S. Trend analysis of streamflow in Turkey. J. Hydrol. 2004, 289, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, O.; Gassmann, M.; Wegerich, K.; Bauer, M. Identification of the effective water availability from streamflows in the Zerafshan river basin, Central Asia. J. Hydrol. 2010, 390, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, D.K.; Kumar, A.; Mohanty, S. Recent trends in sediment load of the tropical (Peninsular) river basins of India. Glob. Planet Chang. 2011, 75, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.; Hisdal, H.; Lawrence, D. Has streamflow changed in the Nordic countries?—Recent trends and comparisons to hydrological projections. J. Hydrol. 2010, 394, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libiseller, C.; Grimvall, A. Performance of partial Mann-Kendall tests for trend detection in the presence of covariates. Environmetrics 2002, 13, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Wang, C.Y. Applicability of prewhitening to eliminate the influence of serial correlation on the Mann-Kendall test. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mount, N.J.; Tate, N.J.; Sarker, M.H.; Thorne, C.R. Evolutionary, multi-scale analysis of river bank line retreat using continuous wavelet transforms: Jamuna River, Bangladesh. Geomorphology 2013, 183, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A.K. Spectral-temporal characterization of riverflow variability in England and Wales for the period 1865–2002. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.A.; Schmidt, J.C.; Topping, D.J. Application of wavelet analysis for monitoring the hydrologic effects of dam operation: Glen Canyon Dam and the Colorado River at Lees Ferry, Arizona. River Res. Appl. 2005, 21, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Guo, S.; Yin, J.; Yang, G.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, D. On the event-based extreme precipitation across China: Time distribution patterns, trends, and return levels. J. Hydrol. 2018, 562, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinsted, A.; Moore, J.C.; Jevrejeva, S. Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2004, 11, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Lai, C.; Zeng, Z.; Zhong, R.; Chen, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, M. Does drought in China show a significant decreasing trend from 1961 to 2009? Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Xu, K.H.; Milliman, J.D.; Yang, H.F.; Wu, C.S. Decline of Yangtze River water and sediment discharge: Impact from natural and anthropogenic changes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, N.; Wang, L. Characteristics of runoff and sediment discharge in Yangtze river in recent 60 years. J. Sediment Res. 2016, 5, 40–46. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yao, S.; Zhou, Y. Review on river sediment resources utilization in China. J. Sediment Res. 2019, 44, 73–80. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.C.; Lian, Y.Q.; Qin, X.Q. Rocky desertification in Southwest China: Impacts, causes, and restoration. Earth Sci. Rev. 2014, 132, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Liu, Z.; Shao, H.; Yang, Z. Karst bare slope soil erosion and soil quality: A simulation case study. Solid Earth 2015, 6, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.J.; Dai, Q.H.; Yuan, Y.F.; Peng, X.D.; Zhao, L.S.; Yang, J. Effects of rainfall intensity on runoff and sediment yields on bare slopes in a karst area. SW China. Geoderma 2018, 330, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.G.; Chen, X.H.; Wang, Z.L.; Wu, X.S.; Zhao, S.W.; Wu, X.Q.; Bai, W.K. Spatio-temporal variation in rainfall erosivity during 1960–2012 in the Pearl River Basin, China. Catena 2016, 137, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Cai, Y.L. Multi-Scale Anthropogenic Driving Forces of Karst Rocky Desertification in Southwest China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Park, T.; Wang, X.; Piao, S.; Xu, B.; Chaturvedi, R.K.; Fuchs, R.; Brovkin, V.; Ciais, P.; Fensholt, R.; et al. China and India lead in greening of the world through land-use management. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.Y.; Yang, X.H.; Wang, K.J.; Xiao, L.L. Is Forest Restoration in the Southwest China Karst Promoted Mainly by Climate Change or Human-Induced Factors? Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9895–9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Brandt, M.; Yue, Y.; Horion, S.; Wang, K.; Keersmaecker, W.D.; Tian, F.; Schurgers, G.; Xiao, X.; Luo, Y.; et al. Increased vegetation growth and carbon stock in China karst via ecological engineering. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.S.; Yang, S.L.; Huang, S.C.; Mu, J.B. Delta changes in the Pearl River estuary and its response to human activities (1954–2008). Quat. Int. 2016, 392, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Guo, S.; Liu, D.; Hong, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, P.; Chen, H. Characterization of rainstorm modes along the upper mainstream of Yangtze River during 2003–2016. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 1976–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zeng, Z.; Lai, C.; Chen, X. Variability of annual peak flows in the Beijiang River Basin, South China, and possible underlying causes. Hydrol. Res. 2017, 48, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]




| River | Control Station | Drainage Area (104 km2) | Runoff Data Availability | Mean Annual Runoff (109 m3/year) | Sediment Data Availability | Mean Annual Sediment Load (106 tons/year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanpanjiang River | XLT | 1.54 | 1953–2015 | 3.595 | 1964–2015 | 4.48 |
| Hongshui River | QJ | 12.89 | 1954–2015 | 64.66 | 1954–2015 | 35.3 |
| Liujiang River | LZ | 4.54 | 1954–2015 | 39.33 | 1955–2015 | 4.96 |
| Xunjiang River | DHJK | 7.27 | 1954–2015 | 169.6 | 1954–2015 | 50.1 |
| West River | WZ | 28.85 | 1954–2015 | 201.6 | 1954–2015 | 55.7 |
| Yujiang River | NN | 32.70 | 1954–2015 | 36.83 | 1954–2015 | 8.15 |
| West River | GY | 35.15 | 1957–2015 | 217.3 | 1957–2015 | 59.6 |
| North River | SL | 3.84 | 1954–2015 | 41.71 | 1954–2015 | 5.38 |
| East River | BL | 2.53 | 1954–2015 | 23.10 | 1954–2015 | 2.26 |
| River | Reservoir | Number | Normal Pool Level (m) | Storage Capacity (108 m3) | Date of Impoundment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanpanjiang | Tianshengqiao | 1 | 780 | 103 | 2000 |
| Hongshuihe | Longtan | 2 | 400 | 273 | 2009 |
| Yujiang | Baise | 3 | 228 | 56 | 2002 |
| Yujiang | Xijin | 4 | 63 | 14 | 1979 |
| West | Datengxia | 5 | 61 | 34 | Unfinished |
| North | Feilaixia | 6 | 52 | 19 | 1993 |
| East | Xinfengjiang | 7 | 116 | 140 | 1969 |
| East | Fengshuba | 8 | 166 | 19 | 1973 |
| Station | Location | Annual Runoff | Annual Sediment Load | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| z Statistics | p-Value | T | z Statistics | p-Value | T | ||
| XLT | Upper reach | −2.47 | <0.05 | ↓ | −3.09 | <0.05 | ↓ |
| QJ | Middle reach | −1.96 | <0.05 | ↓ | −5.34 | <0.05 | ↓ |
| LZ | Middle reach | 0.46 | 0.647 | - | 4.53 | <0.05 | ↑ |
| DHJK | Middle reach | 0.06 | 0.949 | - | −4.33 | <0.05 | ↓ |
| WZ | Middle reach | −0.12 | 0.903 | - | −5.44 | <0.05 | ↓ |
| NN | Middle reach | −0.99 | 0.325 | - | −3.20 | <0.05 | ↓ |
| GY | Lower reach | −0.12 | 0.906 | - | −4.47 | <0.05 | ↓ |
| SJ | Lower reach | 0.52 | 0.606 | - | −1.00 | 0.3182 | - |
| BL | Lower reach | 0.23 | 0.821 | - | −5.10 | <0.05 | ↓ |
| Stations | Abrupt Change Year of Annual Runoff | Abrupt Change Year of Annual Sediment Load |
|---|---|---|
| XLT | 2003 | 1999 |
| QJ | 2001 | 2003 |
| LZ | / | 2005 |
| DHJK | / | 2001 |
| WZ | / | 1999 |
| NN | / | 2004 |
| GY | / | 1999 |
| SJ | / | / |
| BL | / | 1992 |
| Stations | Annual Runoff | Annual Sediment Load | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Availability | Multiple Time-Scale Periodicity (years) | Prominent Periodicity (years) | Data Availability | Multiple Time-Scale Periodicity (year) | Prominent Periodicity (year) | |
| Xiaolongtan | 1953–2017 | 2.6; 10.4; 17.5; 29.5 | 2.6 | 1964–2017 | 2.6; 6.2; 17.5; 29.5 | 2.6 |
| Qianjiang | 1954–2017 | 3.1; 7.4; 14.7; 24.8 | 3.1 | 1954–2017 | 3.7; 17.5 | 3.7 |
| liuzhou | 1954–2017 | 3.1; 7.4; 20.9 | 3.1 | 1954–2017 | 2.2; 3.7; 7.4; 12.4 | 2.2 |
| Dahuangjiangkou | 1954–2017 | 2.6; 3.1; 7.4; 24.8 | 2.6; 3.1 | 1954–2017 | 3.1; 14.7 | 3.1 |
| Wuzhou | 1954–2017 | 2.6; 7.4; 20.9 | 2.6 | 1954–2017 | 3.7; 14.7 | 3.7 |
| Nanning | 1954–2017 | 2.6; 3.7; 6.2; 14.7; 24.8 | 2.6; 3.7; 6.2 | 1954–2017 | 3.7; 8.8; 24.8 | 3.7 |
| Gaoyao | 1957–2017 | 2.6; 7.4; 24.8 | 2.6 | 1957–2017 | 3.1; 8.8; 12.4 | 3.1 |
| Shijiao | 1956–2017 | 2.6; 4.4; 10.4; 20.9 | 2.6; 4.4 | 1975–2017 | 2.2; 4.4; 6.2; 14.7; 29.5 | 2.2; 4.4 |
| Boluo | 1954–2017 | 2.6; 4.4; 8.8; 20.9 | 2.6; 4.4 | 1954–2017 | 2.2; 7.4; 12.4; 20.9 | 2.2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, H.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Guo, S.; Chen, X. Spatiotemporal Variation of Annual Runoff and Sediment Load in the Pearl River during 1953–2017. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5007. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11185007
Zhou H, Wang Z, Wu X, Chen Y, Zhong Y, Li Z, Chen J, Li J, Guo S, Chen X. Spatiotemporal Variation of Annual Runoff and Sediment Load in the Pearl River during 1953–2017. Sustainability. 2019; 11(18):5007. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11185007
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Huanyang, Zhaoli Wang, Xushu Wu, Yuhong Chen, Yixuan Zhong, Zejun Li, Jiachao Chen, Jun Li, Shenglian Guo, and Xiaohong Chen. 2019. "Spatiotemporal Variation of Annual Runoff and Sediment Load in the Pearl River during 1953–2017" Sustainability 11, no. 18: 5007. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11185007
APA StyleZhou, H., Wang, Z., Wu, X., Chen, Y., Zhong, Y., Li, Z., Chen, J., Li, J., Guo, S., & Chen, X. (2019). Spatiotemporal Variation of Annual Runoff and Sediment Load in the Pearl River during 1953–2017. Sustainability, 11(18), 5007. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11185007









