Urban Expansion and the Loss of Prairie and Agricultural Lands: A Satellite Remote-Sensing-Based Analysis at a Sub-Watershed Scale
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
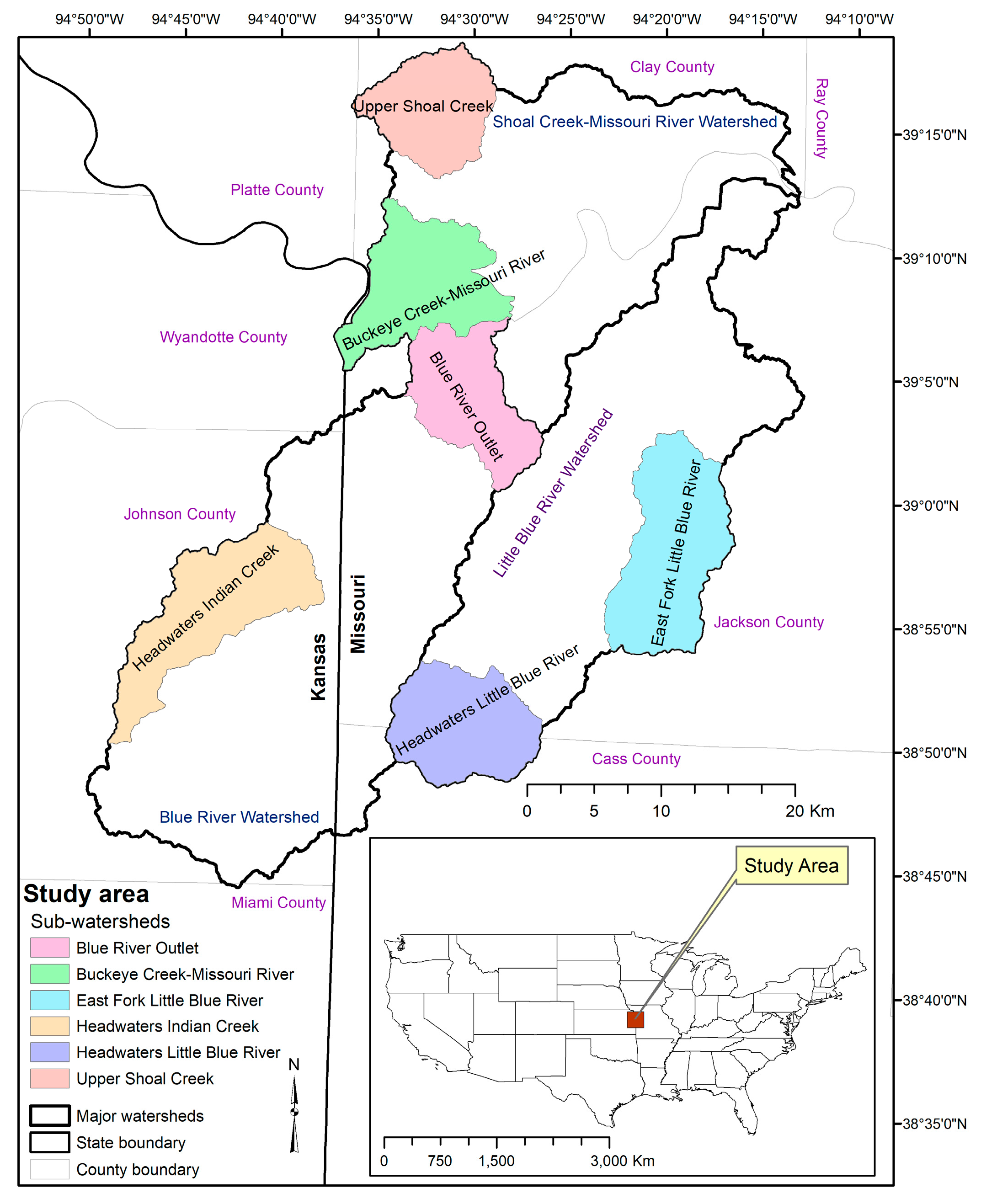
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Processing
2.3. Methodology
Image Classification and Accuracy Assessment
2.4. Analysis of Urban Expansion in Study Area (Six Sub-Watersheds)
2.4.1. Percent Change in Urban Expansion
2.4.2. Rate of Urban Expansion
2.5. Dynamics of Agricultural Land/Grassland Loss in the Six Sub-Watersheds
3. Results
3.1. Accuracy Assessment
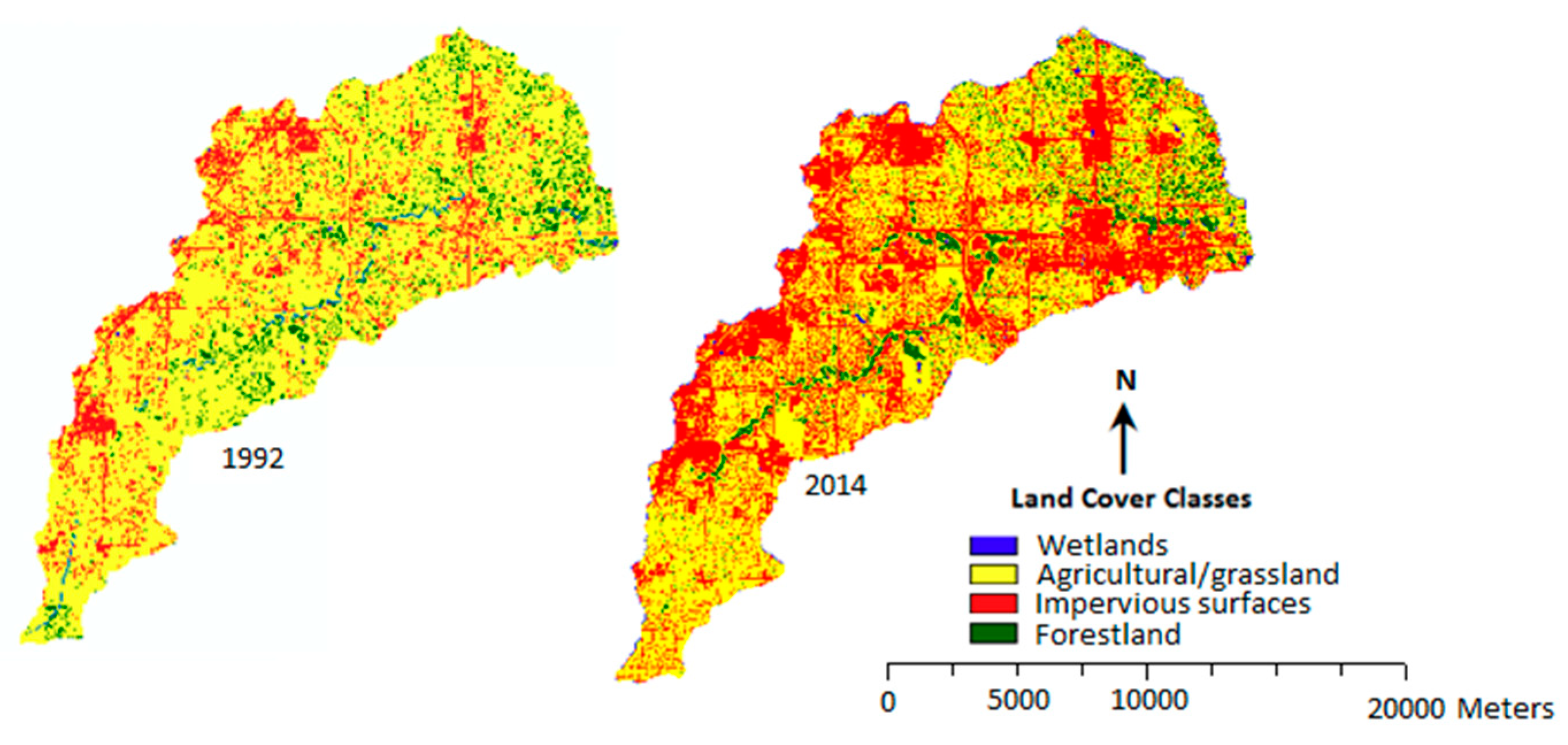
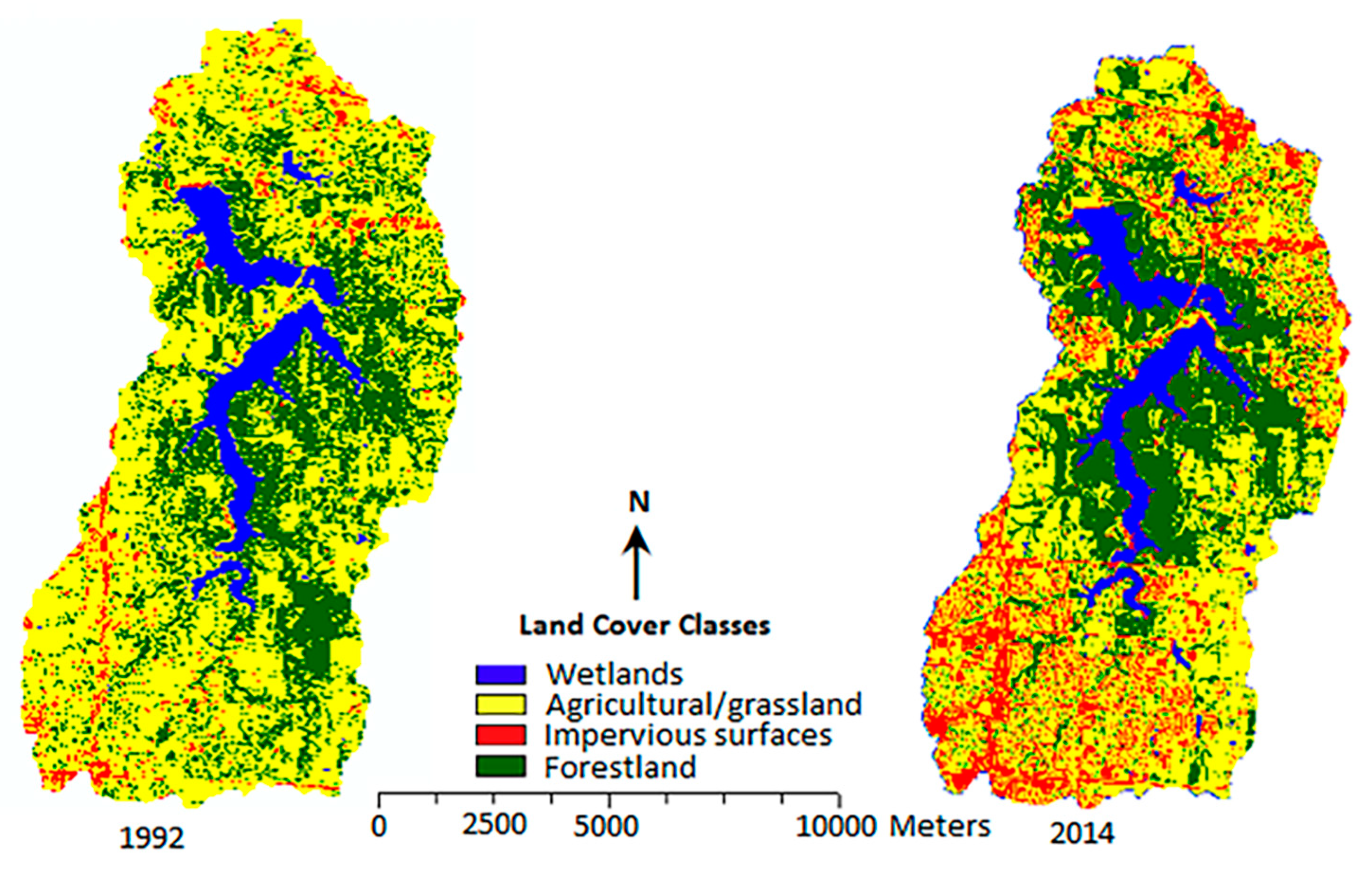
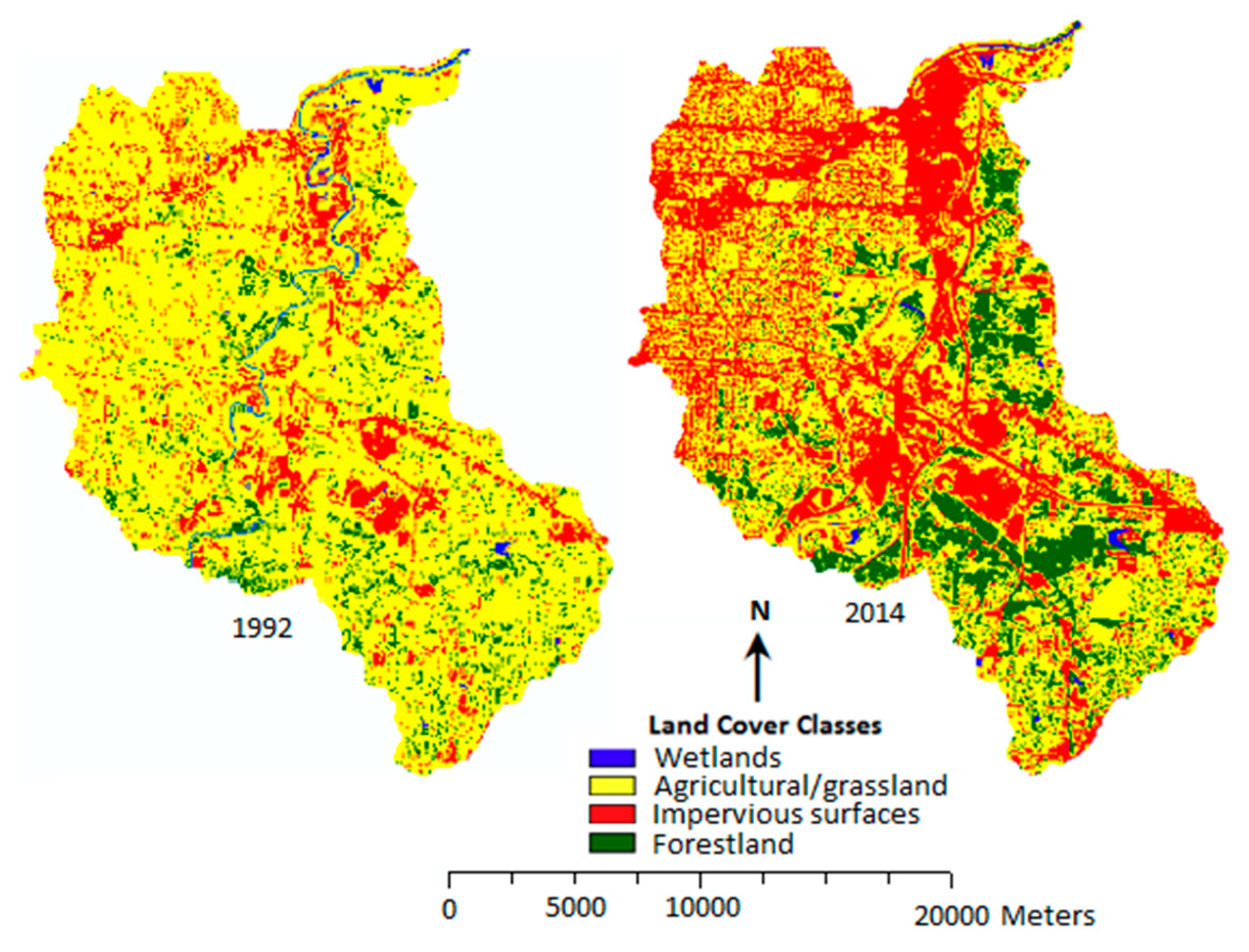
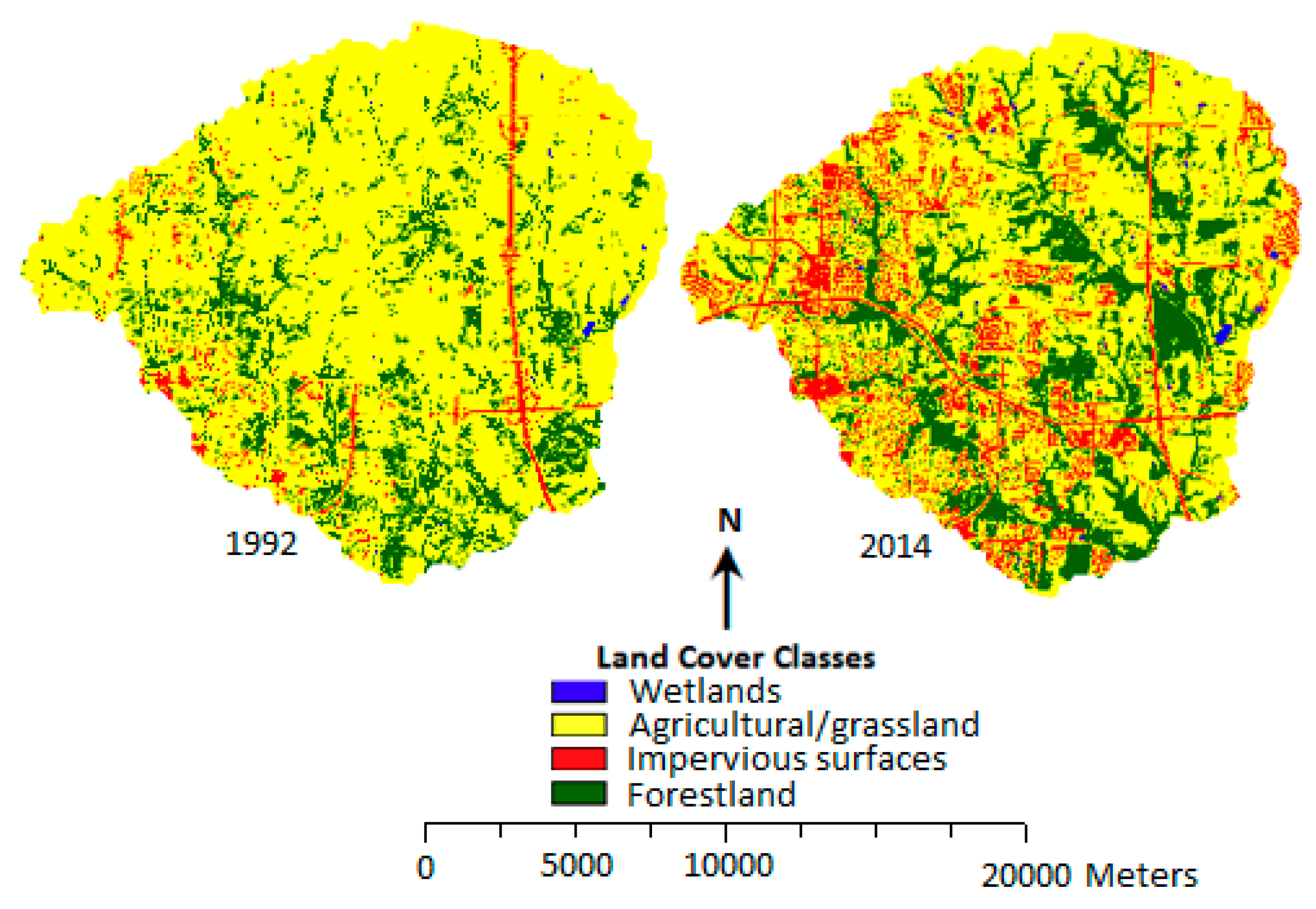
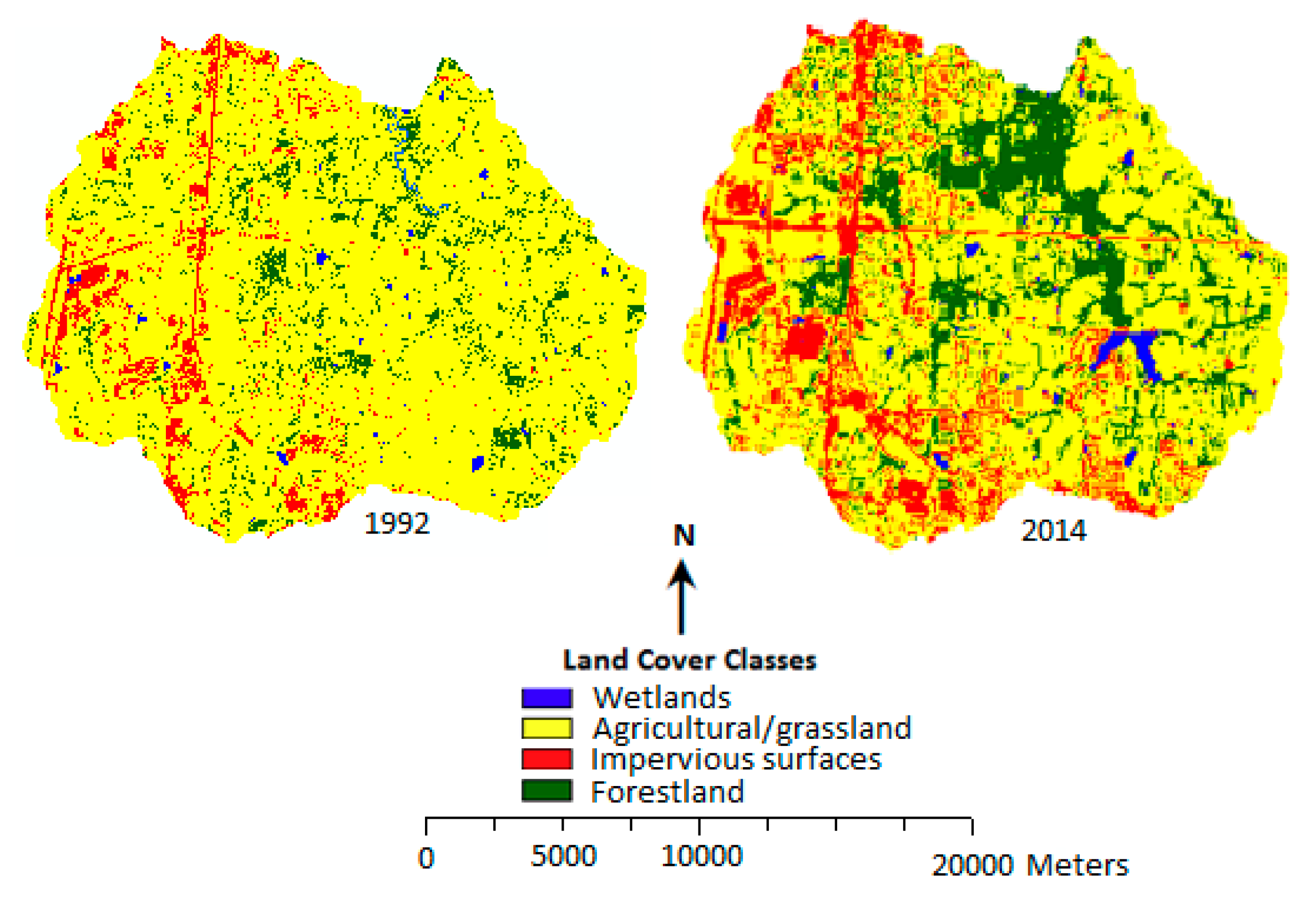
3.2. Change in LULC for the Six Sub-Watersheds
3.3. Urban Expansion and Loss of Agricultural Land/Grassland in the Six Sub-Watersheds
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohen, B. Urbanization in developing countries: Current trends, future projections, and key challenges for sustainability. Technol. Soc. 2006, 28, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenta, A.A.; Yasuda, H.; Haregeweyn, N.; Belay, S.A.; Hadush, Z.; Gebremedhin, A.M.; Mekonnen, G. The dynamics of urban expansion and land use/land cover changes using remote sensing and spatial metrics: The case of Mekelle City of northern Ethiopia. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 4107–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soffanian, A.; Nadoushan, A.M.; Yaghmaei, L.; Falahatkar, S. Mapping and analyzing urban expansion using remotely sensed imagery in Isfahan, Iran. World Appl. Sci. J. 2010, 9, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Tewolde, M.G.; Cabral, P. Urban sprawl analysis and modelling in Asmara, Eritrea. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 2148–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, Y.H.; Cabral, P. Analysis and modelling of urban land cover change in Setubal and Sesimbra, Portugal. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 1549–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundia, C.N.; Murayama, Y. Modelling spatial processes of urban growth in African cities: A case study of Nairobi City. Urban Geogr. 2010, 31, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.; Francis, C. Multifunctional Rural Landscapes; University Nebraska Center for Applied Rural Innovation (CARI): Lincoln, NE, USA, 2007; Available online: http://cari.unl.edu/SustainableAg/pdf/ MultifunctionalRuralLandscapes.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- World Bank. World Bank Database. 2015. Available online: http://data.worldbank.org (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- United Nations. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2014 Revision. Available online: http://esa.un.org/unpd/wup/index.htm (accessed on 3 June 2019).
- Francis, A.C.; Hansen, E.T.; Fox, A.A.; Hesje, J.P.; Nelson, E.H.; Lawseth, E.A.; English, A. Farmland conversion to non-agricultural uses in the US and Canada: Current impacts and concerns for the future. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2012, 10, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Lu, C.; Cheng, X. Spatiotemporal evolution of urban land uses in modern urbanization of China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, M.K.; York, A.M.; Boone, C.G.; Zhang, S. Land fragmentation due to rapid urbanization in the Phoenix Metropolitan Area: Analyzing the spatiotemporal patterns and drivers. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 32, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, D.; Wu, S.; Zhou, S.; Wang, T.; Chen, H. Spatio-temporal assessment of urbanization impacts on ecosystem services: Case study of Nanjing City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 71, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Li, H.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, L. Vulnerability of ecosystem services provisioning to urbanization: A case of China. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 57, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Hong, S. Global urbanization research from 1991 to 2009: A systematic research review. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 104, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, S.; Parent, J.; Civco, D.L.; Blei, A.; Potere, D. The dimensions of global urban expansion: Estimates and projections for all countries 2000–2050. Prog. Plan. 2011, 75, 53–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Pozzi, F.; Elvidge, C.D. Spatial analysis of global urban extents from the DMSP-OLS night-lights. Remote Sens. Environ 2005, 96, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Li, X.; Xie, H.; Lu, C. Urban land expansion and arable land loss in China—A case study of Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region. Land Use Policy 2005, 22, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Deng, X.; Seto, K.C. The impact of urban expansion on agricultural land use intensity in China. Land Use Policy 2013, 35, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Ma, J.; Twibell, R.W.; Underhill, K. Characterizing urban sprawl using multi-stage remote sensing images and landscape metrics. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2006, 30, 861–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, L.; Pandey, C.P.; Nathawat, S.M. Assessment of land consumption rate with urban dynamics change using geospatial techniques. J. Land Use Sci. 2012, 7, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boori, S.M.; Netzband, M.; Choudhary, K.; Voženílek, V. Monitoring and modeling of urban sprawl through remote sensing and GIS in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Ecol. Process. 2015, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, A.O.; Ji, W.; Weilert, E.T. Modeling the Impact of Urban Landscape Change on Urban Wetlands Using Similarity Weighted Instance-Based Machine Learning and Markov Model. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MARC (Mid-America Regional Council). Census Data for the MARC Region. 2010. Available online: http://www.marc.org/Data-Economy/Metrodataline/Population/Census-2010 (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- Weilert, E.T.; Ji, W.; Zubair, A.O. Article Assessing the Impacts of Streamside Ordinance Protection on the Spatial and Temporal Variability in Urban Riparian Vegetation. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, O.A.; Ji, W. Assessing the Impact of Land Cover Classification Methods on the Accuracy of Urban Land Change Prediction. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 41, 170–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Stow, D. The effect of training strategies on supervised classification at different spatial resolutions. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2002, 68, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson, P.; Food, M.G.; Herold, M.; Stehmand, V.S.; Woodcock, E.C.; Wulder, A.M. Good practices for estimating area and assessing accuracy of land change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 148, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Shen, Y.; Ge, J.; Tateishi, R.; Tang, C.; Liang, Y.; Huang, Z. Evaluating urban expansion and land use change in Shijiazhuang, China, by using GIS and remote sensing. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 75, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Mausel, P.; Brondi’Zio, E.; Moran, E. Change detection techniques. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 2365–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ERDAS Field Guide. 1999. Available online: http://web.pdx.edu/~emch/ip1/FieldGuide.pdf (accessed on 3 June 2019).
- Ji, W.; Xu, X.; Murambadoro, D. Understanding urban wetland dynamics: Cross-scale detection and analysis of remote sensing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 1763–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagan, H.; Yamagata, Y. Land-cover change analysis in 50 global cities by using a combination of Landsat data and analysis of grid cells. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 064015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megahed, Y.; Cabral, P.; Silva, J.; Caetano, M. Land Cover Mapping Analysis and Urban Growth Modelling Using Remote Sensing Techniques in Greater Cairo Region—Egypt. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2015, 4, 1750–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Liu, J.; Fu, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, G.; Yang, G.; Luo, L. Urban Expansion and Its Impact on the Land Use Pattern in Xishuangbanna since the Reform and Opening up of China. Remote Sens. 2017, 2, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Agriculture. Forests of Missouri. 2014. Available online: https://www.fs.fed.us/nrs/pubs/ru/ru_fs40.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2019).
- Kansas Forest Service. Forest in Kansas. 2018. Available online: https://www.kansasforests.org/kansas_forest_services/forestsinkansas.html (accessed on 28 February 2019).
- The World Bank Open Data. World Bank Database. 2019. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/AG.LND.FRST.ZS?end=2016&locations=US&start=1990&view=chart (accessed on 28 February 2019).
- Rouse. Assessing Urban Wetlands. Final Report to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Region 7. 2004. Available online: https://dnr.mo.gov/geology/wrc/docs/urban-wetlands.pdf?/env/wrc/docs/urban-wetlands.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2019).

| Sensor | Date | Spectral Mode | No. of Bands | Processing Level | Spatial Resolution (m) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPOT 2 | 29 January 1992 | XS | 3 | 1A | 20 | SPOT image corporation |
| SPOT 5 | 11 August 2014 | J | 4 | 2A | 10 | SPOT image corporation |
| Land Cover Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Impervious surfaces | Residential areas, shopping centers, industrial and commercial facilities, highways and major streets, and associated properties and parking lots |
| Forestland | Areas of land with collection of trees |
| Agricultural land/grasslands | Areas with grasses, brush, crops, and in general, non-forest vegetation |
| Wetlands | Open water bodies and vegetated lowlands such as riparian areas |
| Accuracy Assessment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land Use/Cover Classes | 1992 | 2014 | ||
| Accuracy Assessment (%) | ||||
| Producer’s | User’s | Producer’s | User’s | |
| Agricultural land/grassland | 88.7 | 93.4 | 95.52 | 90.14 |
| Forestland | 94.8 | 87.3 | 87.27 | 85.71 |
| Impervious surfaces | 91.5 | 86.1 | 86.79 | 97.87 |
| Wetland | 92.1 | 90.3 | 62.50 | 100.00 |
| Overall classification accuracy | 90.1 | 90.8 | ||
| Land Cover Classes | HIC | EFLBR | BC-MR | BRO | USC-MR | HLBR | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (%) | Area (%) | Area (%) | Area (%) | Area (%) | Area (%) | |||||||
| 1992 | 2014 | 1992 | 2014 | 1992 | 2014 | 1992 | 2014 | 1992 | 2014 | 1992 | 2014 | |
| Wetlands | 0.70 | 0.31 | 7.06 | 7.94 | 4.45 | 4.86 | 1.11 | 0.49 | 0.15 | 1.26 | 0.65 | 1.26 |
| Agricultural land/grassland | 77.82 | 55.13 | 60.04 | 47.95 | 65.47 | 38.34 | 79.88 | 50.45 | 81.52 | 67.63 | 85.44 | 67.63 |
| Impervious surfaces | 15.23 | 37.64 | 3.32 | 15.56 | 20.03 | 45.07 | 12.82 | 35.14 | 3.35 | 14.65 | 6.53 | 14.65 |
| Forest | 6.25 | 6.92 | 29.58 | 28.55 | 10.05 | 12.46 | 6.19 | 13.92 | 14.98 | 16.46 | 7.38 | 16.46 |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Sub-Watersheds | Rate of Urban Expansion |
|---|---|
| Headwaters Indian Creek | 5.7 |
| East Fork Little Blue River | 16.8 |
| Buckeye Creek-Missouri River | 6.8 |
| Blue River Outlet | 5.5 |
| Upper Shoal Creek-Missouri River | 14.4 |
| Headwaters Little Blue River | 7.9 |
| Sub-Watersheds | Area in Hectares | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urbanized Areas | Agricultural Land/Grassland | |||||
| 1992 (ha) | 2014 (ha) | % Change | 1992 (ha) | 2014 (ha) | % Change | |
| Headwaters Indian Creek | 1710.96 | 3868.80 | 126 | 5590.92 | 3291.12 | −41 |
| East Fork Little Blue River | 342.32 | 1604.88 | 369 | 6184.68 | 4946.88 | −20 |
| Buckeye Creek-Missouri River | 1501.16 | 3731.44 | 149 | 7671.48 | 5465.32 | −29 |
| Blue River Outlet | 510.44 | 1147.24 | 125 | 6677.32 | 5293.92 | −21 |
| Upper Shoal Creek-Missouri River | 219.44 | 915.4 | 317 | 5344.36 | 4166.68 | −22 |
| Headwaters Little Blue River | 920.92 | 2528.64 | 175 | 5735.72 | 3629.44 | −37 |
| Sub-Watershed | Total Loss (ha) | Loss Due to Urban Expansion | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (ha) | (%) | ||
| Headwaters Indian Creek | 2299.8 | 2225.72 | 96.77 |
| East Fork Little Blue River | 1237.8 | 1140.00 | 92.09 |
| Buckeye Creek-Missouri River | 2206.16 | 2193.52 | 99.43 |
| Blue River Outlet | 1383.40 | 810.56 | 58.59 |
| Upper Shoal Creek-Missouri River | 1177.68 | 722.48 | 61.35 |
| Headwaters Little Blue River | 2106.28 | 1763.12 | 83.71 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zubair, O.A.; Ji, W.; Festus, O. Urban Expansion and the Loss of Prairie and Agricultural Lands: A Satellite Remote-Sensing-Based Analysis at a Sub-Watershed Scale. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4673. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11174673
Zubair OA, Ji W, Festus O. Urban Expansion and the Loss of Prairie and Agricultural Lands: A Satellite Remote-Sensing-Based Analysis at a Sub-Watershed Scale. Sustainability. 2019; 11(17):4673. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11174673
Chicago/Turabian StyleZubair, Opeyemi A., Wei Ji, and Olusola Festus. 2019. "Urban Expansion and the Loss of Prairie and Agricultural Lands: A Satellite Remote-Sensing-Based Analysis at a Sub-Watershed Scale" Sustainability 11, no. 17: 4673. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11174673
APA StyleZubair, O. A., Ji, W., & Festus, O. (2019). Urban Expansion and the Loss of Prairie and Agricultural Lands: A Satellite Remote-Sensing-Based Analysis at a Sub-Watershed Scale. Sustainability, 11(17), 4673. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11174673




