A Spatial Fuzzy Multicriteria Analysis of Accessibility: A Case Study in Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
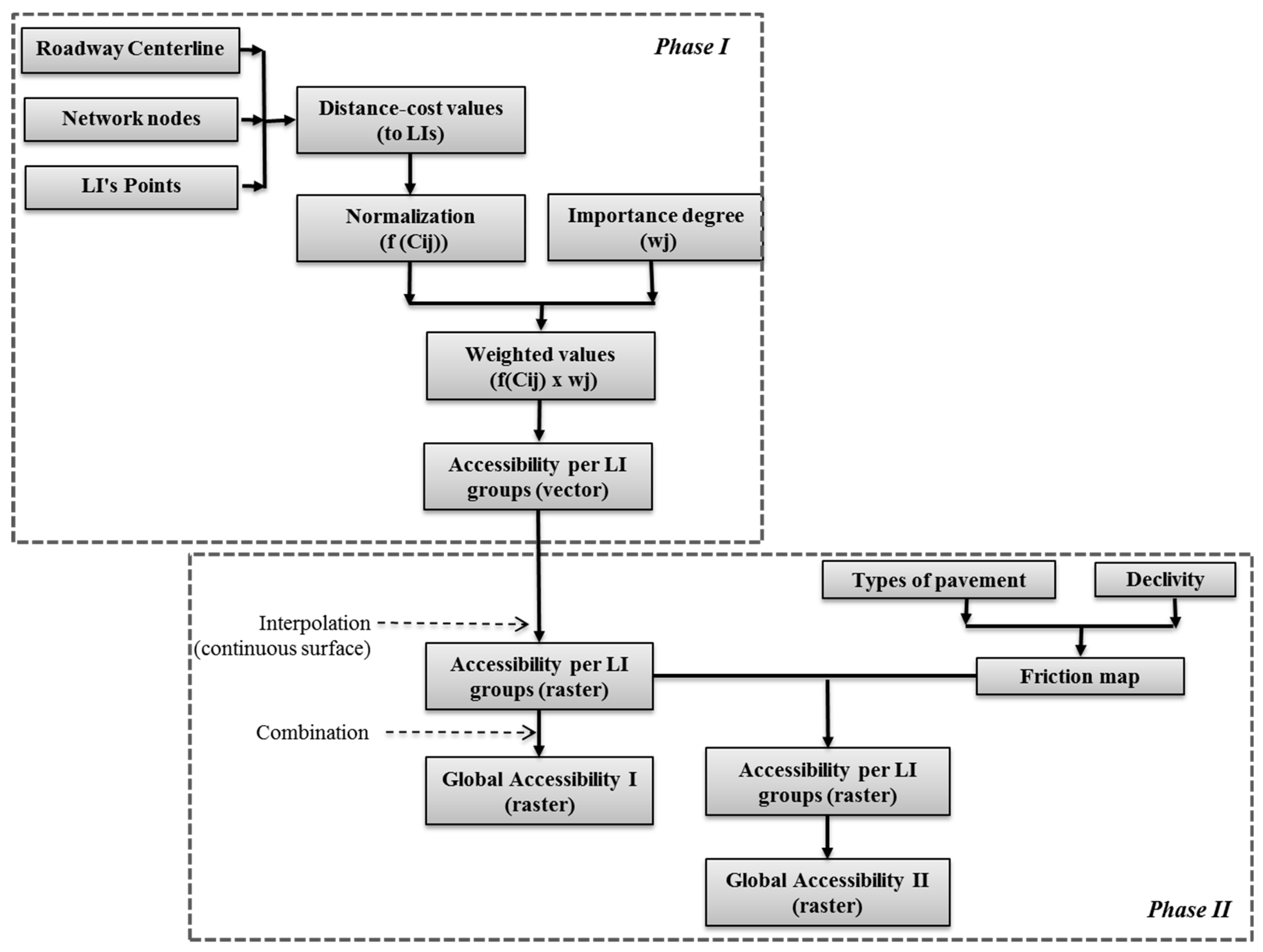
2. Materials and Methods
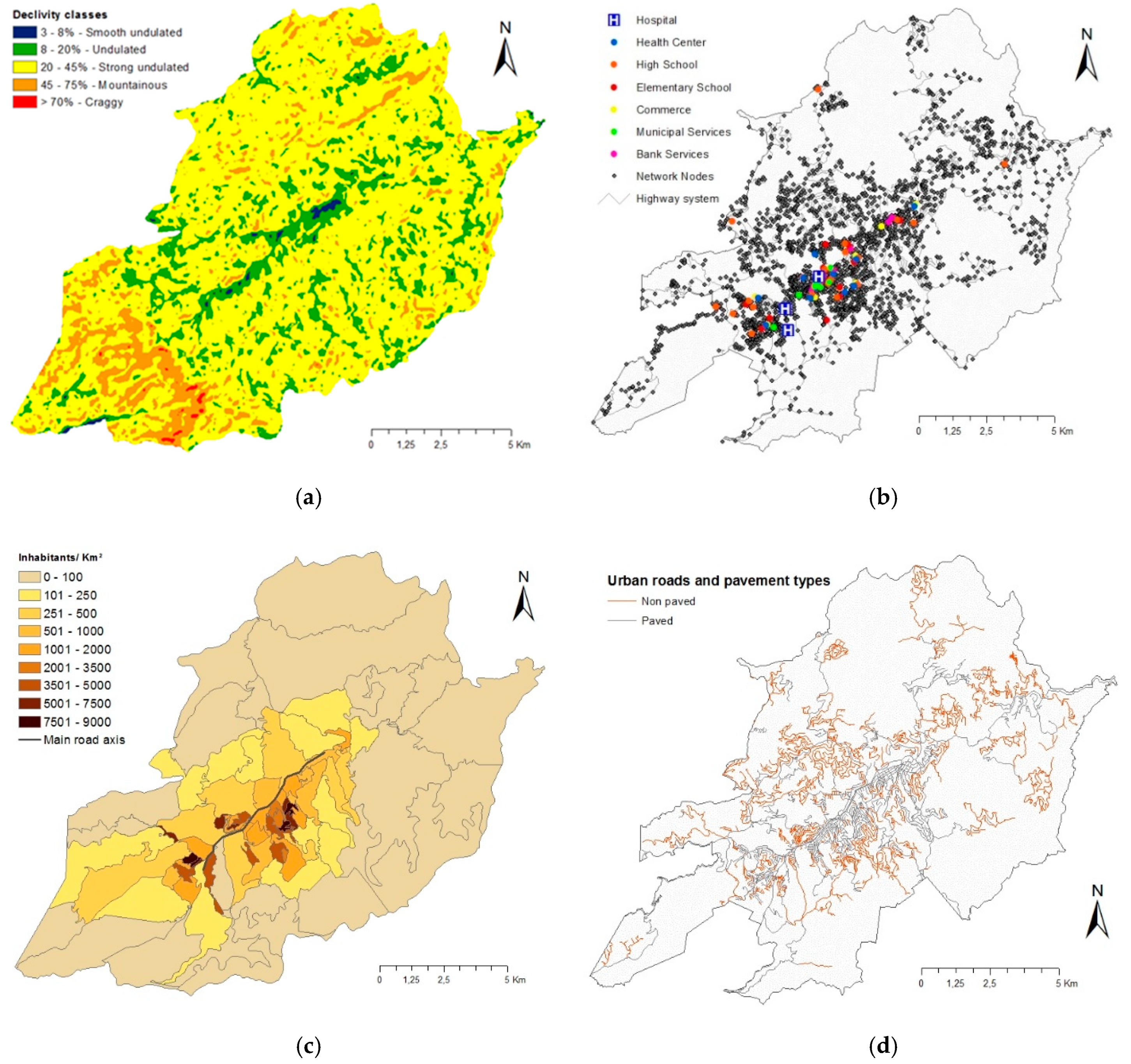
3. Results
3.1. Importance of Locations of Interests and Distance–Cost Definition
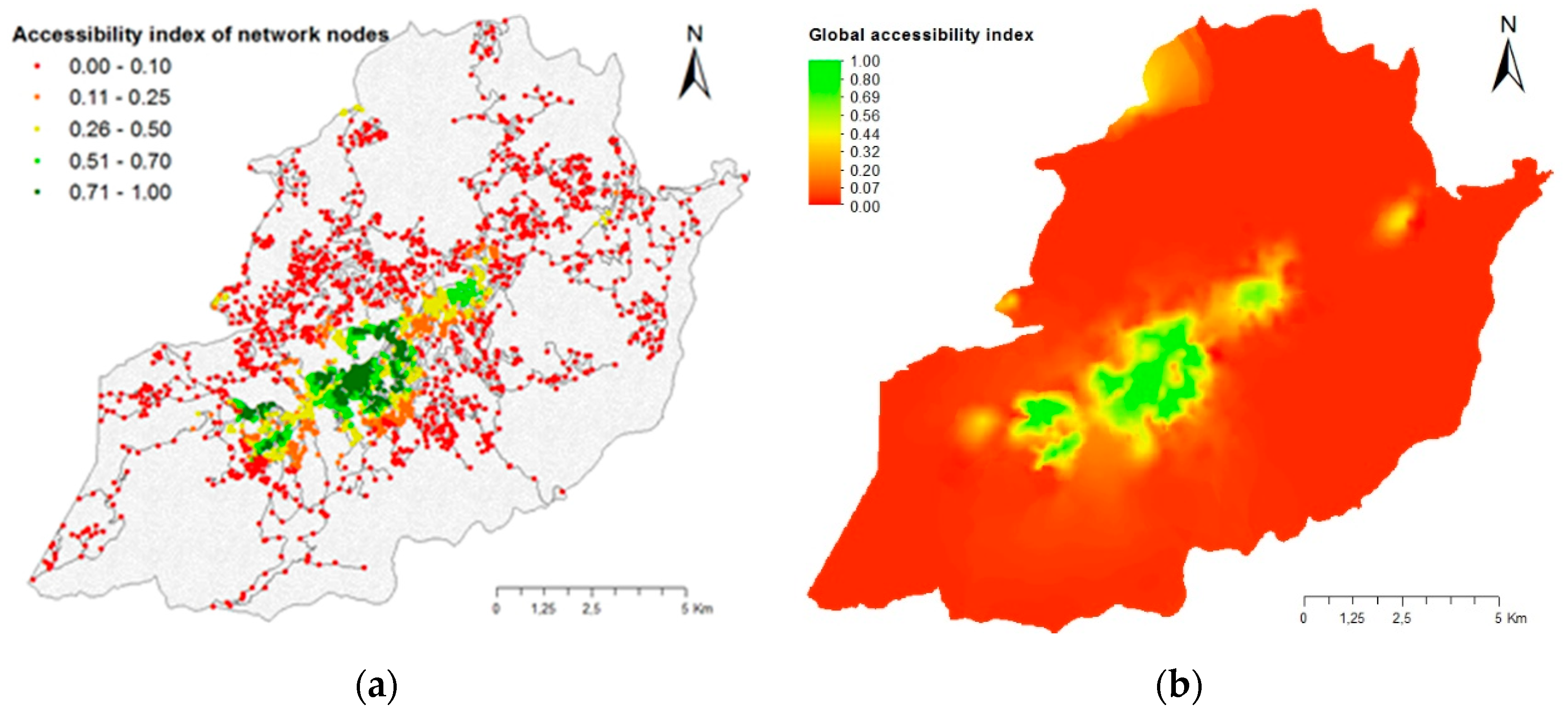
3.2. Cost–Distance Accessibility Index
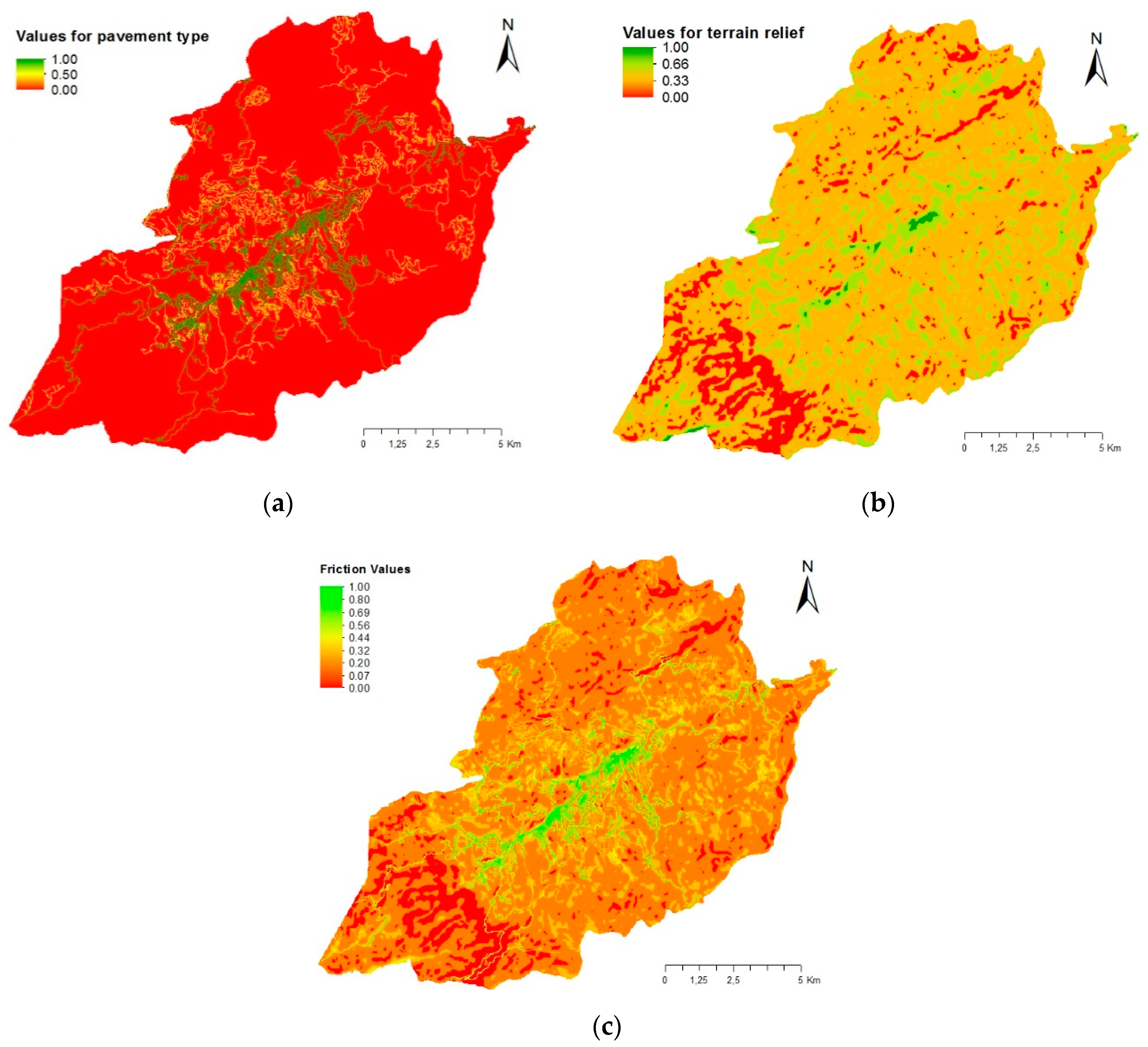
3.3. Accessibility Index with Friction Factors
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levinson, D.M. Accessibility and the journey to work. J. Transp. Geogr. 1998, 6, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascetta, E.; Cartenì, A.; Montanino, M. A new measure of accessibility based on perceived opportunities. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 87, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K. A Theory of Good City Form; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Geurs, K.T.; Wee, B.V. Accessibility evaluation of land-use and transport strategies: Review and research directions. J. Transp. Geogr. 2004, 12, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litman, T. Active Transportation Policy Issues; Victoria Transport Policy Institute: Victoria, BC, Canadá, 2014; Available online: http:www.vtpi.org (accessed on 8 July 2018).
- Murawskia, L.; Church, R.L. Improving accessibility to rural health services: The maximal covering network improvement problem. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2009, 43, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páez, A.; Scott, D.M.; Morency, C. Measuring accessibility: Positive and normative implementations of various accessibility indicators. J. Transp. Geogr. 2012, 25, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, F.; Waddell, P. Modeling WalkTrips Using a Multi-Modal Accessibility Framework. In Proceedings of the Transportation Research Board 93rd Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 12–16 January 2014; Available online: https://trid.trb.org/view.aspx?id=1289226 (accessed on 1 December 2019).
- Campbell, K.B.; Rising, J.A.; Klopp, J.M.; Mbilo, J.M. Accessibility across transport modes and residential developments in Nairobi. J. Transp. Geogr. 2019, 74, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.Y.; Hsu, C.L.; Chen, M.C. A fuzzy multi-criteria decision model for international tourist hotels location selection. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2008, 27, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocarejo, S.J.P.; Oviedo, H.D.R. Transport accessibility and social inequities: A tool for identification of mobility needs and evaluation of transport investments. J. Transp. Geogr. 2012, 24, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhou, H.Z.; Zhang, T.; Wang, R. Urban spatial structure and commute duration: An empirical study of China. Int. J. Transp. 2016, 10, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, W.; Liu, D.; Singer, S. Accessibillity measures of U.S. Metropolitan areas. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 1993, 27, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, S.L.; Niemeier, D.A. Measuring accessibility: An exploration of issues and alternatives. Environ. Plan. A 1997, 29, 1175–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Zeng, X.; Duan, L.; Lu, X.; Sun, H.; Jiang, T.; Yuli, L.Y. Spatial difference analysis for accessibility to high level hospitals based on travel time in Shenzhen, China. Habitat Int. 2016, 53, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farber, S.; Fub, L. Dynamic public transit accessibility using travel time cubes: Comparing the effects of infrastructure (dis)investments over time. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2017, 62, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.S.; Mendes, J.F.G.; Lima, J.P.; Ramos, R.A.R. A Multicriteria Approach to Accessibility Assessment. In Contributions to Sustainable Development in Portuguese and Brazilian Cities, 1st ed.; Mendes, J.F.G., Silva, A.N.R., Souza, L.C.L., Ramos, R.A.R., Eds.; Coimbra, Portugal: Almedina, Coimbra, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 98–117. [Google Scholar]
- Chaloux, N.; Boisjoly, G.; Grise, E.; El-Geneidy, A.; Levinson, D. I Only Some Satisfaction: Introducing Satisfaction Measures of Accessibility. Trans. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2018, 62, 833–843. [Google Scholar]
- Banai, R.; Rapino, M.A. Urban theory since A Theory of Good City Form 1981—A progress review. J. Urban. 2009, 2, 259–276. [Google Scholar]
- Levinson, D.M.; Marshall, W.; Axhausen, K. Elements of Access: Transport Planning for Engineers, Transport Engineering for Planners; Network Design Lab: Sydney, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Geurs, K. Transport Planning with Accessibility Indices in the Netherlands; International Transport Forum Discussion Papers, No. 2018/09; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, B.Y.; Yuan, H.; Wang, D.; Lam, W.H.; Li, Q. Measuring temporal variation of location-based accessibility using space-time utility perspective. J. Transp. Geogr. 2018, 73, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.G. Land-use/transport Interaction Models: Past and Future. J. Transp. Econ. Policy 1998, 32, 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Badoe, D.A.; Miller, E.J. Transportation–land-use interaction: Empirical findings in North America, and their implications for modeling. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2000, 5, 235–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, S.L.; Xin, X. Integrated land use and transportation interaction: A temporal GIS exploratory data analysis approach. J. Transp. Geogr. 2003, 11, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renne, J.L. Transportation and land development: A global view. Res. Transp. Econ. 2016, 60, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayaud, J.R.; Tran, M.; Pereira, R.H.; Nuttall, R. Future access to essential services in a growing smart city: The case of Surrey, British Columbia. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 73, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, J.L.; Ben-Akiva, M.E. Activity-based disaggregate travel demand model system with activity schedules. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2001, 35, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gärling, T.; Schuitema, G. Travel Demand Management Targeting Reduced Private Car Use: Effectiveness, Public Acceptability and Political Feasibility. J. Soc. Issues 2007, 63, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, D. Demographic determinants of daily travel demand. Transp. Policy 2012, 21, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ghasri, M.; Rashidi, T.H.; Waller, S.T. Developing a disaggregate travel demand system of models using data mining techniques. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2017, 105, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niehausa, M.; Galilea, P.; Hurtubi, R. Accessibility and equity: An approach for wider transport project assessment in Chile. Res. Transp. Econ. 2016, 59, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiler, O.M.; Mohammed, B.M. Exploring transportation equity: Development and application of a transportation justice framework. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2016, 47, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleai, M.; Sliuzas, R.; Flacke, J. An integrated framework to evaluate the equity of urban public facilities using spatial multi-criteria analysis. Cities 2014, 40, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zeng, Z.; Jia, T.; Lie, J. Examining the amenability of urban street networks for locating facilities. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2016, 457, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Tong, D. Incorporating activity space and trip chaining into facility siting for accessibility maximization. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2017, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoya, V.R.; Miralles-Guasch, C. Local accessibility inequalities and willingness to walk in Latin-American cities: Findings from Medellín, Colombia. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2017, 11, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.S.; Ramírez-Gómez, Á. Optimizing the location of a biomass plant with a fuzzy-Decision-Making Trial and Evaluation Laboratory (F-DEMATEL) and multi-criteria spatial decision assessment for renewable energy management and long-term sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 182, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malczewski, J.; Jackson, M. Multicriteria spatial allocation of educational resources: An overview. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2004, 34, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizizadeh, B.; Blaschke, T.; Nazmfar, H.; Rezaei Moghaddam, M.H. Landslide susceptibility mapping for the Urmia Lake basin, Iran: A multi-criteria evaluation approach using GIS. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2013, 7, 319–336. [Google Scholar]
- Malczewski, J. GIS-based multicriteria decision analysis: A survey of literature. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2006, 20, 703–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Câmara, G.D.C.; Monteiro, A.M.V. Introduction to the Science of Geoinformation; National Institute of Space Research (INPE): São José dos Campos, Brazil, 2001; Available online: http://mtc-m12.sid.inpe.br/col/sid.inpe.br/sergio/2004/04.22.07.43/doc/publicacao.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2018).
- Chang, N.B.; Parvathinathan, G.; Breeden, J.B. Combining GIS with fuzzy multicriteria decision-making for landfill siting in a fast-growing urban region. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 87, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malczewski, J. Ordered weighted averaging with fuzzy quantifiers: GIS-based multicriteria evaluation for land-use suitability analysis. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2006, 8, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.A.; Singh, M.; Sahoo, R.N.; Ahmed, N.; Khanna, M.; Sarangi, A.; Mishra, A.K. Land suitability analysis for different crops: A multi criteria decision making approach using remote sensing and GIS. Researcher 2011, 3, 61–84. [Google Scholar]
- Phua, M.H.; Minowa, M. A GIS-based multi-criteria decision making approach to forest conservation planning at a landscape scale: A case study in the Kinabalu Area, Sabah, Malaysia. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2005, 71, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joerin, F.; Thériault, M.; Musy, A. Using GIS and outranking multicriteria analysis for land-use suitability assessment. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2001, 15, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghapour, T.; Moridpour, S.; Thompson, R.G. Public transport accessibility in metropolitan areas: A new approach incorporating population density. J. Transp. Geogr. 2016, 54, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, J.F.; Rodrigues, D.S.; Ramos, R.A. A GIS-based multicriteria model for the evaluation of territorial accessibility. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2005, 84, 805–813. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.; Malczewski, J.; Boroushaki, S. A GIS-based multicriteria decision analysis approach for mapping accessibility patterns of housing development sites: A case study in Canmore, Alberta. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2011, 3, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Zhang, J. Multicriteria evaluation on accessibility-based transportation equity in road network design problem. J. Adv. Transp. 2014, 48, 526–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, S.; Yeow, M.C. Accessibility analysis for housing development in Singapore with GIS and multi-criteria analysis methods. Appl. Gis 2006, 2, 13-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbenyo, F.; Nunbogua, A.M.; Dongzagla, A. Accessibility mapping of health facilities in rural Ghana. J. Transp. Health 2017, 6, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, C.; Cebeci, U.; Ulukan, Z. Multi-criteria supplier selection using fuzzy AHP. Logist. Inf. Manag. 2003, 16, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, J.F.G. Multicriteria accessibility evaluation using GIS as Applied to Industrial Location in Portugal. Earth Obs. Mag. 2001, 10, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto, E.; Lima, J.P. Accessibility in the rural environment: A multicriteria approach using GIS. Transportation 2016, 24, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragićević, S.; Lai, T.; Balram, S. GIS-based multicriteria evaluation with multiscale analysis to characterize urban landslide susceptibility in data-scarce environments. Habitat Int. 2015, 45, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelokhani-Niaraki, M.; Malczewski, J. Decision complexity and consensus in Web-based spatial decision making: A case study of site selection problem using GIS and multicriteria analysis. Cities 2015, 45, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronesi, F.; Schito, J.; Grassi, S.; Raubal, M. Automatic selection of weights for GIS-based multicriteria decision analysis: Site selection of transmission towers as a case study. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 83, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahdat, K.; Smith, N.J.; Amiri, G.G. Fuzzy multicriteria for developing a risk management system in seismically prone areas. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2014, 48, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Duanmu, L.; Lahdelma, R.; Li, X. A fuzzy-grey multicriteria decision making model for district heating system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 128, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D.; Pedrycz, W.; Yu, D. Gaussian kernel based fuzzy rough sets: Model, uncertainty measures and applications. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2010, 51, 453–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.H.; Lima, J.P. Multicriteria evaluation of people with reduced mobility accessibility: A study in downtown Itajubá (MG). Urbe. Braz. J. Urban Manag. 2015, 7, 368–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawas, Y.E.; Hassan, M.N.; Abulibdeh, A. A multi-criteria approach of assessing public transport accessibility at a strategic level. J. Transp. Geogr. 2016, 57, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.; Kahraman, C.; Kaya, I. A new fuzzy multicriteria decision making approach: An application for European Quality Award assessment. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2012, 32, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engau, A.; Moffattm, C.; Dyk, W. Multicriteria modeling and tradeoff analysis for oil load dispatch and hauling operations at Noble energy. Optim. Eng. 2015, 16, 73–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banai, R. Public Transportation Decision-Making: A Case Analysis of the Memphis Light Rail Corridor and Route Selection with Analytic Hierarchy Process. J. Public Transp. 2006, 9, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process. Int. J. Serv. Sci. 2008, 1, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banai, R. Evaluation of land use-transportation systems with the Analytic Network Process. J. Transp. Land Use. 2010, 3, 85–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. Fundamentals of the analytic network process. J. Syst. Sci. Syst. Eng. 2004, 13, 129–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidou, A.V.; Vlachokostas, C.; Moussiopoulos, N. Interactions between climate change and the tourism sector: Multiple-criteria decision analysis to assess mitigation and adaptation options in tourism areas. Tourism Manag. 2016, 55, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.S.; García-Moruno, L.; Hernández-Blanco, J. Alonso Sánchez-Ríos, Planning of rural housings in reservoir areas under (mass) tourism based on a fuzzy DEMATEL-GIS/MCDA hybrid and participatory method for Alange, Spain. Habitat Int. 2016, 57, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, G.; Zsigraiová, Z.; Semiao, V. Multi-criteria GIS-based siting of an incineration plant for municipal solid waste. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 1960–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariz, H.A.; Dönmez, C.C.; Sennaroglu, B. Siting of a central healthcare waste incinerator using GIS-based Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 166, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akıncı, H.; Özalp, A.Y.; Turgut, B. Agricultural land use suitability analysis using GIS and AHP technique. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2013, 97, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolekar, R.B.; Bhagat, V.S. Multi-criteria land suitability analysis for agriculture in hilly zone: Remote sensing and GIS approach. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 118, 300–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, M.S.G.; Ramos Rui, A.R.; Rodrigues, D.S. Spatial Analysis of Accessibility to Support Decision-Making in Urban Investments: A case in Amazonia–Brazil. In Proceedings of the 13th WCTR–World Conference Transport Research, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 15–18 July 2013; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, J.P.; Ramos, R.A.R.; Fernandes Júnior, J.L. A multicriteria approach to the prioritization of paved roads. Transportes 2009, 17, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, y.; Chen, R.S.; Meng, X.Z.; Xu, J.; Qadeer, A.; Liu, M. Modeling and evaluating spatial variation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban lake surface sediments in Shanghai. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.P.; Machado, M.H. Walking accessibility for individuals with reduced mobility: A brazilian case study. Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stillwell, W.G.; Seaver, D.A.; Edwards, W. A Comparison of Weight Approximation Techniques in Multiattribute Utility Decision-Making. Org. Behav. Hum. Perform. 1981, 28, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banai, R.; Wakolbingerb, T. A measure of regional influence with the analytic network process. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2011, 45, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, M.J. Problem Solving and Decision Making: Hard, Soft and Creative Approaches; Cengage Learn: Stamford, CT, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Osborn, A.F. Applied Imagination; Oxford: England, UK, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Kohn, N.H.; Paulus, P.B.; Choi, Y. Building on the ideas of others: An examination of the idea combination process. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2011, 47, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, P.B.; Brown, V.R. Toward more creative and innovative group idea generation: A cognitive-social-motivational perspective of brainstorming. Soc. Personal. Psychol. Compass 2007, 1, 248–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietzschel, E.F.; Nijstad, B.; Stroebe, W. Productivity is not enough: A comparison of interactive and nominal brainstorming groups on idea generation and selection. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2006, 42, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.L. Concepts in Composition: Theory and Practice in the Teaching of Writing, 2rd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- IBGE Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics 2010 Cities. Available online: http://cod.ibge.gov.br/2AJ (accessed on 20 September 2018).
- Peuré-Tartaruga, L.A.; Gomeñuka, N.A. Walk Biomechanics on Slopes. Tecnicouro 2010, 4, 76–84. [Google Scholar]
- IPT. Slopes Occupation Manual; Institute of Technological Research: São Paulo, Brazil, 1991; p. 216. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, P.; Kenworthy, J. Urban Design to Reduce Automobile Dependence. Opolis 2006, 2, 35–52. [Google Scholar]
- Albino, V.; Berardi, U.; Dangelico, R.M. Smart Cities: Definitions, Dimensions, Performance, and Initiatives. Int. J. Urban Technol. 2015, 22, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarstad, H. Constructing the sustainable city: Examining the role of sustainability in the ‘smart city’ discourse. Int. J. Environ. Policy Plan. 2016, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
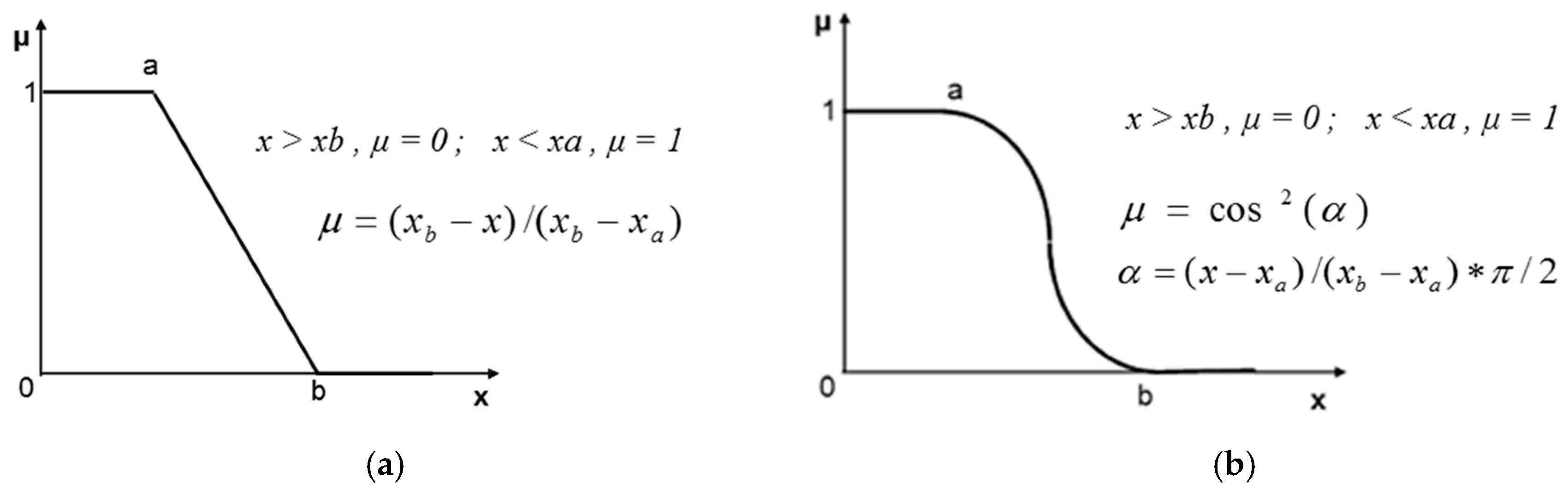


| Contribution | Reference |
|---|---|
| Accessibility addressed transportation planning and transport/land-use interactions | Geurs & Wee [4], Litman [5], Páez et al. [7], Geurs [21], Wang et al. [22] Wilson [23], Badoe & Miller [24], Shaw & Xin [25], Renne [26], Mayaud et al. [27] |
| Accessibility addressed the relation of transportation projects with equity and sustainable territorial development | Bocarejo & Oviedo [11], Niehausa et al. [32], Beiler & Mohammed [33] |
| Accessibility addressed location problems for urban facilities | Campbell et al. [9], Taleai et al. [34], Zhang et al. [35], Li & Tong [37], |
| Accessibility analysis using a multicriteria approach | Banai & Rapino [19], Taleai et al. [34], Meng et al. [50], Mendes [55], Sakamoto & Lima [56], Hawas et al. [64], Tobias et al. [77] |
| Accessibility and sustainability studies using Geographic Information System (GIS) | Malczewski & Jackson [39], Feizizadeh et al. [40], Malczewski [41], Câmara & Monteiro [42], Chang et al. [43], Malczewski [44], Mustafa et al. [45], Phua & Minowa [46], Joerin et al. [47], Agbenyo et al. [53], Dragićević et al. [57], Jelokhani-Niaraki & Malczewski [58], Veronesi et al. [59], Hariz et al. [74] |
| Accessibility index with a fuzzy multicriteria approach | Chou et al. [10], Kahraman et al. [54], Mendes [55], Sakamoto & Lima [56], Vahdat et al. [60], Wang et al. [61], Hu et al. [62], Machado & Lima [63], Aydin et al. [65], Lima et al. [78] |
| Group | Location of Interest | Number of Locations |
|---|---|---|
| 1—Education | Elementary School | 25 |
| High School | 22 | |
| 2—Health Services | Health Centers | 11 |
| Hospitals | 3 | |
| 3—Services and Goods | Commerce | 10 |
| Bank Services | 15 | |
| Municipal Services | 18 | |
| Total | 104 | |
| Group | Weight | Location of Interest | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Education | 0.40 | Elementary School | 0.60 |
| High School | 0.40 | ||
| Health | 0.35 | Health Centers | 0.70 |
| Hospitals | 0.30 | ||
| Services and Goods | 0.25 | Commerce | 0.40 |
| Bank Services | 0.30 | ||
| Municipal Services | 0.30 |
| LI | Dmax (Meters) |
|---|---|
| Elementary School | 960.00 |
| High School | 1400.00 |
| Health Centers | 1600.00 |
| Hospitals | 7500.00 |
| Commerce | 1660.00 |
| Bank Services | 4300.00 |
| Municipal Services | 5000.00 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lima, J.P.; Abitante, J.d.C.; Pons, N.A.D.; Senne, C.M. A Spatial Fuzzy Multicriteria Analysis of Accessibility: A Case Study in Brazil. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3407. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123407
Lima JP, Abitante JdC, Pons NAD, Senne CM. A Spatial Fuzzy Multicriteria Analysis of Accessibility: A Case Study in Brazil. Sustainability. 2019; 11(12):3407. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123407
Chicago/Turabian StyleLima, Josiane Palma, Juliana da Camara Abitante, Nívea Adriana Dias Pons, and Clara Moreira Senne. 2019. "A Spatial Fuzzy Multicriteria Analysis of Accessibility: A Case Study in Brazil" Sustainability 11, no. 12: 3407. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123407
APA StyleLima, J. P., Abitante, J. d. C., Pons, N. A. D., & Senne, C. M. (2019). A Spatial Fuzzy Multicriteria Analysis of Accessibility: A Case Study in Brazil. Sustainability, 11(12), 3407. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123407





