Selective Elimination of Parental Chromatin from Introgression Cultivars of xFestulolium (Festuca × Lolium)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
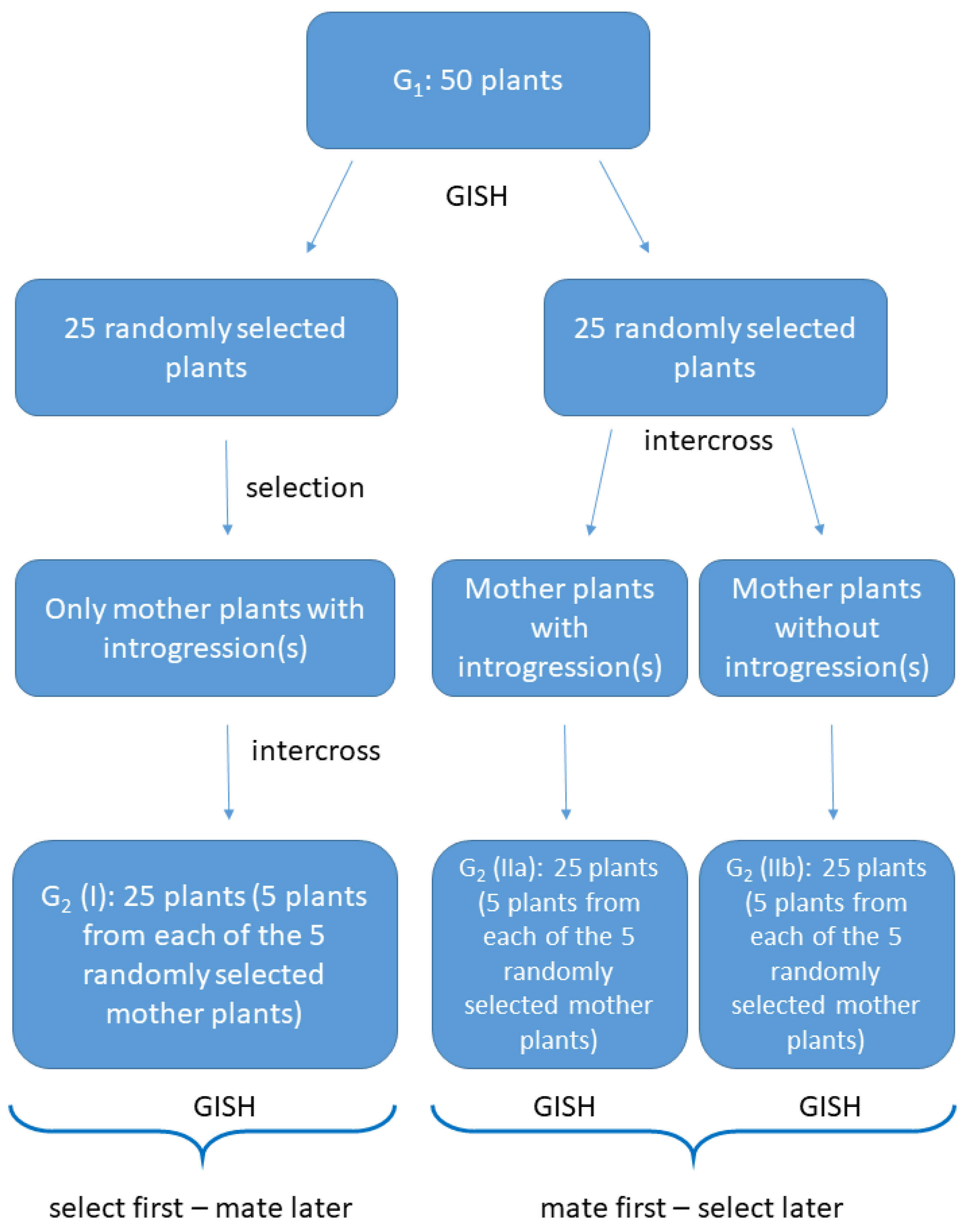
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Crossings and Selection
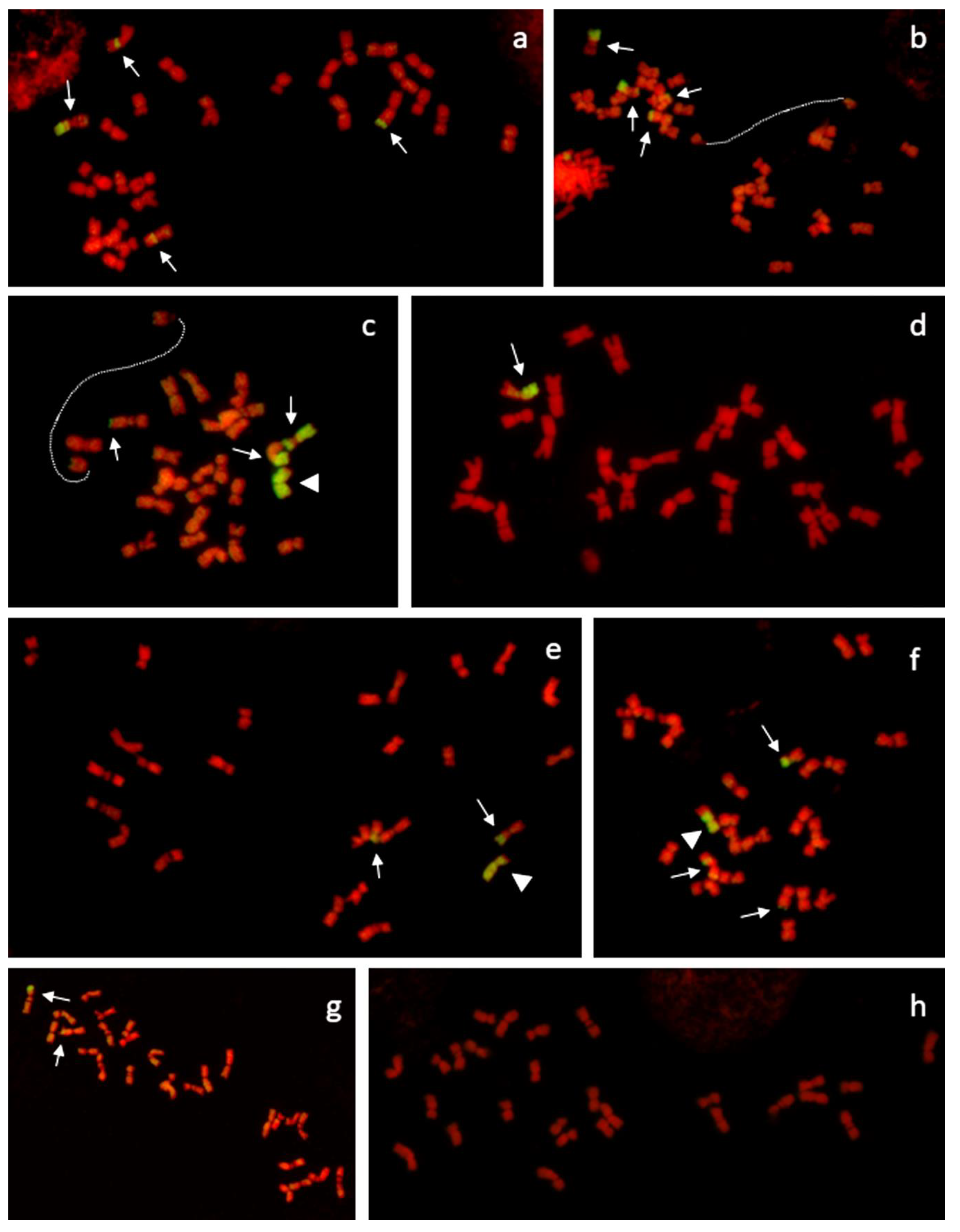
2.3. Genomic in Situ Hybridization (GISH) and Microscopy
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cultivars with Higher Proportion of Festuca chromatin (FL1 and FL2)
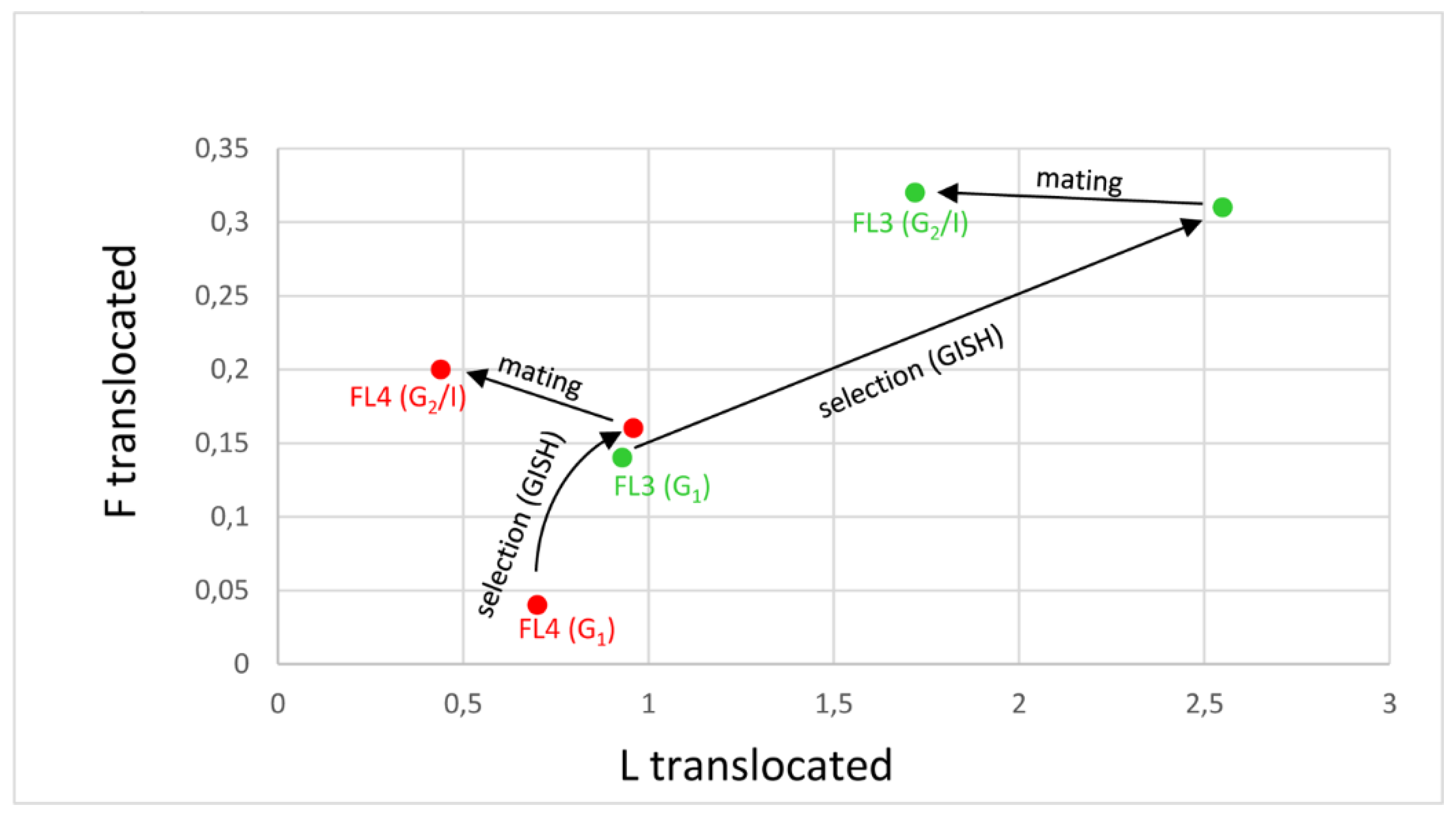
3.2. Cultivars with Lower Proportions of Festuca chromatin (FL3 and FL4)
3.3. Transmission of Individual F. pratensis chromosomes in Consecutive Generation
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soltis, P.S.; Soltis, D.E. The Role of Hybridization in Plant Speciation. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2009, 60, 561–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sears, E.R.; Okamoto, M. Intergenomic chromosome relationships in hexaploid wheat. In Proceedings of the 10th International Congress of Genetics, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–27 August 1958; pp. 258–259. [Google Scholar]
- Riley, R.; Chapman, V. Genetic control of the cytologically diploid behavior of hexaploid wheat. Nature 1958, 182, 713–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermeer, Q.P.; Devries, J.N. An interspecific cross between Allium roylei Stearn. and Allium cepa L. and its backcross to Allium cepa. Euphytica 1990, 47, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopecky, D.; Lukaszewski, A.J.; Dolezel, J. Meiotic behaviour of individual chromosomes of Festuca pratensis in tetraploid Lolium multiflorum. Chromosome Res. 2008, 16, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopecky, D.; Lukaszewski, A.J.; Dolezel, J. Cytogenetics of festulolium (Festuca x Lolium hybrids). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2008, 120, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, B.D.; Kopecky, D.; Lukaszewski, A.J.; Baird, J.H. Evaluation of Turf-type Interspecific Hybrids of Meadow Fescue with Perennial Ryegrass for Improved Stress Tolerance. Crop Sci. 2014, 54, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmala, A.; Zwierzykowski, Z.; Gasior, D.; Rapacz, M.; Zwierzykowska, E.; Humphreys, M.W. GISH/FISH mapping of genes for freezing tolerance transferred from Festuca pratensis to Lolium multiflorum. Heredity 2006, 96, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, M.W.; Thomas, H. Improved drought resistance in introgression lines derived from Lolium multiflorum x Festuca arundinacea hybrids. Plant Breed. 1993, 111, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, M.W.; Pasakinskiene, I. Chromosome painting to locate genes for drought resistance transferred from Festuca arundinacea into Lolium multiflorum. Heredity 1996, 77, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesniewska, A.; Ponitka, A.; Slusarkiewicz-Jarzina, A.; Zwierzykowska, E.; Zwierzykowski, Z.; James, A.R.; Thomas, H.; Humphreys, M.W. Androgenesis from Festuca pratensis x Lolium multiflorum amphidiploid cultivars in order to select and stabilize rare gene combinations for grass breeding. Heredity 2001, 86, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopecky, D.; Loureiro, J.; Zwierzykowski, Z.; Ghesquiere, M.; Dolezel, J. Genome constitution and evolution in Lolium x Festuca hybrid cultivars (Festulolium). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 113, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwierzykowski, Z.; Kosmala, A.; Zwierzykowska, E.; Jones, N.; Joks, W.; Bocianowski, J. Genome balance in six successive generations of the allotetraploid Festuca pratensis x Lolium perenne. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 113, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwierzykowski, Z.; Ksiazczyk, T.; Taciak, M.; Zwierzykowska, E.; Jones, N.; Kosmala, A. Genome constitution in selected and unselected plants of F2-F4 generations derived from an allotet-raploid Festuca pratensis x Lolium perenne hybrid. In Breeding Strategies for Sustainable Forage and Turf Grass Improvement; Barth, S., Milbourne, D., Eds.; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2012; pp. 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Van Heusden, A.W.; van Ooijen, J.W.; Vrielink-van Ginkel, R.; Verbeek, W.H.J.; Wietsma, W.A.; Kik, C. A genetic map of an interspecific cross in Allium based on amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP (TM)) markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2000, 100, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.; Pasakinskiene, I. Genome conflict in the gramineae. New Phytol. 2005, 165, 391–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risso-Pascotto, C.; Pagliarini, M.S.; do Valle, C.B.; Jank, L. Asynchronous meiotic rhythm as the cause of selective chromosome elimination in an interspecific Brachiaria hybrid. Plant Cell Rep. 2004, 22, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopecky, D.; Simonikova, D.; Ghesquiere, M.; Dolezel, J. Stability of Genome Composition and Recombination between Homoeologous Chromosomes in Festulolium (Festuca x Lolium) Cultivars. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2017, 151, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, A.; Akiyama, Y.; Fujimori, M.; Kiyoshi, T. No decrease in f ratio (ratio of Festuca-specific genome region to the whole genome) in maternally derived progeny of festulolium (Festuca pratensis x Lolium species) across generations. Grassl. Sci. 2016, 62, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwierzykowski, Z.; Zwierzykowska, E.; Taciak, M.; Kosmala, A.; Jones, R.N.; Zwierzykowski, W.; Ksiazczyk, T.; Krajewski, P. Genomic structure and fertility in advanced breeding populations derived from an allotetraploid Festuca pratensis x Lolium perenne cross. Plant Breed. 2011, 130, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopecky, D.; Havrankova, M.; Loureiro, J.; Castro, S.; Lukaszewski, A.J.; Bartos, J.; Kopecka, J.; Dolezel, J. Physical Distribution of Homoeologous Recombination in Individual Chromosomes of Festuca pratensis in Lolium multiflorum. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2010, 129, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudi-Nejad, A.; Nasuda, S.; McIntosh, R.A.; Endo, T.R. Transfer of rye chromosome segments to wheat by a gametocidal system. Chromosome Res. 2002, 10, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, J.; Cermeno, M.C.; Lacadena, J.R. Meiotic pairingin wheat-rye addition and substitution lines. Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 1984, 26, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo, T. Dynamics of Rye Telomeres in a Wheat Background during Early Meiosis. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2014, 143, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernickova, K.; Linc, G.; Gaal, E.; Kopecky, D.; Samajova, O.; Lukaszewski, A.J. Out-of-position telomeres in meiotic leptotene appear responsible for chiasmate pairing in an inversion heterozygote in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Chromosoma 2019, 128, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, R.A.; Timmerman, G.M.; Cromey, M.G.; Melz, G. Characterization of progeny from backcrosses of triploid hybrids between Hordeum vulgare L. (2x) and H. bulbosum L. (4x) to Hordeum vulgare. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1994, 88, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, R. The chromosome stability of Hordeum vulgare L. x H. bulbosum L. chromosome substitution plants grown at 2 temperatures. Hereditas 1994, 121, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Lavalle, L.A.B.; Brubaker, C.L. Frequency and fidelity of alien chromosome transmission in Gossypium hexaploid bridging populations. Genome 2007, 50, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.; Armstead, I.; Harper, J.; King, I. Transmission frequencies of introgressed Festuca pratensis chromosomes and chromosome segments in Lolium perenne. Crop Sci. 2013, 53, 1968–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cultivar | L complete | L translocated | F translocated | F complete |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FL1 G1 (male) | 22.50 ± 2.97 | 3.55 ± 2.33 | 0.80 ± 0.98 | 0.50 ± 0.87 |
| FL1 G1 female | 22.80 ± 2.14 | 3.20 ± 1.17 | 0.80 ± 1.30 | 0.40 ± 0.89 |
| FL1 G2 | 23.77 ± 2.23 **↑ | 2.52 ± 2.16 *↓ | 0.68 ± 0.74 | 0.16 ± 0.47 *↓ |
| Change in proportion G2-G1 (%) | 4.59 | −;3.10 | −0.43 | −1.06 |
| FL2 G1 (male) | 23.68 ± 1.61 | 2.32 ± 1.06 | 0.82 ± 0.98 | 0.36 ± 0.64 |
| FL2 G1 female | 23.75 ± 2.06 | 2.25 ± 1.25 | 1.25 ± 1.89 | 0.25 ± 0.50 |
| FL2 G2 | 24.83 ± 1.31 (*)↑ | 1.88 ± 1.48 | 0.54 ± 0.72 *↓ | 0.04 ± 0.20 ***↓ |
| Change in proportion G2-G1 (%) | 4.29 | −1.48 | −1.82 | −0.99 |
- L = Lolium chromosome;
- F = Festuca chromosome;
- translocated = chromosome bearing homoeologous translocation(s);
- (*)P ≤ 0.10, * P ≤ 0.05, ** P ≤ 0.01, *** P ≤ 0.001.
| Cultivar | L complete | L translocated | F translocated |
|---|---|---|---|
| FL3 G1 male for G2/I | 25.00 ± 2.39 | 2.43 ± 1.99 | 0.29 ± 0.70 |
| FL3 G1 female for G2/I | 24.67 ± 2.66 | 2.67 ± 2.25 | 0.33 ± 0.81 |
| FL3 G2/I | 25.58 ± 1.28 **↑ | 1.72 ± 1.14 ***↓ | 0.32 ± 0.62 |
| Change in proportion G2-G1 (%) | 2.94 | -2.98 | 0.04 |
| FL4 G1 male for G2/I | 25.78 ± 0.92 | 1.11 ± 0.74 | 0.11 ± 0.31 |
| FL4 G1 female for G2/I | 26.40 ± 0.55 | 0.80 ± 0.45 | 0.20 ± 0.44 |
| FL4 G2/I | 26.36 ± 1.22 | 0.44 ± 0.77 **↓ | 0.20 ± 0.41 |
| Change in proportion G2-G1 (%) | 1.75 | -1.90 | 0.15 |
- L = Lolium chromosome;
- F = Festuca chromosome;
- translocated = chromosome bearing homoeologous translocation(s);
- ** P ≤ 0.01, *** P ≤ 0.001.
| Cultivar | L complete | L translocated | F translocated |
|---|---|---|---|
| FL3 G1 male for G2/II | 26.86 ± 1.52 | 0.43 ± 0.79 | 0.10 ± 0.29 |
| FL3 G1 female for G2/IIa | 25.60 ± 1.94 | 1.60 ± 0.89 | 0.40 ± 0.54 |
| FL3 G2/IIa | 25.79 ± 2.06 | 1.21 ± 1.14 | 0.33 ± 0.48 |
| Change in proportion G2-G1 (%) | –1.02 | 0.72 | 0.30 |
| FL3 G1 female for G2/IIb | 28.40 ± 1.52 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| FL3 G2/IIb | 27.64 ± 1.18 | 0.04 ± 0.20 ***↓ | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Change in proportion G2−G1 (%) | 0.82 | –0.64 | –0.18 |
| FL4 G1 male for G2/II | 26.46 ± 0.94 | 0.61 ± 0.66 | 0.02 ± 0.15 |
| FL4 G1 female for G2/IIa | 26.20 ± 0.44 | 1.20 ± 0.44 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| FL4 G2/IIa | 25.96 ± 1.06 (*)↑ | 1.36 ± 0.99 *↑ | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Change in proportion G2−G1 (%) | –1.60 | 1.64 | –0.04 |
| FL4 G1 female for G2/IIb | 27.00 ± 0.71 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| FL4 G2/IIb | 26.76 ± 1.09 | 0.08 ± 0.28 ***↓ | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Change in proportion G2-G1 (%) | 0.89 | –0.85 | –0.04 |
- L = Lolium chromosome;
- F = Festuca chromosome;
- (*) P ≤ 0.10, * P ≤ 0.05, *** P ≤ 0.001.
| Chromosome | Number of plants | Transmission (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1F | 111 | 46 n.s. |
| 2F | 96 | 49 n.s. |
| 3F | 114 | 44 n.s. |
| 4F | 88 | 47 n.s. |
| 5F | 88 | 34 ** |
| 6F | 131 | 48 n.s. |
| 7F | 136 | 48 n.s. |
- n.s. non-significant;
- ** significant deviation from the expected transmission frequency (0.50) at P ≤ 0.01 (Student’s t-test).
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kopecký, D.; Horáková, L.; Duchoslav, M.; Doležel, J. Selective Elimination of Parental Chromatin from Introgression Cultivars of xFestulolium (Festuca × Lolium). Sustainability 2019, 11, 3153. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11113153
Kopecký D, Horáková L, Duchoslav M, Doležel J. Selective Elimination of Parental Chromatin from Introgression Cultivars of xFestulolium (Festuca × Lolium). Sustainability. 2019; 11(11):3153. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11113153
Chicago/Turabian StyleKopecký, David, Lucie Horáková, Martin Duchoslav, and Jaroslav Doležel. 2019. "Selective Elimination of Parental Chromatin from Introgression Cultivars of xFestulolium (Festuca × Lolium)" Sustainability 11, no. 11: 3153. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11113153
APA StyleKopecký, D., Horáková, L., Duchoslav, M., & Doležel, J. (2019). Selective Elimination of Parental Chromatin from Introgression Cultivars of xFestulolium (Festuca × Lolium). Sustainability, 11(11), 3153. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11113153






