The Effect of Fertilizers on Biomass and Biodiversity on a Semi-Arid Grassland of Northern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
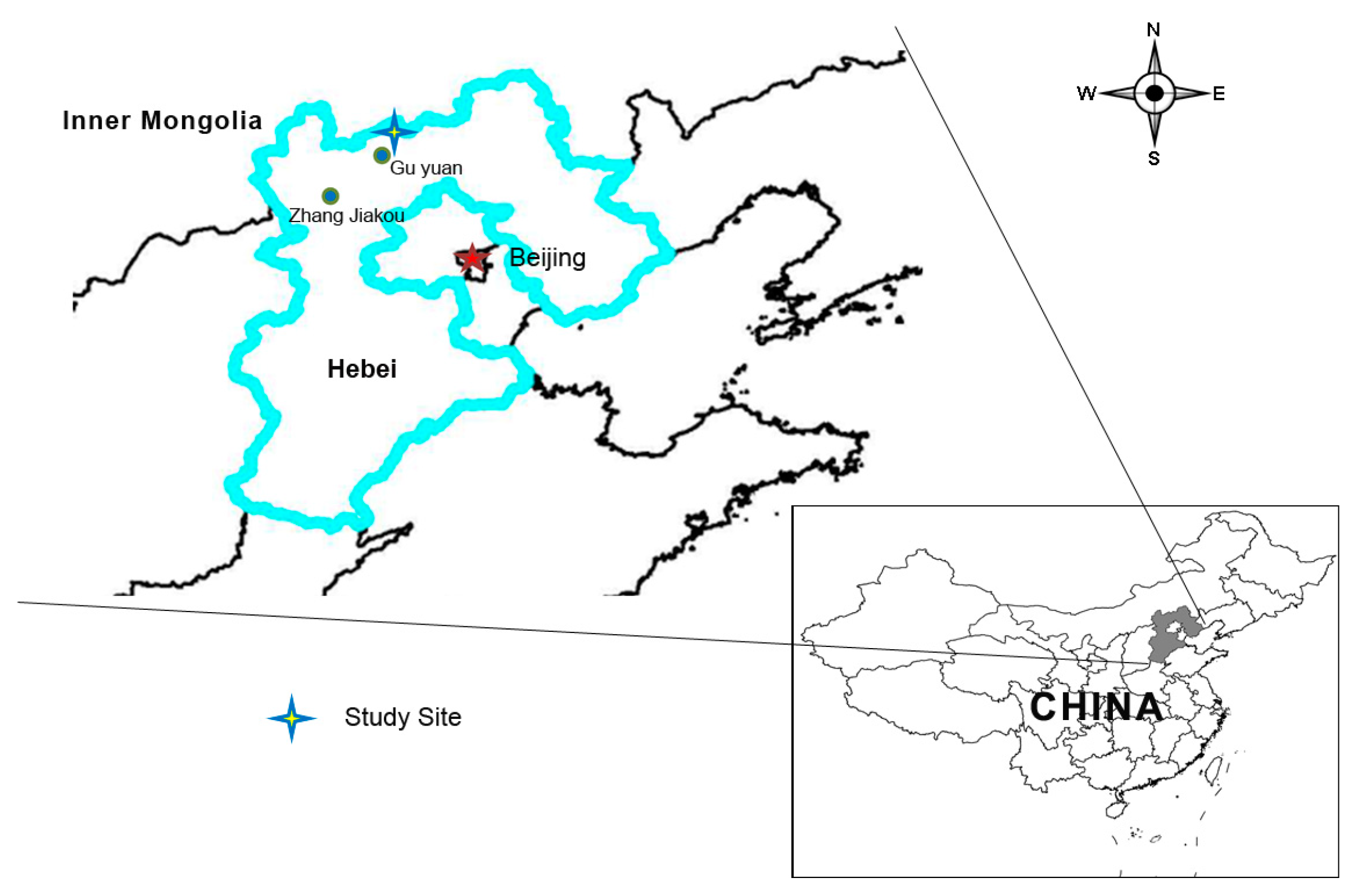
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design and Measurement
2.3. Statistical Analysis
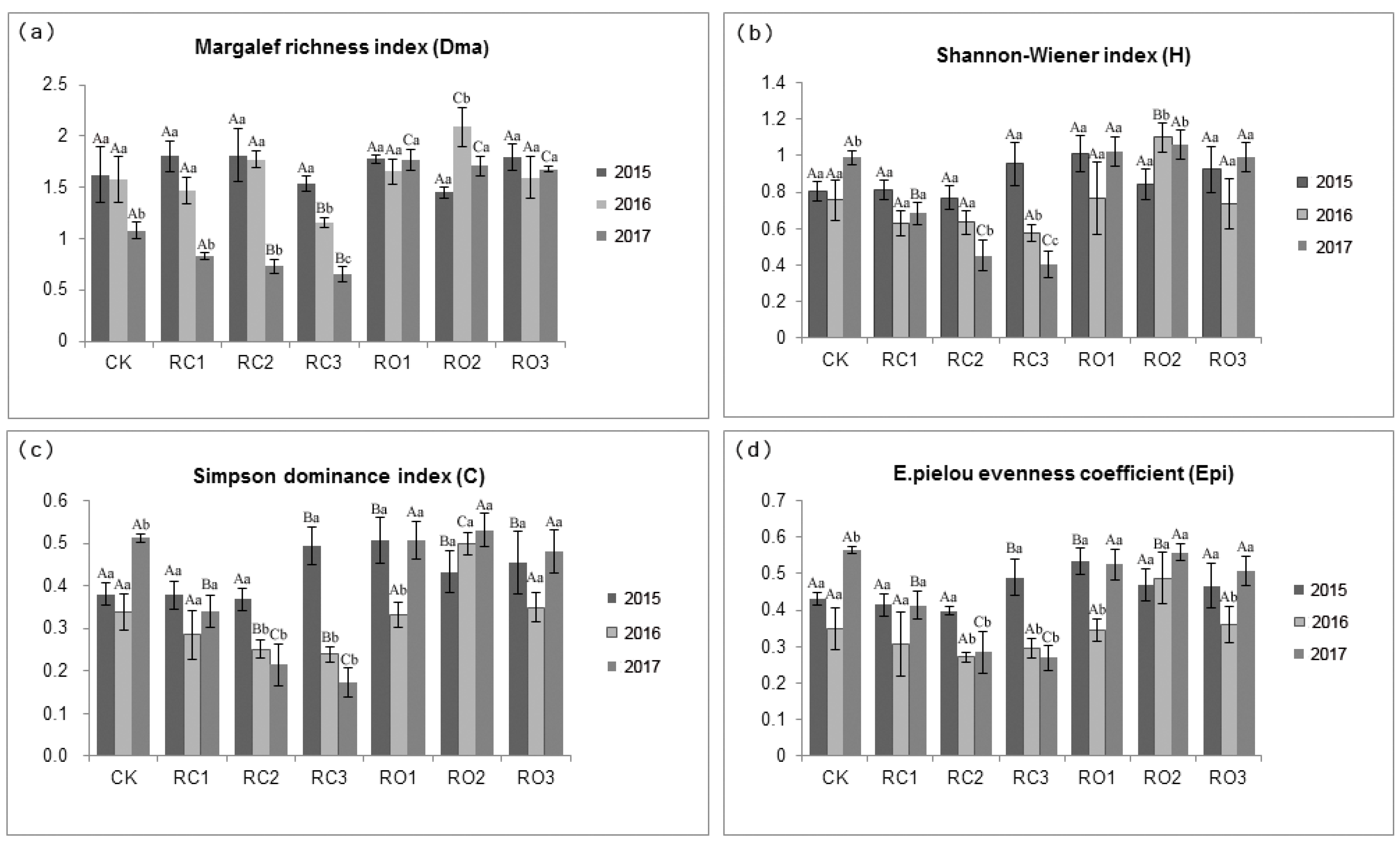
3. Results
3.1. The Effect of Different Treatments on Plant Traits
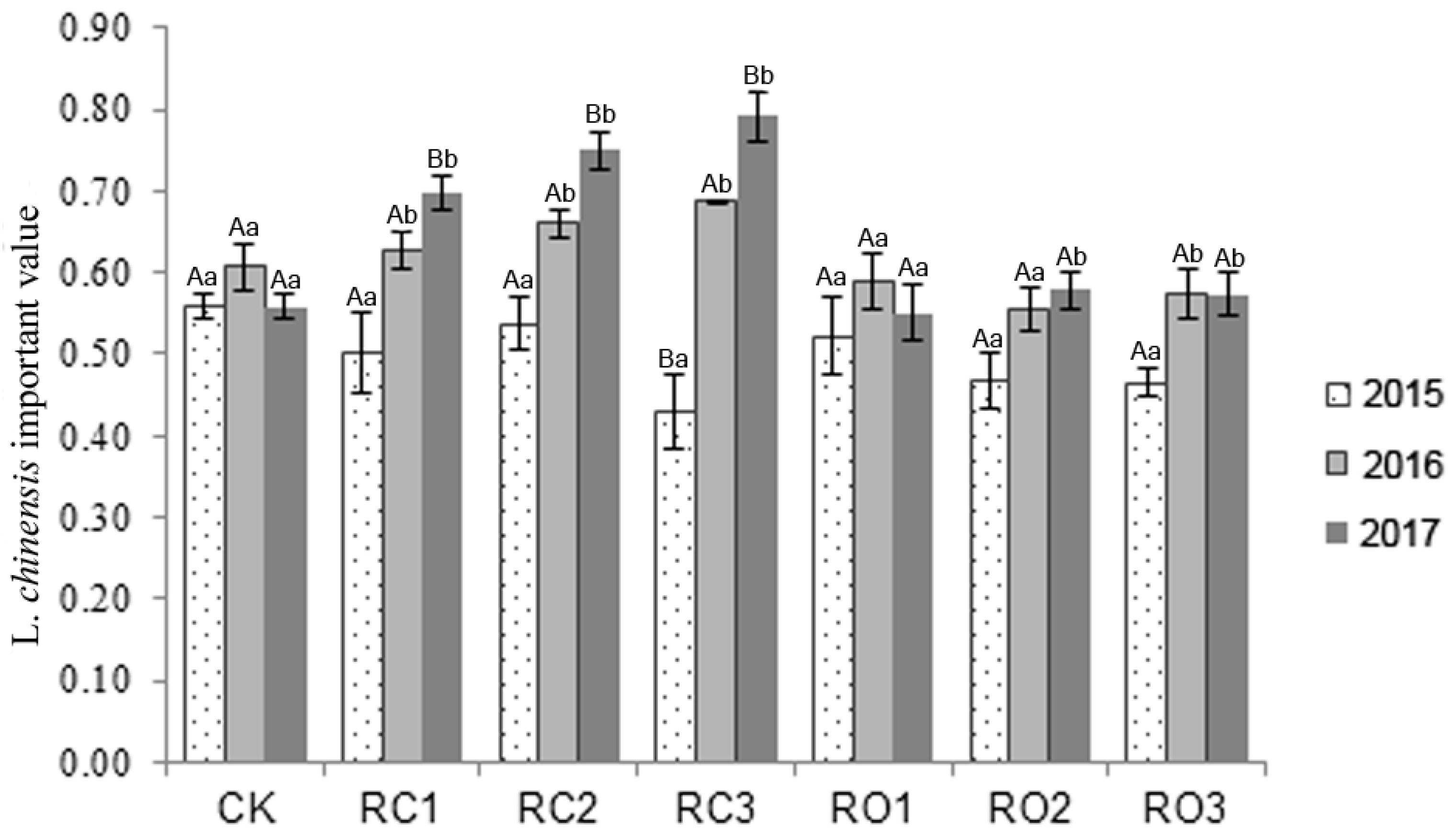
3.2. The Importance Value Index of L. chinensis in Three Years
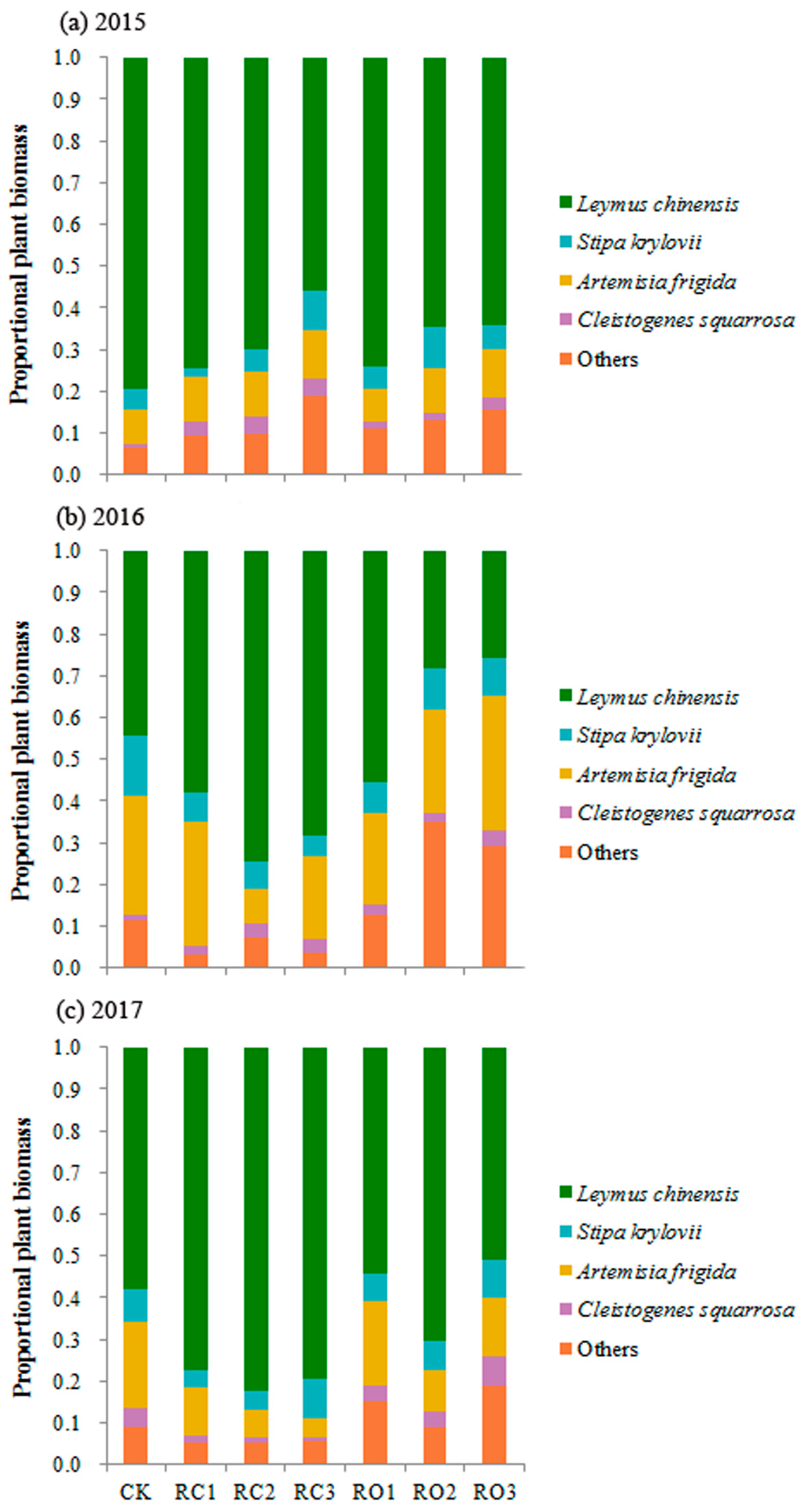
3.3. Species Proportion of Plant Community
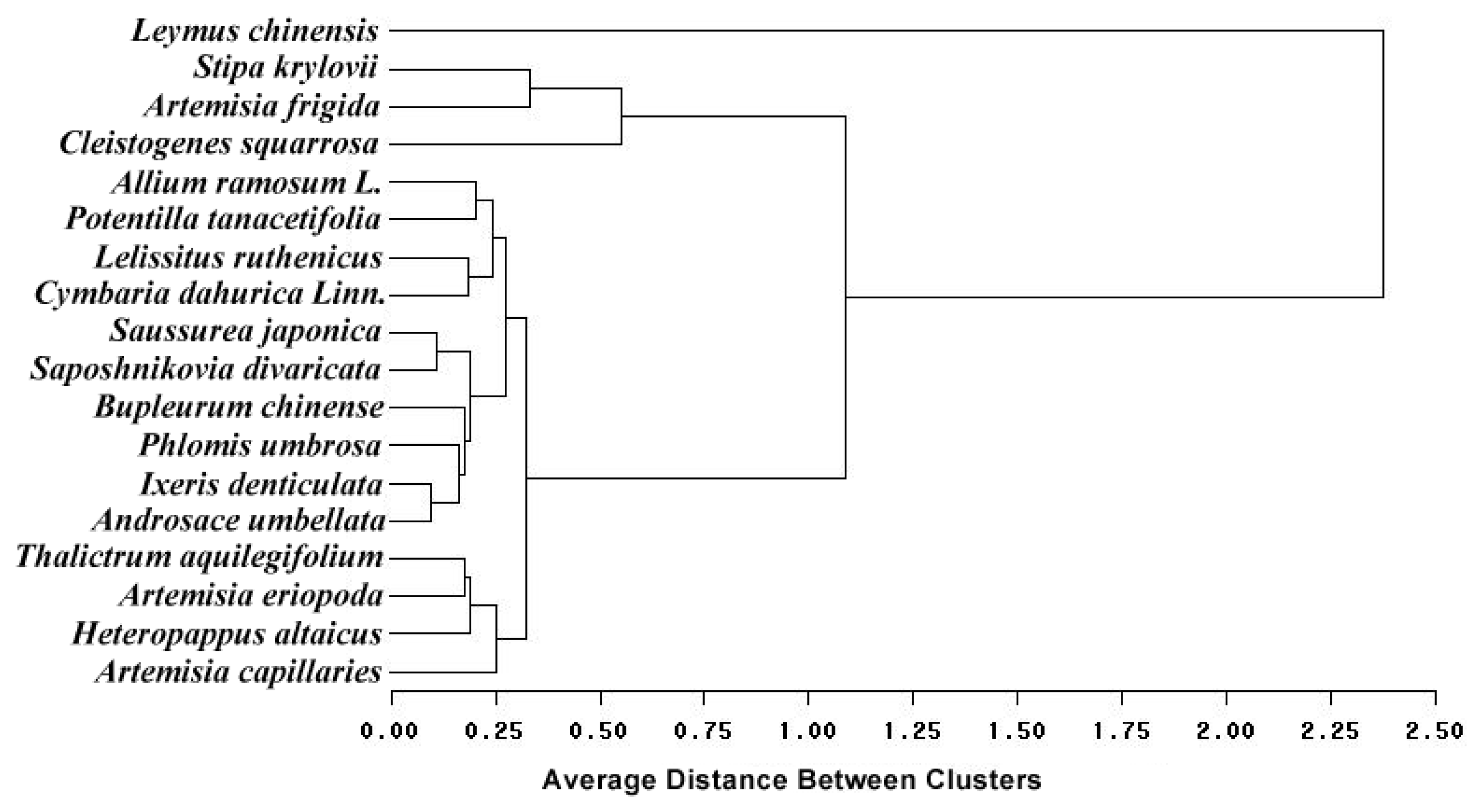
3.4. Changes of Species Biodiversity During Different Years
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qin, H.; Lu, K.P.; Strong, P.J.; Xu, Q.F.; Wu, Q.F.; Xu, Z.X.; Xu, J.; Wang, H.L. Long-term fertilizer application effects on the soil, root arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and community composition in rotation agriculture. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 89, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frossard, E.; Bünemann, E.; Jansa, J.; Oberson, A.; Feller, C. Concepts and practices of nutrient management in agro-ecosystems: Can we draw lessons from history to design future sustainable agricultural production systems? Bodenkultur 2009, 60, 43–60. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, C.A.; Atkinson, D.; Gosling, P.; Jackson, L.R.; Rayns, F.W. Managing soil fertility in organic farming systems. Soil Use Manag. 2002, 18, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Hattenschwiler, S.; Olander, L.; Allison, S. Nitrogen and nature. Ambio 2002, 31, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Li, J.; Ma, L.; Wang, F.; Sisak, I.; Cushman, G.; Zhang, F. Nitrogen flow and use efficiency in production and utilization of wheat, rice, and maize in China. Agric. Syst. 2008, 99, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, G.P.; Vitousek, P.M. Nitrogen in Agriculture: Balancing the Cost of an Essential Resource. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2009, 34, 97–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A. Response of mustard to ethrel spray and basal and foliar application of nitrogen. J. Agron. Crop Sci. -Z. Fur Acker Und Pflanzenbau 1996, 176, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F.S. Significant Acidification in Major Chinese Croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.X.; Jiang, L.; Hu, S.J.; Li, L.H.; Liu, L.L.; Wan, S.Q. Decoupling of soil microbes and plants with increasing anthropogenic nitrogen inputs in a temperate steppe. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 72, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.L.; Greaver, T.L. A global perspective on belowground carbon dynamics under nitrogen enrichment. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millett, J.; Foot, G.W.; Svensson, B.M. Nitrogen deposition and prey nitrogen uptake control the nutrition of the carnivorous plant Drosera rotundifolia. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tylianakis, J.M.; Didham, R.K.; Bascompte, J.; Wardle, D.A. Global change and species interactions in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, R.J.; Dise, N.B.; Stevens, C.J.; Gowing, D.J.; Partners, B. Impact of nitrogen deposition at the species level. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 984–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, C.J.; Dise, N.B.; Mountford, J.O.; Gowing, D.J. Impact of nitrogen deposition on the species richness of grasslands. Science 2004, 303, 1876–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wan, S.; Ren, H.; Han, X.; Li, M.-H.; Cheng, W.; Jiang, Y. Effects of Water and Nitrogen Addition on Species Turnover in Temperate Grasslands in Northern China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, T.N.; Macdonald, A.J.; McGrath, S.P.; Zhao, F.-J. Historical arsenic contamination of soil due to long-term phosphate fertiliser applications. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 180, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, E.M.; El-Neklawy, A.S.; Soad, M.E.A. Beneficial effects of humic substances ferrtigation on soil fertility to potato grown on sandy soil. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2009, 3, 4351–4358. [Google Scholar]
- Demirsoy, L.; Demirsoy, H.; Balci, G. Different growing conditions affect nutritient content, fruit yield and growth in strawberry. Pak. J. Bot. 2012, 44, 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrunisa, M.; Jamro, G.M.; Noor-un-Nisa, M.; Memon, K.S.; Akhtar, M.S. Micronutrient availability assessment of tomato grown in Taluka Badin, Sindh. Pak. J. Bot. 2012, 44, 649–654. [Google Scholar]
- Tejada, M.; Gonzalez, J.L.; Garcia-Martinez, A.M.; Parrado, J. Application of a green manure and green manure composted with beet vinasse on soil restoration: Effects on soil properties. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4949–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, M.; Gonzalez, J.L. Influence of two organic amendments on the soil physical properties, soil losses, sediments and runoff water quality. Geoderma 2008, 145, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wu, G.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, W.; Meng, J.; Liu, H.; Yu, X.; Jiang, G. Effects of cattle manure compost combined with mineral fertilizer on topsoil organic matter, bulk density and earthworm activity in a wheat-maize rotation system in Eastern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 156, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Yan, X.Y.; Wang, J.Y. The effect of mineral fertilizer application on carbon input and export in soil-A pot experiment with wheat using natural C-13 abundance method. Geoderma 2012, 189, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.C.; Zhao, N.; Huang, F.; Lv, Y. Long-term effects of different organic and inorganic fertilizer treatments on soil organic carbon sequestration and crop yields on the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 146, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramberger, B.; Podvrsnik, M.; Gselman, A.; Sustar, V.; Kristl, J.; Mursec, M.; Lesnik, M.; Skorjanc, D. The effects of cutting frequencies at equal fertiliser rates on bio-diverse permanent grassland: Soil organic C and apparent N budget. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 212, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A.; Holz, B. Grassland for agriculture and nature conservation: Production, quality and multi-functionality. Agron. Res. 2006, 4, 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kampmann, D.; Herzog, F.; Jeanneret, P.; Konold, W.; Peter, M.; Walter, T.; Wildi, O.; Luescher, A. Mountain grassland biodiversity: Impact of site conditions versus management type. J. Nat. Conserv. 2008, 16, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B. The rangeland degradation in North China and its preventive strategy. Sci. Agric. Sin. 1997, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- YaJing, B.A.O.; ZhengHai, L.I.; XingGuo, H.A.N.; GuoDong, H.A.N.; YanKai, Z. The caloric content of plant species and its role in a Leymus chinensis steppe community of Inner Mongolia, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2007, 27, 4443–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.W.; Li, L.H.; Han, X.G.; Ming, D. Do rhizome severing and shoot defoliation affect clonal growth of Leymus chinensis at ramet population level? Acta Oecologica-Int. J. Ecol. 2004, 26, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, E.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Yun, J. Effect of grassland degradation on arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis of Leymus chinensis (Trin.) Tzvel. in typical steppe. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2009, 17, 731–734. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H. Analysis on causal factors for degradation and desertification of Hulunbeier grassland. Pratacultural Sci. 2007, 24, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Magurran, A.E. Measuring richness and evenness. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1998, 13, 165–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, R.J.; Willis, K.J.; Field, R. Scale and species richness: Towards a general, hierarchical theory of species diversity. J. Biogeogr. 2001, 28, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, F.; Chen, Y.; Gao, J.; Lu, G.; Tian, M. Identification of hyperspectra characteristic bands of grassland degradation indicator plant species in Bashang Region of Hebei Province. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2016, 32, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Zheng, D. Inner Mongolia Artemisia frigida degraded rangeland and restoration strategies. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2004, 13, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Hao, M.; Guo, S.; Shi, X.; Ma, T.; Liu, P.; Liu, G. Fertilization effects on hay yield and quality of Leymus chinensis. Pratacultural Sci. 2014, 31, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Y. Primary study on fertilizer application to alpine rangeland in Qinghai, China. Pratacultural Sci. 2002, 19, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wen-Ye, C.; Deng-Chen, Q.I.; Guang-Yu, L.I.; Qiang, W.E.I.; Fang, W.; Fei-Da, S.U.N.; Zhen-Heng, L.I.U.; Li, Z.H.U. Study on Degraded Grassland Niche Characteristics and Productivity of Alpine Meadow at Maqu in South of Gansu Province. J. Nat. Resour. 2010, 25, 80–90. [Google Scholar]
- Vance-Chalcraft, H.D.; Willig, M.R.; Cox, S.B.; Lugo, A.E.; Scatena, F.N. Relationship Between Aboveground Biomass and Multiple Measures of Biodiversity in Subtropical Forest of Puerto Rico. Biotropica 2010, 42, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, C.F.; Morgan, E.D. Anomalies in the gas-liquid chromatography of cholesterol heptafluorobutyrate. J. Chromatogr. 1974, 90, 380–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finger, R.; Buchmann, N. An ecological economic assessment of risk-reducing effects of species diversity in managed grasslands. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 110, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Treatment | Nutrition Amount (kg/ha) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P2O5 | Organic Matter | ||
| - | no fertilizer | - | - | - |
| RC1 | 75 kg/ha urea, 45 kg/ha DAP | 42.6 | 20.7 | - |
| RC2 | 150 kg/ha urea, 90 kg/ha DAP | 85.2 | 41.4 | - |
| RC3 | 225 kg/ha urea, 135 kg/ha DAP | 127.8 | 62.1 | - |
| RO1 | 1400 kg/ha organic fertilizer | 42 | 21 | 630 |
| RO2 | 2800 kg/ha organic fertilizer | 84 | 42 | 1260 |
| RO3 | 4200 kg/ha organic fertilizer | 126 | 63 | 1890 |
| 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | L. chinensis | Total | L. chinensis | Total | L. chinensis | |
| CK | 126.82 ± 9.58 b | 100.57 ± 10.20 a | 122.81 ± 7.80 c | 54.64 ± 3.65 b | 102.41 ± 6.19b | 59.24 ± 6.15b |
| RC1 | 176.30 ± 6.30 ab | 131.62 ± 12.86 a | 245.10 ± 4.68 ab | 141.96 ± 20.15 b | 242.64 ± 21.82ab | 188.25 ± 8.89ab |
| RC2 | 210.14 ± 27.10 a | 147.47 ± 21.27 a | 363.99 ± 25.69 a | 270.88 ± 35.56 a | 264.87 ± 64.34a | 218.68 ± 37.79a |
| RC3 | 175.67 ± 18.58 ab | 98.45 ± 9.20 a | 202.94 ± 14.29 abc | 138.60 ± 14.82 b | 255.70 ± 44.44ab | 203.60 ± 17.95ab |
| RO1 | 136.36 ± 5.31 ab | 101.18 ± 8.72 a | 131.12 ± 5.45 bc | 72.92 ± 9.19 b | 143.47 ± 14.83ab | 77.60 ± 15.35b |
| RO2 | 152.60 ± 3.36 ab | 98.78 ± 9.87 a | 187.54 ± 5.09 bc | 52.92 ± 6.56 b | 178.69 ± 15.09ab | 125.98 ± 4.57ab |
| RO3 | 151.01 ± 2.54 ab | 97.12 ± 4.59 a | 207.06 ± 7.35 bc | 52.96 ± 9.27 b | 144.24 ± 4.31ab | 73.43 ± 6.63b |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tong, Z.; Quan, G.; Wan, L.; He, F.; Li, X. The Effect of Fertilizers on Biomass and Biodiversity on a Semi-Arid Grassland of Northern China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11102854
Tong Z, Quan G, Wan L, He F, Li X. The Effect of Fertilizers on Biomass and Biodiversity on a Semi-Arid Grassland of Northern China. Sustainability. 2019; 11(10):2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11102854
Chicago/Turabian StyleTong, Zongyong, Guoling Quan, Liqiang Wan, Feng He, and Xianglin Li. 2019. "The Effect of Fertilizers on Biomass and Biodiversity on a Semi-Arid Grassland of Northern China" Sustainability 11, no. 10: 2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11102854
APA StyleTong, Z., Quan, G., Wan, L., He, F., & Li, X. (2019). The Effect of Fertilizers on Biomass and Biodiversity on a Semi-Arid Grassland of Northern China. Sustainability, 11(10), 2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11102854






