Application of Time-Lapse Ion Exchange Resin Sachets (TIERS) for Detecting Illegal Effluent Discharge in Mixed Industrial and Agricultural Areas, Taiwan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of Time-Lapse Ion Exchange Resin Sachet (TIERS)
2.2. X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) Spectrometry
2.3. Preparation for Resin Detection Modules in XRF
2.4. Field Application
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Development of Resin Detection Modules in XRF
3.2. Field Monitoring Results
3.3. Standardization of Zn and Cu by Sr
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trujillo-González, J.M.; Torres-Mora, M.A.; Keesstra, S.; Brevik, E.C.; Jiménez-Ballesta, R. Heavy metal accumulation related to population density in road dust samples taken from urban sites under different land uses. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 553, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, S.; Dai, S.; Li, Y.; Tang, J.; Ren, Y. Analysis of heavy metal sources in the soil of riverbanks across an urbanization gradient. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, S.; Shahid, M.; Natasha; Bibi, I.; Sarwar, T.; Shah, A.H.; Niazi, N.K. A review of environmental contamination and health risk assessment of wastewater use for crop irrigation with a focus on low and high-income countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtaza, G.; Ghafoor, A.; Qadir, M.; Owens, G.; Aziz, M.; Zia, M.; Ullah, S. Disposal and use of sewage on agricultural lands in Pakistan: A review. Pedosphere 2010, 20, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.A.; Drechsel, P.; Raschid-Sally, L.; Bahri, A.; Mara, D.; Redwood, M.; Jiménez, B. Wastewater irrigation and health: Challenges and outlook for mitigating risks in low-income countries. In Wastewater Irrigation and Health: Assessing and Mitigating Risk in Low-Income Countries; Earthscan: London, UK, 2010; pp. 381–394. [Google Scholar]
- Raychaudhuri, S.; Raychaudhuri, M.; Rautaray, S.K.; Parida, S.; Kumar, A. Urban wastewater – A potential irrigation source for summer paddy (Oryza sativa L.) in India. Int. J. Agric. Innov. Res. 2017, 5, 986–995. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y. Wastewater irrigation: Past, present, and future. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2019, 6, e1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattan, R.; Datta, S.; Chhonkar, P.; Suribabu, K.; Singh, A. Long-term impact of irrigation with sewage effluents on heavy metal content in soils, crops and groundwater—A case study. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 109, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Cao, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, Y. Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 152, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qadir, M.; Wichelns, D.; Raschid-Sally, L.; McCornick, P.G.; Drechsel, P.; Bahri, A.; Minhas, P. The challenges of wastewater irrigation in developing countries. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, R.K.; Agrawal, M.; Marshall, F.M. Health risk assessment of heavy metals via dietary intake of foodstuffs from the wastewater irrigated site of a dry tropical area of India. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muamar, A.; Zouahri, A.; Tijane, M.; El Housni, A.; Mennane, Z.; Yachou, H.; Bouksaim, M. Evaluation of heavy metals pollution in groundwater, soil and some vegetables irrigated with wastewater in the Skhirat region Morocco. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2014, 5, 961–966. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, S.; Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Niazi, N.K.; Bibi, I.; Gul Bakhat, H.F.S.; Abbas, G.; Murtaza, B.; Javeed, H.M.R. Influence of groundwater and wastewater irrigation on lead accumulation in soil and vegetables: Implications for health risk assessment and phytoremediation. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2017, 19, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Tang, J.; Wang, T.; Wu, D.; Busso, C.A.; Jiao, R.; Ren, X. Impacts of sewage irrigation on soil properties of farmland in China: A review. Solid Earth Discuss. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.H.; Zhao, J.Z.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Soderlund, L.G.; Liu, H. Impact of sewage irrigation on heavy metal distribution and contamination in Beijing, China. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Chen, C.; Song, X.; Han, Y.; Liang, Z. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in soil and plants form Dunhua sewage irrigation area. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2011, 6, 5314–5324. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Z.; Wu, W.; Liu, H.; Chen, H.; Yin, S. Impact of long-term irrigation with sewage on heavy metals in soils, crops, and groundwater—A case study in Beijing. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 23, 309–318. [Google Scholar]
- Camargo, M.A.F.; Pereira, T.A.R. Evaluation of concentration of heavy metals in water used in agriculture irrigation. Open Access Libr. J. 2018, 5, e4959. [Google Scholar]
- Ravera, O.; Cenci, R.; Beone, G.M.; Dantas, M.; Lodigiani, P. Trace element concentrations in freshwater mussels and macrophytes as related to those in their environment. J. Limnol. 2003, 62, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapanda, F.; Mangwayana, E.; Nyamangara, J.; Giller, K. The effect of long-term irrigation using wastewater on heavy metal contents of soils under vegetables in Harare, Zimbabwe. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 107, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Malik, R.N. Human health risk assessment of heavy metals via consumption of contaminated vegetables collected from different irrigation sources in Lahore, Pakistan. Arab. J. Chem. 2014, 7, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.; Dumat, C.; Pierart, A.; Shahid, M.; Kang, Y.; Li, N.; Bertoni, G.; Laplanche, C. Measurement of metal bioaccessibility in vegetables to improve human exposure assessments: Field study of soil-plant-atmosphere transfers in urban areas, South China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2016, 38, 1283–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, S. Heavy metal enrichments in the Changjiang (Yangtze river) catchment and on the inner shelf of the east China sea over the last 150 years. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 543, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Zhao, R.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, B.; Li, Y.; Shi, Z. Heavy metal pollution delineation based on uncertainty in a coastal industrial city in the Yangtze river delta, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaseghi, S.; Afyuni, M.; Shariatmadari, H.; Mobli, M. Effect of sewage sludge on some nutrients concentration and soil chemical properties. J. Isfahan Water Wastewater 2005, 53, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Khaskhoussy, K.; Kahlaoui, B.; Nefzi, B.M.; Jozdan, O.; Dakheel, A.; Hachicha, M. Effect of treated wastewater irrigation on heavy metals distribution in a tunisian soil. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2015, 5, 805–810. [Google Scholar]
- Arefin, M.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Wahid-U-Zzaman, M.; Kim, J.-E. Heavy metal contamination in surface water used for irrigation: Functional assessment of the Turag river in Bangladesh. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2016, 59, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroon, B.; Ping, A.; Pervez, A.; Faridullah; Irshad, M. Characterization of heavy metal in soils as affected by long-term irrigation with industrial wastewater. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2018, 9, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Javid, S.; Muhmood, A.; Mjeed, T.; Niaz, A.; Majeed, A. Heavy metal status of soil and vegetables grown on peri-urban area of Lahore district. Soil Environ. 2013, 32, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Gatta, G.; Gagliardi, A.; Disciglio, G.; Lonigro, A.; Francavilla, M.; Tarantino, E.; Giuliani, M.M. Irrigation with treated municipal wastewater on artichoke crop: Assessment of soil and yield heavy metal content and human risk. Water 2018, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suruchi; Khanna, P. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in different vegetables grown in and around urban areas. Res. J. Environ. Toxicol. 2011, 5, 162–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkay, F.; Kiran, S.; Taş, I.; Kuşvuran, S. Effects of Copper, Zinc, Lead and Cadmium Applied with Irrigation Water on Some Eggplant Plant Growth Parameters and Soil Properties. Turk. J. Agric. Nayrural Sci. 2014, 1, 377–383. [Google Scholar]
- Nassr, M.M.I.; Moursi, E.A.; Kassab, M.M. Effect of irrigation water quality on some soil properties, productivity of some wheat cultivars and their contents of heavy metals. J. Soil Sci. Agric. Eng. Mansoura Univ. 2014, 5, 1317–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, S.; Zhao, C. Study on heavy metal element detection of china tea based on ICP-MS method. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2017, 12, 1516–1520. [Google Scholar]
- Hutton, L.A.; O’Neil, G.D.; Read, T.L.; Ayres, Z.J.; Newton, M.E.; Macpherson, J.V. Electrochemical X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy for trace heavy metal analysis: Enhancing X-ray fluorescence detection capabilities by four orders of magnitude. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 4566–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Dong, H.; Liu, K.; He, N. Progress on sensors based on nanomaterials for rapid detection of heavy metal ions. Sci. China Chem. 2017, 60, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liang, X.; Niyungeko, C.; Zhou, J.; Xu, J.; Tian, G. A review of the identification and detection of heavy metal ions in the environment by voltammetry. Talanta 2018, 178, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritschel, A.; Wobrauschek, P.; Chinea, E.; Grass, F.; Fabjan, C. An electrochemical enrichment procedure for the determination of heavy metals by total-reflection X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 1999, 54, 1449–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, T.; Diamond, D. Comparison of soil pollution concentrations determined using AAS and portable XRF techniques. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 1168–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Choi, Y.; Charlesworth, S. Assessing statistically significant heavy metal concentrations in abandoned mine areas via hot spot analysis of portable XRF data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, R.S.; Wang, Y.C. Ligand-enhanced separation of divalent heavy metals from aqueous solutions using a strong-acid ion-exchange resin. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 1948–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.Y.; Lee, J.U.; Moon, S.H.; Kim, K.W. Competitive adsorption characteristic of Co2+, Ni2+ and Cr3+ by IRN77 cation exchange resin in synthesized wastewater. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, T.H.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, C.H. Development of an ion exchange system for plating wastewater treatment. Desalination 2005, 180, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremer, E.; Miller, J.; Curtis, T.; Miller, J. Placement of ion-exchange membranes for monitoring nutrient release from flooded soils. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 98, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbaş, A. Adsorption of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) ions from aqueous solutions on to modified lignin. Energy Sources 2005, 27, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donia, A.M.; Atia, A.A.; El-Boraey, H.; Mabrouk, A.D.H. Uptake studies of copper(II) on glycidyl methacrylate chelating resin containing Fe2O3 particles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 49, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, R.; Fahim, N.K. Application of polypyrrole coated on wood sawdust for removal of Cr(VI) ion from aqueous solutions. React. Funct. Polym. 2007, 67, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammerer, J.; Carle, R.; Kammerer, D.R. Adsorption and ion exchange: Basic principles and their application in food processing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 22–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shefsky, S. Comparing field portable X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) to laboratory analysis of heavy metal in soil. Presented at the International Symposium of Field Screening Methods for Hazardous Wastes and Toxic Chemicals, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 29–31 January 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.-J.S.; Lin, S.-C.; Löwemark, L.; Liou, S.Y.H.; Chang, Q.; Chang, T.-K.; Wei, K.-Y.; Croudace, I.W. Rapid assessment of heavy metal pollution using ion-exchange resin sachets and micro-XRF core-scanning. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Joint FAO/WHO Expert Standards Program Codex Alimentation Commission; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; Available online: http://www.who.int (accessed on 1 February 2019).
- Radojevic, M.; Bashkin, V.N. Practical Environmental Analysis, 2nd ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.J.; Severin, K.P. Otolith chemistry analyses indicate that water Sr:Ca is the primary factor influencing otolith Sr:Ca for freshwater and diadromous fish but not for marine fish. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2009, 66, 1790–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coggon, R.M.; Teagle, D.A.H.; Smith-Duque, C.E.; Alt, J.C.; Cooper, M.J.; Hsieh, M.-H.; Brun, T.; Devetak, I. Reconstructing past seawater Mg/Ca and Sr/Ca from Mid-Ocean Ridge Flank Calcium Carbonate Veins. Science 2010, 327, 1114–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, K.L.; Quinn, T.M.; Taylor, F.W.; Lin, K.; Shen, C.-C. Sea surface temperature variability in the southwest tropical Pacific since AD 1649. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gode, F.; Pehlivan, E. Removal of chromium (III) from aqueous solutions using Lewatit S 100: The effect of pH, time, metal concentration and temperature. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.L.; Brunner, G. Desorption of heavy metals from ion exchange resin with water and carbon dioxide. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2006, 23, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.-H.; Kuan, Y.-C.; Chern, J.-M. Equilibrium and kinetics of heavy metal ion exchange. J. Chin. Inst. Chem. Eng. 2007, 38, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandramohan, K.; Marimuthu, S. Adsorptive removal of Copper from aqueous solution by Amberlite cation-exchange resin-equilibrium and kinetic studies. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Biology, Environment and Chemistry, Dubai, UAE, 28–30 December 2011; Volume 24, pp. 357–361. [Google Scholar]
- Tamilmani, S.; Huang, W.; Raghavan, S.; Smallb, R. Potential-pH diagrams of interest to chemical mechanical planarization of copper. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2002, 149, G638–G642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-H. The Eh-pH diagram and its advances. Metals 2016, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philp, R.P.; Allen, J.; Kuder, T. The use of the isotopic composition of individual compounds for correlating spilled oils and refined products in the environment with suspected sources. Environ. Forensics 2002, 3, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, G.; Kalin, R.M. Investigation of the range of carbon and hydrogen isotopes within a global set of gasolines. Environ. Forensics 2008, 9, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundegard, P.D.; Sweeney, R.E.; Ririe, G.T. Soil gas methane at petroleum contaminated sites: Forensic determination of origin and source. Environ. Forensics 2000, 1, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, S.A.; Wasielewski, T.N. Historical and chemical assessment of the sources of PAHs in soils at a former coal-burning power plant, New Haven, Connecticut. Environ. Forensics 2004, 5, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.R.; Ging, P.B.; Lee, R.W.; Ebbert, C.; Tesoriero, A.J.; Inkpen, E.L. Forensic applications of nitrogen and oxygen isotopes in tracing nitrate sources in urban environments. Environ. Forensics 2002, 3, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machemer, S.D.; Hosick, T.J.; Ingamells, R.L. Source identification of lead contamination in residential and undisturbed soil adjacent to a battery manufacturing facility (Part 1). Environ. Forensics 2007, 8, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegeman, W.J.M.; van Der Weijden, C.H.; Zwolsman, J.J.G. Sorption of Zinc on suspended particles along a salinity gradient: A laboratory study using illite and suspended matter from the river Rhine. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1992, 28, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millward, G.E.; Liu, Y.P. Modelling metal desorption kinetics in estuaries. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 314, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owsianiak, M.; Holm, P.E.; Fantke, P.; Christiansen, K.S.; Borggaard, O.K.; Hauschild, M.Z. Assessing comparative terrestrial ecotoxicity of Cd, Co, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn: The influence of aging and emission source. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, A.L.; Smolders, E.; Van den Brande, K.; Merckx, R.; Wright, S.M.; Naylor, C. Prediction of in situ solid/liquid distribution of radiocaesium in soils. J. Environ. Radioact. 2002, 63, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatje, V.; Payne, T.E.; Hill, D.M.; McOrist, G.; Birch, G.F.; Scymczak, R. Kinetics of trace element uptake and release by particles in estuarine waters: Effects of pH, salinity, and particle loading. Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, J.M.; Ciffroy, P.; Benyahya, L. Implications of short and long term (30 days) sorption on the desorption kinetic of trace metals (Cd, Zn, Co, Mn, Fe, Ag, Cs) associated with river suspended matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 366, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Davison, W.; Tye, A.M.; Crout, N.M.J.; Young, S.D. Kinetics of zinc and cadmium release in freshly contaminated soils. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.Y.; Fang, W.T.; Shyu, G.S.; Chang, T.K. Distribution of heavy metals in the sediments of agricultural fields adjacent to urban areas in Central Taiwan. Paddy Water Environ. 2012, 11, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, T.N.; Ozaki, A.; Tho, H.N.; Duc, A.N.; Thi, Y.T.; Kurosawa, K.; Charlesworth, S. Arsenic and heavy metal contamination in soils under different land use in an estuary in Northern Vietnam. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, Y. Soil heavy metal dynamics and risk assessment under long-term land use and cultivation conversion. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 22, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, D.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, W.; Charlesworth, S. Impact from land use pattern on spatial distribution of cultivated soil heavy metal pollution in typical rural-urban fringe of Northeast China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalavrouziotis, I.K.; Koukoulakis, P.H.; Papadopoulos, A.H. Heavy metal interrelationships in soil in the presence of treated wastewater. Glob. NEST J. 2009, 11, 497–509. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Yu, H. Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and sources of heavy metals in agricultural soil in Dehui, Northeast China. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ağca, N. Spatial distribution of heavy metal content in soils around an industrial area in Southern Turkey. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 1111–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
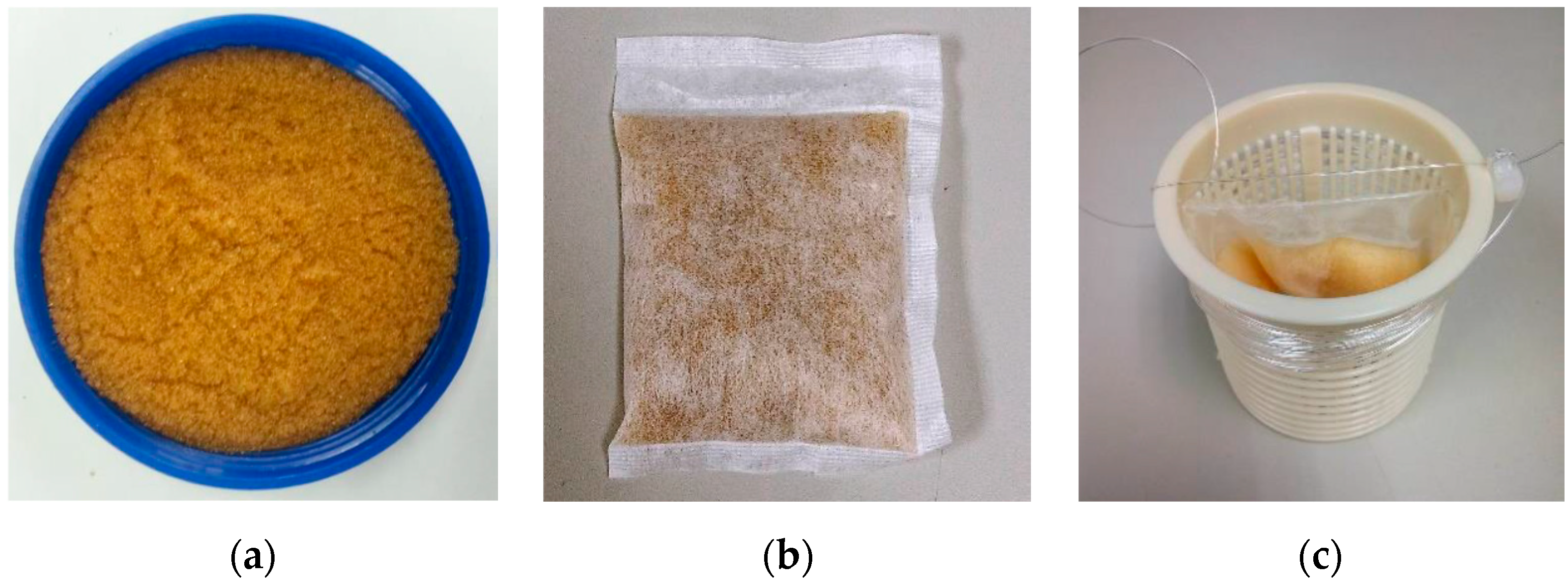

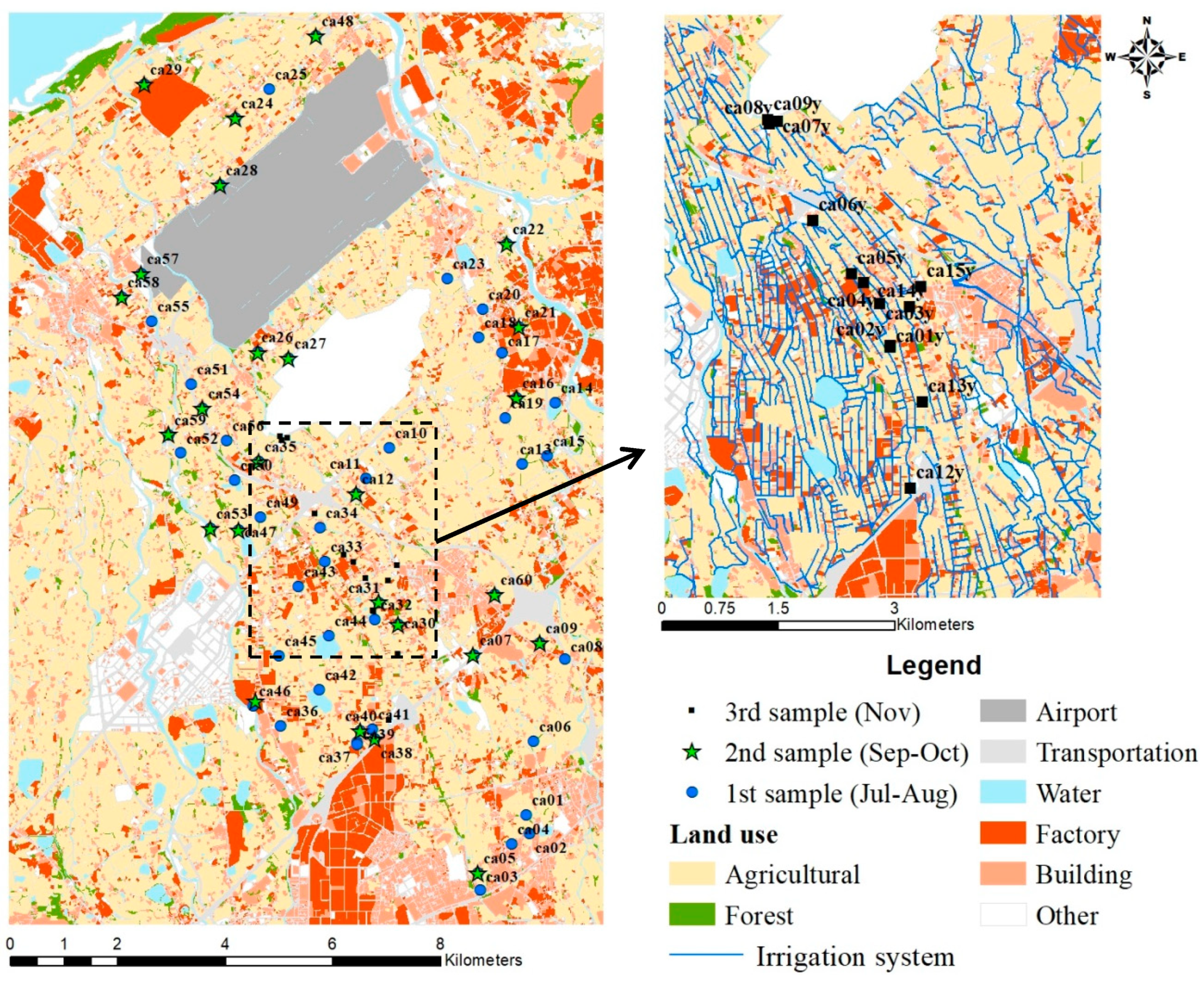

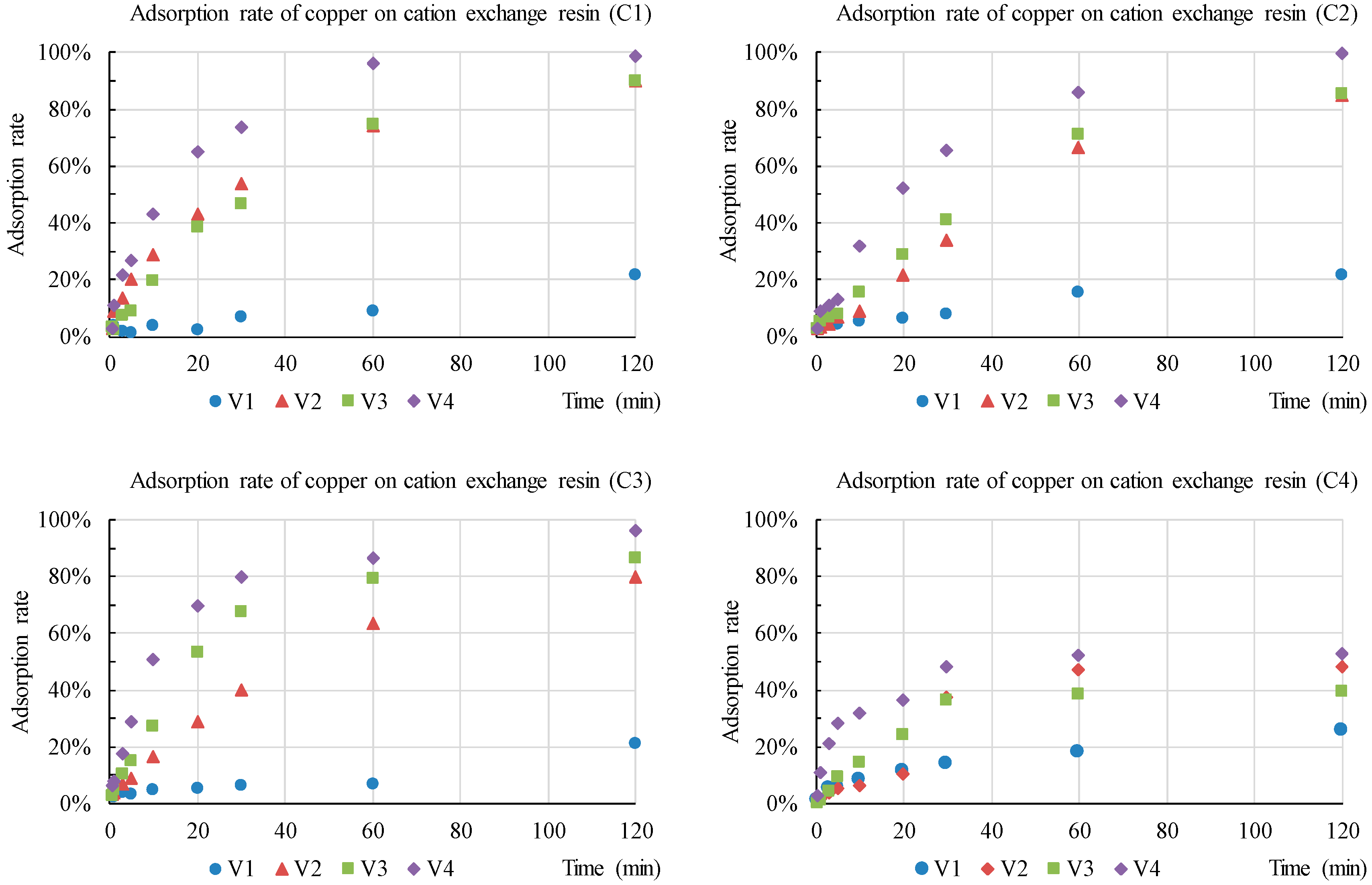
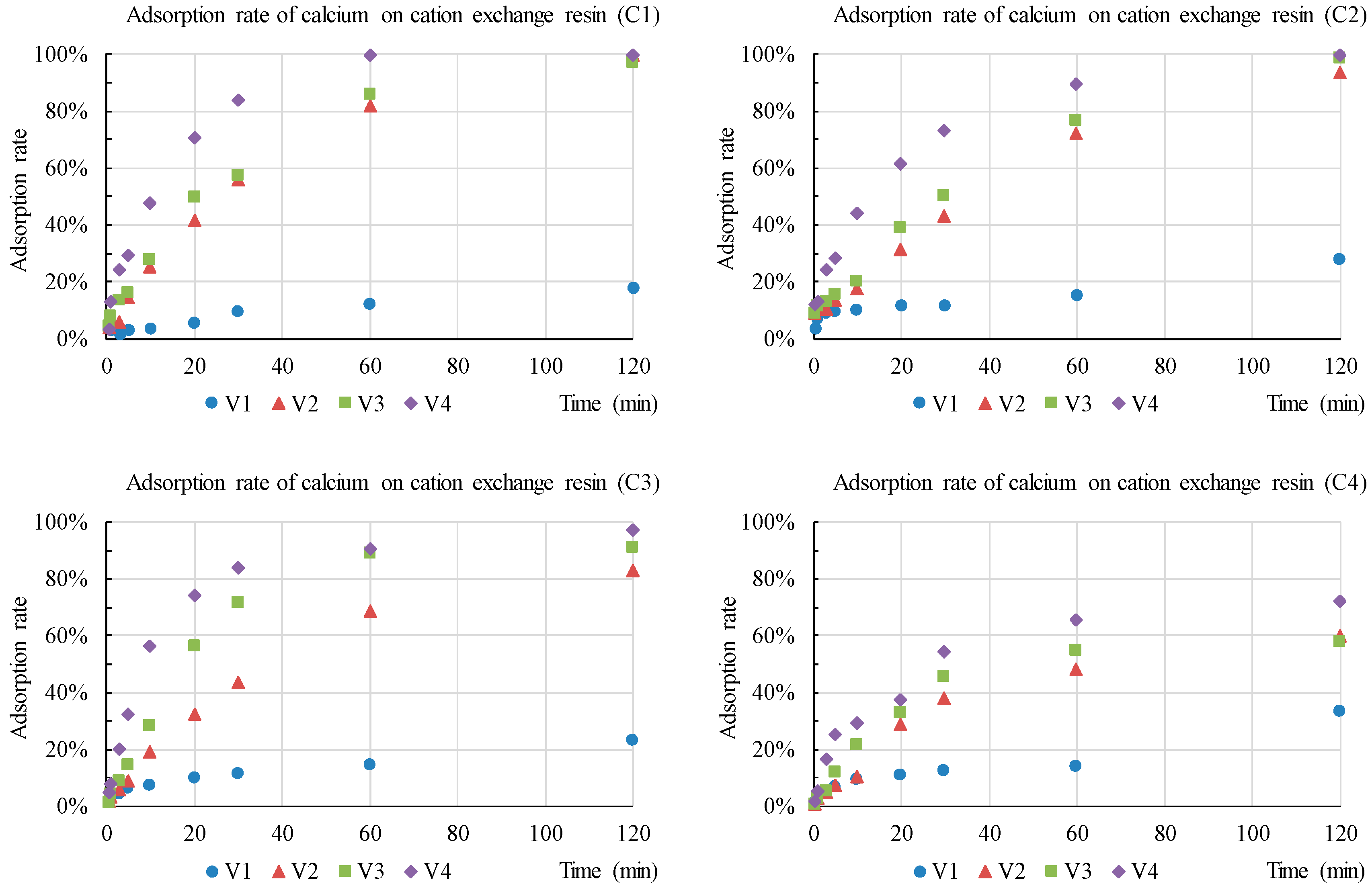

| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Product name | Purolite C100 |
| Application | Softening, Demineralization |
| Polymer structure | Gel polystyrene crosslinked with divinylbenzene |
| Appearance | Spherical beads |
| Functional group | Sulfonic acid |
| Ionic form | Na+ form |
| Cation exchange capacity (CEC) | 2.0 eq/L (Na+ form) |
| Moisture retention | 44–48% (Na+ form) |
| Particle size range | 300–1200 μm |
| Particle density | 1.29 g/cm3 |
| Temperature tolerance | 120 °C |
| Concentration (mg/L) | Zn | Cu | Ca | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | Trace | 0.5 | 0.3 | 2 |
| C2 1 | Low | 5.0 | 3.0 | 20 |
| C3 | Medium | 50 | 30 | 100 |
| C4 | High | 100 | 60 | 200 |
| Sampling Batch | Sample Date | No. of Sample Placement | No. of Collected Sample | Recycle Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 28–29 July | 180 | 137 | 76.11 |
| 4–5 August | 180 | 149 | 82.78 | |
| 11–12 August | 180 | 136 | 75.56 | |
| All | 540 | 422 | 78.15 | |
| 2nd | 30 September | 78 | 61 | 78.21 |
| 7 October | 78 | 63 | 80.77 | |
| 14 October | 78 | 69 | 88.46 | |
| All | 234 | 193 | 82.48 | |
| 3rd | 4 November | 27 | 24 | 88.89 |
| 11 November | 27 | 23 | 85.19 | |
| 18 November | 15 | 9 | 60.00 | |
| All | 69 | 56 | 81.16 |
| Metal and Trace Element | Sampling Batch 1 | Mean (mg/kg) | Median (mg/kg) | Std. Dev. (mg/kg) | Relative Std. Dev. (%) | Max. (mg/kg) | Min. (mg/kg) | Number of Data | Number of Data Smaller than LOD 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | 1st | 8.83 | 5.60 | 11.58 | 131.11 | 139.00 | 1.00 | 422 | 18 |
| 2nd | 15.02 | 13.10 | 10.35 | 68.89 | 53.10 | 1.60 | 193 | 0 | |
| 3rd | 11.72 | 5.65 | 21.33 | 182.09 | 145.10 | 1.10 | 56 | 8 | |
| All | 10.90 | 7.60 | 12.53 | 114.92 | 145.10 | 1.00 | 671 | 26 | |
| Cu | 1st | 5.97 | 3.25 | 12.02 | 201.30 | 163.00 | 1.70 | 422 | 160 |
| 2nd | 8.89 | 5.25 | 12.43 | 139.81 | 118.00 | 1.70 | 193 | 27 | |
| 3rd | 79.20 | 13.40 | 170.85 | 215.71 | 823.00 | 1.80 | 56 | 13 | |
| All | 13.69 | 4.00 | 56.37 | 411.80 | 823.00 | 1.70 | 671 | 200 | |
| Ca | 1st | 40,843.09 | 48,824.00 | 20,611.93 | 50.47 | 81,872.00 | 1540.00 | 422 | 0 |
| 2nd | 37,304.76 | 43,930.00 | 19,618.51 | 52.59 | 63,731.00 | 962.00 | 193 | 0 | |
| 3rd | 31,890.07 | 26,984.00 | 19,035.76 | 59.69 | 58,452.00 | 4682.00 | 56 | 0 | |
| All | 39,078.16 | 45,568.00 | 20,351.59 | 52.08 | 81,872.00 | 962.00 | 671 | 0 | |
| Sr | 1st | 483.85 | 519.50 | 262.90 | 54.33 | 1222.00 | 18.40 | 422 | 0 |
| 2nd | 391.85 | 430.00 | 220.55 | 56.28 | 808.00 | 7.50 | 193 | 0 | |
| 3rd | 356.11 | 389.50 | 196.56 | 55.20 | 675.00 | 52.40 | 56 | 0 | |
| All | 446.73 | 481.00 | 250.92 | 56.17 | 1222.00 | 7.50 | 671 | 0 |
| Ratio of Sr/Ca | Sampling Batch | Mean | Median | Std. Dev. | Relative Std. Dev. (%) | Max. | Min. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sr/Ca | 1st | 0.0119 | 0.0115 | 0.0019 | 16.23 | 0.0230 | 0.0080 |
| 2nd | 0.0104 | 0.0105 | 0.0015 | 14.50 | 0.0142 | 0.0064 | |
| 3rd | 0.0116 | 0.0112 | 0.0017 | 14.29 | 0.0156 | 0.0088 | |
| All | 0.0115 | 0.0112 | 0.0019 | 16.69 | 0.0230 | 0.0064 |
| Sampling Batch | Mean | Median | Std. Dev. | Relative Std. Dev. (%) | Max. | Min. | Threshold 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn/Sr | 1st | 0.0265 | 0.0139 | 0.0455 | 171.50 | 0.6521 | 0.0014 | 0.1176 |
| 2nd | 0.0604 | 0.0340 | 0.0752 | 124.42 | 0.5333 | 0.0054 | 0.2107 | |
| 3rd | 0.0299 | 0.0183 | 0.0431 | 143.81 | 0.2523 | 0.0038 | 0.1161 | |
| Cu/Sr | 1st | 0.0147 | 0.0069 | 0.0314 | 213.04 | 0.4338 | 0.0021 | 0.0775 |
| 2nd | 0.0266 | 0.0174 | 0.0329 | 123.72 | 0.2933 | 0.0039 | 0.0925 | |
| 3rd | 0.2176 | 0.0560 | 0.3848 | 176.80 | 1.4313 | 0.0051 | 0.9871 |
| Sample No. | Zn (mg/kg) | Cu (mg/kg) | Ca (mg/kg) | Sr (mg/kg) | Zn/Sr | Cu/Sr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ca07m 1-1 2 | 9.00 | 1.80 | 3474.00 | 52.10 | 0.1727 3 | 0.0345 |
| ca07d-3 | 15.80 | 3.00 | 7482.00 | 113.70 | 0.1390 | 0.0264 |
| ca07m-3 | 21.00 | 5.50 | 4690.00 | 76.90 | 0.2731 | 0.0715 |
| ca09u-3 | 50.50 | 20.40 | 17,285.00 | 222.00 | 0.2275 | 0.0919 |
| ca15u-3 | 7.20 | 3.80 | 3077.00 | 39.10 | 0.1841 | 0.0972 |
| ca21m-1 | 7.40 | <LOD | 4485.00 | 57.40 | 0.1289 | * 4 |
| ca21d-3 | 105.40 | 24.90 | 40,772.00 | 459.00 | 0.2296 | 0.0542 |
| ca21m-3 | 47.80 | 31.80 | 5691.00 | 73.30 | 0.6521 | 0.4338 |
| ca26d-1 | 22.80 | 2.30 | 18,160.00 | 190.00 | 0.1200 | 0.0121 |
| ca46d-1 | 38.10 | 73.90 | 53,529.00 | 686.00 | 0.0555 | 0.1077 |
| ca46u-3 | 36.50 | 54.20 | 60,608.00 | 684.00 | 0.0534 | 0.0792 |
| ca47d-2 | 139.00 | 163.00 | 81,872.00 | 1204.00 | 0.1154 | 0.1354 |
| ca53u-3 | 14.70 | 14.70 | 11,086.00 | 122.90 | 0.1196 | 0.1196 |
| ca58d-1 | 22.90 | 6.40 | 18,998.00 | 192.00 | 0.1193 | 0.0333 |
| Sample No. | Zn (mg/kg) | Cu (mg/kg) | Ca (mg/kg) | Sr (mg/kg) | Zn/Sr | Cu/Sr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ca21u 1-4 2 | 46.80 | 4.90 | 11,827.00 | 123.70 | 0.3783 3 | 0.0396 |
| ca21m-6 | 23.20 | 5.30 | 9859.00 | 105.70 | 0.2195 | 0.0501 |
| ca26u-5 | 37.10 | 10.00 | 7482.00 | 87.10 | 0.4259 | 0.1148 |
| ca26m-4 | 40.40 | 12.10 | 7548.00 | 95.10 | 0.4248 | 0.1272 |
| ca26u-4 | 39.80 | 9.60 | 9647.00 | 111.10 | 0.3582 | 0.0864 |
| ca30u-6 | 53.10 | 118.00 | 63,594.00 | 781.00 | 0.0680 | 0.1511 |
| ca46u-6 | 48.30 | 55.20 | 57,446.00 | 570.00 | 0.0847 | 0.0968 |
| ca53u-6 | 9.60 | 5.70 | 6929.00 | 60.90 | 0.1576 | 0.0936 |
| ca60d-5 | 4.00 | 2.20 | 962.00 | 7.50 | 0.5333 | 0.2933 |
| ca60m-5 | 4.10 | 2.80 | 3536.00 | 29.30 | 0.1399 | 0.0956 |
| ca61m-6 | 15.20 | 48.30 | 37,820.00 | 346.00 | 0.0439 | 0.1396 |
| Sample No. | Zn (mg/kg) | Cu (mg/kg) | Ca (mg/kg) | Sr (mg/kg) | Zn/Sr | Cu/Sr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ca05ym 1-1 2 | 3.50 | 567.00 | 26,282.00 | 411.00 | 0.0085 | 1.3796 3 |
| ca05yu-1 | 4.00 | 476.00 | 25,420.00 | 392.00 | 0.0102 | 1.2143 |
| ca07ym-2 | 13.60 | <LOD | 6084.00 | 75.80 | 0.1794 | * 4 |
| ca12yu-3 | 145.10 | 823.00 | 53,642.00 | 575.00 | 0.2523 | 1.4313 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shih, P.-K.; Chiang, L.-C.; Lin, S.-C.; Chang, T.-K.; Hsu, W.-C. Application of Time-Lapse Ion Exchange Resin Sachets (TIERS) for Detecting Illegal Effluent Discharge in Mixed Industrial and Agricultural Areas, Taiwan. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11113129
Shih P-K, Chiang L-C, Lin S-C, Chang T-K, Hsu W-C. Application of Time-Lapse Ion Exchange Resin Sachets (TIERS) for Detecting Illegal Effluent Discharge in Mixed Industrial and Agricultural Areas, Taiwan. Sustainability. 2019; 11(11):3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11113129
Chicago/Turabian StyleShih, Po-Kang, Li-Chi Chiang, Sheng-Chi Lin, Tsun-Kuo Chang, and Wei-Chan Hsu. 2019. "Application of Time-Lapse Ion Exchange Resin Sachets (TIERS) for Detecting Illegal Effluent Discharge in Mixed Industrial and Agricultural Areas, Taiwan" Sustainability 11, no. 11: 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11113129
APA StyleShih, P.-K., Chiang, L.-C., Lin, S.-C., Chang, T.-K., & Hsu, W.-C. (2019). Application of Time-Lapse Ion Exchange Resin Sachets (TIERS) for Detecting Illegal Effluent Discharge in Mixed Industrial and Agricultural Areas, Taiwan. Sustainability, 11(11), 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11113129





