A New Approach to Land-Use Structure: Patch Perimeter Metrics as a Spatial Analysis Tool
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Landscape Analysis
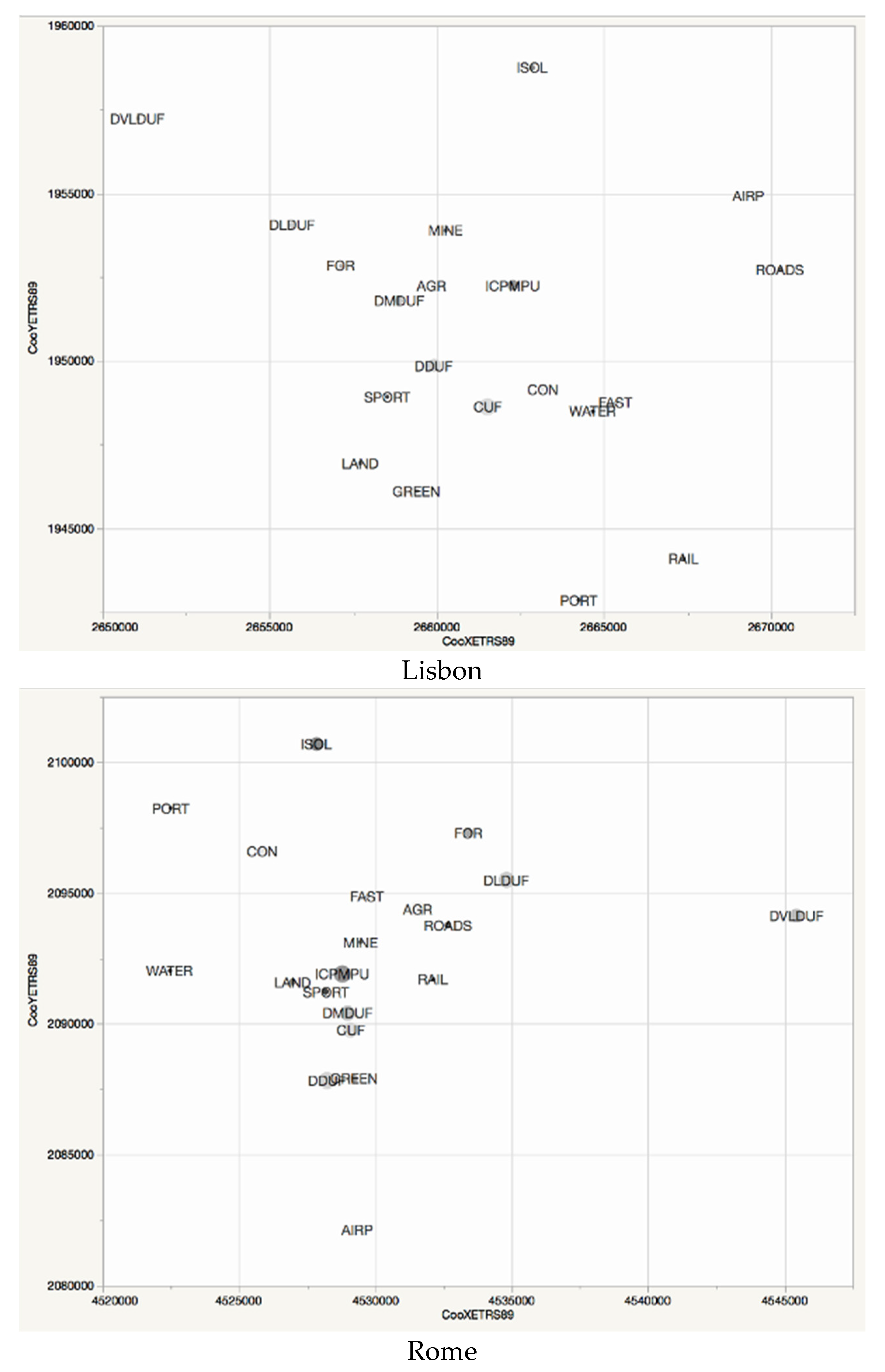
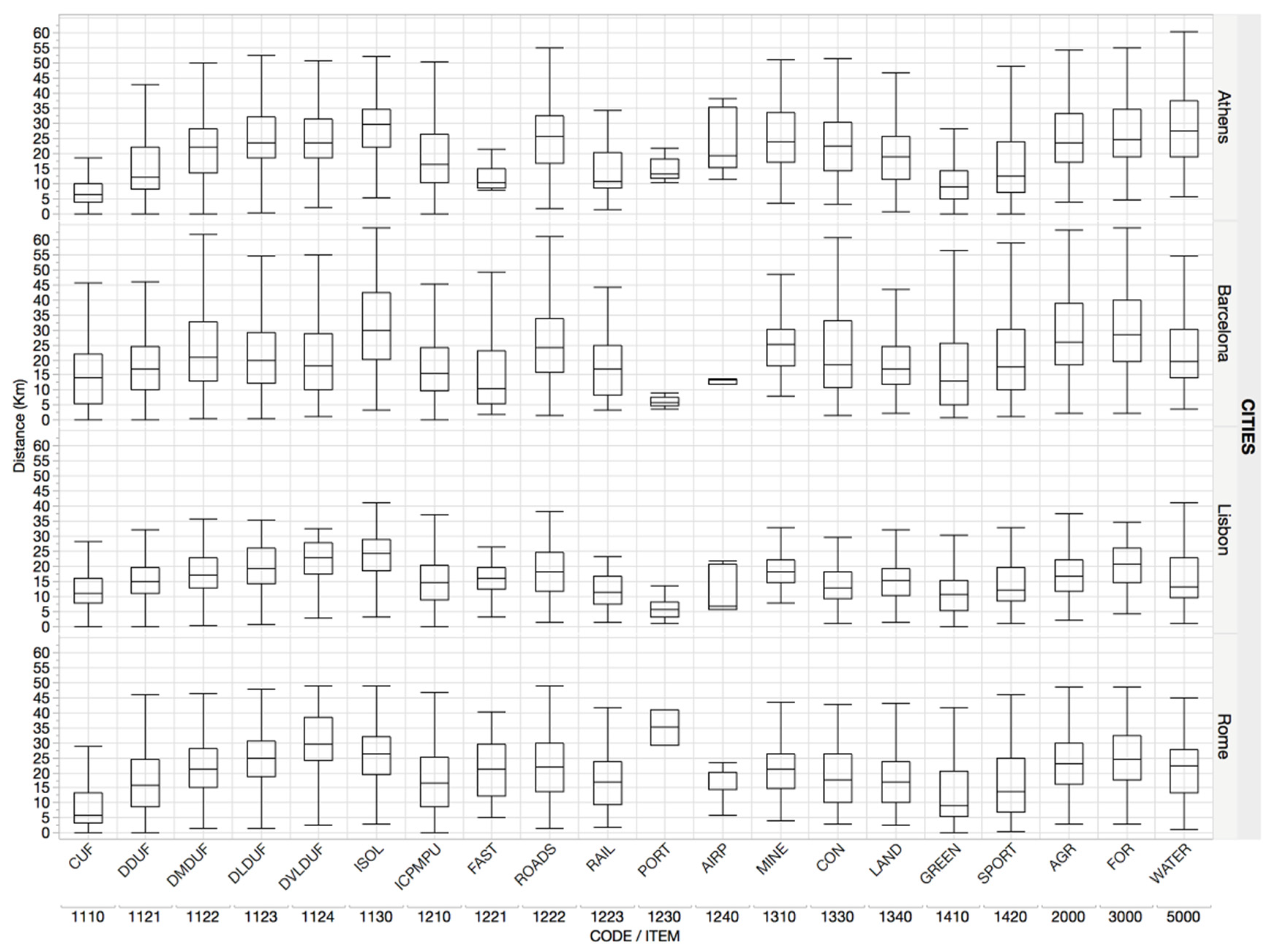
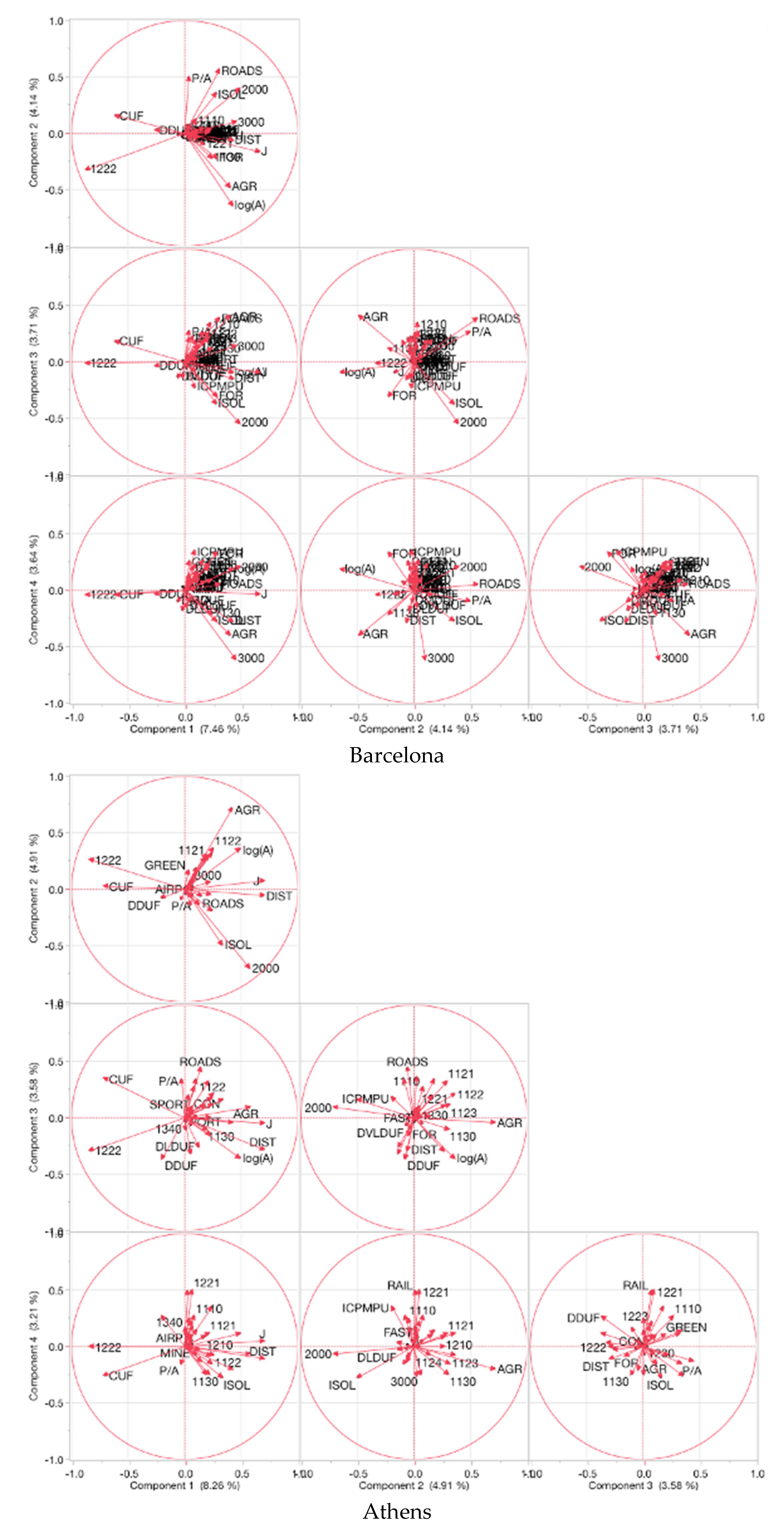
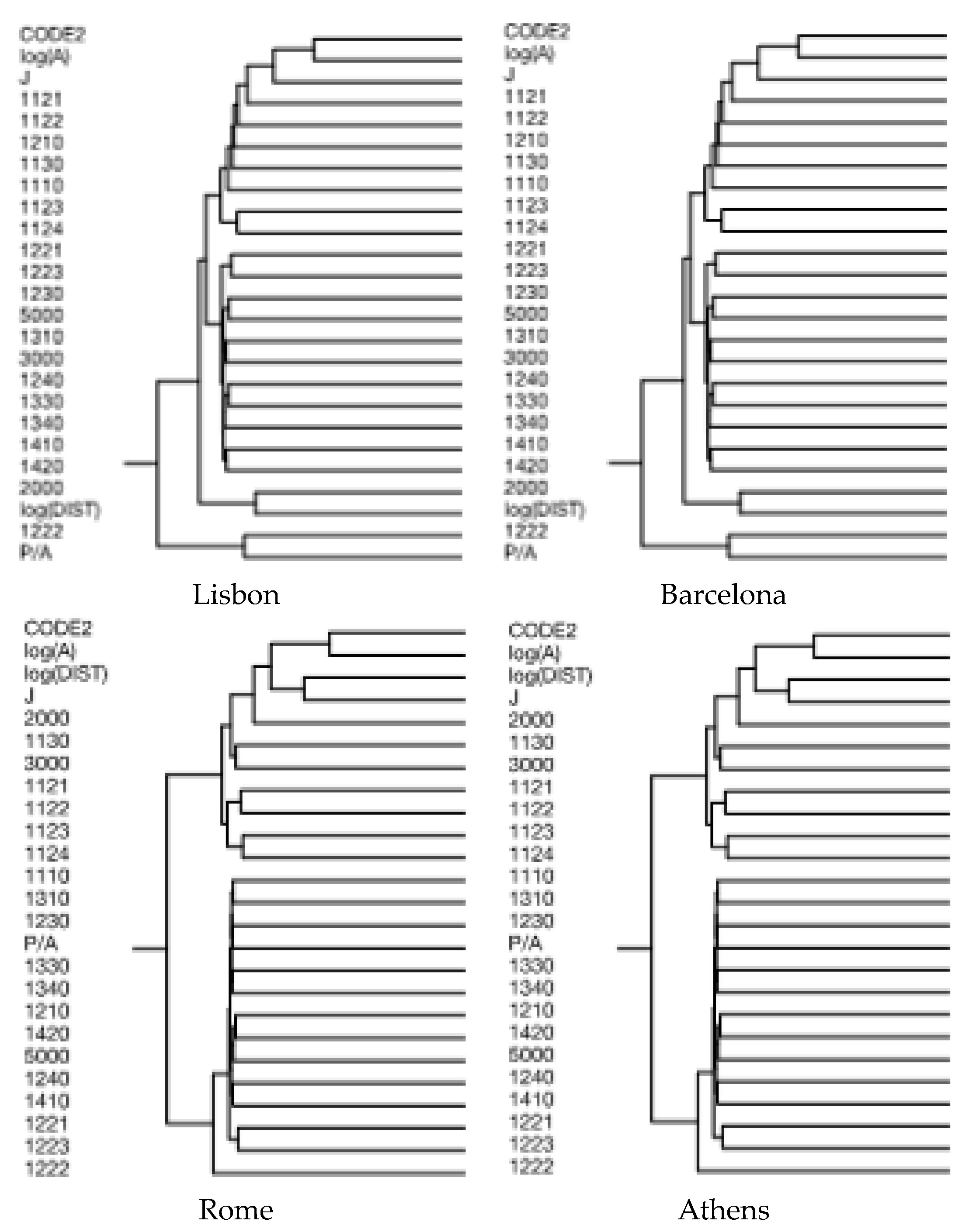
2.3. Spatial Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
Basic Characteristics of Patches and Nearest Neighbor Landscape
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antrop, M. Landscape change and the urbanization process in Europe. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 67, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, A.; Salvati, L.; Sateriano, A.; Carlucci, M.; Gitas, I.; Biasi, R. Unraveling the ‘stable’ landscape: A multi-factor analysis of unchanged agricultural and forest land (1987–2007) in a rapidly-expanding urban region. Urban Ecosyst. 2016, 19, 835–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, B.; Saraswati, S.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Quantifying the degree-of-freedom, degree-of-sprawl, and degree-of-goodness of urban growth from remote sensing data. Appl. Geogr. 2010, 30, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pili, S.; Grigoriadis, E.; Carlucci, M.; Clemente, M.; Salvati, L. Towards Sustainable Growth? A Multi-criteria Assessment of (Changing) Urban Forms. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 76, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radeloff, V.C.; Hammer, R.B.; Stewart, S.I. Rural and suburban sprawl in the US Midwest from 1940 to 2000 and its relation to forest fragmentation. Conserv. Biol. 2005, 19, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, P.; Pons, X.; Saurí, D. Land-cover and land-use change in a Mediterranean landscape: A spatial analysis of driving forces integrating biophysical and human factors. Appl. Geogr. 2008, 28, 189–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, M.K.; York, A.M.; Boone, C.G.; Zhang, S. Land fragmentation due to rapid urbanization in the Phoenix Metropolitan Area: Analyzing the spatiotemporal patterns and drivers. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 32, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvernoy, I.; Zambon, I.; Sateriano, A.; Salvati, L. Pictures from the other side of the fringe: Urban growth and peri-urban agriculture in a post-industrial city (Toulouse, France). J. Rural Stud. 2018, 57, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, A. Environmental planning and management of the peri-urban interface: Perspectives on an Emerging field. Environ. Urban. 2003, 15, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colantoni, A.; Mavrakis, A.; Sorgi, T.; Salvati, L. Towards a ‘polycentric’ landscape? Reconnecting fragments into an integrated network of coastal forests in Rome. Rend. Lincei 2015, 26, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeger, T.; Casey, F. An assessment of market-based approaches to providing ecosystem services on agricultural lands. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 64, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, C.; Walker, R.; Perz, S.; Arima, E.; Aldrich, S.; Caldas, M. Spatial patterns of frontier settlement: Balancing conservation and development. J. Lat. Am. Geogr. 2016, 15, 33–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasi, R.; Brunori, E.; Ferrara, C.; Salvati, L. Towards sustainable rural landscapes? a multivariate analysis of the structure of traditional tree cropping systems along a human pressure gradient in a Mediterranean region. Agroforest. Syst. 2017, 91, 1199–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopoulou, O.; Polyzos, S.; Minetos, D. Peri-urban and urban forests in Greece: Obstacle or advantage to urban development? J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 18, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feranec, J.; Jaffrain, G.; Soukup, T.; Hazeu, G. Determining changes and flows in European landscapes 1990–2000 using CORINE land cover data. Appl. Geogr. 2010, 30, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frondoni, R.; Mollo, B.; Capotorti, G. A landscape analysis of land cover change in the Municipality of Rome (Italy), Spatio-temporal characteristics and ecological implications of land cover transitions from 1954 to 2001. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 100, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchini, M.; Zambon, I.; Pontrandolfi, A.; Turco, R.; Colantoni, A.; Mavrakis, A.; Salvati, L. Urban sprawl and the ‘olive’ landscape: Sustainable land management for ‘crisis’ cities. GeoJournal 2018, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Sateriano, A.; Grigoriadis, E.; Carlucci, M. New wine in old bottles: The (changing) socioeconomic attributes of sprawl during building boom and stagnation. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 131, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, I.; Benedetti, A.; Ferrara, C.; Salvati, L. Soil Matters? A Multivariate Analysis of Socioeconomic Constraints to Urban Expansion in Mediterranean Europe. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 146, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, J. Boundary organizations for sustainable land management: The example of Dutch Environmental Co-operatives. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 70, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, I.; Serra, P.; Sauri, D.; Carlucci, M.; Salvati, L. Beyond the ‘Mediterranean city’: Socioeconomic disparities and urban sprawl in three Southern European cities. Geogr. Ann. Ser. B Hum. Geogr. 2017, 99, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnoletti, M. Rural landscape, nature conservation and culture: Some notes on research trends and management approaches from a (southern) European perspective. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 126, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasanko, M.; Barredo, J.I.; Lavalle, C.; McCormick, N.; Demicheli, L.; Sagris, V.; Brezger, A. Are European Cities Becoming Dispersed? A Comparative Analysis of Fifteen European Urban Areas. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 77, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhi, C.; Musolesi, A. European cities in the process of economic integration: Towards structural convergence. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2007, 41, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turok, I.; Mykhnenko, V. The trajectories of European cities, 1960–2005. Cities 2007, 24, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonewald-Cox, C.M.; Bayless, J.W. The boundary model: A geographical analysis of design and conservation of nature reserves. Biol. Conserv. 1986, 38, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Carlin, B.P.; Gelfand, A.E. Hierarchical Modeling and Analysis for Spatial Data; Crc Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Allmendinger, P.; Haughton, G. Soft spaces, fuzzy boundaries, and metagovernance: The new spatial planning in the Thames Gateway. Environ. Plan. A 2009, 41, 617–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, R.T. Land Mosaics: The Ecology of Landscapes and Regions; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Blumer, H. Race prejudice as a sense of group position. Pac. Sociol. Rev. 1958, 1, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackman, M.R.; Crane, M. “Some of my best friends are black …”: Interracial friendship and whites’ racial attitudes. Public Opin. Q. 1986, 50, 459–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J. The Death and Life of Great American Cities; Random House: New York, NY, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, K.; Hewstone, M.; Hughes, J.; Jenkins, R.; Cairns, E. Residential segregation and intergroup contact: Consequences for intergroup relations, social capital and social identity. In Theorizing Identities and Social Action; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2009; pp. 177–197. [Google Scholar]
- Wessel, T. Does diversity in urban space enhance intergroup contact and tolerance? Geogr. Ann. Ser. B Hum. Geogr. 2009, 91, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opdam, P.F.M.; Westerink, J.; Vos, C.C.; Vries, E.A.D. The role and evolution of boundary concepts in transdisciplinary landscape planning. Plan. Theory Pract. 2015, 16, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerink, J.; Opdam, P.; Van Rooij, S.; Steingröver, E. Landscape services as boundary concept in landscape governance: Building social capital in collaboration and adapting the landscape. Land Use Policy 2017, 60, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Huang, B.; Wang, S.; Lin, H. Sustainable land use optimization using Boundary-based Fast Genetic Algorithm. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2015, 36, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M. Monitoring land use/land cover change, urban growth dynamics and landscape pattern analysis in five fastest urbanized cities in Bangladesh. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2017, 7, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, M.; Liu, X.; Clarke, K.C. Spatial metrics and image texture for mapping urban land use. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riitters, K.H.; O’neill, R.V.; Hunsaker, C.T.; Wickham, J.D.; Yankee, D.H.; Timmins, S.P.; Jackson, B.L. A factor analysis of landscape pattern and structure metrics. Landsc. Ecol. 1995, 10, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, M.; Longley, P.A. The morphology of urban land use. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 1988, 15, 461–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.; Engelen, G. Cellular automata and fractal urban form: A cellular modelling approach to the evolution of urban land-use patterns. Environ. Plan. A 1993, 25, 1175–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, T.; Jorgensen, K.E. Transnational governance ‘above’ and ‘below’ the state: The changing nature of borders in the New Europe. Reg. Fed. Stud. 2000, 10, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, I.N. Time-variant GIS databases of changing historical administrative boundaries: A European comparison. Trans. GIS 2002, 6, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquez, G.M.; Maruca, S.; Fortin, M.J. From fields to objects: A review of geographic boundary analysis. J. Geogr. Seymss 2000, 2, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerink, J.; Kempenaar, A.; Van Lierop, M.; Groot, S.; Van der Valk, A.; Van den Brink, A. The participating government: Shifting boundaries in collaborative spatial planning of urban regions. Environ. Plan. C Govern. Policy 2017, 35, 147–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R. Categories, borders and boundaries. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2009, 33, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.; Paasi, A. Fences and neighbours in the postmodern world: Boundary narratives in political geography. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 1998, 22, 186–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machlis, G.E.; Tichnell, D.L. The State of the World’s Parks; Westview Press: Boulder, CO, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- European Environment Agency. Mapping Guide for a European Urban Atlas; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell, M.J.; Hahs, A.K. The use of gradient analysis studies in advancing our understanding of the ecology of urbanizing landscapes: Current status and future directions. Landsc. Ecol. 2008, 23, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modica, G.; Vizzari, M.; Pollino, M.; Fichera, C.R.; Zoccali, P.; Di Fazio, S. Spatio-temporal analysis of the urban-rural gradient structure: An application in a Mediterranean mountainous landscape (Serra San Bruno, Italy). Earth Syst. Dyn. 2012, 3, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Gong, J.; Wang, Y. Gradient analysis of landscape spatial and temporal pattern changes in Beijing metropolitan area. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2010, 53, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Carlucci, M. The economic and environmental performances of rural districts in Italy: Are 405 competitiveness and sustainability compatible targets? Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 2446–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colantoni, A.; Grigoriadis, E.; Sateriano, A.; Venanzoni, G.; Salvati, L. Cities as selective land predators? A Lesson on Urban Growth, (Un)effective planning and Sprawl Containment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 545–546, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munafò, M.; Salvati, L.; Zitti, M. Estimating soil sealing rate at national level-Italy as a case study. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 26, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, A. The potential effect of national growth-management policy on urban sprawl and the depletion of open spaces and farmland. Land-Use Policy 2004, 21, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrion-Flores, C.; Irwin, E.G. Determinants of residential land-use conversion and sprawl at the rural-urban fringe. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2004, 86, 889–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Morelli, V.G.; Rontos, K.; Sabbi, A. Latent exurban development: City expansion along the rural-to-urban gradient in growing and declining regions of southern Europe. Urban Geogr. 2013, 34, 376–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlucci, M.; Grigoriadis, E.; Rontos, K.; Salvati, L. Revisiting a Hegemonic Concept: Long-term ‘Mediterranean Urbanization’ in Between City Re-polarization and Metropolitan Decline. Appl. Spat. Anal. Policy 2017, 10, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado-Ciuraneta, S.; Durà-Guimerà, A.; Salvati, L. Not only tourism: Unravelling suburbanization, second-home expansion and “rural” sprawl in Catalonia, Spain. Urban Geogr. 2017, 38, 66–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Gargiulo Morelli, V. Unveiling Urban Sprawl in the Mediterranean Region: Towards a Latent Urban Transformation? Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2014, 38, 1935–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L. Agro-forest Landscape and the ‘Fringe’ City: A Multivariate Assessment of Land-use Changes in a Sprawling Region and Implications for Planning. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambon, I.; Colantoni, A.; Carlucci, M.; Morrow, N.; Sateriano, A.; Salvati, L. Land quality, sustainable development and environmental degradation in agricultural districts: A computational approach based on entropy indexes. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2017, 64, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monarca, D.; Cecchini, M.; Guerrieri, M.; Colantoni, A. Conventional and alternative use of biomasses derived by hazelnut cultivation and processing. VII Int. Congr. Hazelnut 2008, 845, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colantoni, A.; Delfanti, L.; Recanatesi, F.; Tolli, M.; Lord, R. Land use planning for utilizing biomass residues in Tuscia Romana (central Italy): Preliminary results of a multi criteria analysis to create an agro-energy district. Land Use Policy 2016, 50, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, I.; Sabbi, A.; Schuetze, T.; Salvati, L. Exploring forest ‘fringescapes’: Urban growth, society and swimming pools as a sprawl landmark in coastal Rome. Rend. Lincei 2015, 26, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marraccini, E.; Debolini, M.; Moulery, M.; Abrantes, P.; Bouchier, A.; Chéry, J.P.; Napoleone, C. Common features and different trajectories of land cover changes in six Western Mediterranean urban regions. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 62, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallinis, G.; Koutsias, N.; Arianoutsou, M. Monitoring land-use/land cover transformations from 1945 to 2007 in two peri-urban mountainous areas of Athens metropolitan area, Greece. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 262–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, A.; Salvati, L.; Sabbi, A.; Colantoni, A. Urbanization, Soil Quality and Rural Areas: Towards a Spatial Mismatch? Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 478, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laidley, T. Measuring Sprawl. A New Index, Recent Trends, and Future Research. Urban Aff. Rev. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grekousis, G.; Manetos, P.; Photis, Y.N. Modeling urban evolution using neural networks, fuzzy logic and GIS: The case of the Athens metropolitan area. Cities 2013, 30, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable’s Name | Abbreviation |
|---|---|
| Continuous Urban Fabric (S.L. > 80%) | CUF |
| Discontinuous Dense Urban Fabric (S.L.: 50–80%) | DDUF |
| Discontinuous Medium Density Urban Fabric (S.L.: 30–50%) | DMDUF |
| Discontinuous Low Density Urban Fabric (S.L.: 10–30%) | DLDUF |
| Discontinuous Very Low Density Urban Fabric (S.L. < 10%) | DVLDUF |
| Industrial, commercial, public, military and private units | ICPMPU |
| Agricultural + Semi-natural areas + Wetlands | AGR |
| Isolated Structures | ISOL |
| Airports | AIRP |
| Construction sites | CON |
| Fast transit roads and associated land | FAST |
| Forests | FOR |
| Green urban areas | GREEN |
| Land without current use | LAND |
| Mineral extraction and dump sites | MINE |
| Other roads and associated lands | ROADS |
| Port areas | PORT |
| Railways and associated land | RAIL |
| Sports and leisure facilities | SPORT |
| Patch perimeter (m) | P |
| Patch size (m2) | A |
| Perimeter to area ratio | P/A |
| Distance from downtown (m) | Dist |
| Pielou J evenness index | J |
| Variable | Lisbon | Barcelona | Rome | Athens |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1110 | 229 | 218 | 114 | |
| 1121 | 508 | 52 | 695 | |
| 1122 | 538 | 196 | 1549 | |
| 1123 | 568 | 1053 | 1297 | |
| 1124 | 1802 | 304 | ||
| 1130 | 1625 | 2290 | 2764 | 7148 |
| 1210 | 496 | 77 | 555 | |
| 1221 | 403 | 81 | 185 | |
| 1222 | 638 | 5476 | 1345 | 5021 |
| 1310 | 148 | 90 | 132 | |
| 1330 | 105 | |||
| 1340 | 329 | 386 | 652 | 1269 |
| 1410 | 215 | 622 | 847 | 2069 |
| 1420 | 101 | |||
| 2000 | 1045 | 5252 | 2639 | 6627 |
| 3000 | 108 | |||
| 5000 | 250 | 308 | 115 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zambon, I.; Serra, P.; Pili, S.; Bernardini, V.; Ferrara, C.; Salvati, L. A New Approach to Land-Use Structure: Patch Perimeter Metrics as a Spatial Analysis Tool. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10072147
Zambon I, Serra P, Pili S, Bernardini V, Ferrara C, Salvati L. A New Approach to Land-Use Structure: Patch Perimeter Metrics as a Spatial Analysis Tool. Sustainability. 2018; 10(7):2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10072147
Chicago/Turabian StyleZambon, Ilaria, Pere Serra, Silvia Pili, Vincenzo Bernardini, Carlotta Ferrara, and Luca Salvati. 2018. "A New Approach to Land-Use Structure: Patch Perimeter Metrics as a Spatial Analysis Tool" Sustainability 10, no. 7: 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10072147
APA StyleZambon, I., Serra, P., Pili, S., Bernardini, V., Ferrara, C., & Salvati, L. (2018). A New Approach to Land-Use Structure: Patch Perimeter Metrics as a Spatial Analysis Tool. Sustainability, 10(7), 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10072147








