Soil Physical Properties and Soybean Yield as Influenced by Long-Term Tillage Systems and Cover Cropping in the Midsouth USA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
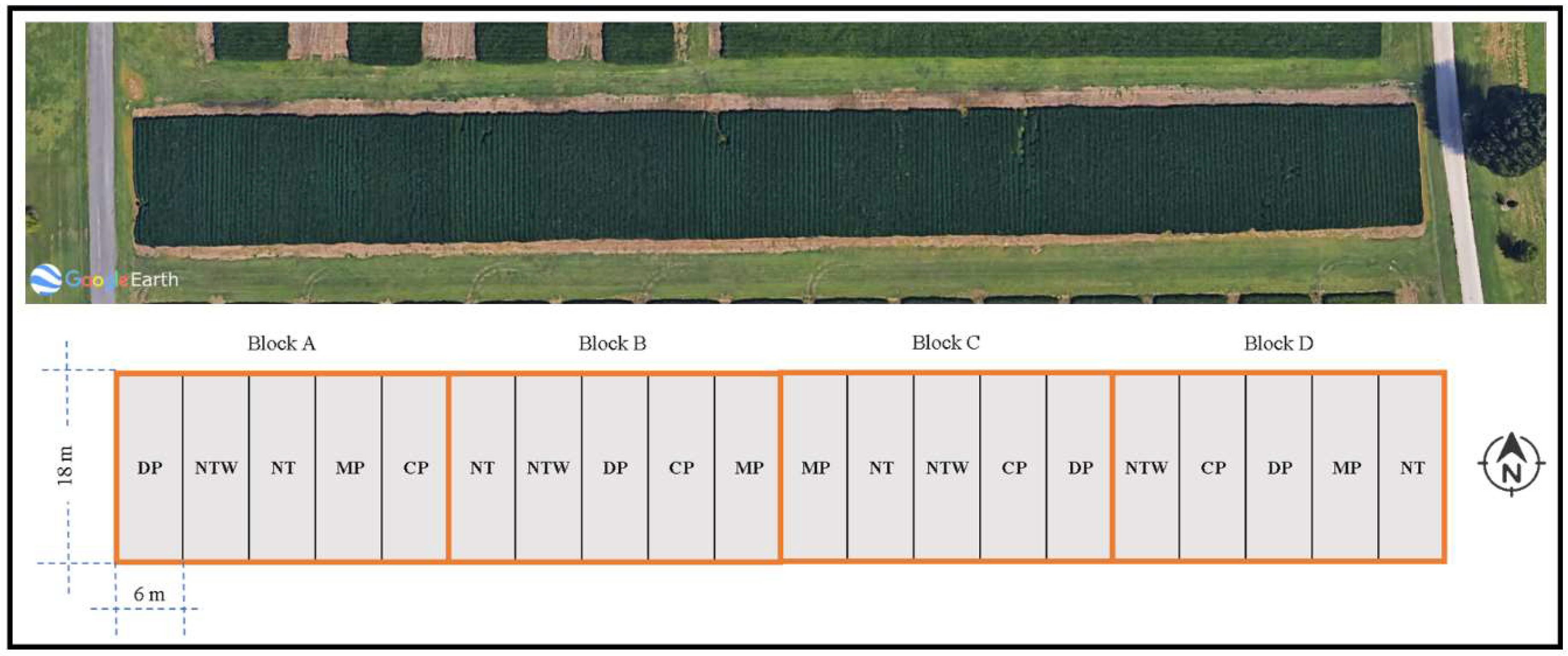
2.1. Study Site and Experimental Setting
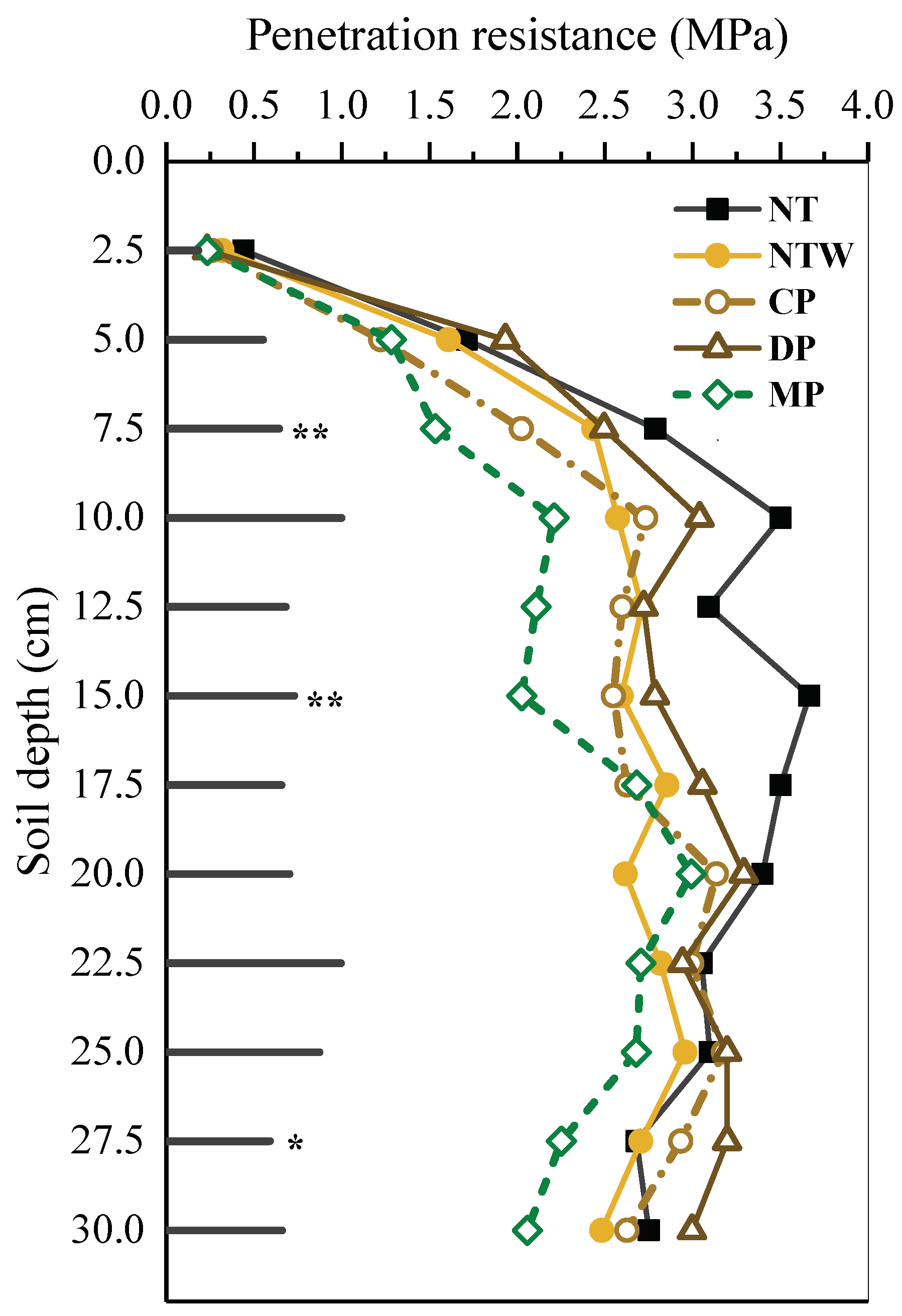
2.2. Bulk Density, Penetration Resistance and Field Moisture Content
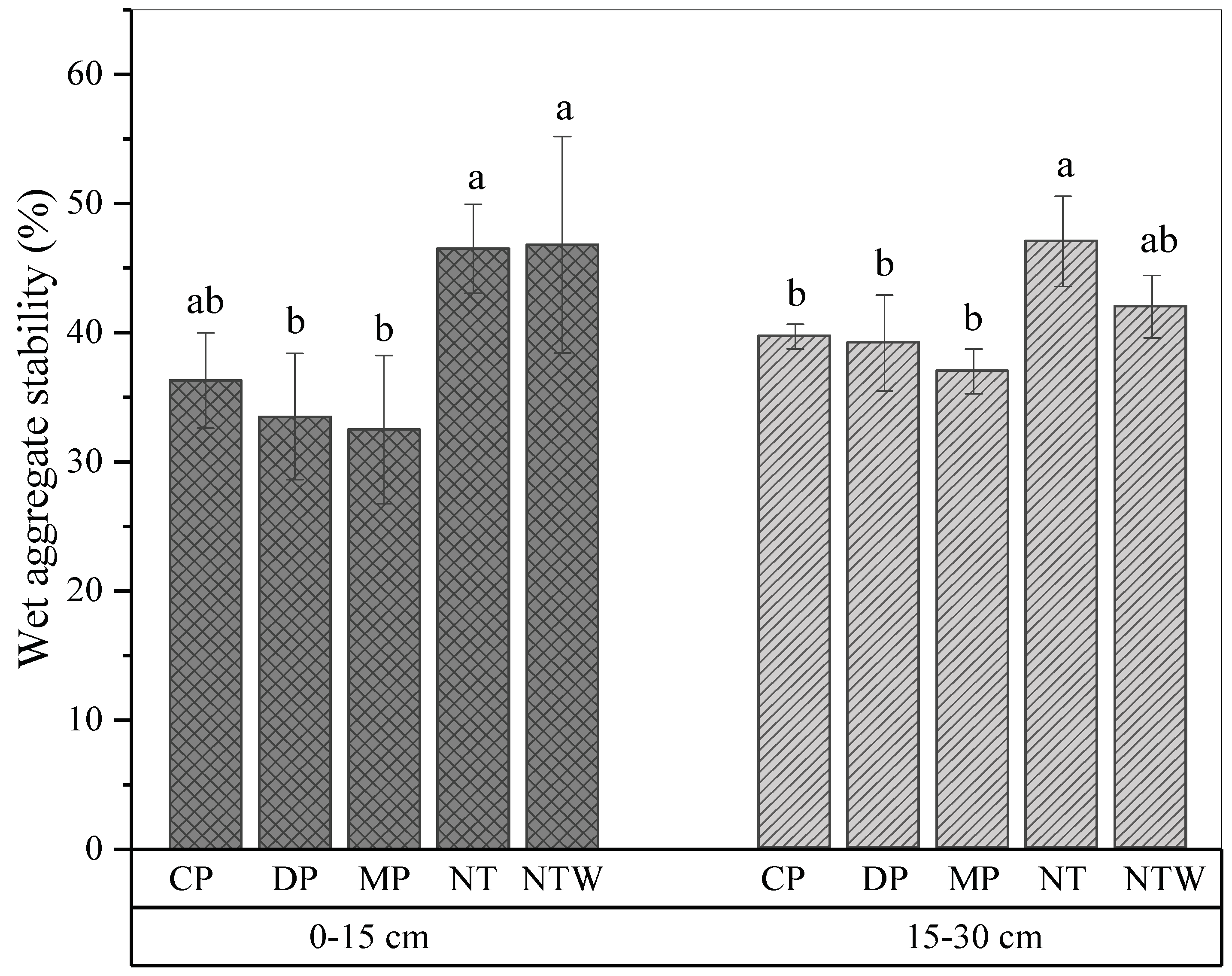
2.3. Wet Aggregate Stability and Dry Aggregate Size Distribution
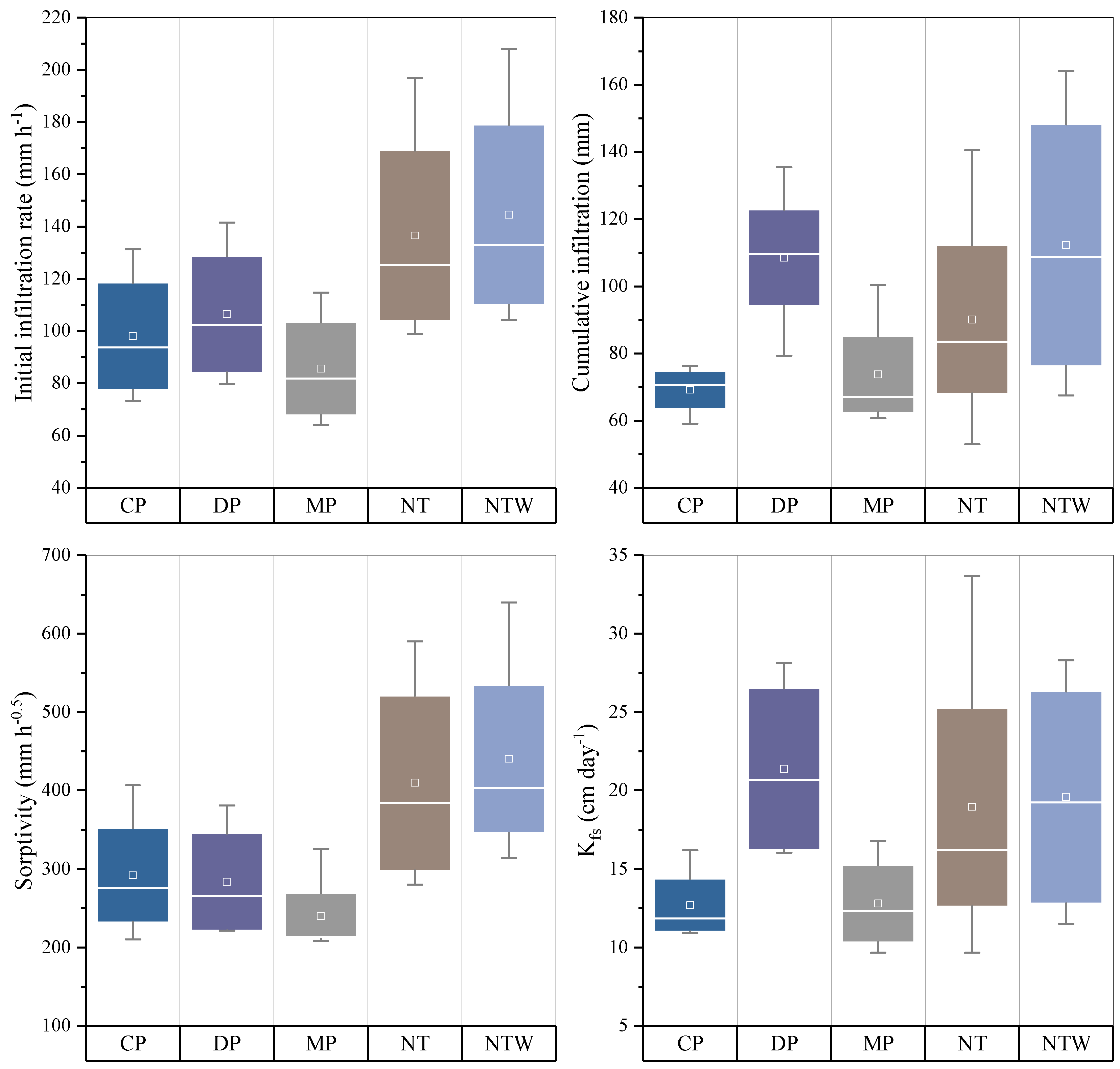
2.4. Water Infiltration and Field-Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Tillage Systems on Soil Hydro-Physical Properties
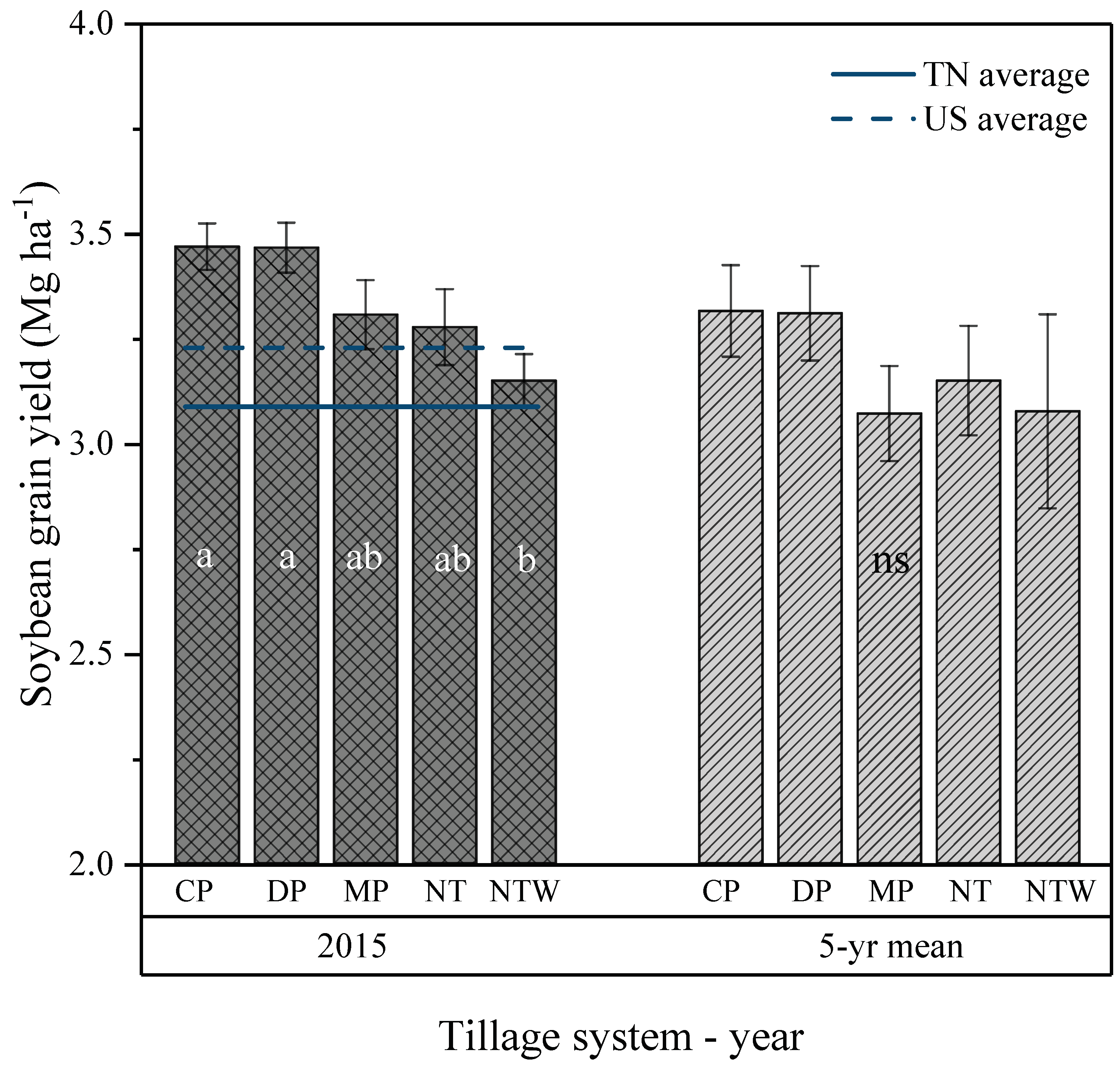
3.2. Effect of Tillage Systems on Soybean Yield
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dubois, O. The State of the World’s Land and Water Resources for Food and Agriculture: Managing Systems at Risk; Earthscan: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rockström, J.; Williams, J.; Daily, G.; Noble, A.; Matthews, N.; Gordon, L.; Wetterstrand, H.; DeClerck, F.; Shah, M.; Steduto, P. Sustainable intensification of agriculture for human prosperity and global sustainability. Ambio 2017, 46, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudel, B.; Radovich, T.J.; Chan-Halbrendt, C.; Crow, S.; Tamang, B.; Halbrendt, J.; Thapa, K. Effect of conservation agriculture on maize-based farming system in the mid-hills of Nepal. Procedia Eng. 2014, 78, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Putte, A.; Govers, G.; Diels, J.; Gillijns, K.; Demuzere, M. Assessing the effect of soil tillage on crop growth: A meta-regression analysis on European crop yields under conservation agriculture. Eur. J. Agron. 2010, 33, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegar, A.; Asoodar, M.; Khadish, A.; Hashemi, A.; Herbert, S. Soil physical characteristics and chickpea yield responses to tillage treatments. Soil Tillage Res. 2003, 71, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Canqui, H.; Francis, C.A. Building resilient soils through agroecosystem redesign under fluctuating climatic regimes. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 71, 127A–133A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, O.; Kaplan, S.; Basaran, M.; Deviren Saygın, S.; Youssef, F.; Nouri, A.; Ozcan, A.U.; Erpul, G. Spatial distribution of wind-driven sediment transport rate in a fallow plot in Central Anatolia, Turkey. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2017, 31, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, A.; Youssef, F.; Basaran, M.; Lee, J.; Saxton, A.M.; Erpul, G. The Effect of Fallow Tillage Management on Aeolian Soil Losses in Semiarid Central Anatolia, Turkey. Agrosyst. Geosci. Environ. 2018, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, T.; Claassen, R.L.; Wallander, S. Conservation-Practice Adoption Rates Vary Widely by Crop and Region; United States Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2015.
- Denton, H.; Tyler, D. Making no-till “conventional” in Tennessee. Mak. Conserv. Tillage Conv. Build. Future 2002, 25, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Boyer, C.N.; Lambert, D.M.; Larson, J.A.; Tyler, D.D. Investment Analysis of Cover Crop and No-Tillage Systems on Tennessee Cotton. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, D.; Gwathmey, C.; Roberts, R.; Lessman, G. Potassium fertilization of cotton produced on a low K soil with contrasting tillage systems. J. Prod. Agric. 1998, 11, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbuthia, L.W.; Acosta-Martínez, V.; DeBruyn, J.; Schaeffer, S.; Tyler, D.; Odoi, E.; Mpheshea, M.; Walker, F.; Eash, N. Long term tillage, cover crop, and fertilization effects on microbial community structure, activity: Implications for soil quality. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 89, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottinelli, N.; Angers, D.A.; Hallaire, V.; Michot, D.; Le Guillou, C.; Cluzeau, D.; Heddadj, D.; Menasseri-Aubry, S. Tillage and fertilization practices affect soil aggregate stability in a Humic Cambisol of Northwest France. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 170, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibet, L.C.; Blanco-Canqui, H.; Jasa, P. Long-term tillage impacts on soil organic matter components and related properties on a Typic Argiudoll. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, G.; von Bertoldi, A.P.; McCoy, A.J. Effect of tillage on soil water content and temperature under freeze–thaw conditions. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentz, R.D.; Bjorneberg, D.L. Polyacrylamide and straw residue effects on irrigation furrow erosion and infiltration. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2003, 58, 312–318. [Google Scholar]
- Acar, M.; Celik, I.; Günal, H. Effects of long-term tillage systems on aggregate-associated organic carbon in the eastern Mediterranean region of Turkey. Eurasian J. Soil Sci. 2018, 7, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kaisi, M.; Douelle, A.; Kwaw-Mensah, D. Soil microaggregate and macroaggregate decay over time and soil carbon change as influenced by different tillage systems. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 69, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.K.; Salahin, N.; Islam, S.; Begum, R.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Islam, M.; Rahman, M. Patterns of change in soil organic matter, physical properties and crop productivity under tillage practices and cropping systems in Bangladesh. J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 155, 216–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamil, M.B.; Little, J.; Nafziger, E.D. Corn residue, tillage, and nitrogen rate effects on soil properties. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 151, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Lal, R. Tillage and drainage management effect on soil gas diffusivity. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 135, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroulík, M.; Hůla, J.; Šindelář, R.; Illek, F. Water infiltration into soil related to the soil tillage intensity. Soil Water Res. 2007, 2, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittelkow, C.M.; Linquist, B.A.; Lundy, M.E.; Liang, X.; Van Groenigen, K.J.; Lee, J.; Van Gestel, N.; Six, J.; Venterea, R.T.; Van Kessel, C. When does no-till yield more? A global meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2015, 183, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouwakpo, S.K.; Song, J.; Gonzalez, J.M. Soil structural stability assessment with the fluidized bed, aggregate stability, and rainfall simulation on long-term tillage and crop rotation systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 178, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, R.; Franti, T.; Doran, J.W.; Powers, T.O.; Zanner, C. Tillage effects on soil quality indicators and nematode abundance in Loessial soil under long-term no-till production. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2008, 39, 2169–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Canqui, H.; Lal, R. Soil and crop response to harvesting corn residues for biofuel production. Geoderma 2007, 141, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, H.; Dersch, G.; Hösch, J.; Baumgarten, A. Tillage effects on soil organic carbon and nutrient availability in a long-term field experiment in Austria. Die Bodenkultur 2007, 58, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- López-Garrido, R.; Madejón, E.; León-Camacho, M.; Girón, I.; Moreno, F.; Murillo, J. Reduced tillage as an alternative to no-tillage under Mediterranean conditions: A case study. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 140, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Grossman, R.; Reinsch, T. 2.1 Bulk density and linear extensibility. Methods Soil Anal. Part 4 Phys. Methods 2002, 4, 201–228. [Google Scholar]
- Kemper, W.; Rosenau, R. Aggregate Stability and Size Distribution. Methods Soil Anal. 1986, 9, 425–442. [Google Scholar]
- Larney, F.J.; Lindwall, C.W.; Bullock, M.S. Fallow management and overwinter effects on wind erodibility in southern Alberta. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1994, 58, 1788–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youker, R.; McGuinness, J. A short method of obtaining mean weight-diameter values of aggregate analyses of soils. Soil Sci. 1957, 83, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, W.; Elrick, D.; Youngs, E.; Amoozegar, A.; Booltink, H.; Bouma, J. 3.4 Saturated and field-saturated water flow parameters. Methods Soil Anal. 2002, 4, 797–801. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, J.R. The theory of infiltration: 4. Sorptivity and algebraic infiltration equations. Soil Sci. 1957, 84, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS Institute. Base SAS 9.4 Procedures Guide: Statistical Procedures; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Saxton, A. DandA. sas: Design and Analysis Macro Collection Version 2.11; University of Tennessee: Knoxville, TN, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Ugalde, O.; Virto, I.; Bescansa, P.; Imaz, M.; Enrique, A.; Karlen, D. No-tillage improvement of soil physical quality in calcareous, degradation-prone, semiarid soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 106, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Leij, F.J.; Ghezzehei, T.A.; Or, D. Modeling the dynamics of the soil pore-size distribution. Soil Tillage Res. 2002, 64, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Canqui, H.; Stone, L.; Schlegel, A.J.; Lyon, D.; Vigil, M.; Mikha, M.; Stahlman, P.; Rice, C. No-till induced increase in organic carbon reduces maximum bulk density of soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 1871–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schjønning, P.; Rasmussen, K.J. Soil strength and soil pore characteristics for direct drilled and ploughed soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2000, 57, 69–82. [Google Scholar]
- Tabaglio, V.; Gavazzi, C.; Menta, C. Physico-chemical indicators and microarthropod communities as influenced by no-till, conventional tillage and nitrogen fertilisation after four years of continuous maize. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 105, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.; Sanderson, J.; Ivany, J.; White, R. Influence of rotation and tillage on forage maize productivity, weed species, and soil quality of a fine sandy loam in the cool–humid climate of Atlantic Canada. Soil Tillage Res. 2002, 67, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, H.M.; Valero, C.; Muñoz, M.Á.; Rodríguez, M.G.; Silva, L.L. Short-term effects of four tillage practices on soil physical properties, soil water potential, and maize yield. Geoderma 2015, 237, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihara, J.; Martius, C.; Bationo, A.; Thuita, M.; Lesueur, D.; Herrmann, L.; Amelung, W.; Vlek, P.L. Soil aggregation and total diversity of bacteria and fungi in various tillage systems of sub-humid and semi-arid Kenya. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2012, 58, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegar, A.; Yousefi, A.; Daryashenas, A. The effect of addition of different amounts and types of organic materials on soil physical properties and yield of wheat. Plant Soil 2002, 247, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikha, M.M.; Rice, C.W. Tillage and manure effects on soil and aggregate-associated carbon and nitrogen. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angers, D.; Samson, N.; Legere, A. Early changes in water-stable aggregation induced by rotation and tillage in a soil under barley production. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1993, 73, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Elliott, E.; Paustian, K. Soil macroaggregate turnover and microaggregate formation: A mechanism for C sequestration under no-tillage agriculture. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 2099–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, A.; Jedari, S. Investigating the consolidation behavior of contaminated clay. Sharif Civ. Eng. J. 2011, 29, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Farahani, C.J.M. Permeability and Compression Characteristics of Clay Contaminated with Kerosene and Gasoil. Mapta 2018, 1, 26–36. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Malhi, S. Response of soil physical properties to tillage and residue management on two soils in a cool temperate environment. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 85, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, N.C.; Weil, R. Nature and Properties of Soils, The Pearson New International Edition; Pearson Higher: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- De Rouw, A.; Huon, S.; Soulileuth, B.; Jouquet, P.; Pierret, A.; Ribolzi, O.; Valentin, C.; Bourdon, E.; Chantharath, B. Possibilities of carbon and nitrogen sequestration under conventional tillage and no-till cover crop farming (Mekong valley, Laos). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 136, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Canqui, H.; Wienhold, B.J.; Jin, V.L.; Schmer, M.R.; Kibet, L.C. Long-term tillage impact on soil hydraulic properties. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 170, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strudley, M.W.; Green, T.R.; Ascough, J.C., II. Tillage effects on soil hydraulic properties in space and time: State of the science. Soil Tillage Res. 2008, 99, 4–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soracco, C.G.; Villarreal, R.; Lozano, L.A.; Vittori, S.; Melani, E.M.; Marino, D.J. Glyphosate dynamics in a soil under conventional and no-till systems during a soybean growing season. Geoderma 2018, 323, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Anderson, S.H.; Udawatta, R.P.; Kallenbach, R.L. Water infiltration influenced by agroforestry and grass buffers for a grazed pasture system. Agrofor. Syst. 2012, 84, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Liang, T.; Wang, L.; Zhou, C. Effects of no-tillage systems on soil physical properties and carbon sequestration under long-term wheat–maize double cropping system. Catena 2015, 128, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacigaluppo, S.; Bodrero, M.; Balzarini, M.; Gerster, G.; Andriani, J.; Enrico, J.; Dardanelli, J. Main edaphic and climatic variables explaining soybean yield in Argiudolls under no-tilled systems. Eur. J. Agron. 2011, 35, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchini, J.C.; Debiasi, H.; Junior, A.A.B.; Tonon, B.C.; Farias, J.R.B.; de Oliveira, M.C.N.; Torres, E. Evolution of crop yields in different tillage and cropping systems over two decades in southern Brazil. Field Crops Res. 2012, 137, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, A.; Lee, J.; Yin, X.; Tyler, D.D.; Saxton, A.M. Thirty-four years of no-tillage and cover crops improve soil quality and increase cotton yield in Alfisols, Southeastern USA. Geoderma 2019, 337, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlen, D.L.; Kovar, J.L.; Cambardella, C.A.; Colvin, T.S. Thirty-year tillage effects on crop yield and soil fertility indicators. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 130, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA-NASS. Quick Stats; USDA-NASS: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.

| BD | PR | TP | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Mg m−3) | (MPa) | (%) | |
| Tillage treatments | 0–15 cm | ||
| CP | 1.47(0.005) a | 1.60(0.08) cd | 44.6(0.18) b |
| DP | 1.43(0.01) b | 1.92(0.15) ab | 45.9(0.49) a |
| MP | 1.45(0.009) ab | 1.34(0.07) d | 45.2(0.33) ab |
| NT | 1.46(0.01) a | 2.17(0.15) a | 44.9(0.45) b |
| NTW | 1.48(0.006) a | 1.77(0.11) bc | 44.1(0.24) b |
| 15–30 cm | |||
| CP | 1.50(0.03) ns | 2.96(0.30) ns | 43.4(1.32) ns |
| DP | 1.44(0.03) | 3.11(0.09) | 45.7(1.30) |
| MP | 1.50(0.01) | 2.56(0.18) | 43.4(0.31) |
| NT | 1.46(0.03) | 3.08(0.07) | 44.9(1.19) |
| NTW | 1.49(0.01) | 2.74(0.26) | 43.7(0.26) |
| ANOVA (p value) | |||
| Depth (A) | 0.03 | 0.001 | 0.03 |
| Depth (B) | 0.45 | 0.11 | 0.44 |
| Depth | 0.21 | <0.0001 | 0.21 |
| T*D | 0.74 | 0.53 | 0.74 |
| GMD (mm) | MWD (mm) | MA% | SMA% | MIA% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Management | 0–15 cm soil depth | ||||
| CP | 1.45(0.11) bc | 2.50(0.07) c | 47.97(2.63) cd | 42.68(0.94) a | 5.65(1.15) ab |
| DP | 1.82(0.12) b | 2.77(0.07) b | 52.45(1.90) bc | 40.40(1.35) ab | 4.60(0.78) bc |
| MP | 1.26(0.09) c | 2.34(0.08) c | 42.52(1.92) d | 44.42(1.57) a | 7.35(0.76) a |
| NT | 2.32(0.19) a | 2.99(0.05) a | 56.91(1.11) ab | 37.53(0.63) b | 3.26(0.43) c |
| NTW | 2.35(0.13) a | 3.04(0.05) a | 58.33(1.58) a | 36.51(2.28) b | 2.44(0.34) c |
| 15–30 cm soil depth | |||||
| CP | 1.29(0.06) bc | 2.34(0.05) bc | 40.69(1.49) bc | 48.67(1.01) ns | 5.82(0.48) ns |
| DP | 1.34(0.13) bc | 2.39(0.11) b | 42.95(2.32) ab | 45.68(1.04) | 7.03(0.59) |
| MP | 1.13(0.01) c | 2.14(0.06) c | 37.11(1.09) c | 49.98(0.38) | 7.45(0.65) |
| NT | 1.51(0.05) b | 2.51(0.02) ab | 44.09(0.96) ab | 48.57(1.88) | 4.63(0.79) |
| NTW | 1.76(0.10) a | 2.68(0.10) a | 46.59(1.38) a | 45.63(1.64) | 5.68(1.08) |
| ANOVA (p value) | |||||
| Depth (A) | 0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0004 | 0.009 | 0.004 |
| Depth (B) | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.009 | 0.12 | 0.05 |
| Depth | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.004 |
| T*D | 0.02 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.09 | 0.14 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nouri, A.; Lee, J.; Yin, X.; D. Tyler, D.; Jagadamma, S.; Arelli, P. Soil Physical Properties and Soybean Yield as Influenced by Long-Term Tillage Systems and Cover Cropping in the Midsouth USA. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4696. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124696
Nouri A, Lee J, Yin X, D. Tyler D, Jagadamma S, Arelli P. Soil Physical Properties and Soybean Yield as Influenced by Long-Term Tillage Systems and Cover Cropping in the Midsouth USA. Sustainability. 2018; 10(12):4696. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124696
Chicago/Turabian StyleNouri, Amin, Jaehoon Lee, Xinhua Yin, Donald D. Tyler, Sindhu Jagadamma, and Prakash Arelli. 2018. "Soil Physical Properties and Soybean Yield as Influenced by Long-Term Tillage Systems and Cover Cropping in the Midsouth USA" Sustainability 10, no. 12: 4696. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124696
APA StyleNouri, A., Lee, J., Yin, X., D. Tyler, D., Jagadamma, S., & Arelli, P. (2018). Soil Physical Properties and Soybean Yield as Influenced by Long-Term Tillage Systems and Cover Cropping in the Midsouth USA. Sustainability, 10(12), 4696. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124696






