Preservation of the Mediterranean Identity: An Intra-City Analysis Towards a Macro-Regional Approach for the Characterisation of Urban Sustainability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
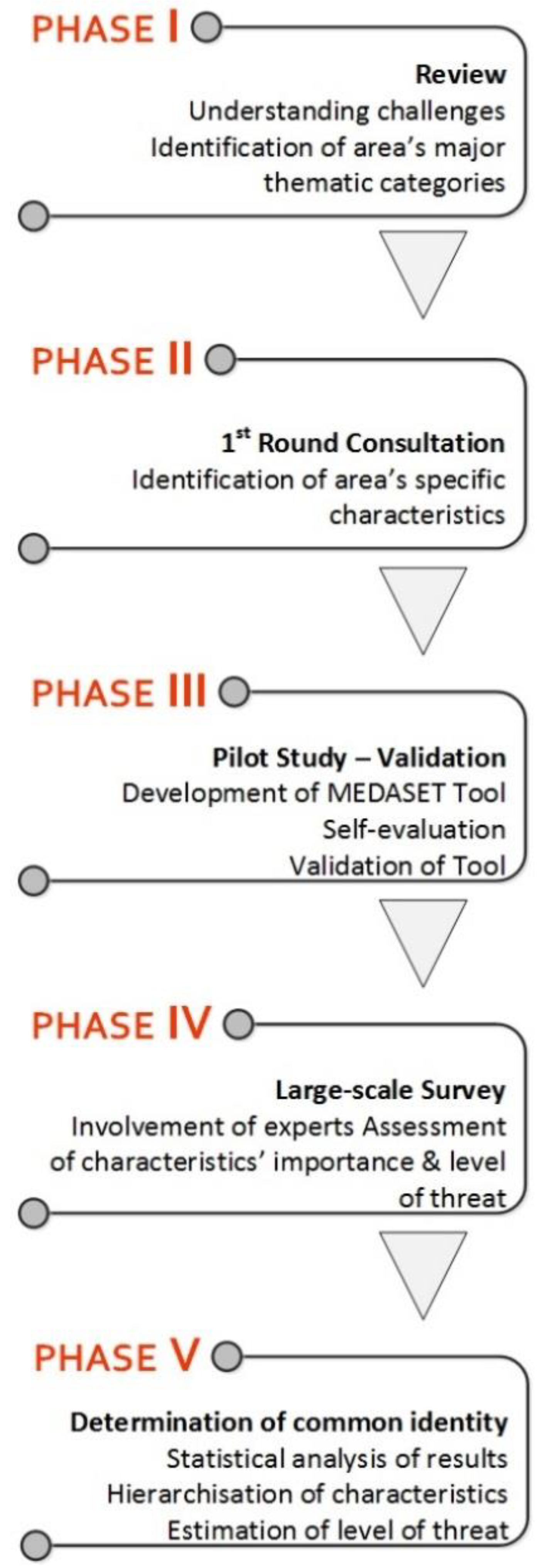
2.1. Review (Phase I)
2.2. First-Round Consultation (Phase II)
2.3. Pilot Study—Validation (Phase III)
2.4. Large-Scale Survey (Phase IV)
2.5. Determination of Common Identity in Areas with Common Characteristics (Phase V)
3. Results
3.1. Phase I: Review
3.2. Phase II: First Round Consultation
3.3. Phase III: Pilot Study—Validation
3.4. Phase IV: Large-Scale Survey
3.5. Phase V: Common Identity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Monetary Fund (IMF). 2018. Available online: www.imf.org/en (accessed on 15 April 2018).
- Balli, F.; Pericoli, F.; Pierucci, E. Globalisation and international risk-sharing: The role of social and political integration. Eur. J. Polit. Econ. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, J.; Thoenig, M.; Verdier, T. Globalisation and the dynamics of cultural identity. J. Int. Econ. 2008, 76, 356–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Q. The trends, promises and challenges of urbanisation in the world. Habitat Int. 2016, 54, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, A. Retailing in a multicultural world: The interplay of retailing, ethnic identity and consumption. J. Retail. Consumer. Serv. 2003, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantaras, K.; Philippas, D.; Siriopoulos, C. Trade asymmetries in the Mediterranean basin. J. Econ. Asymmetries 2018, 17, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S. Gradual Globalisation and Inequality between and within Countries. Can. J. Econ. 2005, 38, 852–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercelli, A.; Borghesi, S. Sustainable globalisation Ecological Economics. Sustain. Econ. 2003, 44, 77–89. [Google Scholar]
- Amico, A.D.; Currà, E. The Role of Urban Built Heritage in Qualify and Quantify Resilience. Specific Issues in Mediterranean City. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2014, 18, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, P.K.; Pavcnik, N. Distributional Effects of Globalisation in Developing Countries. J. Econ. Lit. 2007, 45, 39–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, E.; Rogoff, K.; Wei, S.J.; Kose, M.A. Effects of Financial Globalisation on Developing Countries: Some Empirical Evidence. In India’s and China’s Recent Experience with Reform and Growth. Procyclicality of Financial Systems in Asia; Tseng, W., Cowen, D., Eds.; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cassalia, G.; Tramontana, C.; Ventura, C. New Networking Perspectives towards Mediterranean Territorial Cohesion: The Multidimensional Approach of Cultural Routes. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2017, 223, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas-Mateos, N. The Mediterranean in the Age of Globalisation: Migration, Welfare, and Borders; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Haller, D. Transceding locality, creating identity—A diasporic perspective on the Mediterranean. Anthropol. J. Eur. Cult. 2000, 9, 3–30. [Google Scholar]
- King, R.; Proudfoot, L.; Smith, B. The Mediterranean: Environment and Society; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Eurostat. Tourism Statistics. 2018. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/ index.php/Tourism_statistics (accessed on 27 April 2018).
- Eurostat. Tourism Statistics at Regional Level. 2018. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Tourism_statistics_at_regional_level (accessed on 27 April 2018).
- Karlis, T.; Polemis, D. Cruise homeport competition in the Mediterranean. Tour. Manag. 2018, 68, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Educational; Scientific and Cultural Organisation; World Heritage Committee. World Heritage 40 COM Item 7B: State of the Conservation of Properties Inscribed on the World Heritage List; United Nations Educational: Paris, France, 27 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission Directorate-General Environment. The Costs of Not Implementing the Environmental Acquis-Final Report. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/enveco/economics_policy/pdf/report_sept2011.pdf (accessed on 16 June 2018).
- European Disability Strategy 2010–2020. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=COM:2010:0636:FIN:en:PDF (accessed on 16 June 2018).
- European Industrial Policy. Available online: https://www.cece.eu/industry-and-market/european-industrial-policy (accessed on 16 June 2018).
- Europe Statistics Explained, Employment Statistics. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Employment_statistics (accessed on 16 June 2018).
- Europe 2020 Indicators—R&D and Innovation. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Europe_2020_indicators_-_R%26D_and _innovation (accessed on 16 June 2018).
- Gallopin, G.C. Indicators and Their Use: Information for Decision-Making; Moldan, B., Billharz, S., Eds.; Sustainability indicators; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 13–28. [Google Scholar]
- Athanassiadis AChristis, M.; Bouillard, P.; Vercalsteren, A.; Crawford, R.H.; Khan, A.Z. Comparing a territorial-based and a consumption-based approach to assess the local and global environmental performance of cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 173, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, M.J.; MacGregor-Fors, I. The ecological future of cities. Science 2016, 20, 936–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meadows, D. Indicators and Information Systems for Sustainable Development—A Report to the Balaton Group; The Sustainability Institute: Hartland, VT, USA, 1998; Available online: http://www.sustainabilityinstitute.org/resources.html#SIpapers (accessed on 16 June 2018).
- Michailidou, A.V.; Vlachokostas, C.; Moussiopoulos, N. A methodology to assess the overall environmental pressure attributed to tourism areas: A combined approach for typical all-sized hotels in Chalkidiki, Greece. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 50, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldan, B.; Janoušková, S.; Hák, T. How to understand and measure environmental sustainability: Indicators and targets. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 17, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Yamashita, T. Methodological framework of sustainability assessment in City Sustainability Index (CSI): A concept of constraint and maximization indicators. Habitat Int. 2015, 45, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CAT-MED Project. Available online: http://www.catmed.eu/indicator (accessed on 20 June 2017).
- Cobb, C.; Halstead, T.; Rowe, J. The Genuine Progress Indicator: Summary of Data and Methodology; Redefining Progress: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Esty, D.C.; Levy, M.A.; Srebotnjak, T.; de Sherbinin, A.; Kim, C.H.; Anderson, B. Pilot Environmental Performance Index; Yale Center for Environmental Law & Policy: New Haven, CT, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Science for Environment Policy. 2018 Indicators for sustainable cities. In-depth Report 12. Produced for the European Commission DG Environment by the Science Communication Unit, UWE, Bristol. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/integration/research/newsalert/pdf/indicators_for_sustainable_cities_IR12_en.pdf (accessed on 30 August 2018).
- Marsal-Llacuna, M.-L.; Colomer-Llinàs, J.; Meléndez-Frigola, J. Lessons in urban monitoring taken from sustainable and livable cities to better address the Smart Cities initiative. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2015, 90, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas, A.; Coelho, P.; Subtil, E. The role of common local indicators in regional sustainability assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2009, 10, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas, A.; Nunes, L.M.; Ramos, T.B. Selection of sustainability indicators for planning: Combining stakeholders; participation and data reduction techniques. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 92, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapelan, Z.; Savic, D.A.; Walters, G.A. Decision-support tools for sustainable urban development. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers—Engineering. Sustainability 2005, 158, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, N.; Simms, A.; Thompson, S.; Abdallah, S. The Happy Planet Index: An Index of Human Well-Being and Environmental Impact; New Economics Foundation: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 37120:2014. Sustainable Development of Communities—Indicators for City Services and Quality of Life; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Baabou, W.; Grunewald, N.; Ouellet-Plamondon, C.; Gressot, M.; Galli, A. The Ecological Footprint of Mediterranean cities: Awareness creation and policy implications. Environ. Sci. Policy 2017, 69, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrini, M.; Bono, L. Measuring Urban Sustainability: Analysis of the European Green Capital Award; Ambiente Italia: Milano, Italy, 2011; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Air Quality in Europe. Compare the Current Air Quality in Different European Cities. Available online: Https://www.airqualitynow.eu/index.php (accessed on 16 June 2018).
- Kumar, P.; Bansod, B.K.S.; Debnath, S.K.; Thakur, P.K.; Ghanshyam, C. Index-based groundwater vulnerability mapping models using hydrogeological settings: A critical evaluation. J. Environ. Impact Assess. 2015, 51, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feleki, E.; Vlachokostas, C.; Moussiopoulos, N. Characterisation of sustainability in urban areas: An analysis of assessment tools with emphasis on European cities. J. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leontidou, L. Repolarization in the Mediterranean: Spanish and Greek cities in neoliberal Europe. Eur. Plan. Stud. 1995, 3, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitti, M.; Ferrara, C.; Perini, L.; Carlucci, M.; Salvati, L. Long-term Urban Growth and Land-use Efficiency in Southern Europe: Implications for Sustainable Land Management. Sustainability 2015, 7, 3359–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICOMOS. 2018. Available online: https://www.icomos.org/en/charters-and-texts/179-articles-en-francais/ressources/charters-and-standards/167-the-athens-charter-for-the-restoration-of-historic-monuments (accessed on 27 April 2018).
- Chorianopoulos, I.; Pagonis, T.; Koukoulas, S.; Drymoniti, S. Planning, competitiveness and sprawl in the Mediterranean city: The case of Athens. Cities 2010, 27, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.K. Department of Transport, 2018. Analyses from the National Travel Survey; Statistical release; U.K. Department of Transport: London, UK, 18 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Verband der Automobilindustrie (VDA). 2018. Available online: https://www.vda.de/en/topics/economic-policy-and-infrastructure/traffic/passenger-traffic.html (accessed on 27 April 2018).
- Proceedings of Plea. Environmentally Friendly Cities: Passive and Low Energy Architecture, 1st ed.; Kindle: Lisbon, Portugal, June 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez Riera, M.G.; Rise, M.; Rey, E. Fostering sustainable urban renewal at the neighborhood scale with a spatial decision support system. J. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 38, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESPON. European Territorial Review—Territorial Cooperation for the Future of Europe. 2018. Available online: https://territorial-review.espon.eu/doc/ESPON_Territorial_Review.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2018).
- Gálvez Pérez, J.C.; Granda, M.J.; Guzmán-López, T.; Corone Reinoso, J. Local gastronomy, culture and tourism sustainable cities: The behavior of the American tourist. J. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 32, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sustainable Urban Models Work Methodology and Results. 2012. CAT-MED Project (Financed by Interreg Med Programme 2007–2013). Available online: http://www.catmed.eu/archivos/desc9_CatMed%20Ita-Eng.pdf (accessed on 24 July 2017).
- Ciommi, M.; Chelli, F.M.; Carlucci Luca Salvati, M. Urban Growth and Demographic Dynamics in Southern Europe: Toward a New Statistical Approach to Regional Science. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediterranean Identity and Embodiment of the Traditional Symbolic Characteristics into the Alternative Routes. Report in the Framework of the ALTER ECO Project. (Financed by Interreg Med Programme, 2014–2020). Official Project’s Website. Available online: https://alter-eco.interreg-med.eu (accessed on 24 May 2018).
- Grenon, M.; Baitsse, M. Futures for the Mediterranean Basin: The Blue Plan; New York Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Houston, J.M. The Western Mediterranean World; Academic Pr.: London, UK, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Carli, E.; Frondoni, R.; Pinna, M.-S.; Bacchetta, G.; Fenu, G.; Fois, M.; Marignani, M.; Puddu, S.; Blasi, C. Spatially assessing plant diversity for conservation: A Mediterranean case study. J. Nat. Conserv. 2018, 41, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ara, I. The Mediterranean lifestyle: Not only diet but also socializing. In The Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease through the Mediterranean Diet; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 159–167. [Google Scholar]
- Benhammou, S.; Heras-González, L.; Ibáñez-Peinado, D.; Barceló, C.; Hamdan, M.; Rivas, A.; Mariscal-Arcas, M.; Olea-Serrano, F.; Monteagudo, C. Comparison of Mediterranean diet compliance between European and non-European populations in the Mediterranean basin. Appetite 2016, 107, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renna, M.; Rinaldi, V.A.; Gonnella, M. The Mediterranean Diet between traditional foods and human health: The culinary example of Puglia (Southern Italy). Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2015, 2, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, R. Reinventing the gastronomic identity of Croatian tourist destinations. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2007, 26, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santich, B. The study of gastronomy and its relevance to hospitality education and training. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2004, 23, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, M.; Piroddi, C.; Steenbeek, J.; Kaschner, K.; Ben Rais Lasram, F.; Aguzzi, J. The Biodiversity of the Mediterranean Sea: Estimates, Patterns, and Threats. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsoka, S.; Tsikaloudaki, K.; Theodosiou, T. Urban space’s morphology and microclimatic analysis: A study for a typical urban district in the Mediterranean city of Thessaloniki, Greece. Energy Build. 2017, 156, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.; Dabaieh, M.; Mateus, R.; Bragança, L. The influence of the Mediterranean climate on vernacular architecture: A comparative analysis between the vernacular responsive architecture of southern Portugal and north of Egypt. In Proceedings of the World SB14, Barcelona, Spain, 28–30 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Malek, Ž.; Verburg, P. Mediterranean land systems: Representing diversity and intensity of complex land systems in a dynamic region. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 165, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Philokyprou, M.; Michael, A.; Malaktou, E.; Savvides, A. Environmentally responsive design in Eastern Mediterranean. The case of vernacular architecture in the coastal, lowland and Mountainous regions of Cyprus. Build. Environ. 2017, 111, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, V.G.; Salvati, L. Ad Hoc Urban Sprawl in the Mediterranean City: Dispersing a Compact Tradition? Edizioni Nuova Cultura: Roma, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Salvati, A.; Coch, H.; Morganti, M. Effects of urban compactness on the building energy performance in Mediterranean climate. Energy Procedia 2017, 122, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartholomaios, A. A parametric sensitivity analysis of the influence of urban form on domestic energy consumption for heating and cooling in a Mediterranean city. J. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 28, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, F. Lock living: Urban sprawl in Mediterranean cities. Cities 2003, 20, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, C.; Petschel-held, G.; Leontidou, L. Urban sprawl. In Europe: Landscapes, Land-Use Change and Policy; Blackwell: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Centre for Administrative Innovation in the Euro-Mediterannean Region. Shared Identities and Cultures in the Mediterranean. 2017. Available online: http://unpan1.un.org/intradoc/groups/public/documents/caimed/unpan021020.pdf (accessed on 16 October 2017).
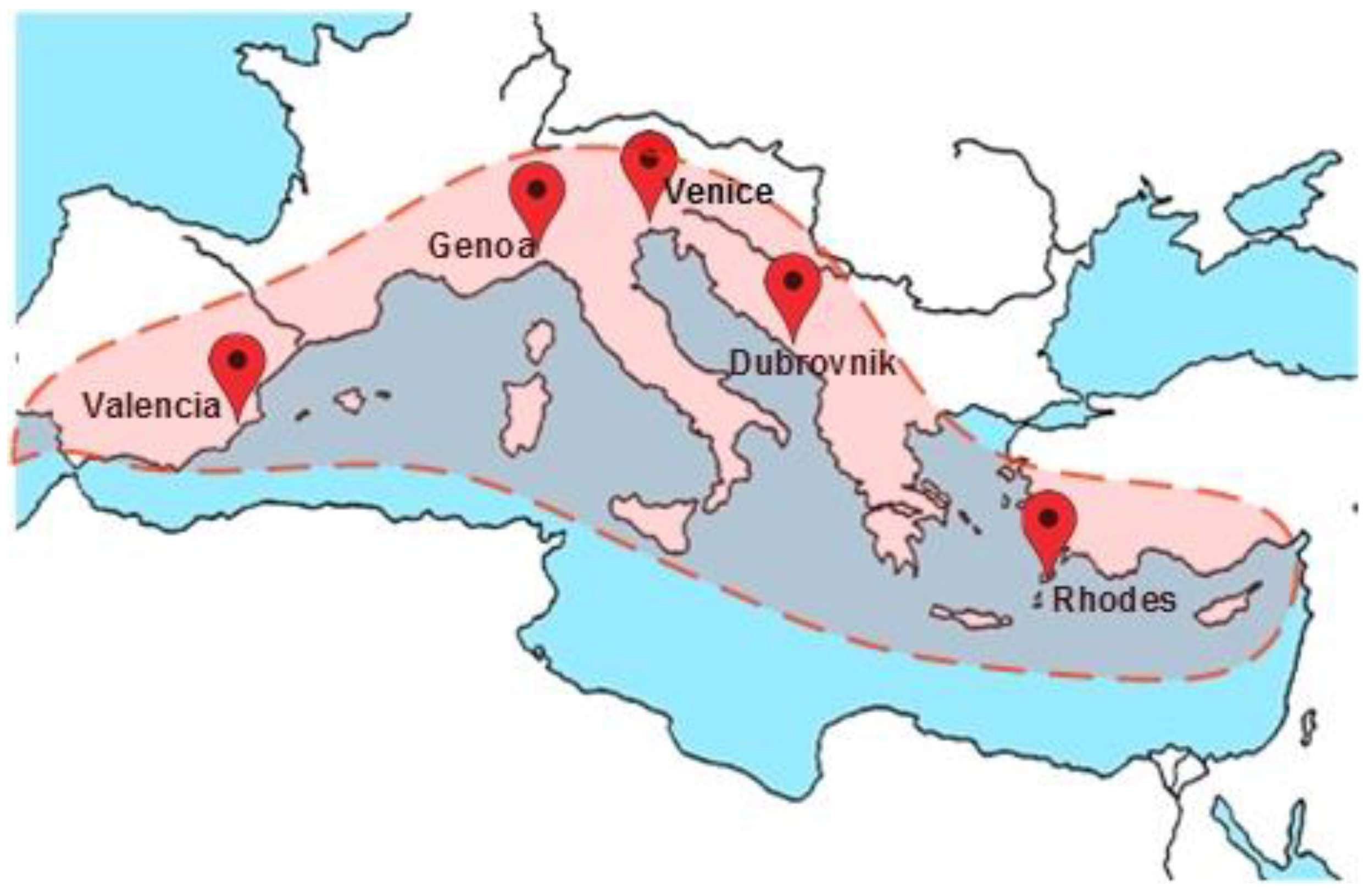


| Common Elements | Description | References |
|---|---|---|
| Landscape, climate, vegetation, and crops | Common graphical and topographical features, climatic conditions, coastal environment, high biodiversity, and specific plants that dominate the regional environment and landscape (e.g., olive trees, vineyards, oaks, pines). | [60,61,62] |
| Gastronomy, commerce, and professional activity | Common dietary habits, dominant role of sea (economic driver, booster of the tourism activity, and meteorological catalyst), high concentration of port-cities. | [63,64,65,66,67,68,69] |
| Structural and architectural characteristics of the urban fabric | Fashioned lifestyles, complexity of urban fabrics, dense/compact urban structure, small size of cities (compared to sprawling, mono-functional cities), squares, and neighbourhood spaces. | [70,71,72,73,74,75] |
| Civilisation and patterns of social behaviour | Notable history, cultural heritage, historical sites and districts inside cities, Christian urban forms, open central squares, places of social exchange and placing of events, large town halls, and prominent churches. | [12] |
| Thematic Categories | Specific Characteristics (Codification) | |
|---|---|---|
| I | Landscape surrounding the city | Olive groves (I1), vineyards (I2), nearby mountains (I3), aromatic scrubland (I4), bare rock (I5), nearby islands or beaches (I6), cork oak forest (I7), pine forest (I8), palm trees (I9), umbrella pines (I10), citrus trees (I11), cliffs and bare rock (I12). |
| II | Urban structure | Big central squares (II1), small residential squares (II2), narrow streets (II3), grand central fountains (II4), small local fountains (II5), cathedrals or grand mosques (II6), historic palaces (II7), fortresses (II8), port area (II9), sea-front promenade (II10), urban density (II11), proximity to basic services (II12), buildings compactness (II13), complexity of uses/functions (II14), mobility (II15). |
| III | Urban architecture | Distinctive colour(s) (III1), distinctive shape/style of houses (III2), decoration of houses (III3), shape/materials of roofs (III4), doors/windows/shutters (III5), balconies (III6), courtyards behind or inside the houses (III7), gardens attached to the houses (III8). |
| IV | Commerce and professional activity | Small shops in town centre (IV1), small shops in residential areas (IV2), local cafés (IV3), local restaurants (IV4), central cafés at town squares (IV5), professional services in the town centre (IV6), busy commerce (IV7), regular fish and/or vegetable markets (IV8), temporary open district markets (IV9). |
| V | Food that is served | Local specialties at restaurants (V1), local specialties at bakeries/delis (V2), street food (V3), fish bought daily from ports/beaches (V4), vegetables/meat bought daily from market stalls (V5), local specialties in grocery stores (V6), bowls/dishes where food is served (V7). |
| VI | Festivals and Events | Religious processions (VI1), traditional parades (VI2), food events in the streets (VI3), communal meals (VI4), competitions between neighbourhoods (VI5). |
| VII | Patterns of social behaviour | Distinctive everyday dress (VII1), distinctive dress on special occasions (VII2), use of local language or dialect (VII3), signage in local language (VII4), social exchange at café terraces (VII5), Mediterranean schedule (VII6), evening “passeggiata” (VII7), late-evening social activity (VII8), close family relations (VII9), open social events (VII10), social life and lifestyle (VII11), religious beliefs (VII12). |
| City | Number of Experts |
|---|---|
| Dubrovnik | 11 |
| Genoa | 13 |
| Rhodes | 10 |
| Valencia | 14 |
| Venice | 16 |
| Thematic Category | Importance * | Level of Threat * |
|---|---|---|
| Landscape (I) | 4.05 | 3.54 |
| Urban structure (II) | 4.46 | 3.97 |
| Urban architecture (III) | 3.99 | 3.62 |
| Commerce and professional activity (IV) | 4.00 | 3.58 |
| Food that is served (V) | 4.13 | 3.49 |
| Festivals and events (VI) | 4.23 | 3.13 |
| Patterns of social behaviour (VII) | 4.05 | 3.30 |
| Importance | A: >4.00 | B: 3.50–3.99 | C: 3.00–3.49 | D: 2.00–2.99 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific characteristics | II7 | III2 | II14 | II5 |
| II9 | IV3 | VII6 | VII4 | |
| II3 | II15 | I10 | V3 | |
| V1 | VI1 | III5 | I11 | |
| IV5 | VII9 | IV9 | I9 | |
| VII10 | IV8 | IIII4 | I5 | |
| II10 | V5 | I3 | VII12 | |
| VII11 | V2 | I4 | V7 | |
| II1 | IV4 | I2 | VII1 | |
| V4 | III1 | VI5 | I7 | |
| VII8 | IV2 | II4 | ||
| VI2 | II6 | III6 | ||
| II13 | VII7 | I1 | ||
| II11 | VI3 | I8 | ||
| II2 | IV7 | VII2 | ||
| II12 | I6 | I12 | ||
| IV1 | IV6 | VI4 | ||
| VII5 | II8 | |||
| V6 | ||||
| III7 | ||||
| VII3 | ||||
| III3 | ||||
| III8 |
| Level of Threat | A: >4.00 | B: 3.50–3.99 | C: 3.00–3.49 | D: 2.00–3.00 | E: <2.00 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific characteristics | V4 | V5 | II14 | VI2 | I5 |
| II15 | V1 | II11 | VI3 | VII1 | |
| IV1 | IV2 | VII3 | I2 | ||
| V6 | IV4 | VI1 | |||
| II3 | VII9 | III6 | |||
| II10 | IV8 | II13 | |||
| III3 | IV7 | I4 | |||
| III2 | VII10 | I9 | |||
| II7 | III5 | II5 | |||
| II12 | III7 | II4 | |||
| II1 | VII8 | VII6 | |||
| II2 | IV3 | VII7 | |||
| V2 | IV6 | VI5 | |||
| III1 | I10 | I11 | |||
| VII11 | II6 | IV5 | |||
| II9 | I6 | I3 | |||
| IIII4 | VII12 | ||||
| VII5 | VI4 | ||||
| II8 | VII4 | ||||
| III8 | VII2 | ||||
| IV9 | V7 | ||||
| I8 | I12 | ||||
| V3 | I7 | ||||
| I1 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feleki, E.; Achillas, C.; Vlachokostas, C.; Michailidou, A.V.; Ortega, L.; Moussiopoulos, N. Preservation of the Mediterranean Identity: An Intra-City Analysis Towards a Macro-Regional Approach for the Characterisation of Urban Sustainability. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3551. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10103551
Feleki E, Achillas C, Vlachokostas C, Michailidou AV, Ortega L, Moussiopoulos N. Preservation of the Mediterranean Identity: An Intra-City Analysis Towards a Macro-Regional Approach for the Characterisation of Urban Sustainability. Sustainability. 2018; 10(10):3551. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10103551
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeleki, Eleni, Charisios Achillas, Christos Vlachokostas, Alexandra V. Michailidou, Leticia Ortega, and Nicolas Moussiopoulos. 2018. "Preservation of the Mediterranean Identity: An Intra-City Analysis Towards a Macro-Regional Approach for the Characterisation of Urban Sustainability" Sustainability 10, no. 10: 3551. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10103551
APA StyleFeleki, E., Achillas, C., Vlachokostas, C., Michailidou, A. V., Ortega, L., & Moussiopoulos, N. (2018). Preservation of the Mediterranean Identity: An Intra-City Analysis Towards a Macro-Regional Approach for the Characterisation of Urban Sustainability. Sustainability, 10(10), 3551. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10103551









