Magnetic Resonance Imaging Techniques for Post-Treatment Evaluation After External Beam Radiation Therapy of Prostate Cancer: Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Role of PSA on Follow-Up
1.2. The Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI on Follow-Up
1.2.1. Prostate Imaging for Recurrence Reporting (PI-RR) System
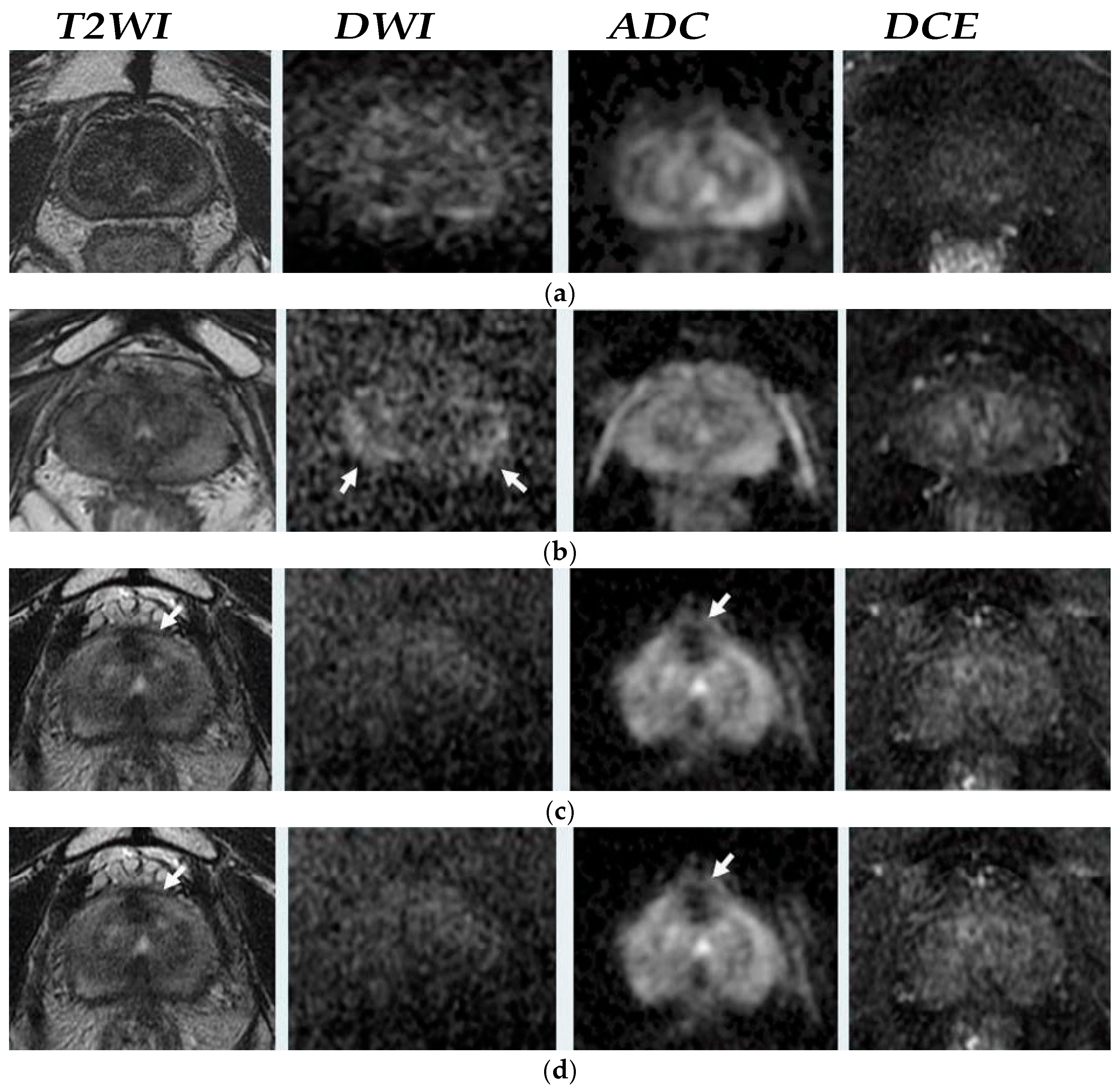
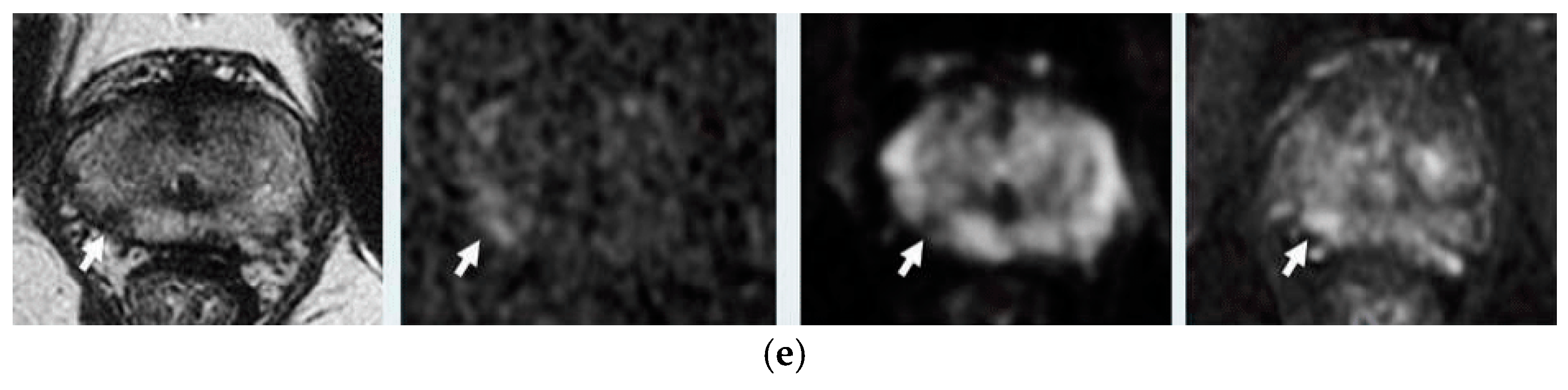
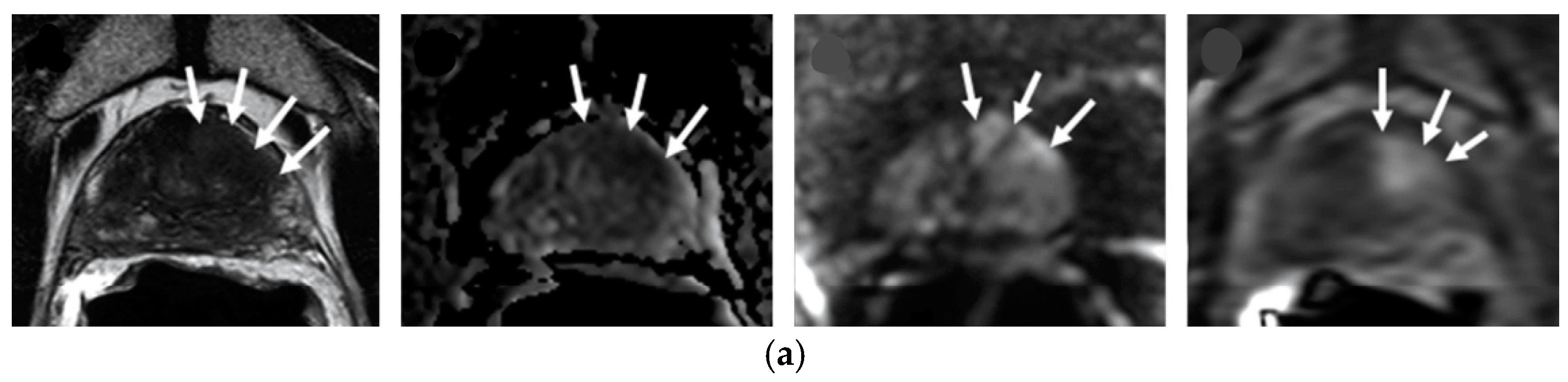
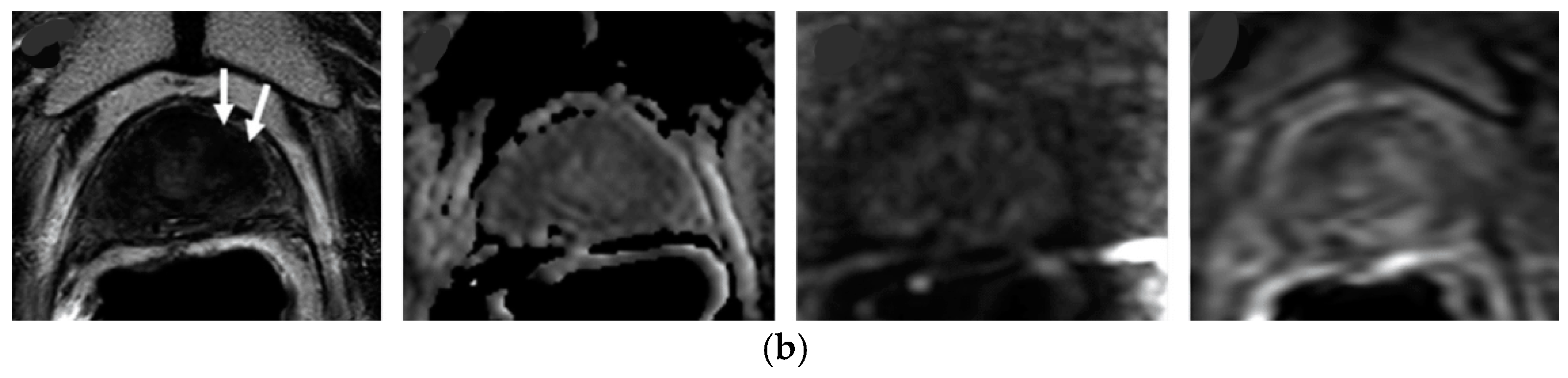
1.2.2. MRI Sequences Suggestions on EBRT
1.2.3. Multiparametric MRI Suggestion on Recurrence
T2—Weighted Imaging T2WI
Diffusion Weighted Imaging DWI-MRI
Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced DCE-MRI
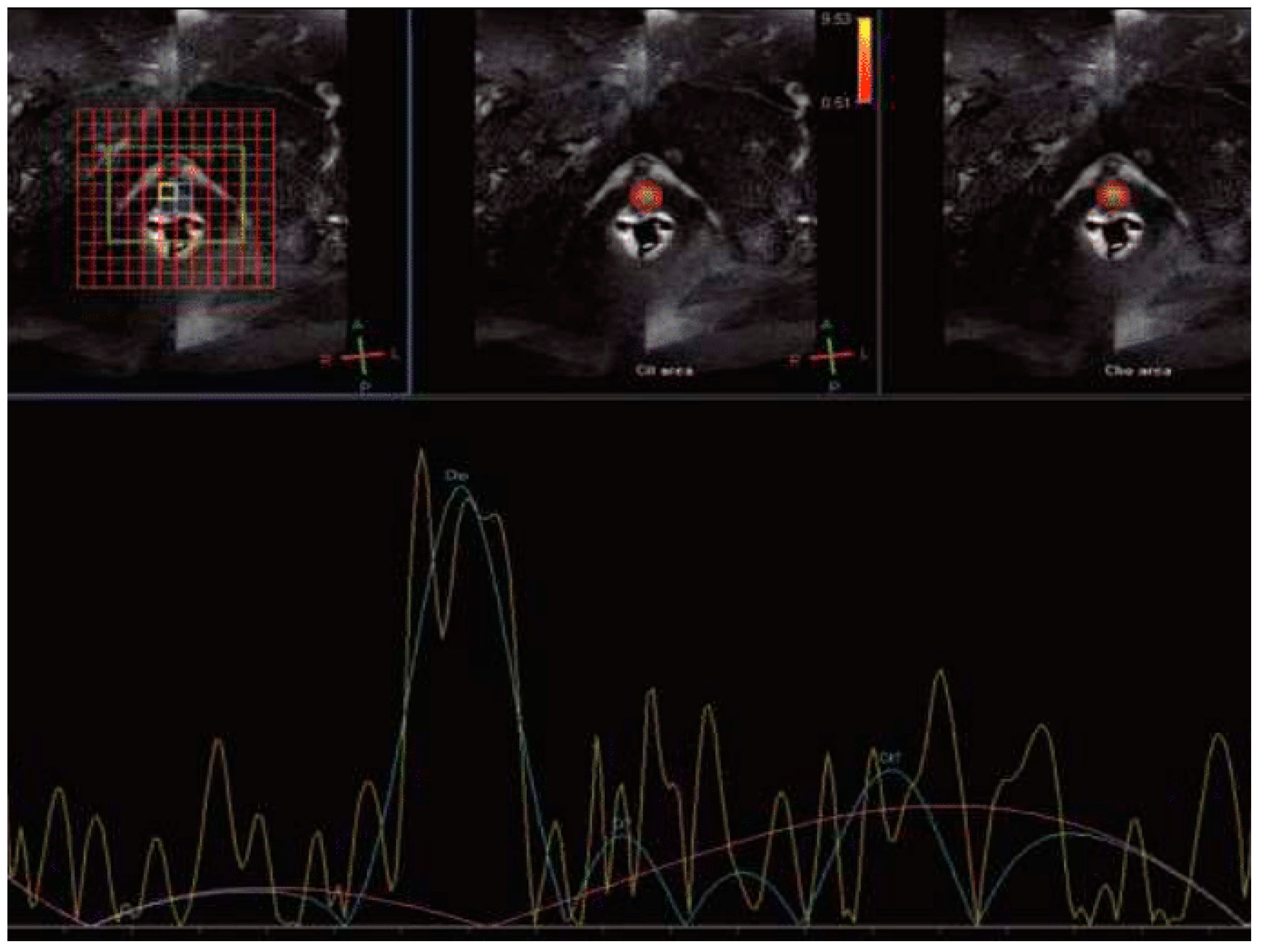
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS)
Blood Oxygenation Level Dependent (BOLD) and Tissue Oxygen Level Dependent (TOLD) MRI
Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MRI
1.2.4. The Role of MRI-Based Radiomics on RT Evaluation
| Study, Year | No. of Subjects | MRI Technique | Biomarkers Change on PCaRelapse | Sensitivity | Specificity | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Westphalen et al., 2009 [21] | 22 patients | T2-Weighted Imaging (T2WI) | Hypointense lesion with a capsular bulge | Reader 1: 62% (95% CI: 0.45–0.76) Reader 2:74% (95% CI: 0.57–0.86) | Reader 1: 64% (95% CI: 0.45–0.80) Reader 2: 68% (95% CI: 0.49–0.82) | Localization of lesion | Background signal changes reduce the diagnostic accuracy |
| Koopman et al., 2020 [22] | review | Diffusion Weighted Imaging (DWI) | Increase DWI intensity and reduce ADC | Range: 94–100% | Range: 75% to 100% | High accuracy in post-treatment changes | False indications of lesions due to radiation inflammatory changes |
| Koopman et al., 2020 [22] | review | Dynamic contrast-enhanced DCE | Increased wash-in and wash-out patterns | Range: 70% to 74% | Range: 73% to 85%. | Key role on the treatment’s effectiveness. | Radiation causes inflammatory changes in blood volume |
| Liao et al., 2018 [23] | review | Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS) | Increase concentration of choline and citrate. | 69% (95% CI: 0.58–0.78) | 86% (95% CI: 0.79–0.92) | Indicative biomarkers of prostate energy metabolism tumor membrane cellular activity | Long image acquisition High cost Low sensitivity |
| Arai et al., 2021 [24] | Animal study | Blood Oxygenation Level Dependent (BOLD) and Tissue Oxygen Level Dependent (TOLD) MRI | Decrease R2* and T1 signal. | N/A | N/A | Capable biomarkersforthe prediction of RT failure outcomes | Limited studies on animals |
| Kooreman et al., 2021, 2022 [34,35] | 20 and 22 patients, respectively | Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) | Decrease in D, f, and D* parameters. | N/A | N/A | Perfusion and diffusion information without the use of contrast agents | Absence of standard protocol sensitivity acquisition parameters (b-values and TE) and segmentation method. |
| Gnep et al., 2017 [37] | 74 patients | T2WI and Radiomics Analysis | Haralick features correlated with PCa relapse | N/A | N/A | Reliable tool for accurate interpretation and objective evaluation of RT response. | Absence of standard method |
2. Discussion
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cancer Today. Available online: https://gco.iarc.who.int/today/ (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- EAU Guidelines on Prostate Cancer—Epidemiology and Aetiology—Uroweb. Uroweb—European Association of Urology. Available online: https://uroweb.org/guidelines/prostate-cancer/chapter/epidemiology-and-aetiology (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Boukaram, C.; Hannoun-Levi, J.-M. Management of prostate cancer recurrence after definitive radiation therapy. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2010, 36, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roach, M.; Hanks, G.; Thames, H.; Schellhammer, P.; Shipley, W.U.; Sokol, G.H.; Sandler, H. Defining biochemical failure following radiotherapy with or without hormonal therapy in men with clinically localized prostate cancer: Recommendations of the RTOG-ASTRO Phoenix Consensus Conference. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 65, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.D.; Grignon, D.J.; Kaplan, R.S.; Parsons, J.T.; Schellhammer, P.F. Consensus statement: Guidelines for PSA following radiation therapy. American Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology Consensus Panel. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1997, 37, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar]
- PSA Test—Mayo Clinic. Available online: https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/psa-test/about/pac-20384731 (accessed on 12 April 2024).
- Muller, B.G.; van den Bos, W.; Brausi, M.; Fütterer, J.J.; Ghai, S.; Pinto, P.A.; Popeneciu, I.V.; de Reijke, T.M.; Robertson, C.; de la Rosette, J.J.M.C.H.; et al. Follow-up modalities in focal therapy for prostate cancer: Results from a Delphi consensus project. World J. Urol. 2015, 33, 1503–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, M.C.; Yildirim, O.; Woo, S.; Vargas, H.A.; Hricak, H. The Role of MRI in Prostate Cancer, Current and Future Directions. MAGMA 2022, 35, 503–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaur, S.; Turkbey, B. Prostate MR Imaging for Posttreatment Evaluation and Recurrence. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 45, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panebianco, V.; Barchetti, F.; Sciarra, A.; Ciardi, A.; Indino, E.L.; Papalia, R.; Gallucci, M.; Tombolini, V.; Gentile, V.; Catalano, C. Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging vs. standard care in men being evaluated for prostate cancer: A randomized study. Urol. Oncol. 2015, 33, 17.e1–17.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PI-RADS|American College of Radiology. Available online: https://www.acr.org/Clinical-Resources/Reporting-and-Data-Systems/PI-RADS (accessed on 28 March 2024).
- Chandarana, H.; Wang, H.; Tijssen, R.H.N.; Das, I.J. Emerging role of MRI in radiation therapy. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 48, 1468–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overview|Prostate Cancer: Diagnosis and Management|Guidance|NICE. 2019. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng131 (accessed on 11 April 2024).
- Panebianco, V.; Villeirs, G.; Weinreb, J.C.; Turkbey, B.I.; Margolis, D.J.; Richenberg, J.; Schoots, I.G.; Moore, C.M.; Futterer, J.; Macura, K.J.; et al. Prostate Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Local Recurrence Reporting (PI-RR): International Consensus-based Guidelines on Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Prostate Cancer Recurrence after Radiation Therapy and Radical Prostatectomy. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 4, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu-Gomez, J.; Dias, A.B.; Ghai, S. PI-RR: The Prostate Imaging for Recurrence Reporting System for MRI Assessment of Local Prostate Cancer Recurrence After Radiation Therapy or Radical Prostatectomy—A Review. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2023, 220, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecoraro, M.; Turkbey, B.; Purysko, A.S.; Girometti, R.; Giannarini, G.; Villeirs, G.; Roberto, M.; Catalano, C.; Padhani, A.R.; Barentsz, J.O.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy and Observer Agreement of the MRI Prostate Imaging for Recurrence Reporting Assessment Score. Radiology 2022, 304, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panebianco, V.; Turkbey, B. Magnetic resonance imaging for prostate cancer recurrence: It’s time for precision diagnostic with Prostate Imaging for Recurrence Reporting (PI-RR) score. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 748–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergaglio, C.; Giasotto, V.; Marcenaro, M.; Barra, S.; Turazzi, M.; Bauckneht, M.; Casaleggio, A.; Sciabà, F.; Terrone, C.; Mantica, G.; et al. The Role of mpMRI in the Assessment of Prostate Cancer Recurrence Using the PI-RR System: Diagnostic Accuracy and Interobserver Agreement in Readers with Different Expertise. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, P.N.; Frade-Santos, S.; García-Baizán, A.; Paredes-Velázquez, L.; Aymerich, M.; Sironi, S.; Otero-García, M.M. An MRI assessment of prostate cancer local recurrence using the PI-RR system: Diagnostic accuracy, inter-observer reliability among readers with variable experience, and correlation with PSA values. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 1790–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Velasco, C.; Ye, H.; Lindner, T.; Grech-Sollars, M.; O’Callaghan, J.; Hiley, C.; Chouhan, M.D.; Niendorf, T.; Koh, D.-M.; et al. Current Applications and Future Development of Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting in Diagnosis, Characterization, and Response Monitoring in Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphalen, A.C.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Cunha, R.M.G.; Hsu, I.; Kornak, J.; Zhao, S.; Coakley, F.V. T2-weighted endorectal magnetic resonance imaging of prostate cancer after external beam radiation therapy. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2009, 35, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, A.G.M.M.; Jenniskens, S.F.M.; Fütterer, J.J. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Assessment After Therapy in Prostate Cancer. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 29, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.-L.; Wei, J.Y.; Li, Y.-Q.; Zhong, J.-H.; Liao, C.-C.; Wei, C.-Y. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Diagnosis of Locally Recurrent Prostate Cancer: Are All Pulse Sequences Helpful? Korean J. Radiol. 2018, 19, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, T.J.; Yang, D.M.; Campbell, J.W., III; Chiu, T.; Cheng, X.; Stojadinovic, S.; Peschke, P.; Mason, R.P. Oxygen-Sensitive MRI: A Predictive Imaging Biomarker for Tumor Radiation Response? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. *Biol. *Phys. 2021, 110, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deal, M.; Bardet, F.; Walker, P.-M.; de la Vega, M.F.; Cochet, A.; Cormier, L.; Bentellis, I.; Loffroy, R. Three-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: A complementary tool to multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging in the identification of aggressive prostate cancer at 3.0t. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 3749–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, D.A.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Gerberich, J.; Stojadinovic, S.; Peschke, P.; Mason, R.P. Developing Oxygen-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging as a Prognostic Biomarker of Radiation Response. Cancer Lett. 2016, 380, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Padgett, K.R.; Su, M.-Y.; Mellon, E.A.; Maziero, D.; Chang, Z. Multi-parametric MRI (mpMRI) for treatment response assessment of radiation therapy. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belfatto, A.; White, D.A.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Cerveri, P.; Baroni, G.; Mason, R.P. Mathematical modeling of tumor response to radiation: Radio-sensitivity correlation with BOLD, TOLD, ΔR1 and ΔR2* investigated in large Dunning R3327-AT1 rat prostate tumors. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; Volume 2015, pp. 3266–3269. [Google Scholar]
- Asuncion, A.; Walker, P.M.; Bertaut, A.; Blanc, J.; Labarre, M.; Martin, E.; Bardet, F.; Cassin, J.; Cormier, L.; Crehange, G.; et al. Prediction of prostate cancer recurrence after radiation therapy using multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy: Assessment of prognostic factors on pretreatment imaging. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2022, 12, 5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, C.; Foudi, F.; Charton, J.; Jung, M.; Lang, H.; Saussine, C.; Jacqmin, D. Comparative Sensitivities of Functional MRI Sequences in Detection of Local Recurrence of Prostate Carcinoma After Radical Prostatectomy or External-Beam Radiotherapy. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 200, W361–W368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallac, R.R.; Zhou, H.; Pidikiti, R.; Song, K.; Stojadinovic, S.; Zhao, D.; Solberg, T.; Peschke, P.; Mason, R.P. Correlations of noninvasive BOLD and TOLD MRI with pO2 and relevance to tumor radiation response. Magn. Reason. Med 2014, 71, 1863–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bihan, D. What can we see with IVIM MRI? NeuroImage 2019, 187, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesny, E.; Leporq, B.; Chapet, O.; Beuf, O. Intravoxel incoherent motion magnetic resonance imaging to assess early tumor response to radiation therapy: Review and future directions. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2024, 108, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooreman, E.S.; van Houdt, P.J.; Keesman, R.; van Pelt, V.W.J.; Nowee, M.E.; Pos, F.; Sikorska, K.; Wetscherek, A.; Müller, A.-C.; Thorwarth, D.; et al. Daily Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) In Prostate Cancer Patients During MR-Guided Radiotherapy-A Multicenter Study. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 705964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooreman, E.S.; van Pelt, V.; Nowee, M.E.; Pos, F.; van der Heide, U.A.; van Houdt, P.J. Longitudinal Correlations Between Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced (DCE) MRI During Radiotherapy in Prostate Cancer Patients. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 897130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgadillo, R.; Ford, J.C.; Abramowitz, M.C.; Dal Pra, A.; Pollack, A.; Stoyanova, R. The role of radiomics in prostate cancer radiotherapy. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2020, 196, 900–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnep, K.; Fargeas, A.; Gutiérrez-Carvajal, R.E.; Commandeur, F.; Mathieu, R.; Ospina, J.D.; Rolland, Y.; Rohou, T.; Vincendeau, S.; Hatt, M.; et al. Haralick textural features on T2 -weighted MRI are associated with biochemical recurrence following radiotherapy for peripheral zone prostate cancer. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2017, 45, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiradkar, R.; Ghose, S.; Jambor, I.; Taimen, P.; Ettala, O.; Purysko, A.S.; Madabhushi, A. Radiomic features from pretreatment biparametric MRI predict prostate cancer biochemical recurrence: Preliminary findings. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 48, 1626–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, H.; Mofid, B.; Shiri, I.; Razzaghdoust, A.; Saadipoor, A.; Mahdavi, A.; Galandooz, H.M.; Mahdavi, S.R. Machine learning-based radiomic models to predict intensity-modulated radiation therapy response, Gleason score and stage in prostate cancer. Radiol. Med. 2019, 124, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Li, S.; Yang, J.; Ye, Y.; Zou, J.; Wang, L.; Long, R.; Zurkiya, O.; Zhao, T.; Johnson, J.; et al. Protein-based MRI contrast agents for molecular imaging of prostate cancer. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2011, 13, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Blasiak, B.; MacDonald, D.; Jasiński, K.; Cheng, F.-Y.; Tomanek, B. Application of H2N-Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Prostate Cancer Magnetic Resonance Imaging in an Animal Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grancharova, T.; Zagorchev, P.; Pilicheva, B. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Parameters for Optimized Photoconversion Efficiency in Synergistic Cancer Treatment. J. Funct. Biomater. 2024, 15, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, J.C.L. Magnetic nanoparticles as contrast agents in magnetic resonance imaging and radiosensitizers in radiotherapy. In Fundamentals and Industrial Applications of Magnetic Nanoparticles; Hussain, C.M., Patankar, K.K., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2022; pp. 291–316. [Google Scholar]
- Valle, L.F.; Greer, M.D.; Shih, J.H.; Barrett, T.; Law, Y.M.; Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Shebel, H.; Muthigi, A.; Su, D.; Merino, M.J.; et al. Multiparametric MRI for the detection of local recurrence of prostate cancer in the setting of biochemical recurrence after low dose rate brachytherapy. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 24, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiella, E.; Santucci, D.; D’Amone, G.; Cirimele, V.; Vertulli, D.; Bruno, A.; Beomonte Zobel, B.; Grasso, R.F. Focal Minimally Invasive Treatment in Localized Prostate Cancer: Comprehensive Review of Different Possible Strategies. Cancers 2024, 16, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitag, M.T.; Radtke, J.P.; Afshar-Oromieh, A.; Roethke, M.C.; Hadaschik, B.A.; Gleave, M.; Bonekamp, D.; Kopka, K.; Eder, M.; Heusser, T.; et al. Local recurrence of prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy is at risk to be missed in 68Ga-PSMA-11-PET of PET/CT and PET/MRI: Comparison with mpMRI integrated in simultaneous PET/MRI. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 44, 776–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glemser, P.A.; Rotkopf, L.T.; Ziener, C.H.; Beuthien-Baumann, B.; Weru, V.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Schlemmer, H.P.; Dimitrakopoulou-Strauss, A.; Sachpekidis, C. Hybrid imaging with [68Ga]PSMA-11 PET-CT and PET-MRI in biochemically recurrent prostate cancer. Cancer Imaging 2022, 22, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattabriga, A.; Renzetti, B.; Galuppi, F.; Bartalena, L.; Gaudiano, C.; Brocchi, S.; Rossi, A.; Schiavina, R.; Bianchi, L.; Brunocilla, E.; et al. Multiparametric Whole-Body MRI: A Game Changer in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jentjens, S.; Mai, C.; Ahmadi Bidakhvidi, N.; De Coster, L.; Mertens, N.; Koole, M.; Everaerts, W.; Joniau, S.; Oyen, R.; Van Laere, K.; et al. Prospective comparison of simultaneous [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 PET/MR versus PET/CT in patients with biochemically recurrent prostate cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, F.; Dupont-Roettger, D.; Dehmeshki, J.; Kubassova, O.; Quraishi, M.I. Advanced Imaging of Biochemical Recurrent Prostate Cancer With PET, MRI, and Radiomics. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Light, A.; Lazic, S.; Houghton, K.; Bayne, M.; Connor, M.J.; Tam, H.; Ahmed, H.U.; Shah, T.T.; Barwick, T.D. Diagnostic Performance of 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT Versus Multiparametric MRI for Detection of Intraprostatic Radiorecurrent Prostate Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2024, 65, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bekou, E.; Mulita, A.; Seimenis, I.; Kotini, A.; Courcoutsakis, N.; Koukourakis, M.I.; Mulita, F.; Karavasilis, E. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Techniques for Post-Treatment Evaluation After External Beam Radiation Therapy of Prostate Cancer: Narrative Review. Clin. Pract. 2025, 15, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15010004
Bekou E, Mulita A, Seimenis I, Kotini A, Courcoutsakis N, Koukourakis MI, Mulita F, Karavasilis E. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Techniques for Post-Treatment Evaluation After External Beam Radiation Therapy of Prostate Cancer: Narrative Review. Clinics and Practice. 2025; 15(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleBekou, Eleni, Admir Mulita, Ioannis Seimenis, Athanasia Kotini, Nikolaos Courcoutsakis, Michael I. Koukourakis, Francesk Mulita, and Efstratios Karavasilis. 2025. "Magnetic Resonance Imaging Techniques for Post-Treatment Evaluation After External Beam Radiation Therapy of Prostate Cancer: Narrative Review" Clinics and Practice 15, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15010004
APA StyleBekou, E., Mulita, A., Seimenis, I., Kotini, A., Courcoutsakis, N., Koukourakis, M. I., Mulita, F., & Karavasilis, E. (2025). Magnetic Resonance Imaging Techniques for Post-Treatment Evaluation After External Beam Radiation Therapy of Prostate Cancer: Narrative Review. Clinics and Practice, 15(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15010004








